1_lesson_circulatory_system_1_part.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 28
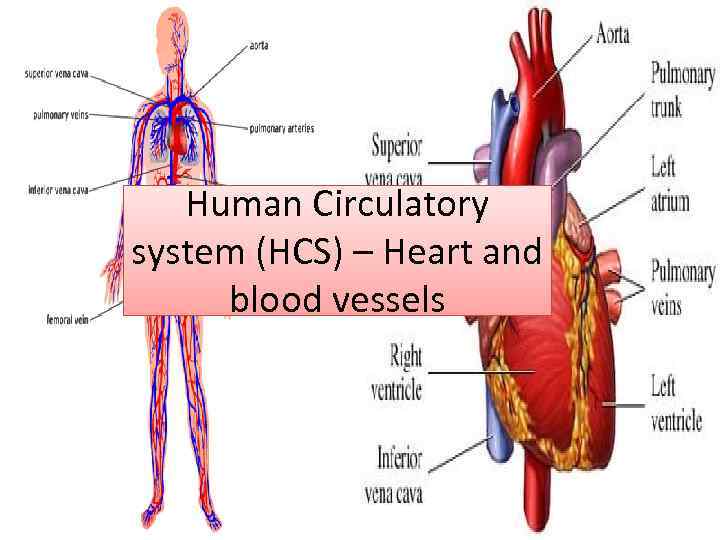
Human Circulatory system (HCS) – Heart and blood vessels
Circulatory system • HCS transports materials throughout the body. • -Oxygen • -Carbon dioxide • -Digested food • -Hormones • -Waste chemicals – urea • -Heat
HCS • HCS is composed of the heart, blood and blood vessels. • Heart and vessels form an internal transport system within the body for substances to and from the cells. • This system is also known as the cardiovascular system (cardio- means heart, while vascular means vessels).
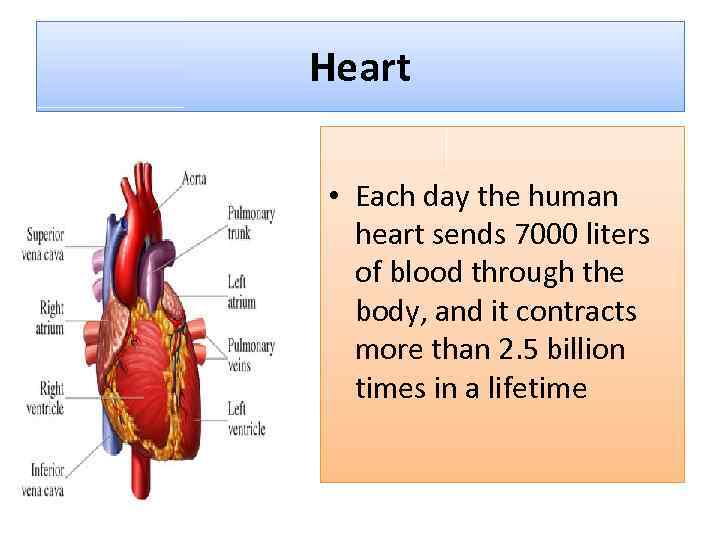
Heart • Each day the human heart sends 7000 liters of blood through the body, and it contracts more than 2. 5 billion times in a lifetime
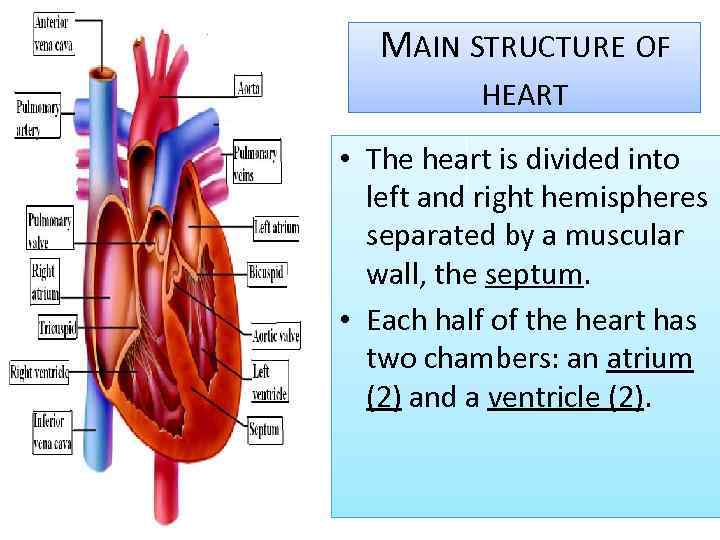
MAIN STRUCTURE OF HEART • The heart is divided into left and right hemispheres separated by a muscular wall, the septum. • Each half of the heart has two chambers: an atrium (2) and a ventricle (2).
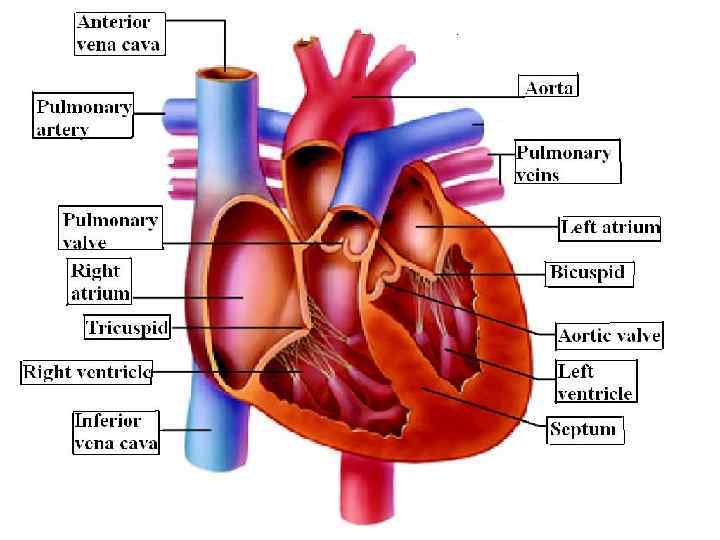
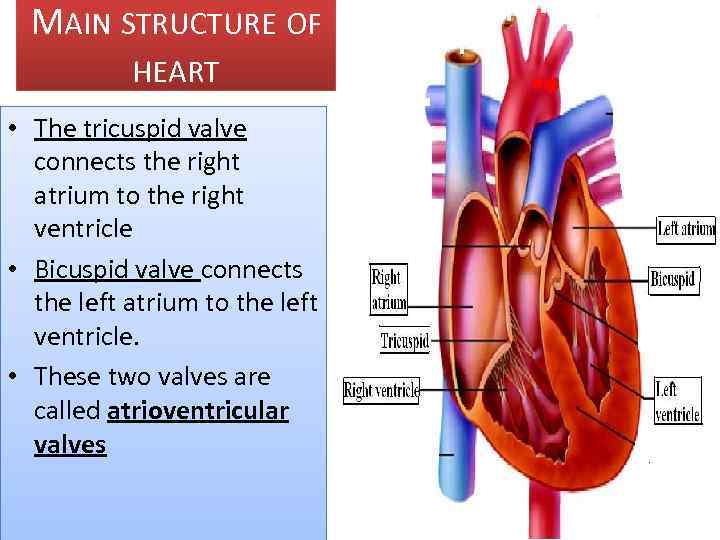
MAIN STRUCTURE OF HEART • The tricuspid valve connects the right atrium to the right ventricle • Bicuspid valve connects the left atrium to the left ventricle. • These two valves are called atrioventricular valves
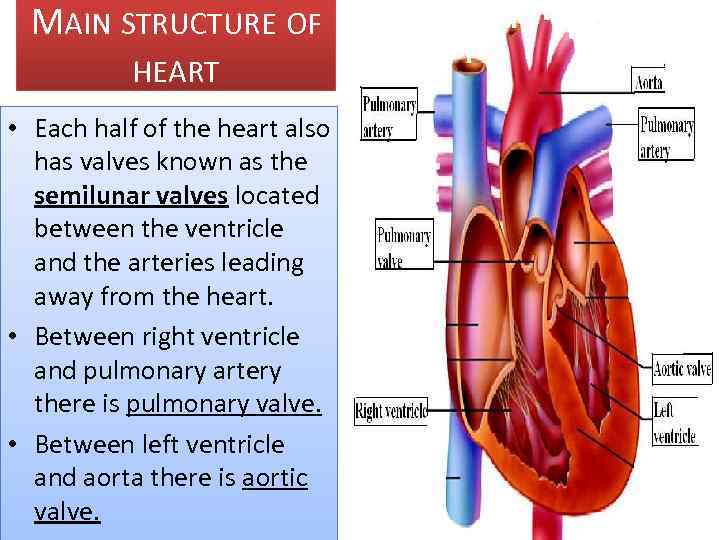
MAIN STRUCTURE OF HEART • Each half of the heart also has valves known as the semilunar valves located between the ventricle and the arteries leading away from the heart. • Between right ventricle and pulmonary artery there is pulmonary valve. • Between left ventricle and aorta there is aortic valve.
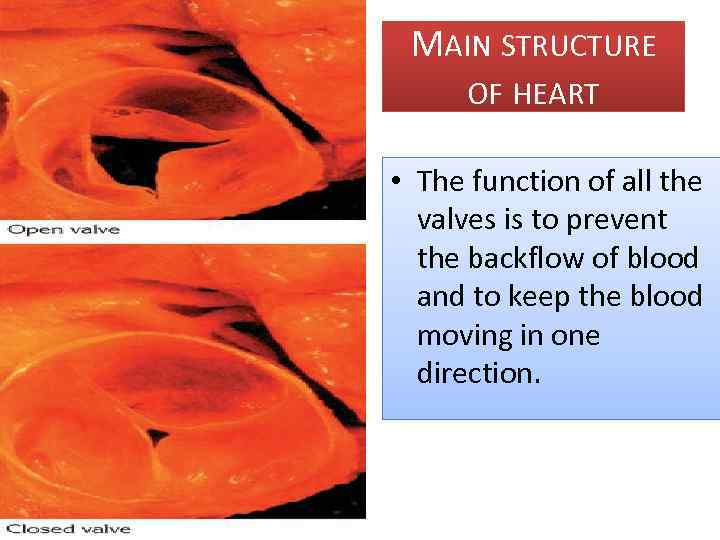
MAIN STRUCTURE OF HEART • The function of all the valves is to prevent the backflow of blood and to keep the blood moving in one direction.
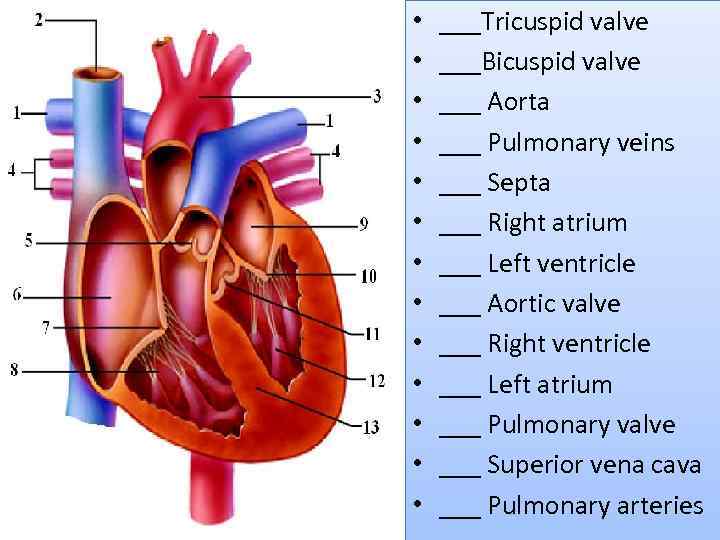
• • • • ___Tricuspid valve ___Bicuspid valve ___ Aorta ___ Pulmonary veins ___ Septa ___ Right atrium ___ Left ventricle ___ Aortic valve ___ Right ventricle ___ Left atrium ___ Pulmonary valve ___ Superior vena cava ___ Pulmonary arteries
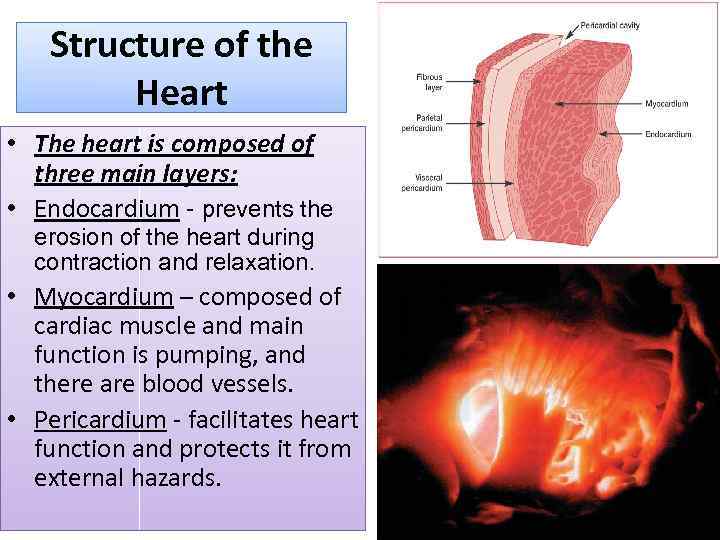
Structure of the Heart • The heart is composed of three main layers: • Endocardium - prevents the erosion of the heart during contraction and relaxation. • Myocardium – composed of cardiac muscle and main function is pumping, and there are blood vessels. • Pericardium - facilitates heart function and protects it from external hazards.
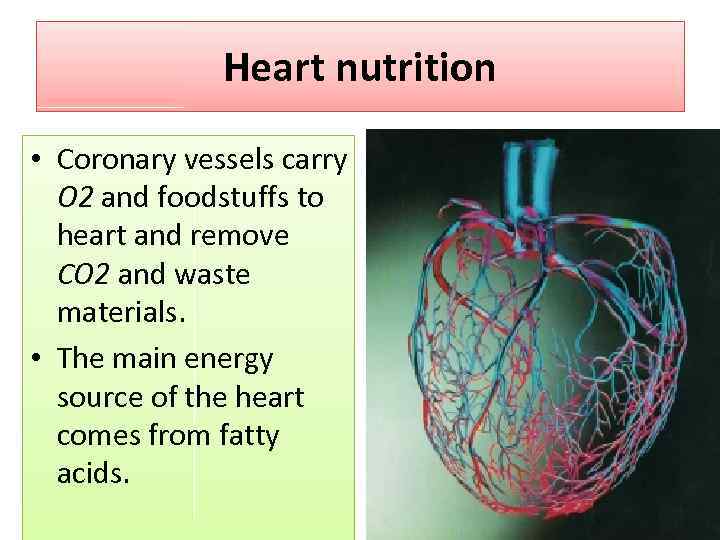
Heart nutrition • Coronary vessels carry O 2 and foodstuffs to heart and remove CO 2 and waste materials. • The main energy source of the heart comes from fatty acids.
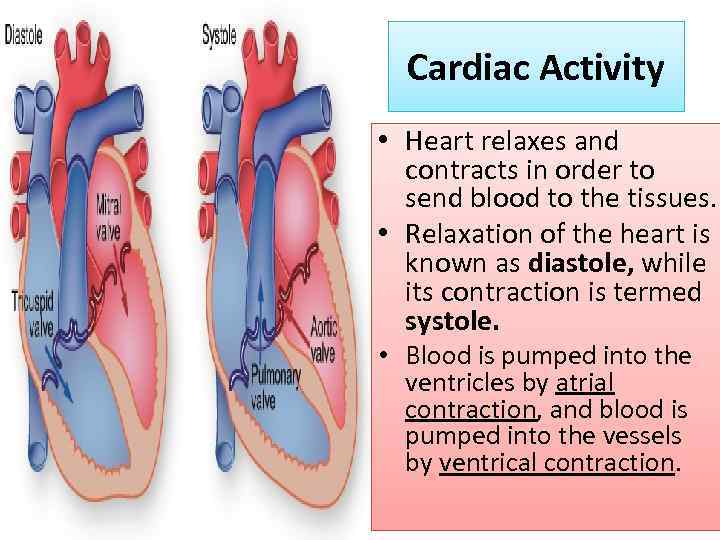
Cardiac Activity • Heart relaxes and contracts in order to send blood to the tissues. • Relaxation of the heart is known as diastole, while its contraction is termed systole. • Blood is pumped into the ventricles by atrial contraction, and blood is pumped into the vessels by ventrical contraction.
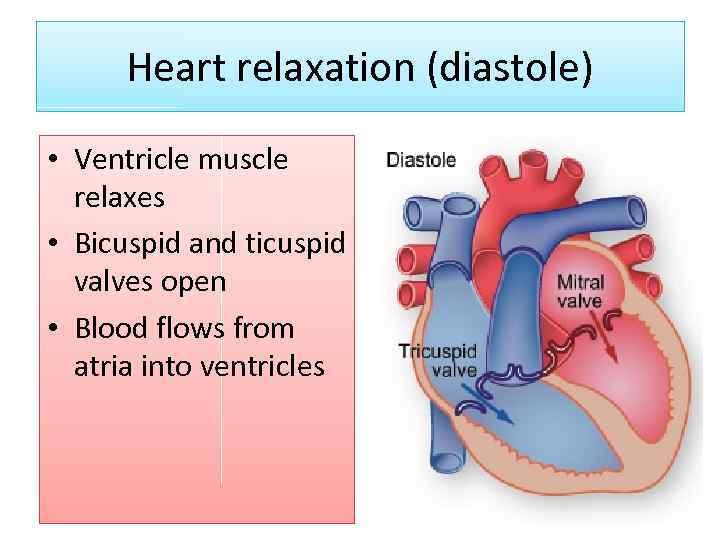
Heart relaxation (diastole) • Ventricle muscle relaxes • Bicuspid and ticuspid valves open • Blood flows from atria into ventricles
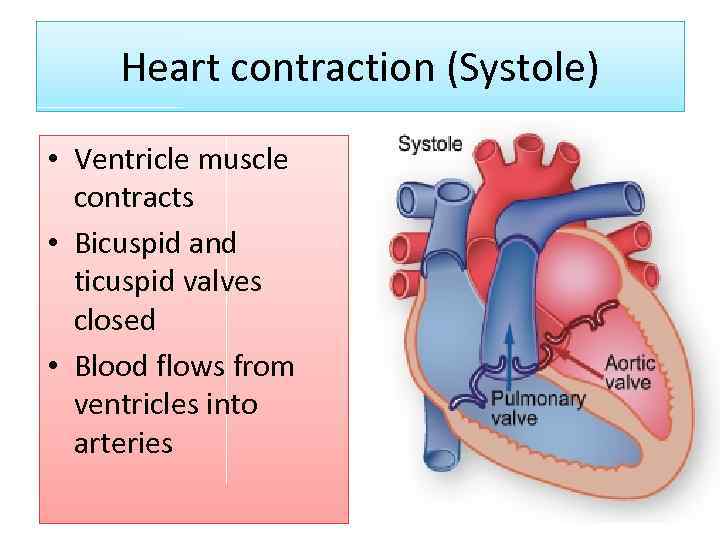
Heart contraction (Systole) • Ventricle muscle contracts • Bicuspid and ticuspid valves closed • Blood flows from ventricles into arteries
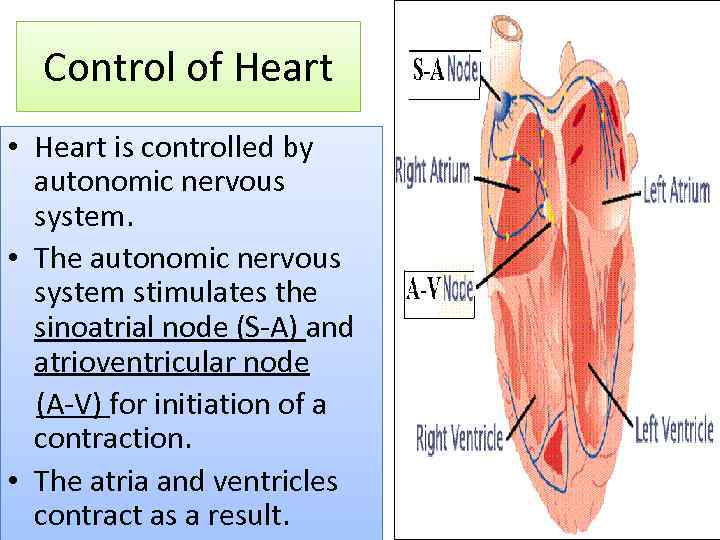
Control of Heart • Heart is controlled by autonomic nervous system. • The autonomic nervous system stimulates the sinoatrial node (S-A) and atrioventricular node (A-V) for initiation of a contraction. • The atria and ventricles contract as a result.

Factors affecting heart function • Nerves, hormones, temperature and severe diseases can all affect heart performance.
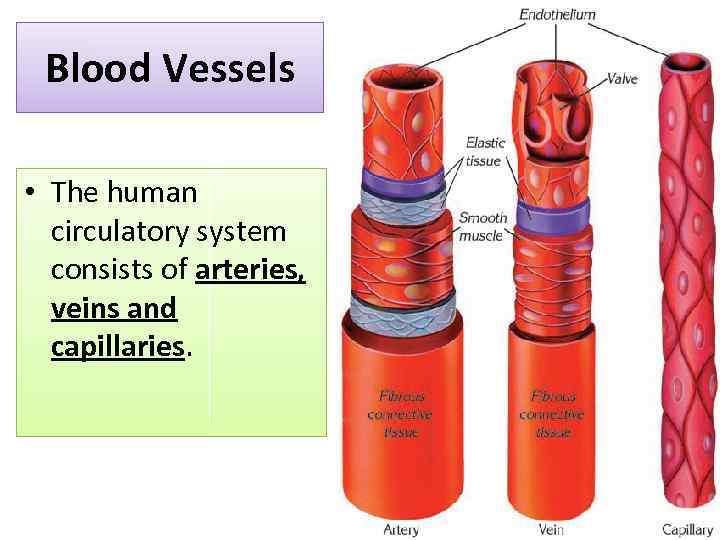
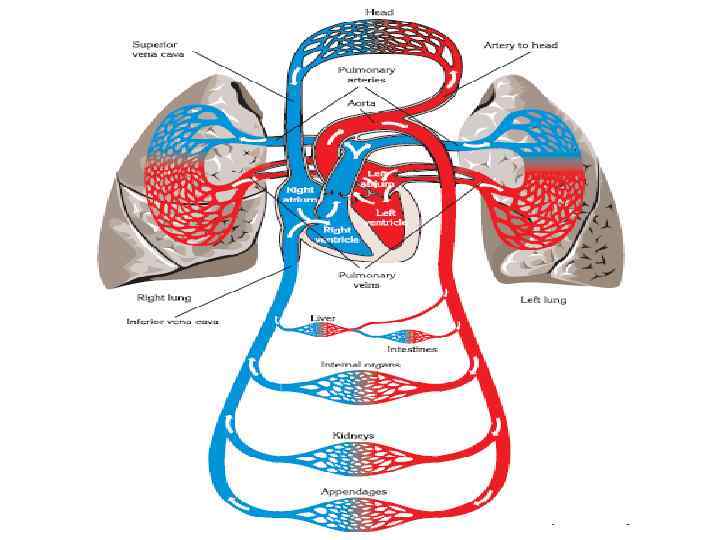
Blood Vessels • The human circulatory system consists of arteries, veins and capillaries.
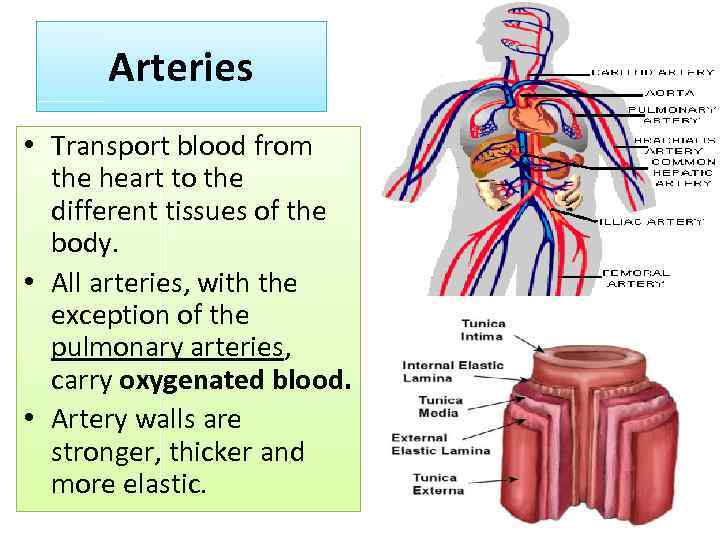
Arteries • Transport blood from the heart to the different tissues of the body. • All arteries, with the exception of the pulmonary arteries, carry oxygenated blood. • Artery walls are stronger, thicker and more elastic.
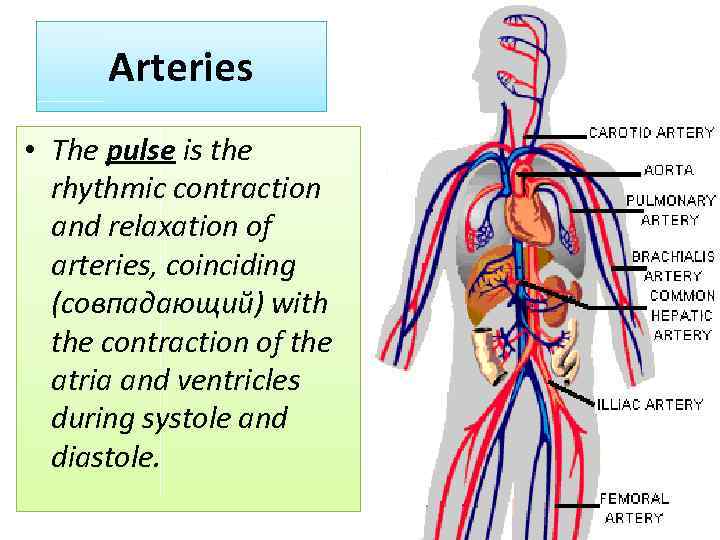
Arteries • The pulse is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of arteries, coinciding (совпадающий) with the contraction of the atria and ventricles during systole and diastole.
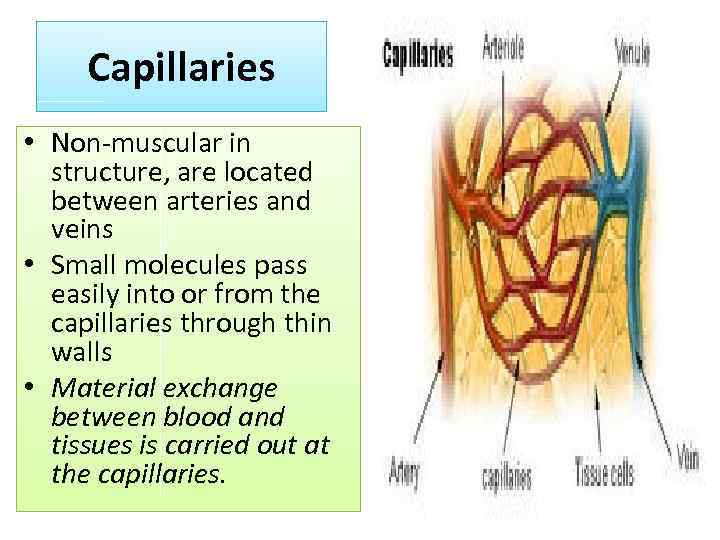
Capillaries • Non-muscular in structure, are located between arteries and veins • Small molecules pass easily into or from the capillaries through thin walls • Material exchange between blood and tissues is carried out at the capillaries.
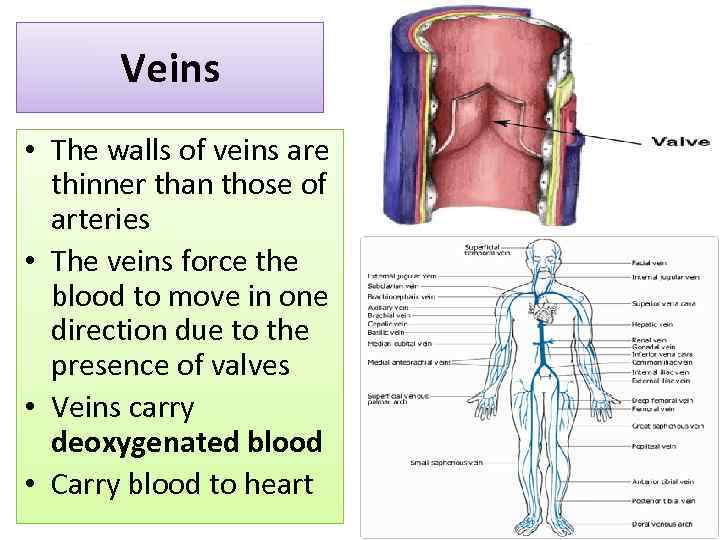
Veins • The walls of veins are thinner than those of arteries • The veins force the blood to move in one direction due to the presence of valves • Veins carry deoxygenated blood • Carry blood to heart
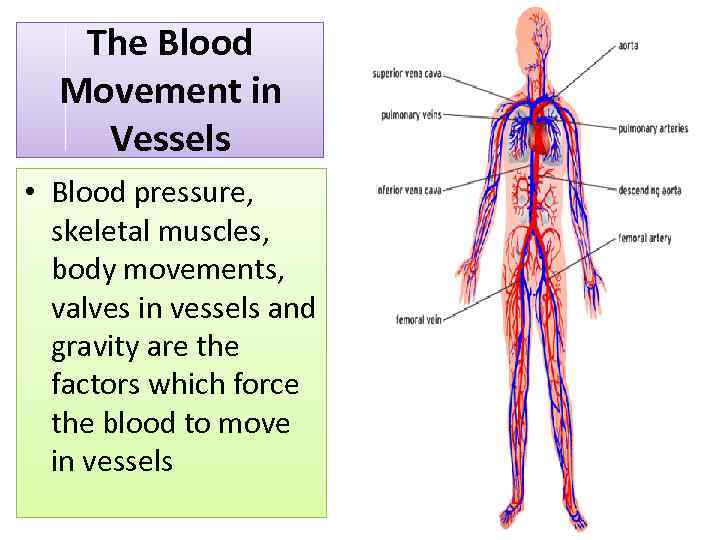
The Blood Movement in Vessels • Blood pressure, skeletal muscles, body movements, valves in vessels and gravity are the factors which force the blood to move in vessels
Blood flow rate • The rate of blood flow is influenced by the diameter of the blood vessels and by blood pressure. • It is most rapid in arteries, approximately 500 mm/sec and slightly slower in veins, approximately 150 mm/sec. • However, it is slowest in the capillaries, 1 mm/sec.
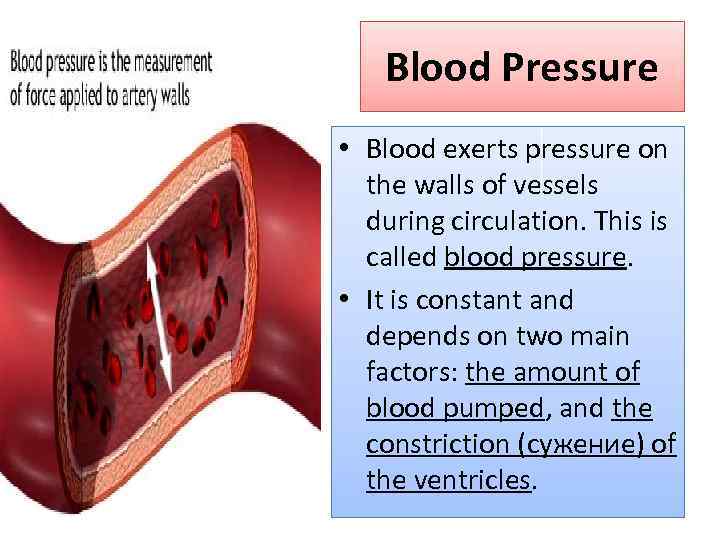
Blood Pressure • Blood exerts pressure on the walls of vessels during circulation. This is called blood pressure. • It is constant and depends on two main factors: the amount of blood pumped, and the constriction (сужение) of the ventricles.
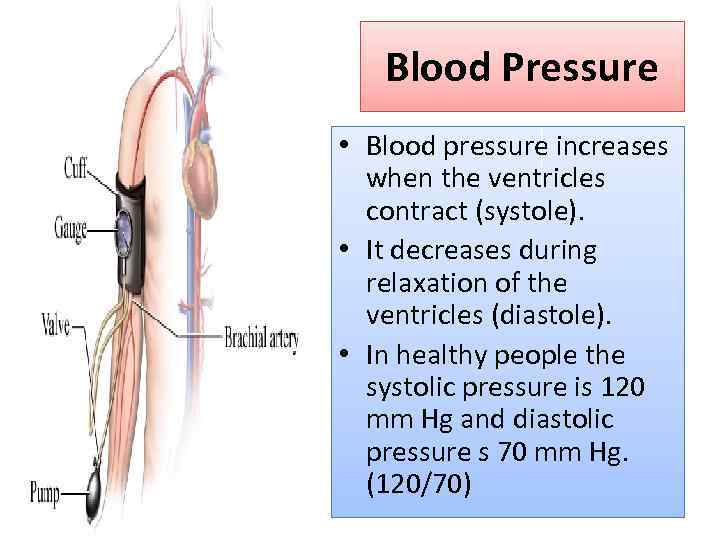
Blood Pressure • Blood pressure increases when the ventricles contract (systole). • It decreases during relaxation of the ventricles (diastole). • In healthy people the systolic pressure is 120 mm Hg and diastolic pressure s 70 mm Hg. (120/70)
Blood Pressure • The blood pressure increases during physical exertion, but slows down during rest and sleep. • Abnormal increase of blood pressure due to illness is termed hypertension, and abnormal decrease in blood pressure is called hypotension.
1_lesson_circulatory_system_1_part.pptx