Human Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase 1 : new activities and







dna_repair_enzymes_as_key_targets_to_develop_anticancer_drugs.ppt
- Размер: 10.2 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 38
Описание презентации Human Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase 1 : new activities and по слайдам
 Human Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase 1 : new activities and development of enzyme inhibitors as anticancer drugs Olga Lavrik SB RAS Institute of Chemical Biology and Fundamental Medicine, Department of Physicochemical Biology and Biotechnology of ASU, Novosibirsk, Barnaul, Russia
Human Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase 1 : new activities and development of enzyme inhibitors as anticancer drugs Olga Lavrik SB RAS Institute of Chemical Biology and Fundamental Medicine, Department of Physicochemical Biology and Biotechnology of ASU, Novosibirsk, Barnaul, Russia
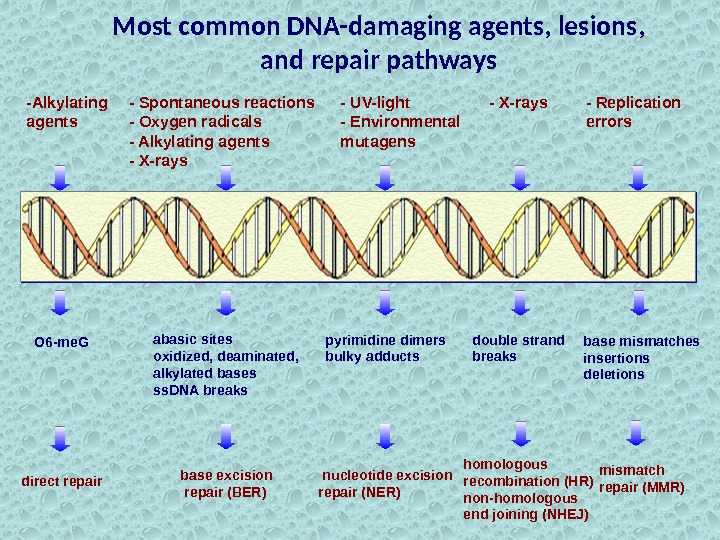
 -Alkylating agents O 6 -me. G direct repair — UV-light — Environmental mutagens pyrimidine dimers bulky adducts nucleotide excision repair (NER) — X-rays double strand breaks homologous recombination (HR) non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) — Replication errors base mismatches insertions deletions mismatch repair (MMR)Most common DNA-damaging agents, lesions, and repair pathways abasic sites oxidized, deaminated, alkylated bases ss. DNA breaks base excision repair (BER)- Spontaneous reactions — Oxygen radicals — Alkylating agents — X-rays
-Alkylating agents O 6 -me. G direct repair — UV-light — Environmental mutagens pyrimidine dimers bulky adducts nucleotide excision repair (NER) — X-rays double strand breaks homologous recombination (HR) non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) — Replication errors base mismatches insertions deletions mismatch repair (MMR)Most common DNA-damaging agents, lesions, and repair pathways abasic sites oxidized, deaminated, alkylated bases ss. DNA breaks base excision repair (BER)- Spontaneous reactions — Oxygen radicals — Alkylating agents — X-rays
 Defects in DNA repair systems Cancer Aging. Cataract Progressive cerebralpalsy Intellectual and immune inadequacy. Cockayne’s syndrom Xeroderma pigmentosum (melanoma, carcinoma) Trichothio- distrophy
Defects in DNA repair systems Cancer Aging. Cataract Progressive cerebralpalsy Intellectual and immune inadequacy. Cockayne’s syndrom Xeroderma pigmentosum (melanoma, carcinoma) Trichothio- distrophy
 DNA repair systems suppress the efficiency of a number of antitumor drugs that have to reveal their cytotoxic effects by damaging DNA of the cancer cells. Therefore inhibiting of DNA repair can improve the anticancer treatment. DNA repair systems are targets for development of anticancer drugs
DNA repair systems suppress the efficiency of a number of antitumor drugs that have to reveal their cytotoxic effects by damaging DNA of the cancer cells. Therefore inhibiting of DNA repair can improve the anticancer treatment. DNA repair systems are targets for development of anticancer drugs
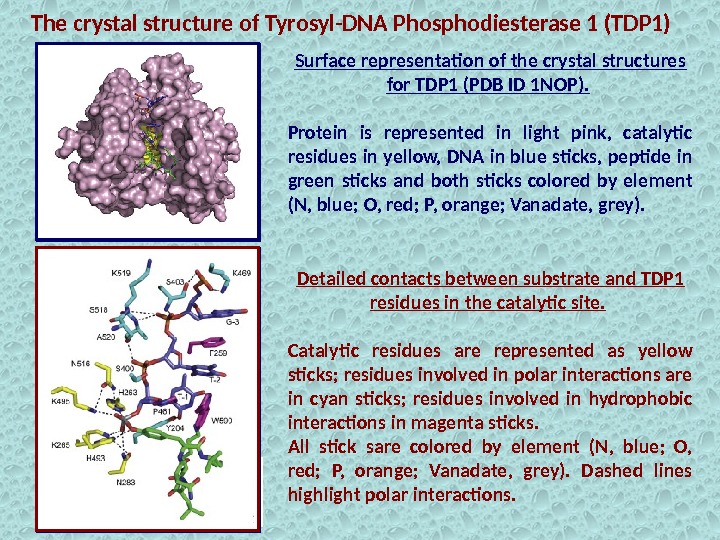
 Surface representation of the crystal structures for TDP 1 (PDB ID 1 NOP). Protein is represented in light pink, catalytic residues in yellow, DNA in blue sticks, peptide in green sticks and both sticks colored by element (N, blue; O, red; P, orange; Vanadate, grey). The crystal structure of Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP 1) Detailed contacts between substrate and TDP 1 residues in the catalytic site. Catalytic residues are represented as yellow sticks; residues involved in polar interactions are in cyan sticks; residues involved in hydrophobic interactions in magenta sticks. All stick sare colored by element (N, blue; O, red; P, orange; Vanadate, grey). Dashed lines highlight polar interactions.
Surface representation of the crystal structures for TDP 1 (PDB ID 1 NOP). Protein is represented in light pink, catalytic residues in yellow, DNA in blue sticks, peptide in green sticks and both sticks colored by element (N, blue; O, red; P, orange; Vanadate, grey). The crystal structure of Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP 1) Detailed contacts between substrate and TDP 1 residues in the catalytic site. Catalytic residues are represented as yellow sticks; residues involved in polar interactions are in cyan sticks; residues involved in hydrophobic interactions in magenta sticks. All stick sare colored by element (N, blue; O, red; P, orange; Vanadate, grey). Dashed lines highlight polar interactions.
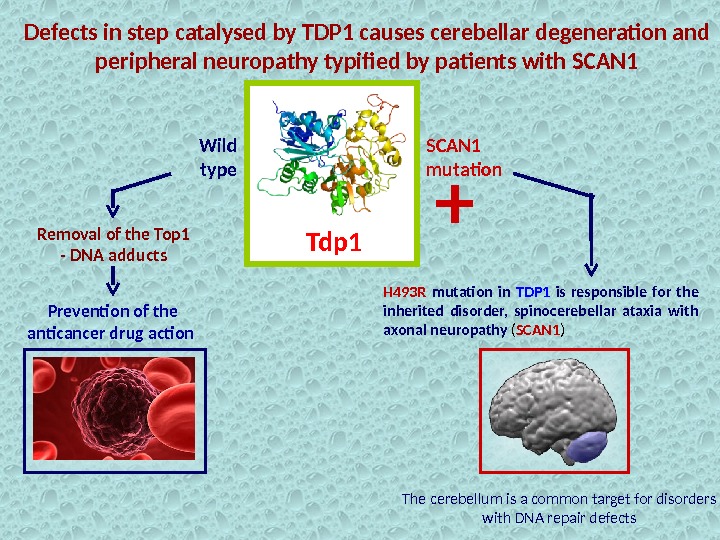
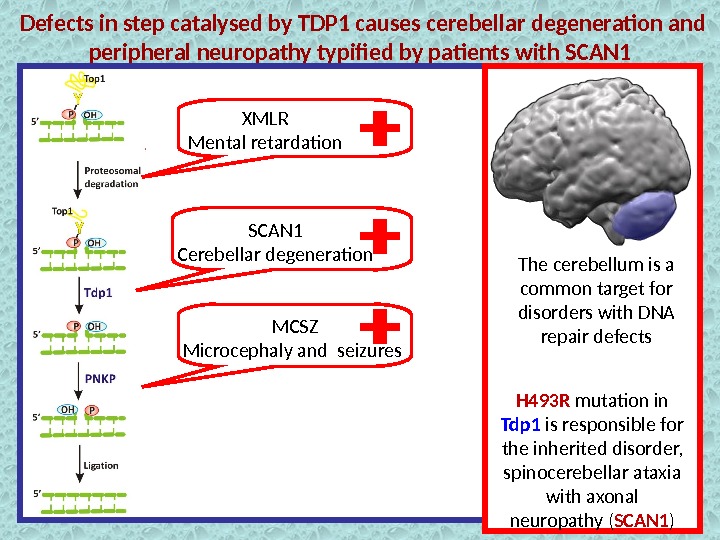
 Defects in step catalysed by TDP 1 causes cerebellar degeneration and peripheral neuropathy typified by patients with SCAN 1 Tdp 1 Removal of the Top 1 — DNA adducts Prevention of the anticancer drug action H 493 R mutation in TDP 1 is responsible for the inherited disorder, spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy ( SCAN 1 )Wild type SCAN 1 mutation + The cerebellum is a common target for disorders with DNA repair defects
Defects in step catalysed by TDP 1 causes cerebellar degeneration and peripheral neuropathy typified by patients with SCAN 1 Tdp 1 Removal of the Top 1 — DNA adducts Prevention of the anticancer drug action H 493 R mutation in TDP 1 is responsible for the inherited disorder, spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy ( SCAN 1 )Wild type SCAN 1 mutation + The cerebellum is a common target for disorders with DNA repair defects
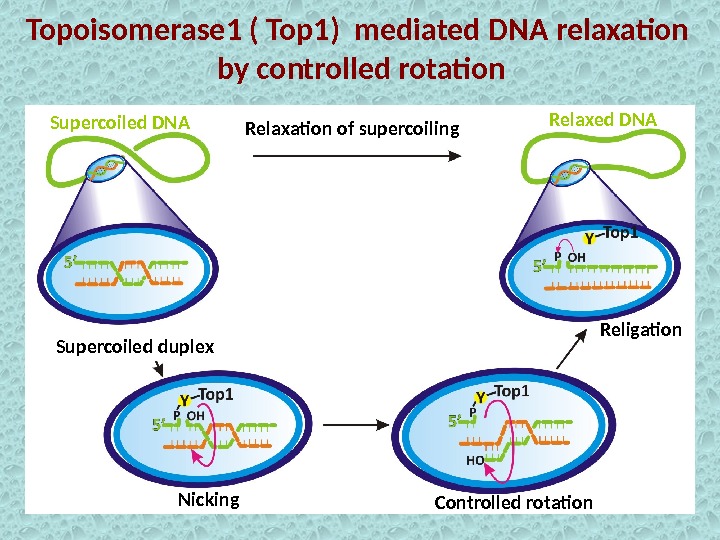
 Topoisomerase 1 ( Top 1) mediated DNA relaxation by controlled rotation Controlled rotation. Relaxation of supercoiling Religation Supercoiled duplex Nicking. Supercoiled DNA Relaxed DN
Topoisomerase 1 ( Top 1) mediated DNA relaxation by controlled rotation Controlled rotation. Relaxation of supercoiling Religation Supercoiled duplex Nicking. Supercoiled DNA Relaxed DN
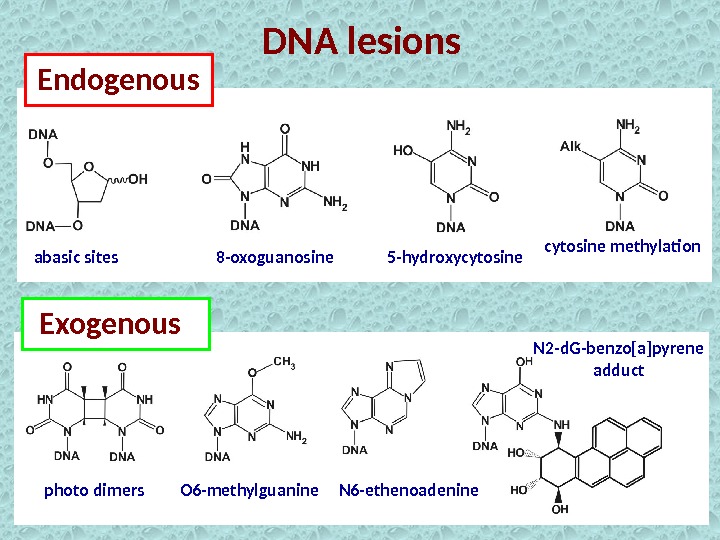
 DNA lesions Endogenous Exogenousabasic sites 8 -oxoguanosine 5 -hydroxycytosine methylation photo dimers O 6 -methylguanine N 6 -ethenoadenine N 2 -d. G-benzo[a]pyrene adduct
DNA lesions Endogenous Exogenousabasic sites 8 -oxoguanosine 5 -hydroxycytosine methylation photo dimers O 6 -methylguanine N 6 -ethenoadenine N 2 -d. G-benzo[a]pyrene adduct
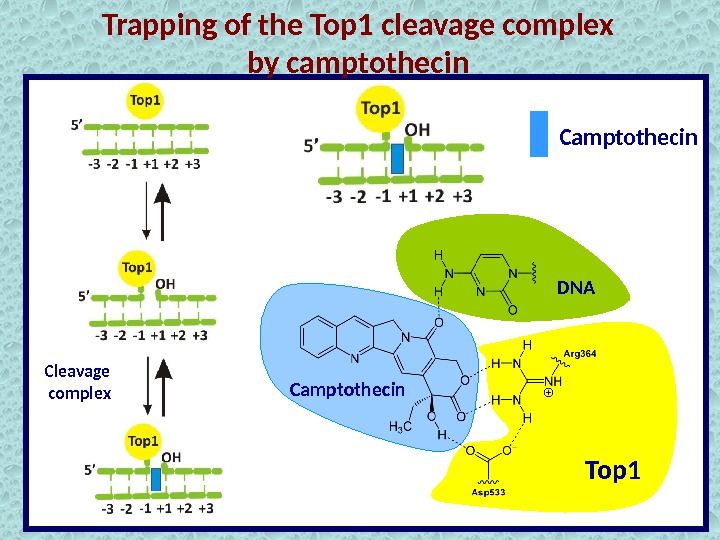
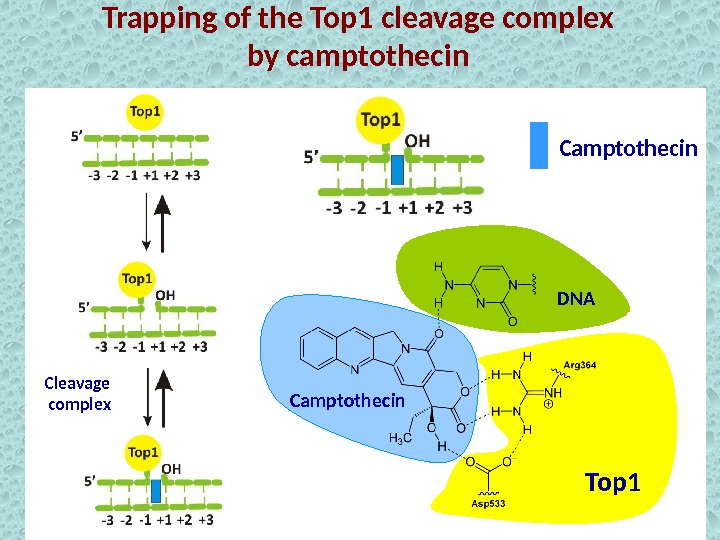
 Trapping of the Top 1 cleavage complex by camptothecin Cleavage complex Top 1 Camptothecin DN
Trapping of the Top 1 cleavage complex by camptothecin Cleavage complex Top 1 Camptothecin DN
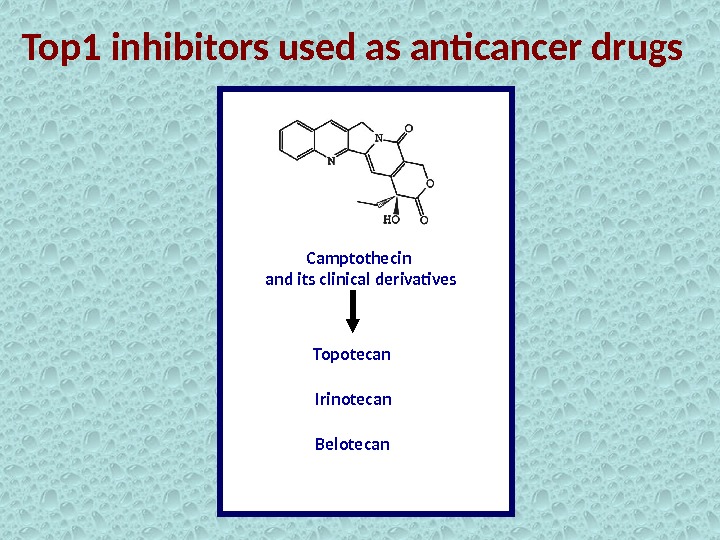
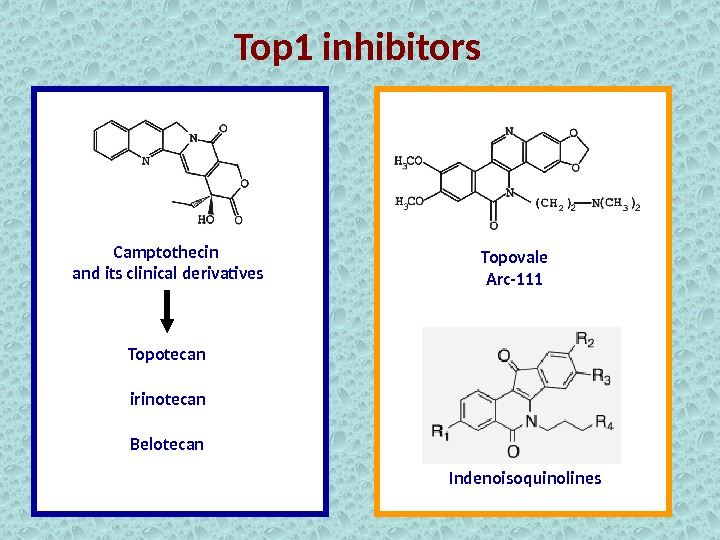
 Top 1 inhibitors used as anticancer drugs Camptothecin and its clinical derivatives Topotecan Irinotecan Belotecan
Top 1 inhibitors used as anticancer drugs Camptothecin and its clinical derivatives Topotecan Irinotecan Belotecan
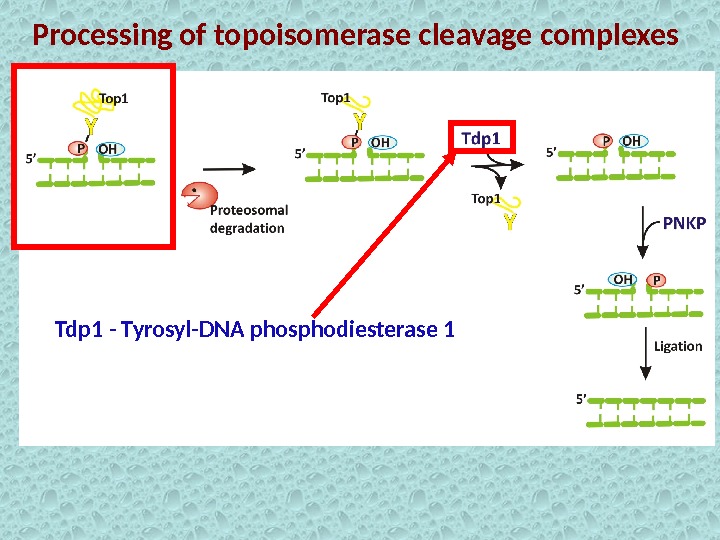
 Processing of topoisomerase cleavage complexes Tdp 1 — Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase
Processing of topoisomerase cleavage complexes Tdp 1 — Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase
 Trapping of the Top 1 cleavage complex by camptothecin Cleavage complex Top 1 Camptothecin DN
Trapping of the Top 1 cleavage complex by camptothecin Cleavage complex Top 1 Camptothecin DN
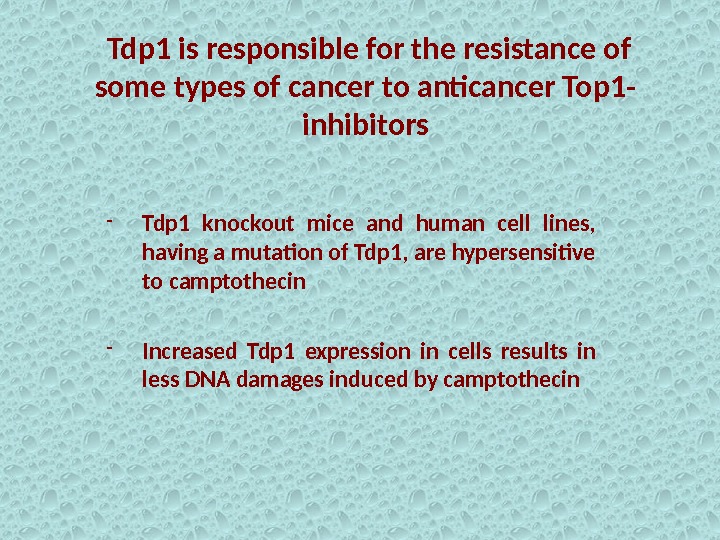
 Tdp 1 is responsible for the resistance of some types of cancer to anticancer Top 1 — inhibitors — Tdp 1 knockout mice and human cell lines, having a mutation of Tdp 1, are hypersensitive to camptothecin — Increased Tdp 1 expression in cells results in less DNA damages induced by camptothecin
Tdp 1 is responsible for the resistance of some types of cancer to anticancer Top 1 — inhibitors — Tdp 1 knockout mice and human cell lines, having a mutation of Tdp 1, are hypersensitive to camptothecin — Increased Tdp 1 expression in cells results in less DNA damages induced by camptothecin
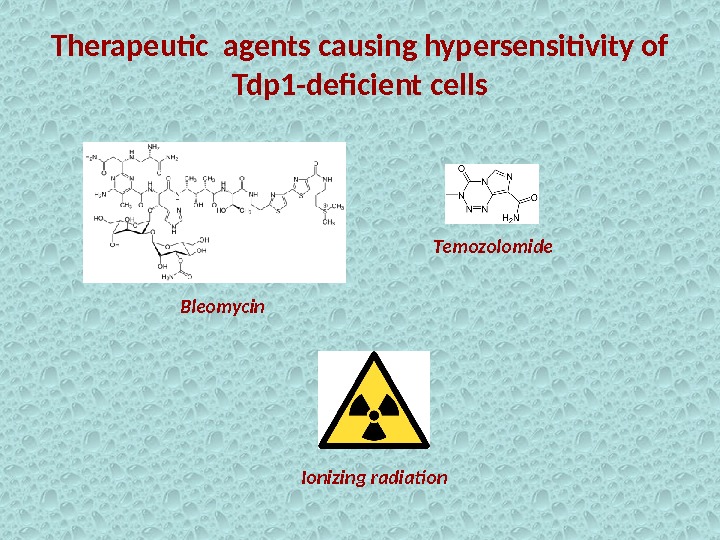
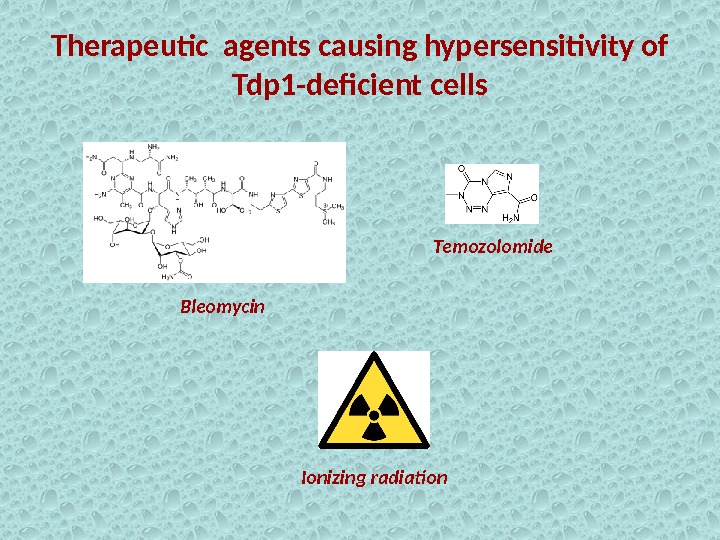
 Therapeutic agents causing hypersensitivity of Tdp 1 -deficient cells Bleomycin Temozolomide Ionizing radiation
Therapeutic agents causing hypersensitivity of Tdp 1 -deficient cells Bleomycin Temozolomide Ionizing radiation
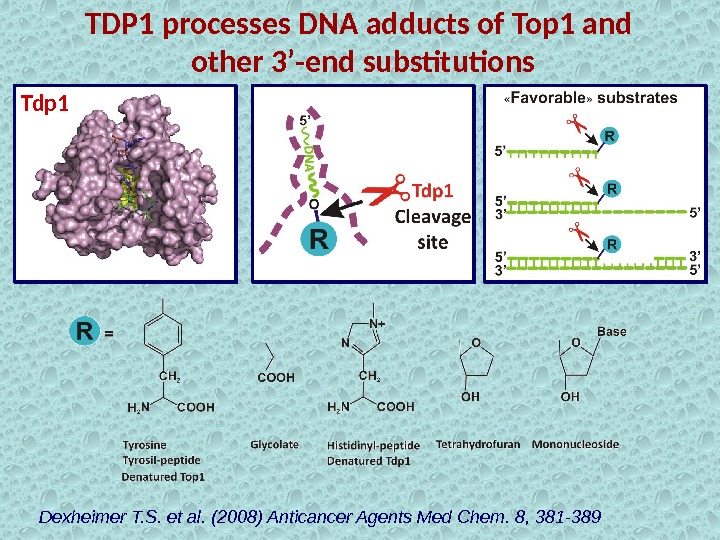
 TDP 1 processes DNA adducts of Top 1 and other 3’-end substitutions Dexheimer T. S. et al. (2008) Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 8, 381 -389 Tdp
TDP 1 processes DNA adducts of Top 1 and other 3’-end substitutions Dexheimer T. S. et al. (2008) Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 8, 381 -389 Tdp
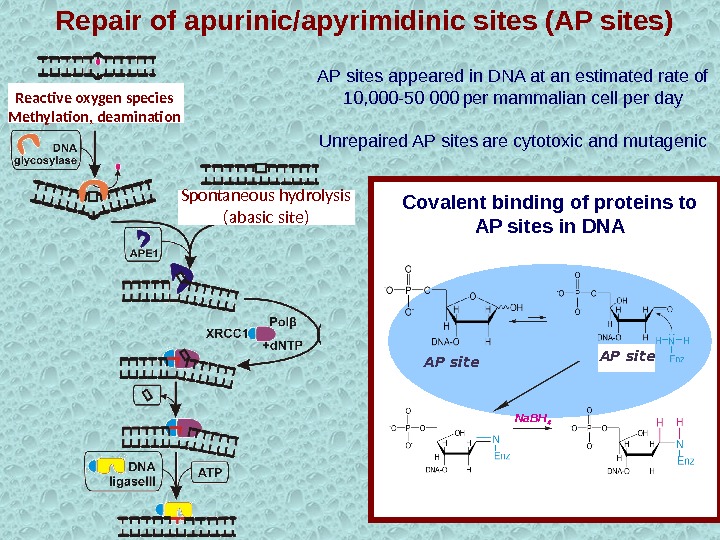
 АР sites appeared in DNA at an estimated rate of 10, 000 -50 000 per mammalian cell per day Unrepaired AP sites are cytotoxic and mutagenic Na. BH 4 АР site. Covalent binding of proteins to AP sites in DNASpontaneous hydrolysis (abasic site)Reactive oxygen species Methylation, deamination Repair of apurinic/apyrimidinic sites (AP sites)
АР sites appeared in DNA at an estimated rate of 10, 000 -50 000 per mammalian cell per day Unrepaired AP sites are cytotoxic and mutagenic Na. BH 4 АР site. Covalent binding of proteins to AP sites in DNASpontaneous hydrolysis (abasic site)Reactive oxygen species Methylation, deamination Repair of apurinic/apyrimidinic sites (AP sites)
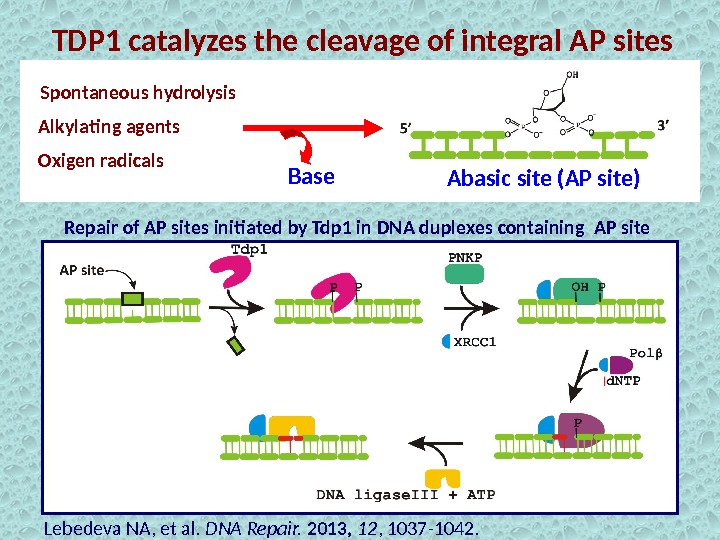
 TDP 1 catalyzes the cleavage of integral AP sites Alkylating agents Spontaneous hydrolysis Oxigen radicals Abasic site (AP site) Repair of AP sites initiated by Tdp 1 in DNA duplexes containing AP site Base Lebedeva NA, et al. DNA Repair. 2013, 12 , 1037 -1042.
TDP 1 catalyzes the cleavage of integral AP sites Alkylating agents Spontaneous hydrolysis Oxigen radicals Abasic site (AP site) Repair of AP sites initiated by Tdp 1 in DNA duplexes containing AP site Base Lebedeva NA, et al. DNA Repair. 2013, 12 , 1037 -1042.
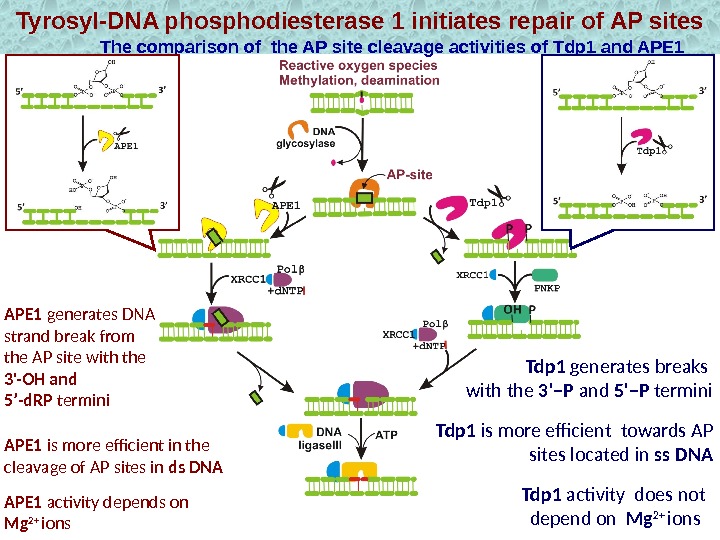
 Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 initiates repair of AP sites The comparison of the AP site cleavage activities of Tdp 1 and APE 1 Tdp 1 is more efficient towards AP sites located in ss DNA Tdp 1 generates breaks with the 3’–P and 5’–P termini. APE 1 generates DNA strand break from the AP site with the 3′-OH and 5’-d. RP termini APE 1 activity depends on Mg 2+ ions. APE 1 is more efficient in the cleavage of AP sites in ds DNA Tdp 1 activity does not depend on Mg 2+ ions
Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 initiates repair of AP sites The comparison of the AP site cleavage activities of Tdp 1 and APE 1 Tdp 1 is more efficient towards AP sites located in ss DNA Tdp 1 generates breaks with the 3’–P and 5’–P termini. APE 1 generates DNA strand break from the AP site with the 3′-OH and 5’-d. RP termini APE 1 activity depends on Mg 2+ ions. APE 1 is more efficient in the cleavage of AP sites in ds DNA Tdp 1 activity does not depend on Mg 2+ ions
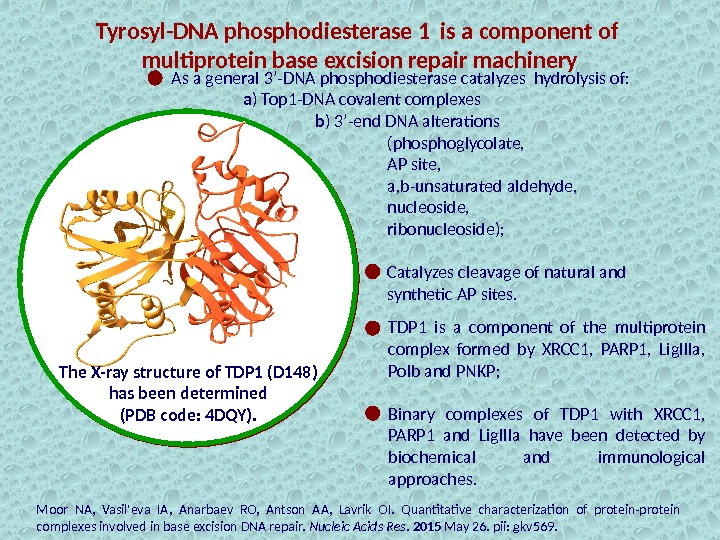
 Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 is a component of multiprotein base excision repair machinery TDP 1 is a component of the multiprotein complex formed by XRCC 1, PARP 1, Lig. IIIa, Polb and PNKP; Binary complexes of TDP 1 with XRCC 1, PARP 1 and Lig. IIIa have been detected by biochemical and immunological approaches. Moor NA, Vasil’eva IA, Anarbaev RO, Antson AA, Lavrik OI. Quantitative characterization of protein-protein complexes involved in base excision DNA repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 May 26. pii: gkv 569. The X-ray structure of TDP 1 (D 148) has been determined (PDB code: 4 DQY). As a general 3’-DNA phosphodiesterase catalyzes hydrolysis of: a ) Top 1 -DNA covalent complexes b ) 3’-end DNA alterations (phosphoglycolate, AP site, a, b-unsaturated aldehyde, nucleoside, ribonucleoside); Catalyzes cleavage of natural and synthetic AP sites.
Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 is a component of multiprotein base excision repair machinery TDP 1 is a component of the multiprotein complex formed by XRCC 1, PARP 1, Lig. IIIa, Polb and PNKP; Binary complexes of TDP 1 with XRCC 1, PARP 1 and Lig. IIIa have been detected by biochemical and immunological approaches. Moor NA, Vasil’eva IA, Anarbaev RO, Antson AA, Lavrik OI. Quantitative characterization of protein-protein complexes involved in base excision DNA repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 May 26. pii: gkv 569. The X-ray structure of TDP 1 (D 148) has been determined (PDB code: 4 DQY). As a general 3’-DNA phosphodiesterase catalyzes hydrolysis of: a ) Top 1 -DNA covalent complexes b ) 3’-end DNA alterations (phosphoglycolate, AP site, a, b-unsaturated aldehyde, nucleoside, ribonucleoside); Catalyzes cleavage of natural and synthetic AP sites.
 Defects in step catalysed by TDP 1 causes cerebellar degeneration and peripheral neuropathy typified by patients with SCAN 1 The cerebellum is a common target for disorders with DNA repair defects H 493 R mutation in Tdp 1 is responsible for the inherited disorder, spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy ( SCAN 1 )XMLR Mental retardation SCAN 1 Cerebellar degeneration MCSZ Microcephaly and seizures
Defects in step catalysed by TDP 1 causes cerebellar degeneration and peripheral neuropathy typified by patients with SCAN 1 The cerebellum is a common target for disorders with DNA repair defects H 493 R mutation in Tdp 1 is responsible for the inherited disorder, spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy ( SCAN 1 )XMLR Mental retardation SCAN 1 Cerebellar degeneration MCSZ Microcephaly and seizures
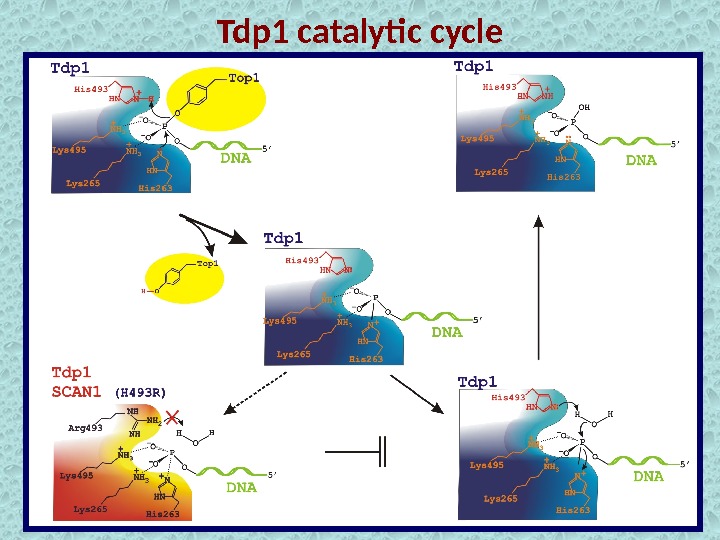
 Tdp 1 catalytic cycle
Tdp 1 catalytic cycle
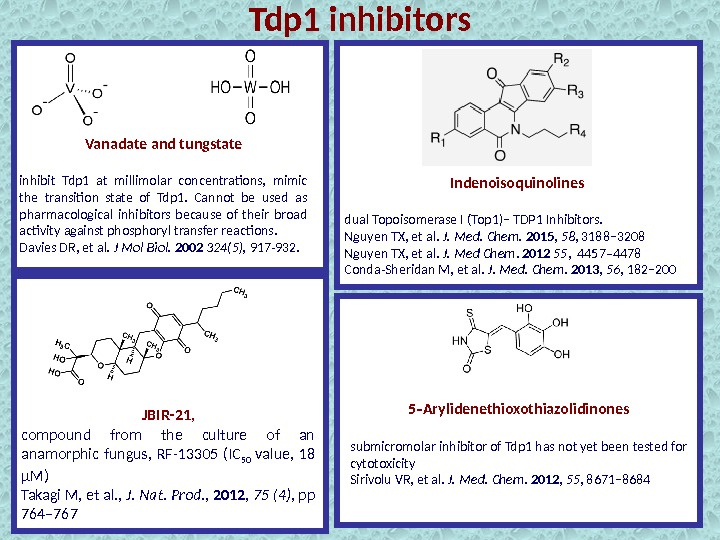
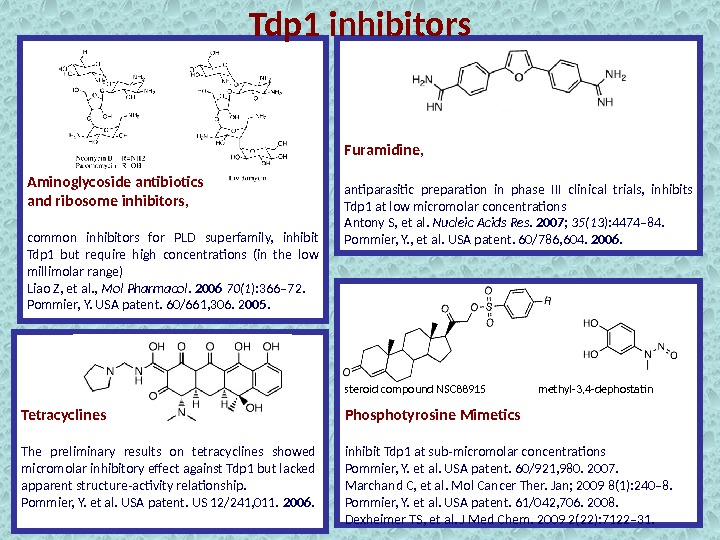
 Vanadate and tungstate inhibit Tdp 1 at millimolar concentrations, mimic the transition state of Tdp 1. Cannot be used as pharmacological inhibitors because of their broad activity against phosphoryl transfer reactions. Davies DR, et al. J Mol Biol. 2002 324(5), 917 -932. Indenoisoquinolines dual Topoisomerase I (Top 1)− TDP 1 Inhibitors. Nguyen TX, et al. J. Med. Chem. 2015 , 58 , 3188− 3208 Nguyen TX, et al. J. Med Chem. 2012 55 , 4457– 4478 Conda-Sheridan M, et al. J. Med. Chem. 2013 , 56 , 182− 200 5 Arylidenethioxothiazolidinones‑ submicromolar inhibitor of Tdp 1 has not yet been tested for cytotoxicity Sirivolu VR, et al. J. Med. Chem. 2012 , 55 , 8671− 8684 JBIR-21 , compound from the culture of an anamorphic fungus, RF-13305 (IC 50 value, 18 μM) Takagi M, et al. , J. Nat. Prod. , 2012 , 75 (4) , pp 764– 767 Tdp 1 inhibitors
Vanadate and tungstate inhibit Tdp 1 at millimolar concentrations, mimic the transition state of Tdp 1. Cannot be used as pharmacological inhibitors because of their broad activity against phosphoryl transfer reactions. Davies DR, et al. J Mol Biol. 2002 324(5), 917 -932. Indenoisoquinolines dual Topoisomerase I (Top 1)− TDP 1 Inhibitors. Nguyen TX, et al. J. Med. Chem. 2015 , 58 , 3188− 3208 Nguyen TX, et al. J. Med Chem. 2012 55 , 4457– 4478 Conda-Sheridan M, et al. J. Med. Chem. 2013 , 56 , 182− 200 5 Arylidenethioxothiazolidinones‑ submicromolar inhibitor of Tdp 1 has not yet been tested for cytotoxicity Sirivolu VR, et al. J. Med. Chem. 2012 , 55 , 8671− 8684 JBIR-21 , compound from the culture of an anamorphic fungus, RF-13305 (IC 50 value, 18 μM) Takagi M, et al. , J. Nat. Prod. , 2012 , 75 (4) , pp 764– 767 Tdp 1 inhibitors
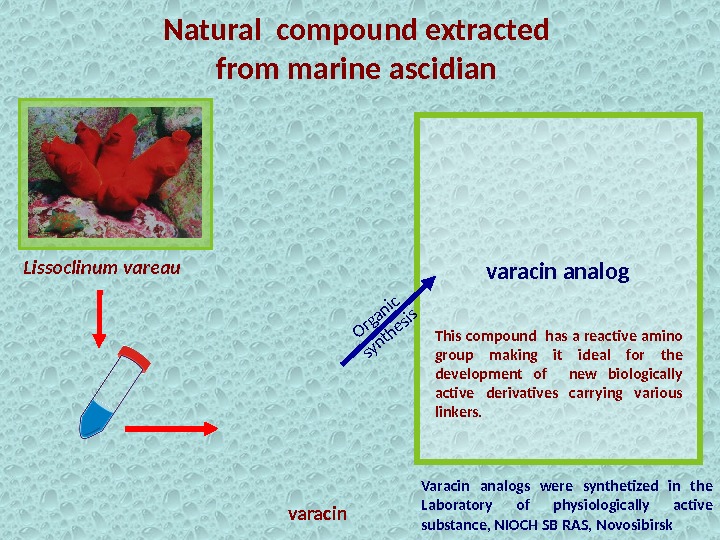
 Natural compound extracted from marine ascidian Varacin analogs were synthetized in the Laboratory of physiologically active substance, NIOCH SB RAS, Novosibirsk. Lissoclinum vareau varacin This compound has a reactive amino group making it ideal for the development of new biologically active derivatives carrying various linkers. varacin analog. Organic synthesis
Natural compound extracted from marine ascidian Varacin analogs were synthetized in the Laboratory of physiologically active substance, NIOCH SB RAS, Novosibirsk. Lissoclinum vareau varacin This compound has a reactive amino group making it ideal for the development of new biologically active derivatives carrying various linkers. varacin analog. Organic synthesis
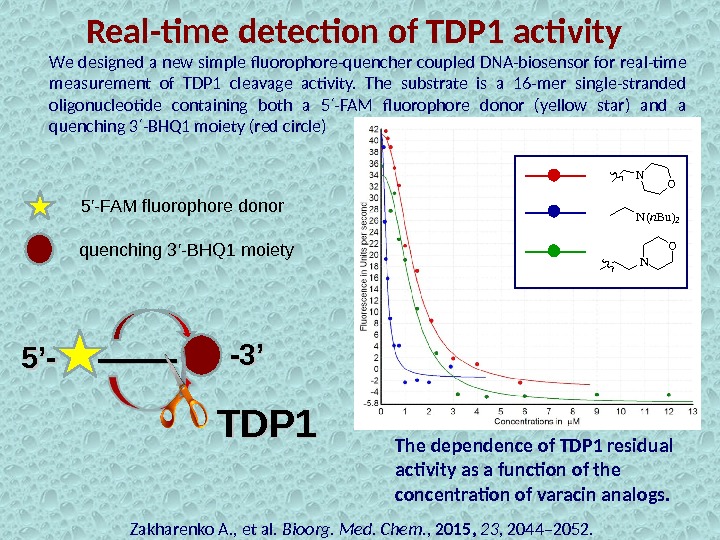
 Real-time detection of TDP 1 activity Zakharenko A. , et al. Bioorg. Med. Chem. , 2015, 23 , 2044– 2052. 5’-5’- -3’-3’We designed a new simple fluorophore-quencher coupled DNA-biosensor for real-time measurement of TDP 1 cleavage activity. The substrate is a 16 -mer single-stranded oligonucleotide containing both a 5 -FAM fluorophore donor (yellow star) and a ′ quenching 3 -BHQ 1 moiety (red circle) ′ 5′-FAM fluorophore donor quenching 3′-BHQ 1 moiety TDP 1 The dependence of TDP 1 residual activity as a function of the concentration of varacin analogs. N O N(n. Bu)2 NO
Real-time detection of TDP 1 activity Zakharenko A. , et al. Bioorg. Med. Chem. , 2015, 23 , 2044– 2052. 5’-5’- -3’-3’We designed a new simple fluorophore-quencher coupled DNA-biosensor for real-time measurement of TDP 1 cleavage activity. The substrate is a 16 -mer single-stranded oligonucleotide containing both a 5 -FAM fluorophore donor (yellow star) and a ′ quenching 3 -BHQ 1 moiety (red circle) ′ 5′-FAM fluorophore donor quenching 3′-BHQ 1 moiety TDP 1 The dependence of TDP 1 residual activity as a function of the concentration of varacin analogs. N O N(n. Bu)2 NO
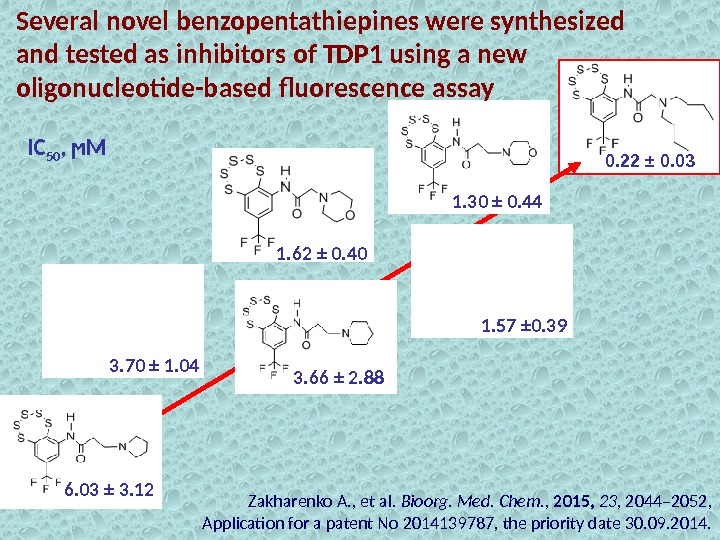
 Several novel benzopentathiepines were synthesized and tested as inhibitors of TDP 1 using a new oligonucleotide-based fluorescence assay 0. 22 ± 0. 03 1. 30 ± 0. 44 1. 57 ± 0. 391. 62 ± 0. 40 3. 70 ± 1. 04 3. 66 ± 2. 88 6. 03 ± 3. 12 IC 50 , ϻМ Zakharenko A. , et al. Bioorg. Med. Chem. , 2015, 23 , 2044– 2052, Application for a patent No 2014139787, the priority date 30. 09. 2014.
Several novel benzopentathiepines were synthesized and tested as inhibitors of TDP 1 using a new oligonucleotide-based fluorescence assay 0. 22 ± 0. 03 1. 30 ± 0. 44 1. 57 ± 0. 391. 62 ± 0. 40 3. 70 ± 1. 04 3. 66 ± 2. 88 6. 03 ± 3. 12 IC 50 , ϻМ Zakharenko A. , et al. Bioorg. Med. Chem. , 2015, 23 , 2044– 2052, Application for a patent No 2014139787, the priority date 30. 09. 2014.
 Molecular Modeling of the most potent TDP 1 inhibitor (J. Reynisson, School of Chemical Sciences, University of Auckland, New Zealand) According to the molecular modeling, the conformational flexibility of the dibutylamine group of the most effective inhibitor allows it to occupy an advantageous position for effective binding. The protein surface is rendered. The tertiary amine occupies a cleft exposed to the water environment. Red depicts a positive partial charge on the surface, blue depicts negative partial charge and grey shows neutral/lipophilic areas. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as green lines between the ligand the amino acids ASN 516 and HIS 263. 2 -(Dibutylamino)-N-(8 -(trifluoro- methyl)benzo[f][1, 2, 3, 4, 5] pentathiepin-6 -yl) acetamide IC 50 = 0, 22 µM.
Molecular Modeling of the most potent TDP 1 inhibitor (J. Reynisson, School of Chemical Sciences, University of Auckland, New Zealand) According to the molecular modeling, the conformational flexibility of the dibutylamine group of the most effective inhibitor allows it to occupy an advantageous position for effective binding. The protein surface is rendered. The tertiary amine occupies a cleft exposed to the water environment. Red depicts a positive partial charge on the surface, blue depicts negative partial charge and grey shows neutral/lipophilic areas. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as green lines between the ligand the amino acids ASN 516 and HIS 263. 2 -(Dibutylamino)-N-(8 -(trifluoro- methyl)benzo[f][1, 2, 3, 4, 5] pentathiepin-6 -yl) acetamide IC 50 = 0, 22 µM.
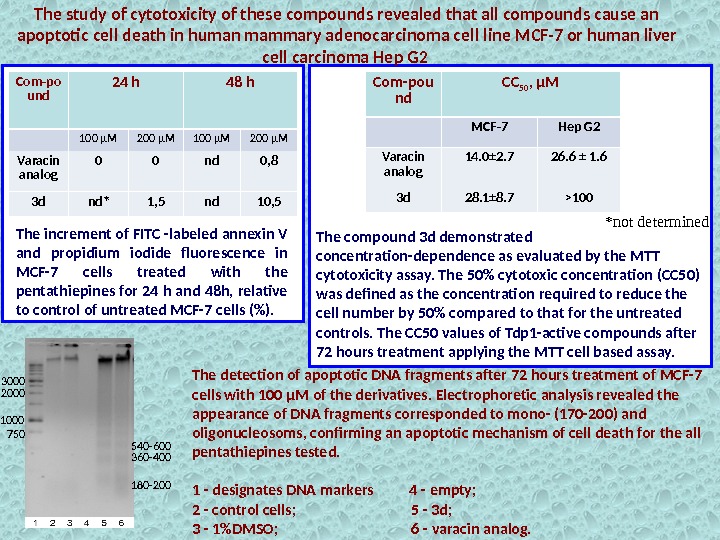
 — The cytotoxicity study of the compounds showed that they caused apoptotic cell death in human mammary adenocarcinoma cell line MCF-7 and human liver cell carcinoma Hep G 2. — Several apoptotic features were observed with light microscopy: condensation of nuclei, shrinkage of the cytoplasm, convolution of outlines and formation of apoptotic bodies. — The most potent TDP 1 inhibitor (dibutylamine derivative) with 200 μM concentration caused 10. 5% of the cells to enter apoptosis Cytotoxicity of varacin analogs
— The cytotoxicity study of the compounds showed that they caused apoptotic cell death in human mammary adenocarcinoma cell line MCF-7 and human liver cell carcinoma Hep G 2. — Several apoptotic features were observed with light microscopy: condensation of nuclei, shrinkage of the cytoplasm, convolution of outlines and formation of apoptotic bodies. — The most potent TDP 1 inhibitor (dibutylamine derivative) with 200 μM concentration caused 10. 5% of the cells to enter apoptosis Cytotoxicity of varacin analogs
 The X-ray structure of TDP 1 (D 148) Conclusions — Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiestherase 1 is the beneficial target to design the new classes of anticancer drugs. These drugs are extremely important to improve anticancer therapy by topoisomerase inhibitors. — A new class of TDP 1 benzopentathiepine inhibitors active in the low micromolar or high nanomolar range. The derivative containing dibutylamine substituent demonstrates the highest activity. Its potency can be attributed to its high lipophility and a greater conformational flexibility allowing it to effectively fit to the TDP 1 active center. — Tdp 1 inhibitors caused apoptotic cell death in cancer cell lines — The most potent TDP 1 inhibitor has the greatest potential to be developed further as an anticancer drug in combination with the established Top 1 inhibitors.
The X-ray structure of TDP 1 (D 148) Conclusions — Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiestherase 1 is the beneficial target to design the new classes of anticancer drugs. These drugs are extremely important to improve anticancer therapy by topoisomerase inhibitors. — A new class of TDP 1 benzopentathiepine inhibitors active in the low micromolar or high nanomolar range. The derivative containing dibutylamine substituent demonstrates the highest activity. Its potency can be attributed to its high lipophility and a greater conformational flexibility allowing it to effectively fit to the TDP 1 active center. — Tdp 1 inhibitors caused apoptotic cell death in cancer cell lines — The most potent TDP 1 inhibitor has the greatest potential to be developed further as an anticancer drug in combination with the established Top 1 inhibitors.
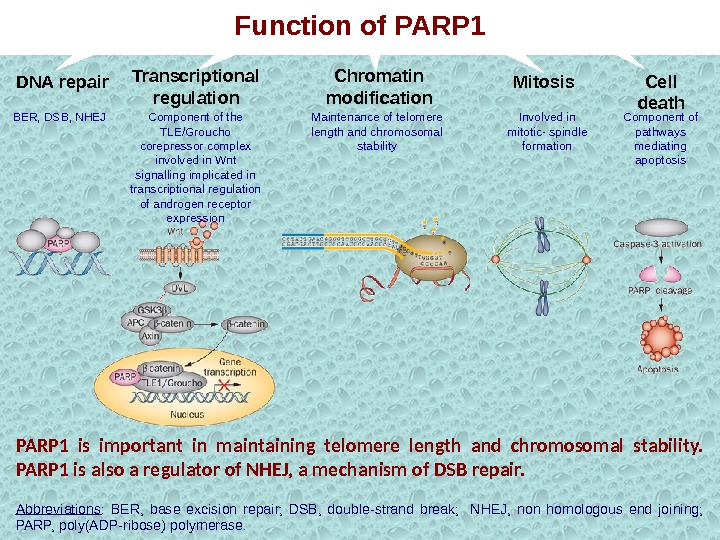
 PARP 1 is important in maintaining telomere length and chromosomal stability. PARP 1 is also a regulator of NHEJ, a mechanism of DSB repair. Abbreviations : BER, base excision repair; DSB, double-strand break; NHEJ, non homologous end joining; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. DNA repair BER, DSB, NHEJ Transcriptional regulation Component of the TLE/Groucho corepressor complex involved in Wnt signalling implicated in transcriptional regulation of androgen receptor expression Chromatin modification Mitosis Cell death Maintenance of telomere length and chromosomal stability Involved in mitotic- spindle formation Component of pathways mediating apoptosis. Function of PARP
PARP 1 is important in maintaining telomere length and chromosomal stability. PARP 1 is also a regulator of NHEJ, a mechanism of DSB repair. Abbreviations : BER, base excision repair; DSB, double-strand break; NHEJ, non homologous end joining; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. DNA repair BER, DSB, NHEJ Transcriptional regulation Component of the TLE/Groucho corepressor complex involved in Wnt signalling implicated in transcriptional regulation of androgen receptor expression Chromatin modification Mitosis Cell death Maintenance of telomere length and chromosomal stability Involved in mitotic- spindle formation Component of pathways mediating apoptosis. Function of PARP
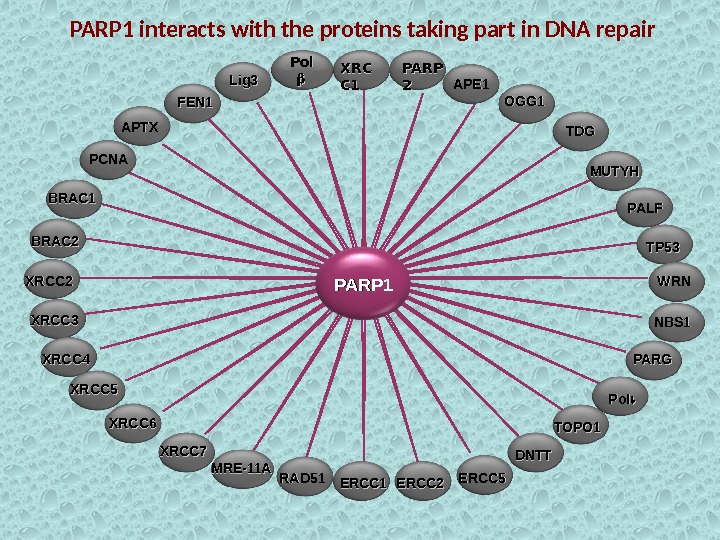
 PARP 1 Pol XRCXRC C 1 C 1 PARP 22 FEN 1 APE 1 PALFOGG 1 Lig 3 APTX PCNA MUTYHTDGTDG BRAC 1 BRAC 2 XRCC 3 XRCC 4 XRCC 5 XRCC 6 XRCC 7 RAD 51 MRE-11 A TP 53 ERCC 1 ERCC 2 ERCC 5 NBS 1 WRNWRN PARG Pol DNTT TOPO 1 PARP 1 interacts with the proteins taking part in DNA repair
PARP 1 Pol XRCXRC C 1 C 1 PARP 22 FEN 1 APE 1 PALFOGG 1 Lig 3 APTX PCNA MUTYHTDGTDG BRAC 1 BRAC 2 XRCC 3 XRCC 4 XRCC 5 XRCC 6 XRCC 7 RAD 51 MRE-11 A TP 53 ERCC 1 ERCC 2 ERCC 5 NBS 1 WRNWRN PARG Pol DNTT TOPO 1 PARP 1 interacts with the proteins taking part in DNA repair
 NAD and ATP store depletion Neurodegenerative diseases Stroke. Craniocerebral injury Ischemia and infarction. Diabetes Inflammatory. Usnic acid derivatives – selective PARP 1 inhibitors. Enhancement of the effect of anticancer agents Protective effect. PARP 1 is multifunctional protein involved in DNA damage response and a number of inflammatory processes. New antitumor drugs (PARP 1 inhibitors) are based on modified natural compounds. PARP 1 inhibition (inactivation) Hyperactivation. Moderate activation DNA repair Piperazine derivatives of betulonic acid the universal inhibitors of DNA repair enzymes Necrosis
NAD and ATP store depletion Neurodegenerative diseases Stroke. Craniocerebral injury Ischemia and infarction. Diabetes Inflammatory. Usnic acid derivatives – selective PARP 1 inhibitors. Enhancement of the effect of anticancer agents Protective effect. PARP 1 is multifunctional protein involved in DNA damage response and a number of inflammatory processes. New antitumor drugs (PARP 1 inhibitors) are based on modified natural compounds. PARP 1 inhibition (inactivation) Hyperactivation. Moderate activation DNA repair Piperazine derivatives of betulonic acid the universal inhibitors of DNA repair enzymes Necrosis
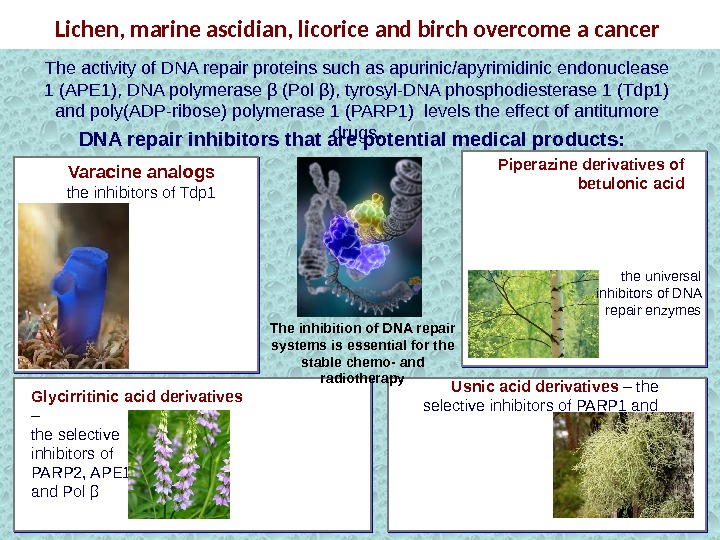
 Lichen, marine ascidian, licorice and birch overcome a cancer Piperazine derivatives of betulonic acid. Varacine analogs the inhibitors of Tdp 1 Glycirritinic acid derivatives – the selective inhibitors of PARP 2, APE 1 and Pol β Usnic acid derivatives – the selective inhibitors of PARP 1 and Tdp 1 DNA repair inhibitors that are potential medical products: The inhibition of DNA repair systems is essential for the stable chemo- and radiotherapy. The activity of DNA repair proteins such as apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (АРЕ 1), DNA polymerase β (Pol β), tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (Tdp 1) and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP 1) levels the effect of antitumore drugs. the universal inhibitors of DNA repair enzymes
Lichen, marine ascidian, licorice and birch overcome a cancer Piperazine derivatives of betulonic acid. Varacine analogs the inhibitors of Tdp 1 Glycirritinic acid derivatives – the selective inhibitors of PARP 2, APE 1 and Pol β Usnic acid derivatives – the selective inhibitors of PARP 1 and Tdp 1 DNA repair inhibitors that are potential medical products: The inhibition of DNA repair systems is essential for the stable chemo- and radiotherapy. The activity of DNA repair proteins such as apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (АРЕ 1), DNA polymerase β (Pol β), tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (Tdp 1) and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP 1) levels the effect of antitumore drugs. the universal inhibitors of DNA repair enzymes
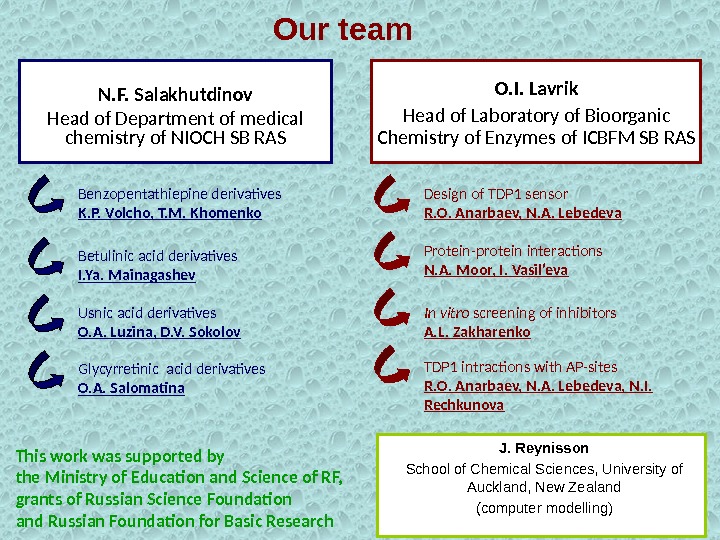
 Our team N. F. Salakhutdinov Head of Department of medical chemistry of NIOCH SB RAS Benzopentathiepine derivatives K. P. Volcho, T. M. Khomenko Usnic acid derivatives O. A. Luzina, D. V. Sokolov. Betulinic acid derivatives I. Ya. Mainagashev Glycyrretinic acid derivatives O. A. Salomatina O. I. Lavrik Head of Laboratory of Bioorganic Chemistry of Enzymes of ICBFM SB RAS Design of TDP 1 sensor R. O. Anarbaev, N. A. Lebedeva In vitro screening of inhibitors A. L. Zakharenko TDP 1 intractions with AP-sites R. O. Anarbaev, N. A. Lebedeva, N. I. Rechkunova J. Reynisson School of Chemical Sciences, University of Auckland, New Zealand (computer modelling)Protein-protein interactions N. A. Moor, I. Vasil’eva This work was supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of RF, grants of Russian Science Foundation and Russian Foundation for Basic Research
Our team N. F. Salakhutdinov Head of Department of medical chemistry of NIOCH SB RAS Benzopentathiepine derivatives K. P. Volcho, T. M. Khomenko Usnic acid derivatives O. A. Luzina, D. V. Sokolov. Betulinic acid derivatives I. Ya. Mainagashev Glycyrretinic acid derivatives O. A. Salomatina O. I. Lavrik Head of Laboratory of Bioorganic Chemistry of Enzymes of ICBFM SB RAS Design of TDP 1 sensor R. O. Anarbaev, N. A. Lebedeva In vitro screening of inhibitors A. L. Zakharenko TDP 1 intractions with AP-sites R. O. Anarbaev, N. A. Lebedeva, N. I. Rechkunova J. Reynisson School of Chemical Sciences, University of Auckland, New Zealand (computer modelling)Protein-protein interactions N. A. Moor, I. Vasil’eva This work was supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of RF, grants of Russian Science Foundation and Russian Foundation for Basic Research
 Thank you for your attention!
Thank you for your attention!
 Therapeutic agents causing hypersensitivity of Tdp 1 -deficient cells Bleomycin Temozolomide Ionizing radiation
Therapeutic agents causing hypersensitivity of Tdp 1 -deficient cells Bleomycin Temozolomide Ionizing radiation
 Top 1 inhibitors Camptothecin and its clinical derivatives Topotecan irinotecan Belotecan Topovale Arc-111 Indenoisoquinolines
Top 1 inhibitors Camptothecin and its clinical derivatives Topotecan irinotecan Belotecan Topovale Arc-111 Indenoisoquinolines
 The increment of FITC -labeled annexin V and propidium iodide fluorescence in MCF-7 cells treated with the pentathiepines for 24 h and 48 h, relative to control of untreated MCF-7 cells (%). *not determined. Com-po und 24 h 48 h 100 µM 200 µM Varacin analog 0 0 nd 0, 8 3 d nd* 1, 5 nd 10, 5 The study of cytotoxicity of these compounds revealed that all compounds cause an apoptotic cell death in human mammary adenocarcinoma cell line MCF-7 or human liver cell carcinoma Hep G 2 Com-pou nd CC 50 , µM MCF-7 Hep G 2 Varacin analog 14. 0± 2. 7 26. 6 ± 1. 6 3 d 28. 1± 8. 7 >100 The compound 3 d demonstrated concentration-dependence as evaluated by the MTT cytotoxicity assay. The 50% cytotoxic concentration (CC 50) was defined as the concentration required to reduce the cell number by 50% compared to that for the untreated controls. The CC 50 values of Tdp 1 -active compounds after 72 hours treatment applying the MTT cell based assay. The detection of apoptotic DNA fragments after 72 hours treatment of MCF-7 cells with 100 μM of the derivatives. Electrophoretic analysis revealed the appearance of DNA fragments corresponded to mono- (170 -200) and oligonucleosoms, confirming an apoptotic mechanism of cell death for the all pentathiepines tested. 1 — designates DNA markers 4 — empty; 2 — control cells; 5 — 3 d; 3 — 1%DMSO; 6 — varacin analog. 750 1000 2000 3000 180 -200360 -400540 —
The increment of FITC -labeled annexin V and propidium iodide fluorescence in MCF-7 cells treated with the pentathiepines for 24 h and 48 h, relative to control of untreated MCF-7 cells (%). *not determined. Com-po und 24 h 48 h 100 µM 200 µM Varacin analog 0 0 nd 0, 8 3 d nd* 1, 5 nd 10, 5 The study of cytotoxicity of these compounds revealed that all compounds cause an apoptotic cell death in human mammary adenocarcinoma cell line MCF-7 or human liver cell carcinoma Hep G 2 Com-pou nd CC 50 , µM MCF-7 Hep G 2 Varacin analog 14. 0± 2. 7 26. 6 ± 1. 6 3 d 28. 1± 8. 7 >100 The compound 3 d demonstrated concentration-dependence as evaluated by the MTT cytotoxicity assay. The 50% cytotoxic concentration (CC 50) was defined as the concentration required to reduce the cell number by 50% compared to that for the untreated controls. The CC 50 values of Tdp 1 -active compounds after 72 hours treatment applying the MTT cell based assay. The detection of apoptotic DNA fragments after 72 hours treatment of MCF-7 cells with 100 μM of the derivatives. Electrophoretic analysis revealed the appearance of DNA fragments corresponded to mono- (170 -200) and oligonucleosoms, confirming an apoptotic mechanism of cell death for the all pentathiepines tested. 1 — designates DNA markers 4 — empty; 2 — control cells; 5 — 3 d; 3 — 1%DMSO; 6 — varacin analog. 750 1000 2000 3000 180 -200360 -400540 —
 Tdp 1 inhibitors Aminoglycoside antibiotics and ribosome inhibitors, common inhibitors for PLD superfamily, inhibit Tdp 1 but require high concentrations (in the low millimolar range) Liao Z, et al. , Mol Pharmacol. 2006 70(1 ): 366– 72. Pommier, Y. USA patent. 60/661, 306. 2 005. Furamidine, antiparasitic preparation in phase III clinical trials, inhibits Tdp 1 at low micromolar concentrations Antony S, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 ; 35(13 ): 4474– 84. Pommier, Y. , et al. USA patent. 60/786, 604. 2006. Tetracyclines The preliminary results on tetracyclines showed micromolar inhibitory effect against Tdp 1 but lacked apparent structure-activity relationship. Pommier, Y. et al. USA patent. US 12/241, 011. 2006. Phosphotyrosine Mimetics inhibit Tdp 1 at sub-micromolar concentrations Pommier, Y. et al. USA patent. 60/921, 980. 2007. Marchand C, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. Jan; 2009 8(1): 240– 8. Pommier, Y. et al. USA patent. 61/042, 706. 2008. Dexheimer TS, et al. J Med Chem. 2009 2(22): 7122– 31. methyl-3, 4 -dephostatinsteroid compound NS
Tdp 1 inhibitors Aminoglycoside antibiotics and ribosome inhibitors, common inhibitors for PLD superfamily, inhibit Tdp 1 but require high concentrations (in the low millimolar range) Liao Z, et al. , Mol Pharmacol. 2006 70(1 ): 366– 72. Pommier, Y. USA patent. 60/661, 306. 2 005. Furamidine, antiparasitic preparation in phase III clinical trials, inhibits Tdp 1 at low micromolar concentrations Antony S, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 ; 35(13 ): 4474– 84. Pommier, Y. , et al. USA patent. 60/786, 604. 2006. Tetracyclines The preliminary results on tetracyclines showed micromolar inhibitory effect against Tdp 1 but lacked apparent structure-activity relationship. Pommier, Y. et al. USA patent. US 12/241, 011. 2006. Phosphotyrosine Mimetics inhibit Tdp 1 at sub-micromolar concentrations Pommier, Y. et al. USA patent. 60/921, 980. 2007. Marchand C, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. Jan; 2009 8(1): 240– 8. Pommier, Y. et al. USA patent. 61/042, 706. 2008. Dexheimer TS, et al. J Med Chem. 2009 2(22): 7122– 31. methyl-3, 4 -dephostatinsteroid compound NS

