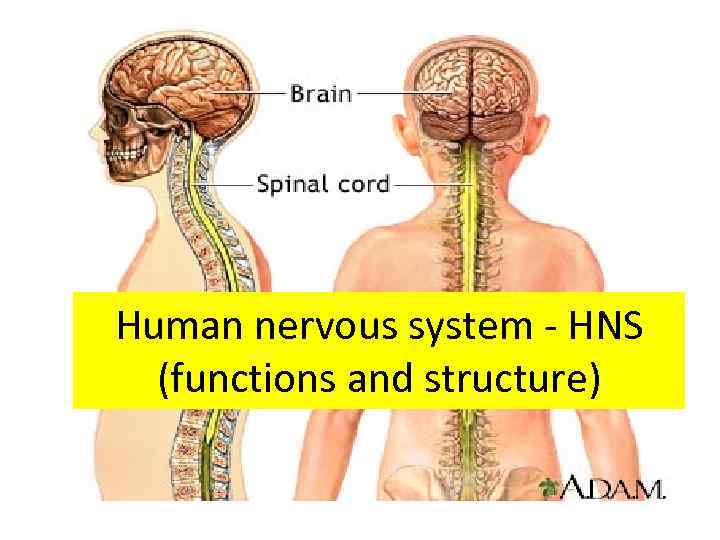
 Human nervous system - HNS (functions and structure)
Human nervous system - HNS (functions and structure)
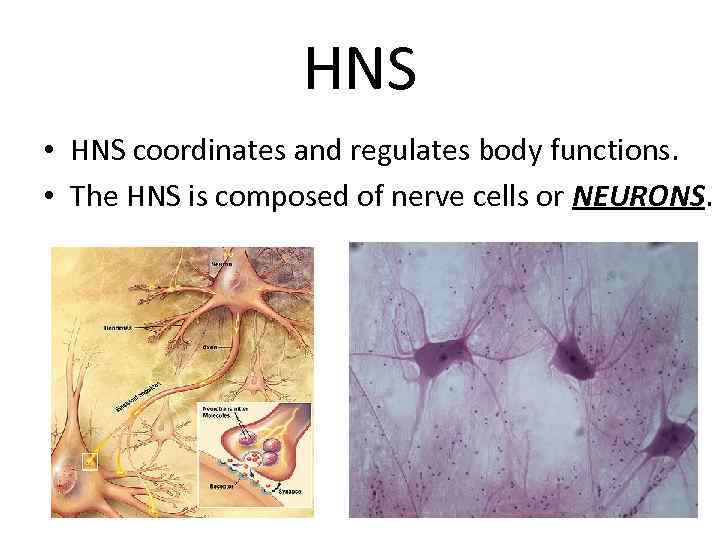 HNS • HNS coordinates and regulates body functions. • The HNS is composed of nerve cells or NEURONS.
HNS • HNS coordinates and regulates body functions. • The HNS is composed of nerve cells or NEURONS.
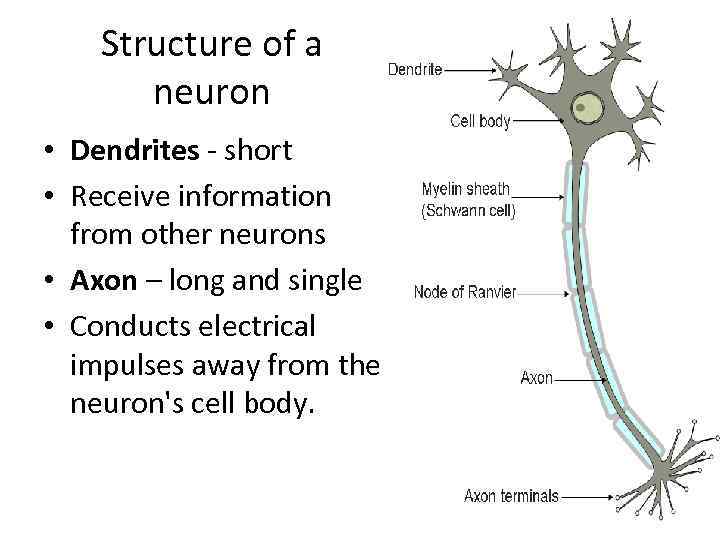 Structure of a neuron • Dendrites - short • Receive information from other neurons • Axon – long and single • Conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body.
Structure of a neuron • Dendrites - short • Receive information from other neurons • Axon – long and single • Conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body.
 Types of neurons • Unipolar – one projection, transmit info from sensory organs (eye, skin…) to central nervous system (CNS). • Bipolar – one axon and dendrite, interpretation of info. • Multipolar – many dendrites and one axon, from CNS to muscles or glands
Types of neurons • Unipolar – one projection, transmit info from sensory organs (eye, skin…) to central nervous system (CNS). • Bipolar – one axon and dendrite, interpretation of info. • Multipolar – many dendrites and one axon, from CNS to muscles or glands
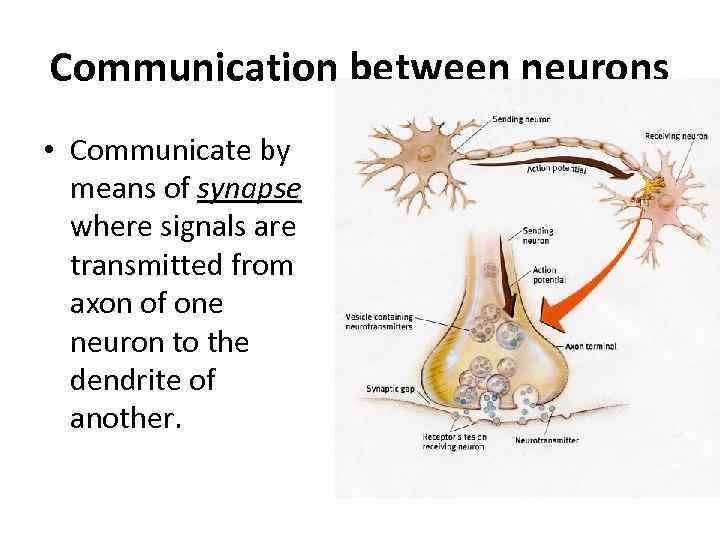 Communication between neurons • Communicate by means of synapse where signals are transmitted from axon of one neuron to the dendrite of another.
Communication between neurons • Communicate by means of synapse where signals are transmitted from axon of one neuron to the dendrite of another.
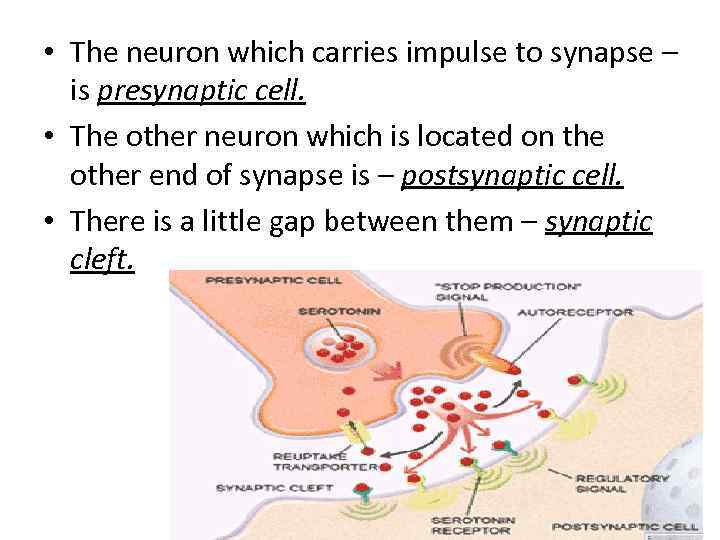 • The neuron which carries impulse to synapse – is presynaptic cell. • The other neuron which is located on the other end of synapse is – postsynaptic cell. • There is a little gap between them – synaptic cleft.
• The neuron which carries impulse to synapse – is presynaptic cell. • The other neuron which is located on the other end of synapse is – postsynaptic cell. • There is a little gap between them – synaptic cleft.
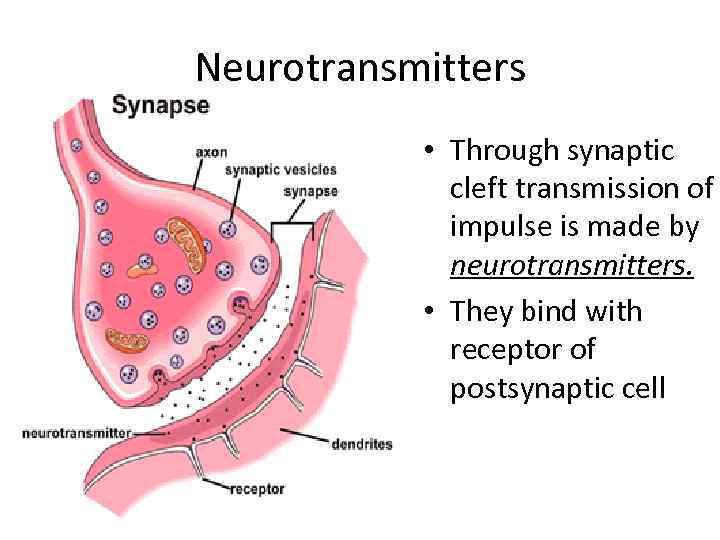 Neurotransmitters • Through synaptic cleft transmission of impulse is made by neurotransmitters. • They bind with receptor of postsynaptic cell
Neurotransmitters • Through synaptic cleft transmission of impulse is made by neurotransmitters. • They bind with receptor of postsynaptic cell
 Parts of HNS • 1. Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord, control center of body • 2. Peripheral nervous system (PNS): contains a) sensory neurons, receive info (eye, skin…) and transmit it to CNS b) motor neurons, send commands from CNS to muscles and organs
Parts of HNS • 1. Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord, control center of body • 2. Peripheral nervous system (PNS): contains a) sensory neurons, receive info (eye, skin…) and transmit it to CNS b) motor neurons, send commands from CNS to muscles and organs