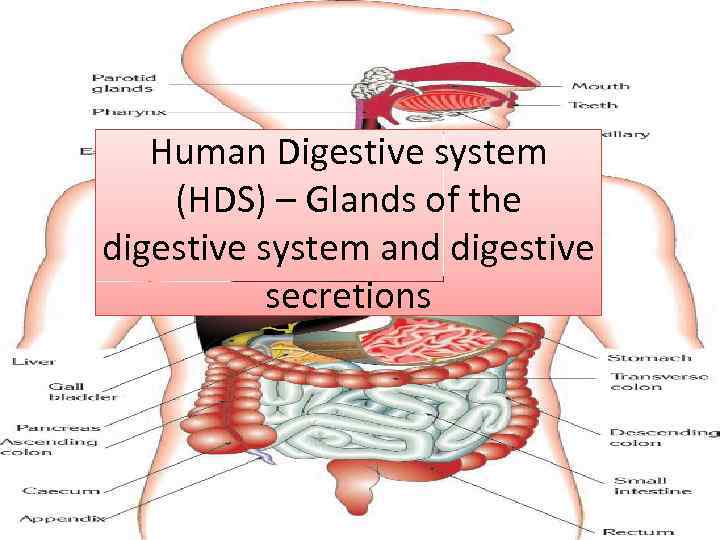
 Human Digestive system (HDS) – Glands of the digestive system and digestive secretions
Human Digestive system (HDS) – Glands of the digestive system and digestive secretions
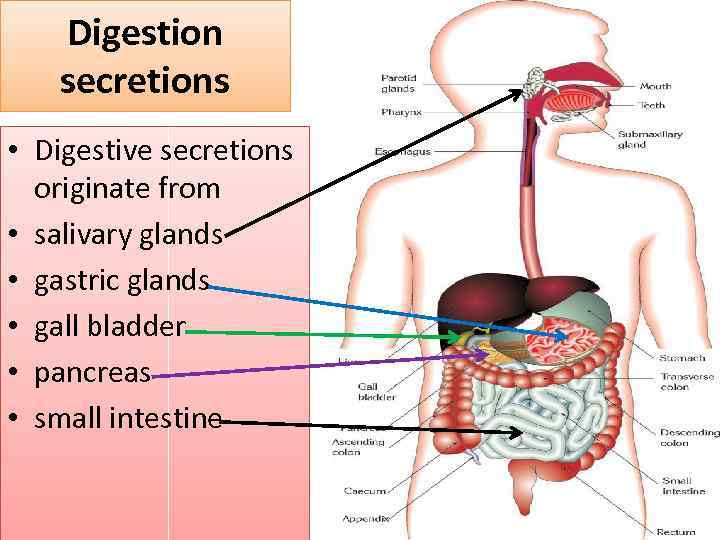 Digestion secretions • Digestive secretions originate from • salivary glands • gastric glands • gall bladder • pancreas • small intestine
Digestion secretions • Digestive secretions originate from • salivary glands • gastric glands • gall bladder • pancreas • small intestine
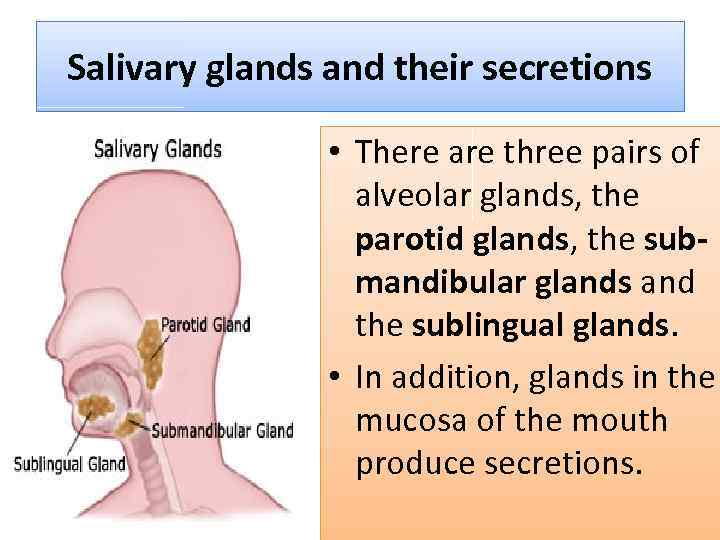 Salivary glands and their secretions • There are three pairs of alveolar glands, the parotid glands, the submandibular glands and the sublingual glands. • In addition, glands in the mucosa of the mouth produce secretions.
Salivary glands and their secretions • There are three pairs of alveolar glands, the parotid glands, the submandibular glands and the sublingual glands. • In addition, glands in the mucosa of the mouth produce secretions.
 Salivary glands and their secretions • Approximately 1 -1. 5 liters of saliva is secreted everyday • These saliva is composed of 3% protein and amylase enzymes (ptyalin). • Amylase breaks down carbohydrates
Salivary glands and their secretions • Approximately 1 -1. 5 liters of saliva is secreted everyday • These saliva is composed of 3% protein and amylase enzymes (ptyalin). • Amylase breaks down carbohydrates
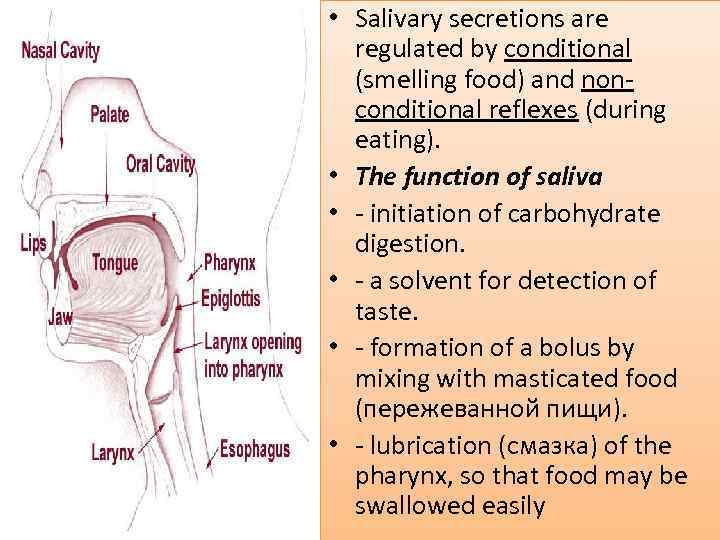 • Salivary secretions are regulated by conditional (smelling food) and nonconditional reflexes (during eating). • The function of saliva • - initiation of carbohydrate digestion. • - a solvent for detection of taste. • - formation of a bolus by mixing with masticated food (пережеванной пищи). • - lubrication (смазка) of the pharynx, so that food may be swallowed easily
• Salivary secretions are regulated by conditional (smelling food) and nonconditional reflexes (during eating). • The function of saliva • - initiation of carbohydrate digestion. • - a solvent for detection of taste. • - formation of a bolus by mixing with masticated food (пережеванной пищи). • - lubrication (смазка) of the pharynx, so that food may be swallowed easily
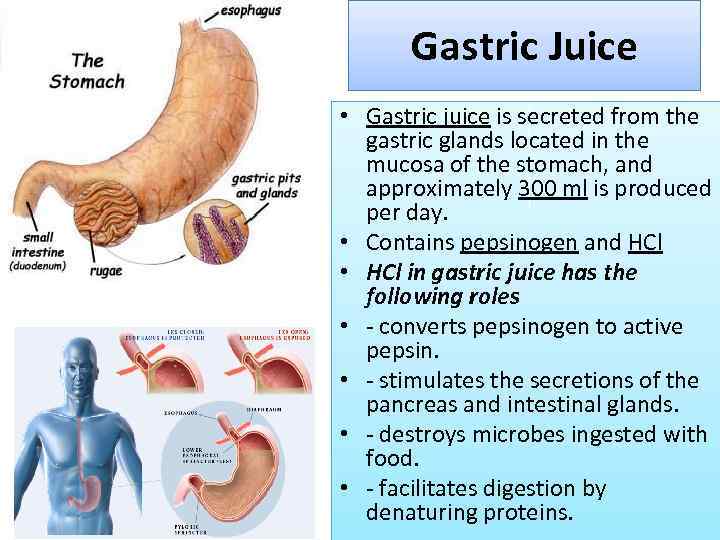 Gastric Juice • Gastric juice is secreted from the gastric glands located in the mucosa of the stomach, and approximately 300 ml is produced per day. • Contains pepsinogen and HCl • HCl in gastric juice has the following roles • - converts pepsinogen to active pepsin. • - stimulates the secretions of the pancreas and intestinal glands. • - destroys microbes ingested with food. • - facilitates digestion by denaturing proteins.
Gastric Juice • Gastric juice is secreted from the gastric glands located in the mucosa of the stomach, and approximately 300 ml is produced per day. • Contains pepsinogen and HCl • HCl in gastric juice has the following roles • - converts pepsinogen to active pepsin. • - stimulates the secretions of the pancreas and intestinal glands. • - destroys microbes ingested with food. • - facilitates digestion by denaturing proteins.
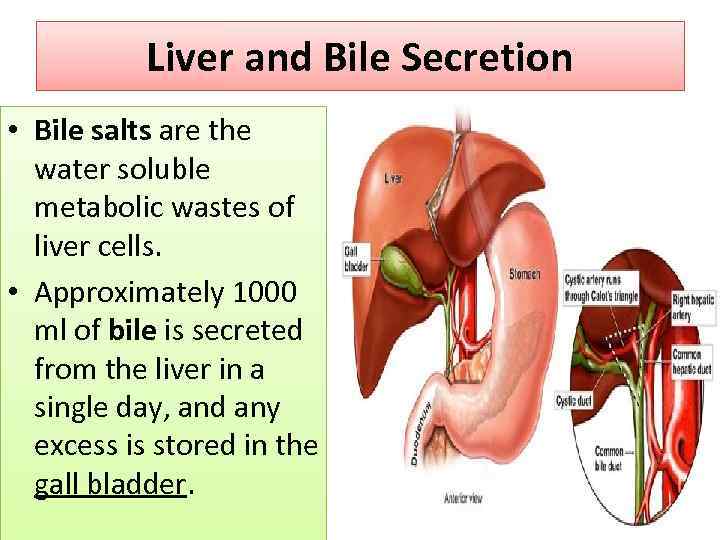 Liver and Bile Secretion • Bile salts are the water soluble metabolic wastes of liver cells. • Approximately 1000 ml of bile is secreted from the liver in a single day, and any excess is stored in the gall bladder.
Liver and Bile Secretion • Bile salts are the water soluble metabolic wastes of liver cells. • Approximately 1000 ml of bile is secreted from the liver in a single day, and any excess is stored in the gall bladder.
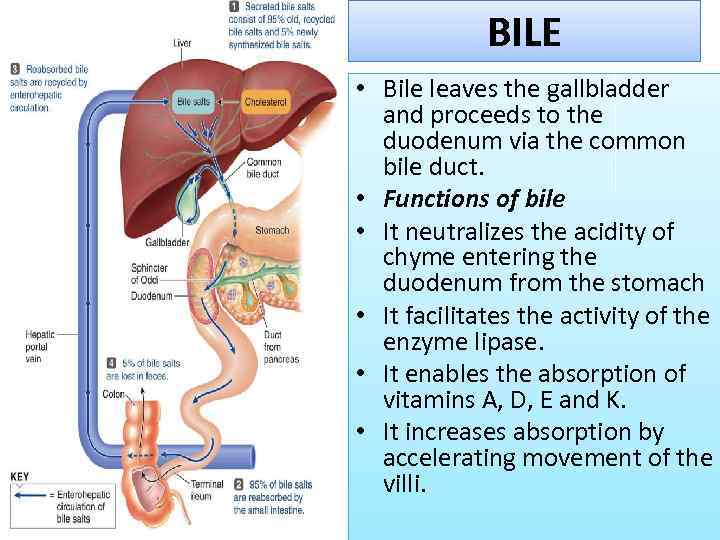 BILE • Bile leaves the gallbladder and proceeds to the duodenum via the common bile duct. • Functions of bile • It neutralizes the acidity of chyme entering the duodenum from the stomach • It facilitates the activity of the enzyme lipase. • It enables the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K. • It increases absorption by accelerating movement of the villi.
BILE • Bile leaves the gallbladder and proceeds to the duodenum via the common bile duct. • Functions of bile • It neutralizes the acidity of chyme entering the duodenum from the stomach • It facilitates the activity of the enzyme lipase. • It enables the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K. • It increases absorption by accelerating movement of the villi.
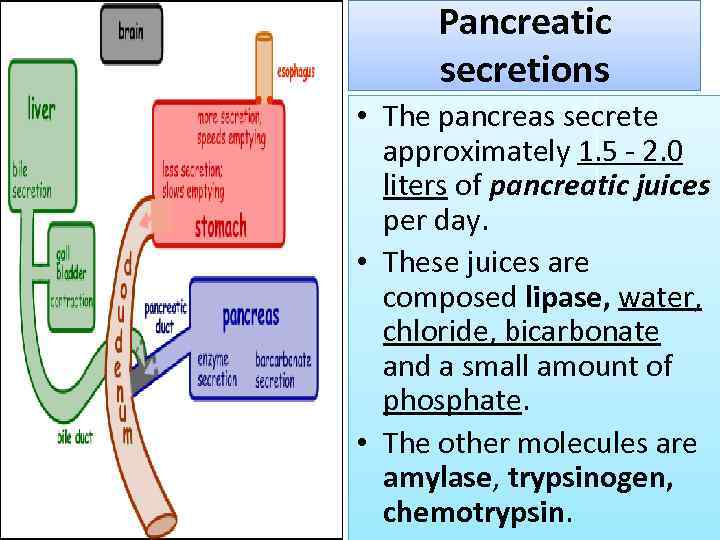 Pancreatic secretions • The pancreas secrete approximately 1. 5 - 2. 0 liters of pancreatic juices per day. • These juices are composed lipase, water, chloride, bicarbonate and a small amount of phosphate. • The other molecules are amylase, trypsinogen, chemotrypsin.
Pancreatic secretions • The pancreas secrete approximately 1. 5 - 2. 0 liters of pancreatic juices per day. • These juices are composed lipase, water, chloride, bicarbonate and a small amount of phosphate. • The other molecules are amylase, trypsinogen, chemotrypsin.
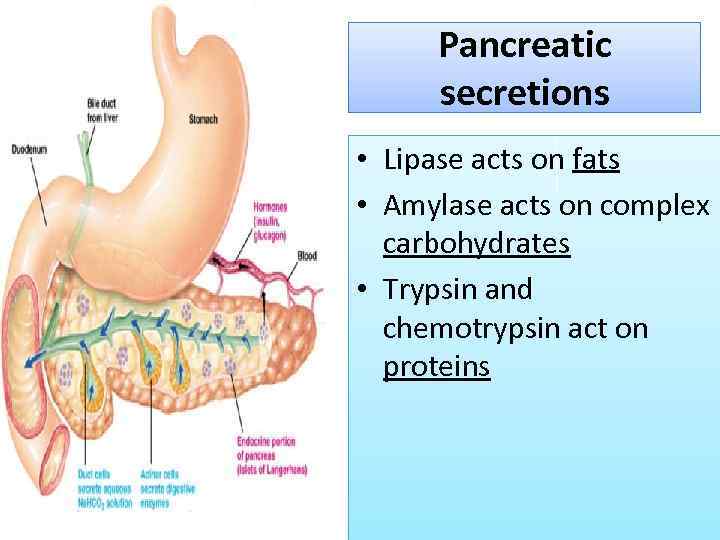 Pancreatic secretions • Lipase acts on fats • Amylase acts on complex carbohydrates • Trypsin and chemotrypsin act on proteins
Pancreatic secretions • Lipase acts on fats • Amylase acts on complex carbohydrates • Trypsin and chemotrypsin act on proteins
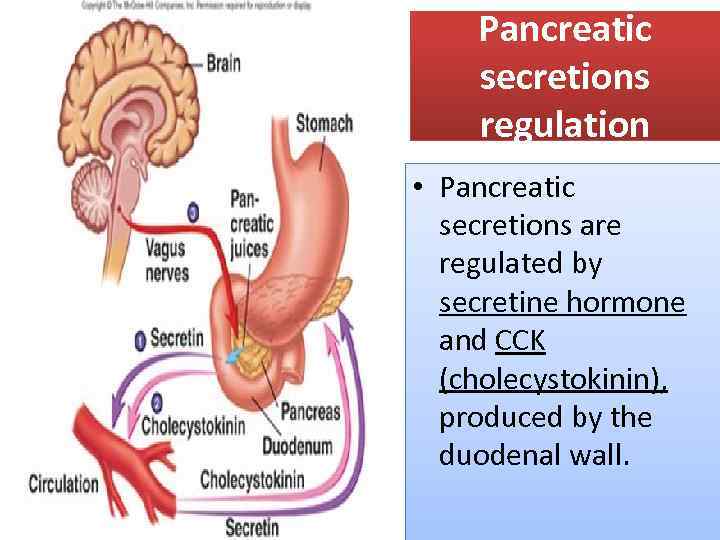 Pancreatic secretions regulation • Pancreatic secretions are regulated by secretine hormone and CCK (cholecystokinin), produced by the duodenal wall.
Pancreatic secretions regulation • Pancreatic secretions are regulated by secretine hormone and CCK (cholecystokinin), produced by the duodenal wall.
 Small Intestine Secretions • The digestion of food finishes in the small intestine. • The digested nutrients are consequently easily absorbed by intestinal cells.
Small Intestine Secretions • The digestion of food finishes in the small intestine. • The digested nutrients are consequently easily absorbed by intestinal cells.