64b25405f3a37d380b2501711626f17b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 HR CHALLENGES IN HEALTHCARE DR NAGENDRA SWAMY PRESIDENT MANPAL HEALTH ENTERPRISES
HR CHALLENGES IN HEALTHCARE DR NAGENDRA SWAMY PRESIDENT MANPAL HEALTH ENTERPRISES
 CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIESHEALTHCARE IN INDIA • CHALLENGES • Affordability of Quality Healthcare. Currently ~3% of population are covered by Insurance/Third Party Funding • Accessibility to Quality Healthcare, especially in rural areas • Brain Drain: Availability of trained Doctors / Nurses / Paramedics • Intense Competition: Entry of private players, and MNCs • Govt. Spending(<1% of GDP): Low healthcare spending by the government and increased load towards the payment of Salaries (80%) • Ailing Government Infrastructure: healthcare with high maintenance costs OPPORTUNITIES • Recognition as an Industry: Transition from “healthcare” as a Social Responsibility to “healthcare” as a business. • Tap Domestic Potential: Increased Health Insurance Cover, improving Domestic affordability • Integrated Urban-Rural Presence: Tele. Medicine and integrated networks of care to help tap the large rural population • Medical Process Out-Sourcing: Clinical Research, Tele-Radiology, Medical Transcription etc. • Medical Tourism: International community recognizing India as a quality care provider
CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIESHEALTHCARE IN INDIA • CHALLENGES • Affordability of Quality Healthcare. Currently ~3% of population are covered by Insurance/Third Party Funding • Accessibility to Quality Healthcare, especially in rural areas • Brain Drain: Availability of trained Doctors / Nurses / Paramedics • Intense Competition: Entry of private players, and MNCs • Govt. Spending(<1% of GDP): Low healthcare spending by the government and increased load towards the payment of Salaries (80%) • Ailing Government Infrastructure: healthcare with high maintenance costs OPPORTUNITIES • Recognition as an Industry: Transition from “healthcare” as a Social Responsibility to “healthcare” as a business. • Tap Domestic Potential: Increased Health Insurance Cover, improving Domestic affordability • Integrated Urban-Rural Presence: Tele. Medicine and integrated networks of care to help tap the large rural population • Medical Process Out-Sourcing: Clinical Research, Tele-Radiology, Medical Transcription etc. • Medical Tourism: International community recognizing India as a quality care provider
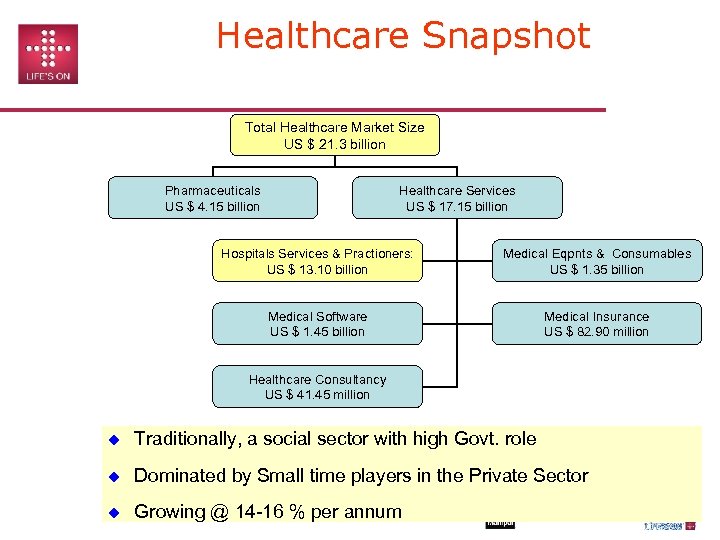 Healthcare Snapshot Total Healthcare Market Size US $ 21. 3 billion Pharmaceuticals US $ 4. 15 billion Healthcare Services US $ 17. 15 billion Hospitals Services & Practioners: US $ 13. 10 billion Medical Eqpnts & Consumables US $ 1. 35 billion Medical Software US $ 1. 45 billion Medical Insurance US $ 82. 90 million Healthcare Consultancy US $ 41. 45 million Traditionally, a social sector with high Govt. role Dominated by Small time players in the Private Sector Growing @ 14 -16 % per annum
Healthcare Snapshot Total Healthcare Market Size US $ 21. 3 billion Pharmaceuticals US $ 4. 15 billion Healthcare Services US $ 17. 15 billion Hospitals Services & Practioners: US $ 13. 10 billion Medical Eqpnts & Consumables US $ 1. 35 billion Medical Software US $ 1. 45 billion Medical Insurance US $ 82. 90 million Healthcare Consultancy US $ 41. 45 million Traditionally, a social sector with high Govt. role Dominated by Small time players in the Private Sector Growing @ 14 -16 % per annum
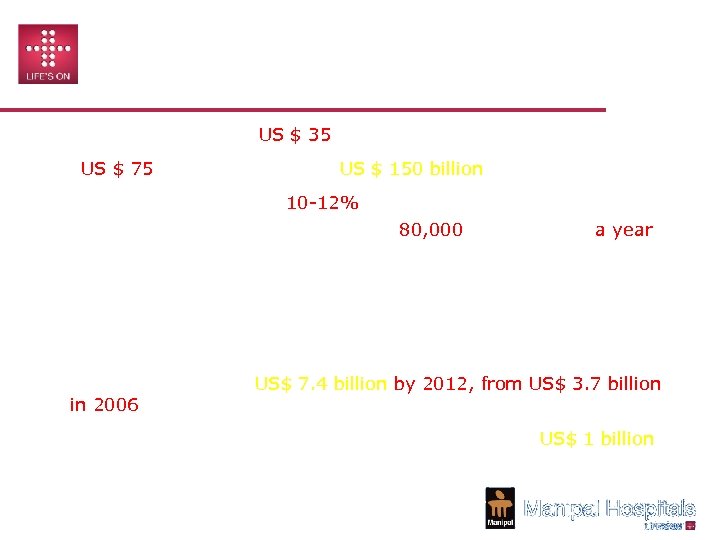 SUMMARY: INDIAN HEALTHCARE MARKET • Indian healthcare a US $ 35 billion industry, expected to reach US $ 75 billion by 2012 and US $ 150 billion by 2017. • • Will grow at the rate of 10 -12% over the next few years. • 4 MN PEOPLE ARE EMPLOYED, MAKING IT ONE OF THE LARGEST SERVICE SECTORS IN THE ECONOMY GOING UP TO 9 MN IN 2015 • Clinical trials have the potential to become a US$ 1 billion industry by 2010 and the health services outsourcing sector has the potential to grow to US$ 7. 4 billion by 2012, from US$ 3. 7 billion in 2006. • Private Equity funds are expected to invest at least US$ 1 billion in the healthcare in the next five years. WHO Recommends India to add 80, 000 hospital beds a year for the next 5 -8 years to meet the demands of healthcare sector
SUMMARY: INDIAN HEALTHCARE MARKET • Indian healthcare a US $ 35 billion industry, expected to reach US $ 75 billion by 2012 and US $ 150 billion by 2017. • • Will grow at the rate of 10 -12% over the next few years. • 4 MN PEOPLE ARE EMPLOYED, MAKING IT ONE OF THE LARGEST SERVICE SECTORS IN THE ECONOMY GOING UP TO 9 MN IN 2015 • Clinical trials have the potential to become a US$ 1 billion industry by 2010 and the health services outsourcing sector has the potential to grow to US$ 7. 4 billion by 2012, from US$ 3. 7 billion in 2006. • Private Equity funds are expected to invest at least US$ 1 billion in the healthcare in the next five years. WHO Recommends India to add 80, 000 hospital beds a year for the next 5 -8 years to meet the demands of healthcare sector
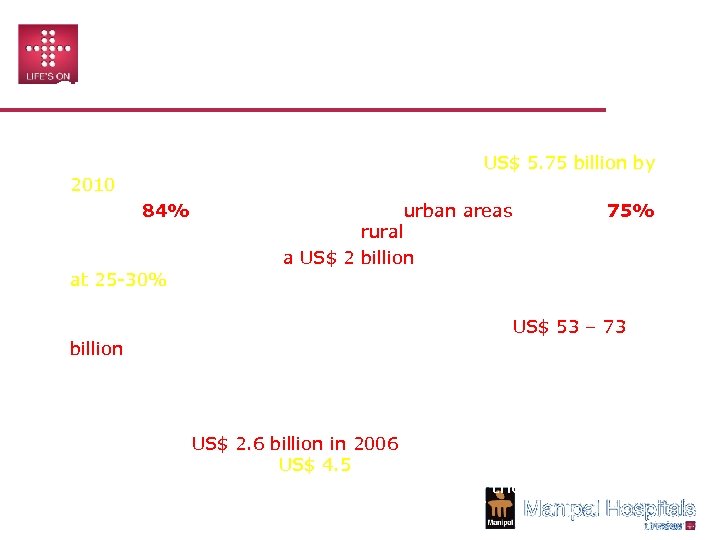 SUMMARY: INDIAN HEALTHCARE MARKET With only 10% of the Indian urban population covered by health insurance, the sector has growth potential of US$ 5. 75 billion by 2010 • In fact, 84% of hospital beds are in urban areas, whereas 75% of the population still resides in rural villages. • Medical tourism will be a US$ 2 billion industry by 2012, growing at 25 -30% annually. In 2007, India treated 450, 000 foreign patients and ranked 2 nd in medical tourism globally. • The total healthcare market with Pharma will be US$ 53 – 73 billion (6. 2 – 8. 5 per cent of the GDP) in the next 5 yrs • The Indian middle class estimated at 300 million has strong Purchase power. Ø According to Ernst & Young, the Indian medical equipment industry was US$ 2. 6 billion in 2006 and is growing at 15 per cent and expected to reach US$ 4. 5 billion by 2012. Only 35 per cent is accounted for by the domestic sector, while the rest is imported •
SUMMARY: INDIAN HEALTHCARE MARKET With only 10% of the Indian urban population covered by health insurance, the sector has growth potential of US$ 5. 75 billion by 2010 • In fact, 84% of hospital beds are in urban areas, whereas 75% of the population still resides in rural villages. • Medical tourism will be a US$ 2 billion industry by 2012, growing at 25 -30% annually. In 2007, India treated 450, 000 foreign patients and ranked 2 nd in medical tourism globally. • The total healthcare market with Pharma will be US$ 53 – 73 billion (6. 2 – 8. 5 per cent of the GDP) in the next 5 yrs • The Indian middle class estimated at 300 million has strong Purchase power. Ø According to Ernst & Young, the Indian medical equipment industry was US$ 2. 6 billion in 2006 and is growing at 15 per cent and expected to reach US$ 4. 5 billion by 2012. Only 35 per cent is accounted for by the domestic sector, while the rest is imported •
 Figures in Rs crore * Projected Source: Healthcare services in India: 2012, the path ahead. ASSOCHAM-YES Bank, 2009; Mc. Kinsey 2007
Figures in Rs crore * Projected Source: Healthcare services in India: 2012, the path ahead. ASSOCHAM-YES Bank, 2009; Mc. Kinsey 2007
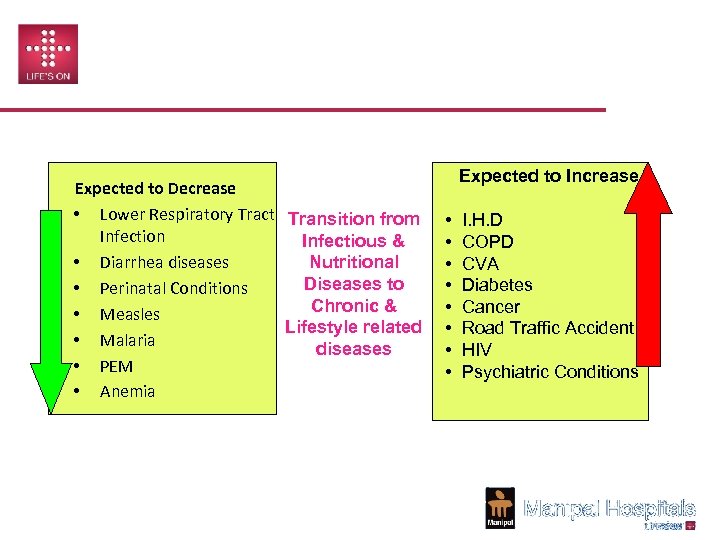 CHANGING – DISEASE PROFILE Expected to Decrease • Lower Respiratory Tract Transition from Infection Infectious & • Diarrhea diseases Nutritional Diseases to • Perinatal Conditions Chronic & • Measles Lifestyle related • Malaria diseases • PEM • Anemia Source: www. cia. gov - Fact Book UK /USA 2007 Expected to Increase • • I. H. D COPD CVA Diabetes Cancer Road Traffic Accident HIV Psychiatric Conditions
CHANGING – DISEASE PROFILE Expected to Decrease • Lower Respiratory Tract Transition from Infection Infectious & • Diarrhea diseases Nutritional Diseases to • Perinatal Conditions Chronic & • Measles Lifestyle related • Malaria diseases • PEM • Anemia Source: www. cia. gov - Fact Book UK /USA 2007 Expected to Increase • • I. H. D COPD CVA Diabetes Cancer Road Traffic Accident HIV Psychiatric Conditions
 CHANGING – DISEASE PROFILE USD 237 Billion in National Income for India Loss due to CNCD in 2015 Globally over 36 million will die of this epidemic- 80% death is lower and middle income groups- amounting to 44% of premature death world wide. This is double the number of deaths dues to infectious diseases. -WHO report -FOCUS ON PREVENTIVE TO CURATIVE: • Life style modification • Early Diagnosis • Ancillary & Auxiliary Therapies • Prophylaxis • Utilization of Genetic & Biotechnology
CHANGING – DISEASE PROFILE USD 237 Billion in National Income for India Loss due to CNCD in 2015 Globally over 36 million will die of this epidemic- 80% death is lower and middle income groups- amounting to 44% of premature death world wide. This is double the number of deaths dues to infectious diseases. -WHO report -FOCUS ON PREVENTIVE TO CURATIVE: • Life style modification • Early Diagnosis • Ancillary & Auxiliary Therapies • Prophylaxis • Utilization of Genetic & Biotechnology
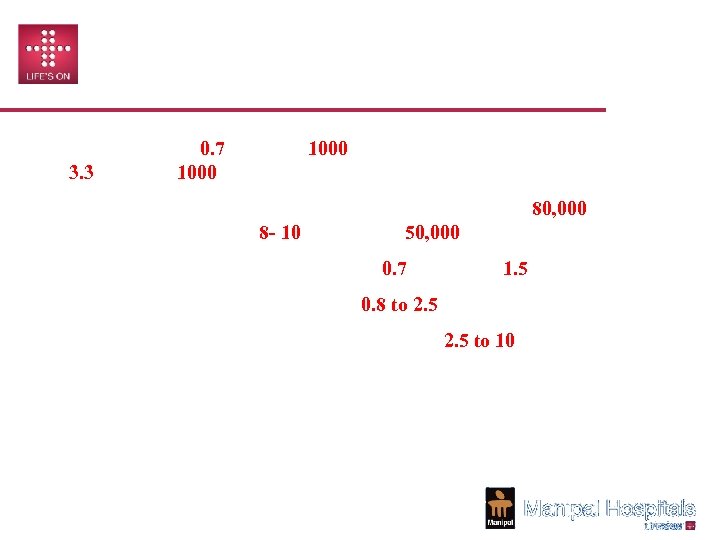 MARKET REALITY • India has only 0. 7 beds per 1000 people in contrast to the average of 3. 3 beds per 1000 in other countries. • The demand completely eclipses capacity. India needs 80, 000 beds each year for the next 8 - 10 years at Rs 50, 000 cr per year. • Double the number of doctors from 0. 7 million to 1. 5 million • Triple the number of nurses from 0. 8 to 2. 5 million. • Four times the number of paramedics from 2. 5 to 10 million. • 60% of the 15, 393 hospitals and 80% of all qualified doctors are in private sector
MARKET REALITY • India has only 0. 7 beds per 1000 people in contrast to the average of 3. 3 beds per 1000 in other countries. • The demand completely eclipses capacity. India needs 80, 000 beds each year for the next 8 - 10 years at Rs 50, 000 cr per year. • Double the number of doctors from 0. 7 million to 1. 5 million • Triple the number of nurses from 0. 8 to 2. 5 million. • Four times the number of paramedics from 2. 5 to 10 million. • 60% of the 15, 393 hospitals and 80% of all qualified doctors are in private sector
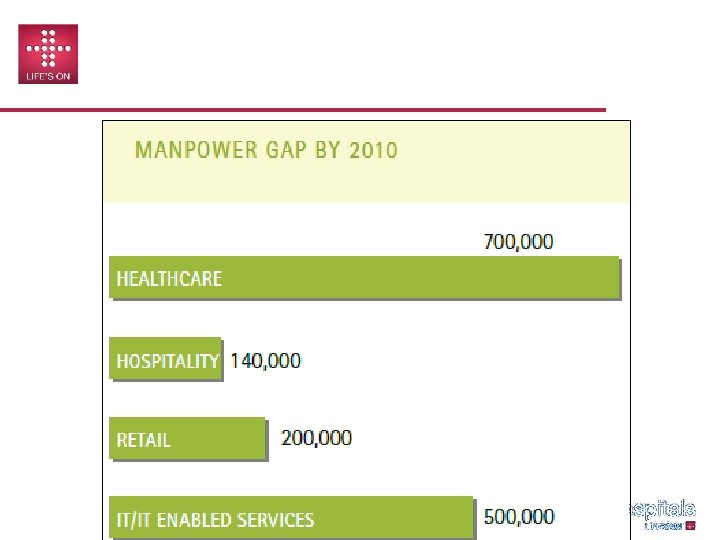 MANPOWER GAP
MANPOWER GAP
 HEALTHCARE TODAY Industrial Age Medicine to Information Age Medicine
HEALTHCARE TODAY Industrial Age Medicine to Information Age Medicine
 UNIQUE CHALLENGES OF HEALTHCARE ( HOSPITALS)
UNIQUE CHALLENGES OF HEALTHCARE ( HOSPITALS)
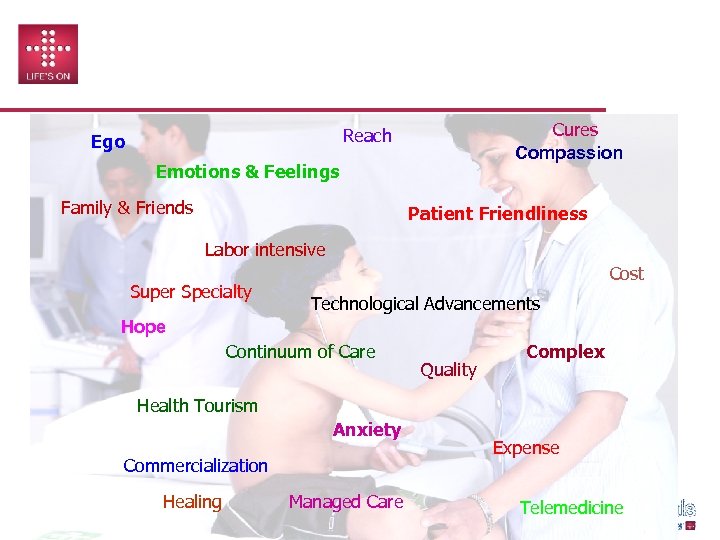 Healthcare Today Cures Compassion Reach Ego Emotions & Feelings Family & Friends Patient Friendliness Labor intensive Super Specialty Cost Technological Advancements Hope Continuum of Care Quality Complex Health Tourism Anxiety Commercialization Healing Managed Care Expense Telemedicine
Healthcare Today Cures Compassion Reach Ego Emotions & Feelings Family & Friends Patient Friendliness Labor intensive Super Specialty Cost Technological Advancements Hope Continuum of Care Quality Complex Health Tourism Anxiety Commercialization Healing Managed Care Expense Telemedicine
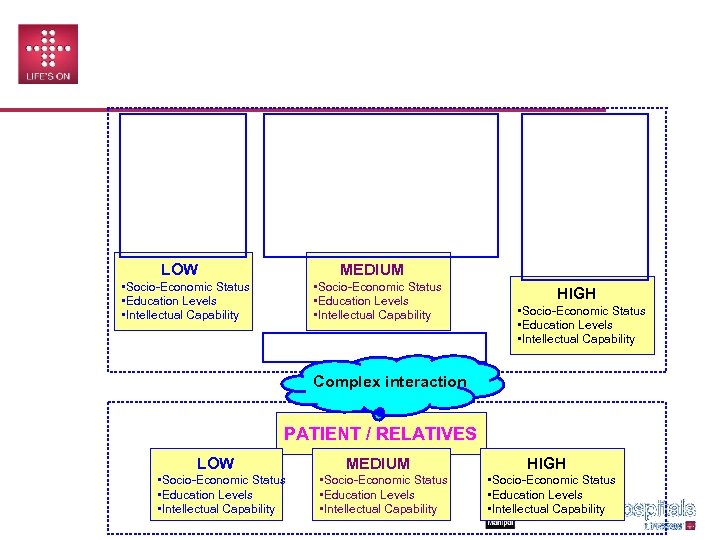 HEALTH CARE TODAY (Spectrum of Skill Sets Involved in Service Delivery) Attendants Counselors Receptionist Super Specialist Security Staff Technicians OT Staff Primary Physician Housekeeping OPD Secretaries Dietician Anesthetist Lift Operators Pt. Care Coordinators Admissions Radiologist Canteen Admin Manager Nursing Physiotherapist Room Boys Pharmacist Cashier Jr. Doctors LOW PRO MEDIUM • Socio-Economic Status • Education Levels • Intellectual Capability Healthcare Organization Sr. Management HIGH • Socio-Economic Status • Education Levels • Intellectual Capability Complex interaction PATIENT / RELATIVES LOW • Socio-Economic Status • Education Levels • Intellectual Capability MEDIUM • Socio-Economic Status • Education Levels • Intellectual Capability HIGH • Socio-Economic Status • Education Levels • Intellectual Capability
HEALTH CARE TODAY (Spectrum of Skill Sets Involved in Service Delivery) Attendants Counselors Receptionist Super Specialist Security Staff Technicians OT Staff Primary Physician Housekeeping OPD Secretaries Dietician Anesthetist Lift Operators Pt. Care Coordinators Admissions Radiologist Canteen Admin Manager Nursing Physiotherapist Room Boys Pharmacist Cashier Jr. Doctors LOW PRO MEDIUM • Socio-Economic Status • Education Levels • Intellectual Capability Healthcare Organization Sr. Management HIGH • Socio-Economic Status • Education Levels • Intellectual Capability Complex interaction PATIENT / RELATIVES LOW • Socio-Economic Status • Education Levels • Intellectual Capability MEDIUM • Socio-Economic Status • Education Levels • Intellectual Capability HIGH • Socio-Economic Status • Education Levels • Intellectual Capability
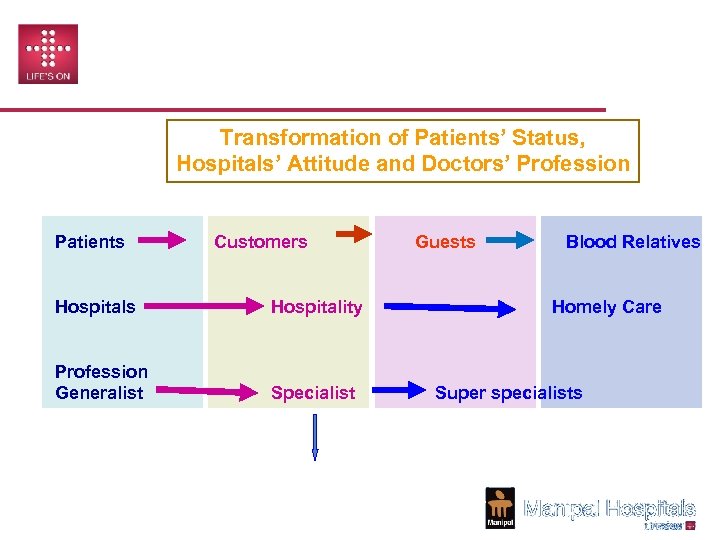 CHANGING TRENDS Transformation of Patients’ Status, Hospitals’ Attitude and Doctors’ Profession Patients Customers Hospitality Profession Generalist Specialist Sub Specialist Guests Blood Relatives Homely Care Super specialists
CHANGING TRENDS Transformation of Patients’ Status, Hospitals’ Attitude and Doctors’ Profession Patients Customers Hospitality Profession Generalist Specialist Sub Specialist Guests Blood Relatives Homely Care Super specialists
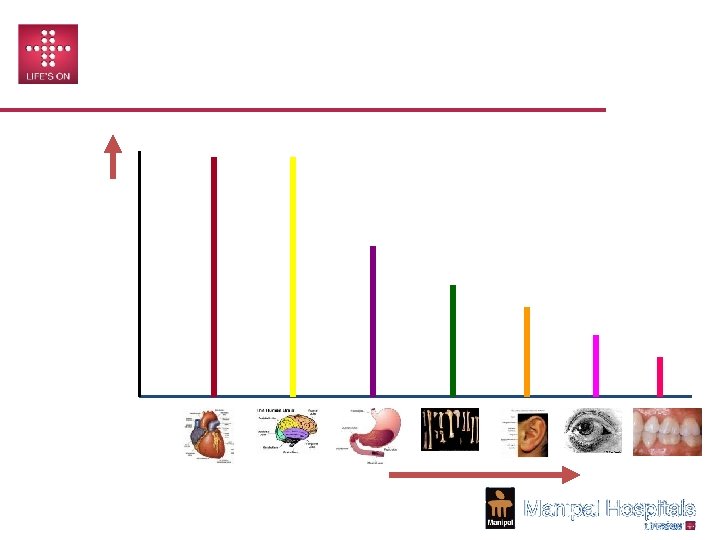 CHANGING EGO LEVELS Ego Levels of Health Professionals Ego Levels vs. Criticality of Organs Anatomy handled
CHANGING EGO LEVELS Ego Levels of Health Professionals Ego Levels vs. Criticality of Organs Anatomy handled
 CHANGING TRENDS-BEHAVIORAL • Doctors – – – • Patients – – • More Communicative, Humility Doctor–Patient Relationship Hospital-Doctor Relationships Encouraging Second Opinion Integrated approach- Respect all systems Patient Safety / Medical Errors Patient Education and Charter of Right More Demanding Nursing, Paramedical & Administrative Staff – – Equipped with Tech Tools Care Beyond Nursing
CHANGING TRENDS-BEHAVIORAL • Doctors – – – • Patients – – • More Communicative, Humility Doctor–Patient Relationship Hospital-Doctor Relationships Encouraging Second Opinion Integrated approach- Respect all systems Patient Safety / Medical Errors Patient Education and Charter of Right More Demanding Nursing, Paramedical & Administrative Staff – – Equipped with Tech Tools Care Beyond Nursing


 PREPARING THE 21 ST CENTURY GLOBAL HEALTHCARE WORKFORCE To meet the growing global demands of caring for the increasing numbers of patients with chronic conditions, we need to develop a new approach to training. A different set of competencies The five basic competencies Patient centred care Partnering Quality improvement Information and communication technology Public health perspective
PREPARING THE 21 ST CENTURY GLOBAL HEALTHCARE WORKFORCE To meet the growing global demands of caring for the increasing numbers of patients with chronic conditions, we need to develop a new approach to training. A different set of competencies The five basic competencies Patient centred care Partnering Quality improvement Information and communication technology Public health perspective
 QUALITY AND QUANTITY OF HUMAN RESOURCE TO ENHANCE • • • The Govt Policy must encourage PG Courses so that Hospitals meeting certain minimum criteria can offer these courses with relaxation in terms of restrictions. ( Fellowship / DNB) Qualitative Educational Institutions to be commenced. Continued medical education (CMEs) for medical, nursing and para-medical professionals, Mandatory credentialing of Medical Professionals while recruiting. The current compulsory rural stint for medical professionals. Huge Health cities/ medi-cities will induce employment and even provide human resources through education facilities. To have 2 nd line – Health Assistants to assist Nursing in non clinical work and Physician assistant programmes To give importance to Healthcare management programmes and make them popular career option. Staff for accreditation programmes- NABH / NABL/ JCI / ISO etc
QUALITY AND QUANTITY OF HUMAN RESOURCE TO ENHANCE • • • The Govt Policy must encourage PG Courses so that Hospitals meeting certain minimum criteria can offer these courses with relaxation in terms of restrictions. ( Fellowship / DNB) Qualitative Educational Institutions to be commenced. Continued medical education (CMEs) for medical, nursing and para-medical professionals, Mandatory credentialing of Medical Professionals while recruiting. The current compulsory rural stint for medical professionals. Huge Health cities/ medi-cities will induce employment and even provide human resources through education facilities. To have 2 nd line – Health Assistants to assist Nursing in non clinical work and Physician assistant programmes To give importance to Healthcare management programmes and make them popular career option. Staff for accreditation programmes- NABH / NABL/ JCI / ISO etc
 FEW DAUNTING CHALLENGES • ACUTE SHORTAGE OF QUALIFIED AND TRAINED STAFF • GETTING REPLACEMENT IN TIME – SERVICE GETS EFFECTED • UP COMING NEW FACILITIES TAKING AWAY TRAINED STAFF WHICH RESULTS IN REPLACEMENT BY UNTRAINED STAFF- GAPS IN SERVICE. • MOST OF THE CONSULTANTS ARE ON CONTRACT, NONEMPLOYEE STATUS WHICH MAKES IT DIFFICULT TO MANAGE THEM. • ABSENCE OF BENCH MARKING FOR STAFF : BED RATIO • QUALITY / PATEINET SAFETY / MEDICAL ERRORS – PROACTIVE REPORTING. • INCREASED MEDICO-LEGAL RISK, COMPLIANCE TO STATUTORY OBLIGATIONS. • IR ISSUES AND LABOR UNION ACTIVITIES. • VICARIOUS RESPONSIBILITY OF CONTRACT EMPLOYEES.
FEW DAUNTING CHALLENGES • ACUTE SHORTAGE OF QUALIFIED AND TRAINED STAFF • GETTING REPLACEMENT IN TIME – SERVICE GETS EFFECTED • UP COMING NEW FACILITIES TAKING AWAY TRAINED STAFF WHICH RESULTS IN REPLACEMENT BY UNTRAINED STAFF- GAPS IN SERVICE. • MOST OF THE CONSULTANTS ARE ON CONTRACT, NONEMPLOYEE STATUS WHICH MAKES IT DIFFICULT TO MANAGE THEM. • ABSENCE OF BENCH MARKING FOR STAFF : BED RATIO • QUALITY / PATEINET SAFETY / MEDICAL ERRORS – PROACTIVE REPORTING. • INCREASED MEDICO-LEGAL RISK, COMPLIANCE TO STATUTORY OBLIGATIONS. • IR ISSUES AND LABOR UNION ACTIVITIES. • VICARIOUS RESPONSIBILITY OF CONTRACT EMPLOYEES.
 THE REAL CHALLENGE IS ……. . ng gi M na a ity s D er iv
THE REAL CHALLENGE IS ……. . ng gi M na a ity s D er iv
 MHB – Awards and Accolades NABH
MHB – Awards and Accolades NABH
 Recognition & Awards 2010 2007 2008 2009 2006 2004 2005 Ranked 1 st in Bangalore for the 7 th consecutive year by ‘The Week’ among ‘India’s Best Hospitals’
Recognition & Awards 2010 2007 2008 2009 2006 2004 2005 Ranked 1 st in Bangalore for the 7 th consecutive year by ‘The Week’ among ‘India’s Best Hospitals’
 Sources: Mc. Kinsey report – Technopark- E&Y – KPMG- WHO-Cygnus -ASSOCHAM-YES Bank. MOH- CRIS-INFAC-IRDA-HOSMAC-NIPER- Netscribe-FIICI THANK YOU VERY MUCH FOR YOUR PATIENCE - Dr Nagendra Swamy
Sources: Mc. Kinsey report – Technopark- E&Y – KPMG- WHO-Cygnus -ASSOCHAM-YES Bank. MOH- CRIS-INFAC-IRDA-HOSMAC-NIPER- Netscribe-FIICI THANK YOU VERY MUCH FOR YOUR PATIENCE - Dr Nagendra Swamy


