http: //www. embryology. ch/anglais /iperiodembry/carnegie 02. html














i-ii-kvira5.ppt
- Размер: 15.4 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 68
Описание презентации http: //www. embryology. ch/anglais /iperiodembry/carnegie 02. html по слайдам
 http: //www. embryology. ch/anglais /iperiodembry/carnegie 02. html
http: //www. embryology. ch/anglais /iperiodembry/carnegie 02. html
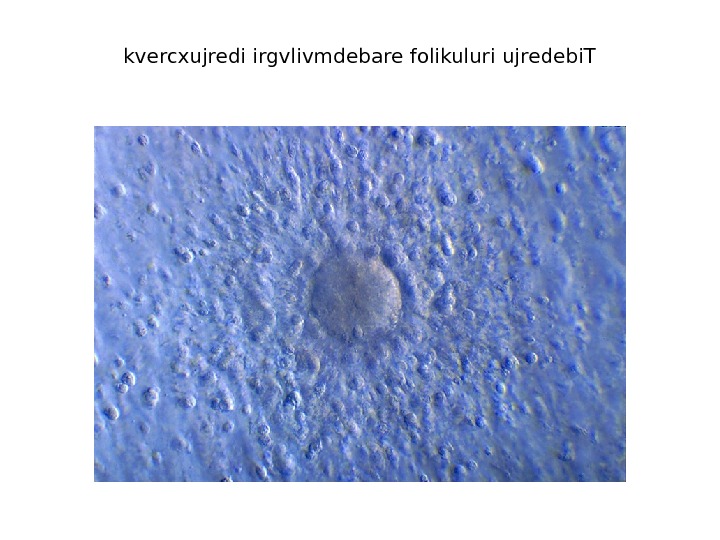
 kvercxujredi irgvlivmdebare folikuluri ujredebi. T
kvercxujredi irgvlivmdebare folikuluri ujredebi. T
 Stage 1 1 Male pronucleus 2 Female pronucleus 3 Doubled paternal centrosome 4 «Inner bodies » Approx. 1 rst day 0. 1 — 0. 15 mm
Stage 1 1 Male pronucleus 2 Female pronucleus 3 Doubled paternal centrosome 4 «Inner bodies » Approx. 1 rst day 0. 1 — 0. 15 mm
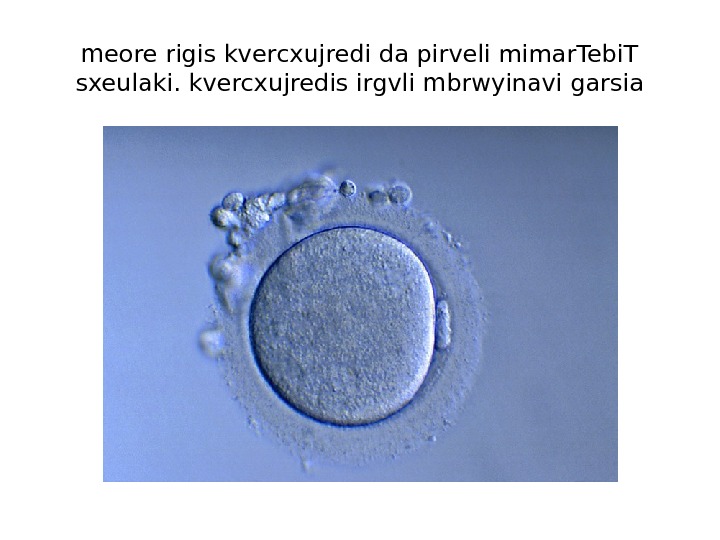
 meore rigis kvercxujredi da pirveli mimar. Tebi. T sxeulaki. kvercxujredis irgvli mbrwyinavi garsia
meore rigis kvercxujredi da pirveli mimar. Tebi. T sxeulaki. kvercxujredis irgvli mbrwyinavi garsia
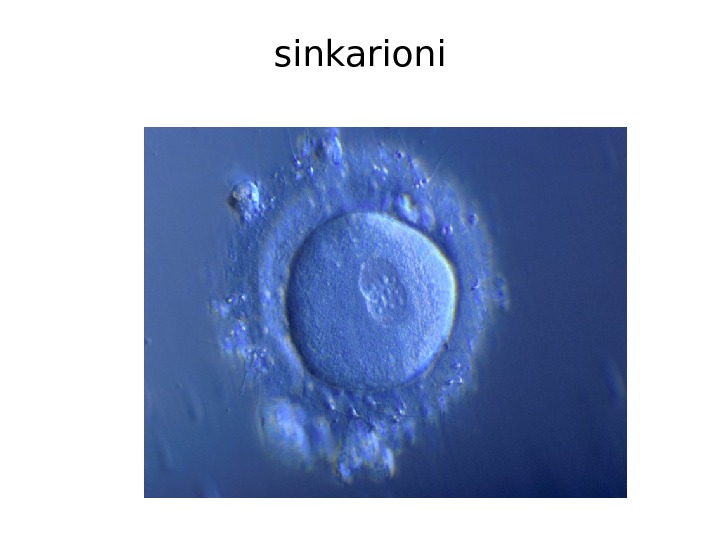
 sinkarioni
sinkarioni
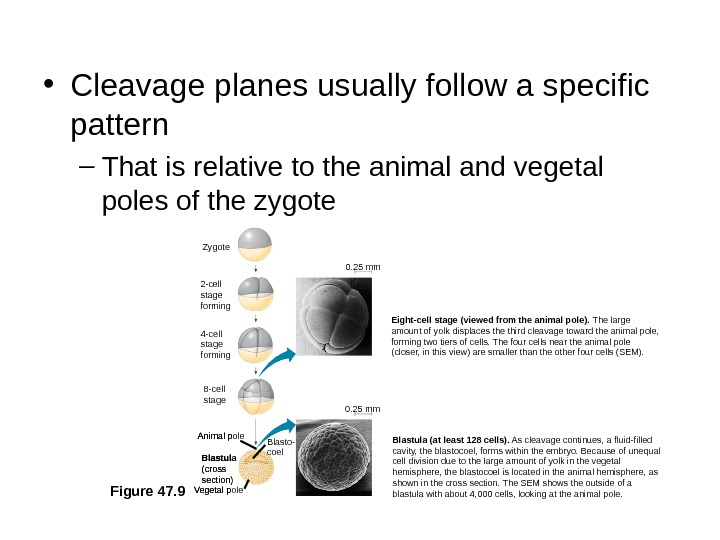
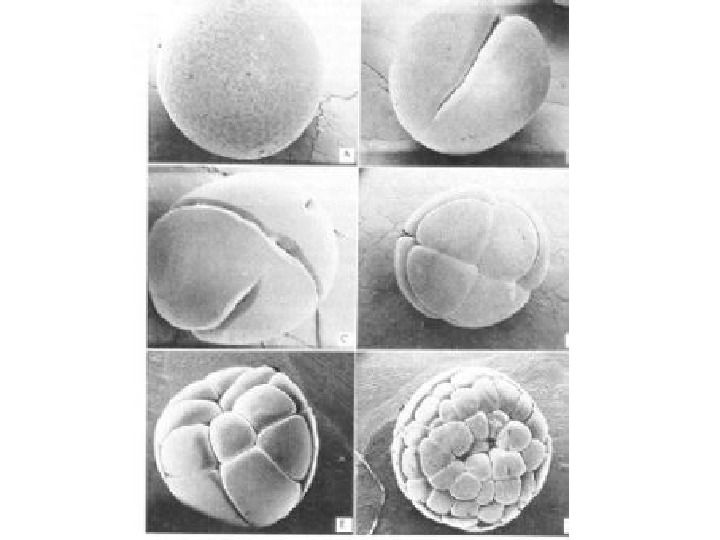
 • Cleavage planes usually follow a specific pattern – That is relative to the animal and vegetal poles of the zygote Figure 47. 9 Zygote 2 -cell stage forming 4 -cell stage forming 8 -cell stage Eight-cell stage (viewed from the animal pole). The large amount of yolk displaces the third cleavage toward the animal pole, forming two tiers of cells. The four cells near the animal pole (closer, in this view) are smaller than the other four cells (SEM). 0. 25 mm Vegetal pole Blastula (cross section)Animal pole Blasto- coel Blastula (at least 128 cells). As cleavage continues, a fluid-filled cavity, the blastocoel, forms within the embryo. Because of unequal cell division due to the large amount of yolk in the vegetal hemisphere, the blastocoel is located in the animal hemisphere, as shown in the cross section. The SEM shows the outside of a blastula with about 4, 000 cells, looking at the animal pole. Vegetal pole Blastula (cross section)Animal pole Blasto- coel 0. 25 mm
• Cleavage planes usually follow a specific pattern – That is relative to the animal and vegetal poles of the zygote Figure 47. 9 Zygote 2 -cell stage forming 4 -cell stage forming 8 -cell stage Eight-cell stage (viewed from the animal pole). The large amount of yolk displaces the third cleavage toward the animal pole, forming two tiers of cells. The four cells near the animal pole (closer, in this view) are smaller than the other four cells (SEM). 0. 25 mm Vegetal pole Blastula (cross section)Animal pole Blasto- coel Blastula (at least 128 cells). As cleavage continues, a fluid-filled cavity, the blastocoel, forms within the embryo. Because of unequal cell division due to the large amount of yolk in the vegetal hemisphere, the blastocoel is located in the animal hemisphere, as shown in the cross section. The SEM shows the outside of a blastula with about 4, 000 cells, looking at the animal pole. Vegetal pole Blastula (cross section)Animal pole Blasto- coel 0. 25 mm

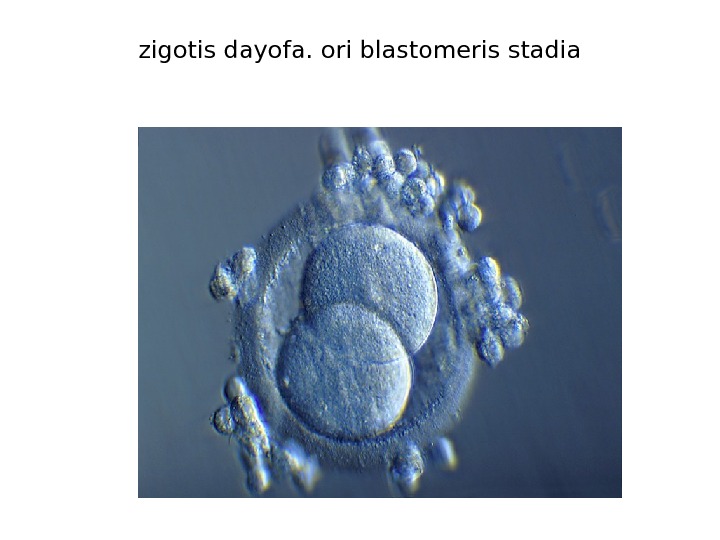
 zigotis dayofa. ori blastomeris stadia
zigotis dayofa. ori blastomeris stadia
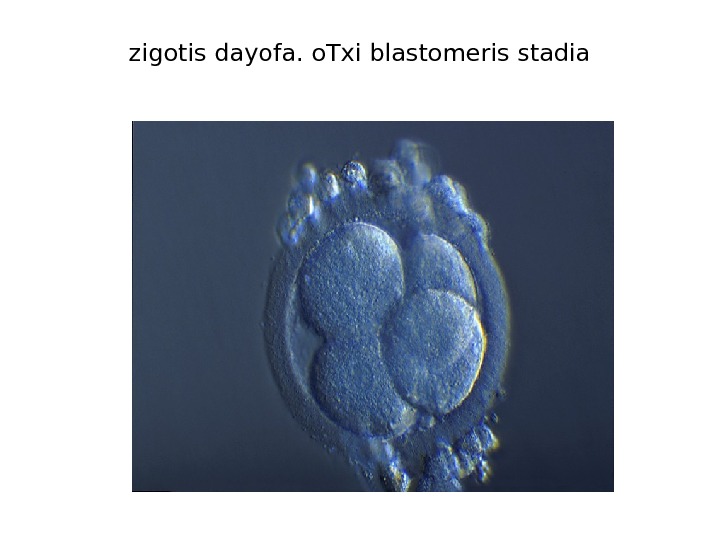
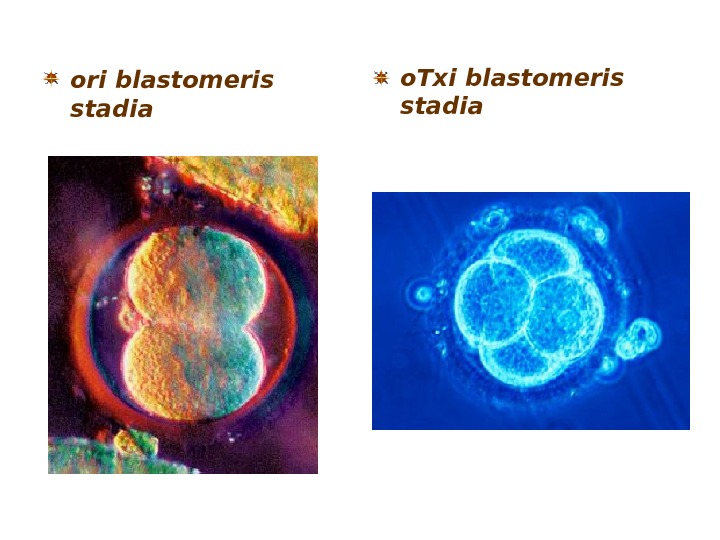
 zigotis dayofa. o. Txi blastomeris stadia
zigotis dayofa. o. Txi blastomeris stadia
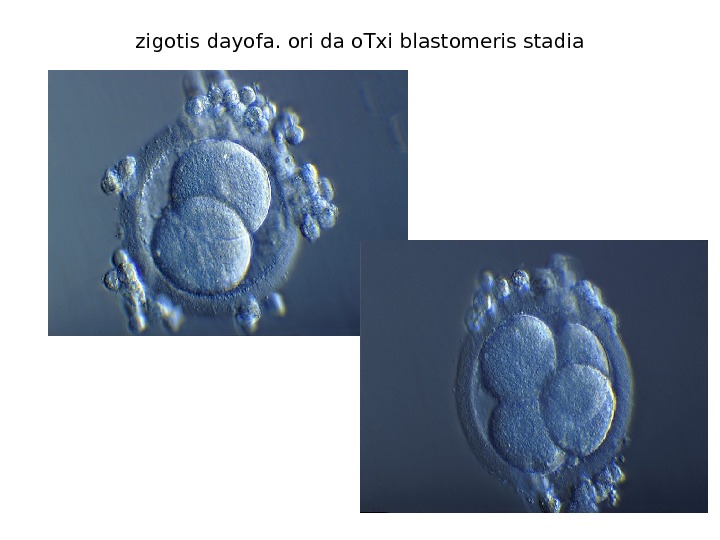
 zigotis dayofa. ori da o. Txi blastomeris stadia
zigotis dayofa. ori da o. Txi blastomeris stadia

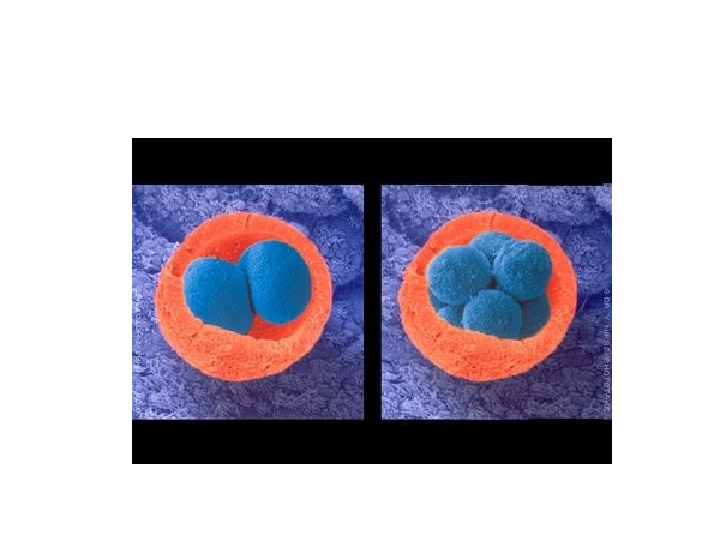
 ori blastomeris stadia o. Txi blastomeris stadia
ori blastomeris stadia o. Txi blastomeris stadia
 Stage 2 Approx. 2 nd — 3 rd day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm The axis (dashed) lies through the two future (embryonic and abembryonic) poles. The embryo is divided into right and left halves (A and B). 1. Zona pellucida 2. Blastomere 3. Polar body
Stage 2 Approx. 2 nd — 3 rd day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm The axis (dashed) lies through the two future (embryonic and abembryonic) poles. The embryo is divided into right and left halves (A and B). 1. Zona pellucida 2. Blastomere 3. Polar body
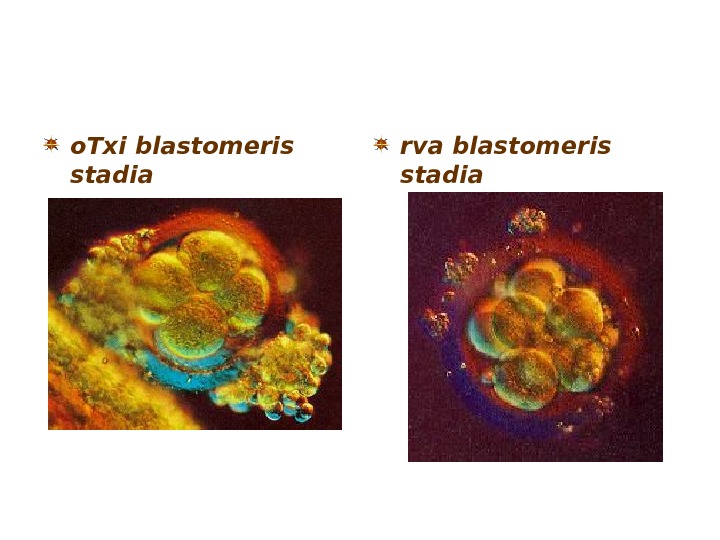
 o. Txi blastomeris stadia rva blastomeris stadia
o. Txi blastomeris stadia rva blastomeris stadia
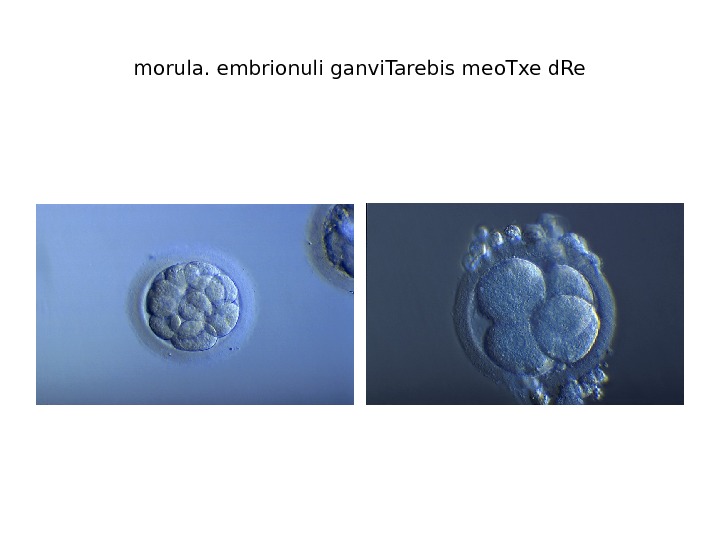
 morula. embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis meo. Txe d. Re
morula. embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis meo. Txe d. Re
 morula. embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis meo. Txe d. Re
morula. embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis meo. Txe d. Re
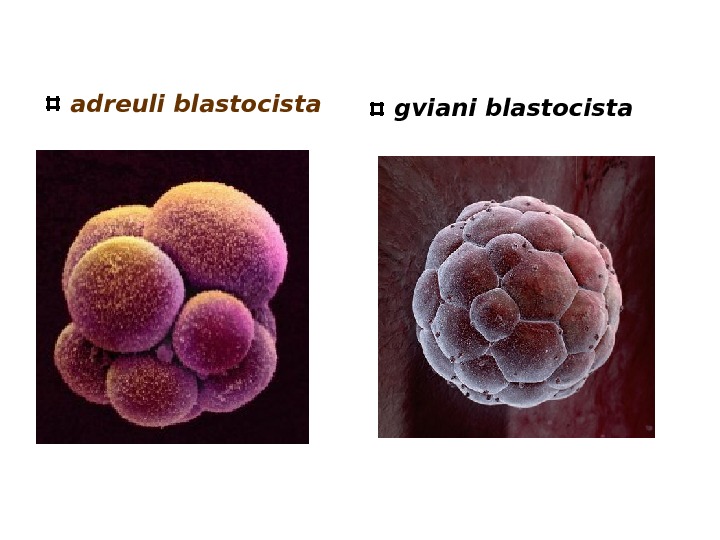
 adreuli blastocista gviani blastocista
adreuli blastocista gviani blastocista
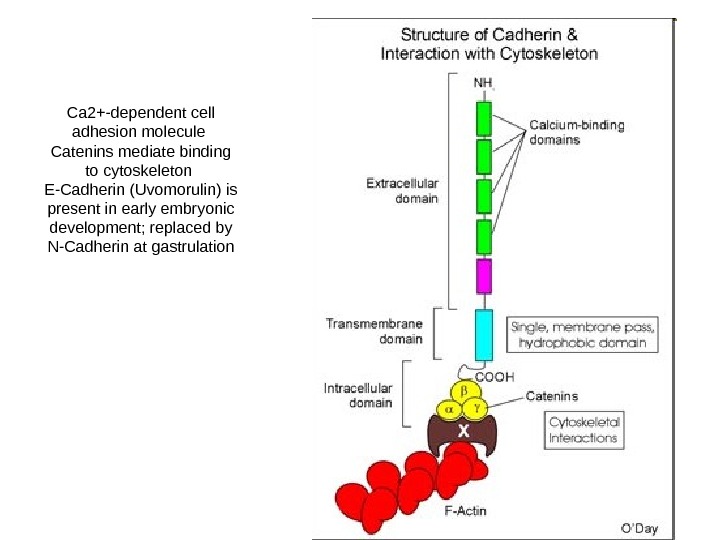
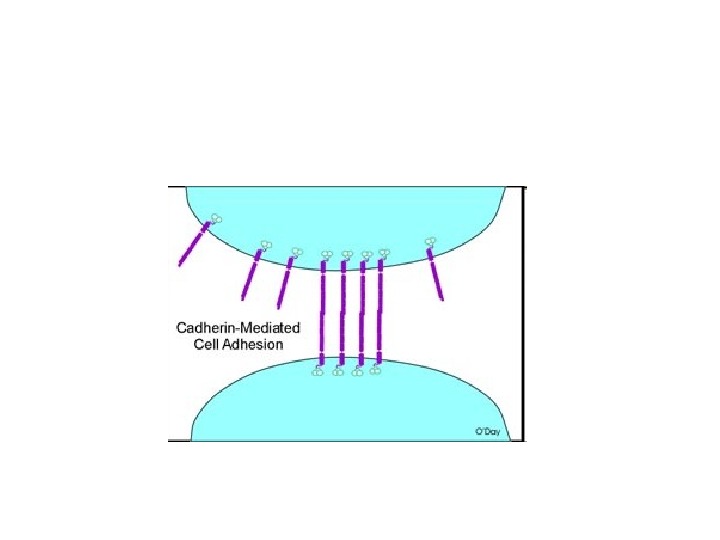
 Ca 2+-dependent cell adhesion molecule Catenins mediate binding to cytoskeleton E-Cadherin (Uvomorulin) is present in early embryonic development; replaced by N-Cadherin at gastrulation
Ca 2+-dependent cell adhesion molecule Catenins mediate binding to cytoskeleton E-Cadherin (Uvomorulin) is present in early embryonic development; replaced by N-Cadherin at gastrulation

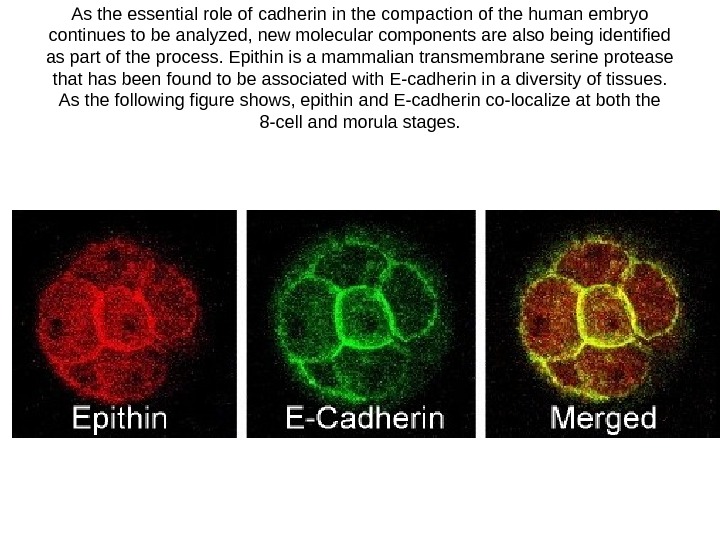
 As the essential role of cadherin in the compaction of the human embryo continues to be analyzed, new molecular components are also being identified as part of the process. Epithin is a mammalian transmembrane serine protease that has been found to be associated with E-cadherin in a diversity of tissues. As the following figure shows, epithin and E-cadherin co-localize at both the 8 -cell and morula stages.
As the essential role of cadherin in the compaction of the human embryo continues to be analyzed, new molecular components are also being identified as part of the process. Epithin is a mammalian transmembrane serine protease that has been found to be associated with E-cadherin in a diversity of tissues. As the following figure shows, epithin and E-cadherin co-localize at both the 8 -cell and morula stages.
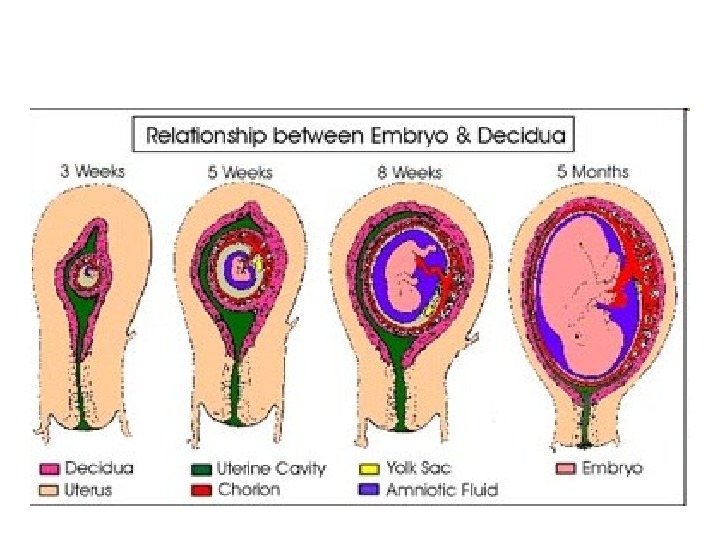
 3 week pregnant
3 week pregnant
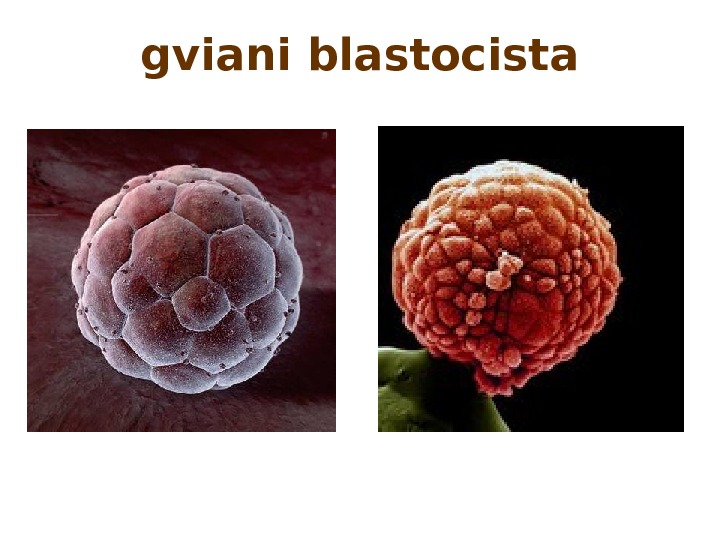
 gviani blastocista
gviani blastocista
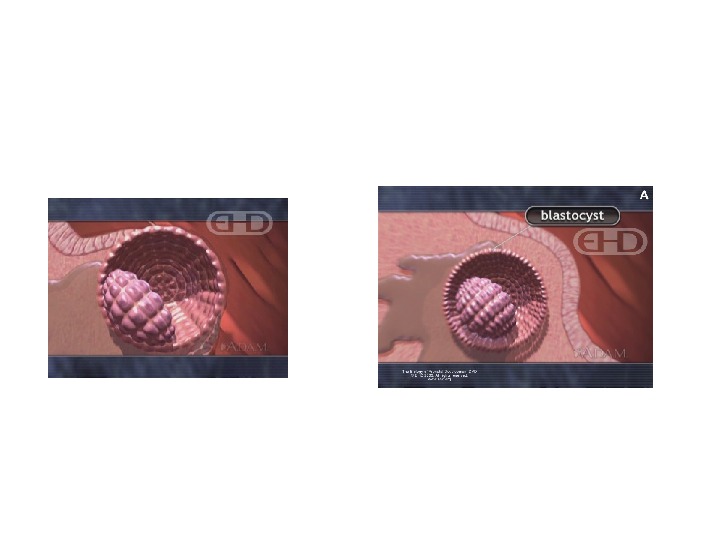
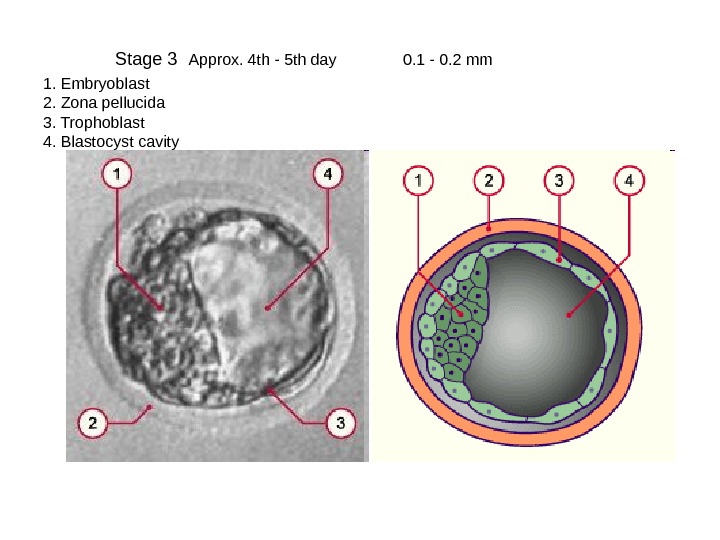
 Stage 3 Approx. 4 th — 5 th day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm 1. Embryoblast 2. Zona pellucida 3. Trophoblast 4. Blastocyst cavity
Stage 3 Approx. 4 th — 5 th day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm 1. Embryoblast 2. Zona pellucida 3. Trophoblast 4. Blastocyst cavity
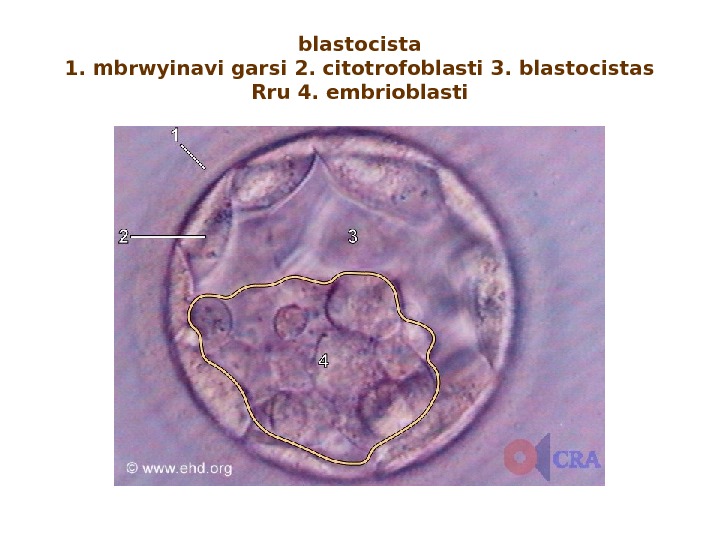
 blastocista 1. mbrwyinavi garsi 2. citotrofoblasti 3. blastocistas Rru 4. embrioblasti
blastocista 1. mbrwyinavi garsi 2. citotrofoblasti 3. blastocistas Rru 4. embrioblasti
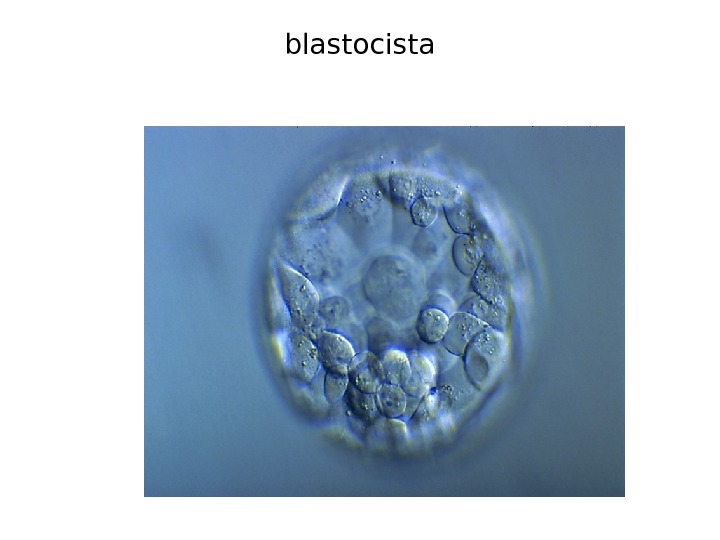
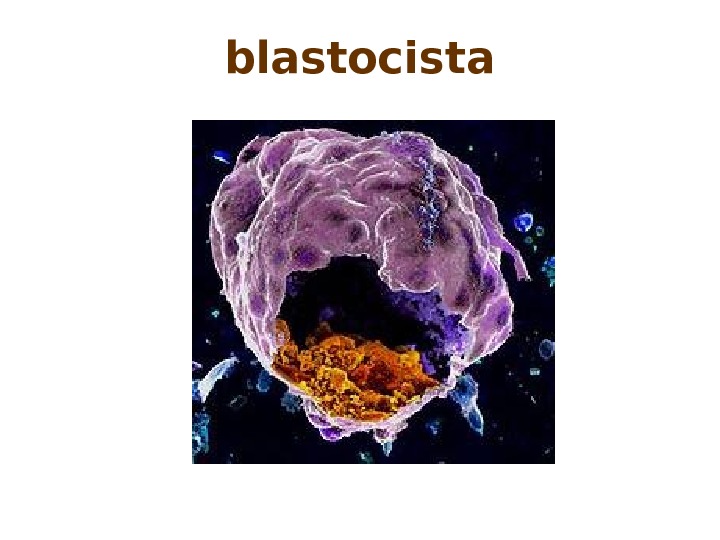
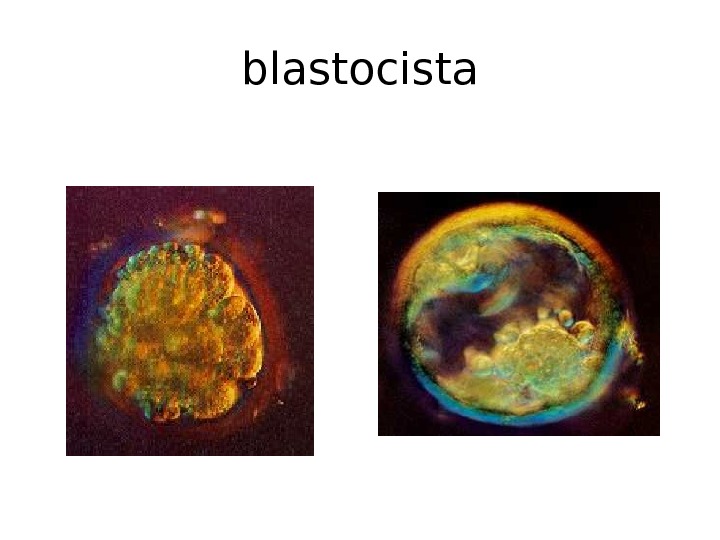
 blastocista
blastocista
 blastocista
blastocista
 blastocista
blastocista
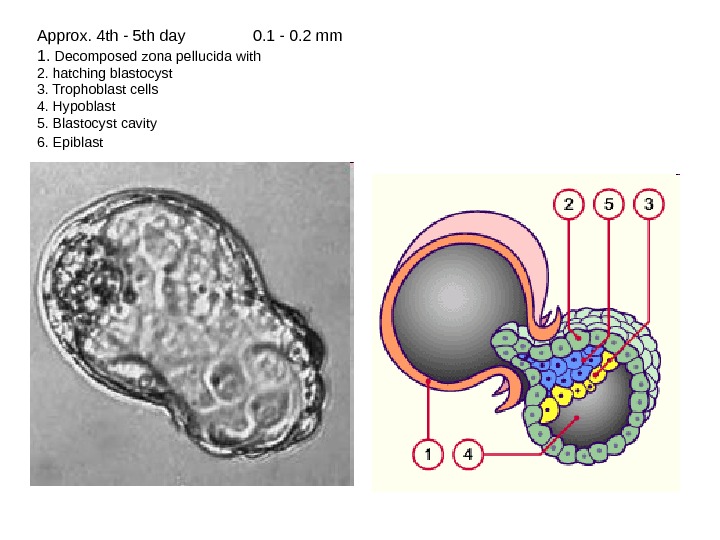
 Approx. 4 th — 5 th day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm 1. Decomposed zona pellucida with 2. hatching blastocyst 3. Trophoblast cells 4. Hypoblast 5. Blastocyst cavity 6. Epiblast
Approx. 4 th — 5 th day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm 1. Decomposed zona pellucida with 2. hatching blastocyst 3. Trophoblast cells 4. Hypoblast 5. Blastocyst cavity 6. Epiblast


 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis I kvira
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis I kvira
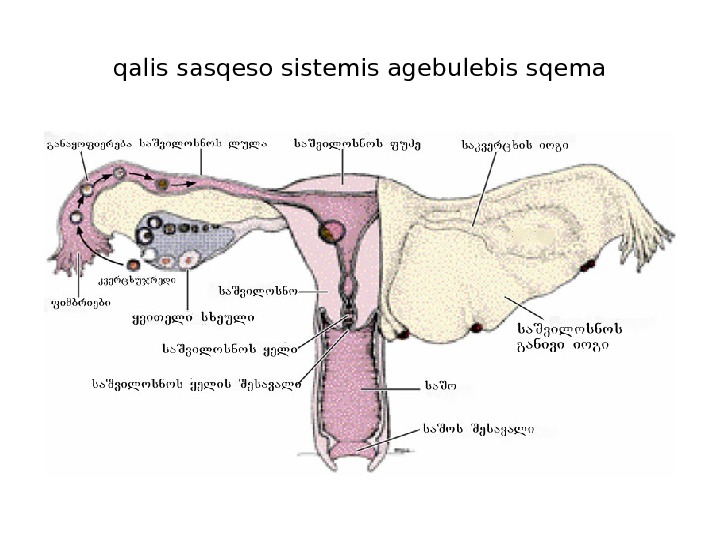
 qalis sasqeso sistemis agebulebis sqema
qalis sasqeso sistemis agebulebis sqema
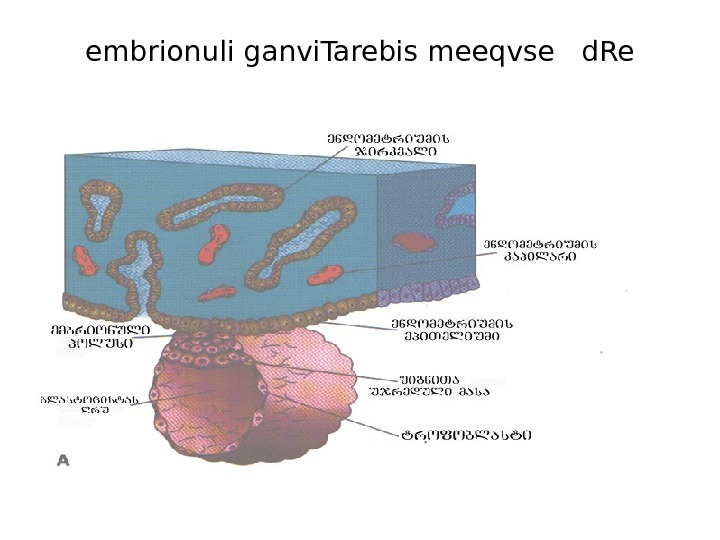
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis meeqvse d. Re
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis meeqvse d. Re
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me. Svide d. Re
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me. Svide d. Re
 » embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis meore kvira
» embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis meore kvira
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis merve d. Re
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis merve d. Re
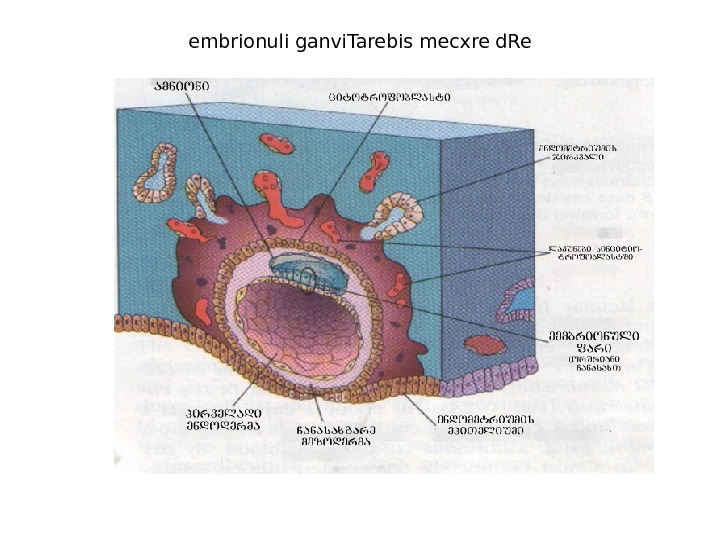
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis mecxre d. Re
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis mecxre d. Re
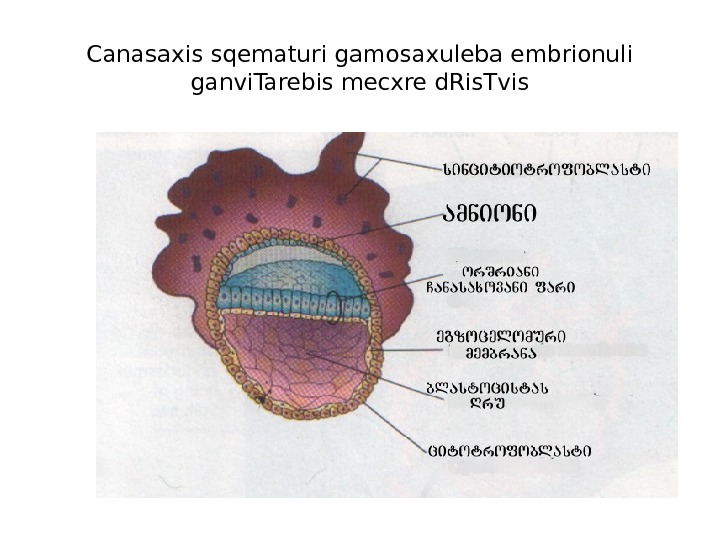
 Canasaxis sqematuri gamosaxuleba embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis mecxre d. Ris. Tvis
Canasaxis sqematuri gamosaxuleba embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis mecxre d. Ris. Tvis
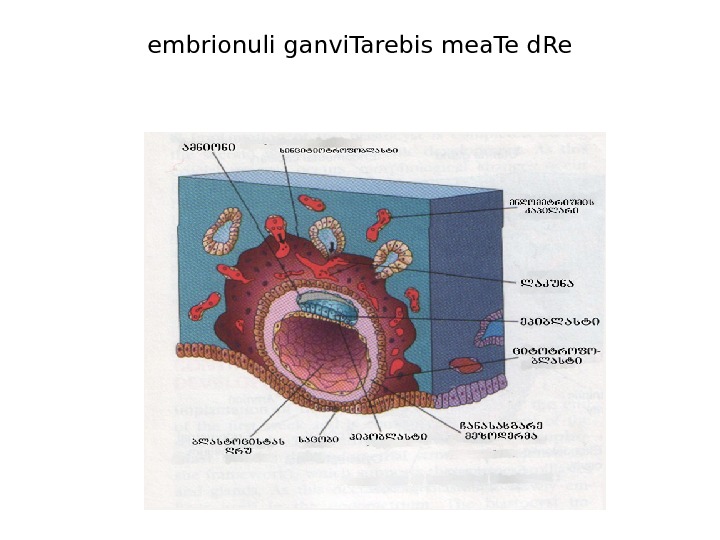
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis mea. Te d. Re
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis mea. Te d. Re
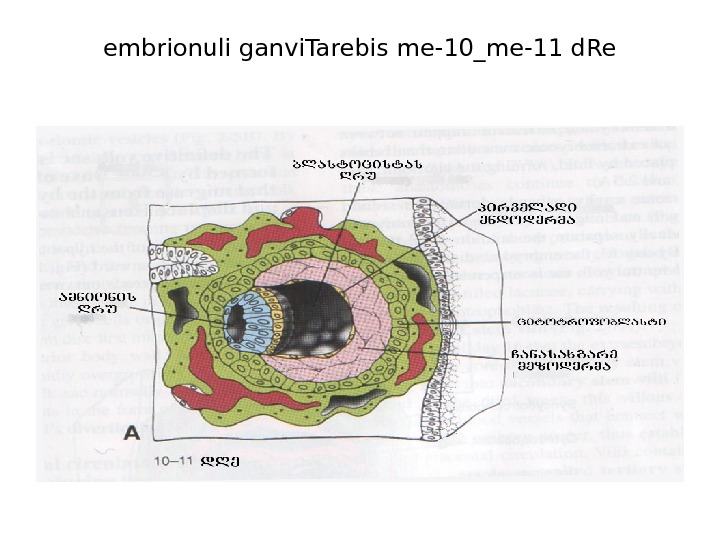
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-10_me-11 d. Re
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-10_me-11 d. Re
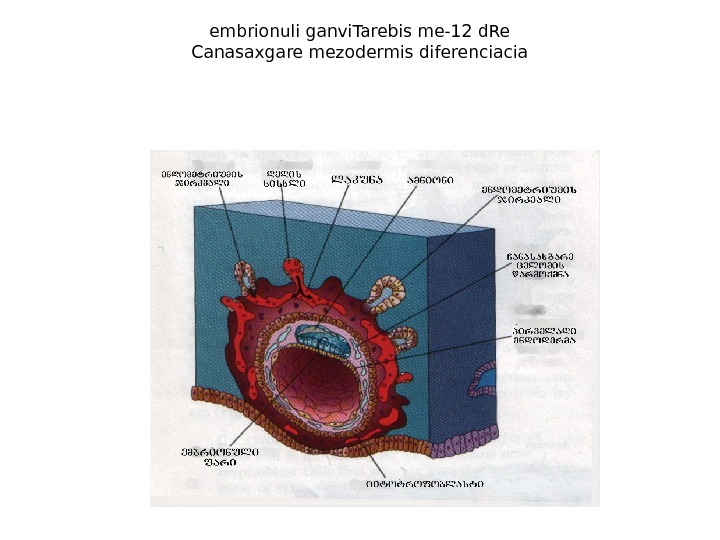
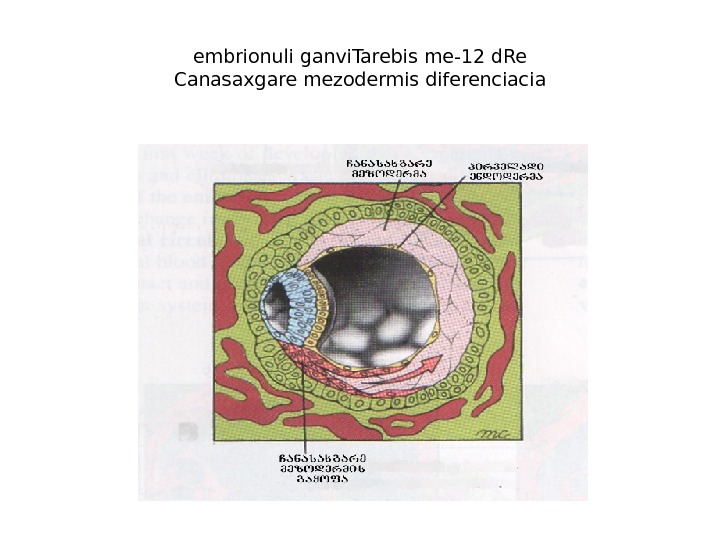
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-12 d. Re Canasaxgare mezodermis diferenciacia
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-12 d. Re Canasaxgare mezodermis diferenciacia
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-12 d. Re Canasaxgare mezodermis diferenciacia
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-12 d. Re Canasaxgare mezodermis diferenciacia
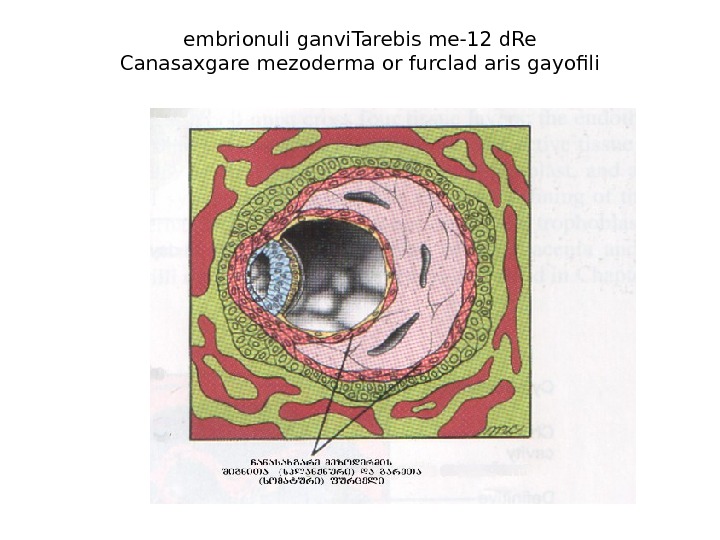
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-12 d. Re Canasaxgare mezoderma or furclad aris gayofili
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-12 d. Re Canasaxgare mezoderma or furclad aris gayofili
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-12_me-13 -e d. Re
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-12_me-13 -e d. Re
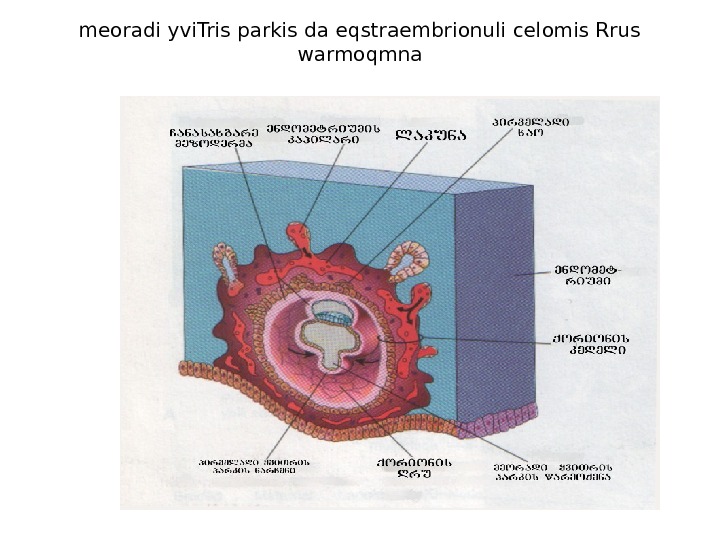
 meoradi yvi. Tris parkis da eqstraembrionuli celomis Rrus warmoqmna
meoradi yvi. Tris parkis da eqstraembrionuli celomis Rrus warmoqmna
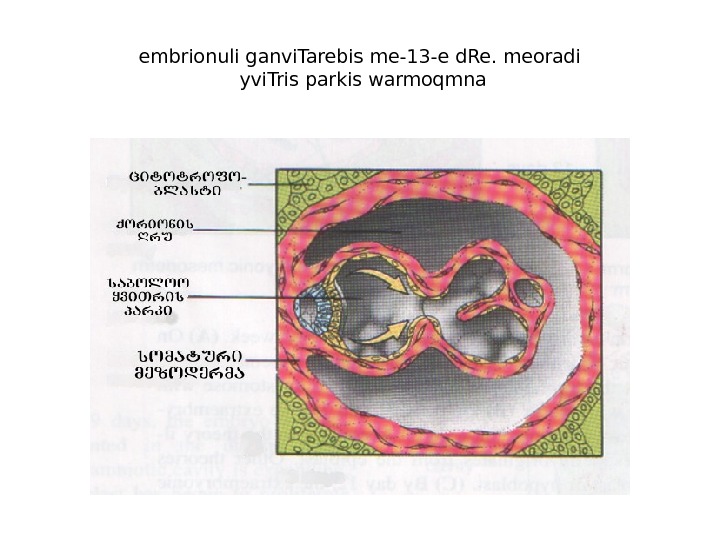
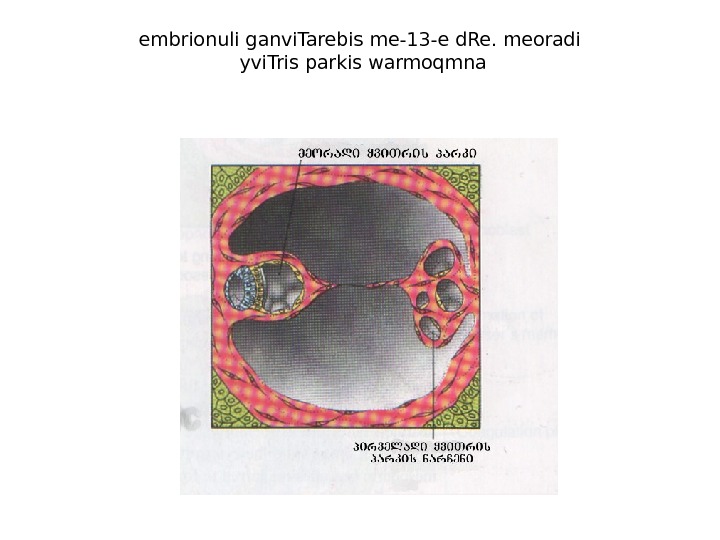
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-13 -e d. Re. meoradi yvi. Tris parkis warmoqmna
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-13 -e d. Re. meoradi yvi. Tris parkis warmoqmna
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-13 -e d. Re. meoradi yvi. Tris parkis warmoqmna
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-13 -e d. Re. meoradi yvi. Tris parkis warmoqmna
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-14 d. Re
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis me-14 d. Re
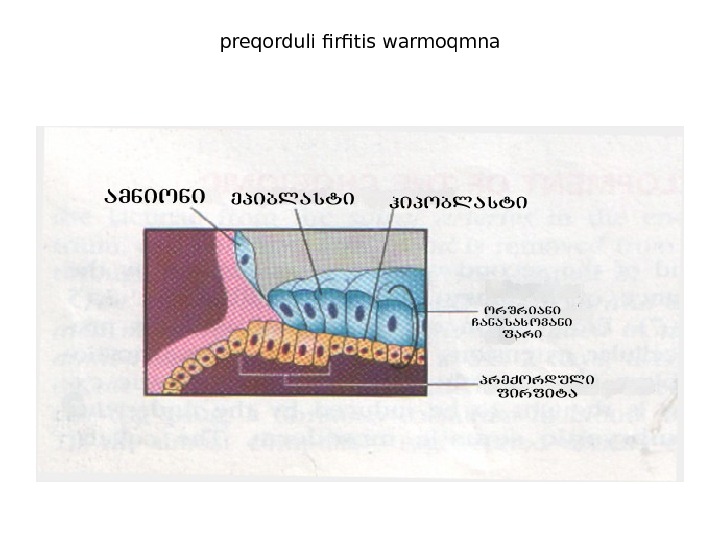
 preqorduli firfitis warmoqmna
preqorduli firfitis warmoqmna
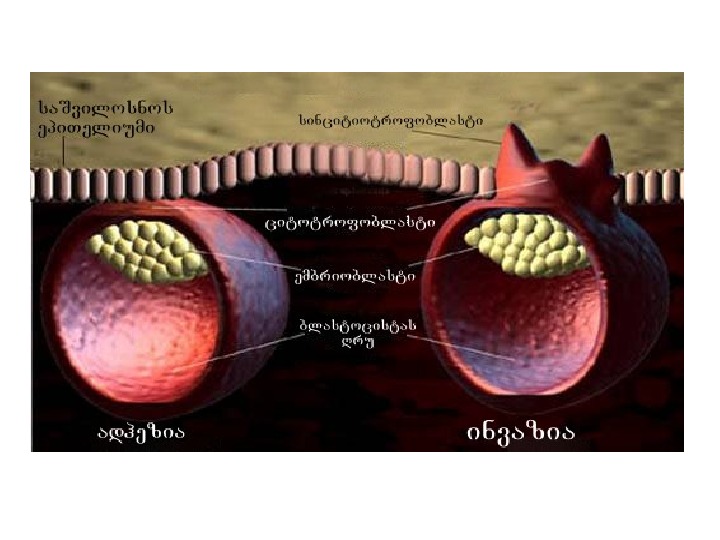
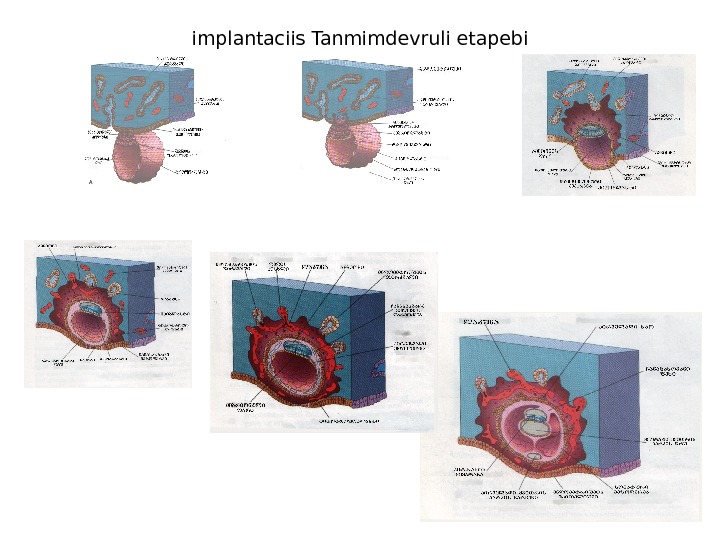
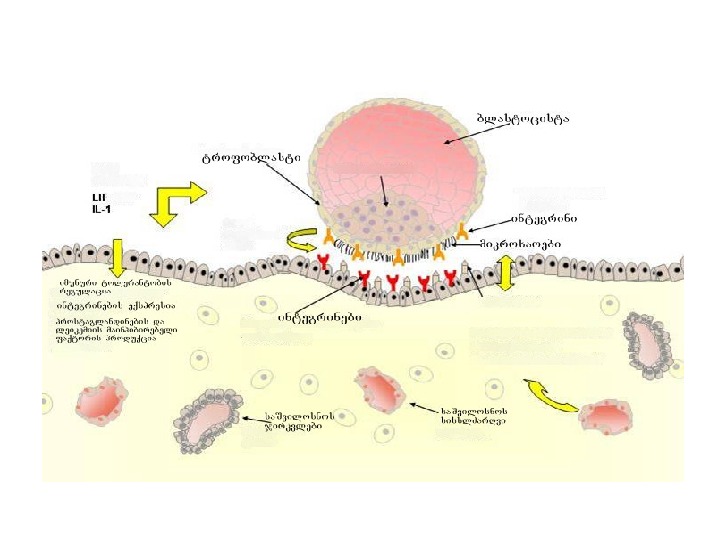
 implantaciis Tanmimdevruli etapebi
implantaciis Tanmimdevruli etapebi

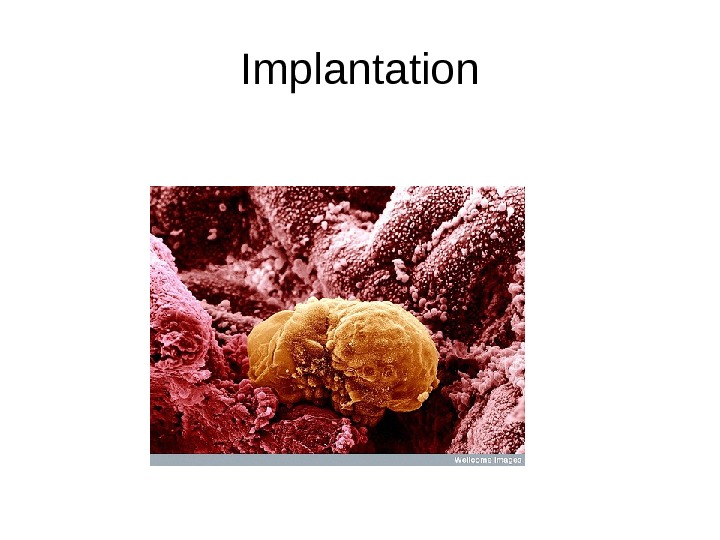
 Implantation
Implantation



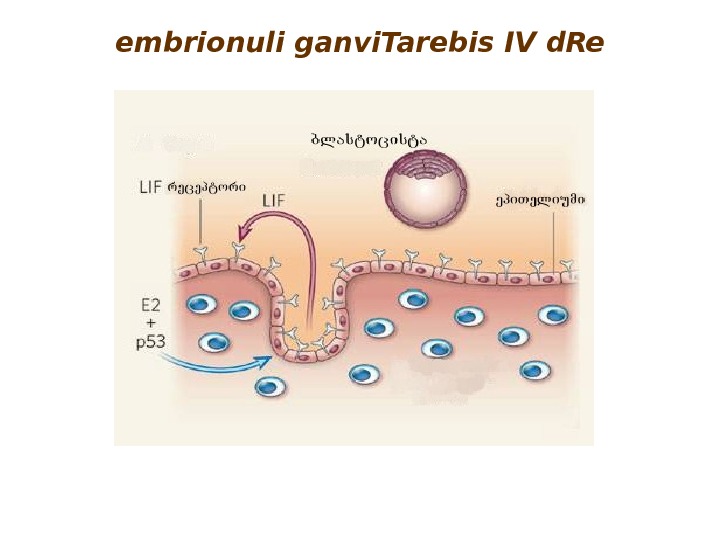
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis IV d. Re
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis IV d. Re
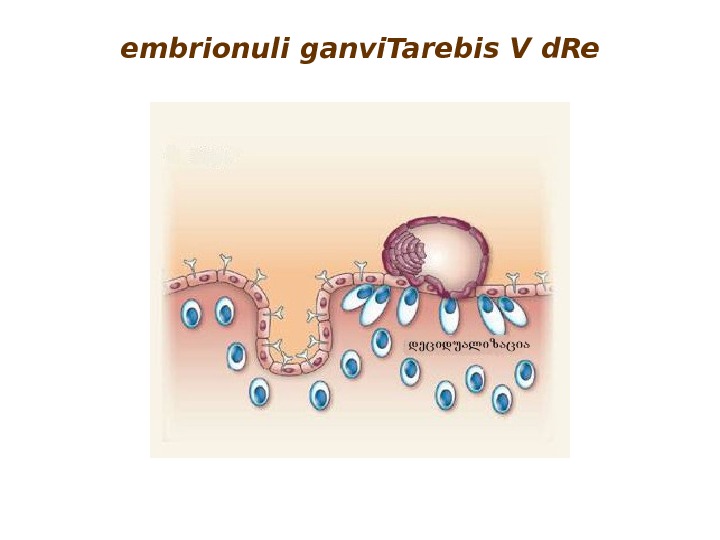
 embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis V d. Re
embrionuli ganvi. Tarebis V d. Re
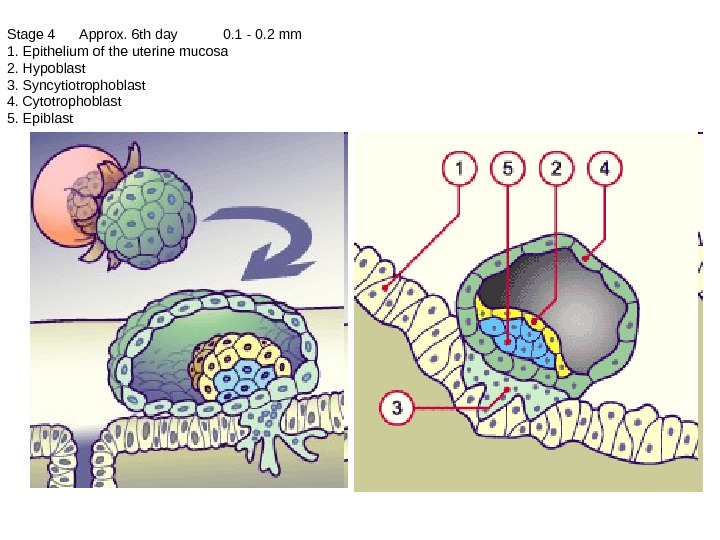
 Stage 4 Approx. 6 th day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm 1. Epithelium of the uterine mucosa 2. Hypoblast 3. Syncytiotrophoblast 4. Cytotrophoblast 5. Epiblast
Stage 4 Approx. 6 th day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm 1. Epithelium of the uterine mucosa 2. Hypoblast 3. Syncytiotrophoblast 4. Cytotrophoblast 5. Epiblast
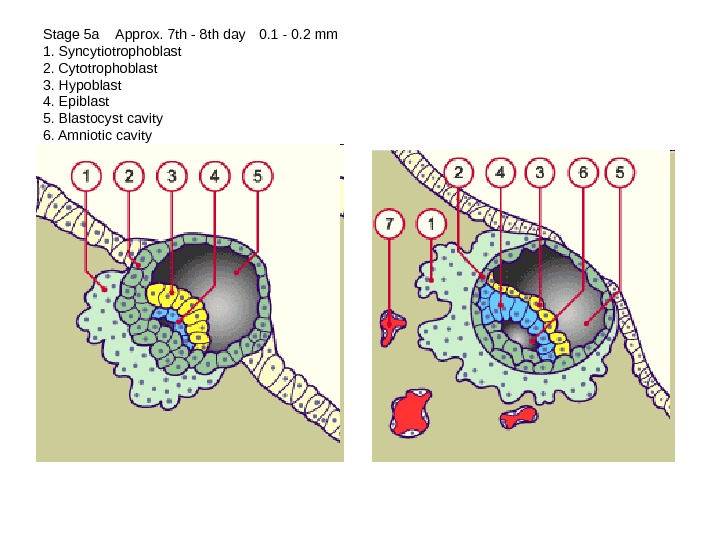
 Stage 5 a Approx. 7 th — 8 th day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm 1. Syncytiotrophoblast 2. Cytotrophoblast 3. Hypoblast 4. Epiblast 5. Blastocyst cavity 6. Amniotic cavity 7. Maternal blood vessels
Stage 5 a Approx. 7 th — 8 th day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm 1. Syncytiotrophoblast 2. Cytotrophoblast 3. Hypoblast 4. Epiblast 5. Blastocyst cavity 6. Amniotic cavity 7. Maternal blood vessels
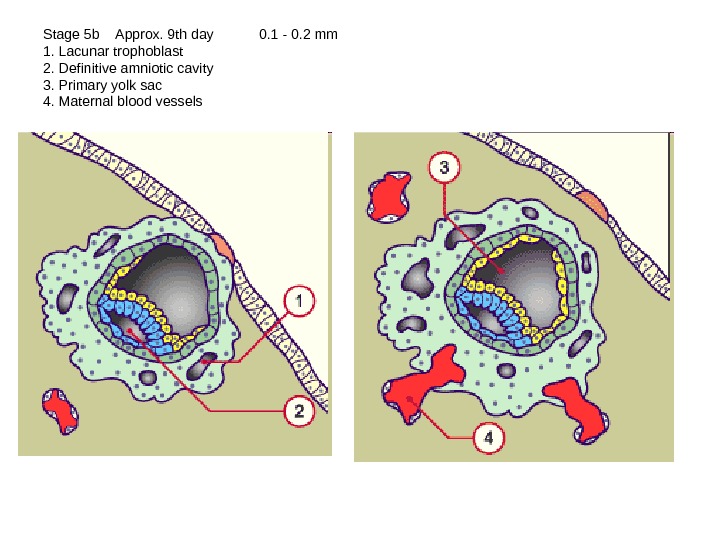
 Stage 5 b Approx. 9 th day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm 1. Lacunar trophoblast 2. Definitive amniotic cavity 3. Primary yolk sac 4. Maternal blood vessels
Stage 5 b Approx. 9 th day 0. 1 — 0. 2 mm 1. Lacunar trophoblast 2. Definitive amniotic cavity 3. Primary yolk sac 4. Maternal blood vessels
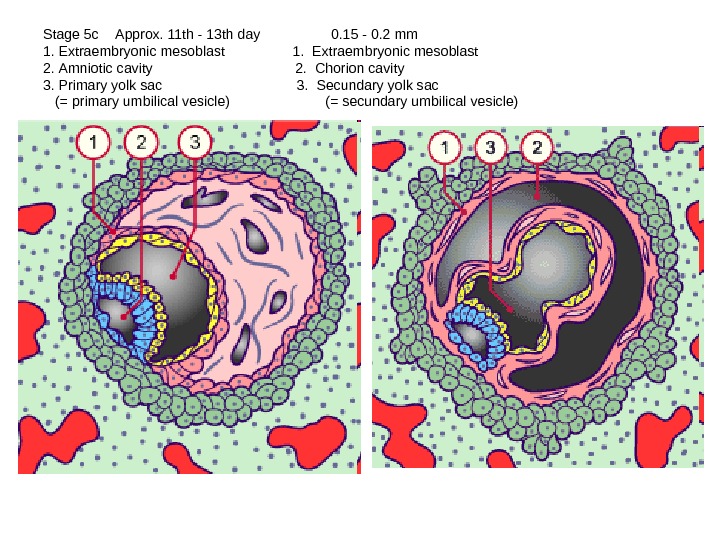
 Stage 5 c Approx. 11 th — 13 th day 0. 15 — 0. 2 mm 1. Extraembryonic mesoblast 2. Amniotic cavity 2. Chorion cavity 3. Primary yolk sac 3. Secundary yolk sac (= primary umbilical vesicle) (= secundary umbilical vesicle)
Stage 5 c Approx. 11 th — 13 th day 0. 15 — 0. 2 mm 1. Extraembryonic mesoblast 2. Amniotic cavity 2. Chorion cavity 3. Primary yolk sac 3. Secundary yolk sac (= primary umbilical vesicle) (= secundary umbilical vesicle)

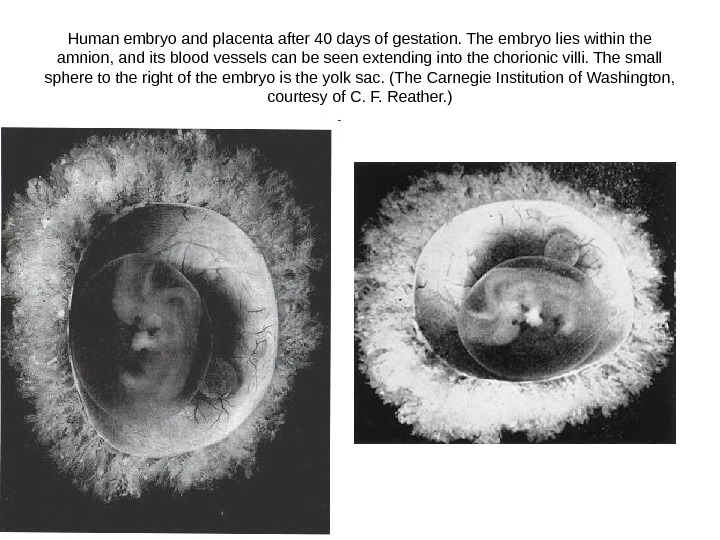
 Human embryo and placenta after 40 days of gestation. The embryo lies within the amnion, and its blood vessels can be seen extending into the chorionic villi. The small sphere to the right of the embryo is the yolk sac. (The Carnegie Institution of Washington, courtesy of C. F. Reather. )
Human embryo and placenta after 40 days of gestation. The embryo lies within the amnion, and its blood vessels can be seen extending into the chorionic villi. The small sphere to the right of the embryo is the yolk sac. (The Carnegie Institution of Washington, courtesy of C. F. Reather. )
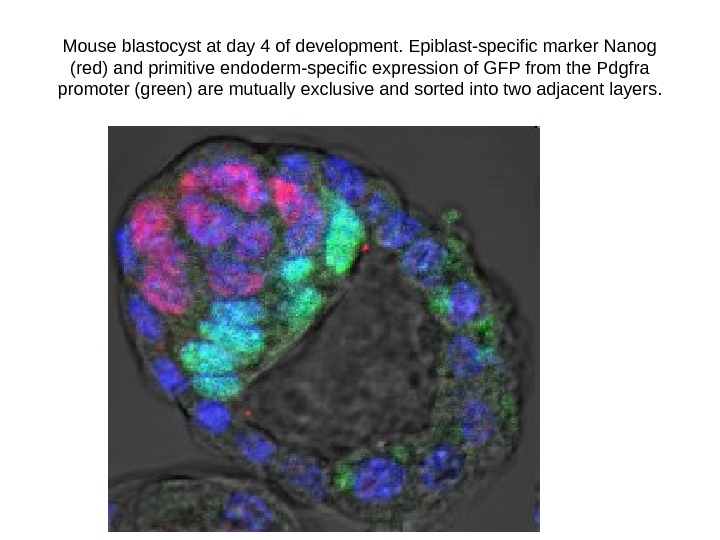
 Mouse blastocyst at day 4 of development. Epiblast-specific marker Nanog (red) and primitive endoderm-specific expression of GFP from the Pdgfra promoter (green) are mutually exclusive and sorted into two adjacent layers.
Mouse blastocyst at day 4 of development. Epiblast-specific marker Nanog (red) and primitive endoderm-specific expression of GFP from the Pdgfra promoter (green) are mutually exclusive and sorted into two adjacent layers.
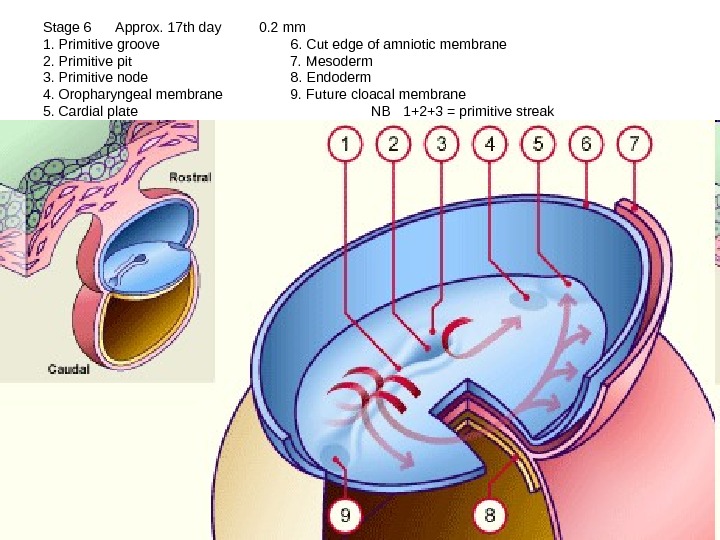
 Stage 6 Approx. 17 th day 0. 2 mm 1. Primitive groove 6. Cut edge of amniotic membrane 2. Primitive pit 7. Mesoderm 3. Primitive node 8. Endoderm 4. Oropharyngeal membrane 9. Future cloacal membrane 5. Cardial plate NB 1+2+3 = primitive streak
Stage 6 Approx. 17 th day 0. 2 mm 1. Primitive groove 6. Cut edge of amniotic membrane 2. Primitive pit 7. Mesoderm 3. Primitive node 8. Endoderm 4. Oropharyngeal membrane 9. Future cloacal membrane 5. Cardial plate NB 1+2+3 = primitive streak
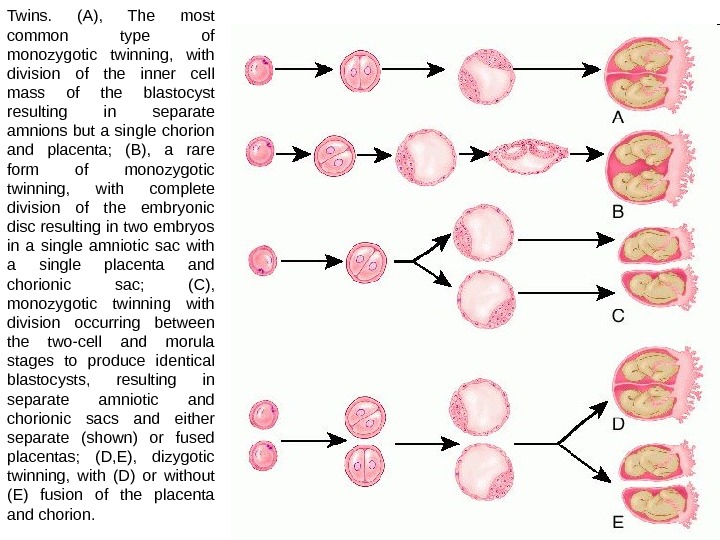
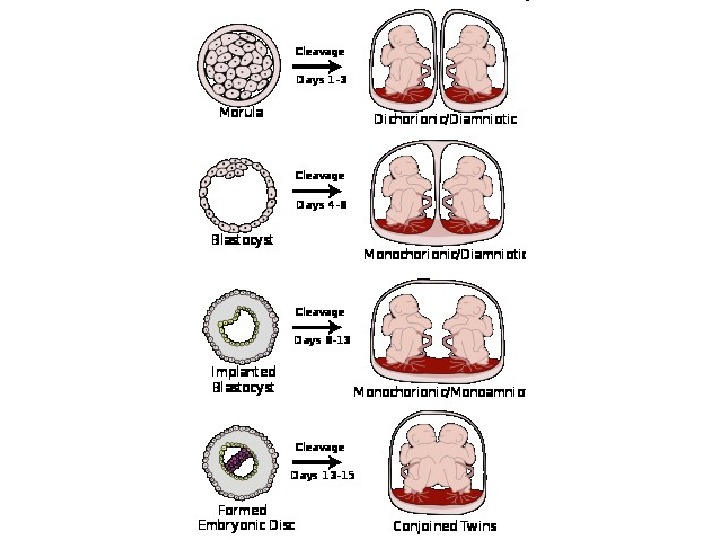
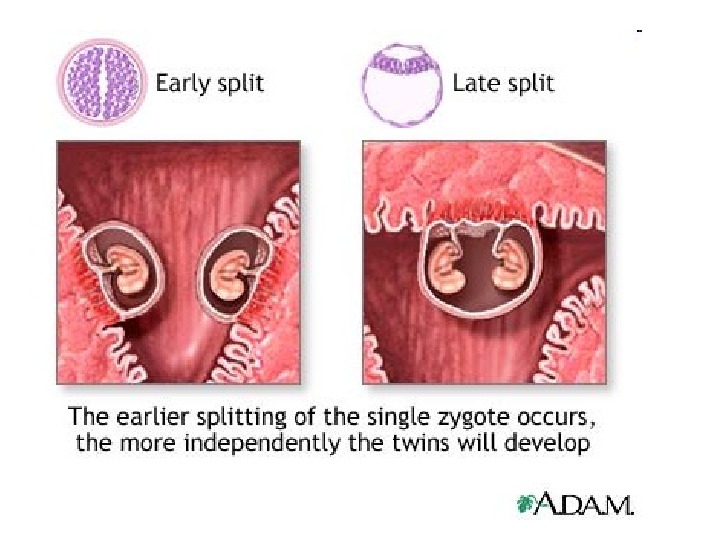
 Twins. (A), The most common type of monozygotic twinning, with division of the inner cell mass of the blastocyst resulting in separate amnions but a single chorion and placenta; (B), a rare form of monozygotic twinning, with complete division of the embryonic disc resulting in two embryos in a single amniotic sac with a single placenta and chorionic sac; (C), monozygotic twinning with division occurring between the two-cell and morula stages to produce identical blastocysts, resulting in separate amniotic and chorionic sacs and either separate (shown) or fused placentas; (D, E), dizygotic twinning, with (D) or without (E) fusion of the placenta and chorion.
Twins. (A), The most common type of monozygotic twinning, with division of the inner cell mass of the blastocyst resulting in separate amnions but a single chorion and placenta; (B), a rare form of monozygotic twinning, with complete division of the embryonic disc resulting in two embryos in a single amniotic sac with a single placenta and chorionic sac; (C), monozygotic twinning with division occurring between the two-cell and morula stages to produce identical blastocysts, resulting in separate amniotic and chorionic sacs and either separate (shown) or fused placentas; (D, E), dizygotic twinning, with (D) or without (E) fusion of the placenta and chorion.



