Howard Gardner’s: Multiple Intelligences Presented to you by























































multiple_intelligence_theory.ppt
- Размер: 2.4 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 61
Описание презентации Howard Gardner’s: Multiple Intelligences Presented to you by по слайдам
 Howard Gardner’s: Multiple Intelligences Presented to you by the: Jr. Gifted and Talented Class 2003 —
Howard Gardner’s: Multiple Intelligences Presented to you by the: Jr. Gifted and Talented Class 2003 —
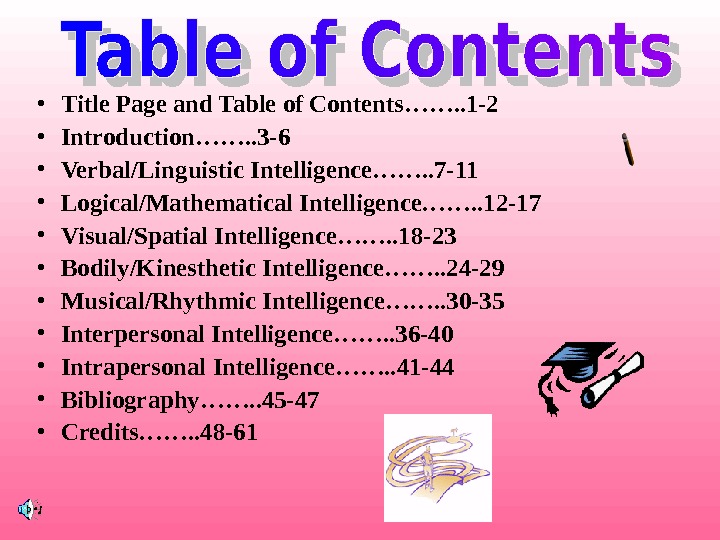
 • Title Page and Table of Contents……. . 1 -2 • Introduction……. . 3 -6 • Verbal/Linguistic Intelligence……. . 7 -11 • Logical/Mathematical Intelligence……. . 12 -17 • Visual/Spatial Intelligence……. . 18 -23 • Bodily/Kinesthetic Intelligence……. . 24 -29 • Musical/Rhythmic Intelligence……. . 30 -35 • Interpersonal Intelligence……. . 36 -40 • Intrapersonal Intelligence……. . 41 -44 • Bibliography……. . 45 -47 • Credits……. . 48 —
• Title Page and Table of Contents……. . 1 -2 • Introduction……. . 3 -6 • Verbal/Linguistic Intelligence……. . 7 -11 • Logical/Mathematical Intelligence……. . 12 -17 • Visual/Spatial Intelligence……. . 18 -23 • Bodily/Kinesthetic Intelligence……. . 24 -29 • Musical/Rhythmic Intelligence……. . 30 -35 • Interpersonal Intelligence……. . 36 -40 • Intrapersonal Intelligence……. . 41 -44 • Bibliography……. . 45 -47 • Credits……. . 48 —
 The theory of multiple intelligences is Howard Gardner’s theory that proposes that people are not born with all of the intelligence they will ever have. It says that intelligence can be learned throughout life. Also, it claims that everyone is intelligent in at least seven different ways and can develop each aspect of intelligence to an average level of competency. Intelligence, as defined by Gardner, is the ability to solve problems or fashion products that are valuable in one or more cultural settings.
The theory of multiple intelligences is Howard Gardner’s theory that proposes that people are not born with all of the intelligence they will ever have. It says that intelligence can be learned throughout life. Also, it claims that everyone is intelligent in at least seven different ways and can develop each aspect of intelligence to an average level of competency. Intelligence, as defined by Gardner, is the ability to solve problems or fashion products that are valuable in one or more cultural settings.
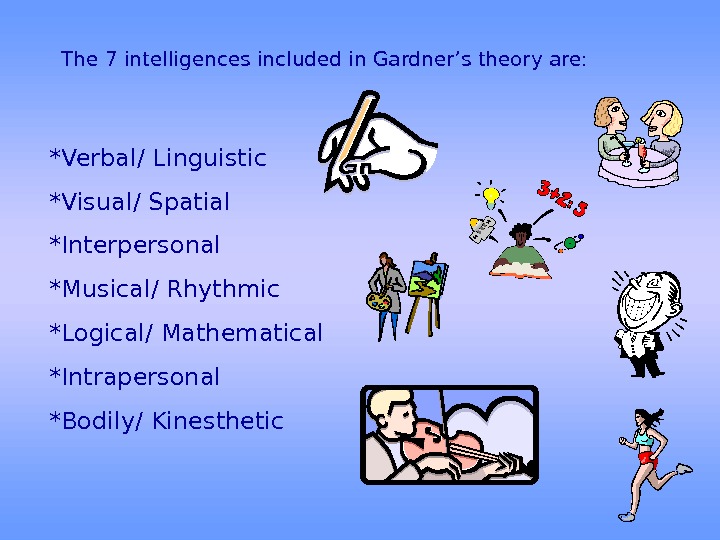
 The 7 intelligences included in Gardner’s theory are: *Verbal/ Linguistic *Visual/ Spatial *Interpersonal *Musical/ Rhythmic *Logical/ Mathematical *Intrapersonal *Bodily/ Kinesthetic
The 7 intelligences included in Gardner’s theory are: *Verbal/ Linguistic *Visual/ Spatial *Interpersonal *Musical/ Rhythmic *Logical/ Mathematical *Intrapersonal *Bodily/ Kinesthetic
 There are 8 Criteria for Defining Multiple Intelligences: *Each of the intelligences can potentially be isolated by brain damage. *Each of the intelligences exists in exceptional people (savants or prodigies). *Each of the intelligences has a process of developing during normal child development and has a peak end-state performance. *Each of the intelligences is evidenced in species other than human beings. *Each of the intelligences has been tested using various measures not necessarily associated with intelligence. *Each of the intelligences can work without the others being present. *Each of the intelligences has a set of identifiable operations. *Each of the intelligences can be symbolized or has its own unique symbol or set of symbols.
There are 8 Criteria for Defining Multiple Intelligences: *Each of the intelligences can potentially be isolated by brain damage. *Each of the intelligences exists in exceptional people (savants or prodigies). *Each of the intelligences has a process of developing during normal child development and has a peak end-state performance. *Each of the intelligences is evidenced in species other than human beings. *Each of the intelligences has been tested using various measures not necessarily associated with intelligence. *Each of the intelligences can work without the others being present. *Each of the intelligences has a set of identifiable operations. *Each of the intelligences can be symbolized or has its own unique symbol or set of symbols.
 The theory of multiple intelligences has encouraged the idea that a person is not born with all the intelligence they will ever possess. In the rest this slide show, each of the intelligences will be explained to give you a better understanding of Howard Gardner’s theory.
The theory of multiple intelligences has encouraged the idea that a person is not born with all the intelligence they will ever possess. In the rest this slide show, each of the intelligences will be explained to give you a better understanding of Howard Gardner’s theory.
 Linguistic Intelligence
Linguistic Intelligence
 ~*Linguistic Intelligence*~ Linguistic Intelligence ( Word Smart ) is the capacity to use language, your native language, and perhaps other languages, to express what’s on your mind and to understand other people. Gardner’s Definition: Criteria Used for Linguistic Intelligence • Can understand words and manipulate the structure of language • Has highly developed communication skills including writing, speaking, and story-telling • Knows and correctly uses rules of grammar • Enjoys reading, writing, and speaking • Has a large vocabulary This person learns best by: • Saying, hearing, and seeing words • Writing • Talking • Reading
~*Linguistic Intelligence*~ Linguistic Intelligence ( Word Smart ) is the capacity to use language, your native language, and perhaps other languages, to express what’s on your mind and to understand other people. Gardner’s Definition: Criteria Used for Linguistic Intelligence • Can understand words and manipulate the structure of language • Has highly developed communication skills including writing, speaking, and story-telling • Knows and correctly uses rules of grammar • Enjoys reading, writing, and speaking • Has a large vocabulary This person learns best by: • Saying, hearing, and seeing words • Writing • Talking • Reading
 • Author • Journalist • Poet • Playwright • Radio Announcer • Speech Pathologist (one who interprets) • Typist • Novelist • Comedian • Politician • Orator • Actor • Curator These people would do well in these careers.
• Author • Journalist • Poet • Playwright • Radio Announcer • Speech Pathologist (one who interprets) • Typist • Novelist • Comedian • Politician • Orator • Actor • Curator These people would do well in these careers.
 Famous People With Linguistic Intelligence • William Shakespeare • Edgar Allen Poe • Earnest Hemmingway • F. Scott Fitzgerald • Emily Dickinson • Agatha Christie • T. S. Eliot • Rudyard Kipling
Famous People With Linguistic Intelligence • William Shakespeare • Edgar Allen Poe • Earnest Hemmingway • F. Scott Fitzgerald • Emily Dickinson • Agatha Christie • T. S. Eliot • Rudyard Kipling
 Activities These People Would Enjoy • Book reporting • Telling jokes • Writing words • Reading • Journal writing • Speaking • Letter writing • Storytelling • Discussing • Creative writing • Debating • Persuading
Activities These People Would Enjoy • Book reporting • Telling jokes • Writing words • Reading • Journal writing • Speaking • Letter writing • Storytelling • Discussing • Creative writing • Debating • Persuading

 Logical-Mathematical Intelligence Logical-mathematical intelligence is the capacity to use numbers effectively and reason well. Someone who has this kind of intelligence is able to see cause and effect really well; also, they are able to identify a problem and solve it right there on the spot. People with this intelligence think by reasoning, and they love experimenting, questioning, figuring out logical puzzles, and calculating.
Logical-Mathematical Intelligence Logical-mathematical intelligence is the capacity to use numbers effectively and reason well. Someone who has this kind of intelligence is able to see cause and effect really well; also, they are able to identify a problem and solve it right there on the spot. People with this intelligence think by reasoning, and they love experimenting, questioning, figuring out logical puzzles, and calculating.
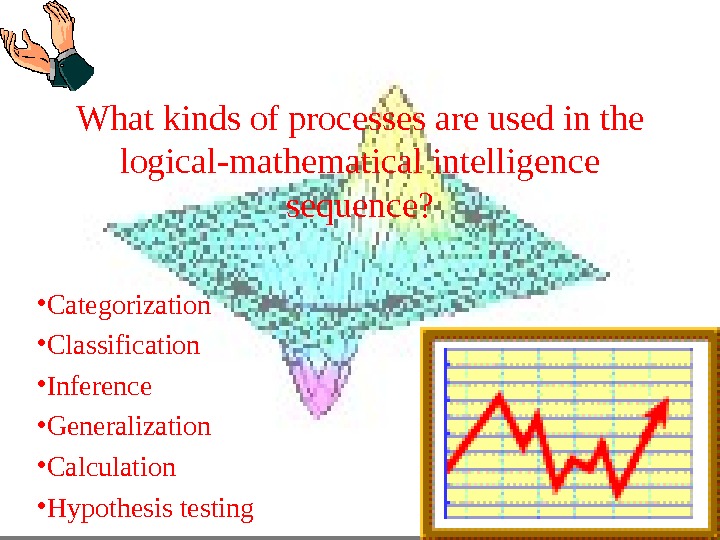
 What kinds of processes are used in the logical-mathematical intelligence sequence? • Categorization • Classification • Inference • Generalization • Calculation • Hypothesis testing
What kinds of processes are used in the logical-mathematical intelligence sequence? • Categorization • Classification • Inference • Generalization • Calculation • Hypothesis testing
 Careers • Accountant • Actuary • Auditor • Banker • Bookkeeper • Businessperson • Computer Analyst • Computer Programmer • Doctor • Economist • Legal Assistant • Mathematician • Purchasing Agent • Science Researcher • Science Teacher • Statistician • Technician • Underwriter
Careers • Accountant • Actuary • Auditor • Banker • Bookkeeper • Businessperson • Computer Analyst • Computer Programmer • Doctor • Economist • Legal Assistant • Mathematician • Purchasing Agent • Science Researcher • Science Teacher • Statistician • Technician • Underwriter
 Famous Mathematicians • Einstein • Pythagoras • Newton • Pascal • Archimedes • Euclid • Copernicus • Plato • Galileo • Aristotle
Famous Mathematicians • Einstein • Pythagoras • Newton • Pascal • Archimedes • Euclid • Copernicus • Plato • Galileo • Aristotle
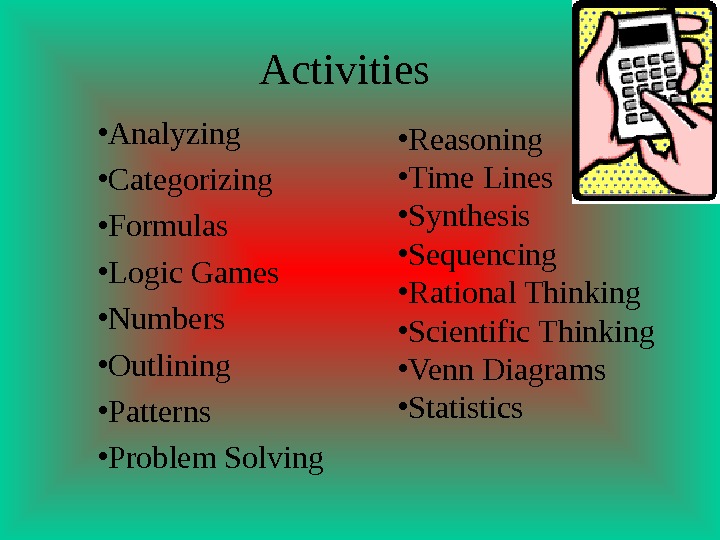
 • Analyzing • Categorizing • Formulas • Logic Games • Numbers • Outlining • Patterns • Problem Solving • Reasoning • Time Lines • Synthesis • Sequencing • Rational Thinking • Scientific Thinking • Venn Diagrams • Statistics. Activities
• Analyzing • Categorizing • Formulas • Logic Games • Numbers • Outlining • Patterns • Problem Solving • Reasoning • Time Lines • Synthesis • Sequencing • Rational Thinking • Scientific Thinking • Venn Diagrams • Statistics. Activities
 Spatial Intelligenc e
Spatial Intelligenc e
 What is spatial intelligence? Spatial intelligence is the brain’s ability to perceive and interpret visual stimuli. In other words, it’s how our minds process what we see. Although not very recognized, spatial intelligence is very important in the arts and in everyday life.
What is spatial intelligence? Spatial intelligence is the brain’s ability to perceive and interpret visual stimuli. In other words, it’s how our minds process what we see. Although not very recognized, spatial intelligence is very important in the arts and in everyday life.
 Why is spatial intelligence important? The way that we visually perceive and interpret the world around us is an important quality to have. In the arts, the ability to transfer a vision to a painting, sculpture, or film is a key quality. Careers such as architecture, require a person to transfer a vision of a structure into a blueprint. Spatial intelligence is even used by average people to remember small, but important facts; like how to travel from your school to your house. Everyone uses spatial intelligence in everyday life.
Why is spatial intelligence important? The way that we visually perceive and interpret the world around us is an important quality to have. In the arts, the ability to transfer a vision to a painting, sculpture, or film is a key quality. Careers such as architecture, require a person to transfer a vision of a structure into a blueprint. Spatial intelligence is even used by average people to remember small, but important facts; like how to travel from your school to your house. Everyone uses spatial intelligence in everyday life.
 Possible Careers • Advertising Agent • Architect • Cartographer(Map Maker) • Drafter • Engineer • Fine Artist • Graphic Designer • Fashion Designer • Interior Designer • Inventor • Painter • Photographer • Pilot • Sculptor • Surveyor • Urban Planner
Possible Careers • Advertising Agent • Architect • Cartographer(Map Maker) • Drafter • Engineer • Fine Artist • Graphic Designer • Fashion Designer • Interior Designer • Inventor • Painter • Photographer • Pilot • Sculptor • Surveyor • Urban Planner
 Famous People With High Spatial Intelligence • Leonardo Da Vinci • Pablo Picasso • Spike Lee • Vincent Van Gogh • Frank Lloyd Wright (architect) • Steven Spielberg • Ansel Adams (photographer) • Amelia Earhart • Auguste Rodin (sculptor) • Robert Fulton (inventor) • Michelangelo
Famous People With High Spatial Intelligence • Leonardo Da Vinci • Pablo Picasso • Spike Lee • Vincent Van Gogh • Frank Lloyd Wright (architect) • Steven Spielberg • Ansel Adams (photographer) • Amelia Earhart • Auguste Rodin (sculptor) • Robert Fulton (inventor) • Michelangelo
 Lesson planning activities for spatial intelligence • Brochures • Collages • Designs • Drawings • Flow Charts • Mapping • Molding Clay • Patterns • Painting • Photography • Posters • Pretending • Sculpting • Visualization • Idea Sketching • Labeling
Lesson planning activities for spatial intelligence • Brochures • Collages • Designs • Drawings • Flow Charts • Mapping • Molding Clay • Patterns • Painting • Photography • Posters • Pretending • Sculpting • Visualization • Idea Sketching • Labeling

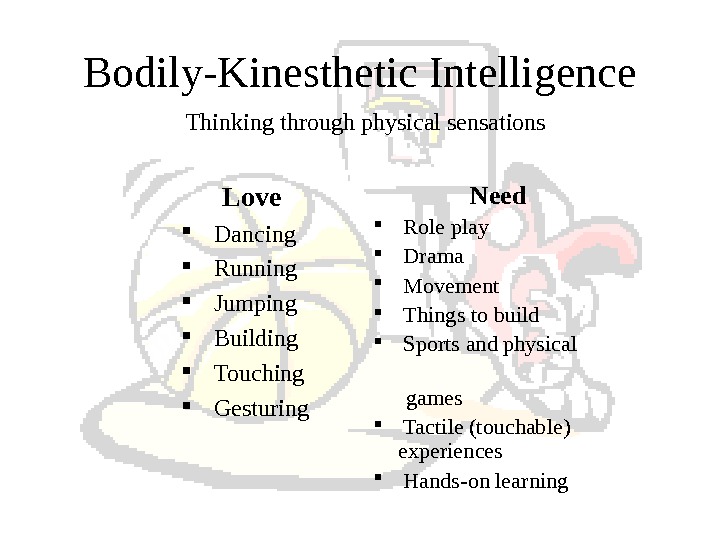
 What is Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence? It is expertise in using one’s whole body to express ideas and feelings. Examples: acting, dancing, sports, and using body language It is the ability to use one’s hands to produce or transform things. Examples: sculpting clay and hands-on learning
What is Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence? It is expertise in using one’s whole body to express ideas and feelings. Examples: acting, dancing, sports, and using body language It is the ability to use one’s hands to produce or transform things. Examples: sculpting clay and hands-on learning
 Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence Love Dancing Running Jumping Building Touching Gesturing Need Role play Drama Movement Things to build Sports and physical games Tactile (touchable) experiences Hands-on learning. Thinking through physical sensations
Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence Love Dancing Running Jumping Building Touching Gesturing Need Role play Drama Movement Things to build Sports and physical games Tactile (touchable) experiences Hands-on learning. Thinking through physical sensations
 Other Activities that Would be Enjoyed • Acting • Charades • Collections • Demonstrations • Experiments • Field Trips • Gymnastics • Impersonations • Inventing • Martial Arts • Miming • Puppetry • Visiting • Exercise
Other Activities that Would be Enjoyed • Acting • Charades • Collections • Demonstrations • Experiments • Field Trips • Gymnastics • Impersonations • Inventing • Martial Arts • Miming • Puppetry • Visiting • Exercise
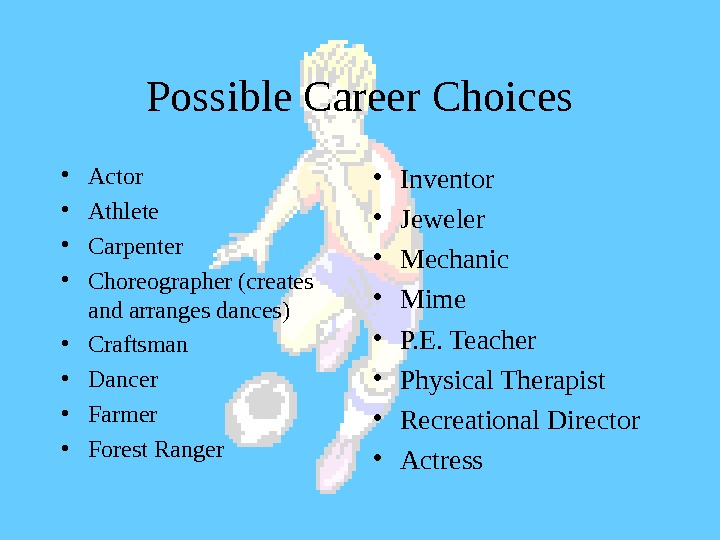
 Possible Career Choices • Actor • Athlete • Carpenter • Choreographer (creates and arranges dances) • Craftsman • Dancer • Farmer • Forest Ranger • Inventor • Jeweler • Mechanic • Mime • P. E. Teacher • Physical Therapist • Recreational Director • Actress
Possible Career Choices • Actor • Athlete • Carpenter • Choreographer (creates and arranges dances) • Craftsman • Dancer • Farmer • Forest Ranger • Inventor • Jeweler • Mechanic • Mime • P. E. Teacher • Physical Therapist • Recreational Director • Actress
 • Babe Ruth • Jim Thorpe • Kristi Yamaguchi • Mickey Mantle • Thomas Edison • Isadora Duncan • Cincinnatus • Fabergè • Wilbur Wright • Orville Wright
• Babe Ruth • Jim Thorpe • Kristi Yamaguchi • Mickey Mantle • Thomas Edison • Isadora Duncan • Cincinnatus • Fabergè • Wilbur Wright • Orville Wright

 What is Musical Intelligence? Being musically intelligent means that you are able to distinguish the sounds around you and that you have the ability to make your own melodies. Even if you are only singing a song or making music, you are using your musical intelligence! If you are musically intelligent, you are able to: • Perceive • Discriminate • Transform • Express All kinds of musical forms
What is Musical Intelligence? Being musically intelligent means that you are able to distinguish the sounds around you and that you have the ability to make your own melodies. Even if you are only singing a song or making music, you are using your musical intelligence! If you are musically intelligent, you are able to: • Perceive • Discriminate • Transform • Express All kinds of musical forms
 Types of Musical Intelligence Figural and Formal (“top-down”) (“ bottom-up”) This means that you are very intuitive about analytic and technical the nature of music and about music and its creation. *Anyone can have either both or one of these forms *
Types of Musical Intelligence Figural and Formal (“top-down”) (“ bottom-up”) This means that you are very intuitive about analytic and technical the nature of music and about music and its creation. *Anyone can have either both or one of these forms *
 Careers This will give you just a taste for the jobs available in this growing field. • Advertising Agent • Conductor • Disc Jockey • Film/Instrument Maker • Composer • Music Teacher • Sound Engineer • Music Therapist • Song Writer • Performing Musician • Piano Turner • Singer • Musical Theater Actor/ Actress • Studio Engineer • Instrument Manager • Rapper
Careers This will give you just a taste for the jobs available in this growing field. • Advertising Agent • Conductor • Disc Jockey • Film/Instrument Maker • Composer • Music Teacher • Sound Engineer • Music Therapist • Song Writer • Performing Musician • Piano Turner • Singer • Musical Theater Actor/ Actress • Studio Engineer • Instrument Manager • Rapper
 Famous Musicians These are just a few of the famous Musicians that helped shape the field of Music. • Joan Baez • Zubin Mehta • Ethel Merman • Jean Redpath • Gustav Mahler • Leonard Bernstein • Ella Fitzgerald • Jenny Lind • Stephen Foster • Antonio Stradivari • Ludwig van Beethoven • Ray Charles • Robert Schumann • Sergei Rachmaninoff • Yehudi Menuhin • Willie Nelson • The Mavericks • Lawerence Welk • George Gershwin
Famous Musicians These are just a few of the famous Musicians that helped shape the field of Music. • Joan Baez • Zubin Mehta • Ethel Merman • Jean Redpath • Gustav Mahler • Leonard Bernstein • Ella Fitzgerald • Jenny Lind • Stephen Foster • Antonio Stradivari • Ludwig van Beethoven • Ray Charles • Robert Schumann • Sergei Rachmaninoff • Yehudi Menuhin • Willie Nelson • The Mavericks • Lawerence Welk • George Gershwin
 Activities The following is a list of activities that can be used in a classroom or anywhere else to enhance one’s own musical intelligence. • Sing Ballads • Create Chants • Create Concept Songs • Discographies (lists of musical selections to enhance what you are learning or teaching. ) • Environmental Sounds • Humming • Illustrate With Sounds • Rhythms • Instrumental sounds • Listening • Lyrics • Mood Music • Music Composition or creation • Musical concepts • Musical Performance • Percussion and Raps • Reproduce sounds and rhythms • Singing and Songs • Vocal Sounds and Tonal Patterns
Activities The following is a list of activities that can be used in a classroom or anywhere else to enhance one’s own musical intelligence. • Sing Ballads • Create Chants • Create Concept Songs • Discographies (lists of musical selections to enhance what you are learning or teaching. ) • Environmental Sounds • Humming • Illustrate With Sounds • Rhythms • Instrumental sounds • Listening • Lyrics • Mood Music • Music Composition or creation • Musical concepts • Musical Performance • Percussion and Raps • Reproduce sounds and rhythms • Singing and Songs • Vocal Sounds and Tonal Patterns
 Interpersonal Intelligence
Interpersonal Intelligence
 Interpersonal Intelligence Gardner’s Definition: • Interpersonal intelligence, (people smart), is understanding other people. It’s an ability we all need, but is at a premium if you are a teacher, clinician, salesperson, or a politician. Anybody who deals with other people has to be skilled in the interpersonal sphere.
Interpersonal Intelligence Gardner’s Definition: • Interpersonal intelligence, (people smart), is understanding other people. It’s an ability we all need, but is at a premium if you are a teacher, clinician, salesperson, or a politician. Anybody who deals with other people has to be skilled in the interpersonal sphere.
 Interpersonally intelligent people enjoy: * Giving feedback to the teacher or to classmates • Understanding other’s feelings • Person-to-person communication • Cooperative learning strategies • Receiving feedback • Group projects • Teaching someone else something new • Learning from someone outside of school • Other points of view • Creating group rules • Acting in a play or simulation • Conducting an interview • Creating «phone buddies» for homework • Sensing others’ motives • Creating group rules
Interpersonally intelligent people enjoy: * Giving feedback to the teacher or to classmates • Understanding other’s feelings • Person-to-person communication • Cooperative learning strategies • Receiving feedback • Group projects • Teaching someone else something new • Learning from someone outside of school • Other points of view • Creating group rules • Acting in a play or simulation • Conducting an interview • Creating «phone buddies» for homework • Sensing others’ motives • Creating group rules
 Famous Interpersonal People • Abraham Lincoln • George Washington • Ghandi • Dr. Joyce Brothers • Oprah Winfrey • Jesse Jackson • Martin Luther King • R ev. Billy Graham
Famous Interpersonal People • Abraham Lincoln • George Washington • Ghandi • Dr. Joyce Brothers • Oprah Winfrey • Jesse Jackson • Martin Luther King • R ev. Billy Graham
 Interpersonal Careers • Administrator • Anthropologist • Arbitrator • Counselor • Manager • Nurse • Personnel Director • Politician • Public Relations • Salesperson • School Principal • Sociologist • Therapist • Teacher • Travel Agent • Religious Leader • Psychologist
Interpersonal Careers • Administrator • Anthropologist • Arbitrator • Counselor • Manager • Nurse • Personnel Director • Politician • Public Relations • Salesperson • School Principal • Sociologist • Therapist • Teacher • Travel Agent • Religious Leader • Psychologist
 “ What is intrapersonal intelligence? ” Intrapersonal intelligence is self-knowledge and the ability to act adaptively on the basis of that knowledge. This intelligence includes having an accurate picture of oneself (one’s strengths and weaknesses); awareness of inner moods, intentions, motivations, temperaments, and desires; and the capacity for self-discipline, self-understanding, and self-esteem. Essentially, it’s how well you know yourself.
“ What is intrapersonal intelligence? ” Intrapersonal intelligence is self-knowledge and the ability to act adaptively on the basis of that knowledge. This intelligence includes having an accurate picture of oneself (one’s strengths and weaknesses); awareness of inner moods, intentions, motivations, temperaments, and desires; and the capacity for self-discipline, self-understanding, and self-esteem. Essentially, it’s how well you know yourself.
 • Clergyman • Entrepreneur • Program planner • Psychiatrist • Psychology Teacher • Philosopher • Theologian • Researcher • Spiritual Counselor • Psychologist
• Clergyman • Entrepreneur • Program planner • Psychiatrist • Psychology Teacher • Philosopher • Theologian • Researcher • Spiritual Counselor • Psychologist
 * Aristotle * Emily Dickinson * General George Patton * Helen Keller * Malcolm X * Mohammed
* Aristotle * Emily Dickinson * General George Patton * Helen Keller * Malcolm X * Mohammed
 *Autobiography *Awareness of Personal Feelings *Concentration *Expression of Feelings *Focusing *Free-Choice Time *Goal Setting *Higher-Order Thinking and Reasoning *Independent Studies Projects *Mood Awareness and Shifting *Personal Application * Personal Priorities *Personal Projection *Sensing the Emotions of the Moment *Self –Identification *Thinking Strategies
*Autobiography *Awareness of Personal Feelings *Concentration *Expression of Feelings *Focusing *Free-Choice Time *Goal Setting *Higher-Order Thinking and Reasoning *Independent Studies Projects *Mood Awareness and Shifting *Personal Application * Personal Priorities *Personal Projection *Sensing the Emotions of the Moment *Self –Identification *Thinking Strategies
 Book References • Multiple Intelligences: In The Classroom by Thomas Armstrong • Multiple Intelligences: Theory in Practice by Howard Gardner • Multiple Intelligence Approaches Assessment : Solving the Assessment Conundrum by David Lazear
Book References • Multiple Intelligences: In The Classroom by Thomas Armstrong • Multiple Intelligences: Theory in Practice by Howard Gardner • Multiple Intelligence Approaches Assessment : Solving the Assessment Conundrum by David Lazear
 • Teaching & Learning Through Multiple Intelligences by Linda Campbell • Multiple Intelligences: Activities by Deirdre Korff Wilkins, M. A.
• Teaching & Learning Through Multiple Intelligences by Linda Campbell • Multiple Intelligences: Activities by Deirdre Korff Wilkins, M. A.
 A Bite From The Internet • http: //www. arches. uga. edu/~hmt/webwrite/linguist ics. htm • http: //www. cookps. act. edu. au/mi_ling. htm • www. 1 stepenglish. com • www. ul. ie/~mearsa/9519211/ • www. chariho. k 12. RI. us • www. chariho. k 12. us/curriculum/MISmart/inter. ht m
A Bite From The Internet • http: //www. arches. uga. edu/~hmt/webwrite/linguist ics. htm • http: //www. cookps. act. edu. au/mi_ling. htm • www. 1 stepenglish. com • www. ul. ie/~mearsa/9519211/ • www. chariho. k 12. RI. us • www. chariho. k 12. us/curriculum/MISmart/inter. ht m

 Junior G/T Class Linguistic Intelligence Michelle Markovich & Rachel Sullivan
Junior G/T Class Linguistic Intelligence Michelle Markovich & Rachel Sullivan
 Logical-Mathematical Intelligence Josh Hughes, Mike Phelps, & Gary De. Witt
Logical-Mathematical Intelligence Josh Hughes, Mike Phelps, & Gary De. Witt
 Spatial Intelligence T. J. Pope & Ashley Torres
Spatial Intelligence T. J. Pope & Ashley Torres
 Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence Kristina Heinecke & Mallary Williams
Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence Kristina Heinecke & Mallary Williams
 Musical Intelligence Rachel Snedecor & Marilynn Pester
Musical Intelligence Rachel Snedecor & Marilynn Pester
 Interpersonal Intelligence Melissa Hamilton & Kyle Gospodarek
Interpersonal Intelligence Melissa Hamilton & Kyle Gospodarek
 Intrapersonal Intelligence Kaitlin Hancock & Ashley Wathen
Intrapersonal Intelligence Kaitlin Hancock & Ashley Wathen
 Cover and Table of Contents Amanda Cappiello
Cover and Table of Contents Amanda Cappiello
 Introduction Kaitlin Hancock
Introduction Kaitlin Hancock
 Bibliography Joel Martinez & Christina Pacheco
Bibliography Joel Martinez & Christina Pacheco
 Credits Bud Sothman & Brittany Claussen Everyone has a special talent!
Credits Bud Sothman & Brittany Claussen Everyone has a special talent!
 Señora Shinovich & Ed Jimenez Our Teacher and Assistant
Señora Shinovich & Ed Jimenez Our Teacher and Assistant
 We hope you had an enjoyable learning experience!!!!!
We hope you had an enjoyable learning experience!!!!!

