187efa53c804e9f4166f009b226bc2a1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

Human Resources Line of Business Performance Reference Model (PRM) Presentation to IT Performance Management Council July 20, 2006 Report Tile UNITED STATES OFFICE OF PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT 1
Agenda § HR Line of Business (HR LOB) Background § HR LOB Enterprise Architecture Overview § The HR LOB PRM v 1 § Approach § Value § Workshop Methodology § Results § Lessons Learned § Questions 2

HR LOB Background 3

HR LOB Vision & Goals Vision: Governmentwide, modern, cost-effective, standardized, and interoperable HR solutions providing common, core functionality to support the strategic management of human capital. Goals: 1. Improve the governmentwide strategic management of human capital 2. Achieve or increase operational efficiencies in the acquisition, development, implementation and operation of human resources management systems 3. Achieve or increase cost savings/avoidance from human resource solution activities 4. Improved Customer Service 4

HR LOB – Two Dimensions 1. Common Solutions 1. Address distinct business improvements that have a direct impact on HR LOB performance goals 2. Achieve economies of scale 3. Utilize shared service centers 2. Standardization 1. Solutions are developed through a set of common and repeatable processes and tools that are compliant with the Federal Enterprise Architecture (FEA) guidance 5

Concept of Operations (CONOPS) § The Shared Service Centers will take a phased approach to delivering HR services § At a minimum, all service centers will offer the same common, core functionalities § The solutions that operate at these service centers will be evaluated and recommended by a multi-agency steering committee that stresses scalability, interoperability, and portability § Shared Service Center solutions can be COTS or GOTS and will be selected on a competitive basis § Agencies will have choices when they shop around for the service centers that best meet their needs § The shared service centers will leverage “plug and play” architecture concepts 6

Shared Service Centers § September 2004 five agencies submitted proposals to OMB to be HR LOB Shared Service Centers (SSCs) § February 2005 OMB announced five “candidate” HR LOB SSCs § March 2005 OPM established a multi agency Technical Panel and Advisory Board to evaluate the SSC candidates from an HR perspective § August 2005 OPM and OMB announced the final selection of 5 HR LOB SSCs § October 2005 a Shared Service Center Advisory Council (SSCAC) consisting of five HR LOB SSCs and four Payroll Providers was established § Additional Federal and Private Sector SSCs may be announced in FY 2006 7
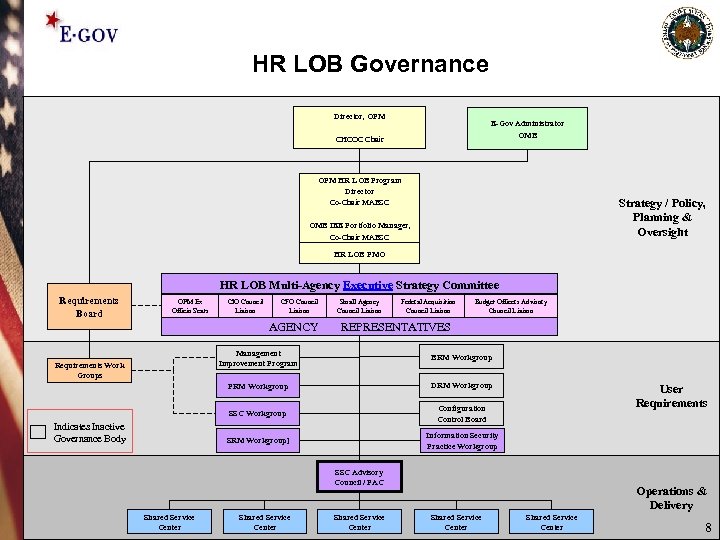
HR LOB Governance Director, OPM E-Gov Administrator OMB CHCOC Chair OPM HR LOB Program Director Co-Chair MAESC Strategy / Policy, Planning & Oversight OMB IEE Portfolio Manager, Co-Chair MAESC HR LOB PMO HR LOB Multi-Agency Executive Strategy Committee Requirements Board OPM Ex Officio Seats CIO Council Liaison CFO Council Liaison AGENCY Small Agency Council Liaison Federal Acquisition Council Liaison Budget Officers Advisory Council Liaison REPRESENTATIVES Management Improvement Program DRM Workgroup SSC Workgroup Configuration Control Board SRM Workgroup] Indicates Inactive Governance Body BRM Workgroup PRM Workgroup Requirements Work Groups Information Security Practice Workgroup User Requirements SSC Advisory Council / PAC Shared Service Center Operations & Delivery Shared Service Center 8

HR LOB Enterprise Architecture 9

Results of the HR LOB EA approach 1. Agency consensus in a variety of areas regarding government-wide view 2. Common vocabulary for processes and activities 3. Management tools 1. Improved decision making 2. Basis for standardization and common solutions 3. Enhanced communication 4. Consistent with OMB’s FEA rationale 1. Alignment 2. Integration 3. Change 4. Time to Market 5. Convergence 10
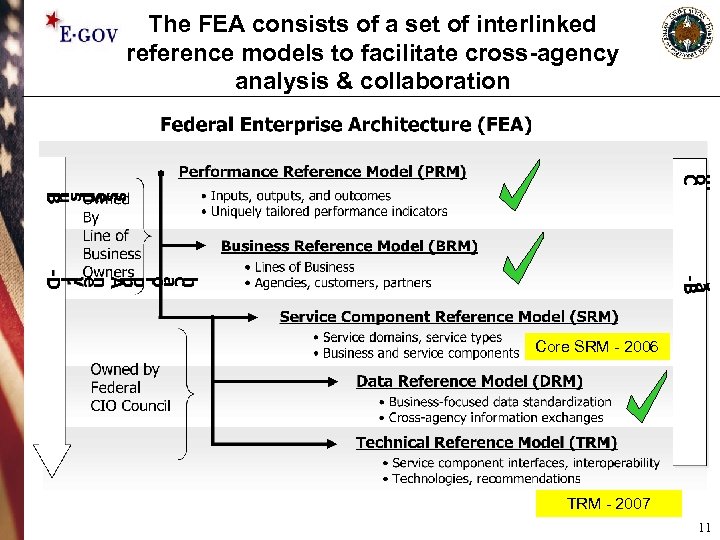
The FEA consists of a set of interlinked reference models to facilitate cross-agency analysis & collaboration Core SRM - 2006 TRM - 2007 11
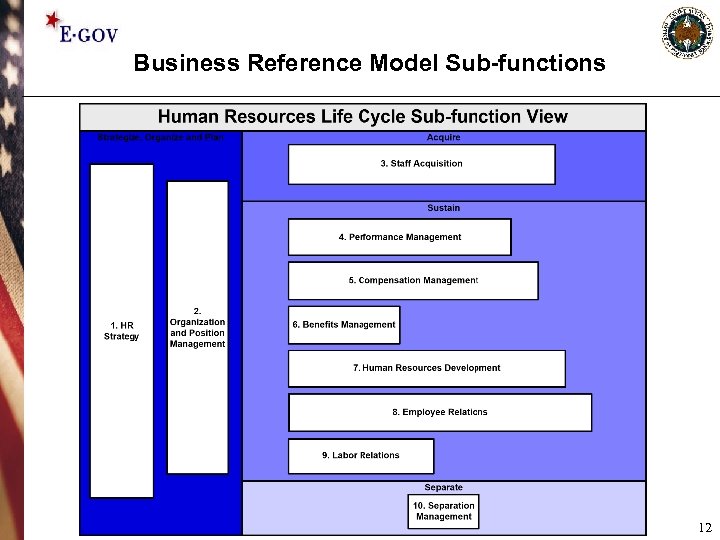
Business Reference Model Sub-functions 12

Target Requirements The HR LOB Target Requirements: § Focus on the common government-wide HR processes that may be delivered by shared service centers § Utilize the HR LOB Business Reference Model (BRM) for processes and activities that have been identified to move to SSCs § Identify a common view of the role of the SSC in Federal HR 13
DRM The HR LOB Data Reference Model (DRM): § Identifies data needed to execute BRM processes § Depicted at the conceptual and logical level – does not describe how the data will be implemented § Enables the government to communicate more accurately and efficiently about the purpose, content and structure of human resources data § Enables standardization for data descriptions, data context, and for data sharing § Reflects a future target 14

SRM The HR LOB Service Component Reference Model (SRM): § Uses FEA guidance to identify service components – potentially reusable self-contained business capabilities § Organizes service components by service type and service domain using FEA as a guide § Proposes a common view of service delivery § Identifies generic enabling technology required to deliver service components to customers 15

HR LOB Performance Reference Model (PRM) Approach 16

Purpose of HR LOB PRM v 1 § Establishes a standardized set of measures based on Business Reference Model (BRM) processes against which to measure Human Resource Management (HRM) processes § Develops a series of measures to assess the performance of services offered by Shared Service Centers (SSCs) § Addresses the sub-function processes § Develops a set of normalized measures across the Federal HR community § Supports the objectives of Human Capital Assessment and Accountability Framework (HCAAF) § The HCAAF offers guidance and integration for transforming human capital management and describes the expectations that guide the assessment of agency human capital efforts 17

FEA guidelines define the PRM for Human Resource Management based on the HR LOB Business Reference Model (BRM) Measurement Category HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT – HRM involves all activities associated with the recruitment and management of personnel Measurement Grouping Measurement Indicators HR Strategy Organization and Position Management Staff Acquisition Performance Management Compensation Management Benefit Management Human Resource Development Labor Relations Employee Relations Separation Management 18
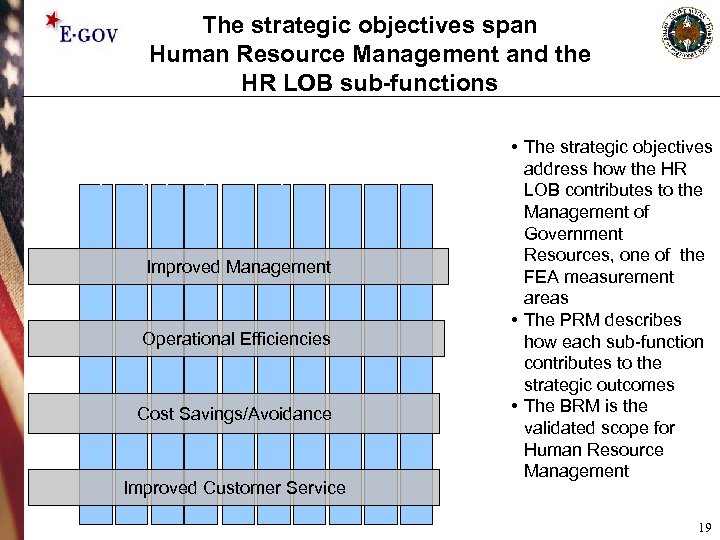
HR St ra te gy O rg M & an P ag os em itio St af en n f A t cq ui sit io Pe n rfo rm an ce Co M m gm pe t M ns gm at t ion Be ne fit s H Mg um m t D an ev R el e o s Em pm ou r Re plo ent ce la ye tio e ns La R el bo at r io ns M Sep an ar ag atio em n en t The strategic objectives span Human Resource Management and the HR LOB sub-functions Improved Management Operational Efficiencies Cost Savings/Avoidance Improved Customer Service • The strategic objectives address how the HR LOB contributes to the Management of Government Resources, one of the FEA measurement areas • The PRM describes how each sub-function contributes to the strategic outcomes • The BRM is the validated scope for Human Resource Management 19
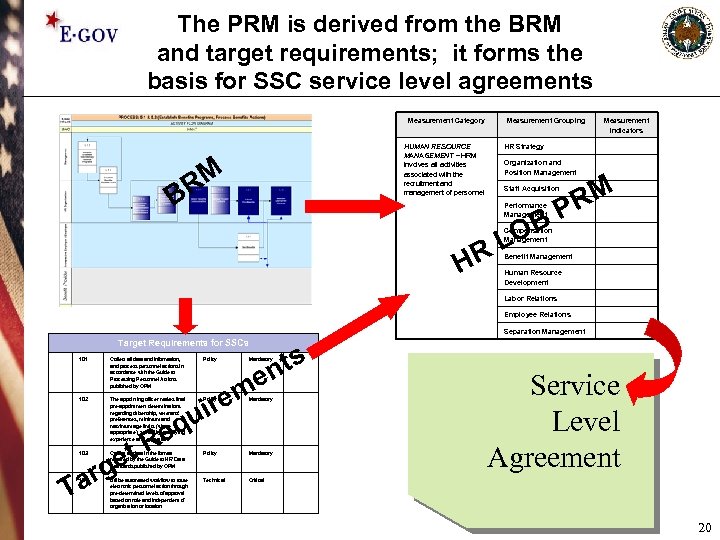
The PRM is derived from the BRM and target requirements; it forms the basis for SSC service level agreements Measurement Category HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT – HRM involves all activities associated with the recruitment and management of personnel RM B Measurement Grouping Measurement Indicators HR Strategy Organization and Position Management RM P B Staff Acquisition Performance Management LO R Compensation Management H Benefit Management Human Resource Development Labor Relations Employee Relations Separation Management Target Requirements for SSCs 101 Collect all data and information, and process personnel actions in accordance with the Guide to Processing Personnel Actions published by OPM 102 The appointing officer makes final pre-appointment determinations regarding citizenship, veterans’ preferences, minimum and maximum age limits (where appropriate), suitability, qualifying experience and education. et eq R ts en m Policy ire u Policy Mandatory 103 Collect all data in the format required by the Guide to HR Data Standards published by OPM Policy Mandatory 104 Utilize automated workflow to route electronic personnel action through pre-determined levels of approval based on role and independent of organization or location Technical Service Level Agreement Critical arg T 20
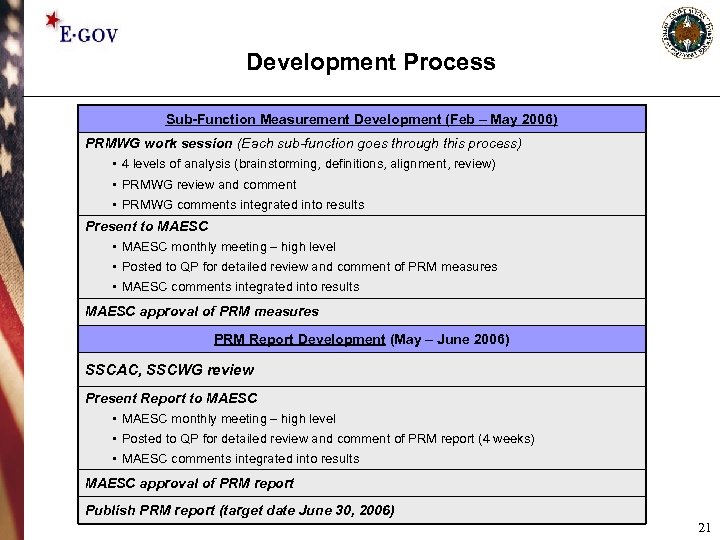
Development Process Sub-Function Measurement Development (Feb – May 2006) PRMWG work session (Each sub-function goes through this process) • 4 levels of analysis (brainstorming, definitions, alignment, review) • PRMWG review and comment • PRMWG comments integrated into results Present to MAESC • MAESC monthly meeting – high level • Posted to QP for detailed review and comment of PRM measures • MAESC comments integrated into results MAESC approval of PRM measures PRM Report Development (May – June 2006) SSCAC, SSCWG review Present Report to MAESC • MAESC monthly meeting – high level • Posted to QP for detailed review and comment of PRM report (4 weeks) • MAESC comments integrated into results MAESC approval of PRM report Publish PRM report (target date June 30, 2006) 21

Work Session Process 22
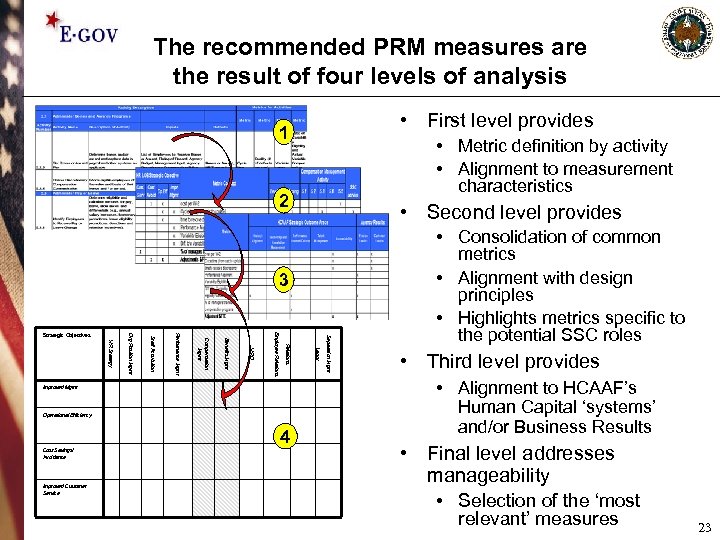
The recommended PRM measures are the result of four levels of analysis • First level provides 1 • Metric definition by activity • Alignment to measurement characteristics 2 • Second level provides 3 Operational Efficiency 4 Cost Savings/ Avoidance Improved Customer Service Labor Improved Mgmt Separation Mgmt Relations Employee Relations HRD Benefits Mgmt Compensation Mgmt Performance Mgmt Staff Acquisition HR Strategy Org Position Mgmt Strategic Objectives • Consolidation of common metrics • Alignment with design principles • Highlights metrics specific to the potential SSC roles • Third level provides • Alignment to HCAAF’s Human Capital ‘systems’ and/or Business Results • Final level addresses manageability • Selection of the ‘most relevant’ measures 23
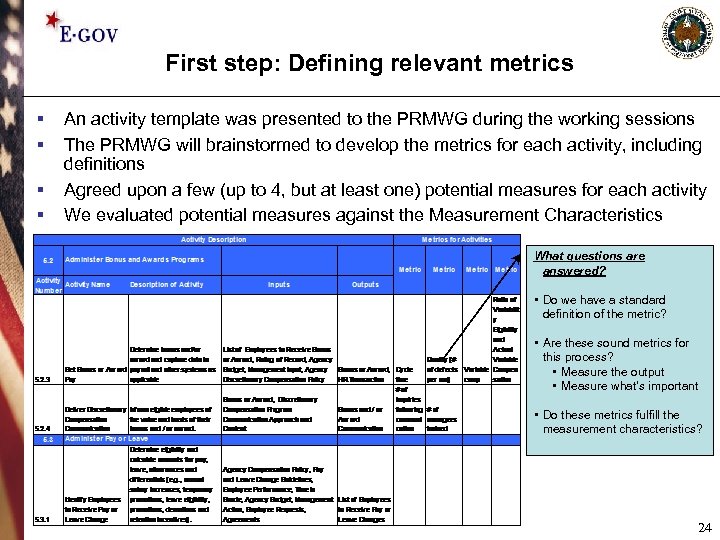
First step: Defining relevant metrics § § An activity template was presented to the PRMWG during the working sessions The PRMWG will brainstormed to develop the metrics for each activity, including definitions Agreed upon a few (up to 4, but at least one) potential measures for each activity We evaluated potential measures against the Measurement Characteristics What questions are answered? • Do we have a standard definition of the metric? • Are these sound metrics for this process? • Measure the output • Measure what’s important • Do these metrics fulfill the measurement characteristics? 24
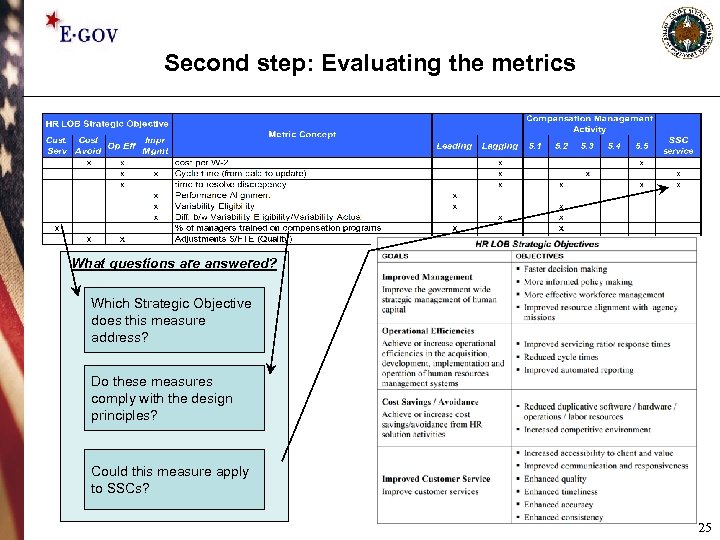
Second step: Evaluating the metrics What questions are answered? Which Strategic Objective does this measure address? Do these measures comply with the design principles? Could this measure apply to SSCs? 25
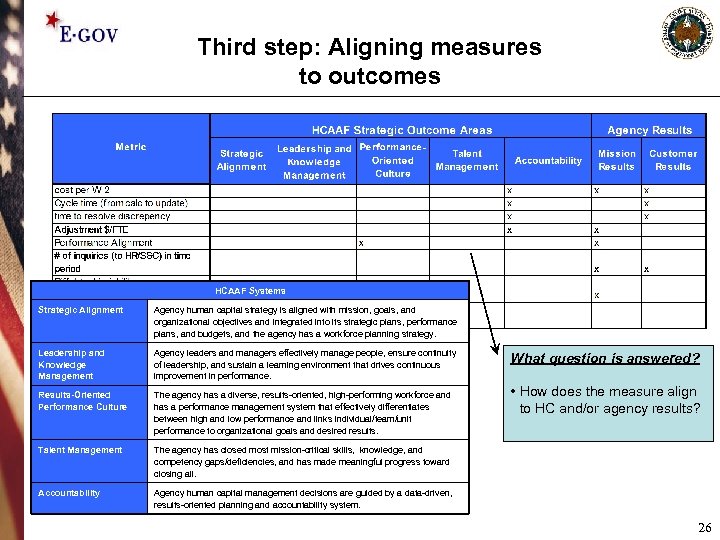
Third step: Aligning measures to outcomes HCAAF Systems Strategic Alignment Agency human capital strategy is aligned with mission, goals, and organizational objectives and integrated into its strategic plans, performance plans, and budgets, and the agency has a workforce planning strategy. Leadership and Knowledge Management Agency leaders and managers effectively manage people, ensure continuity of leadership, and sustain a learning environment that drives continuous improvement in performance. Results-Oriented Performance Culture The agency has a diverse, results-oriented, high-performing workforce and has a performance management system that effectively differentiates between high and low performance and links individual/team/unit performance to organizational goals and desired results. Talent Management The agency has closed most mission-critical skills, knowledge, and competency gaps/deficiencies, and has made meaningful progress toward closing all. Accountability Agency human capital management decisions are guided by a data-driven, results-oriented planning and accountability system. What question is answered? • How does the measure align to HC and/or agency results? 26
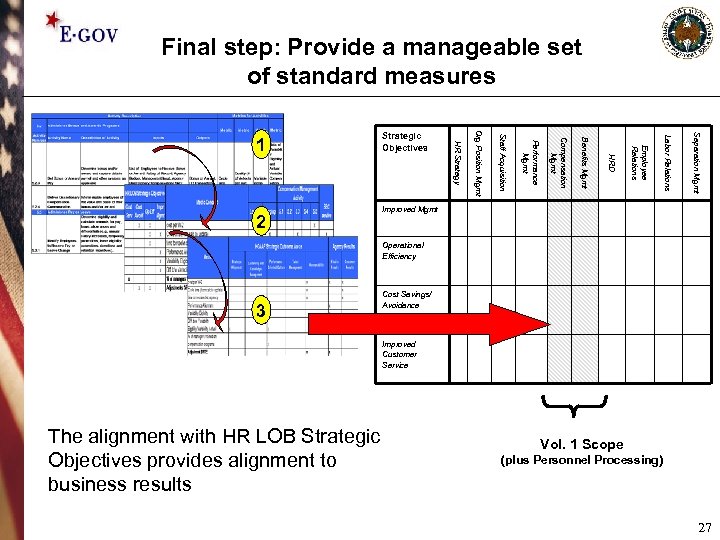
Final step: Provide a manageable set of standard measures Separation Mgmt Labor Relations Employee Relations HRD Benefits Mgmt Compensation Mgmt Performance Mgmt Staff Acquisition Org Position Mgmt 2 Strategic Objectives HR Strategy 1 Improved Mgmt Operational Efficiency 3 Cost Savings/ Avoidance Improved Customer Service The alignment with HR LOB Strategic Objectives provides alignment to business results Vol. 1 Scope (plus Personnel Processing) 27

Results 28
Measurement Indicators Types of indicators for core areas § “Tip of the Iceberg” – Indicators that reflect the health of the process to deliver results § If the measure is not in the expected range, or changes drastically, additional analysis would be performed to understand the causes of the change § Additional analysis may indicate an agency process issue, an SSC process issue, or a issue between the agency and SSC § Transactional measure – Indicators track time or accuracy regarding completion of a task § These measures are typically relevant to SSC service and/or processing 29

Common Themes in Compensation Management Measurements § Customer Service § Measures that track transactional procedures which can reflect an organization’s ability to provide customer service. § Timeliness § Measure that track how long it takes to complete a task. The intent of these measures is to evaluate efficiency. § Quality § Measures that track errors over a period of time. By tracking quality, customers can better understand the impacts of delivering HR service efficiently and could affect the perception of employeecustomers. § Cost § Measures that calculate the cost of a process or transaction. Cost metrics are essential in determining long-term benefits of new technology initiatives. 30
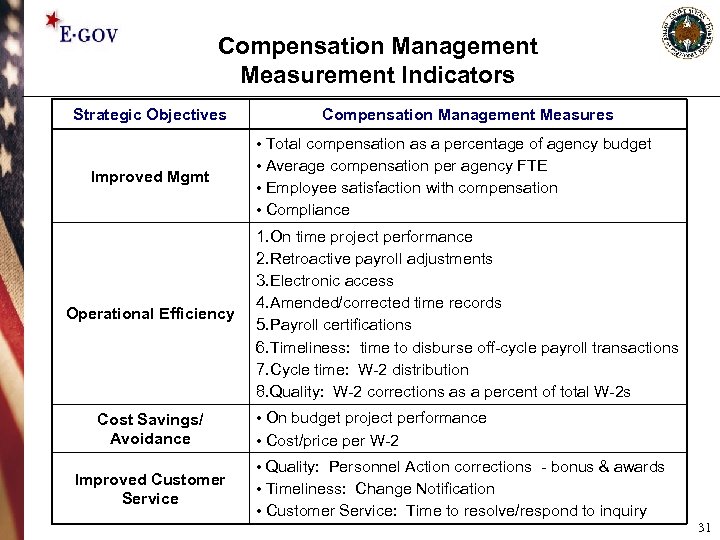
Compensation Management Measurement Indicators Strategic Objectives Improved Mgmt Operational Efficiency Cost Savings/ Avoidance Improved Customer Service Compensation Management Measures • Total compensation as a percentage of agency budget • Average compensation per agency FTE • Employee satisfaction with compensation • Compliance 1. On time project performance 2. Retroactive payroll adjustments 3. Electronic access 4. Amended/corrected time records 5. Payroll certifications 6. Timeliness: time to disburse off-cycle payroll transactions 7. Cycle time: W-2 distribution 8. Quality: W-2 corrections as a percent of total W-2 s • On budget project performance • Cost/price per W-2 • Quality: Personnel Action corrections - bonus & awards • Timeliness: Change Notification • Customer Service: Time to resolve/respond to inquiry 31
Common Themes in Benefits Management Measures § Customer Service § Measures that track transactional procedures which can reflect an organization’s ability to provide customer service § Timeliness § Measures that track how long it takes to complete a task. The intent of these measures is to evaluate efficiency § Quality § Measures that track errors over a period of time. By tracking quality, customers can better understand the impacts of delivering HR service efficiently and could affect the perception of employeecustomers § Cost § Measures that calculate the cost of a process or transaction. Cost metrics are essential in determining long-term benefits of new technology initiatives 32
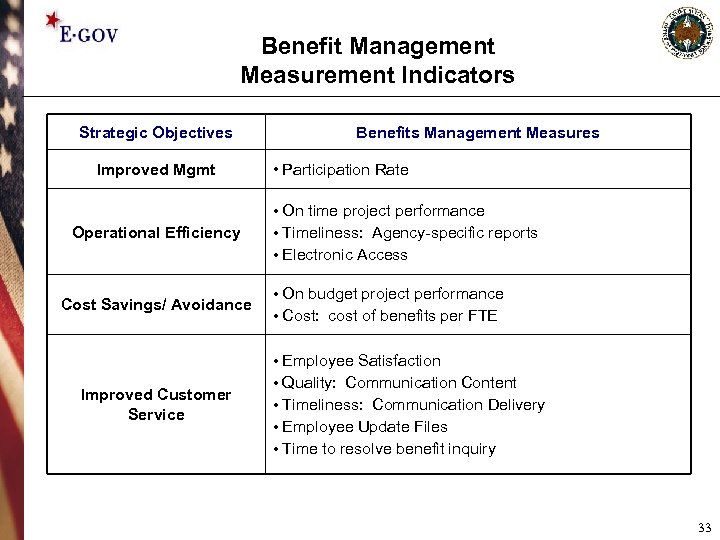
Benefit Management Measurement Indicators Strategic Objectives Improved Mgmt Operational Efficiency Cost Savings/ Avoidance Improved Customer Service Benefits Management Measures • Participation Rate • On time project performance • Timeliness: Agency-specific reports • Electronic Access • On budget project performance • Cost: cost of benefits per FTE • Employee Satisfaction • Quality: Communication Content • Timeliness: Communication Delivery • Employee Update Files • Time to resolve benefit inquiry 33

Common Themes in Personnel Action Measures § Self-Service § Measures that track the availability and usage of self-service applications. § Customer Service § Measures that track transactional procedures which can reflect an organization’s ability to provide customer service. § Processing & Workflow § Measure that track how long it takes to complete a task. § Quality - Measures that track errors over a period of time. By tracking quality, customers can better understand the impacts of delivering HR service and could affect the perception of employeecustomers. § Evaluation & Compliance § HR and SSC ensures that personnel actions are compliant with applicable standards, policies, rules, and regulations. 34
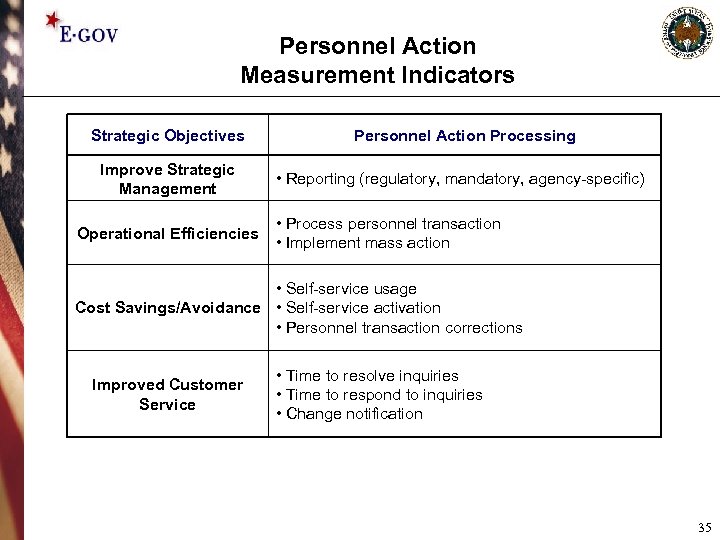
Personnel Action Measurement Indicators Strategic Objectives Personnel Action Processing Improve Strategic Management • Reporting (regulatory, mandatory, agency-specific) Operational Efficiencies • Process personnel transaction • Implement mass action • Self-service usage Cost Savings/Avoidance • Self-service activation • Personnel transaction corrections Improved Customer Service • Time to resolve inquiries • Time to respond to inquiries • Change notification 35

PRM Report Results § Developed measures across three sub-functions § 17 for Compensation Management § 11 for Benefits Management § 9 for Personnel Actions § Some measures were recommended for use with more than one sub -function § While the majority of measures had SSC involvement, some measures are relevant only to agencies. § Measures are being leveraged in the SLA process development 36
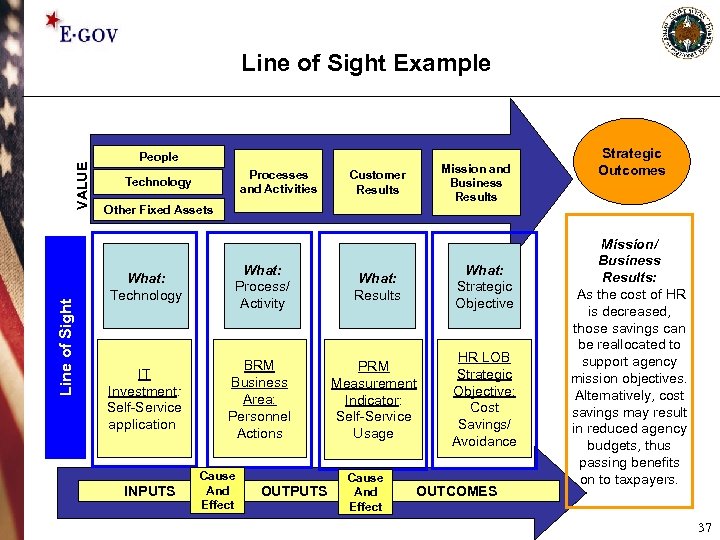
Line of Sight VALUE Line of Sight Example People • Processes and • Activities Processes and Activities Technology Mission and Business Results • Customer • Results Other Fixed Assets What: Technology What: Process/ Activity What: Results What: Strategic Objective IT Investment: Self-Service application BRM Business Area: Personnel Actions PRM Measurement Indicator: Self-Service Usage HR LOB Strategic Objective: Cost Savings/ Avoidance INPUTS Cause And Effect OUTCOMES Strategic Outcomes Mission/ Business Results: As the cost of HR is decreased, those savings can be reallocated to support agency mission objectives. Alternatively, cost savings may result in reduced agency budgets, thus passing benefits on to taxpayers. 37

Value of the PRM v 1 § Provides a common language and set of definitions that can be used to accelerate the development of Service Level Agreements (SLAs) between agencies and SSCs. § Creates a set of measures that are aligned to business results. § Agencies can use to validate HR contributions to agency missioncritical results. § Provides an opportunity to highlight significant process improvement opportunities. § Provides agencies with an approach for developing measures that provide visibility to the business benefits of capital investments. 38

Lessons Learned § Prepare to discuss many measures – hundreds of measures were considered, but didn’t meet characteristics threshold § Start small – agencies agreed with the vision of developing a small, manageable set of measures that are likely to evolve as inputs and outcomes are aligned § Prepare for further analysis – agencies are interested in decomposing the definitions to standardize cost information 39

Questions Kunal Suryavanshi – HR LOB PMO Kunal. Suryavanshi@opm. gov 202. 606. 1273 Tim Biggert – EA Team Leader Timothy. Biggert@opm. gov 202. 606. 4185 Melanie Meador – PRM Lead mmeador@us. ibm. com 703. 633. 4279 40
187efa53c804e9f4166f009b226bc2a1.ppt