Human Body Systems You Can’t Have One Without
























organ_rayhan.pptx
- Размер: 4.3 Мб
- Автор: Райхан Кубайдуллина
- Количество слайдов: 39
Описание презентации Human Body Systems You Can’t Have One Without по слайдам
 Human Body Systems You Can’t Have One Without The Other
Human Body Systems You Can’t Have One Without The Other
 If you damage one system, you may damage several like smoking which irritates the lungs and also destroys the cells of the immune system Body Systems Work Together Ardi Rizal 2 years old Musi Banyuasin, Indonesia May
If you damage one system, you may damage several like smoking which irritates the lungs and also destroys the cells of the immune system Body Systems Work Together Ardi Rizal 2 years old Musi Banyuasin, Indonesia May
 If you get excited, the nervous system works with the circulatory system by increasing your heart rate.
If you get excited, the nervous system works with the circulatory system by increasing your heart rate.
 AIDS destroys the Immune System As a result you may get: 1. pneumonia (respiratory ), 2. yeast infection (reproductive ), 3. Candida affecting esophagus (digestive) 4. Kaposi’s sarcoma (integumentary).
AIDS destroys the Immune System As a result you may get: 1. pneumonia (respiratory ), 2. yeast infection (reproductive ), 3. Candida affecting esophagus (digestive) 4. Kaposi’s sarcoma (integumentary).
 The Human Body Team How does the body get the systems to work together? To answer this question, we need to recall the organizational structure of multicellular organisms.
The Human Body Team How does the body get the systems to work together? To answer this question, we need to recall the organizational structure of multicellular organisms.
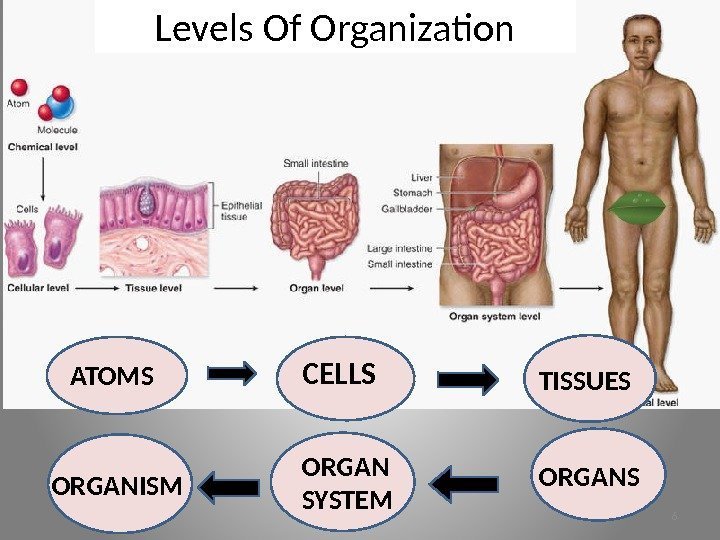
 Levels Of Organization ATOMS CELLS TISSUES ORGANSORGAN SYSTEMORGANISM
Levels Of Organization ATOMS CELLS TISSUES ORGANSORGAN SYSTEMORGANISM
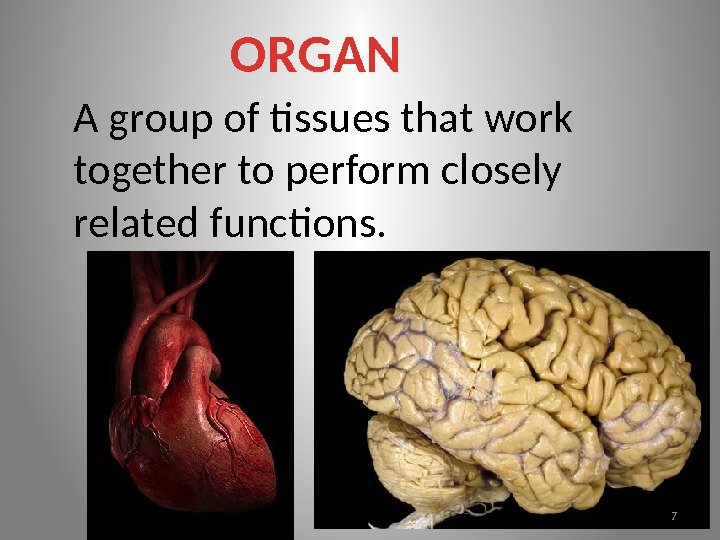
 ORGAN A group of tissues that work together to perform closely related functions.
ORGAN A group of tissues that work together to perform closely related functions.
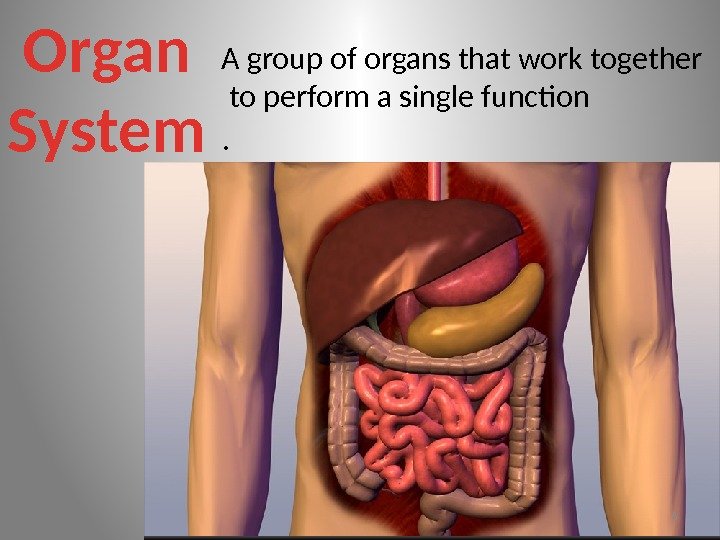
 Organ System A group of organs that work together to perform a single function.
Organ System A group of organs that work together to perform a single function.
 There are 11 organ systems in the human body 1. Integumentary System 2. Skeletal System 3. Muscular System 4. Nervous System 5. Endocrine System 6. Cardiovascular System 7. Lymphatic & Immune System 8. Respiratory System 9. Digestive System 10. Urinary System 11. Reproductive System
There are 11 organ systems in the human body 1. Integumentary System 2. Skeletal System 3. Muscular System 4. Nervous System 5. Endocrine System 6. Cardiovascular System 7. Lymphatic & Immune System 8. Respiratory System 9. Digestive System 10. Urinary System 11. Reproductive System
 Skeletal System Your skeleton has five major functions. • It provides shape and support • Enables you to move • Protects your internal organs • Produces blood cells • Stores certain materials until your body needs them
Skeletal System Your skeleton has five major functions. • It provides shape and support • Enables you to move • Protects your internal organs • Produces blood cells • Stores certain materials until your body needs them
 Major Organs of the Skeletal System • Bones • Tendons connect bones to muscles. • Ligaments connect bone to bone. • Cartilage cushions places where bones connect and offers flexibility.
Major Organs of the Skeletal System • Bones • Tendons connect bones to muscles. • Ligaments connect bone to bone. • Cartilage cushions places where bones connect and offers flexibility.
 Muscular System Your muscles control all movements of the body tissues, organs and bones.
Muscular System Your muscles control all movements of the body tissues, organs and bones.
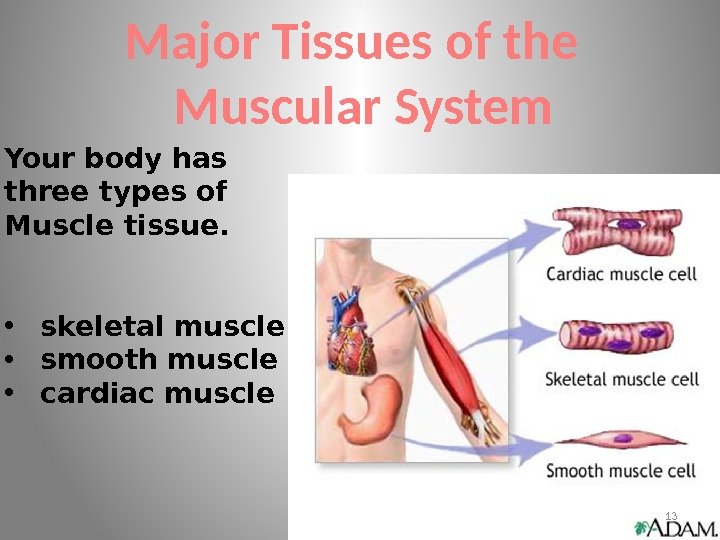
 Major Tissues of the Muscular System Your body has three types of Muscle tissue. • skeletal muscle • smooth muscle • cardiac muscle
Major Tissues of the Muscular System Your body has three types of Muscle tissue. • skeletal muscle • smooth muscle • cardiac muscle
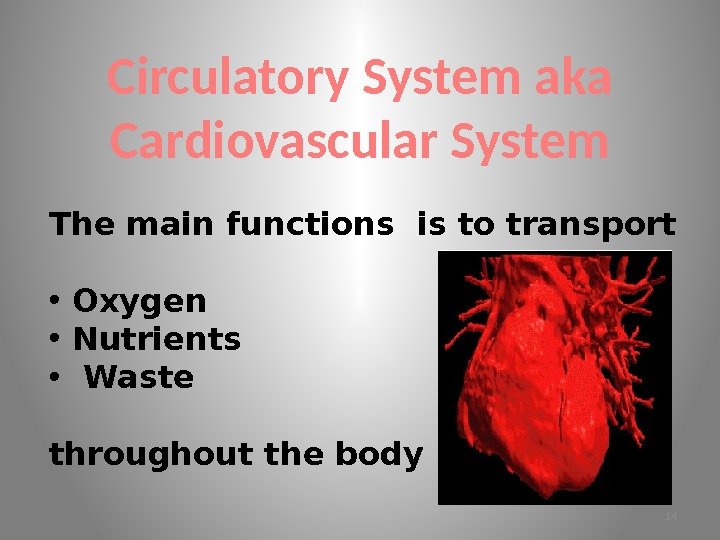
 Circulatory System aka Cardiovascular System The main functions is to transport • Oxygen • Nutrients • Waste throughout the body
Circulatory System aka Cardiovascular System The main functions is to transport • Oxygen • Nutrients • Waste throughout the body
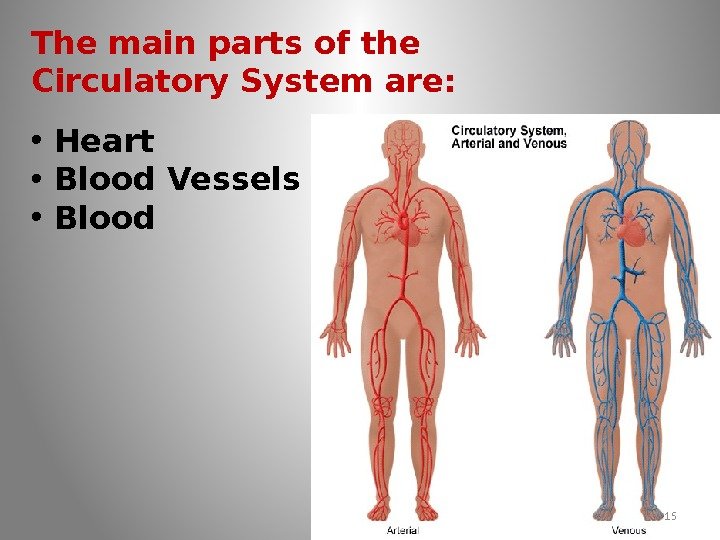
 The main parts of the Circulatory System are: • Heart • Blood Vessels • Blood
The main parts of the Circulatory System are: • Heart • Blood Vessels • Blood
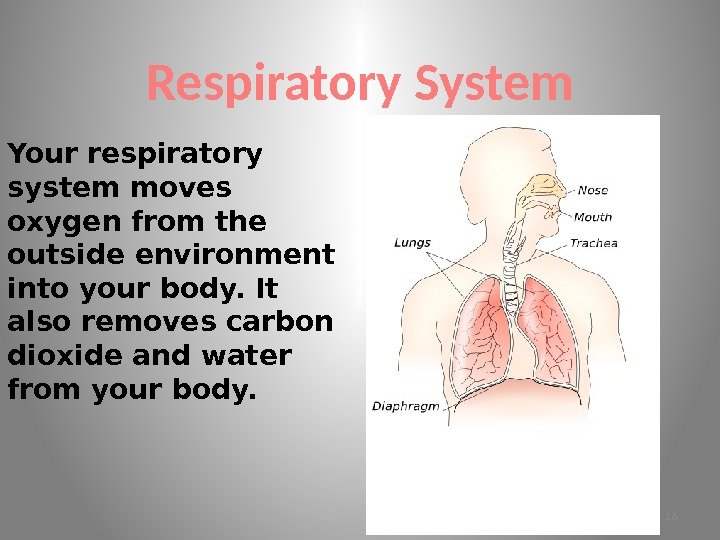
 Respiratory System Your respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into your body. It also removes carbon dioxide and water from your body.
Respiratory System Your respiratory system moves oxygen from the outside environment into your body. It also removes carbon dioxide and water from your body.
 The Main Parts of the Respiratory system are: • Nose • Mouth • Trachea • Lungs • Diaphragm
The Main Parts of the Respiratory system are: • Nose • Mouth • Trachea • Lungs • Diaphragm
 The Digestive System • The main functions of the digestive system • Breaks down food into molecules the body can absorb. • Passes these molecules into the blood to be carried throughout the body. • Eliminates solid wastes from the body.
The Digestive System • The main functions of the digestive system • Breaks down food into molecules the body can absorb. • Passes these molecules into the blood to be carried throughout the body. • Eliminates solid wastes from the body.
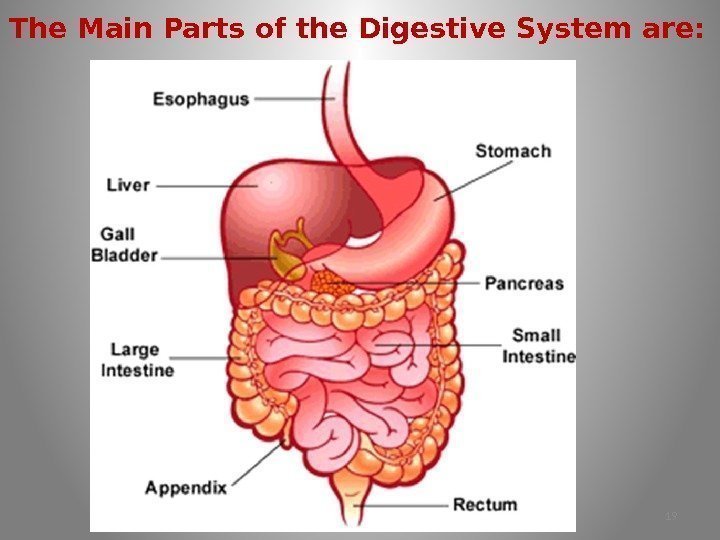
 The Main Parts of the Digestive System are:
The Main Parts of the Digestive System are:
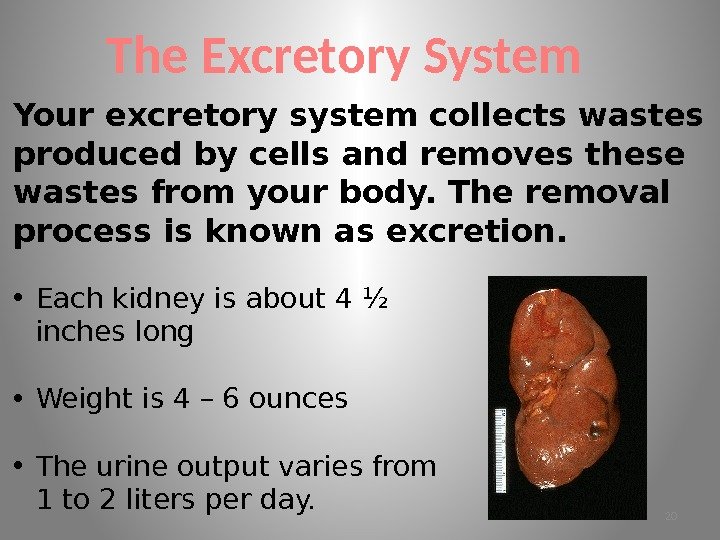
 The Excretory System Your excretory system collects wastes produced by cells and removes these wastes from your body. The removal process is known as excretion. • Each kidney is about 4 ½ inches long • Weight is 4 – 6 ounces • The urine output varies from 1 to 2 liters per day.
The Excretory System Your excretory system collects wastes produced by cells and removes these wastes from your body. The removal process is known as excretion. • Each kidney is about 4 ½ inches long • Weight is 4 – 6 ounces • The urine output varies from 1 to 2 liters per day.
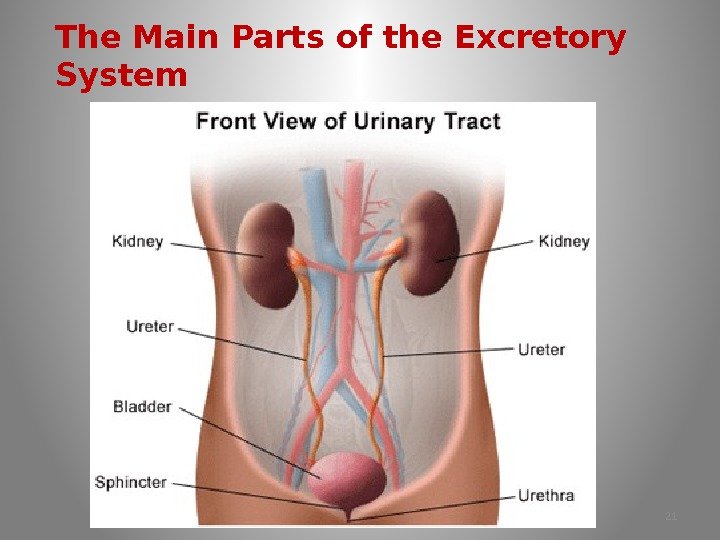
 The Main Parts of the Excretory System
The Main Parts of the Excretory System
 Integumentary System (it’s your skin) Your Skin has many important functions: • Covers body and prevents water loss. • Protects body from injury and infection. • Helps regulate body temperature. • Eliminate wastes • Gathers information about the environment • Produce vitamin
Integumentary System (it’s your skin) Your Skin has many important functions: • Covers body and prevents water loss. • Protects body from injury and infection. • Helps regulate body temperature. • Eliminate wastes • Gathers information about the environment • Produce vitamin
 Major Parts of the Integumentary System • Skin • Hair • Nails
Major Parts of the Integumentary System • Skin • Hair • Nails
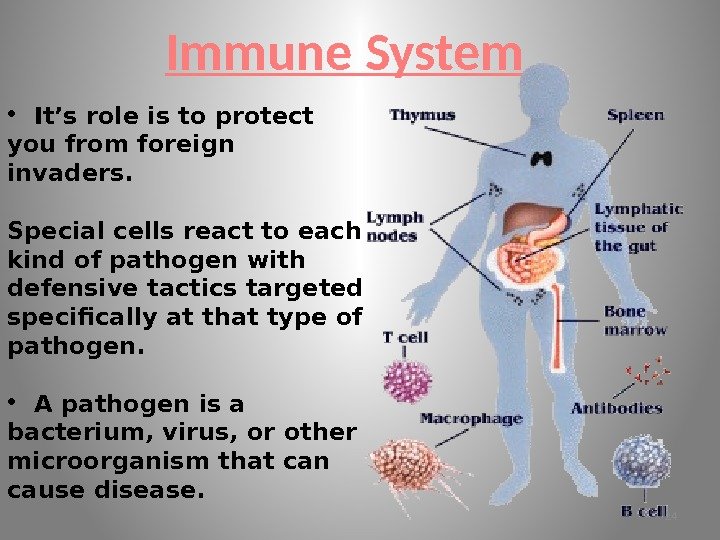
 Immune System • It’s role is to protect you from foreign invaders. Special cells react to each kind of pathogen with defensive tactics targeted specifically at that type of pathogen. • A pathogen is a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease.
Immune System • It’s role is to protect you from foreign invaders. Special cells react to each kind of pathogen with defensive tactics targeted specifically at that type of pathogen. • A pathogen is a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease.
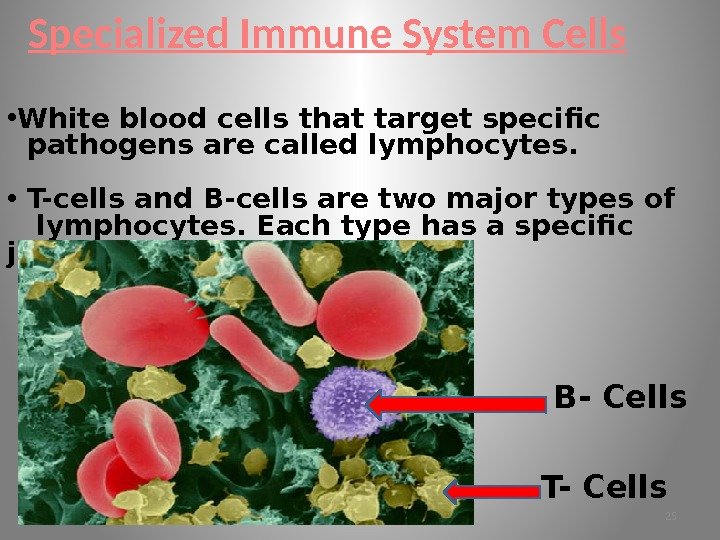
 Specialized Immune System Cells • White blood cells that target specific pathogens are called lymphocytes. • T-cells and B-cells are two major types of lymphocytes. Each type has a specific job. T- Cells B- Cells
Specialized Immune System Cells • White blood cells that target specific pathogens are called lymphocytes. • T-cells and B-cells are two major types of lymphocytes. Each type has a specific job. T- Cells B- Cells
 What are Antibodies? • Antibodies are special proteins that recognize and defeat invading pathogens. • Antibodies are made by the B-cells. • Once a pathogen is encountered by the B-cells it memorizes it and next time it encounters the pathogen it will have antibodies ready to fight the pathogen.
What are Antibodies? • Antibodies are special proteins that recognize and defeat invading pathogens. • Antibodies are made by the B-cells. • Once a pathogen is encountered by the B-cells it memorizes it and next time it encounters the pathogen it will have antibodies ready to fight the pathogen.
 What are Antigens? An antigen is any substance that when introduced into the body stimulates the production of an antibody immune response. Antigens include: Toxins Bacteria Foreign blood cells Cells of transplanted organs.
What are Antigens? An antigen is any substance that when introduced into the body stimulates the production of an antibody immune response. Antigens include: Toxins Bacteria Foreign blood cells Cells of transplanted organs.
 What is Immunity? • Immunity is a state in which the body has sufficient defenses to fight infection, disease or invasion by pathogens. • Non- Specific Immunity refers to the defenses that are in place at all times and are not specific to the pathogen to which the system is responding. • Skin, mucous membranes, hairs in nose and ears, enzymes in mouth and tears in eyes.
What is Immunity? • Immunity is a state in which the body has sufficient defenses to fight infection, disease or invasion by pathogens. • Non- Specific Immunity refers to the defenses that are in place at all times and are not specific to the pathogen to which the system is responding. • Skin, mucous membranes, hairs in nose and ears, enzymes in mouth and tears in eyes.
 Specific Immunity is a specific antibody response to the pathogen and has been acquired in one of several ways. • Antibodies were transferred from mother to fetus across the placenta. • Antibodies were transferred through breast milk from mother to child. • Antibodies were built up due to prior exposure to the pathogen. • Antibodies were be built up through a vaccination process.
Specific Immunity is a specific antibody response to the pathogen and has been acquired in one of several ways. • Antibodies were transferred from mother to fetus across the placenta. • Antibodies were transferred through breast milk from mother to child. • Antibodies were built up due to prior exposure to the pathogen. • Antibodies were be built up through a vaccination process.
 What is a Vaccination? • Most vaccines contain a little bit of a disease germ that is weak or dead. Vaccines do NOT contain the type of germ that makes you sick. • Having this little bit of the germ inside your body makes your body’s immune system build antibodies to it. • Vaccines can be administered by a needle, mouth and some thorough a nasal spray. • In the US children are vaccinated before they can enter school for: Measles, Mumps, Rubella, Pertussis, Hepatitis B, Diphtheria, and Tetanus
What is a Vaccination? • Most vaccines contain a little bit of a disease germ that is weak or dead. Vaccines do NOT contain the type of germ that makes you sick. • Having this little bit of the germ inside your body makes your body’s immune system build antibodies to it. • Vaccines can be administered by a needle, mouth and some thorough a nasal spray. • In the US children are vaccinated before they can enter school for: Measles, Mumps, Rubella, Pertussis, Hepatitis B, Diphtheria, and Tetanus
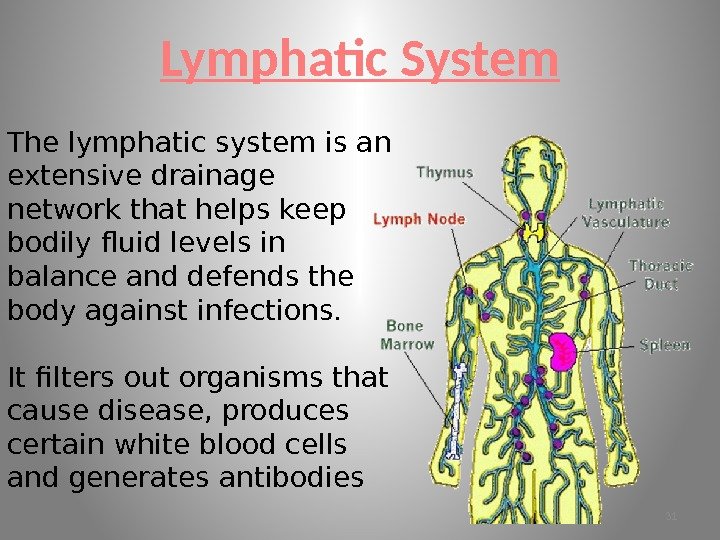
 Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is an extensive drainage network that helps keep bodily fluid levels in balance and defends the body against infections. It filters out organisms that cause disease, produces certain white blood cells and generates antibodies
Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is an extensive drainage network that helps keep bodily fluid levels in balance and defends the body against infections. It filters out organisms that cause disease, produces certain white blood cells and generates antibodies
 • It is made up of a network of lymphatic vessels that carry lymph — a clear, watery fluid that contains protein molecules, salts, glucose, urea, and other substances — throughout the body. • It works closely with the immune system and the circulatory system. • The Spleen stores many of the white blood cells needed for the immune response. Major Parts of the Lymphatic System
• It is made up of a network of lymphatic vessels that carry lymph — a clear, watery fluid that contains protein molecules, salts, glucose, urea, and other substances — throughout the body. • It works closely with the immune system and the circulatory system. • The Spleen stores many of the white blood cells needed for the immune response. Major Parts of the Lymphatic System
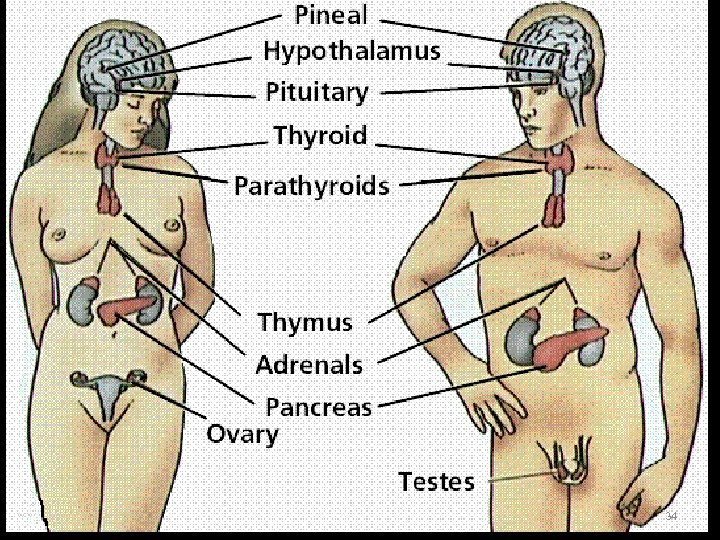
 Endocrine System 1. The endocrine system is a collection of ductless glands that secrete special proteins called hormones. 2. The glands release the hormones into the bloodstream and they travel to the target cells or organs. 3. The main function of the endocrine system is to maintain a stable environment within the body or homeostasis. 4. The hormones also help the body to regulate: Growth Sexual development Metabolism Sugar, salt and fluid levels in the blood
Endocrine System 1. The endocrine system is a collection of ductless glands that secrete special proteins called hormones. 2. The glands release the hormones into the bloodstream and they travel to the target cells or organs. 3. The main function of the endocrine system is to maintain a stable environment within the body or homeostasis. 4. The hormones also help the body to regulate: Growth Sexual development Metabolism Sugar, salt and fluid levels in the blood

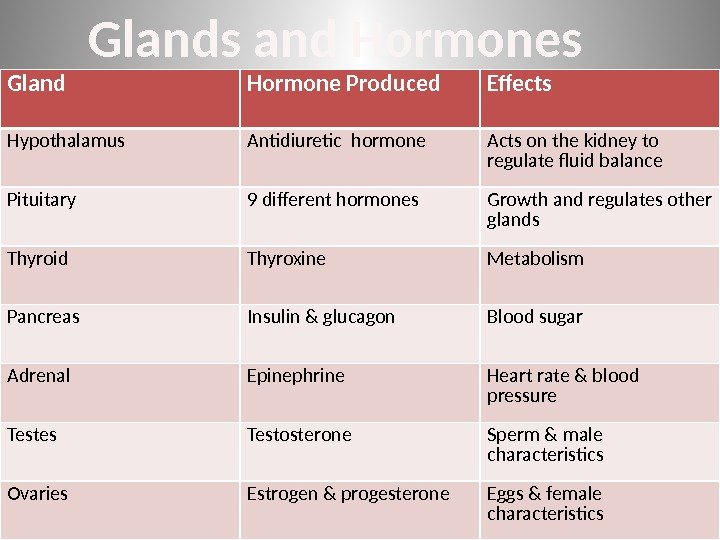
 35 Gland Hormone Produced Effects Hypothalamus Antidiuretic hormone Acts on the kidney to regulate fluid balance Pituitary 9 different hormones Growth and regulates other glands Thyroid Thyroxine Metabolism Pancreas Insulin & glucagon Blood sugar Adrenal Epinephrine Heart rate & blood pressure Testes Testosterone Sperm & male characteristics Ovaries Estrogen & progesterone Eggs & female characteristics. Glands and Hormones
35 Gland Hormone Produced Effects Hypothalamus Antidiuretic hormone Acts on the kidney to regulate fluid balance Pituitary 9 different hormones Growth and regulates other glands Thyroid Thyroxine Metabolism Pancreas Insulin & glucagon Blood sugar Adrenal Epinephrine Heart rate & blood pressure Testes Testosterone Sperm & male characteristics Ovaries Estrogen & progesterone Eggs & female characteristics. Glands and Hormones





