8535e9344c14b26c5e134fcb50617e38.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 90



Human Ecology: • deals with the relationship between humans and their environment

Recall: The ecosystem • ecological system • any portion of the environment • made up of living(biotic factors) and nonliving things (abiotic factors)

Environmental Threats Humans have greater impact on the environment than other organisms by: • altering the environment in pursuit of natural resources, such as food, coal, and wood • generating wastes and pollution that affect the environment • upsetting the basic processes of the ecosystems, such as generation of soils, cycling of waters, flow of energy, and recycling of nutrients

Two Types of Resources • Renewable resources - resources that can be replaced in a relatively short period of time - solar energy, air, water, soil, living things, food supply

Renewable Resources

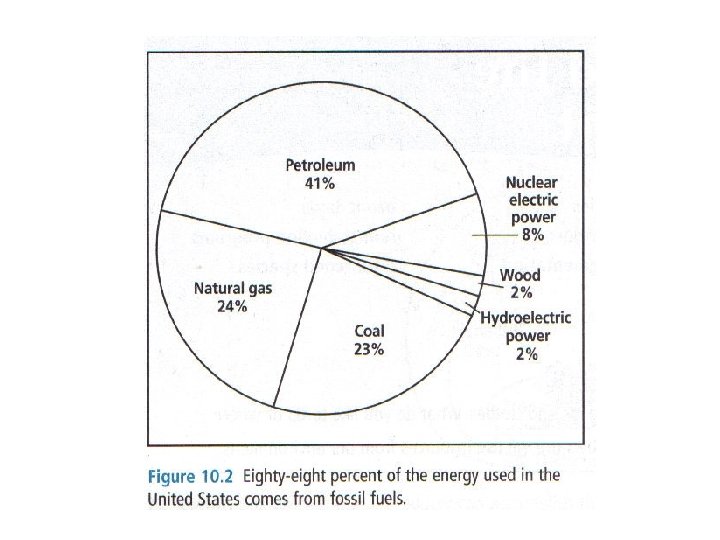
• Nonrenewable resources - once used, can not be replaced - those that are finite (fixed amount on Earth) - those that take a long time to be replaced - fossil fuels, coal, oil, natural gas, metals, minerals

Nonrenewable Resources



Preserving Our Resources The 3 R’s • REDUCE • REUSE • RECYCLE

How Individuals Can Preserve Resources

How much have you learned? 1. Which of the following is a renewable resource? A. wood B. oil C. iron D. coal

2. The best way to ensure that there will be enough aluminum for all future needs is to A. dig more mines and process more aluminum B. buy more aluminum from other countries and save our own C. recycle and reuse aluminum D. increase space exploration and search for new sources of aluminum

3. Some ecologists are concerned that the human population has outgrown the capacity of many of Earth’s ecosystems. The natural limiting factor that will more likely prevent further human population growth in many parts of the world is A. habitat destruction B. political intervention C. food supply D. social intervention

4. Today’s lifestyles have led to increased demands for disposable products. The packaging of these products has caused environmental problems most directly associated with A. food web contamination B. atmosphere depletion C. solid waste disposal D. the use of nuclear fuels

5. When humans use more ground water for industry than is being replaced, the soil above the ground water may collapse and disrupt natural habitats. This human activity is an example of A. species exploitation B. renewal of natural resources C. a disposal problem D. poor use of finite resources

6. In some areas, foresters plant one tree for every tree they cut. This activity is an example of A. lack of management of nonrenewable natural resources B. a good conservation practice for renewable natural resources C. a good conservation practice for nonrenewable natural resources D. lack of concern for renewable resources

Causes of Environmental Damage
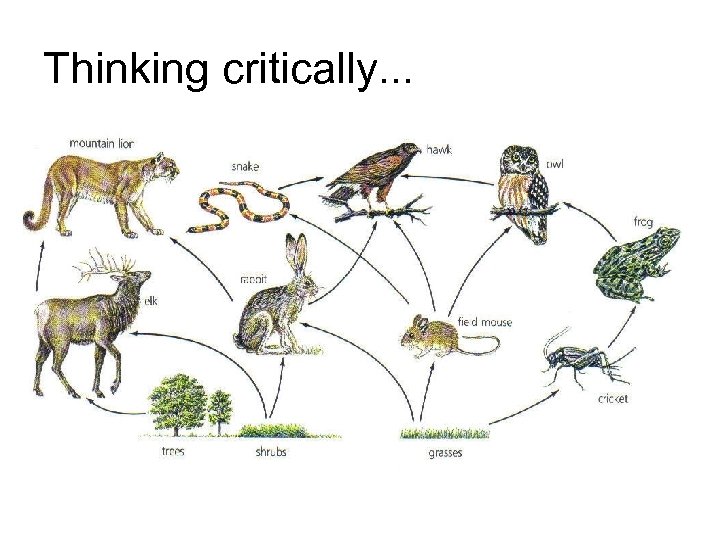
Thinking critically. . .

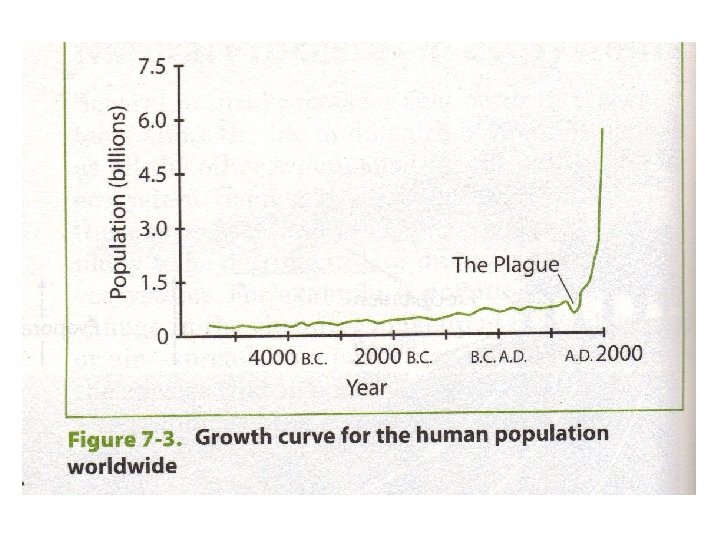
Human Population Growth • most serious environmental problems related to growth in human population • 1850: 1 billion • 1930: 2 billion • mid 1970’s: 4 billion • 1990: 5. 1 billion • 2000: 6. 2 billion

Disruption of the Ecosystem • Urbanization - shift from rural (farming) areas to cities - results in the destruction of farmlands - destroyed or endangered other ecosystems

Industrialization • the development of an economy in which machines produce many of the products people use • may add to quality of life, but can harm the environment • contributes to pollution of air and water • increase demand for energy, water, and other resources

Deforestation • the destruction of forests resulting from human activity • can provide people with land for farming and places to live • causes widespread habitat destruction

Poor Farming Practices • Overfarming and overgrazing

• Misuse of Pesticides - indiscrimate use caused contamination of the air and water - disrupted food chains by killing organisms that are not pests

Pollution • adding anything to the environment or affecting the environment in a way that makes it less fit for living things • processes or changes that are likely detrimental or damaging to the ecosystems • a harmful change in the chemical makeup of the soil, water, or air

Some Forms of Pollution • Water Pollution Sources of pollution: 1. organic wastes 2. inorganic chemicals 3. disease-causing microorganisms 4. changes in water temperature 5. oil spills 6. radioactive wastes
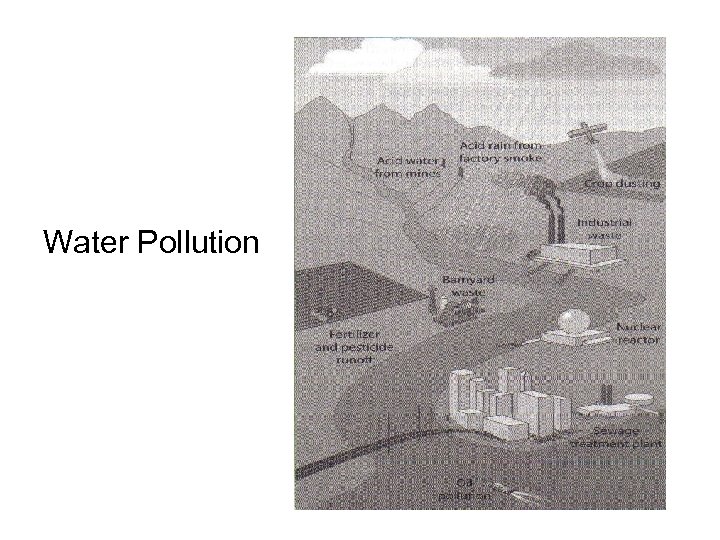
Water Pollution


• Air Pollution Some air pollutants: 1. aerosols - natural (smoke, dust) - artificial ( hair spray, air freshener) 2. gases (SO 2, H 2 S, CO, NO 2)
Global Warming
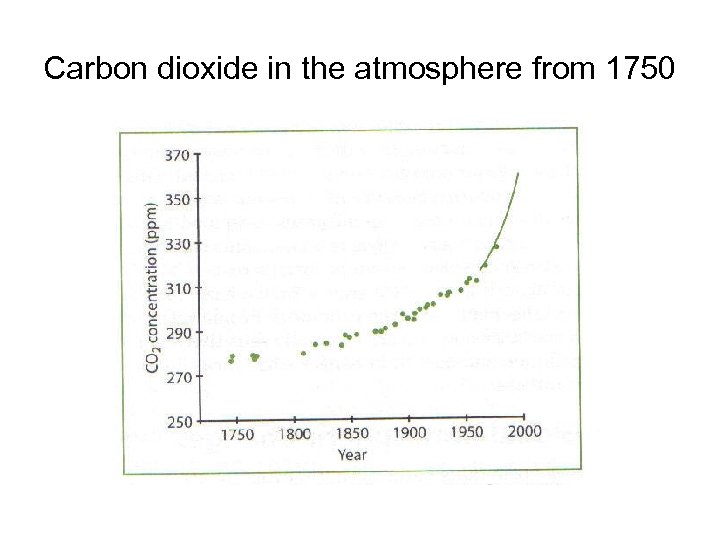
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere from 1750

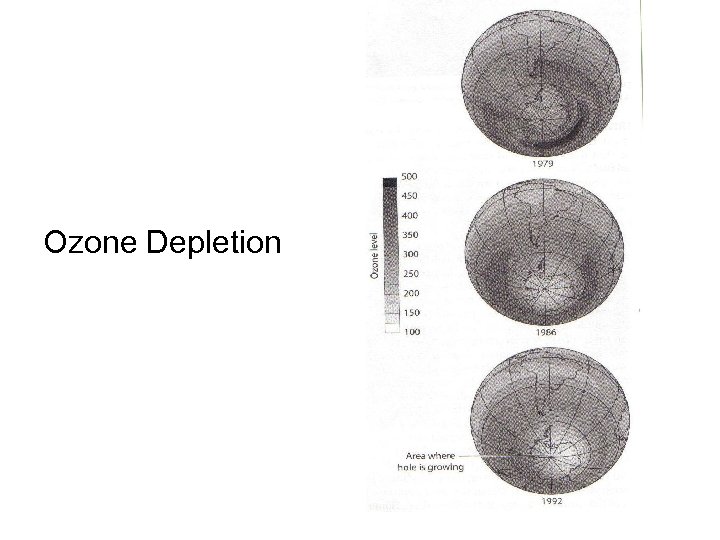
Ozone Depletion

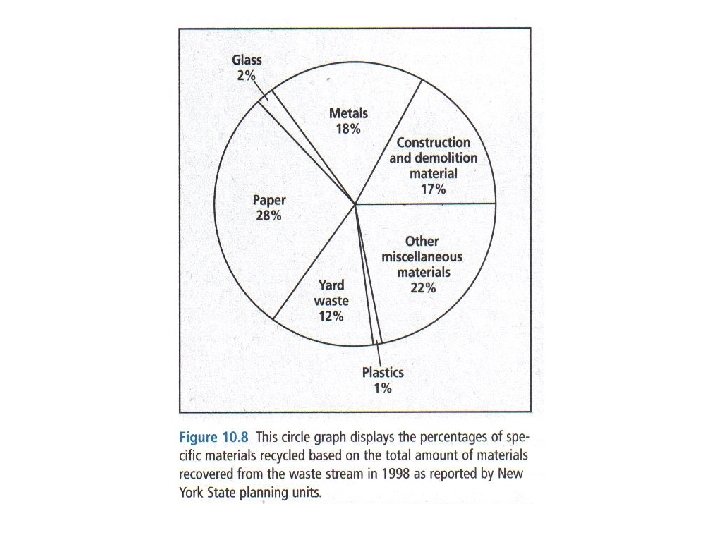
• Land Pollution - caused by many tons of solid waste, or refuse everyday Two ways of disposing waste or refuse: 1. Sanitary landfills 2. Incineration (burning)

How much have you learned? 1. The grasshoppers, spiders, shrews, and other organisms, along with the soil minerals, amount of rainfall, and other factors, constitute A. an ecosystem B. a species C. a biosphere D. a food web
2. Ladybugs were introduced as predators into an agricultural area of the United States to reduce the number of aphids feeding on grain crops. This action is an example of A. preservation of endangered species B. conservation of natural resources C. protection of watershed areas D. use of a nonchemical means of insect control

3. An example of a human activity that has had a positive effect on the environment is the A. disruption of natural habitats through deforestation B. capture and sale of rare South American birds C. use of reforestation to control erosion D. hunting of endangered species of animals
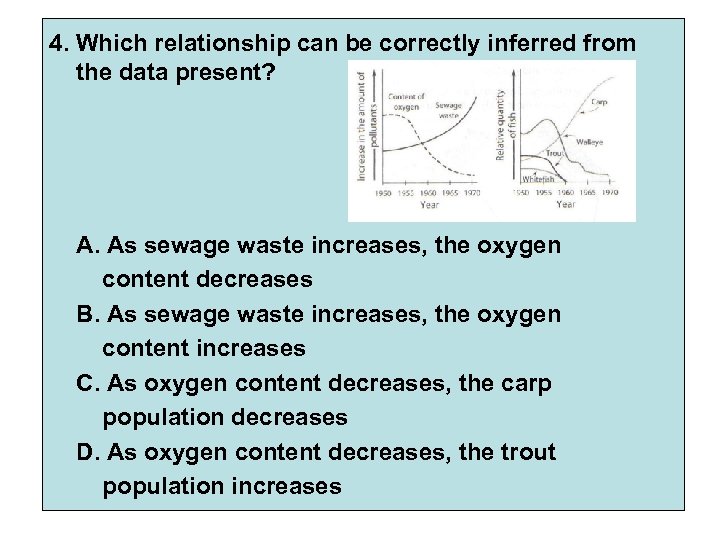
4. Which relationship can be correctly inferred from the data present? A. As sewage waste increases, the oxygen content decreases B. As sewage waste increases, the oxygen content increases C. As oxygen content decreases, the carp population decreases D. As oxygen content decreases, the trout population increases

5. The trees in forest aid in reducing flood damage chiefly because their A. branches store water in the form of sap B. leaves absorb moisture from the air C. root systems hold the soil in place D. stems serve to store food

6. A method of agriculture presently used in many regions of the world where one crop is grown on many acres of land has created serious insect problems. This is primarily because this method A. increase soil erosion B. provides concentrated areas of one kind of food for insects C. increases the effectiveness of insecticides used over long periods of time D. involves the growing of crops in former desert areas
7. Modern methods of agriculture have contributed to the problem of soil depletion because many of these methods A. require smaller amounts of mineral and fertilizer application B. interfere with the natural cycling of elements C. use many varieties of cloned plants D. depend on the practice of planting and harvesting

8. Refer to the chart below, which illustrates some methods of pest control. One likely effect of using these methods of pest control will be to A. prevent the extinction of endangered species B. increase water pollution C. reduce pesticide contamination of the environment D. Harm the atmosphere

9. A desired outcome derived from an understanding of the principles of ecology would be A. the elimination of most predatory species B. an increase in world human population C. a decrease in disruption of existing wildlife habitats D. an increase in the amount of industrialization

10. Which action that humans take in attempting to solve ecological problem has had the most negative effect? A. seeking better means of birth control in the human population B. applying scientific farming techniques C. producing stronger and more effective pesticides D. developing new techniques for the disposal of sewage and industrial chemical wastes

11. DDT is an insecticide that accumulates in the fatty tissues of animals and is transferred through food chains. Its concentration increases at each link of a food chain. Which organism in a food chain is most likely to accumulate the highest concentration of DDT? A. rabbit (a herbivore) B. corn (a producer) C. field mouse (a consumer) D. owl (a predator)

12. Which of these human activities is quite often responsible for the other three human activities? A. increasing demand on limited food production B. rapid increase of loss of farmland due to soil erosion C. rapid increase of human population D. increasing levels of air pollution

13. The least ecologically damaging method for controlling the mosquitoes that spread the disease malaria is by A. draining the swamps where mosquitoes breed B. spraying swamps with chemical pesticides C. spreading oil over swamps D. introducing local fish species to the swamps where mosquitoes breed

14. Which human activity would most likely result in the addition of an organism to the endangered species list? A. the use of cover crops to prevent soil erosion B. the use of pollution controls by industry C. the use of erosion prevention measures by road construction crew D. habitat destruction by shopping mall developers

15. Humans are responsible for some of the negative changes that occur in nature because they A. have controlled the use of many pesticides and other environmentally damaging chemicals B. have passed laws to preserve the environment C. are able to preserve scarce resources D. are able to modify their physical environment to provide for human needs

16. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere A. keep Earth warm B. are related mostly from greenhouses C. are valuable fuels D. reduce holes in the ozone shield

17. Some modern agricultural methods have created serious insect problems, primarily because these methods A. increase soil loss B. provide concentrated areas of food for insects C. aid in the absorption of water D. grow crops in areas where formerly only insects could live

18. Plants help maintain the quality of the atmosphere by A. storing carbon dioxide B. opening holes in the ozone shield C. causing global warming D. storing oxygen

19. The number of industries along New York State’s rivers is increasing. What is the most likely consequence of increased industrialization? A. a decrease in the amount of water needed by industry B. a decrease in the amount of water pollution C. an increase in the destruction of natural ecosystems D. an increase in the amount of water available for recreational use

20. Which human activity has probably contributed MOST to lake acidification in the Adirondack region of New York State? A. passage of environmental protection laws B. reforestation projects in lumbered areas C. production of chemical air pollutants by industry D. use of biological insect controls to eliminate pests

Natural Processes in the Ecosystem Soil Formation • weathering which breaks down rocks • accumulation of organic materials from decaying (dead) plants and animals

The Water Cycle • almost entirely a physical process • consists of the following processes: - evaporation from the surface of land water - transpiration from the leaves of plants - condensation - precipitation
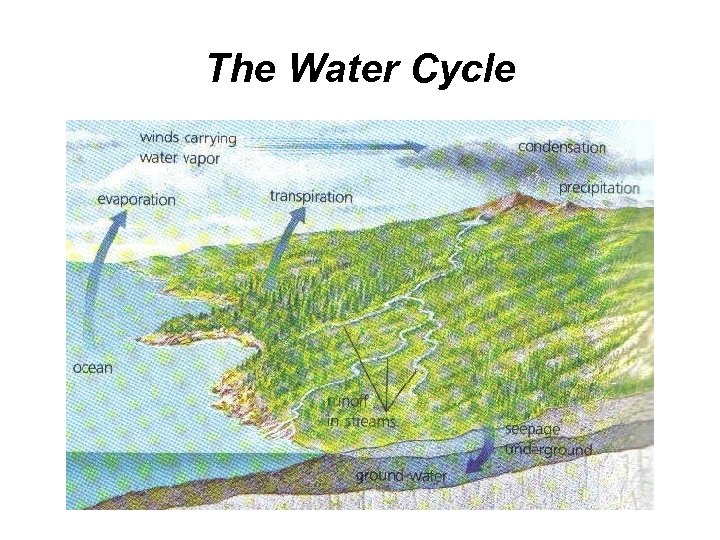
The Water Cycle
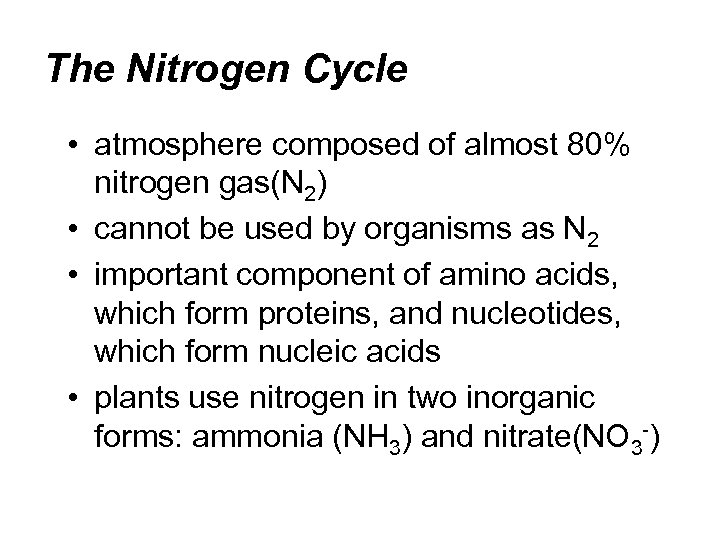
The Nitrogen Cycle • atmosphere composed of almost 80% nitrogen gas(N 2) • cannot be used by organisms as N 2 • important component of amino acids, which form proteins, and nucleotides, which form nucleic acids • plants use nitrogen in two inorganic forms: ammonia (NH 3) and nitrate(NO 3 -)
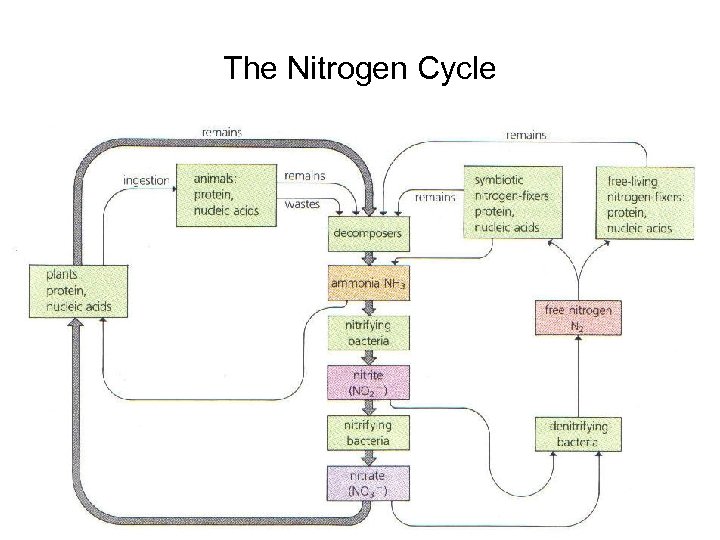
The Nitrogen Cycle
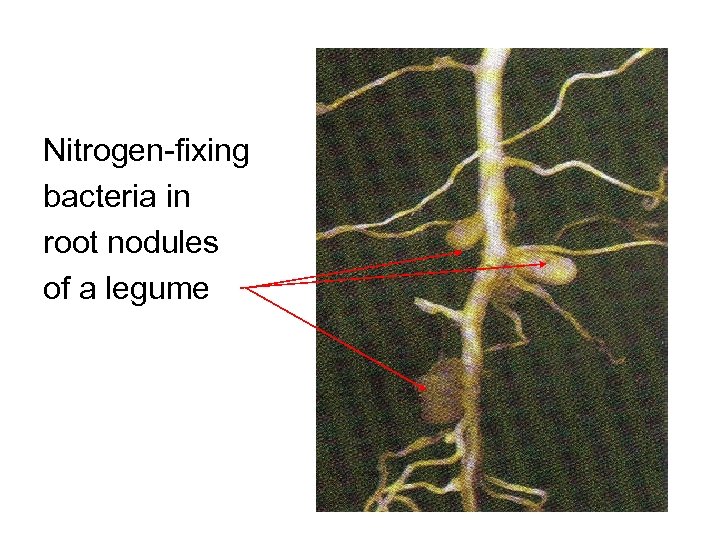
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in root nodules of a legume

The Carbon and Oxygen Cycles Carbon dioxide(CO 2): • makes up 0. 03% of the atmosphere • also found dissolved in the waters of the earth • incorporated into organic compounds during photosynthesis • released when remains of dead plants and animals decompose

Oxygen (O 2): • makes up about 20% of the earth’s atmosphere • formed from the splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen during photosynthesis • used by animals and plants in cellular respiration
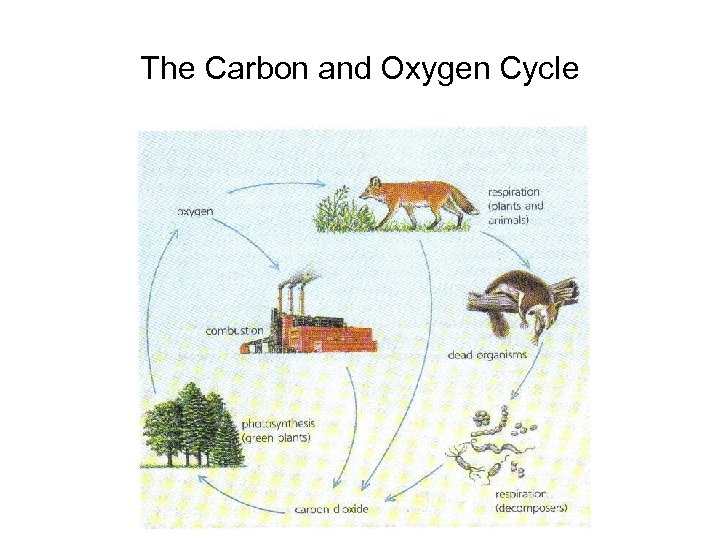
The Carbon and Oxygen Cycle

Waste Removal and the Recycling of Nutrients • nutrients transported from one organism to another through the food chains • those not released in the atmosphere are contained in the dead bodies and wastes of organisms • nutrients restored through break down of wastes and dead bodies of organisms by decomposers

Population Growth • Most species in new environments can have a period of rapid population growth. • The population increase levels off as it approaches the ecosystem’s carrying capacity – the number of individuals the environment can support
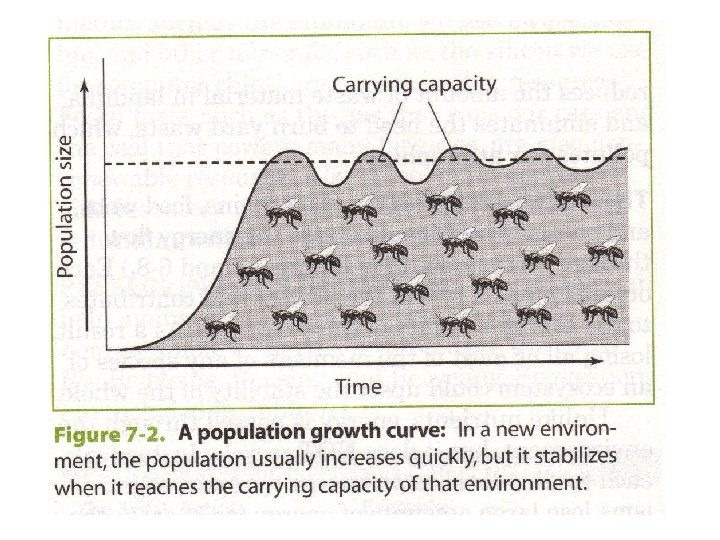

Human Activities and the Loss of Diversity Direct Harvesting • the destruction or removal of species from their habitats • can lead to the extinction of a species

Land Use As human population grows… • More space for places to live • More land needed to grow food • More land to build roads and factories • More land to provide parks and recreational areas • Use of land decreases the space and resources available for other species

Habitat Destruction • Occurs when people take over land for their own use • An important way that species can become endangered – they simple have nowhere to live • Whole ecosystems can be damaged and entire species may become extinct
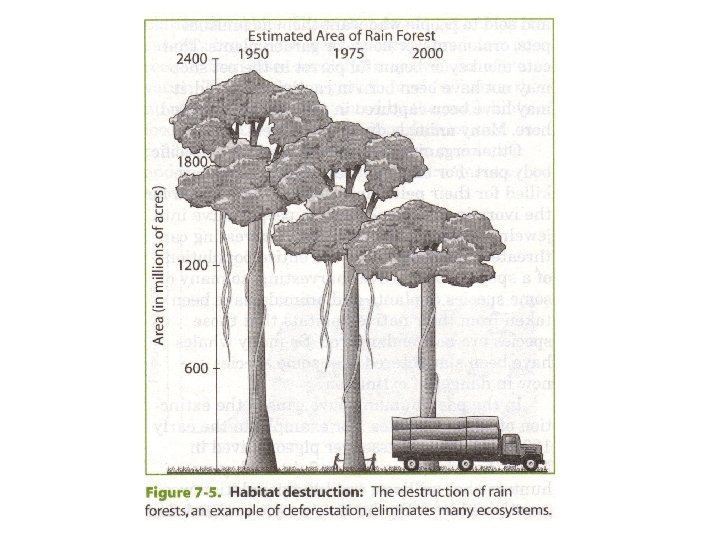

Loss Biodiversity • Occurs when species are lost • Can affect the health of whole ecosystems and food webs • Can affect the proportion of gases in the atmosphere • Can be caused by habitat destruction


Imported Species • Import and release of species from one environment to another reduce biodiversity • Imported species may become a pest creating a serious problem • Many states and countries have laws to restrict the transport of fruits or vegetables


How much have you learned? 1. The creation of wildlife refuges and the enforcement of game laws are conservation measures that promote increased A. use of chemicals to control pests B. preservation of species C. use of natural controls to limit pest populations D. exploitation of wildlife species

2. Which of the following human activities would be most likely to prevent certain species from becoming extinct? A. pass laws to place all endangered species in zoos B. increase the hunting of predators C. increase wildlife management and habitat protection D. mate organisms from different species to create new and stronger organisms

3. Japanese beetles, a major insect pest in the United States, do relatively little damage in Japan because they A. are kept in check by natural enemies B. are kept in check by effective pesticides C. hibernate during the winter months D. have gradually adapted to the environment

4. Gypsy moths were accidentally introduced into North America. The most probable reason these insects have become serious pests in North America is that they A. were bred by research scientists and are resistant to all pesticides B. are protected by environmental laws and feed on other insects C. have few natural enemies and reproduce successfully D. are affected by natural controls and feed on plants
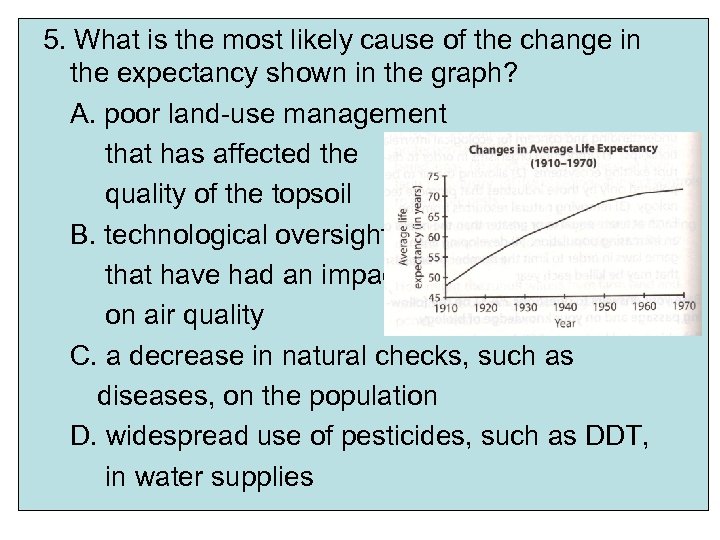
5. What is the most likely cause of the change in the expectancy shown in the graph? A. poor land-use management that has affected the quality of the topsoil B. technological oversights that have had an impact on air quality C. a decrease in natural checks, such as diseases, on the population D. widespread use of pesticides, such as DDT, in water supplies
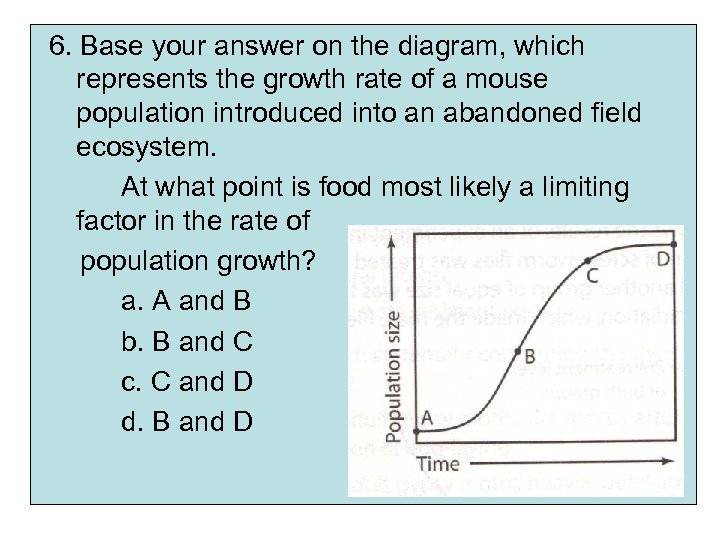
6. Base your answer on the diagram, which represents the growth rate of a mouse population introduced into an abandoned field ecosystem. At what point is food most likely a limiting factor in the rate of population growth? a. A and B b. B and C c. C and D d. B and D
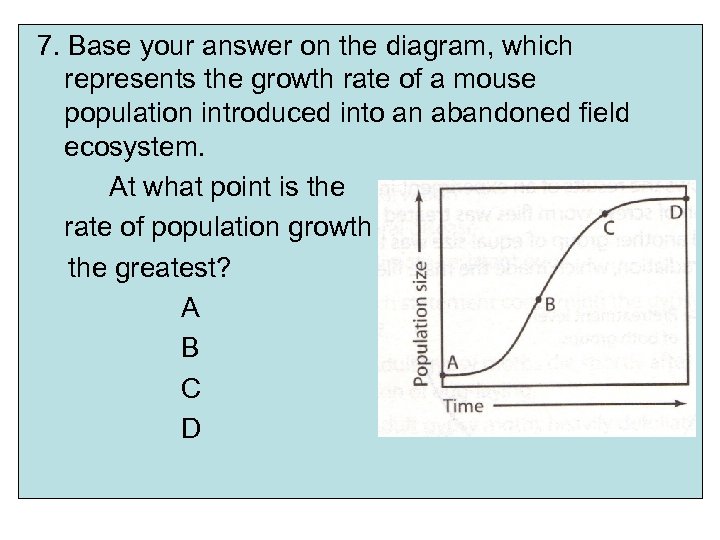
7. Base your answer on the diagram, which represents the growth rate of a mouse population introduced into an abandoned field ecosystem. At what point is the rate of population growth the greatest? A B C D
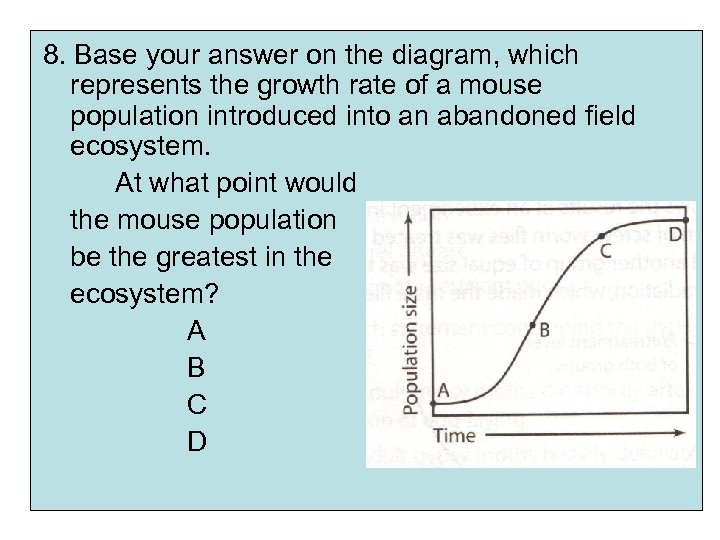
8. Base your answer on the diagram, which represents the growth rate of a mouse population introduced into an abandoned field ecosystem. At what point would the mouse population be the greatest in the ecosystem? A B C D
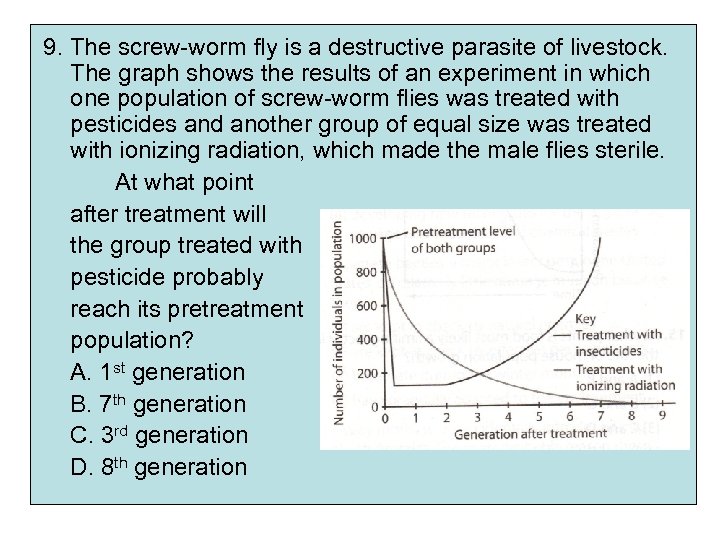
9. The screw-worm fly is a destructive parasite of livestock. The graph shows the results of an experiment in which one population of screw-worm flies was treated with pesticides and another group of equal size was treated with ionizing radiation, which made the male flies sterile. At what point after treatment will the group treated with pesticide probably reach its pretreatment population? A. 1 st generation B. 7 th generation C. 3 rd generation D. 8 th generation
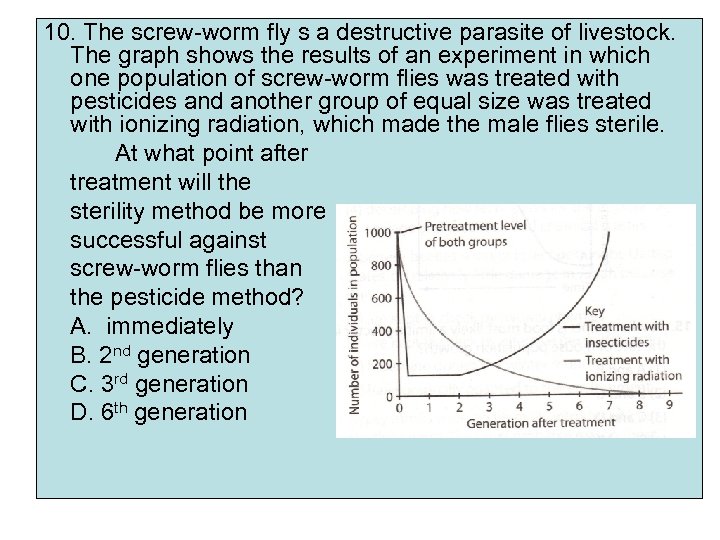
10. The screw-worm fly s a destructive parasite of livestock. The graph shows the results of an experiment in which one population of screw-worm flies was treated with pesticides and another group of equal size was treated with ionizing radiation, which made the male flies sterile. At what point after treatment will the sterility method be more successful against screw-worm flies than the pesticide method? A. immediately B. 2 nd generation C. 3 rd generation D. 6 th generation
8535e9344c14b26c5e134fcb50617e38.ppt