d4cf76fe47464083454c6664445cf6db.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

HTM 3103 Consumer Behavior for Tourism & Hospitality Week 1 2013/2

Consumer Behavior is…? ‘The study of why people buy the products/services they do and how they make their decisions ‘(Horner & Swarbrooke, 1996)

CUSTOMER vs. CONSUMER How differences between these 2 terms? Customer vs. Consumer – Customer = someone who make a purchase ( ‘monetary exchange’ takes place) – Consumer = someone who consume the products or services In Tourism and Hospitality , Customer and Consumer may not be the same person e. g. When having a restaurants meals with family OR when travelling for a trip with family…. one person make a payment but the rest are just eat or travel with the one who make a payment…. . In this case, the person who pay = ? and other people whom not make a payment = ?

An ideal goals for any companies should be to survive and making enough profit Attracting or finding new customers may be an essential… however, it is more desirable and much less expensive to retain current customers. Therefore, loyal customers who will always come back are the necessity. HOW? the first stage is to make them feel satisfied! If we can meet or exceed what they expect , they will feel satisfied.


In order to meet or exceed the expectations of our consumers , - it is needed to understand the consumer’s needs, motives, and preferences ( that generate those expectations ) Although companies & organizations often consider their consumer’s wants & needs , however, they rely more on persuading them to buy products and services rather than putting the consumer at the core

Without knowing real wants and needs , how could the right marketing mixes can be designed and offered? For this reason, Understanding CB is crucial for marketing strategies and 4 Ps which is carried out by organizations to be effective

Understanding CB enabling companies to: 1) Forecast consumer behaviors in the future ( not to be over optimistic or underestimate the situations) 2) Correctly Persuade consumers 3) Developing new products/ services to suit their needs & wants Therefore, it could be said that, understanding CB is crucial for marketing strategies and 4 Ps to be carried out by organizations effectively

Overview of Tourism & Hospitality Tourism : A short term movement of people to places Hospitality: ‘The provision of food, drink, and accommodation away from home’ distancing from their normal place of residence to indulge in pleasurable activities, so as travelling for business purposes ( adapted from Horner & Swarbrooke, 1996) Word’s definitions: ‘The reception and entertainment of guests, visitors, or strangers with liberality and goodwill’ • The term ‘Hospitality’ comes from the word ‘ Hospice’ - In the old days, ‘Hospice’ is a term for the places of rest for travellers and pilgrims

Both hospitality and tourism are umbrella terms for a wide range of commercial activities. For example, the hospitality industry comprised of commercial organizations offering food, beverage and lodging consists of lodging, foodservices in restaurants, planes and cruise ships, clubs, cafeterias, etc. ; and recreational facilities ranging from casinos to resorts The tourism industry supports a traveler's need for transportation, food, lodging, amusement, and entertainment. It involves tour operators, rental cars, hotels, bars, gasoline stations, theme parks, and attractions. While sometimes both terms are used interchangeably, they are not quite synonymous. The tourism industry serves people away from home. Hospitality also includes businesses that serve people in their local town. Source: Zabel, D. (2003). The Best of the Web: Hospitality and Tourism Web Sites. Journal of Business & Finance Librarianship, 8(3/4), 167 -179.

Therefore, Hospitality Industry and Tourism industry are interrelated ◦ Without one of each, another cannot be survived

Top 10 destinations of the world, 2013 ( source : Tripadvisor) http: //www. tripadvisor. co. uk/Trav elers. Choice-Destinations-c. Top-g 1

What is a ‘Tourist’? Tourist could be defined as ‘A person whom travel out of his/her usual environments and stay there at least 24 hours but not more than 1 consecutive year for leisure, business, and other purposes’ (adapted from WTO) 2 forms of travel o Domestic travel ü Tourism activity of residents of one country traveling only within that country o International travel üTourism activity of people visiting destinations outside their own country's boundaries

Majority of tourists are domestic tourist However, In terms of spending, International tourists usually spend much higher and stay longer in general.
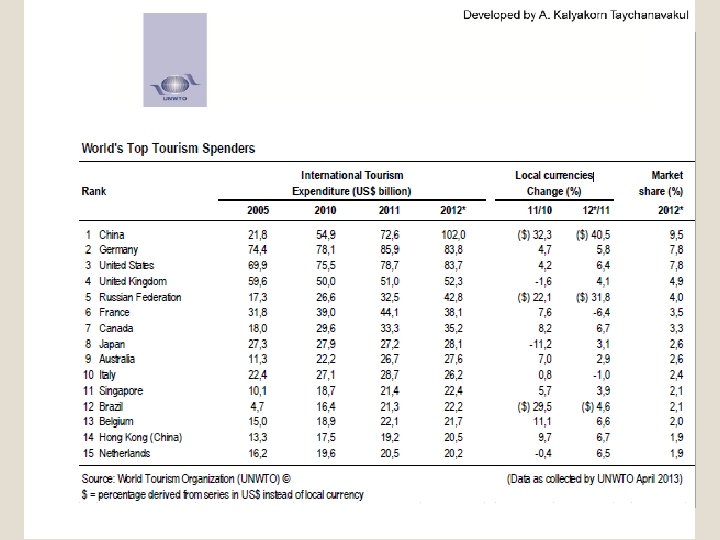

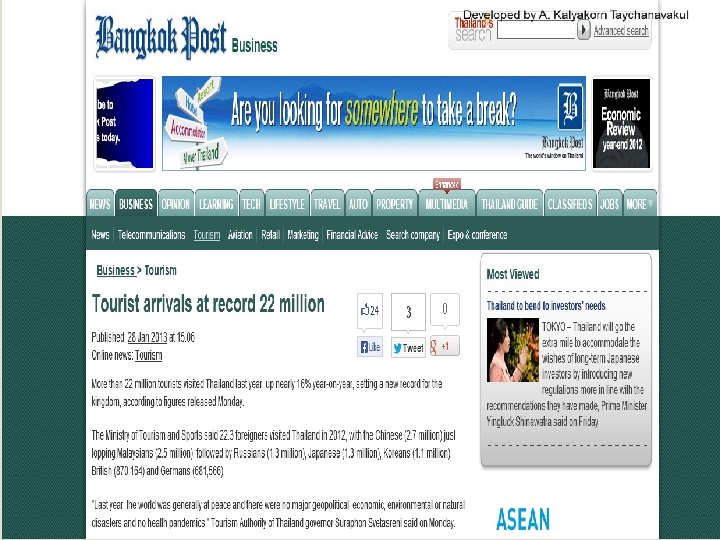
Overview of Tourism in Thailand The main marketing slogan for promoting Thailand internationally was "Amazing Thailand" The main marketing slogan for promoting Thai tourism to the Thai is ‘Unseen Thailand’ 4, 078 baht is the average spend per head per day of foreign visitors to Thailand in 2010. An average stay was 9. 12 days, resulting in 592. 79 billion baht gross foreign tourism revenue The average spend per head per day of domestic tourists was 1, 736 baht. They made 101 million domestic trips and stayed 2. 59 days on average in 2010, contributing 402 billion baht in domestic tourism revenue In 1997 – 7. 2 million visitors In 2012 - 22. 3 million visitors
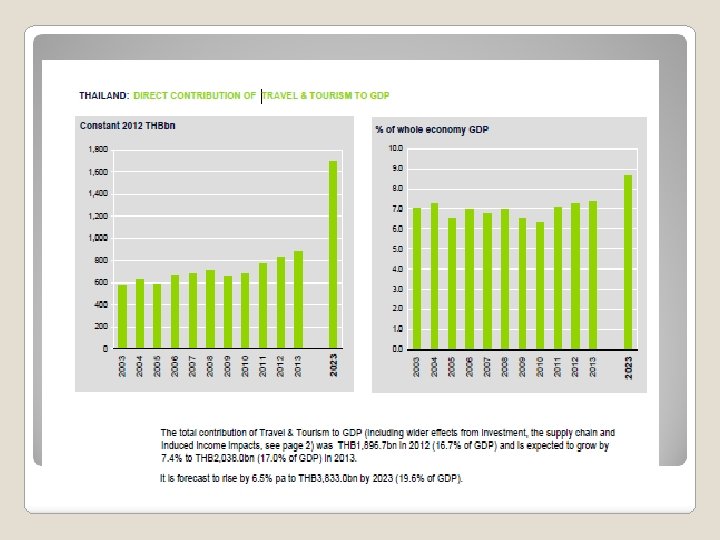

Forces driving growth in Tourism & Hospitality 1) The economy : Economic growth in developed economies during 80 s – 90 s rise in stock market + very low unemployment rate Higher disposable income = People have more leisure time , early retirement Due to higher income, more leisure time , early retirement … People want and can afford more goods & services For many people, consumption of services such as hospitality has become a major form of recreation

Forces driving growth in Tourism & Hospitality 2) The growth of the youth market Companies see the importance of increase in Children’s roles within their family decision-making ü ‘Pester –Power’-- the ability that children have to make their parents buy things, by repeatedly asking them until they agree üThese companies market directly to them E. g. fast-food restaurants Children meals = promotional gifts or premium is the key

Forces driving growth in Tourism & Hospitality 3) Technological change : the most important factor - Development in transportation links as a primary factor e. g. cars, motorways, jet travel - Development of Television and delivery technology Development in Computer : the most important factor , as it linked most of the other developments e. g. hotel reservation via internet<< websites are more attractive and user-friendly, e-payment, e-banking, kiosk-self check in at the airport ü

Forces driving growth in Tourism & Hospitality 4) Social changes üShifting from ‘production oriented ‘ to focus on consumption 5) The Mass media ü Consumption relies on the media to disseminate its messages and to mold its images associating goods and services in particular brand with meanings - Mc. Donald’s , KFC and Burger King spend billions of pounds every year …. breaking traditional eating cultures

Forces driving growth in Tourism & Hospitality 6) Facilitating means (for consumption) üThe growth of credit cards • • ü ‘While earlier generations saved until they could afford to buy in cash, today’s consumers operate on ‘ the buy now, pay later’ phenomena The growth of consumption has been facilitated by this together with mail order, television shopping channels, and internet (increasingly significantly) The growth of store cards

Forces driving growth in Tourism & Hospitality 7) Globalization ürefers to processes that increase world-wide exchanges of national and cultural resources. üAdvances in transportation and telecommunications infrastructure, including the rise of the Internet, are major factors in globalization üThese factors generate further interdependence of economic and cultural activities. ü‘All the world become more interconnected’ e. g. Mc. Donald’s : open up their first store in 1955 By 2000, over 30, 000 stores in more than 100 countries , including China, Russia, India, Israel etc. ,

The value of theory in researching consumer behavior in hospitality • Researchers have developed valuable models and frameworks to simplify complexes variables (factors) which affect hospitality consumption of consumers in regards to consumer preference, his/her choice, and purchase behavior

The development of consumer behavior research • The development of an academic theories within the area of consumption began within the marketing department in the business school of 1950 s • The main purpose for its development was to help marketing managers understand more on specific causes on consumer behavior , particularly, consumer buying decision • This focuses on what the consumer would do under certain specified conditions became known as ‘the positivist ‘ approach

• However, the ‘positivist’ approach is acceptable for a specific, particular sets of situation only, not for more complex situations where other factors come into play

• Therefore, the ‘positivist’ approach is acceptable for a specific, particular sets of situation only, not for more complex situations where other factors come into play • In sum , consumer behavior has to be understood within the context of human interaction, which is known as ‘ the interpretivist school of research, or ‘ the interpretivist approach’

Contemporary reviews of literature would indicate three broad approaches to consumption (cont. , ): The economic consumer 2) The behavioral consumer 3) The experiential consumer 1)

Contemporary reviews of literature would indicate three broad approaches to consumption: 1) The economic, positivist (rational) or cognitive consumer 2) The behavioral, interpretivist consumer (learning) 3) The experiential consumer (postmodern )

The Positivist/economic consumer The fundamental assumption here is… All human behavior has objectively identifiable causes and effects , all of which can be isolated, studied , and measured Consumers are logical and make rational decisions based on analysis of potential and losses Ø When faced with a problem or a decision, people process all the information relevant to it After processing this information, people make a rational decision about the best choice or decision to make Ø E. g. Marketers assumed that ; if best deals/ quality/fair prices are offered--> consumers will buy. Therefore, marketers view consumers as robot/automatons

Interpretivist/ Behavioral consumer Consumption is a learned response to stimuli, punishment or reward - People are not simply rational information processors or decision makers - Each consumers' experience is unique - 'experience' (past experience or experiences of others) lead to buying/consumption decision No emotions are involved in buying decision, what involves is ‘past experience’

Experiential Consumer Rejects a structural response to experience Buy because of emotions Consumption is beyond explanation or prediction Decision and learning are seen as modern constructs and are replaced by fantasy, hedonism, or symbolism

For example: ü To fulfill Fantasy needs : One day, an old woman is fantasizing about being a teen again. In order to suit her fantasy need, she goes to theme park where she always went when she was 17 ü To fulfill Hedonism (pleasure- seeking) needs: People whom love entertainment and want to hang out all night goes to Casino or entertainment venue that operates 24/7

ü To fulfill Symbolism need: üSome persons need something that symbolized or posed meaning within it to express themselves. üE. g. 1 The Fashionista chooses ‘Paris’ as a travel destination because the city is the icon of fashion. üE. g. 2 A high-income honeymoon couple choose Switzerland as a honeymoon destination because the country symbolizes romanticism. üE. g. 3 A person who pay very high price for the hotel room in which famous people used to stay in to acquire status
d4cf76fe47464083454c6664445cf6db.ppt