2_lesson_respiratory_system.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 22
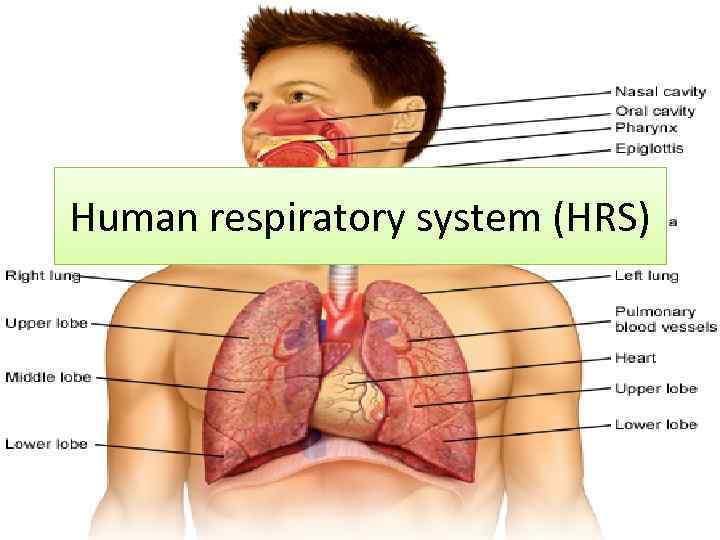 Human respiratory system (HRS)
Human respiratory system (HRS)
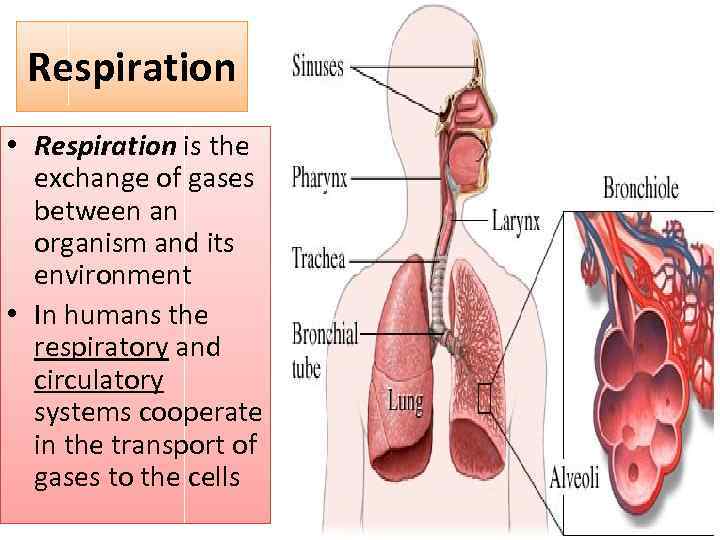 Respiration • Respiration is the exchange of gases between an organism and its environment • In humans the respiratory and circulatory systems cooperate in the transport of gases to the cells
Respiration • Respiration is the exchange of gases between an organism and its environment • In humans the respiratory and circulatory systems cooperate in the transport of gases to the cells
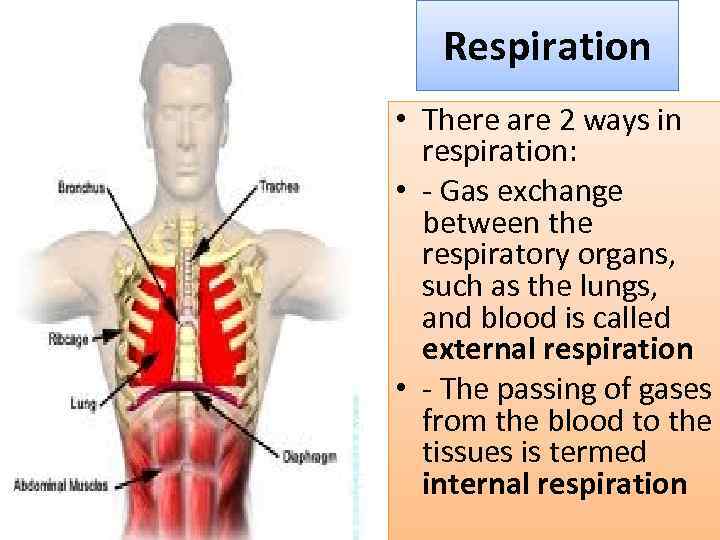 Respiration • There are 2 ways in respiration: • - Gas exchange between the respiratory organs, such as the lungs, and blood is called external respiration • - The passing of gases from the blood to the tissues is termed internal respiration
Respiration • There are 2 ways in respiration: • - Gas exchange between the respiratory organs, such as the lungs, and blood is called external respiration • - The passing of gases from the blood to the tissues is termed internal respiration
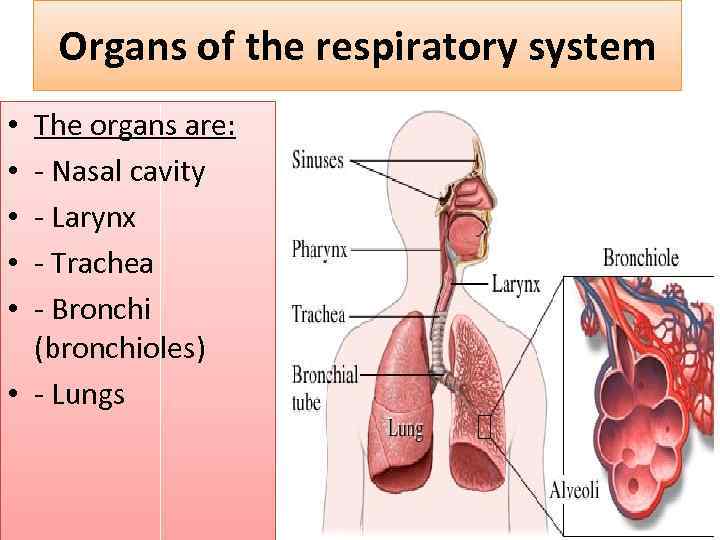 Organs of the respiratory system The organs are: - Nasal cavity - Larynx - Trachea - Bronchi (bronchioles) • - Lungs • • •
Organs of the respiratory system The organs are: - Nasal cavity - Larynx - Trachea - Bronchi (bronchioles) • - Lungs • • •
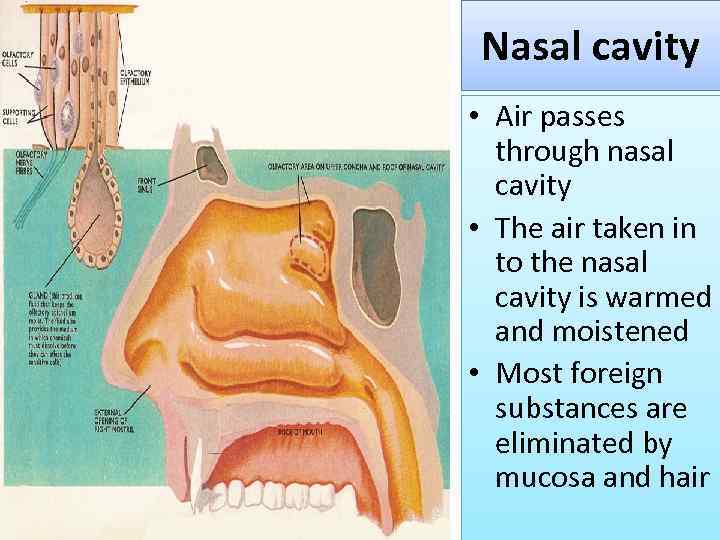 Nasal cavity • Air passes through nasal cavity • The air taken in to the nasal cavity is warmed and moistened • Most foreign substances are eliminated by mucosa and hair
Nasal cavity • Air passes through nasal cavity • The air taken in to the nasal cavity is warmed and moistened • Most foreign substances are eliminated by mucosa and hair
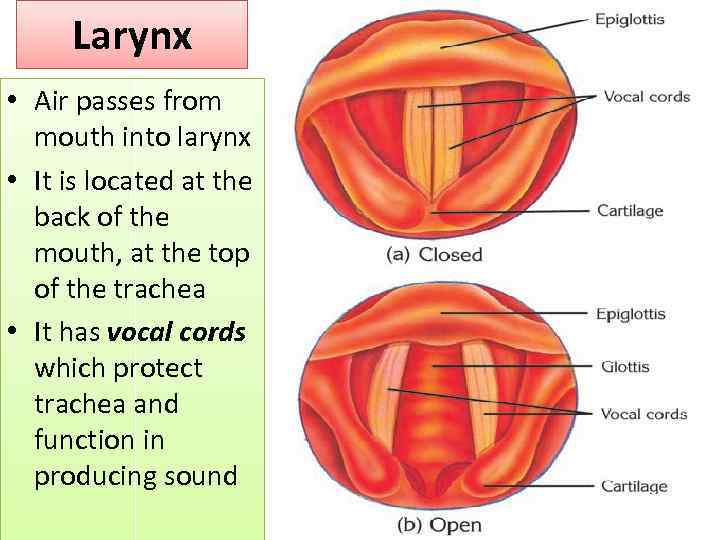 Larynx • Air passes from mouth into larynx • It is located at the back of the mouth, at the top of the trachea • It has vocal cords which protect trachea and function in producing sound
Larynx • Air passes from mouth into larynx • It is located at the back of the mouth, at the top of the trachea • It has vocal cords which protect trachea and function in producing sound
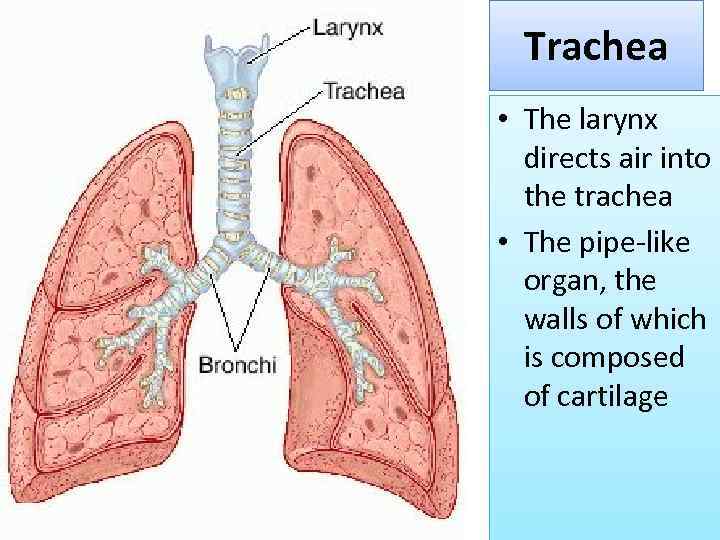 Trachea • The larynx directs air into the trachea • The pipe-like organ, the walls of which is composed of cartilage
Trachea • The larynx directs air into the trachea • The pipe-like organ, the walls of which is composed of cartilage
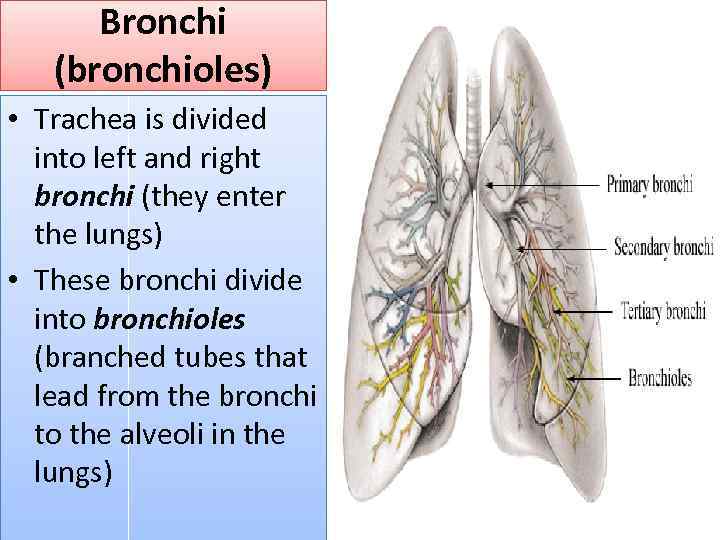 Bronchi (bronchioles) • Trachea is divided into left and right bronchi (they enter the lungs) • These bronchi divide into bronchioles (branched tubes that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli in the lungs)
Bronchi (bronchioles) • Trachea is divided into left and right bronchi (they enter the lungs) • These bronchi divide into bronchioles (branched tubes that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli in the lungs)
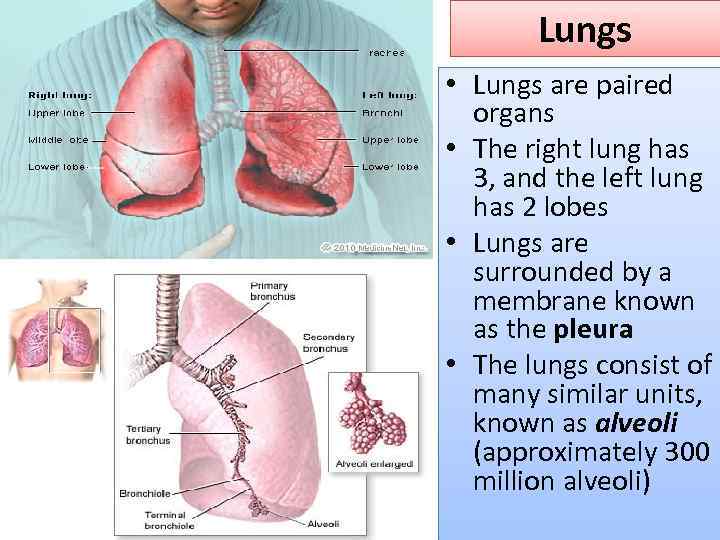 Lungs • Lungs are paired organs • The right lung has 3, and the left lung has 2 lobes • Lungs are surrounded by a membrane known as the pleura • The lungs consist of many similar units, known as alveoli (approximately 300 million alveoli)
Lungs • Lungs are paired organs • The right lung has 3, and the left lung has 2 lobes • Lungs are surrounded by a membrane known as the pleura • The lungs consist of many similar units, known as alveoli (approximately 300 million alveoli)
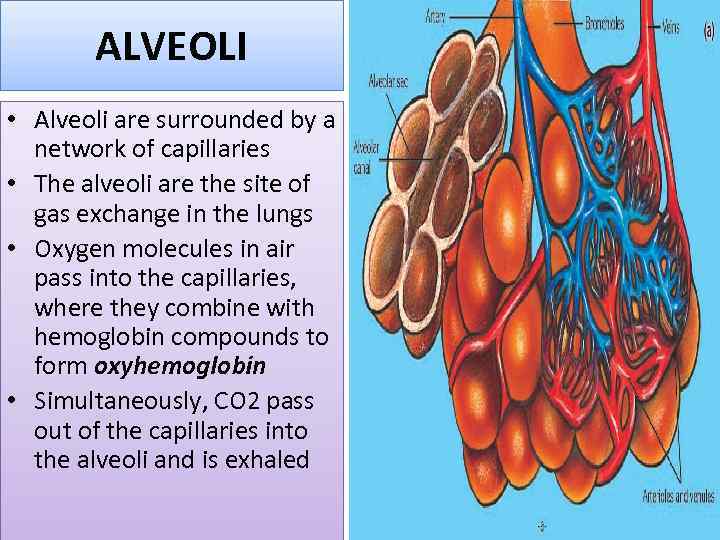 ALVEOLI • Alveoli are surrounded by a network of capillaries • The alveoli are the site of gas exchange in the lungs • Oxygen molecules in air pass into the capillaries, where they combine with hemoglobin compounds to form oxyhemoglobin • Simultaneously, CO 2 pass out of the capillaries into the alveoli and is exhaled
ALVEOLI • Alveoli are surrounded by a network of capillaries • The alveoli are the site of gas exchange in the lungs • Oxygen molecules in air pass into the capillaries, where they combine with hemoglobin compounds to form oxyhemoglobin • Simultaneously, CO 2 pass out of the capillaries into the alveoli and is exhaled
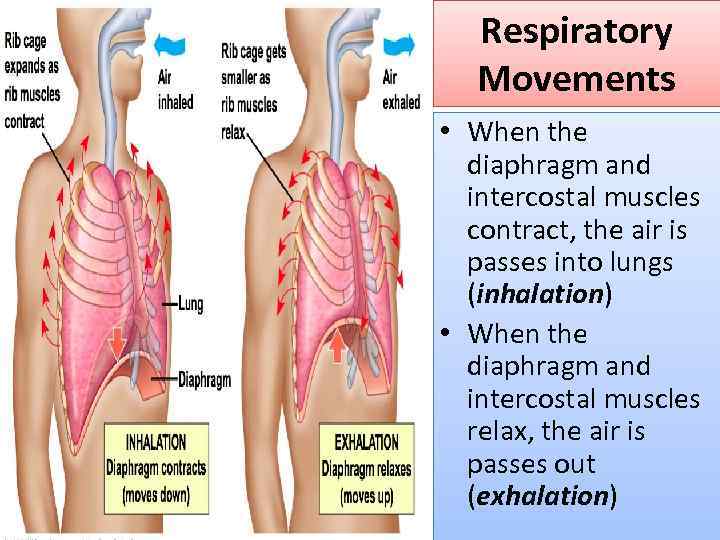 Respiratory Movements • When the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, the air is passes into lungs (inhalation) • When the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, the air is passes out (exhalation)
Respiratory Movements • When the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, the air is passes into lungs (inhalation) • When the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, the air is passes out (exhalation)
 Respiratory air volume • When we breathe, the amount of air moved in and out with each breath is called the tidal volume (normal is 500 m. L) • The maximum volume of air that can be moved in and out during a single breath is called the vital capacity
Respiratory air volume • When we breathe, the amount of air moved in and out with each breath is called the tidal volume (normal is 500 m. L) • The maximum volume of air that can be moved in and out during a single breath is called the vital capacity
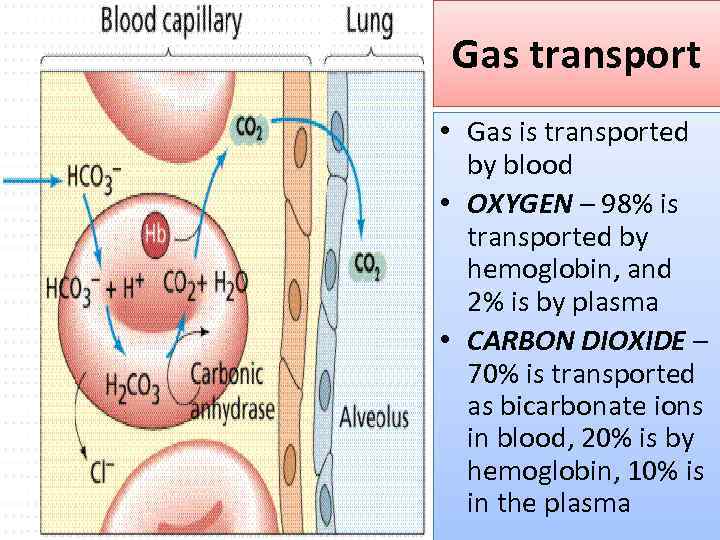 Gas transport • Gas is transported by blood • OXYGEN – 98% is transported by hemoglobin, and 2% is by plasma • CARBON DIOXIDE – 70% is transported as bicarbonate ions in blood, 20% is by hemoglobin, 10% is in the plasma
Gas transport • Gas is transported by blood • OXYGEN – 98% is transported by hemoglobin, and 2% is by plasma • CARBON DIOXIDE – 70% is transported as bicarbonate ions in blood, 20% is by hemoglobin, 10% is in the plasma
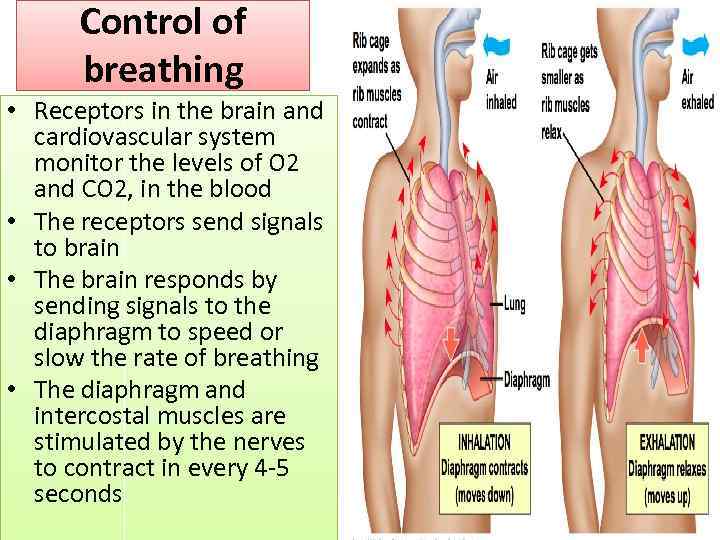 Control of breathing • Receptors in the brain and cardiovascular system monitor the levels of O 2 and CO 2, in the blood • The receptors send signals to brain • The brain responds by sending signals to the diaphragm to speed or slow the rate of breathing • The diaphragm and intercostal muscles are stimulated by the nerves to contract in every 4 -5 seconds
Control of breathing • Receptors in the brain and cardiovascular system monitor the levels of O 2 and CO 2, in the blood • The receptors send signals to brain • The brain responds by sending signals to the diaphragm to speed or slow the rate of breathing • The diaphragm and intercostal muscles are stimulated by the nerves to contract in every 4 -5 seconds
 Respiratory Diseases • • The diseases of the human respiratory system are: - Asthma - Emphysema - Lung cancer
Respiratory Diseases • • The diseases of the human respiratory system are: - Asthma - Emphysema - Lung cancer
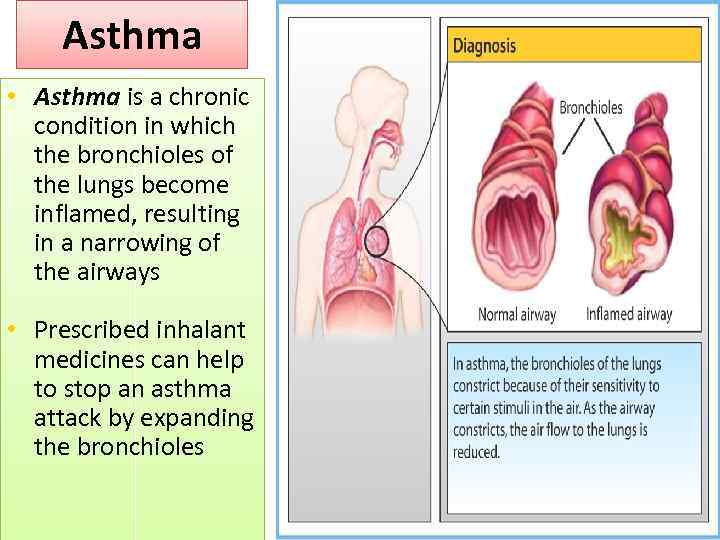 Asthma • Asthma is a chronic condition in which the bronchioles of the lungs become inflamed, resulting in a narrowing of the airways • Prescribed inhalant medicines can help to stop an asthma attack by expanding the bronchioles
Asthma • Asthma is a chronic condition in which the bronchioles of the lungs become inflamed, resulting in a narrowing of the airways • Prescribed inhalant medicines can help to stop an asthma attack by expanding the bronchioles
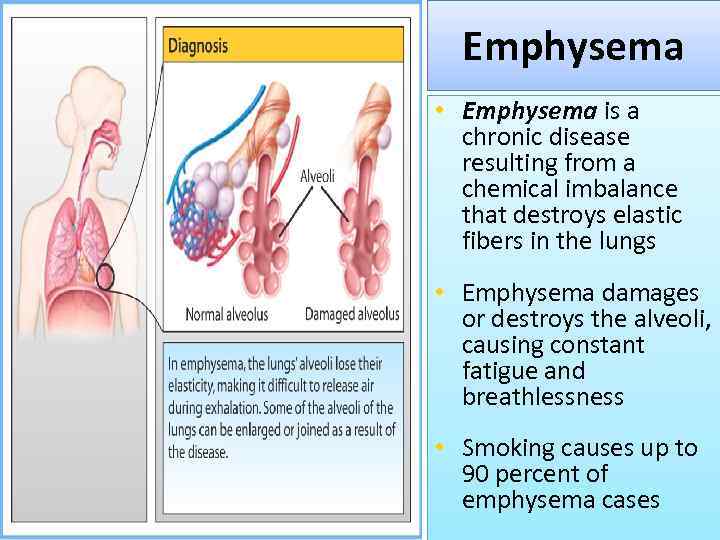 Emphysema • Emphysema is a chronic disease resulting from a chemical imbalance that destroys elastic fibers in the lungs • Emphysema damages or destroys the alveoli, causing constant fatigue and breathlessness • Smoking causes up to 90 percent of emphysema cases
Emphysema • Emphysema is a chronic disease resulting from a chemical imbalance that destroys elastic fibers in the lungs • Emphysema damages or destroys the alveoli, causing constant fatigue and breathlessness • Smoking causes up to 90 percent of emphysema cases
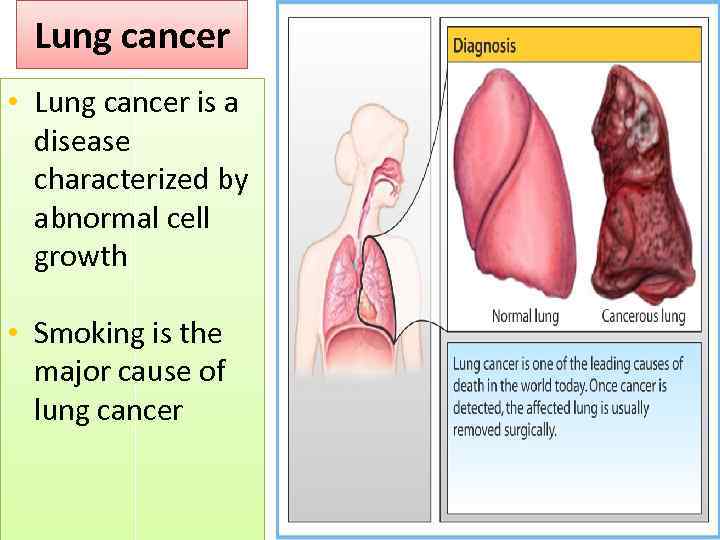 Lung cancer • Lung cancer is a disease characterized by abnormal cell growth • Smoking is the major cause of lung cancer
Lung cancer • Lung cancer is a disease characterized by abnormal cell growth • Smoking is the major cause of lung cancer
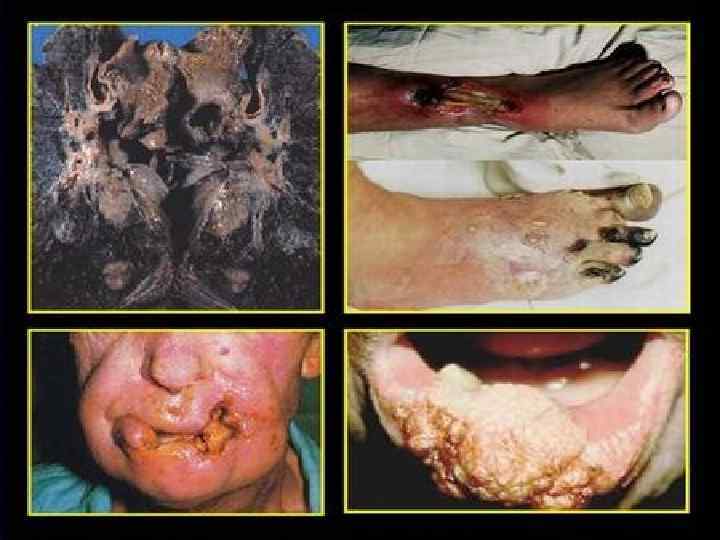
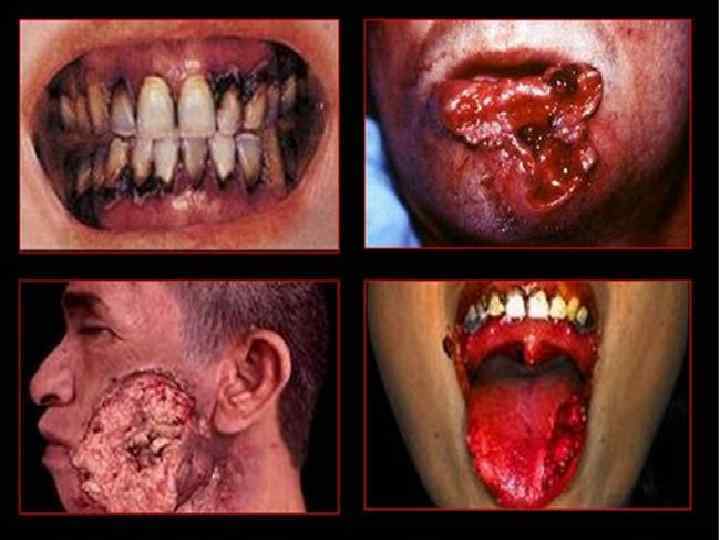
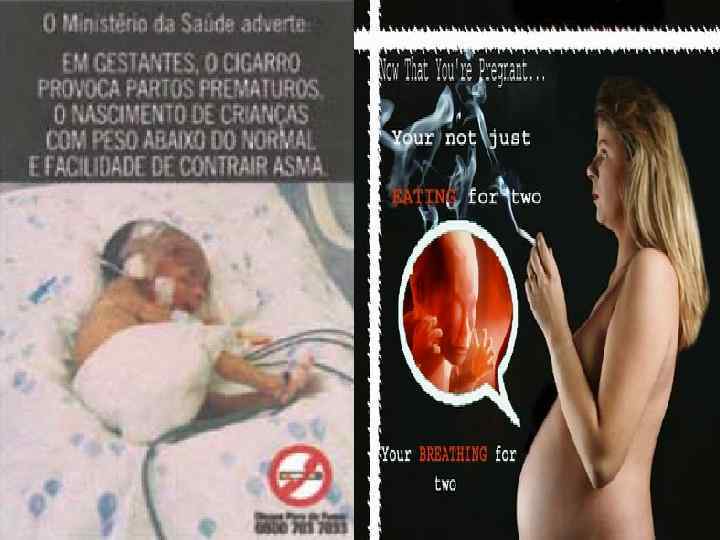
 Smoking • Smoking causes mainly problems with respiratory system, beginning by throat cancer, lung cancer, emphysema, osteoporosis, problems with blood and blood vessels, heart attack and etc
Smoking • Smoking causes mainly problems with respiratory system, beginning by throat cancer, lung cancer, emphysema, osteoporosis, problems with blood and blood vessels, heart attack and etc