77e43ed1014a7292ecac3bf5e8e441db.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Human Resource within The Health System ANDREASTA MELIALA andremeliala@ugm. ac. id
Human Resource within The Health System ANDREASTA MELIALA andremeliala@ugm. ac. id
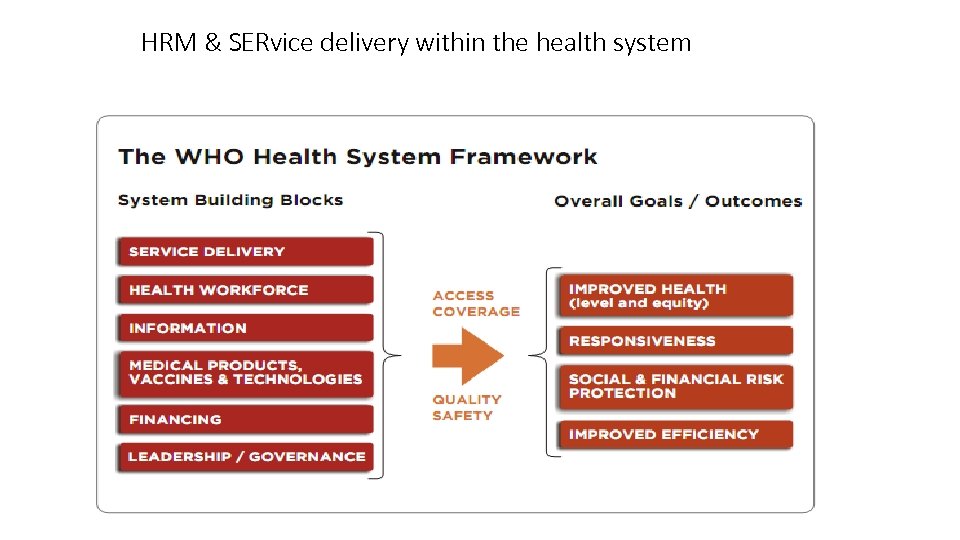 HRM & SERvice delivery within the health system
HRM & SERvice delivery within the health system
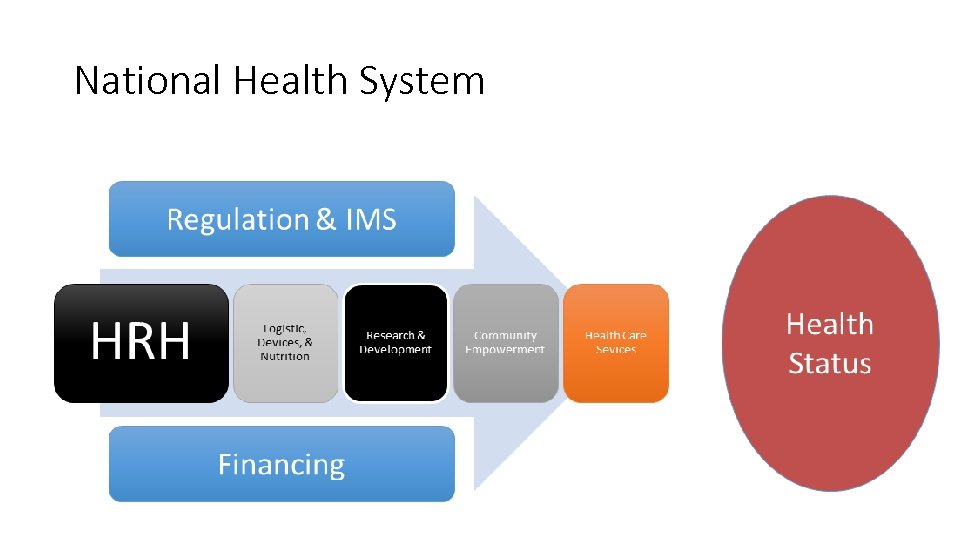 National Health System
National Health System
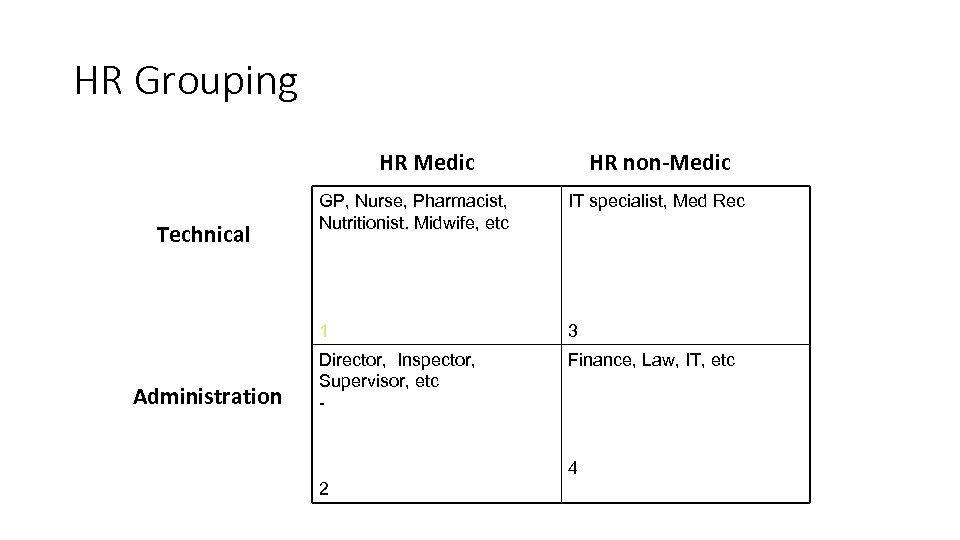 HR Grouping HR Medic HR non-Medic Administration IT specialist, Med Rec 1 Technical GP, Nurse, Pharmacist, Nutritionist. Midwife, etc 3 Director, Inspector, Supervisor, etc - Finance, Law, IT, etc 4 2
HR Grouping HR Medic HR non-Medic Administration IT specialist, Med Rec 1 Technical GP, Nurse, Pharmacist, Nutritionist. Midwife, etc 3 Director, Inspector, Supervisor, etc - Finance, Law, IT, etc 4 2
 The Context
The Context
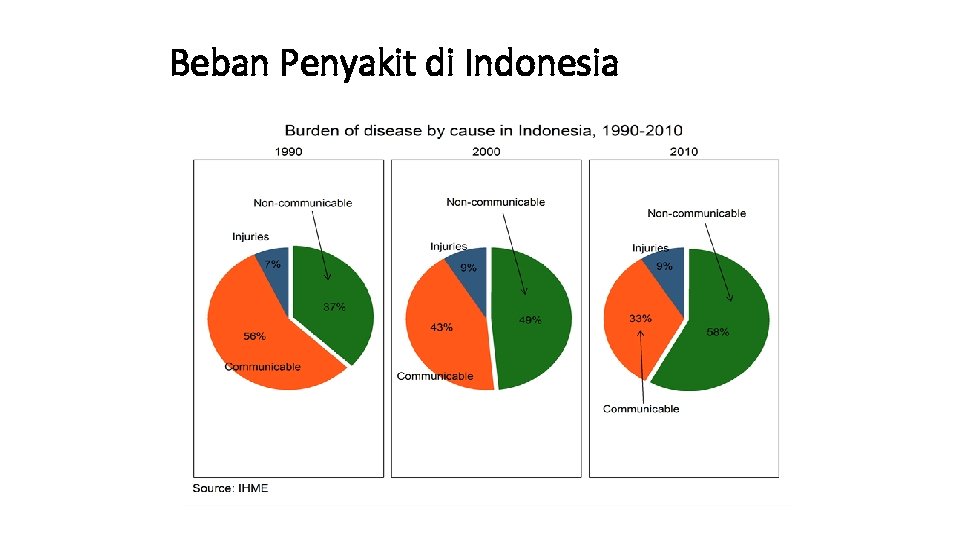 Beban Penyakit di Indonesia
Beban Penyakit di Indonesia
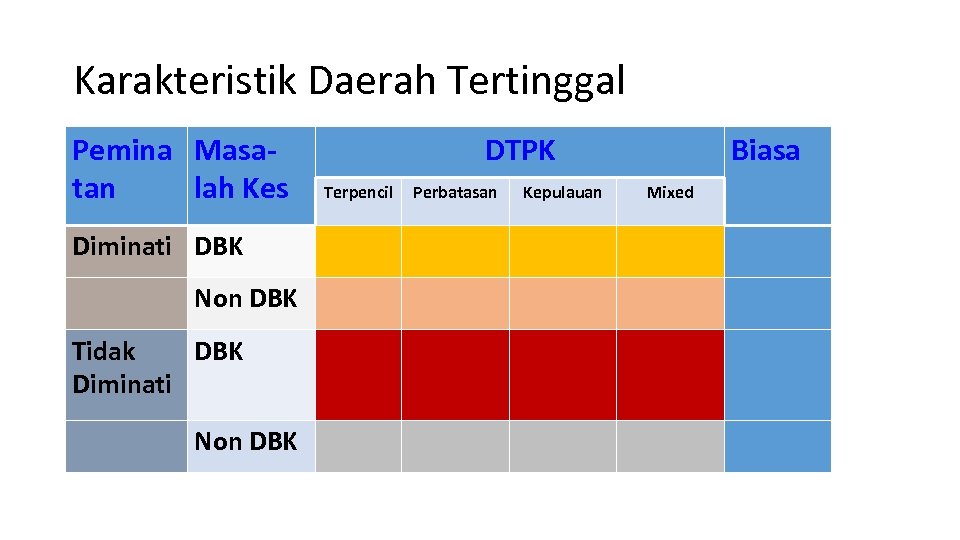 Karakteristik Daerah Tertinggal Pemina Masatan lah Kes Diminati DBK Non DBK Tidak DBK Diminati Non DBK DTPK Terpencil Perbatasan Kepulauan Biasa Mixed
Karakteristik Daerah Tertinggal Pemina Masatan lah Kes Diminati DBK Non DBK Tidak DBK Diminati Non DBK DTPK Terpencil Perbatasan Kepulauan Biasa Mixed
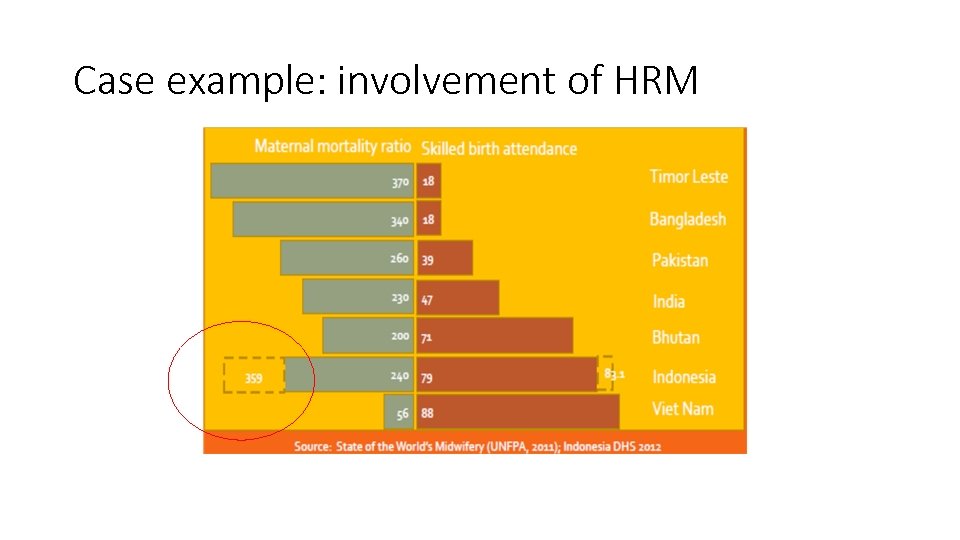 Case example: involvement of HRM
Case example: involvement of HRM
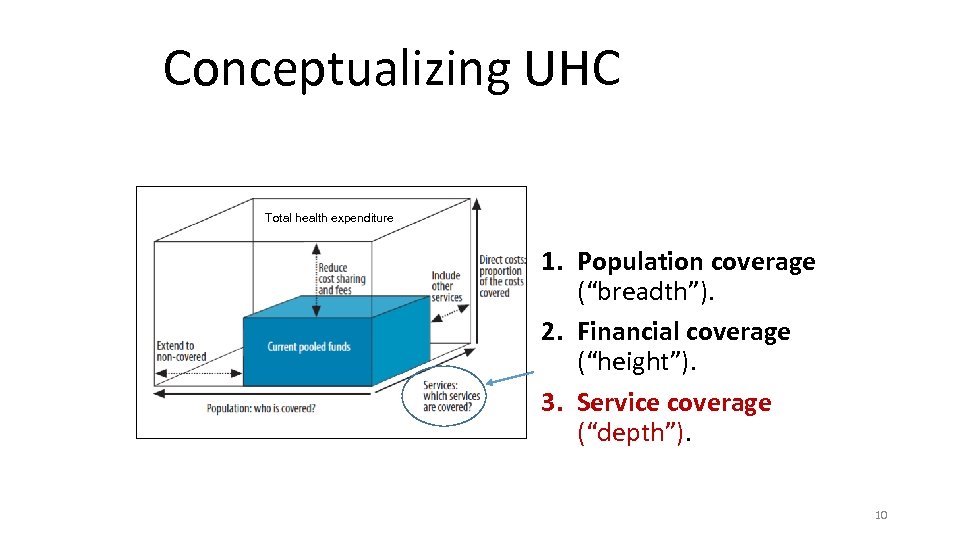 Conceptualizing UHC Total health expenditure 1. Population coverage (“breadth”). 2. Financial coverage (“height”). 3. Service coverage (“depth”). 10
Conceptualizing UHC Total health expenditure 1. Population coverage (“breadth”). 2. Financial coverage (“height”). 3. Service coverage (“depth”). 10
 Assessing supply-side readiness for UHC § Assessing “depth” of UHC also implies examining supply-side readiness in terms of the ability of health facilities (both at the primary care and higher levels) to deliver key tracer components of the benefits package. § WHO’s Service Availability and Readiness Assessment (SARA) toolkit is a very useful instrument that – when combined with national guidelines – can be used for assessing supply-side readiness for UHC. 11
Assessing supply-side readiness for UHC § Assessing “depth” of UHC also implies examining supply-side readiness in terms of the ability of health facilities (both at the primary care and higher levels) to deliver key tracer components of the benefits package. § WHO’s Service Availability and Readiness Assessment (SARA) toolkit is a very useful instrument that – when combined with national guidelines – can be used for assessing supply-side readiness for UHC. 11
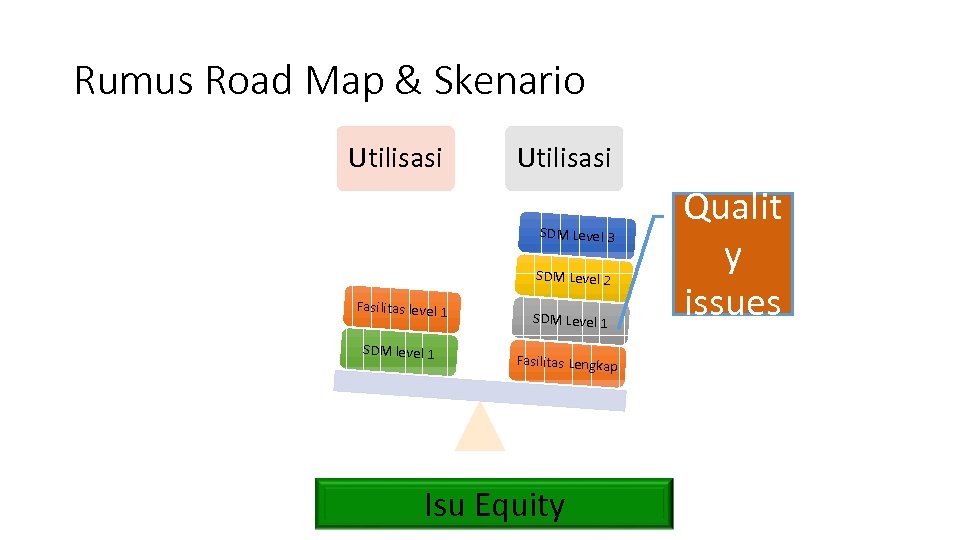 Rumus Road Map & Skenario Utilisasi SDM Level 3 SDM Level 2 Fasilitas level 1 SDM Level 1 Fasilitas Lengkap Isu Equity Qualit y issues
Rumus Road Map & Skenario Utilisasi SDM Level 3 SDM Level 2 Fasilitas level 1 SDM Level 1 Fasilitas Lengkap Isu Equity Qualit y issues
 The Concept
The Concept
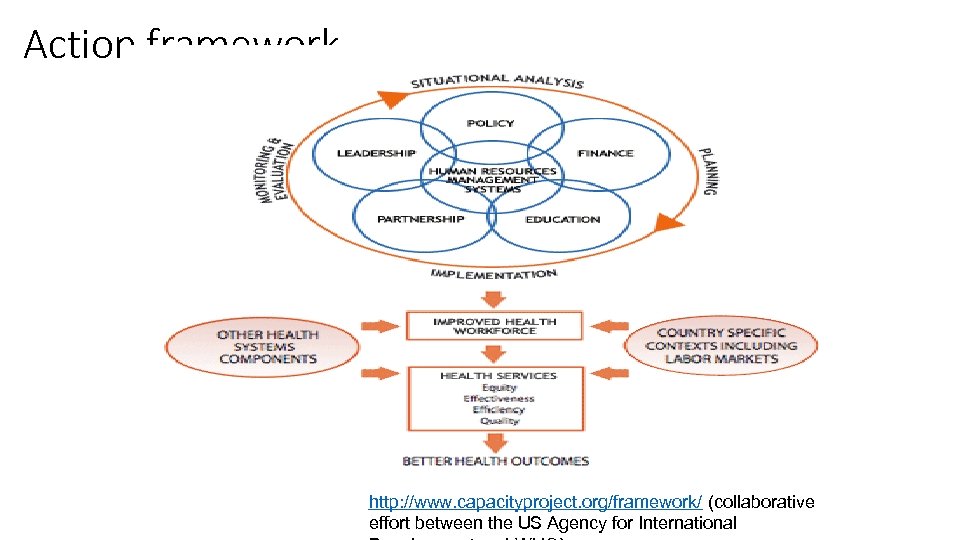 Action framework http: //www. capacityproject. org/framework/ (collaborative effort between the US Agency for International
Action framework http: //www. capacityproject. org/framework/ (collaborative effort between the US Agency for International
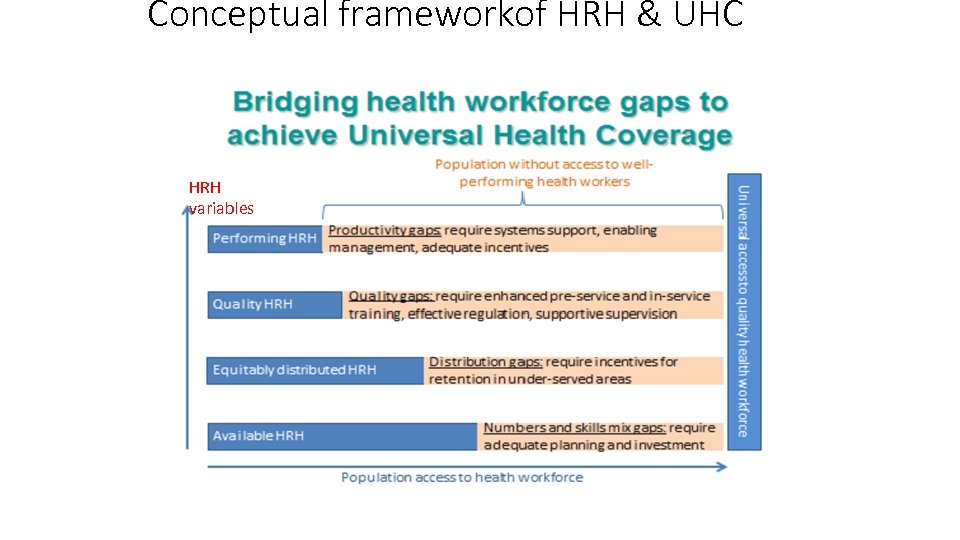 Conceptual frameworkof HRH & UHC HRH variables
Conceptual frameworkof HRH & UHC HRH variables
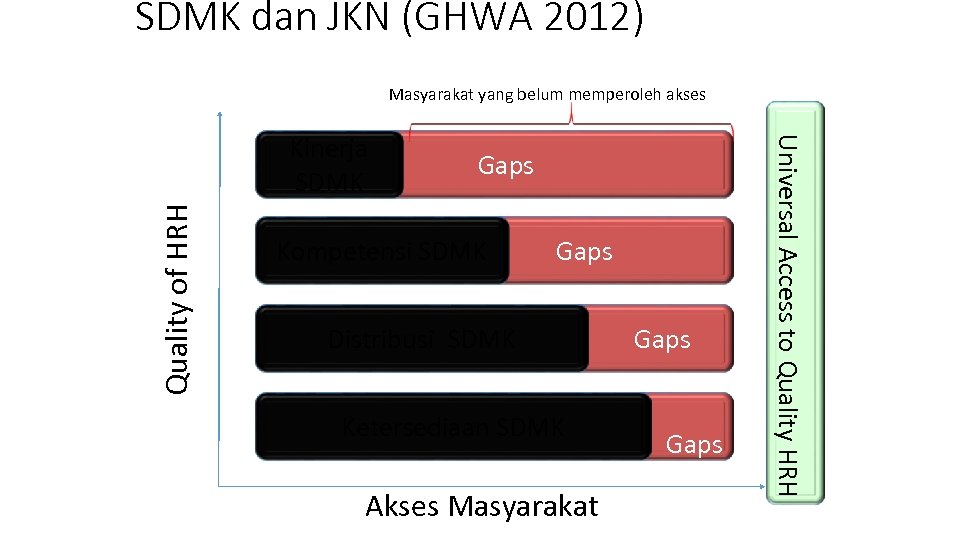 SDMK dan JKN (GHWA 2012) Masyarakat yang belum memperoleh akses Quality of HRH Gaps Kompetensi SDMK Gaps Distribusi SDMK Ketersediaan SDMK Akses Masyarakat Gaps Universal Access to Quality HRH Kinerja SDMK
SDMK dan JKN (GHWA 2012) Masyarakat yang belum memperoleh akses Quality of HRH Gaps Kompetensi SDMK Gaps Distribusi SDMK Ketersediaan SDMK Akses Masyarakat Gaps Universal Access to Quality HRH Kinerja SDMK
 Going forward, the need for beds and skilled manpower will increase significantly Forces at work • Increase in demand for treatments, especially for hospitalisation • Shift in demand to expensive diseases, e. g. , cancer, heart diseases • Increased demand for high quality inpatient and outpatient care Requirements in tangible assets: beds 1. A. Increase of at least 100% in overall number of bed days required 1. B. High likelihood of even greater increase in number of tertiary beds required Requirements in tangible assets: manpower 2. A. Increase in number of physicians per population from current low rate 2. A. Corresponding increase in number of nurses and other healthcare personnel
Going forward, the need for beds and skilled manpower will increase significantly Forces at work • Increase in demand for treatments, especially for hospitalisation • Shift in demand to expensive diseases, e. g. , cancer, heart diseases • Increased demand for high quality inpatient and outpatient care Requirements in tangible assets: beds 1. A. Increase of at least 100% in overall number of bed days required 1. B. High likelihood of even greater increase in number of tertiary beds required Requirements in tangible assets: manpower 2. A. Increase in number of physicians per population from current low rate 2. A. Corresponding increase in number of nurses and other healthcare personnel
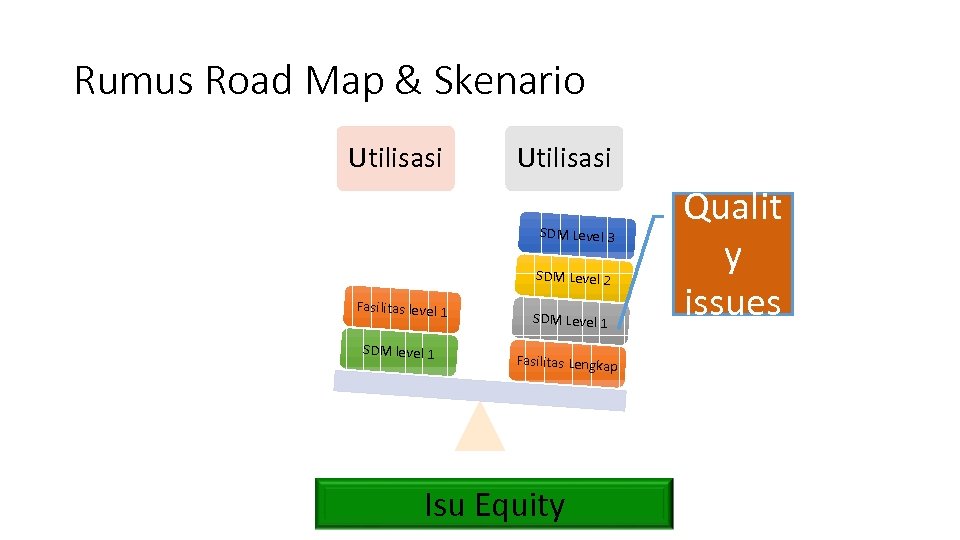 Rumus Road Map & Skenario Utilisasi SDM Level 3 SDM Level 2 Fasilitas level 1 SDM Level 1 Fasilitas Lengkap Isu Equity Qualit y issues
Rumus Road Map & Skenario Utilisasi SDM Level 3 SDM Level 2 Fasilitas level 1 SDM Level 1 Fasilitas Lengkap Isu Equity Qualit y issues
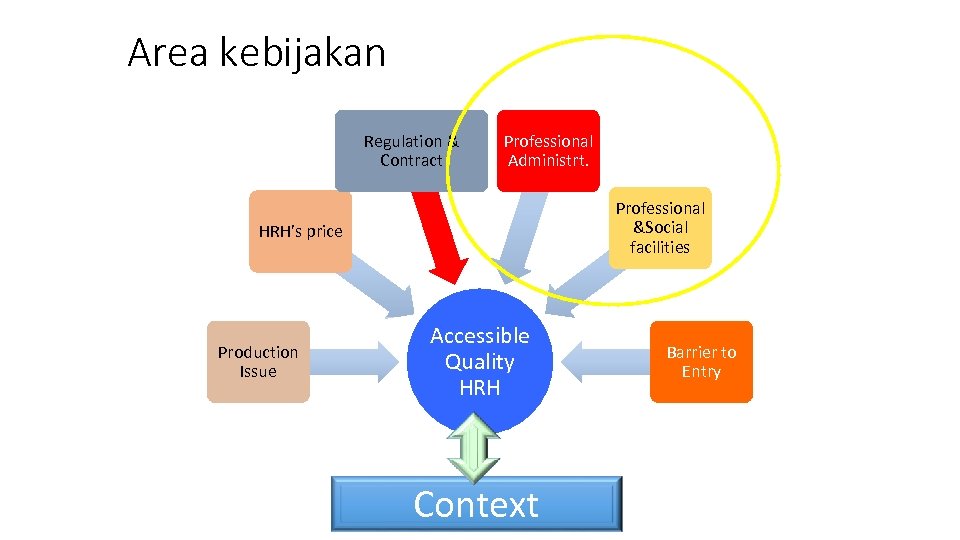 Area kebijakan Regulation & Contract Professional Administrt. Professional &Social facilities HRH’s price Production Issue Accessible Quality HRH Context Barrier to Entry
Area kebijakan Regulation & Contract Professional Administrt. Professional &Social facilities HRH’s price Production Issue Accessible Quality HRH Context Barrier to Entry
 Challenge
Challenge
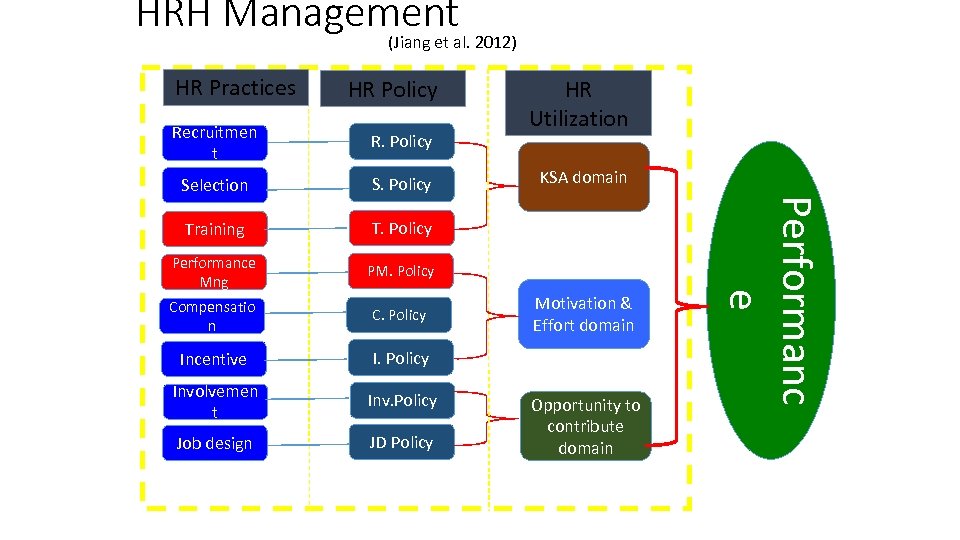 HRH Management (Jiang et al. 2012) HR Practices HR Policy R. Policy Selection S. Policy Training T. Policy Performance Mng PM. Policy Compensatio n C. Policy Incentive I. Policy Involvemen t Inv. Policy Job design JD Policy KSA domain Motivation & Effort domain Opportunity to contribute domain Performanc e Recruitmen t HR Utilization
HRH Management (Jiang et al. 2012) HR Practices HR Policy R. Policy Selection S. Policy Training T. Policy Performance Mng PM. Policy Compensatio n C. Policy Incentive I. Policy Involvemen t Inv. Policy Job design JD Policy KSA domain Motivation & Effort domain Opportunity to contribute domain Performanc e Recruitmen t HR Utilization
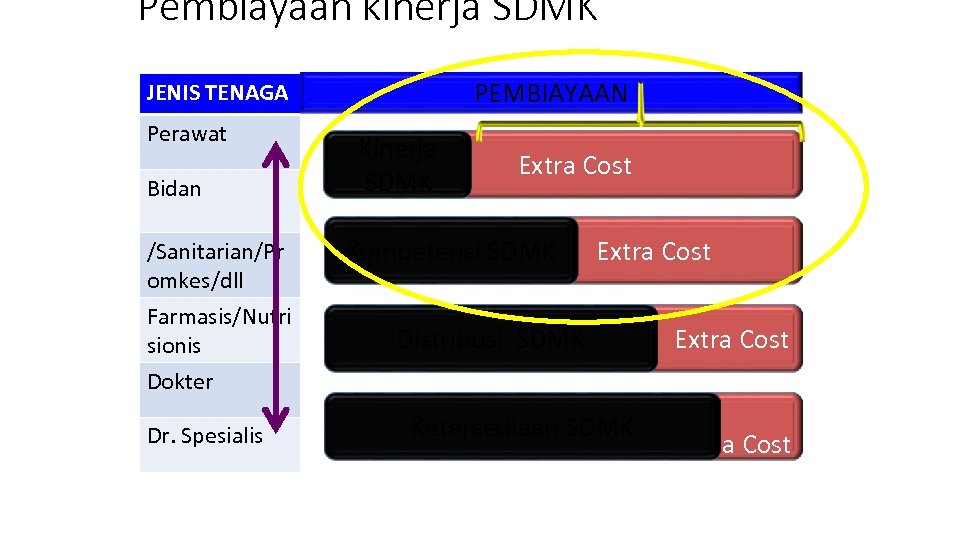 Pembiayaan kinerja SDMK PEMBIAYAAN JENIS TENAGA Perawat Bidan /Sanitarian/Pr omkes/dll Farmasis/Nutri sionis Dokter Dr. Spesialis Kinerja SDMK Extra Cost Kompetensi SDMK Extra Cost Distribusi SDMK Ketersediaan SDMK Extra Cost
Pembiayaan kinerja SDMK PEMBIAYAAN JENIS TENAGA Perawat Bidan /Sanitarian/Pr omkes/dll Farmasis/Nutri sionis Dokter Dr. Spesialis Kinerja SDMK Extra Cost Kompetensi SDMK Extra Cost Distribusi SDMK Ketersediaan SDMK Extra Cost
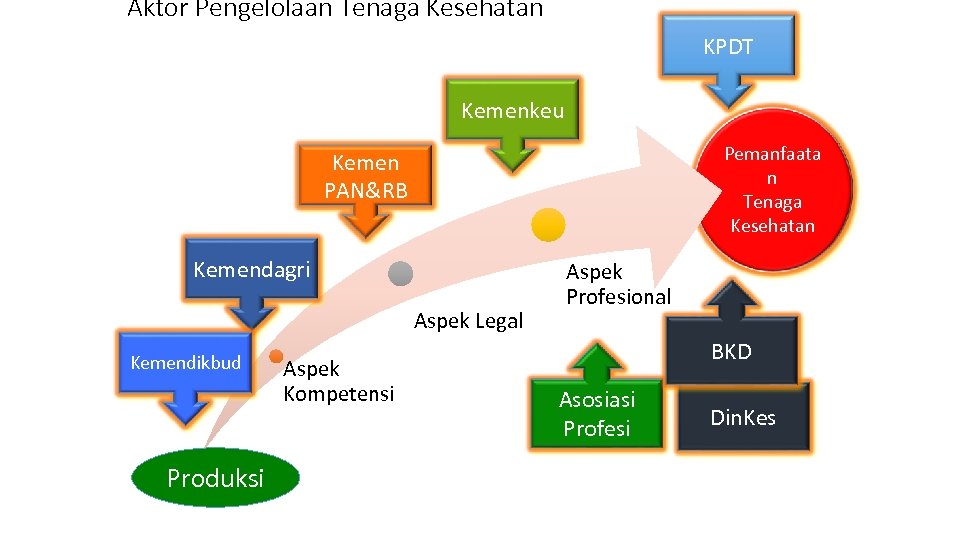 Aktor Pengelolaan Tenaga Kesehatan KPDT Kemenkeu Pemanfaata n Tenaga Kesehatan Kemen PAN&RB Kemendagri Aspek Legal Kemendikbud Produksi Aspek Kompetensi Aspek Profesional BKD Asosiasi Profesi Din. Kes
Aktor Pengelolaan Tenaga Kesehatan KPDT Kemenkeu Pemanfaata n Tenaga Kesehatan Kemen PAN&RB Kemendagri Aspek Legal Kemendikbud Produksi Aspek Kompetensi Aspek Profesional BKD Asosiasi Profesi Din. Kes


