4559726ce26322a634dbe18a804351a8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Planning
 Four Phases to HR Planning n “What will we need? ” u Determine future HR requirements n “What’s available? ” u Determine future HR availabilities Internally F Externally F n Reconcile requirements and availabilities u Anticipate “gaps” u Develop action plans n Control and evaluate
Four Phases to HR Planning n “What will we need? ” u Determine future HR requirements n “What’s available? ” u Determine future HR availabilities Internally F Externally F n Reconcile requirements and availabilities u Anticipate “gaps” u Develop action plans n Control and evaluate
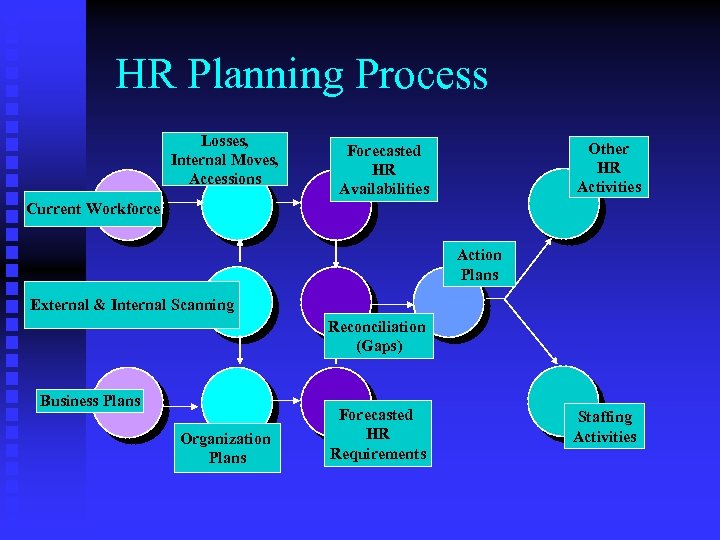 HR Planning Process Losses, Internal Moves, Accessions Other HR Activities Forecasted HR Availabilities Current Workforce Action Plans External & Internal Scanning Reconciliation (Gaps) Business Plans Organization Plans Forecasted HR Requirements Staffing Activities
HR Planning Process Losses, Internal Moves, Accessions Other HR Activities Forecasted HR Availabilities Current Workforce Action Plans External & Internal Scanning Reconciliation (Gaps) Business Plans Organization Plans Forecasted HR Requirements Staffing Activities
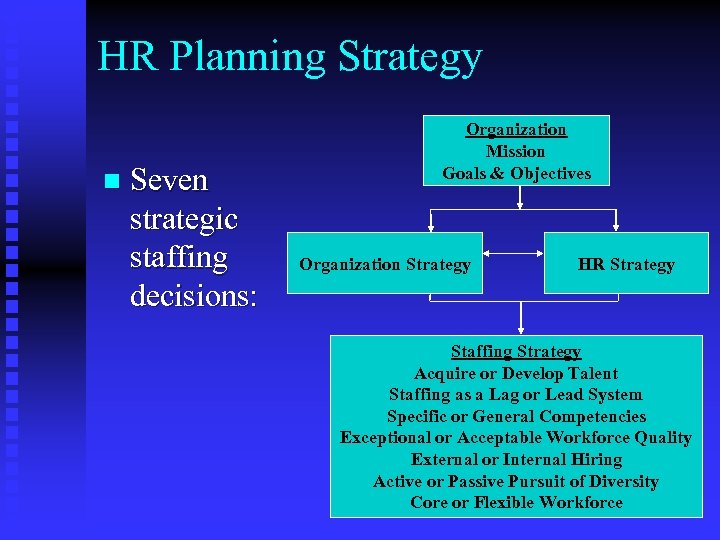 HR Planning Strategy n Seven strategic staffing decisions: Organization Mission Goals & Objectives Organization Strategy HR Strategy Staffing Strategy Acquire or Develop Talent Staffing as a Lag or Lead System Specific or General Competencies Exceptional or Acceptable Workforce Quality External or Internal Hiring Active or Passive Pursuit of Diversity Core or Flexible Workforce
HR Planning Strategy n Seven strategic staffing decisions: Organization Mission Goals & Objectives Organization Strategy HR Strategy Staffing Strategy Acquire or Develop Talent Staffing as a Lag or Lead System Specific or General Competencies Exceptional or Acceptable Workforce Quality External or Internal Hiring Active or Passive Pursuit of Diversity Core or Flexible Workforce
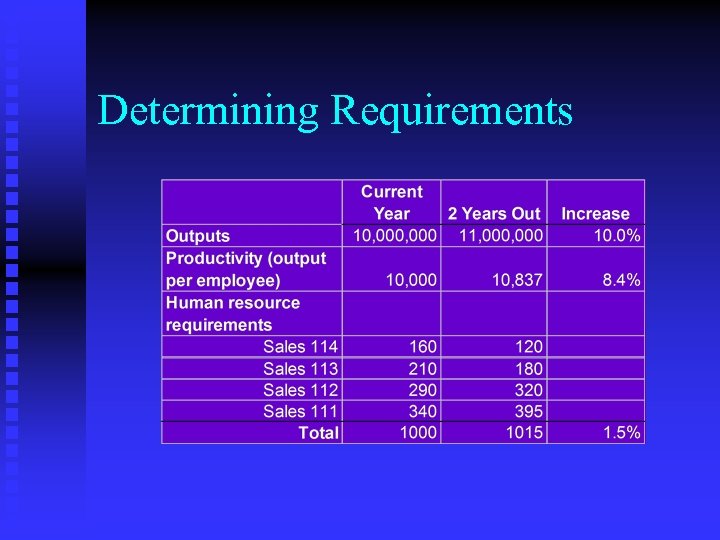
 Determining Requirements Begin with strategic plan n Identify: n u Relevant changes in technologies u Plans to restructure the organization u Business needs or changes n Techniques u Statistical u Judgmental
Determining Requirements Begin with strategic plan n Identify: n u Relevant changes in technologies u Plans to restructure the organization u Business needs or changes n Techniques u Statistical u Judgmental
 Determining Requirements
Determining Requirements
 Determining Availabilities: Internal Inventory current numbers and types of employees available n Anticipate losses through terminations, turnover, etc. n Figure impact of promotions, transfers, recruitment n
Determining Availabilities: Internal Inventory current numbers and types of employees available n Anticipate losses through terminations, turnover, etc. n Figure impact of promotions, transfers, recruitment n
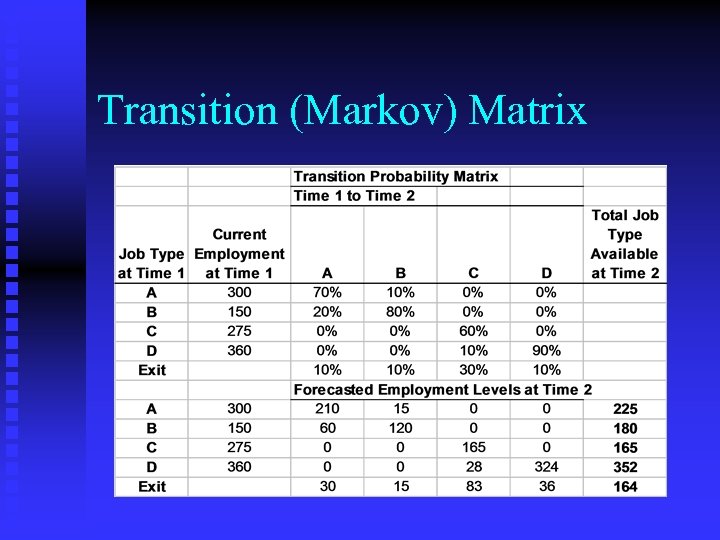 Transition (Markov) Matrix
Transition (Markov) Matrix
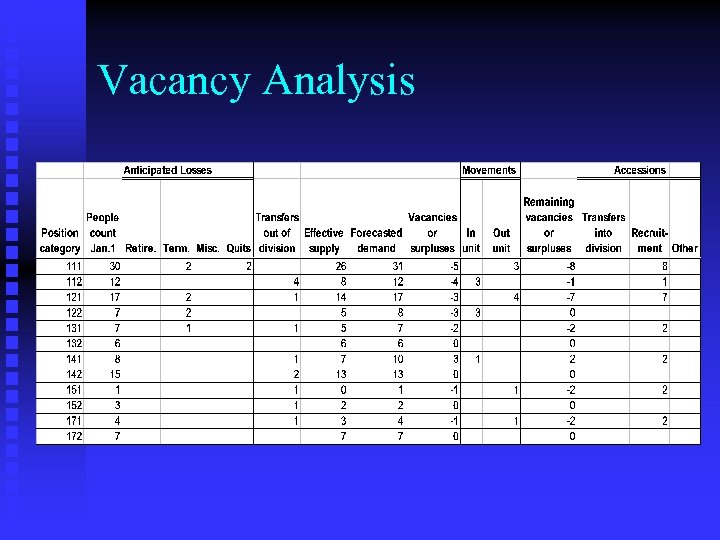 Vacancy Analysis
Vacancy Analysis
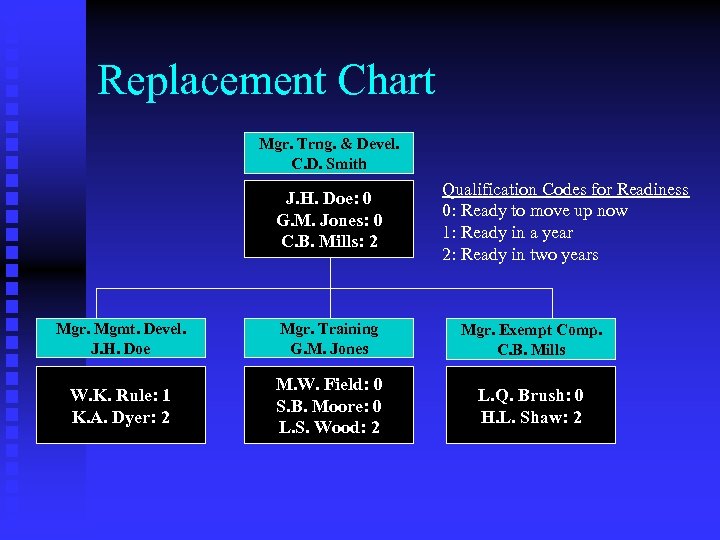 Replacement Chart Mgr. Trng. & Devel. C. D. Smith J. H. Doe: 0 G. M. Jones: 0 C. B. Mills: 2 Qualification Codes for Readiness 0: Ready to move up now 1: Ready in a year 2: Ready in two years Mgr. Mgmt. Devel. J. H. Doe Mgr. Training G. M. Jones Mgr. Exempt Comp. C. B. Mills W. K. Rule: 1 K. A. Dyer: 2 M. W. Field: 0 S. B. Moore: 0 L. S. Wood: 2 L. Q. Brush: 0 H. L. Shaw: 2
Replacement Chart Mgr. Trng. & Devel. C. D. Smith J. H. Doe: 0 G. M. Jones: 0 C. B. Mills: 2 Qualification Codes for Readiness 0: Ready to move up now 1: Ready in a year 2: Ready in two years Mgr. Mgmt. Devel. J. H. Doe Mgr. Training G. M. Jones Mgr. Exempt Comp. C. B. Mills W. K. Rule: 1 K. A. Dyer: 2 M. W. Field: 0 S. B. Moore: 0 L. S. Wood: 2 L. Q. Brush: 0 H. L. Shaw: 2
 Determining Availabilities: Internal n Techniques u Statistical F Past employee flow patterns F Transition or Markhov matrices u Judgmental F Executive reviews F Succession planning F Vacancy analysis
Determining Availabilities: Internal n Techniques u Statistical F Past employee flow patterns F Transition or Markhov matrices u Judgmental F Executive reviews F Succession planning F Vacancy analysis
 Determining Availabilities: External n Monitoring of u Major environmental trends F Publications F Media F Consultants u Labor market(s) F College enrollment F BLS and other labor statistics
Determining Availabilities: External n Monitoring of u Major environmental trends F Publications F Media F Consultants u Labor market(s) F College enrollment F BLS and other labor statistics
 Reconcile n Anticipate, clarify and define “gaps” u Set objectives to satisfy needs u Generate alternatives n Determine action plans u Specific managerial behaviors are identified through decision making F Brainstorming F Delphi technique
Reconcile n Anticipate, clarify and define “gaps” u Set objectives to satisfy needs u Generate alternatives n Determine action plans u Specific managerial behaviors are identified through decision making F Brainstorming F Delphi technique
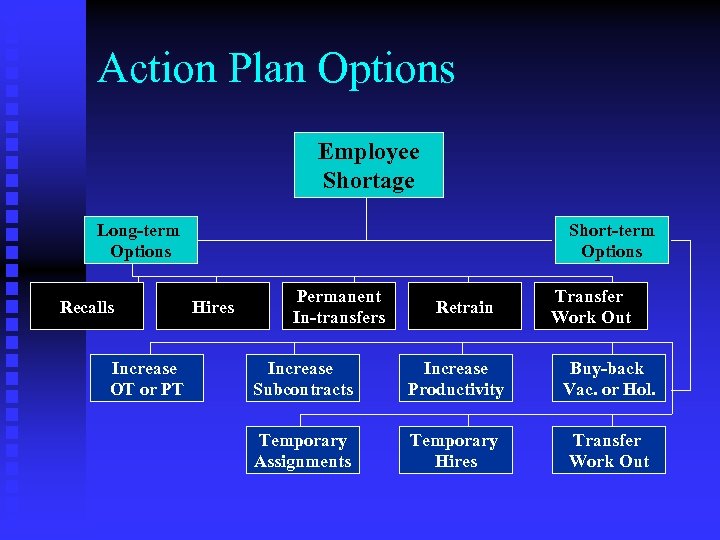 Action Plan Options Employee Shortage Long-term Options Recalls Increase OT or PT Short-term Options Hires Permanent In-transfers Retrain Transfer Work Out Increase Subcontracts Increase Productivity Buy-back Vac. or Hol. Temporary Assignments Temporary Hires Transfer Work Out
Action Plan Options Employee Shortage Long-term Options Recalls Increase OT or PT Short-term Options Hires Permanent In-transfers Retrain Transfer Work Out Increase Subcontracts Increase Productivity Buy-back Vac. or Hol. Temporary Assignments Temporary Hires Transfer Work Out
 Action Plan Options Employee Surplus Long-term Options Freeze Hires Use Attrition Short-term Options Permanent Out-transfers Reduce OT or PT Excused Absences Layoffs Transfer Work In Temporary Assignments Retirement Incentives Retrain Reduce Workweek Train or Retrain Transfer Work In Temp. Shut-Down or Layoff Accumulate Surplus
Action Plan Options Employee Surplus Long-term Options Freeze Hires Use Attrition Short-term Options Permanent Out-transfers Reduce OT or PT Excused Absences Layoffs Transfer Work In Temporary Assignments Retirement Incentives Retrain Reduce Workweek Train or Retrain Transfer Work In Temp. Shut-Down or Layoff Accumulate Surplus
 Control and Evaluate n In new HR plans, qualitative evaluation should assess u Extent to which HR problems and opportunities are correctly assessed u Quality of working relationships with specialists and managers who supply data u Extent to which decision-makers are using the HR plan u Perceived value of the HR plan to the decisionmakers
Control and Evaluate n In new HR plans, qualitative evaluation should assess u Extent to which HR problems and opportunities are correctly assessed u Quality of working relationships with specialists and managers who supply data u Extent to which decision-makers are using the HR plan u Perceived value of the HR plan to the decisionmakers
 Control and Evaluate n In established plans, quantitative evaluation should assess u Actual staffing levels against forecasted requirements u Actual productivity to anticipated productivity u Actual personnel flow against desired rates u Action programs implemented against those planned u Costs relative to the budget u Comparison of benefits to costs
Control and Evaluate n In established plans, quantitative evaluation should assess u Actual staffing levels against forecasted requirements u Actual productivity to anticipated productivity u Actual personnel flow against desired rates u Action programs implemented against those planned u Costs relative to the budget u Comparison of benefits to costs
 STAFFING Recruitment and Selection Human Resource Management
STAFFING Recruitment and Selection Human Resource Management
 Recruitment, Selection and HR n Recruitment and selection are two-way processes that affect each other u Applicants self-select throughout recruitment u Organizations select throughout recruitment u Recruitment goes on throughout evaluation of candidates
Recruitment, Selection and HR n Recruitment and selection are two-way processes that affect each other u Applicants self-select throughout recruitment u Organizations select throughout recruitment u Recruitment goes on throughout evaluation of candidates
 Recruitment, Selection and HR n Recruitment affects other activities u Selection system effectiveness u Training u Compensation u Employee relations u Affirmative action goals u If incumbents are not qualified, recruiters have to look at different populations u Overqualified employees become bored u Public relations activities
Recruitment, Selection and HR n Recruitment affects other activities u Selection system effectiveness u Training u Compensation u Employee relations u Affirmative action goals u If incumbents are not qualified, recruiters have to look at different populations u Overqualified employees become bored u Public relations activities
 Common Recruitment Mistakes n Lack of specificity in job ads u Too many unqualified applicants n Word of mouth recruitment used exclusively u Perpetuates the current workforce n Not communicating accurate information about the job and/or organization u Employees may become dissatisfied and leave
Common Recruitment Mistakes n Lack of specificity in job ads u Too many unqualified applicants n Word of mouth recruitment used exclusively u Perpetuates the current workforce n Not communicating accurate information about the job and/or organization u Employees may become dissatisfied and leave
 Designing Recruitment Programs Must be integrated into the strategic planning process n Must be carefully done n u Potentially qualified candidates may not hear of opening u Treatment candidates receive during recruitment will impact job choices
Designing Recruitment Programs Must be integrated into the strategic planning process n Must be carefully done n u Potentially qualified candidates may not hear of opening u Treatment candidates receive during recruitment will impact job choices
 Recruitment Philosophy n Internal advantages n External advantages u New ideas and innovation u Easier to evaluate u Reduces some training applicants u Less expensive u Faster u More familiar with organization; less training u Motivational for current employees costs u Does not disrupt current organizational chart u Usually more rapid accomplishment of affirmative action goals u Signal to employees that business is changing u Often no viable internal candidate
Recruitment Philosophy n Internal advantages n External advantages u New ideas and innovation u Easier to evaluate u Reduces some training applicants u Less expensive u Faster u More familiar with organization; less training u Motivational for current employees costs u Does not disrupt current organizational chart u Usually more rapid accomplishment of affirmative action goals u Signal to employees that business is changing u Often no viable internal candidate
 Recruitment Strategy Where to recruit n Whom to recruit n How to recruit n When to recruit n Choice of recruiters n Information to communicate n
Recruitment Strategy Where to recruit n Whom to recruit n How to recruit n When to recruit n Choice of recruiters n Information to communicate n
 Recruitment Evaluation n n Number of jobs filled Number and quality of resumes/applications Acceptance to offer ratio Salary offered Analysis of rejected offers n n n Time in which jobs were filled Cost per hire Cost of operations Affirmative action goals met Quality of new employee performance Determination of most effective methods
Recruitment Evaluation n n Number of jobs filled Number and quality of resumes/applications Acceptance to offer ratio Salary offered Analysis of rejected offers n n n Time in which jobs were filled Cost per hire Cost of operations Affirmative action goals met Quality of new employee performance Determination of most effective methods
 Measurement Issues in Selection n Reliability n Validity u Over time u Job-relatedness u Across different u “Content Validity: ” samples of items u Across different raters or judges Content of test is representative of job content u “Criterion-related Validity: ” Strength of predictive relationship between selection test and job performance
Measurement Issues in Selection n Reliability n Validity u Over time u Job-relatedness u Across different u “Content Validity: ” samples of items u Across different raters or judges Content of test is representative of job content u “Criterion-related Validity: ” Strength of predictive relationship between selection test and job performance
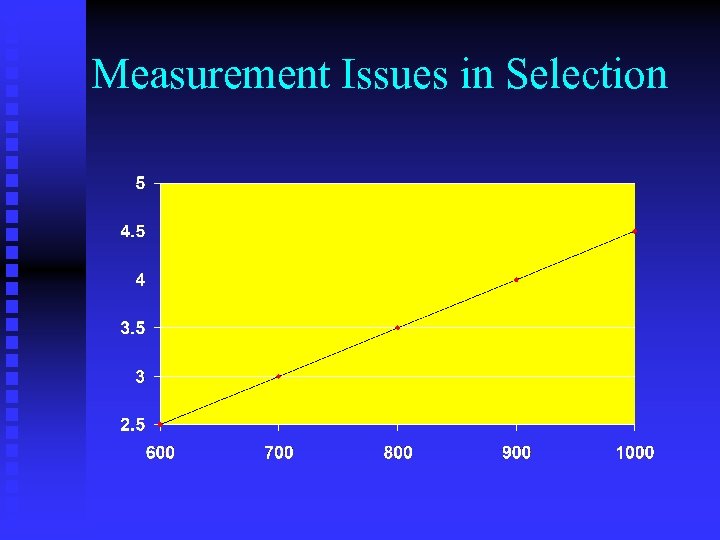 Measurement Issues in Selection
Measurement Issues in Selection
 What is a “Test? ” n EEOC Uniform Guidelines u A “test” is anything that has an impact on the terms and conditions of employment u Application blank? u Interview? u Performance appraisal? u Training programs?
What is a “Test? ” n EEOC Uniform Guidelines u A “test” is anything that has an impact on the terms and conditions of employment u Application blank? u Interview? u Performance appraisal? u Training programs?
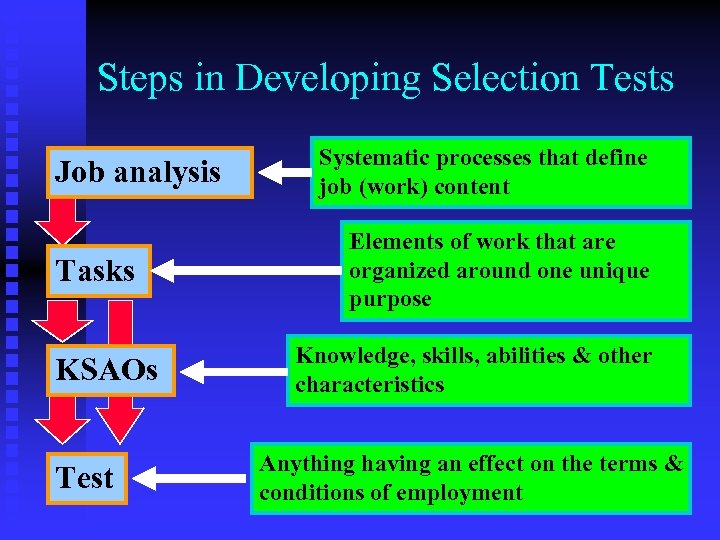 Steps in Developing Selection Tests Job analysis Tasks KSAOs Test Systematic processes that define job (work) content Elements of work that are organized around one unique purpose Knowledge, skills, abilities & other characteristics Anything having an effect on the terms & conditions of employment
Steps in Developing Selection Tests Job analysis Tasks KSAOs Test Systematic processes that define job (work) content Elements of work that are organized around one unique purpose Knowledge, skills, abilities & other characteristics Anything having an effect on the terms & conditions of employment
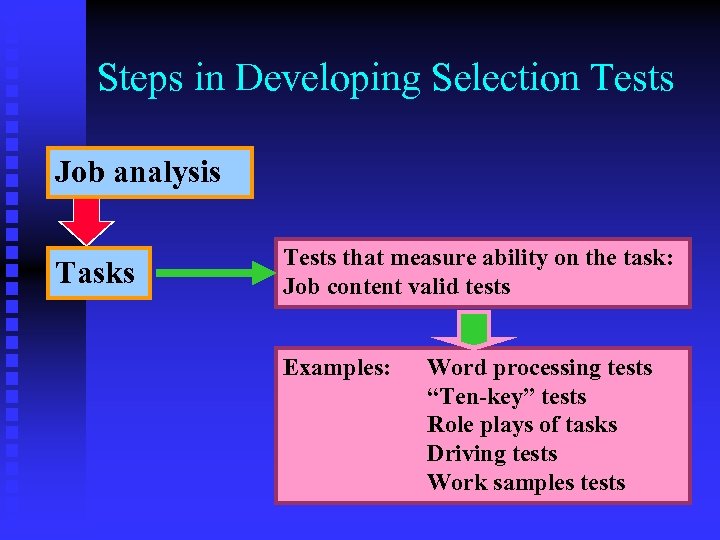 Steps in Developing Selection Tests Job analysis Tasks Tests that measure ability on the task: Job content valid tests Examples: Word processing tests “Ten-key” tests Role plays of tasks Driving tests Work samples tests
Steps in Developing Selection Tests Job analysis Tasks Tests that measure ability on the task: Job content valid tests Examples: Word processing tests “Ten-key” tests Role plays of tasks Driving tests Work samples tests
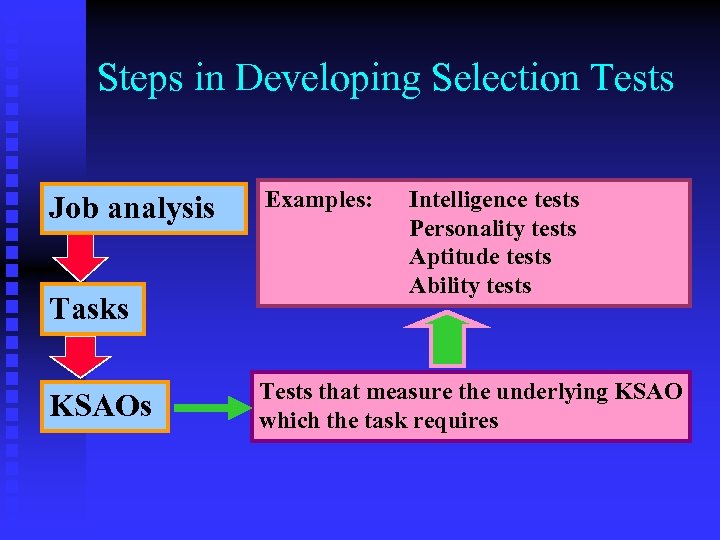 Steps in Developing Selection Tests Job analysis Tasks KSAOs Examples: Intelligence tests Personality tests Aptitude tests Ability tests Tests that measure the underlying KSAO which the task requires
Steps in Developing Selection Tests Job analysis Tasks KSAOs Examples: Intelligence tests Personality tests Aptitude tests Ability tests Tests that measure the underlying KSAO which the task requires
 Screening and Selection Methods Drug testing n Integrity tests n Mental ability tests n Objective personality and interest n Employment interviews n Work sample tests n
Screening and Selection Methods Drug testing n Integrity tests n Mental ability tests n Objective personality and interest n Employment interviews n Work sample tests n
 Choosing the Right Predictor n Depends on u The nature of the job u Established validity of the predictor u Selection ratio (ratio of hires to applicants) u Cost of the predictor u Adverse impact caused by the predictor
Choosing the Right Predictor n Depends on u The nature of the job u Established validity of the predictor u Selection ratio (ratio of hires to applicants) u Cost of the predictor u Adverse impact caused by the predictor


