1939addbba38291b09596e5f652a5279.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn A Convex Method for Locating Regions of Interest with Multi-Instance Learning Yu-Feng Li 1, James T. Kwok 2, Ivor W. Tsang 3 and Zhi-Hua Zhou 1 1 LAMDA Group, Nanjing University, China 2 Hong Kong University of Science & Technology, Hong Kong 3 Nanyang Technological University, Singapore {liyf, zhouzh}@lamda. nju. edu. cn, jamesk@cse. ust. hk, Ivor. Tsang@ntu. edu. sg
http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn A Convex Method for Locating Regions of Interest with Multi-Instance Learning Yu-Feng Li 1, James T. Kwok 2, Ivor W. Tsang 3 and Zhi-Hua Zhou 1 1 LAMDA Group, Nanjing University, China 2 Hong Kong University of Science & Technology, Hong Kong 3 Nanyang Technological University, Singapore {liyf, zhouzh}@lamda. nju. edu. cn, jamesk@cse. ust. hk, Ivor. Tsang@ntu. edu. sg
![Multi-Instance Learning http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn MIL [Dietterich et al. , AIJ 97] Multi-Instance Learning http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn MIL [Dietterich et al. , AIJ 97]](https://present5.com/presentation/1939addbba38291b09596e5f652a5279/image-2.jpg) Multi-Instance Learning http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn MIL [Dietterich et al. , AIJ 97] attempts to learn from a training set consists of bags each containing many instances - A bag is positive if it contains at least one positive instances; otherwise negative. - The labels of training bags are known, however, the labels of instances in the bags are unknown. Traditional supervised learning Multi-instance learning In MIL, identifying positive instances is an important problem üunderstanding the relation between the bag and input patterns. Figure reprinted from [Zhi-Hua Zhou et al. , icml 09] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Multi-Instance Learning http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn MIL [Dietterich et al. , AIJ 97] attempts to learn from a training set consists of bags each containing many instances - A bag is positive if it contains at least one positive instances; otherwise negative. - The labels of training bags are known, however, the labels of instances in the bags are unknown. Traditional supervised learning Multi-instance learning In MIL, identifying positive instances is an important problem üunderstanding the relation between the bag and input patterns. Figure reprinted from [Zhi-Hua Zhou et al. , icml 09] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
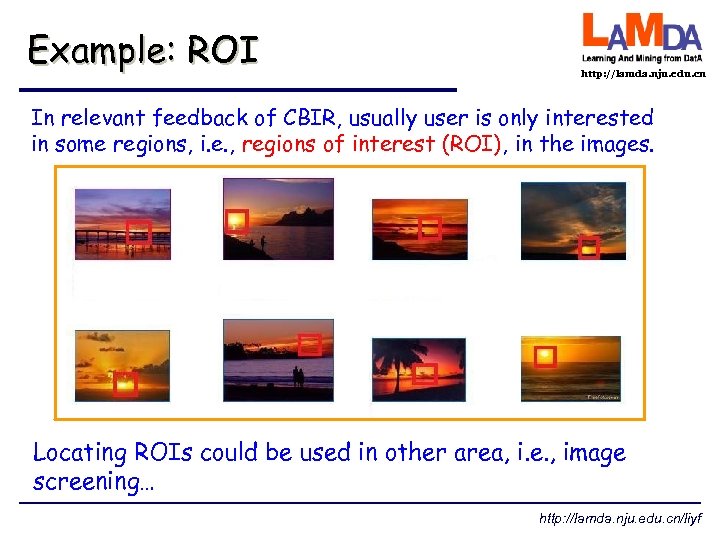 Example: ROI http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn In relevant feedback of CBIR, usually user is only interested in some regions, i. e. , regions of interest (ROI), in the images. Locating ROIs could be used in other area, i. e. , image screening… http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Example: ROI http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn In relevant feedback of CBIR, usually user is only interested in some regions, i. e. , regions of interest (ROI), in the images. Locating ROIs could be used in other area, i. e. , image screening… http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
 The Problem http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn How to develop an efficient and theoretical supported method for locating the ROIs? …This presentation http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
The Problem http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn How to develop an efficient and theoretical supported method for locating the ROIs? …This presentation http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
 Outline http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn p Introduction p Our Methods p Experiments p Conclusion http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Outline http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn p Introduction p Our Methods p Experiments p Conclusion http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
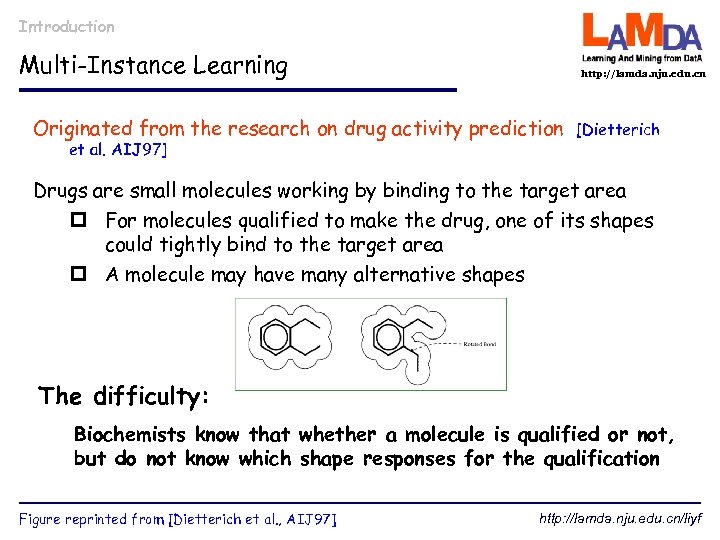 Introduction Multi-Instance Learning http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Originated from the research on drug activity prediction et al. AIJ 97] [Dietterich Drugs are small molecules working by binding to the target area p For molecules qualified to make the drug, one of its shapes could tightly bind to the target area p A molecule may have many alternative shapes The difficulty: Biochemists know that whether a molecule is qualified or not, but do not know which shape responses for the qualification Figure reprinted from [Dietterich et al. , AIJ 97] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Introduction Multi-Instance Learning http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Originated from the research on drug activity prediction et al. AIJ 97] [Dietterich Drugs are small molecules working by binding to the target area p For molecules qualified to make the drug, one of its shapes could tightly bind to the target area p A molecule may have many alternative shapes The difficulty: Biochemists know that whether a molecule is qualified or not, but do not know which shape responses for the qualification Figure reprinted from [Dietterich et al. , AIJ 97] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
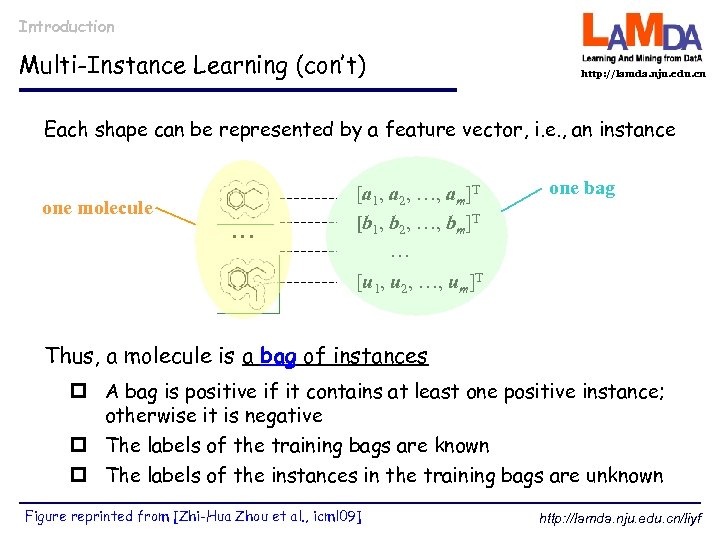 Introduction Multi-Instance Learning (con’t) http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Each shape can be represented by a feature vector, i. e. , an instance one molecule … [a 1, a 2, …, am]T [b 1, b 2, …, bm]T … one bag [u 1, u 2, …, um]T Thus, a molecule is a bag of instances p A bag is positive if it contains at least one positive instance; otherwise it is negative p The labels of the training bags are known p The labels of the instances in the training bags are unknown Figure reprinted from [Zhi-Hua Zhou et al. , icml 09] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Introduction Multi-Instance Learning (con’t) http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Each shape can be represented by a feature vector, i. e. , an instance one molecule … [a 1, a 2, …, am]T [b 1, b 2, …, bm]T … one bag [u 1, u 2, …, um]T Thus, a molecule is a bag of instances p A bag is positive if it contains at least one positive instance; otherwise it is negative p The labels of the training bags are known p The labels of the instances in the training bags are unknown Figure reprinted from [Zhi-Hua Zhou et al. , icml 09] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
 Introduction MIL for Image Analysis http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Various applications ü Image categorization [Maron & Ratan, ICML’ 98; Chen & Wang, JMLR 04; Chen et al. , PAMI 06] ü Image retrieval ü Face detection [Zhang et al. , ICDE’ 02; Zhou et al. , AJCAI’ 05] [Viola et al. , NIPS’ 05; Zhang & Viola, NIPS’ 07] ü Computer-aided medical diagnosis [Fung et al. , NIPS’ 06] ü … … http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Introduction MIL for Image Analysis http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Various applications ü Image categorization [Maron & Ratan, ICML’ 98; Chen & Wang, JMLR 04; Chen et al. , PAMI 06] ü Image retrieval ü Face detection [Zhang et al. , ICDE’ 02; Zhou et al. , AJCAI’ 05] [Viola et al. , NIPS’ 05; Zhang & Viola, NIPS’ 07] ü Computer-aided medical diagnosis [Fung et al. , NIPS’ 06] ü … … http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
 Introduction Related works for locating ROIs http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn • Diverse Density and its variants [Maron & Lozano-Pérez, NIPS 98] [Maron & Ratan, ICML 98] [Zhang & Goldman, NIPS 02] [Ray & Craven, icml 05] – Effective in locating the ROIs – Huge time cost, suffers from local minima • CKNN-ROI [zhou et al. , AJCAI 05] – A variation of Citation-k. NN [wang & zucker, icml 00] – Efficient, but based on heuristic • SVM based methods – Very few focus on locating the ROIs, except MI-SVM al. , nips 03] [Andrew et – Effect and efficient, but still suffers from local minima http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Introduction Related works for locating ROIs http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn • Diverse Density and its variants [Maron & Lozano-Pérez, NIPS 98] [Maron & Ratan, ICML 98] [Zhang & Goldman, NIPS 02] [Ray & Craven, icml 05] – Effective in locating the ROIs – Huge time cost, suffers from local minima • CKNN-ROI [zhou et al. , AJCAI 05] – A variation of Citation-k. NN [wang & zucker, icml 00] – Efficient, but based on heuristic • SVM based methods – Very few focus on locating the ROIs, except MI-SVM al. , nips 03] [Andrew et – Effect and efficient, but still suffers from local minima http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
![Introduction Multi-Instance SVM [Andrew et al, nips 03] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Main Introduction Multi-Instance SVM [Andrew et al, nips 03] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Main](https://present5.com/presentation/1939addbba38291b09596e5f652a5279/image-10.jpg) Introduction Multi-Instance SVM [Andrew et al, nips 03] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Main Idea : Large Margin Principle Positive bag Negative bag Key instance, i. e. , roi Optimal Hyperplane http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Introduction Multi-Instance SVM [Andrew et al, nips 03] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Main Idea : Large Margin Principle Positive bag Negative bag Key instance, i. e. , roi Optimal Hyperplane http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
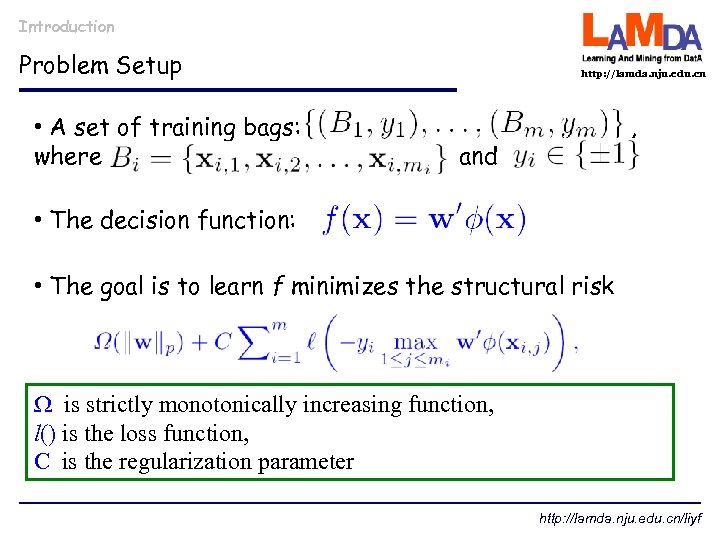 Introduction Problem Setup • A set of training bags: where http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn , and • The decision function: • The goal is to learn f minimizes the structural risk is strictly monotonically increasing function, l() is the loss function, C is the regularization parameter http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Introduction Problem Setup • A set of training bags: where http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn , and • The decision function: • The goal is to learn f minimizes the structural risk is strictly monotonically increasing function, l() is the loss function, C is the regularization parameter http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
 Introduction Problem Setup (cont. ) • consider http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn and square hinge loss • So, (1) becomes where This, however, is a non-convex problem because of the max operator and it may get stuck in local solution. In this paper, we propose a convex-relaxation method to solve such an non-convex problem. http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Introduction Problem Setup (cont. ) • consider http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn and square hinge loss • So, (1) becomes where This, however, is a non-convex problem because of the max operator and it may get stuck in local solution. In this paper, we propose a convex-relaxation method to solve such an non-convex problem. http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
 Outline http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn p Introduction p Our Methods p Experiments p Conclusion http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Outline http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn p Introduction p Our Methods p Experiments p Conclusion http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
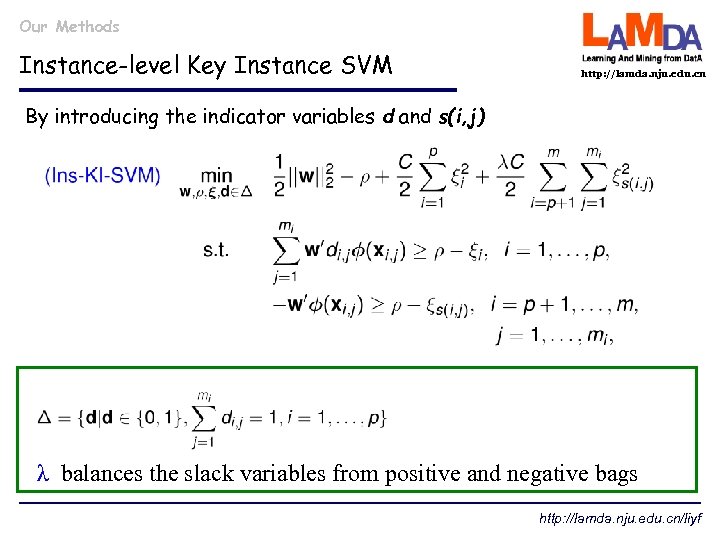 Our Methods Instance-level Key Instance SVM http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn By introducing the indicator variables d and s(i, j) λ balances the slack variables from positive and negative bags http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Our Methods Instance-level Key Instance SVM http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn By introducing the indicator variables d and s(i, j) λ balances the slack variables from positive and negative bags http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
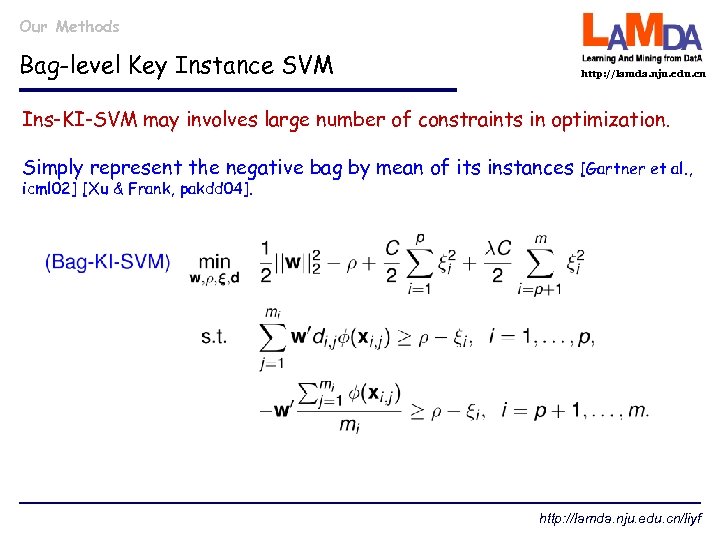 Our Methods Bag-level Key Instance SVM http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Ins-KI-SVM may involves large number of constraints in optimization. Simply represent the negative bag by mean of its instances icml 02] [Xu & Frank, pakdd 04]. [Gartner et al. , http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Our Methods Bag-level Key Instance SVM http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Ins-KI-SVM may involves large number of constraints in optimization. Simply represent the negative bag by mean of its instances icml 02] [Xu & Frank, pakdd 04]. [Gartner et al. , http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
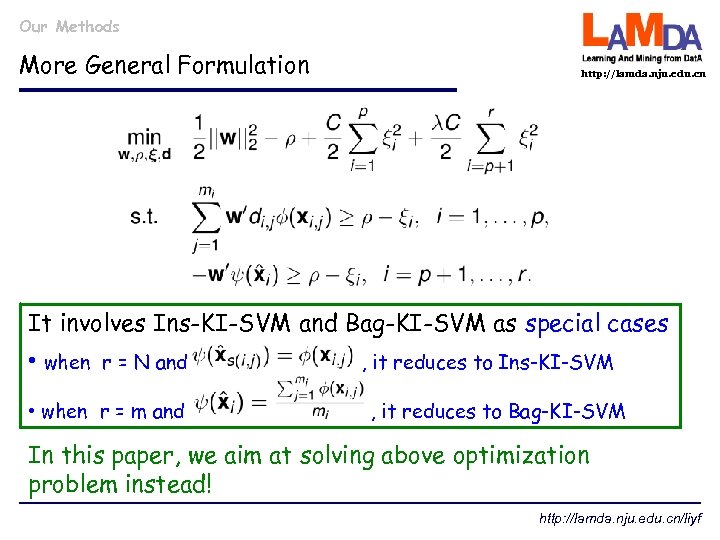 Our Methods More General Formulation http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn It involves Ins-KI-SVM and Bag-KI-SVM as special cases • when r = N and • when r = m and , , it reduces to Ins-KI-SVM , it reduces to Bag-KI-SVM In this paper, we aim at solving above optimization problem instead! http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Our Methods More General Formulation http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn It involves Ins-KI-SVM and Bag-KI-SVM as special cases • when r = N and • when r = m and , , it reduces to Ins-KI-SVM , it reduces to Bag-KI-SVM In this paper, we aim at solving above optimization problem instead! http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
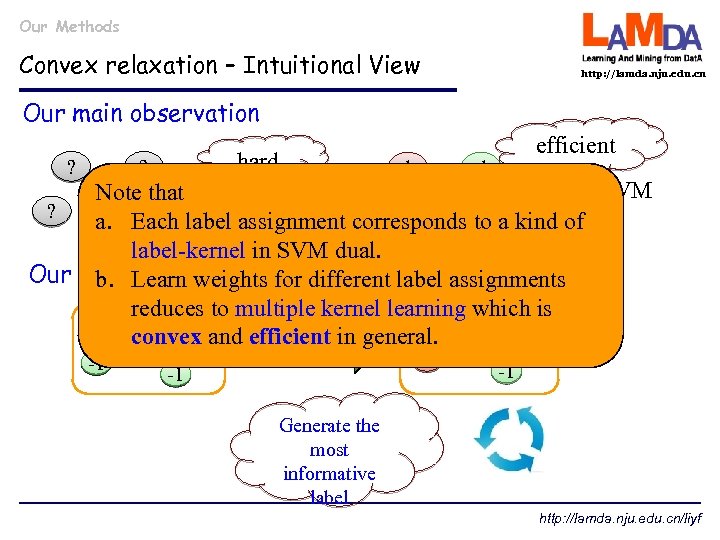 Our Methods Convex relaxation – Intuitional View http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Our main observation efficient hard 1 -1 -1 SVM Note that? SVM 1 ? a. Each label assignment corresponds to a kind of -1 ? label-kernel in SVM dual. Our simple strategy for different label assignments b. Learn weights reduces to multiple kernel learning which is SVM ? ? 1 convex and efficient in general. 1 …-1 1 -1 ? ? ? -1 1 ? -1 -1 Generate the most informative label http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Our Methods Convex relaxation – Intuitional View http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Our main observation efficient hard 1 -1 -1 SVM Note that? SVM 1 ? a. Each label assignment corresponds to a kind of -1 ? label-kernel in SVM dual. Our simple strategy for different label assignments b. Learn weights reduces to multiple kernel learning which is SVM ? ? 1 convex and efficient in general. 1 …-1 1 -1 ? ? ? -1 1 ? -1 -1 Generate the most informative label http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
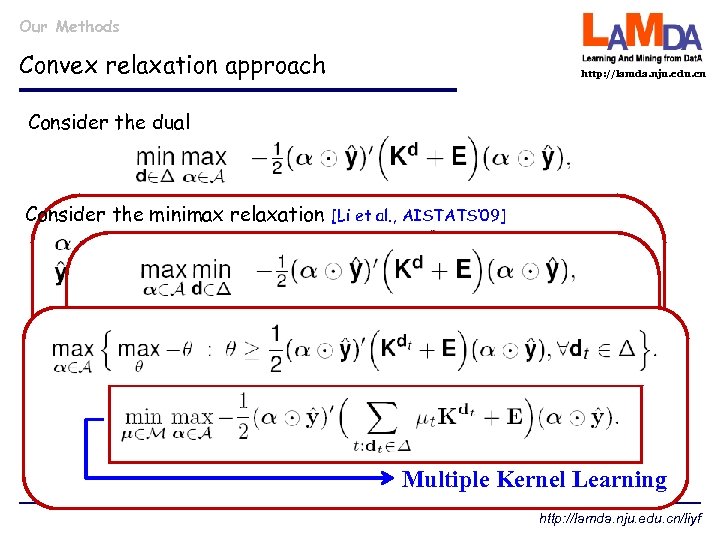 Our Methods Convex relaxation approach http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Consider the dual Consider the minimax relaxation [Li et al. , AISTATS’ 09] Multiple Kernel Learning http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Our Methods Convex relaxation approach http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Consider the dual Consider the minimax relaxation [Li et al. , AISTATS’ 09] Multiple Kernel Learning http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
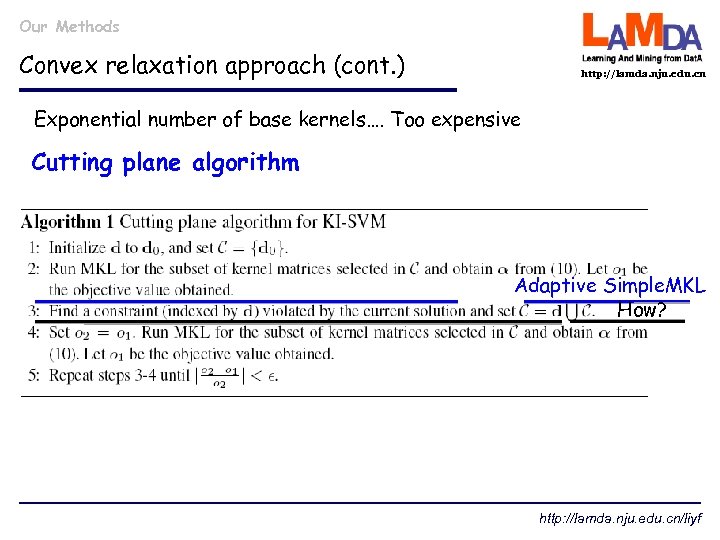 Our Methods Convex relaxation approach (cont. ) http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Exponential number of base kernels…. Too expensive Cutting plane algorithm Adaptive Simple. MKL How? http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Our Methods Convex relaxation approach (cont. ) http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Exponential number of base kernels…. Too expensive Cutting plane algorithm Adaptive Simple. MKL How? http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
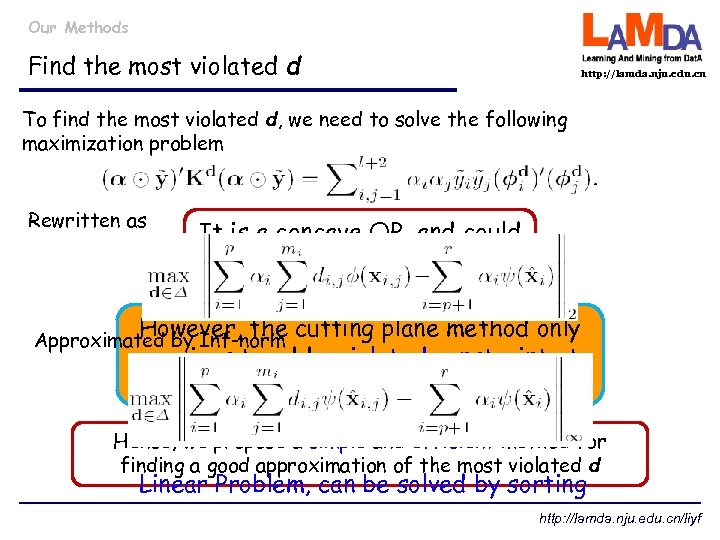 Our Methods Find the most violated d http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn To find the most violated d, we need to solve the following maximization problem Rewritten as It is a concave QP, and could not be solved efficiently… However, the cutting plane method only requires to add a violated constraint at each iteration Approximated by Inf-norm Hence, we propose a simple and efficient method for finding a good approximation of the most violated d Linear Problem, can be solved by sorting http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Our Methods Find the most violated d http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn To find the most violated d, we need to solve the following maximization problem Rewritten as It is a concave QP, and could not be solved efficiently… However, the cutting plane method only requires to add a violated constraint at each iteration Approximated by Inf-norm Hence, we propose a simple and efficient method for finding a good approximation of the most violated d Linear Problem, can be solved by sorting http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
 Outline http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn p Introduction p Our Methods p Experiments p Conclusion http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Outline http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn p Introduction p Our Methods p Experiments p Conclusion http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
 Experiments Two Kinds of Tasks http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn 1. CBIR image data 2. Benchmark data sets http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Experiments Two Kinds of Tasks http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn 1. CBIR image data 2. Benchmark data sets http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
![Experiments CBIR image data [zhou et al. , AJCAI 05] http: //lamda. nju. edu. Experiments CBIR image data [zhou et al. , AJCAI 05] http: //lamda. nju. edu.](https://present5.com/presentation/1939addbba38291b09596e5f652a5279/image-23.jpg) Experiments CBIR image data [zhou et al. , AJCAI 05] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Some statistics Image size: 160 × 160 Feature representation by using SBN [Maron & Ratan ICML 98] Evaluation: success rate, i. e. , the ratio of the number of successes divided by the total number of relevant images http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Experiments CBIR image data [zhou et al. , AJCAI 05] http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Some statistics Image size: 160 × 160 Feature representation by using SBN [Maron & Ratan ICML 98] Evaluation: success rate, i. e. , the ratio of the number of successes divided by the total number of relevant images http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
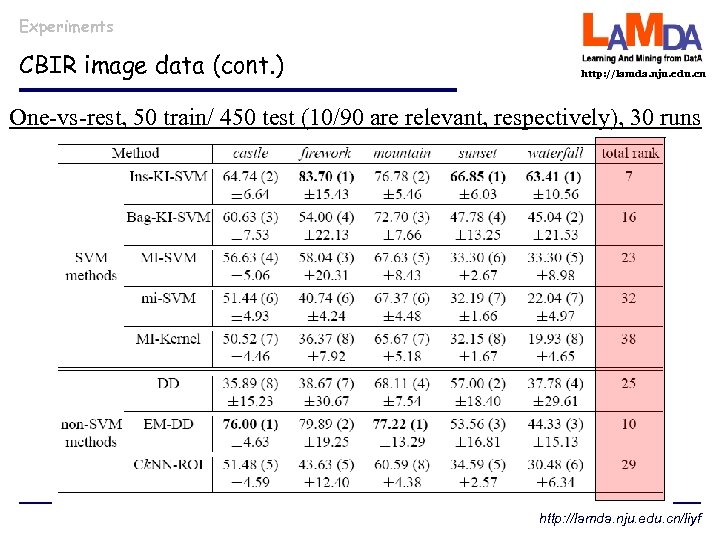 Experiments CBIR image data (cont. ) http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn One-vs-rest, 50 train/ 450 test (10/90 are relevant, respectively), 30 runs http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Experiments CBIR image data (cont. ) http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn One-vs-rest, 50 train/ 450 test (10/90 are relevant, respectively), 30 runs http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
 Experiments Some examples http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Experiments Some examples http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
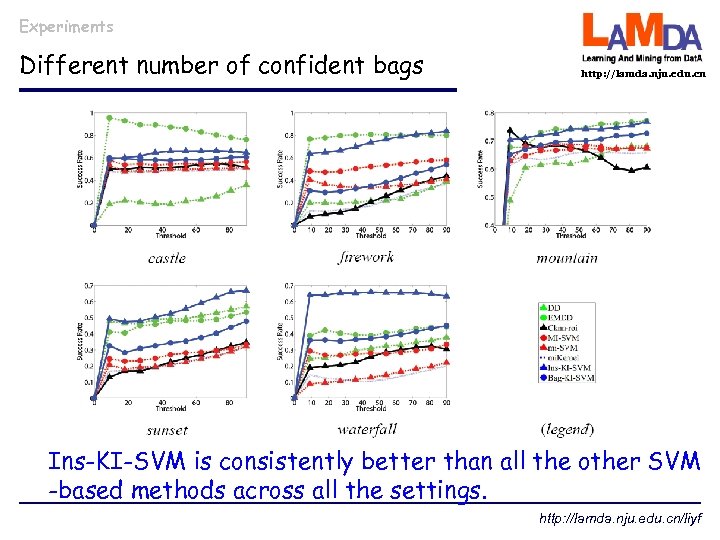 Experiments Different number of confident bags http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Ins-KI-SVM is consistently better than all the other SVM -based methods across all the settings. http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Experiments Different number of confident bags http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Ins-KI-SVM is consistently better than all the other SVM -based methods across all the settings. http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
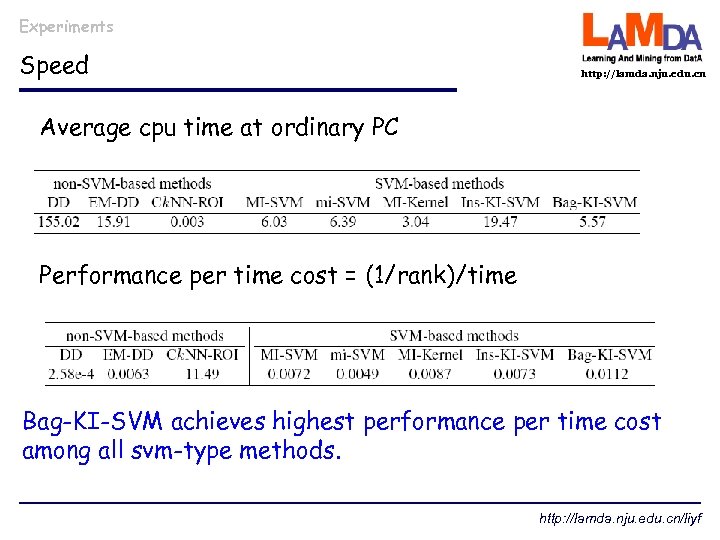 Experiments Speed http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Average cpu time at ordinary PC Performance per time cost = (1/rank)/time Bag-KI-SVM achieves highest performance per time cost among all svm-type methods. http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Experiments Speed http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Average cpu time at ordinary PC Performance per time cost = (1/rank)/time Bag-KI-SVM achieves highest performance per time cost among all svm-type methods. http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
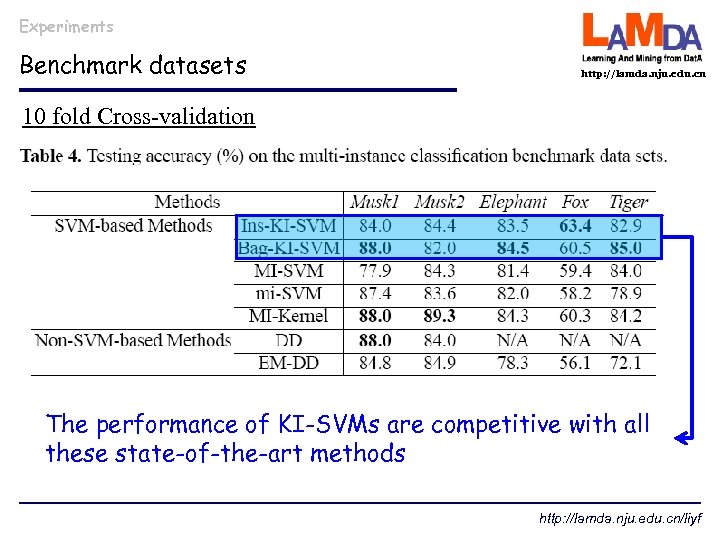 Experiments Benchmark datasets http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn 10 fold Cross-validation The performance of KI-SVMs are competitive with all these state-of-the-art methods http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Experiments Benchmark datasets http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn 10 fold Cross-validation The performance of KI-SVMs are competitive with all these state-of-the-art methods http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
 Conclusion http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Main contribution: ü A convex method for locating ROIs with multiinstance learning Future work: ü Locating multiple rois or roi groups Thanks! http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf
Conclusion http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn Main contribution: ü A convex method for locating ROIs with multiinstance learning Future work: ü Locating multiple rois or roi groups Thanks! http: //lamda. nju. edu. cn/liyf


