3_lesson_integumentary_system.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Human integumentary system (SKIN)
Human integumentary system (SKIN)
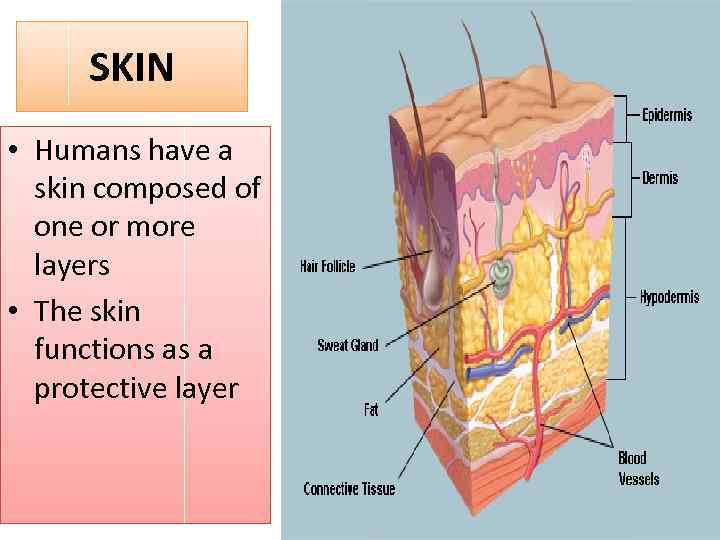 SKIN • Humans have a skin composed of one or more layers • The skin functions as a protective layer
SKIN • Humans have a skin composed of one or more layers • The skin functions as a protective layer
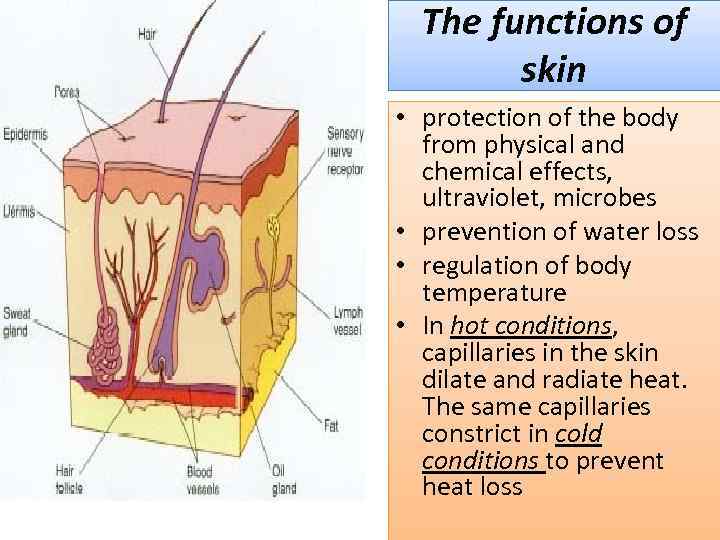 The functions of skin • protection of the body from physical and chemical effects, ultraviolet, microbes • prevention of water loss • regulation of body temperature • In hot conditions, capillaries in the skin dilate and radiate heat. The same capillaries constrict in cold conditions to prevent heat loss
The functions of skin • protection of the body from physical and chemical effects, ultraviolet, microbes • prevention of water loss • regulation of body temperature • In hot conditions, capillaries in the skin dilate and radiate heat. The same capillaries constrict in cold conditions to prevent heat loss
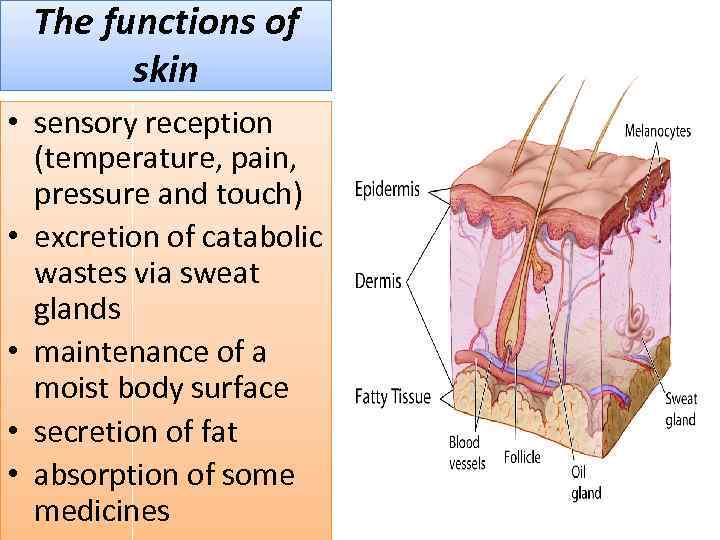 The functions of skin • sensory reception (temperature, pain, pressure and touch) • excretion of catabolic wastes via sweat glands • maintenance of a moist body surface • secretion of fat • absorption of some medicines
The functions of skin • sensory reception (temperature, pain, pressure and touch) • excretion of catabolic wastes via sweat glands • maintenance of a moist body surface • secretion of fat • absorption of some medicines
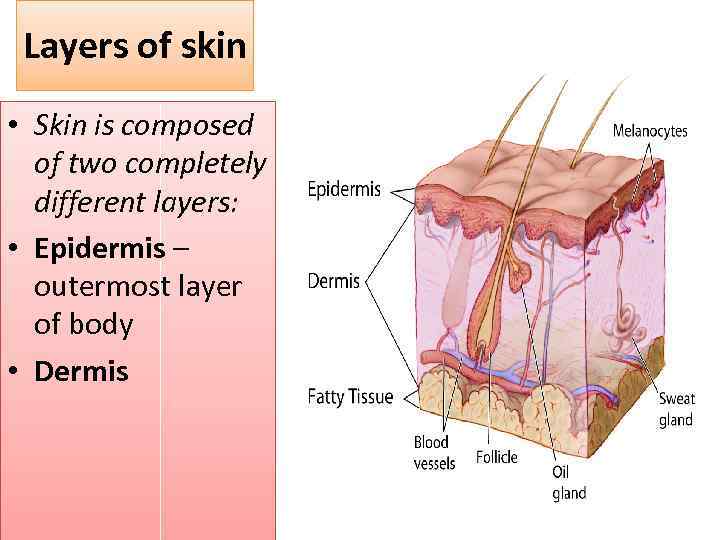 Layers of skin • Skin is composed of two completely different layers: • Epidermis – outermost layer of body • Dermis
Layers of skin • Skin is composed of two completely different layers: • Epidermis – outermost layer of body • Dermis
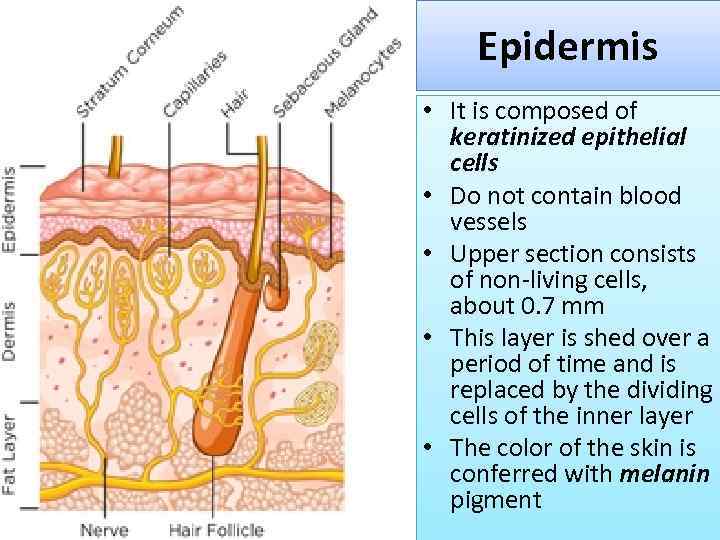 Epidermis • It is composed of keratinized epithelial cells • Do not contain blood vessels • Upper section consists of non-living cells, about 0. 7 mm • This layer is shed over a period of time and is replaced by the dividing cells of the inner layer • The color of the skin is conferred with melanin pigment
Epidermis • It is composed of keratinized epithelial cells • Do not contain blood vessels • Upper section consists of non-living cells, about 0. 7 mm • This layer is shed over a period of time and is replaced by the dividing cells of the inner layer • The color of the skin is conferred with melanin pigment
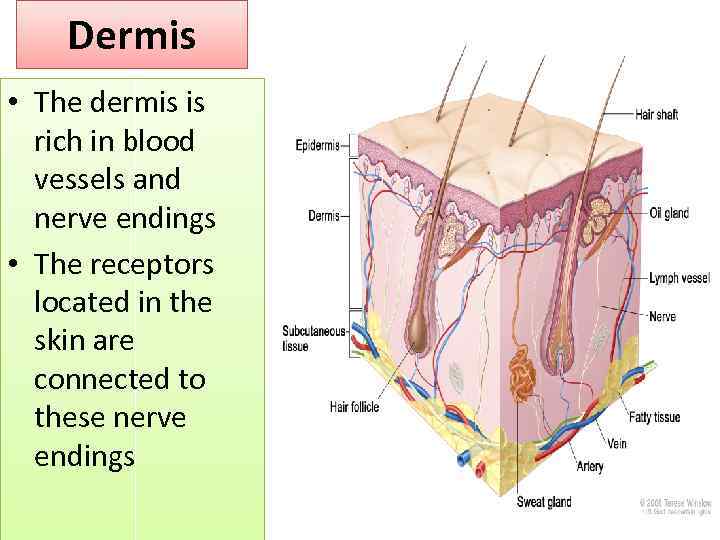 Dermis • The dermis is rich in blood vessels and nerve endings • The receptors located in the skin are connected to these nerve endings
Dermis • The dermis is rich in blood vessels and nerve endings • The receptors located in the skin are connected to these nerve endings
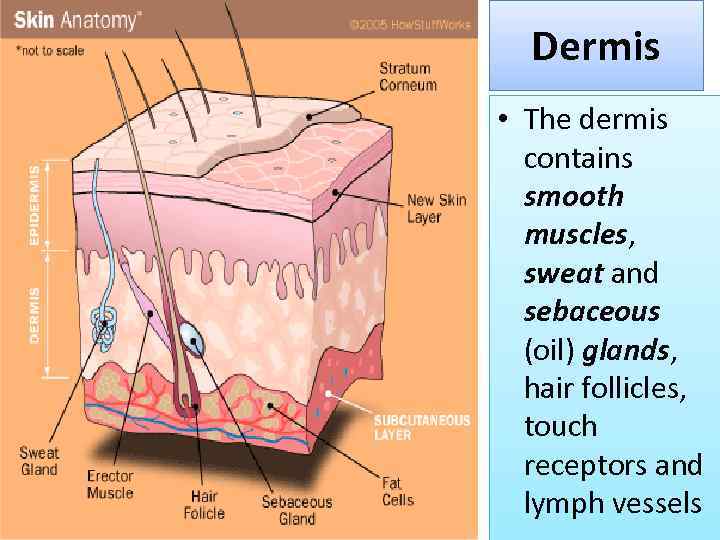 Dermis • The dermis contains smooth muscles, sweat and sebaceous (oil) glands, hair follicles, touch receptors and lymph vessels
Dermis • The dermis contains smooth muscles, sweat and sebaceous (oil) glands, hair follicles, touch receptors and lymph vessels
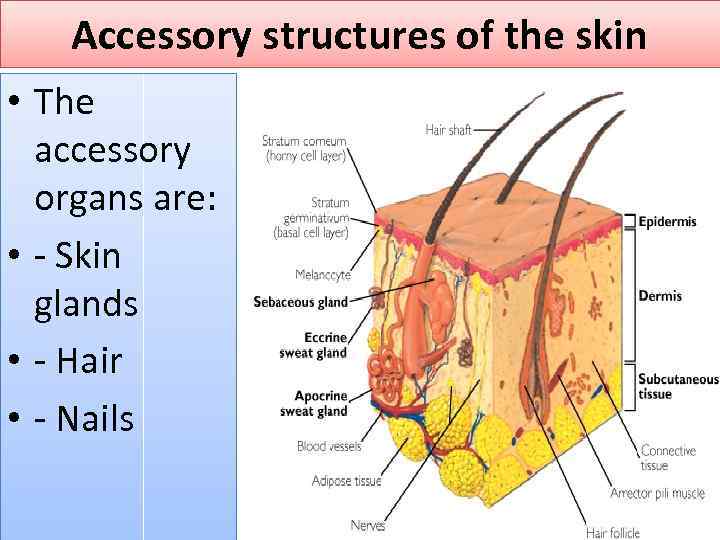 Accessory structures of the skin • The accessory organs are: • - Skin glands • - Hair • - Nails
Accessory structures of the skin • The accessory organs are: • - Skin glands • - Hair • - Nails
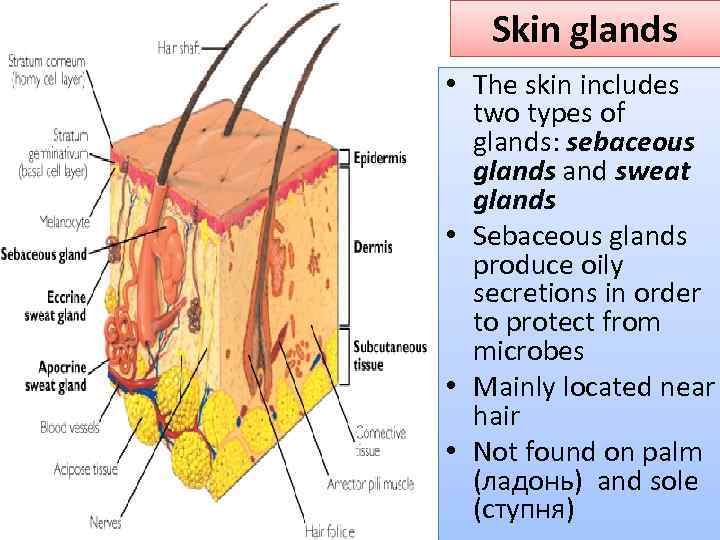 Skin glands • The skin includes two types of glands: sebaceous glands and sweat glands • Sebaceous glands produce oily secretions in order to protect from microbes • Mainly located near hair • Not found on palm (ладонь) and sole (ступня)
Skin glands • The skin includes two types of glands: sebaceous glands and sweat glands • Sebaceous glands produce oily secretions in order to protect from microbes • Mainly located near hair • Not found on palm (ладонь) and sole (ступня)
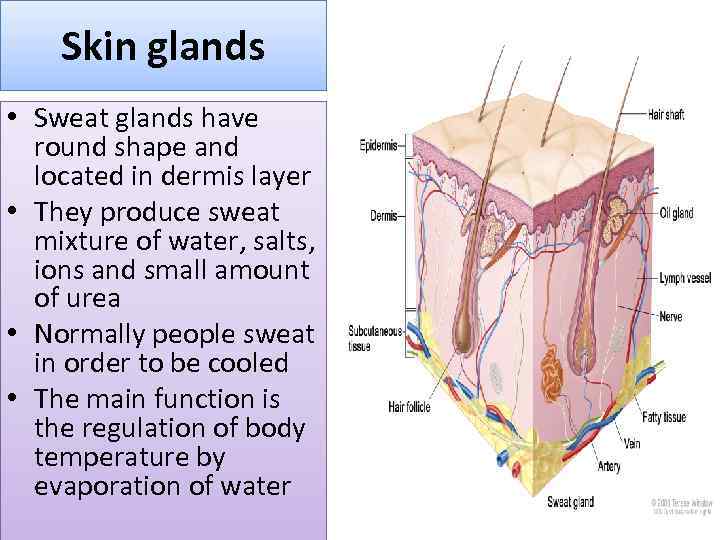 Skin glands • Sweat glands have round shape and located in dermis layer • They produce sweat mixture of water, salts, ions and small amount of urea • Normally people sweat in order to be cooled • The main function is the regulation of body temperature by evaporation of water
Skin glands • Sweat glands have round shape and located in dermis layer • They produce sweat mixture of water, salts, ions and small amount of urea • Normally people sweat in order to be cooled • The main function is the regulation of body temperature by evaporation of water
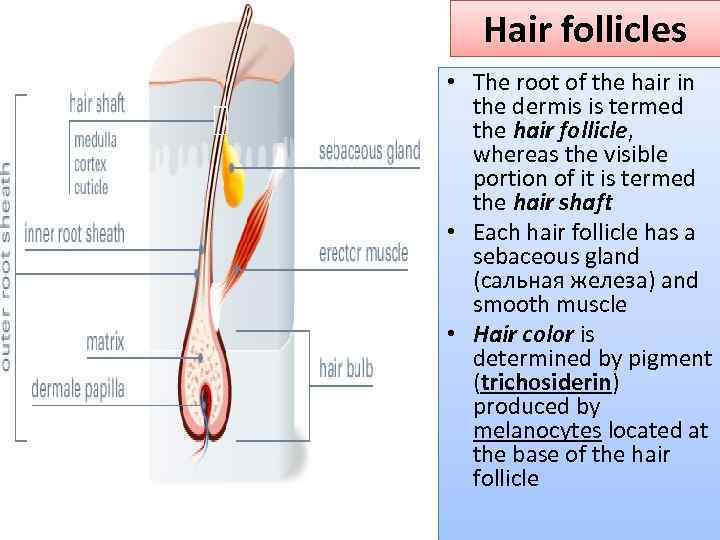 Hair follicles • The root of the hair in the dermis is termed the hair follicle, whereas the visible portion of it is termed the hair shaft • Each hair follicle has a sebaceous gland (сальная железа) and smooth muscle • Hair color is determined by pigment (trichosiderin) produced by melanocytes located at the base of the hair follicle
Hair follicles • The root of the hair in the dermis is termed the hair follicle, whereas the visible portion of it is termed the hair shaft • Each hair follicle has a sebaceous gland (сальная железа) and smooth muscle • Hair color is determined by pigment (trichosiderin) produced by melanocytes located at the base of the hair follicle
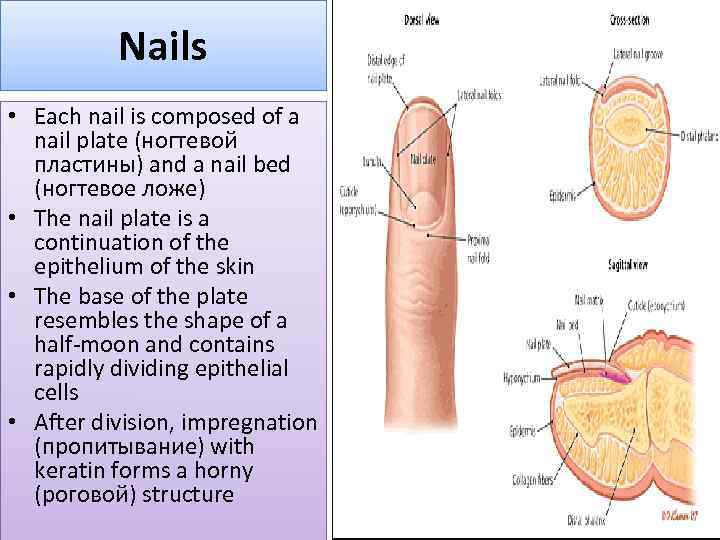 Nails • Each nail is composed of a nail plate (ногтевой пластины) and a nail bed (ногтевое ложе) • The nail plate is a continuation of the epithelium of the skin • The base of the plate resembles the shape of a half-moon and contains rapidly dividing epithelial cells • After division, impregnation (пропитывание) with keratin forms a horny (роговой) structure
Nails • Each nail is composed of a nail plate (ногтевой пластины) and a nail bed (ногтевое ложе) • The nail plate is a continuation of the epithelium of the skin • The base of the plate resembles the shape of a half-moon and contains rapidly dividing epithelial cells • After division, impregnation (пропитывание) with keratin forms a horny (роговой) structure
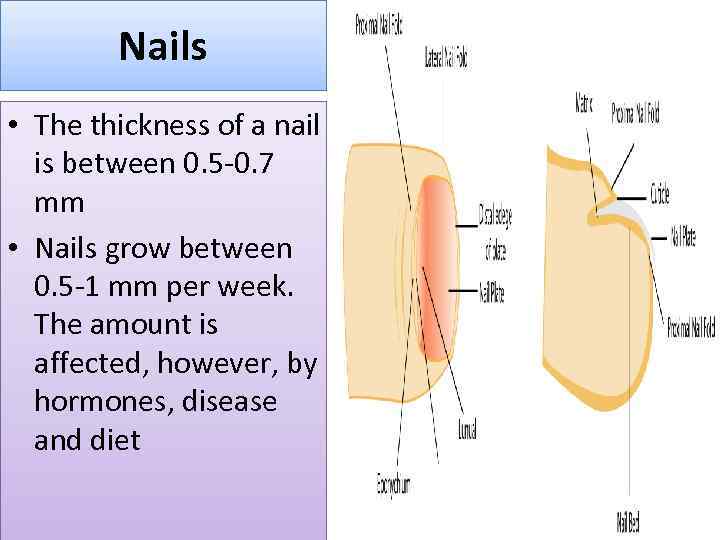 Nails • The thickness of a nail is between 0. 5 -0. 7 mm • Nails grow between 0. 5 -1 mm per week. The amount is affected, however, by hormones, disease and diet
Nails • The thickness of a nail is between 0. 5 -0. 7 mm • Nails grow between 0. 5 -1 mm per week. The amount is affected, however, by hormones, disease and diet
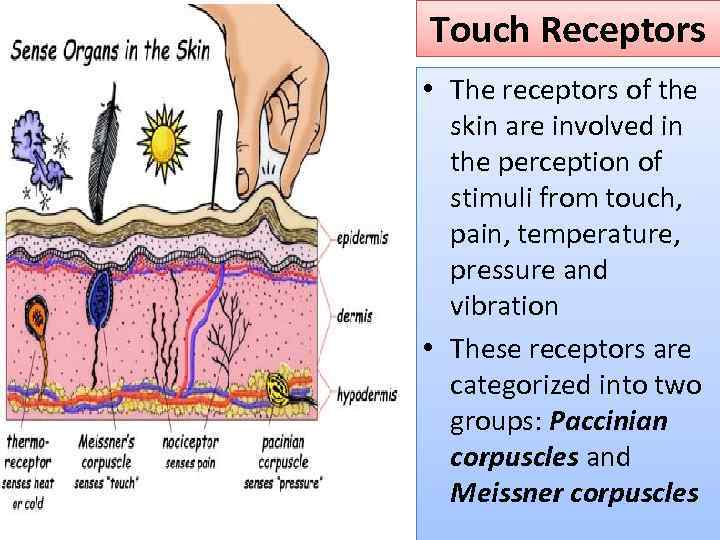 Touch Receptors • The receptors of the skin are involved in the perception of stimuli from touch, pain, temperature, pressure and vibration • These receptors are categorized into two groups: Paccinian corpuscles and Meissner corpuscles
Touch Receptors • The receptors of the skin are involved in the perception of stimuli from touch, pain, temperature, pressure and vibration • These receptors are categorized into two groups: Paccinian corpuscles and Meissner corpuscles
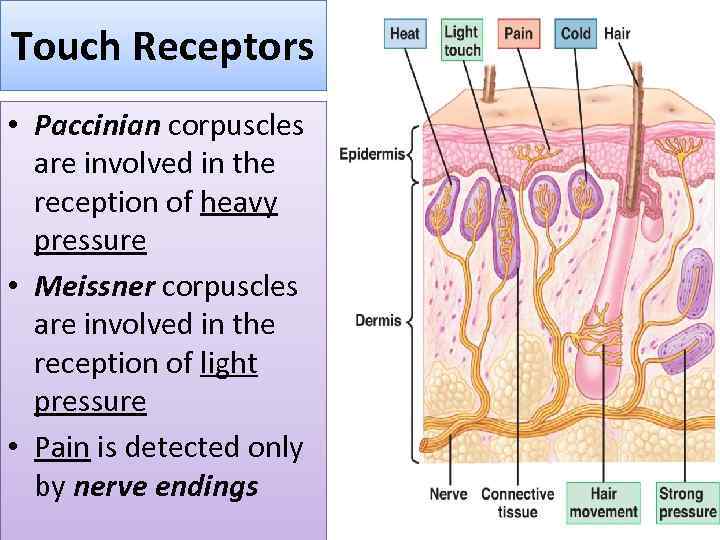 Touch Receptors • Paccinian corpuscles are involved in the reception of heavy pressure • Meissner corpuscles are involved in the reception of light pressure • Pain is detected only by nerve endings
Touch Receptors • Paccinian corpuscles are involved in the reception of heavy pressure • Meissner corpuscles are involved in the reception of light pressure • Pain is detected only by nerve endings


