3d0a29011e5d3972505c85271f2d95ee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Paper code: 2. 23/5. 83/3. 23 Preeti Nigam Faculty, Rai University
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Paper code: 2. 23/5. 83/3. 23 Preeti Nigam Faculty, Rai University
 Acknowledgements These notes have been prepared from the books written by the following authors: V. S. P Rao Schwind, Das, Werther, Davis
Acknowledgements These notes have been prepared from the books written by the following authors: V. S. P Rao Schwind, Das, Werther, Davis
 Unit-I Concepts & Perspectives of HRM; HRM in changing environment, HRM functions, Role of HR Practitioners; HR Policies, Corporate objectives and Human Resource Planning.
Unit-I Concepts & Perspectives of HRM; HRM in changing environment, HRM functions, Role of HR Practitioners; HR Policies, Corporate objectives and Human Resource Planning.
 People are Different Heterogeneous Different reactions Educated (New Technology) Motivation level
People are Different Heterogeneous Different reactions Educated (New Technology) Motivation level
 Definition Human resource may be defined as the art of procuring, developing and maintaining competent workforce to achieve the goals of an organization in an effective and efficient manner.
Definition Human resource may be defined as the art of procuring, developing and maintaining competent workforce to achieve the goals of an organization in an effective and efficient manner.
 Features Pervasive Force Action Oriented Individually oriented People oriented Development oriented Integrating mechanism Comprehensive Function Auxiliary Service Inter-disciplinary function Continuous function
Features Pervasive Force Action Oriented Individually oriented People oriented Development oriented Integrating mechanism Comprehensive Function Auxiliary Service Inter-disciplinary function Continuous function
 Scope of HRM Personnel aspect Welfare aspect Industrial relations aspect
Scope of HRM Personnel aspect Welfare aspect Industrial relations aspect
 Misconceptions 1. Lack of expertise 2. Alienation from the mainstream 3. Fascination with latest fads 4. Lack of respect
Misconceptions 1. Lack of expertise 2. Alienation from the mainstream 3. Fascination with latest fads 4. Lack of respect
 Objectives of HRM 1. To contribute to organizational effectiveness 2. To be efficient and cost effective 3. To be responsive to lager societal concerns 4. To meet personal needs of its employees
Objectives of HRM 1. To contribute to organizational effectiveness 2. To be efficient and cost effective 3. To be responsive to lager societal concerns 4. To meet personal needs of its employees
 Objectives of HRM 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. To help the organization reach its goals To employ the skills and abilities of the workforce efficiently To provide the organization with well trained and well motivated employees To increase to the fullest the employee’s job satisfaction and self-actualization To develop and maintain a quality of work life To communicate HR policies to all employees To help maintain ethical policies and behavior
Objectives of HRM 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. To help the organization reach its goals To employ the skills and abilities of the workforce efficiently To provide the organization with well trained and well motivated employees To increase to the fullest the employee’s job satisfaction and self-actualization To develop and maintain a quality of work life To communicate HR policies to all employees To help maintain ethical policies and behavior
 Importance of HRM 1. Enterprise Level a) 2. Retain best people in the organization Individual Level Promotes team work and spirit b) Excellent growth opportunities c) Work with diligence and commitment a) 3. Society Level Employment opportunities b) Scarce talents are put to best use a)
Importance of HRM 1. Enterprise Level a) 2. Retain best people in the organization Individual Level Promotes team work and spirit b) Excellent growth opportunities c) Work with diligence and commitment a) 3. Society Level Employment opportunities b) Scarce talents are put to best use a)
 New Management Practices 1. Boundary less organization 2. Employee empowerment 3. Diminished corporate layers 4. Changed power base 5. New Manager a sponsor, a team leader 6. Commitment building
New Management Practices 1. Boundary less organization 2. Employee empowerment 3. Diminished corporate layers 4. Changed power base 5. New Manager a sponsor, a team leader 6. Commitment building
 Role of HR Manager Changing from protector and screener to the planner and change agent Planning and implementing downsizing, restructuring and other cost cutting activities
Role of HR Manager Changing from protector and screener to the planner and change agent Planning and implementing downsizing, restructuring and other cost cutting activities
 HRM in India Static Legalistic Ritualistic
HRM in India Static Legalistic Ritualistic
 History of HRM 1. Industrial Revolution Fragmented and Dull jobs, workers did portion of the job, workers were glorified machine tools, interests of workers not protected 2. Scientific Management Taylor advocated, work is broken down into smallest mechanical elements and rearranging them into efficient combination. Individuals should be matched physically and mentally to the requirements of the task. Piece rate system.
History of HRM 1. Industrial Revolution Fragmented and Dull jobs, workers did portion of the job, workers were glorified machine tools, interests of workers not protected 2. Scientific Management Taylor advocated, work is broken down into smallest mechanical elements and rearranging them into efficient combination. Individuals should be matched physically and mentally to the requirements of the task. Piece rate system.
 History of HRM 3. Trade Unionism Collective bargaining, unfair labor practices, grievance handling, disciplinary procedures, pay and benefits 4. Human Relations Movement Hawthorne experiments by Elton Mayo demonstrated that employee productivity was affected not only by the way the job was designed and employee economically rewarded but also by certain social and psychological factors. Includes supervisory training programs, strengthen bonds between labor and management and counseling programs
History of HRM 3. Trade Unionism Collective bargaining, unfair labor practices, grievance handling, disciplinary procedures, pay and benefits 4. Human Relations Movement Hawthorne experiments by Elton Mayo demonstrated that employee productivity was affected not only by the way the job was designed and employee economically rewarded but also by certain social and psychological factors. Includes supervisory training programs, strengthen bonds between labor and management and counseling programs
 History of HRM 5. Human Resources Approach Pet Milk theory that happy workers are productive workers or happy cows give more milk was rejected. Workers are unique with their own needs and motivation levels. This Approach assumes that job is the primary source of satisfaction and motivation to the employees. Emphasis on individual involvement in the decisions made in the organization.
History of HRM 5. Human Resources Approach Pet Milk theory that happy workers are productive workers or happy cows give more milk was rejected. Workers are unique with their own needs and motivation levels. This Approach assumes that job is the primary source of satisfaction and motivation to the employees. Emphasis on individual involvement in the decisions made in the organization.
 Human Resources Approach People do not dislike work if they have helped establish objectives Theory Y- Most people can exercise a great deal more self-direction, self-control and creativity than are required in their current jobs Manager’s job is to use untapped human potential Manager should create a healthy, safe and convenient environment Manager should provide self-direction to the subordinates Expanding subordinates influence Work satisfaction
Human Resources Approach People do not dislike work if they have helped establish objectives Theory Y- Most people can exercise a great deal more self-direction, self-control and creativity than are required in their current jobs Manager’s job is to use untapped human potential Manager should create a healthy, safe and convenient environment Manager should provide self-direction to the subordinates Expanding subordinates influence Work satisfaction
 Terminology Management HRM Empowerment HRD Job Analysis Employee Development
Terminology Management HRM Empowerment HRD Job Analysis Employee Development
 Case Does Sincerity pay?
Case Does Sincerity pay?
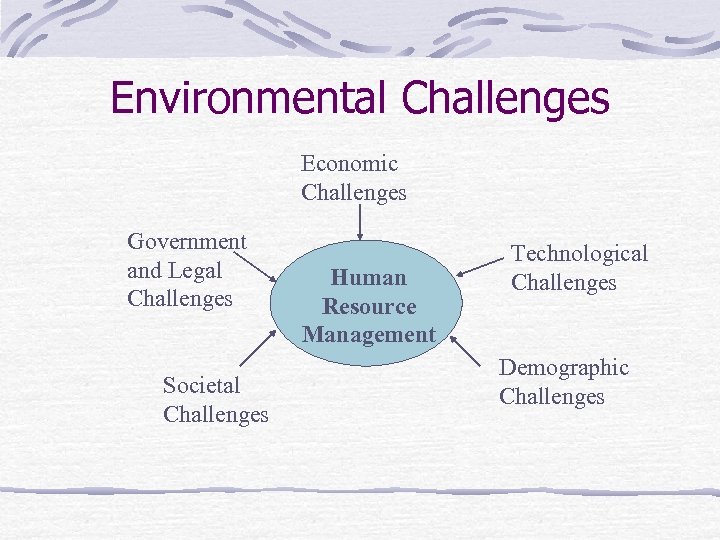 Environmental Challenges Economic Challenges Government and Legal Challenges Societal Challenges Human Resource Management Technological Challenges Demographic Challenges
Environmental Challenges Economic Challenges Government and Legal Challenges Societal Challenges Human Resource Management Technological Challenges Demographic Challenges
 Economic and Societal Challenges 1. Economic Challenges Global Trade Challenge of Productivity Improvement 2. Technological Challenges Computerization Automation 3. Demographic Challenges Increasing number of women in the workforce Shift from Primary to Service jobs Educational attainment of workers Employment of older workers More part time workers Unemployment 4. Cultural Challenges
Economic and Societal Challenges 1. Economic Challenges Global Trade Challenge of Productivity Improvement 2. Technological Challenges Computerization Automation 3. Demographic Challenges Increasing number of women in the workforce Shift from Primary to Service jobs Educational attainment of workers Employment of older workers More part time workers Unemployment 4. Cultural Challenges
 Steps in Dealing with Environmental Challenges 1. Monitor the environment 2. Evaluate the impact 3. Take proactive measures 4. Obtain and analyze feedback
Steps in Dealing with Environmental Challenges 1. Monitor the environment 2. Evaluate the impact 3. Take proactive measures 4. Obtain and analyze feedback
 Factors Influencing Personnel Function. External Technological Economic Political Social Local & Govt. Issues Unions Employer’s demands Workforce diversity Rao Internal Mission Policies Organizational Culture Organizational Structure HR Systems
Factors Influencing Personnel Function. External Technological Economic Political Social Local & Govt. Issues Unions Employer’s demands Workforce diversity Rao Internal Mission Policies Organizational Culture Organizational Structure HR Systems
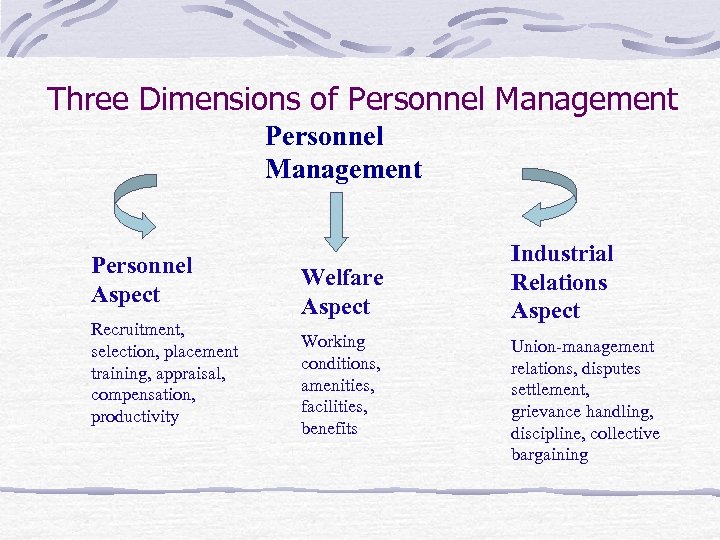 Three Dimensions of Personnel Management Personnel Aspect Recruitment, selection, placement training, appraisal, compensation, productivity Welfare Aspect Working conditions, amenities, facilities, benefits Industrial Relations Aspect Union-management relations, disputes settlement, grievance handling, discipline, collective bargaining
Three Dimensions of Personnel Management Personnel Aspect Recruitment, selection, placement training, appraisal, compensation, productivity Welfare Aspect Working conditions, amenities, facilities, benefits Industrial Relations Aspect Union-management relations, disputes settlement, grievance handling, discipline, collective bargaining
 Functions of Personnel Management Managerial Functions Planning Organizing Directing Controlling Operative Functions 1. Employment Job Analysis HR Planning Recruitment Selection Placement Induction and Orientation
Functions of Personnel Management Managerial Functions Planning Organizing Directing Controlling Operative Functions 1. Employment Job Analysis HR Planning Recruitment Selection Placement Induction and Orientation
 Functions of Personnel Management 2. Human Resource Development Performance Appraisal Training Management Development Career Planning and Development Organization Development 3. Compensation Job Evaluation Wage and salary administration Incentives Bonus Fringe benefits Social security measures
Functions of Personnel Management 2. Human Resource Development Performance Appraisal Training Management Development Career Planning and Development Organization Development 3. Compensation Job Evaluation Wage and salary administration Incentives Bonus Fringe benefits Social security measures
 Functions of Personnel Management Human relations 5. Effectiveness of Human resource Management 4. Organization health Human resource auditing, audit and research
Functions of Personnel Management Human relations 5. Effectiveness of Human resource Management 4. Organization health Human resource auditing, audit and research
 Personnel Policy Brewster and Richbell defined Personnel policies as “a set of proposals and actions that act as a reference point for managers in their dealings with employees. Personnel policies constitute guides to action. They furnish the general standards or bases on which decisions are reached. Their genesis lies in an organization's values, philosophy, concepts and principles”. E. g. equal employment opportunity to minorities
Personnel Policy Brewster and Richbell defined Personnel policies as “a set of proposals and actions that act as a reference point for managers in their dealings with employees. Personnel policies constitute guides to action. They furnish the general standards or bases on which decisions are reached. Their genesis lies in an organization's values, philosophy, concepts and principles”. E. g. equal employment opportunity to minorities
 Procedures are action guidelines. They are derived from policies.
Procedures are action guidelines. They are derived from policies.
 Advantages of Personnel Policies Delegation Uniformity Better control Standards of efficiency Confidence Speedy decisions Coordinating devices
Advantages of Personnel Policies Delegation Uniformity Better control Standards of efficiency Confidence Speedy decisions Coordinating devices
 Obstacles in Administering Personnel Policies Reluctant managers Conflicts in policy specially employment Difficult to review and update Freedom to managers dangerous
Obstacles in Administering Personnel Policies Reluctant managers Conflicts in policy specially employment Difficult to review and update Freedom to managers dangerous
 Characteristics of Personnel Policy Related to objectives Easy to understand Precise Stable and flexible Based on facts Appropriate number Just, fair and equitable Reasonable Review
Characteristics of Personnel Policy Related to objectives Easy to understand Precise Stable and flexible Based on facts Appropriate number Just, fair and equitable Reasonable Review
 Coverage of Personnel Policies. Michael Armstrong Social responsibility Equity Consideration Quality of Work Life Employment policies Promotion policies Development policies Relations policies
Coverage of Personnel Policies. Michael Armstrong Social responsibility Equity Consideration Quality of Work Life Employment policies Promotion policies Development policies Relations policies
 Line and Staff Relationships Line Relationships exists between superior and subordinate. Line refers to those positions of an organization which have responsibility, authority and are accountable for accomplishment of primary objectives.
Line and Staff Relationships Line Relationships exists between superior and subordinate. Line refers to those positions of an organization which have responsibility, authority and are accountable for accomplishment of primary objectives.
 Line and Staff Relationships Staff Relations When positions are created to secure advice, guidance, information, help or assistance, counseling etc. in the process of attaining organizational goals Staff authority is advisory. A staff manager helps serve, investigate, plan, solve special problems, supports line effort, provides ideas and has special expertise.
Line and Staff Relationships Staff Relations When positions are created to secure advice, guidance, information, help or assistance, counseling etc. in the process of attaining organizational goals Staff authority is advisory. A staff manager helps serve, investigate, plan, solve special problems, supports line effort, provides ideas and has special expertise.
 Personnel Management- Line or Staff The personnel management is a line management responsibility but a staff function. Personnel managers perform the various functions of personnel management viz. employment, training, development, wage and salary administration, motivation, grievance redressal, workers’ participation in management, collective bargaining etc. Also personnel managers perform certain staff functions relating to management of personnel like advising, assisting, guiding, suggesting, counseling and providing information to line managers.
Personnel Management- Line or Staff The personnel management is a line management responsibility but a staff function. Personnel managers perform the various functions of personnel management viz. employment, training, development, wage and salary administration, motivation, grievance redressal, workers’ participation in management, collective bargaining etc. Also personnel managers perform certain staff functions relating to management of personnel like advising, assisting, guiding, suggesting, counseling and providing information to line managers.
 Human Resource Planning The process of getting the right number of qualified people into the right job at the right time.
Human Resource Planning The process of getting the right number of qualified people into the right job at the right time.
 Objectives Forecast personnel requirements Cope with changes Use existing manpower productively Promote employees in a systematic manner
Objectives Forecast personnel requirements Cope with changes Use existing manpower productively Promote employees in a systematic manner
 Benefits Reservoir of Talent Prepare people for future Expand or contract Cut costs Succession Planning
Benefits Reservoir of Talent Prepare people for future Expand or contract Cut costs Succession Planning
 HRM at Different Levels 1. National level 2. Sectoral Level 3. Industry Level 4. Unit level 5. Departmental level 6. Job Level
HRM at Different Levels 1. National level 2. Sectoral Level 3. Industry Level 4. Unit level 5. Departmental level 6. Job Level
 The Process Of HRP 1. Forecasting the demand for Human resources 2. Preparing Manpower Inventory 3. Determining Manpower Gaps 4. Formulating Manpower Plans
The Process Of HRP 1. Forecasting the demand for Human resources 2. Preparing Manpower Inventory 3. Determining Manpower Gaps 4. Formulating Manpower Plans
 Human Resource Planning (cont’d) Small Business and HR Planning Issues Attracting and retaining qualified outsiders Management succession between generations of owners Evolution of HR activities as business grows Family relationships and HR policies
Human Resource Planning (cont’d) Small Business and HR Planning Issues Attracting and retaining qualified outsiders Management succession between generations of owners Evolution of HR activities as business grows Family relationships and HR policies
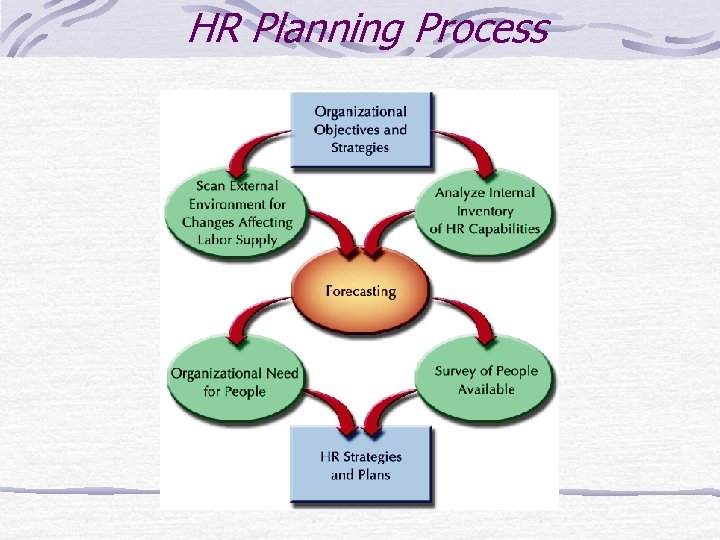 HR Planning Process
HR Planning Process
 Manpower Plan: Strategies Recruitment Plan Redeployment Plan Redundancy plan Training Plan Productivity Plan Retention Plan Control Points
Manpower Plan: Strategies Recruitment Plan Redeployment Plan Redundancy plan Training Plan Productivity Plan Retention Plan Control Points
 Benefits of HR Planning Better view of the HR dimensions of business decisions Lower HR costs through better HR management. More timely recruitment for anticipate HR needs More inclusion of protected groups through planned increases in workforce diversity. Better development of managerial talent
Benefits of HR Planning Better view of the HR dimensions of business decisions Lower HR costs through better HR management. More timely recruitment for anticipate HR needs More inclusion of protected groups through planned increases in workforce diversity. Better development of managerial talent
 Responsibility for HRP Prof. Geisler outlined the responsibilities. Assist and counsel operating managers to plan and set objectives Collect and summarize manpower data keeping long run objectives and organizational interests in mind Monitor and measure performance against the plan and keep top management informed Provide proper research base for effective manpower and organizational planning
Responsibility for HRP Prof. Geisler outlined the responsibilities. Assist and counsel operating managers to plan and set objectives Collect and summarize manpower data keeping long run objectives and organizational interests in mind Monitor and measure performance against the plan and keep top management informed Provide proper research base for effective manpower and organizational planning
 Problems in HRP Accuracy Support Number’s game
Problems in HRP Accuracy Support Number’s game
 Indian Organizations Inadequate records Improper retrieval systems Non-computerized personnel information Current technologies and knowledge not put to use optimally Changes in labor market Difficulties in forecasting resignations, deaths, turnovers etc.
Indian Organizations Inadequate records Improper retrieval systems Non-computerized personnel information Current technologies and knowledge not put to use optimally Changes in labor market Difficulties in forecasting resignations, deaths, turnovers etc.
 Guidelines Objectives Top Management Support Manpower Inventory Human Resource Information System Coordination
Guidelines Objectives Top Management Support Manpower Inventory Human Resource Information System Coordination
 Suggested Readings: 1. Dessler, Gary, Human Resource Management, Pearson 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Education Asia, New Delhi. Rao, V. S. P. , Human Resource Management-Text & Cases, Excel Books, New Delhi. Ramaswamy, E; Managing Human Resources, Oxford University Press, New Delhi Irancevich, John, Human Resource Management, Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill. Casio, Wayne F; Managing Human Resources, Mc. Graw Hill Inc. Subba Rao, P; Essentials of Human Resource Management & Industrial Relations, Text, Cases & Games, Mimbai, Himalaya Publishing House. Mondy R. W; Noe, R. M. , Premeaux, S. r. and Mondy J. B; Human Resource Management, Prentice Hall Inc. Saiyodain, Human Resource Management, TMH, N. Delhi. Aswthappa, Human Resource Management, TMH, N. Delhi.
Suggested Readings: 1. Dessler, Gary, Human Resource Management, Pearson 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Education Asia, New Delhi. Rao, V. S. P. , Human Resource Management-Text & Cases, Excel Books, New Delhi. Ramaswamy, E; Managing Human Resources, Oxford University Press, New Delhi Irancevich, John, Human Resource Management, Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill. Casio, Wayne F; Managing Human Resources, Mc. Graw Hill Inc. Subba Rao, P; Essentials of Human Resource Management & Industrial Relations, Text, Cases & Games, Mimbai, Himalaya Publishing House. Mondy R. W; Noe, R. M. , Premeaux, S. r. and Mondy J. B; Human Resource Management, Prentice Hall Inc. Saiyodain, Human Resource Management, TMH, N. Delhi. Aswthappa, Human Resource Management, TMH, N. Delhi.


