 HTML
HTML
 What is HTML? n n HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language An HTML file is a text file containing markup tags n n HTML files must have an htm or html file extension n The markup tags tell the Web browser how to display the page. html is preferred. htm is from very old operating systems that can only handle “ 8+3” names (eight characters, dot, three characters) HTML files can be created using a simple text editor n Formatted text, such as Microsoft Word’s. doc files, cannot be used in HTML files 2
What is HTML? n n HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language An HTML file is a text file containing markup tags n n HTML files must have an htm or html file extension n The markup tags tell the Web browser how to display the page. html is preferred. htm is from very old operating systems that can only handle “ 8+3” names (eight characters, dot, three characters) HTML files can be created using a simple text editor n Formatted text, such as Microsoft Word’s. doc files, cannot be used in HTML files 2
 HTML Tags n n n n HTML tags are used to mark up HTML elements HTML tags are surrounded by angle brackets, < and > Most HTML tags come in pairs, like and The tags in a pair are the start tag and the end tag The text between the start and end tags is the element content The tags act as containers (they contain the element content), and should be properly nested HTML tags are not case sensitive; means the same as 3
HTML Tags n n n n HTML tags are used to mark up HTML elements HTML tags are surrounded by angle brackets, < and > Most HTML tags come in pairs, like and The tags in a pair are the start tag and the end tag The text between the start and end tags is the element content The tags act as containers (they contain the element content), and should be properly nested HTML tags are not case sensitive; means the same as 3
Paragraph  Some simple tags n n n
Some simple tags n n n Preformatted text; preserve spaces and don’t wrap lines 4
 Structure of an HTML document n An HTML document is contained within tags n n n It consists of a
Structure of an HTML document n An HTML document is contained within tags n n n It consists of a
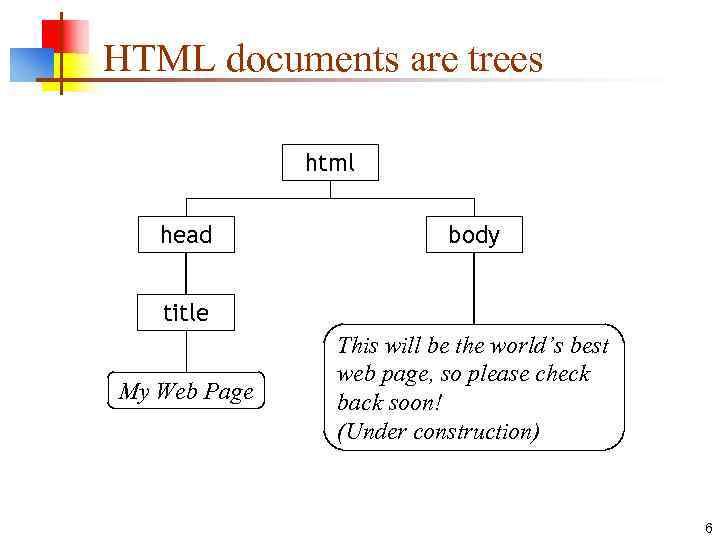 HTML documents are trees html head body title My Web Page This will be the world’s best web page, so please check back soon! (Under construction) 6
HTML documents are trees html head body title My Web Page This will be the world’s best web page, so please check back soon! (Under construction) 6
 Whitespace n n Whitespace is any non-printing characters (space, tab, newline, and a few others) HTML treats all whitespace as word separators, and automatically flows text from one line to the next, depending on the width of the page To group text into paragraphs, with a blank line between paragraphs, enclose each paragraph in
Whitespace n n Whitespace is any non-printing characters (space, tab, newline, and a few others) HTML treats all whitespace as word separators, and automatically flows text from one line to the next, depending on the width of the page To group text into paragraphs, with a blank line between paragraphs, enclose each paragraph in
and
tags To force HTML to use whitespace exactly as you wrote it, enclose your text inandtags (“pre” stands for “preformatted”) n n
also uses a monospace fontis handy for displaying programs 7
 Lists n n Two of the kinds of lists in HTML are ordered,
Lists n n Two of the kinds of lists in HTML are ordered,
- to
- to
- Sugar
- Chips
- Caffeine
- Chocolate
 Attributes n n Some markup tags may contain attributes of the form name="value" to provide additional information Example: To have an ordered list with letters A, B, C, . . . instead of numbers, use
Attributes n n Some markup tags may contain attributes of the form name="value" to provide additional information Example: To have an ordered list with letters A, B, C, . . . instead of numbers, use
- to
" src="https://present5.com/presentation/65685405_27027355/image-10.jpg" alt="Links n To link to another page, enclose the link text in " />
Links n To link to another page, enclose the link text in to n Example: I'm taking Dr. Dave's CIT 597 course this semester. n n To link to another part of the same page, n n n Link text will automatically be underlined and blue (or purple if recently visited) Insert a named anchor: References And link to it with: My references To link to a named anchor from a different page, use My references 10
 Images n n Images (pictures) are not part of an HTML page; the HTML just tells where to find the image To add an image to a page, use:
Images n n Images (pictures) are not part of an HTML page; the HTML just tells where to find the image To add an image to a page, use: n The src attribute is required; the others are optional n Attributes may be in any order n The URL may refer to any. gif, . jpg, or. png file n Other graphic formats are not recognized n The alt attribute provides a text representation of the image if the actual image is not downloaded n The height and width attributes, if included, will improve the display as the page is being downloaded n n If height or width is incorrect, the image will be distorted There is no end tag, because
is not a container 11
 Entities n n n Certain characters, such as <, have special meaning in HTML To put these characters into HTML without any special meaning, we have to use entities Here are some of the most common entities: n n n < represents < > represents > & represents & ' represents ' " represents " represents a “nonbreaking space”--one that HTML does not treat as whitespace 12
Entities n n n Certain characters, such as <, have special meaning in HTML To put these characters into HTML without any special meaning, we have to use entities Here are some of the most common entities: n n n < represents < > represents > & represents & ' represents ' " represents " represents a “nonbreaking space”--one that HTML does not treat as whitespace 12
 Forms n n
Forms n n
 Forms and Java. Script n The Java. Script language can be used to make pages that “do something” n n n You can use Java. Script to write complete programs, but. . . Usually you just use snippets of Java. Script here and there throughout your Web page Java. Script code snippets can be attached to various form elements n n For example, you might want to check that a zipcode field contains a 5 -digit integer before you send that information to the server Microsoft calls its version of Java. Script “active scripting” HTML forms can be used without Java. Script, and Java. Script can be used without HTML forms, but they work well together Java. Script for HTML is covered in a separate lecture 14
Forms and Java. Script n The Java. Script language can be used to make pages that “do something” n n n You can use Java. Script to write complete programs, but. . . Usually you just use snippets of Java. Script here and there throughout your Web page Java. Script code snippets can be attached to various form elements n n For example, you might want to check that a zipcode field contains a 5 -digit integer before you send that information to the server Microsoft calls its version of Java. Script “active scripting” HTML forms can be used without Java. Script, and Java. Script can be used without HTML forms, but they work well together Java. Script for HTML is covered in a separate lecture 14
 The
The
 The tag n Most, but not all, form elements use the input tag, with a type=". . . " argument to tell which kind of element it is n n type can be text, checkbox, radio, password, hidden, submit, reset, button, file, or image Other common input tag arguments include: n n name: the name of the element value: the “value” of the element; used in different ways for different values of type readonly: the value cannot be changed disabled: the user can’t do anything with this element Other arguments are defined for the input tag but have meaning only for certain values of type 16
The tag n Most, but not all, form elements use the input tag, with a type=". . . " argument to tell which kind of element it is n n type can be text, checkbox, radio, password, hidden, submit, reset, button, file, or image Other common input tag arguments include: n n name: the name of the element value: the “value” of the element; used in different ways for different values of type readonly: the value cannot be changed disabled: the user can’t do anything with this element Other arguments are defined for the input tag but have meaning only for certain values of type 16
A multi-line" src="https://present5.com/presentation/65685405_27027355/image-17.jpg" alt="Text input A text field: A multi-line" />
Text input A text field: A multi-line text field A password field: • Note that two of these use the input tag, but one uses textarea 17
A reset button:" src="https://present5.com/presentation/65685405_27027355/image-18.jpg" alt="Buttons n n n A submit button: A reset button:" />
Buttons n n n A submit button: A reset button: A plain button: n submit: send data reset: restore all form elements to their initial state n button: take some action as specified by Java. Script • Note that the type is input, not “button” n 18
n n type: "checkbox" name:" src="https://present5.com/presentation/65685405_27027355/image-19.jpg" alt="Checkboxes n A checkbox: n n type: "checkbox" name:" />
Checkboxes n A checkbox: n n type: "checkbox" name: used to reference this form element from Java. Script value: value to be returned when element is checked Note that there is no text associated with the checkbox— you have to supply text in the surrounding HTML 19
male male
Radio buttons: male female n If two or more radio buttons have the same name, the user can only select one of them at a time n n n This is how you make a radio button “group” If you ask for the value of that name, you will get the value specified for the selected radio button As with checkboxes, radio buttons do not contain any text 20
< -- right there, don't" src="https://present5.com/presentation/65685405_27027355/image-22.jpg" alt="Hidden fields n n < -- right there, don't" />
Hidden fields n n < -- right there, don't you see it? What good is this? n n n All input fields are sent back to the server, including hidden fields This is a way to include information that the user doesn’t need to see (or that you don’t want her to see) The value of a hidden field can be set programmatically (by Java. Script) before the form is submitted 22
Who are you?
23 The rest of HTML n HTML is a large markup language, with a lot of options n n If you aren’t already familiar with it, you should study one or more of the tutorials (there are many online) Your browser’s View -> Source command is a great way to see how things are done in HTML pages often contain Java. Script code There is no such “thing” as DHTML (Dynamic HTML) n DHTML is simply HTML with several other technologies mixed in, such as Java. Script 24
The rest of HTML n HTML is a large markup language, with a lot of options n n If you aren’t already familiar with it, you should study one or more of the tutorials (there are many online) Your browser’s View -> Source command is a great way to see how things are done in HTML pages often contain Java. Script code There is no such “thing” as DHTML (Dynamic HTML) n DHTML is simply HTML with several other technologies mixed in, such as Java. Script 24
 The End 25
The End 25


