Topic 9.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 39

Human Resources and Labor Productivity 1. Human Resources: Definition & Meaning, Classification 2. Human Resources Planning in Enterprise. Working Time Balance of 1 Worker. 3. Labor Productivity: Definition & Meaning, calculation methodology, methodology factors and enhancement 1

1. Human Resources: Definition & Meaning, Classification 2

Human Resources Actual Potential 3

Personnel of Enterprise – people employed in an organization or engaged in an organized undertaking such as military service (Oxford Dictionary) - All full-time employees with the professional trainings/education and/or practical experience. - (Ukrainian Business Practice) 4

Classification of Personnel According to executive functions (managers, engineers, clerks, workers) According to profession and specialization) According to qualification According to age According to gender identity According to occupational life etc 5

Human Resource Management (1) Staff Planning: needed staff, professions, specialization, qualification etc; Recruiting: selection, orientation, employment, adaptation; Disposition of personnel according to industrial and organizational structure of enterprise; Allocation of responsibilities; Personnel development; Stimulation and motivation, work discipline; Hygiene and security control: labor medicine, security of people and materiality 6

Human Resource Management (2) Provide connections between top-management and labor union; Enhance job arrangement; Estimate staff: age, education, qualification, dedication, discipline etc); Certificate employees and career development; Implement social functions: family help, meals on enterprise, support of ex-employees etc); Develop corporate culture. 7

Indicators of the Staff Size MOMENT: Accounting staff size Number present Number of employees, that actually have started to work INTERVAL: Average payroll (number) Average number present Average number of employees, that actually have started to work 8

2. Human Resources Planning in Enterprise. Working Time Balance of 1 Worker. 9

Human Resources Planning a) workers 10

Working Time Balance of 1 Worker 3 stages: stages Calculate average number of working days in year for 1 worker; Fix average duration of 1 working day; Define yearly effective working time in hours 11
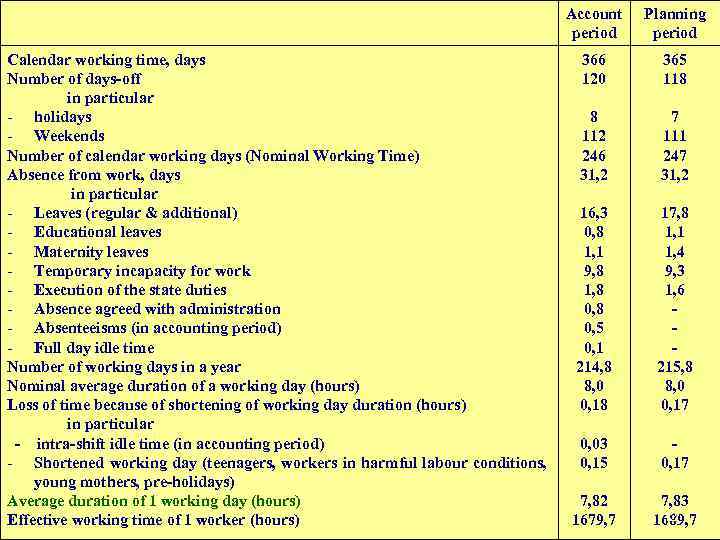
Account period Calendar working time, days Number of days-off in particular - holidays - Weekends Number of calendar working days (Nominal Working Time) Absence from work, days in particular - Leaves (regular & additional) - Educational leaves - Maternity leaves - Temporary incapacity for work - Execution of the state duties - Absence agreed with administration - Absenteeisms (in accounting period) - Full day idle time Number of working days in a year Nominal average duration of a working day (hours) Loss of time because of shortening of working day duration (hours) in particular - intra-shift idle time (in accounting period) - Shortened working day (teenagers, workers in harmful labour conditions, young mothers, pre-holidays) Average duration of 1 working day (hours) Effective working time of 1 worker (hours) Planning period 366 120 365 118 8 112 246 31, 2 7 111 247 31, 2 16, 3 0, 8 1, 1 9, 8 1, 8 0, 5 0, 1 214, 8 8, 0 0, 18 17, 8 1, 1 1, 4 9, 3 1, 6 215, 8 8, 0 0, 17 0, 03 0, 15 0, 17 7, 82 1679, 7 7, 83 12 1689, 7

Case study: how to calculate a number of workers Suppose: 1. Servicemen - Service standard - 10 units; - Number of machine units to be served - 50 units; Milling-machine operator - Output quota - Production volume (plan) Installers - Number of working places 4. Number of shifts 5. Annual nominal working time of 1 worker 6. Annual effective working time of 1 worker - 370 pieces per month; - 7400 pieces in month - 12 WP. - 248 days - 219 days 13

Case study: how to calculate a number of workers Define: Number of workers on payroll in this section in planning period. 14

number of workers on payroll for labor: де T – Labour hours for accomplishment of the manufacturing program (man-hours); WTE – annual effective working time of 1 worker in planning period, according to working time balance k. LP – planning labor performance for certain group of workers (according to profession and qualification) 15

number of workers on payroll for output quata: де Q – planning production volume in natural parameters; Quota. OP – output quota per hour. 16

number of workers on payroll For service standard where NS – number of machines under service (units); S - number of machine-shifts per day; k. PR – reduction factor to consider the number present in number of workers on payroll; STS – service standard for 1 WP 17

number of workers on payroll for number of working places: where WP – кількість робочих місць. 18

Human Resources Planning b) managers, engineers, clerks 19

Challenges by Human Resource Planning One person executes different functions and solves many different problems, thus works of certain kinds are small; Work is interval, thus there is not even loading of employees; It is impossible to evaluate and measure certain kinds of works (operations). 20

Payroll for standard time: where ТD&M – Labour hours of design and managerial efforts (man-hours); WTE – annual effective working time of 1 manager/ engineer/ clerk in planning period (hours). 21

Payroll for standard personnel number Standard personnel number – a fixed number of employees (according to profession & qualification structure) needed for accomplishment of curtain engineering or managerial function/ efforts/ works. 22

Payroll for span of control A manager's span of control is the number of employees that he or she can effectively be in control of at any one time. 23

Payroll for information flows where QINFO – general information volume (document flow) in curtain managerial function in a year, number of documents; q. INFO – average annual information volume (document flow), that one manager is able to process. 24

Payroll for authorized staff size Number of employees for every position is to calculate by one of mentioned above methods. 25

Human Resource Planning c) serving employee for service standard for number of working places 26

3. Labor Productivity: Definition & Meaning calculation methodology, methodology factors and enhancement 27

Labor The aggregate of all human physical and mental effort used in creation of goods and services. Labor is a primary factor of production. The size of a nation’s labor force is determined by the size of its adult population, and the extent to which the adults are either working or are prepared to offer their labor for wages. 28

Labor Productivity (LP) 29

Kinds of Labor Productivity of public labor Productivity of individual labor 30

Indicators of public labor productivity Labor productivity : LPеc = GDP / Number of engaged in economics Labor productivity : LPеc = GDP / Aggregate hours of labor in the country Where GDP – gross domestic product (₴). 31

Indicators of individual labor productivity Production output in time unit (direct ratio); Labour hours per 1 product (adverse ratio). 32

Labour hours for 1 Product t = T/Q where Q – Production volume, in natural parameters; T – total labour requirements, man-hours. 33

Types of Labour Hours: Technological Labour Hours include all labour requirements of all main workers (piece ans time workers), t. ТЕCH; Service Labour Hours include labour requirements of helpers, t. SERV; Production Labour Hours include labour requirements of all workers (main workers and helpers) t. PRO; Managerial Labour Hours includes labour requirements of all managers, engineers and clerks, t. MAN; Full Labour Hours are labour requirements of all personnel, t. FULL: t. FULL = t. ТЕCH + t. SERV + t. MAN 34

Output in time unit OP = Q/T Output per hour, Output per day, Output per year, quarter, month for one average worker. 35

How to enhance the Labour Productivity Factors of LP Enhancement – the driving forces, conditions, requirements that affect the labour productivity. Reserves of LP Enhancement – unutilized opportunities to save the labour requirements and labour inpur. 36

Factors affecting labour productivity 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. physical-organic, location, and technological factors; . cultural belief-value and individual attitudinal, motivational and behavioural factors international influences – e. g. levels of innovativeness and efficiency on the part of the owners and managers of inward investing foreign companies managerial-organizational and wider economic and political-legal environments levels of flexibility in internal labour markets and the organization of work activities individual rewards and payment systems, and the effectiveness of personnel managers 37

Classification of Factors of LP Enhancement External Internal 38

Planning LP can be defined by two methods : Direct Calculation. Planning Production output / average number of employees ratio; ratio Factor Planning. 39
Topic 9.pptx