b2f06a0af55aea45f2d046f89125add4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 96

How to Write a Web Page By Mimi Opkins

What We’ll Cover Today u. Basic HTML Tags u. How to Make a Simple Page

What Is HTML u. Hypertext Markup Language u. Instructions to the Web Browser u. Like proofreading instructions u. Made up of “tags”

Anatomy of a Tag u. Start Tag: u<TAGNAME ATTRIBUTE=value> u. End Tag: u</TAGNAME> OR u. Tag: u<TAGNAME ATTRIBUTE=value>

What You Need to Know About Tags u. NOT case-sensitive u. Doesn’t matter where you put them on a line u. Don’t have to be on the same line as the text u. Not all tags have ending tags u. Browsers will ignore invalid tags

Basic HTML Tags u. Titles u. Headings u. Line Spacing u. Graphics u. Fonts u. Links u. Lists u. Tables

HTML Tag u. Lets the browser know that this is an HTML document u. Must start and every web page u<HTML> u</HTML>

HEAD Tag u. First part of every Web Page u. Defines the heading section u<HEAD> u</HEAD>

TITLE Tag u. Displays information on the top line of your browser u<TITLE>Title Line</TITLE>

TITLE Example <HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>My First Web Page</TITLE> </HEAD>
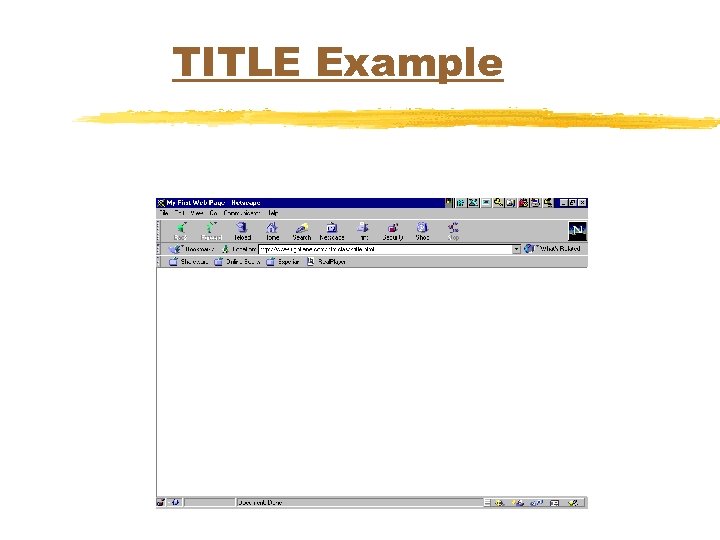
TITLE Example

BODY Tag u. Defines the main section of your web page u<BODY BGCOLOR=color name BACKGROUND=picturename> u</BODY>

BODY Example u. BACKGROUND specifies a background picture <BODY BACKGROUND=lionimg. gif> u. BGCOLOR specifies a background color <BODY BGCOLOR=cyan>

BODY Background Example

BODY BGCOLOR Example

Heading Tag u. Used to display headings u 6 different levels u<H 1> </H 1> u<H 2> </H 2> u<H 3> </H 3> u<H 4> </H 4> u<H 5> </H 5> u<H 6> </H 6>

Heading Example <H 1>Heading <H 2>Heading <H 3>Heading <H 4>Heading <H 5>Heading <H 6>Heading Level Level 1</H 1> 2</H 2> 3</H 3> 4</H 4> 5</H 5> 6</H 6>
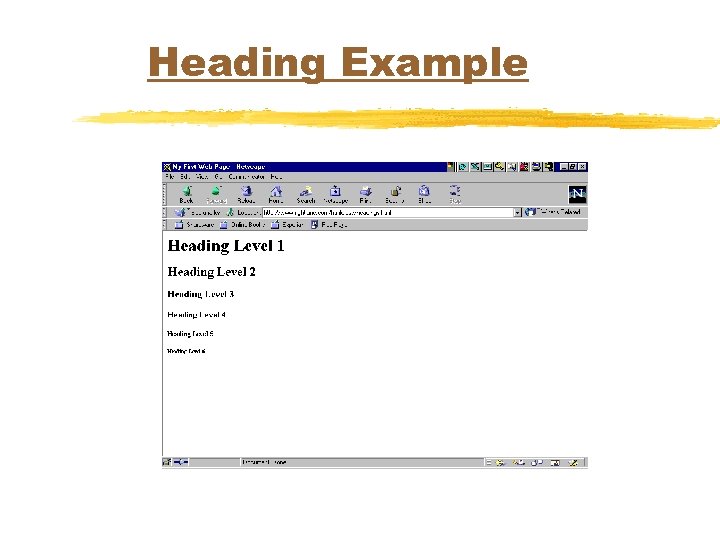
Heading Example

Adding Text u. Just type in the information you want u. Browser will format it for you based on screen width and other HTML tags

Adding Text Example <HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>My First Web Page</TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY> This is the text of my first web page. </BODY> </HTML>

Adding Text Example

Line Spacing Tags u. Break Tag - starts a new line u<BR> u. Paragraph Tag - starts a new line and inserts a blank line u<P>

Line Spacing Tags (con’t. ) u. Center Tag - centers the following text or picture u<CENTER> </CENTER> u. Horizontal Rule - draws a straight line across the screen u<HR WIDTH=xx%>

Line Spacing Example <BODY> This is the first paragraph of my web page. <BR>This text will start on a new line <P>This will start on a new line with a blank space. <CENTER>This text is centered on the page </CENTER> <!--this is a comment stating that following is a straight line that is 50% of the page wide--> <HR WIDTH=50%>
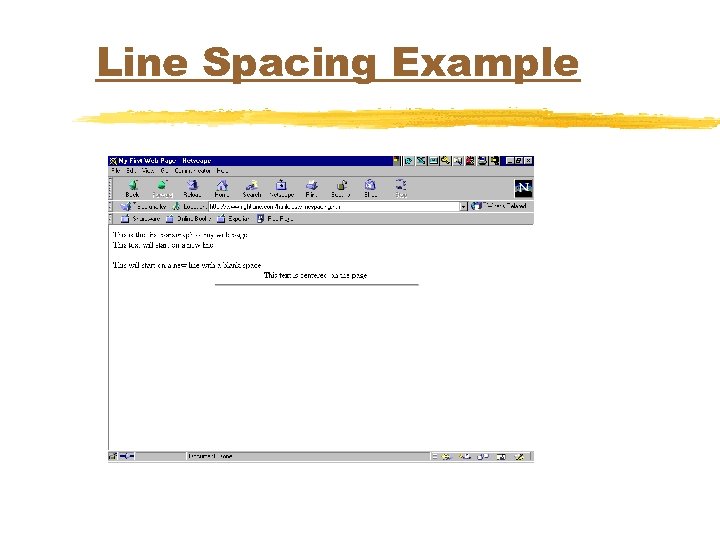
Line Spacing Example

Let’s Put It Together (so far) <html> <head> <title>My First Web Page</title> </head> <body> <h 1>Welcome to My Web Page</h 1> This is my very own web page. Just learning how so I'm experimenting with different tags. <BR>This text will start on a new line <h 2>This is the next section of my first web page</h 2> <P>This will start on a new line with a blank space. <CENTER>This text is centered on the page <h 3>So is this heading</h 3> <!--this a comment before a straight line--> <hr> </CENTER> </body> </html>
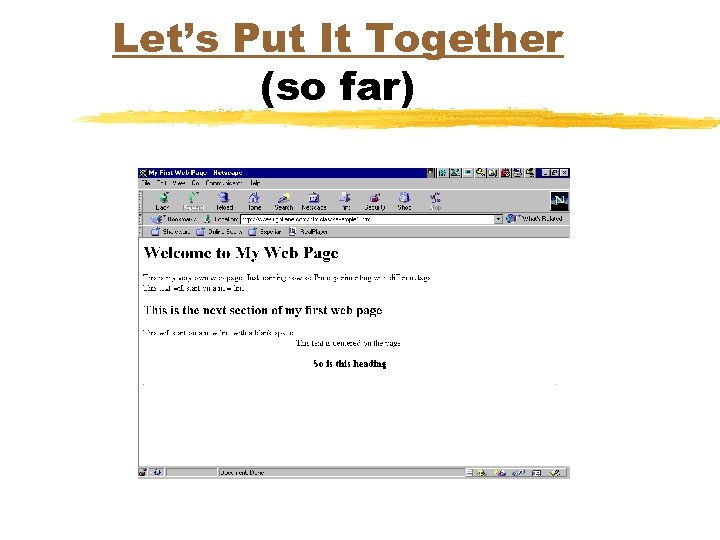
Let’s Put It Together (so far)

IMG Tag u. Add pictures to a web page u<IMG SRC=name of the picture ALIGN=alignment option WIDTH=width HEIGHT=height ALT=alternate text>

IMG Tag (con’t. ) u. Alignment controls where picture is placed in relationship to the text u. LEFT, RIGHT, TOP, MIDDLE, BOTTOM u. WIDTH and HEIGHT control the size of the picture in pixels
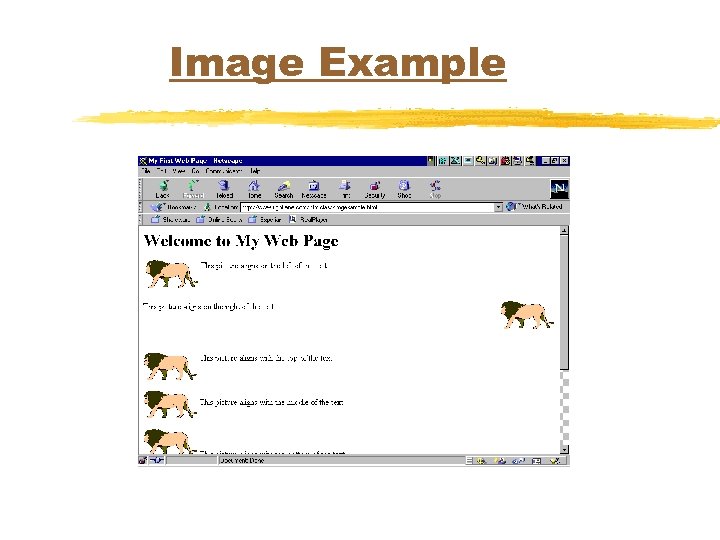
Image Example
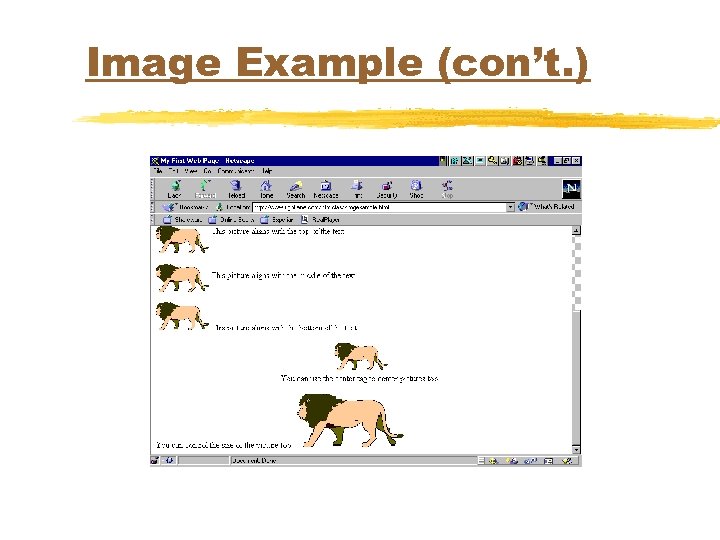
Image Example (con’t. )

FONT Tag u<FONT SIZE=size COLOR=color> u</FONT>

FONT Tag (con’t. ) u. SIZE Ranges from 1 to 7 u. COLOR changes the color of the text between the <FONT> and </FONT> tags

Font Example <html> <head><title>My First Web Page</title></head> <body> This is normal size text. It is font size 3. <font size=7>This is font size 7</font> <font size=6>This is font size 6</font> <font size=5>This is font size 5</font> <font size=4>This is font size 4</font> <font size=3>This is font size 3</font> <font size=2>This is font size 2</font> <font size=1>This is font size 1</font> <font color=red>This is red text</font> <font color=blue>This is blue text</font> This is normal color text. It is black. </body> </html>
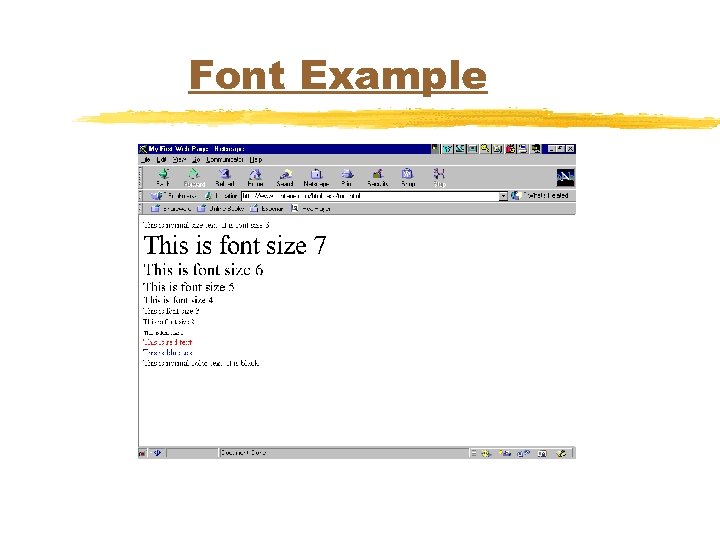
Font Example

Other Font Related Tags u. Bold u<B> </B> u. Underline u<U> </U> u. Italic u<I> </I>

More Font Examples <html> <head> <title>My First Web Page</title> </head> <body> This is normal size text. <b>This is bold text. </b> <i>This text is in italics. </i> <u>This text is underlined. </u> You can combine these tags also. <b><i>This is bold, italic text. </i></b> </body> </html>

More Font Examples

A Word About Color u. Color is really expressed in three parts u. RED GREEN BLUE u. COLOR=#RRGGBB u. Cyan is COLOR=#00 FFFF u. Yellow is COLOR=#FFFF 00 u. Black is COLOR=#000000 u. White is COLOR=#FFFFFF

More About Color u. Some browsers will accept color names u. Common color names are: u. RED u. GREEN u. BLUE u. CYAN u. YELLOW

Anchor Tag (How to Make Links) u<A HREF=web page address> link description u</A>

Anchor Example <A HREF=“http: //www. csulb. edu”> Cal State University Long Beach</A> <A HREF=“mailto: mopkins@csulb. edu”> Teacher Extraordinaire</A>

Anchor Example <html> <head> <title>My First Web Page</title> </head> <body> <h 2>How to Add a Link to a Web Page</h 2> <p> To add a link to a web page you use the anchor < A> tag. This takes three parts: <ol> <li>The < A HREF="web page name"> is the actually place where you want the link to go <li>Next you put the title of the web page <li>Finally, you end the link with the < /A> tag. </ol> <p> For example: <b><font color=red>

Anchor Example (con’t. ) < A HREF=http: //www. experian. com> Experian Information Solutions Home Page < /A> </font></b> is a link to the Experian Information Solutions page. <p> It will look like this on the web page: <a href=http: //www. experian. com>Experian Information Solutions</a> <p> You can also set up a link to automatically open up the email program. It goes like this: <b><font color=red> < A HREF=mailto: email address> email recipient< /A> </font></b> <p>It will look like this on the web page: <A HREF=mailto: mimi. opkins@experian. com>Employee Extraodinaire</a> </body> </html>
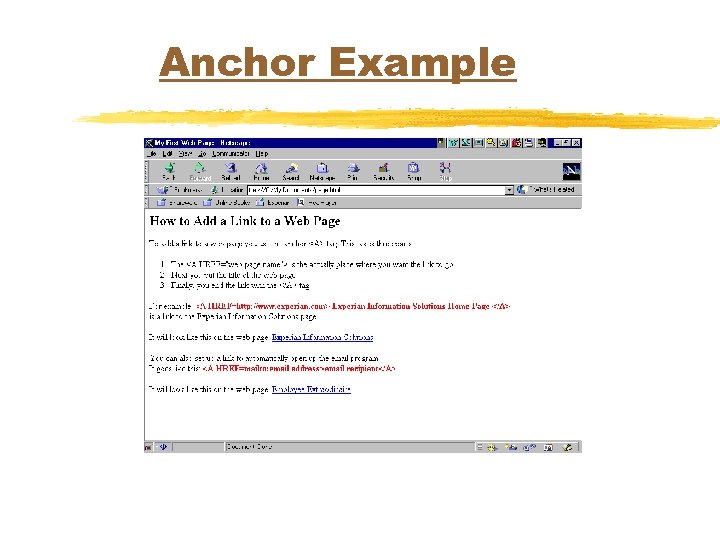
Anchor Example
How Do I View the HTML u. Internet Explorer: u View…Source u. Mozilla: u View…Page Source

How Do I Test My Page u. Internet Explorer: u File…Open…Browse u. Mozilla u File…Open File

Lists u. Unordered List u. Simple List u. Ordered List u. Definition List

Unordered List Tag u. Used when the items in a list can be displayed in any order u. Items are displayed following a “bullet” character

Unordered List Tag (con’t. ) u. All list items must be enclosed between unordered list tags u<UL> u</UL> u. List items are identified by the list item tags u<LI> u</LI>

Unordered List Example <UL> <LI>Milk</LI> <LI>Bread</LI> <LI>Eggs</LI> </UL>
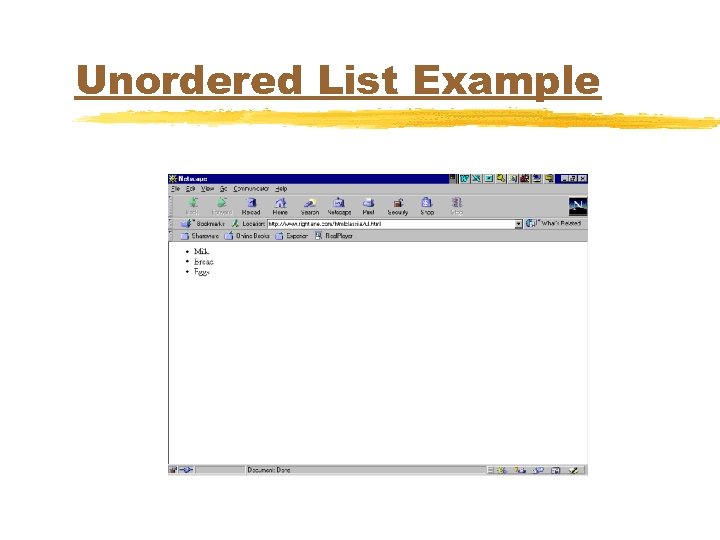
Unordered List Example
Changing the Bullet u. Change the bullet type in the <UL TYPE=bullet-type> tag u<UL TYPE=DISC> displays a solid disc u<UL TYPE=CIRCLE> displays a circle u<UL TYPE=SQUARE> display a square
Bullet Type Example <UL TYPE=DISC> <LI>List item 1 disc</LI> <LI>List item 2 disc</LI> </UL> <UL TYPE=CIRCLE> <LI>List item 1 circle</LI> <LI>List item 2 circle</LI> </UL> <UL TYPE=SQUARE> <LI>List item 1 square</LI> <LI>List item 2 square</LI> </UL>
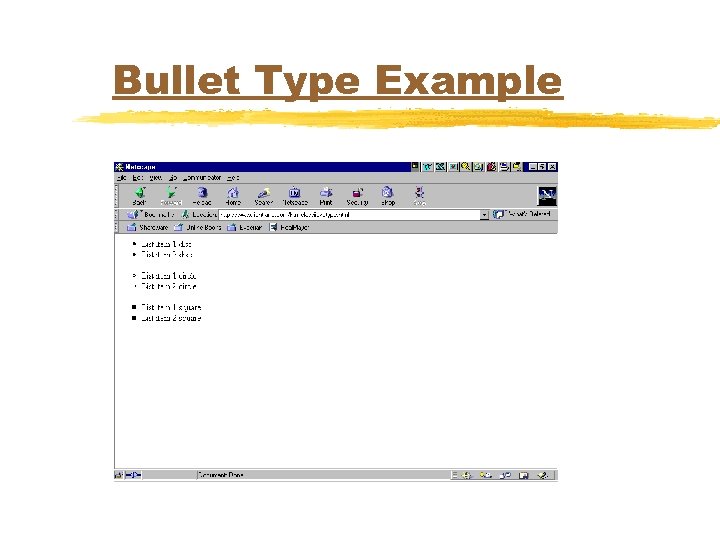
Bullet Type Example

Simple List Tag u. Another type of unordered list u. Browser may not display it differently than an ordered list u. All list items must be enclosed between simple list tags u<SL> u</SL>

Simple List Example <SL> <LI>Milk</LI> <LI>Bread</LI> <LI>Eggs</LI> </SL>
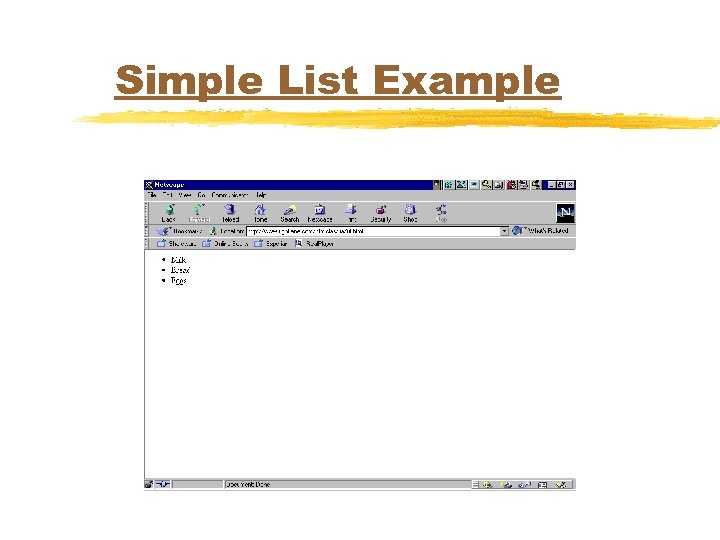
Simple List Example

Ordered List Tag u. Numbered Lists u. Used when order is important u. All list items must be enclosed between ordered list tags u<OL> u</OL>

Ordered List Example <OL> <LI>Drop of the kids</LI> <LI>Pick up the dry cleaning</LI> <LI>Go to the market</LI> </OL>
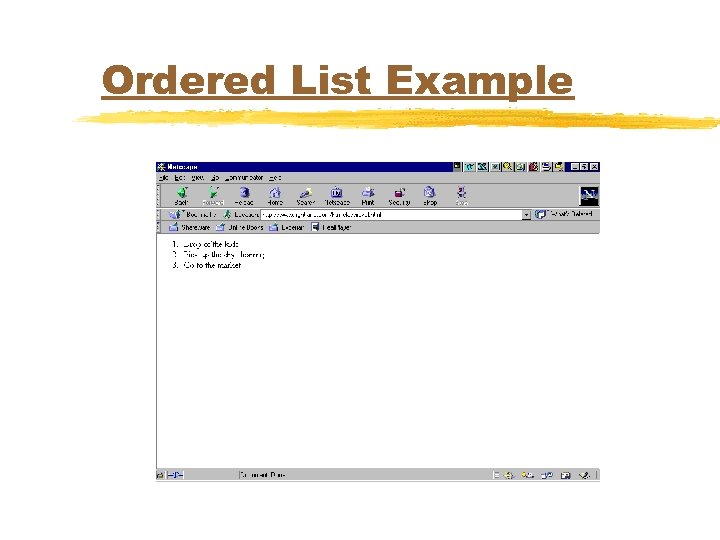
Ordered List Example
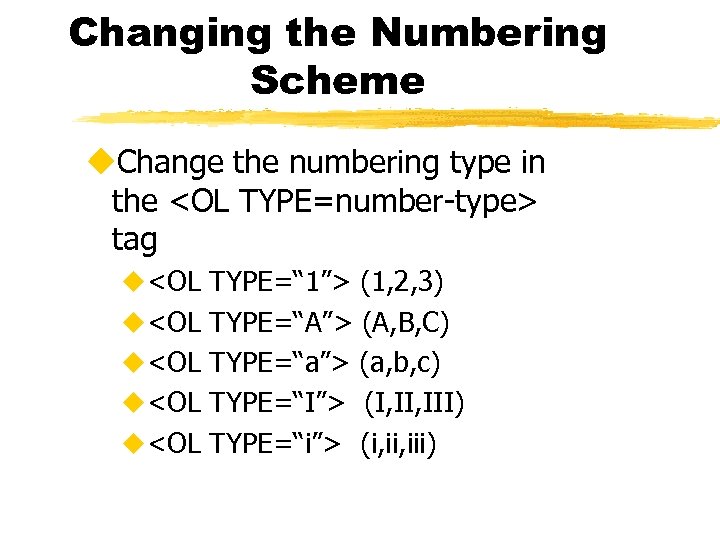
Changing the Numbering Scheme u. Change the numbering type in the <OL TYPE=number-type> tag u<OL TYPE=“ 1”> (1, 2, 3) u<OL TYPE=“A”> (A, B, C) u<OL TYPE=“a”> (a, b, c) u<OL TYPE=“I”> (I, III) u<OL TYPE=“i”> (i, iii)

Number Type Example <OL TYPE="1"> <LI>List item 1 type 1</LI> <LI>List item 2 type 1</LI> <LI>List item 3 type 1</LI> </OL> <OL TYPE="A"> <LI>List item 1 type A</LI> <LI>List item 2 type A</LI> <LI>List item 3 type A</LI> </OL>

Number Type Example <OL TYPE="a"> <LI>List item 1 type a</LI> <LI>List item 2 type a</LI> <LI>List item 3 type a</LI> </OL> <OL TYPE="I"> <LI>List item 1 type I</LI> <LI>List item 2 type I</LI> <LI>List item 3 type I</LI> </OL> <OL TYPE="i"> <LI>List item 1 type i</LI> <LI>List item 2 type i</LI> <LI>List item 3 type i</LI> </OL>
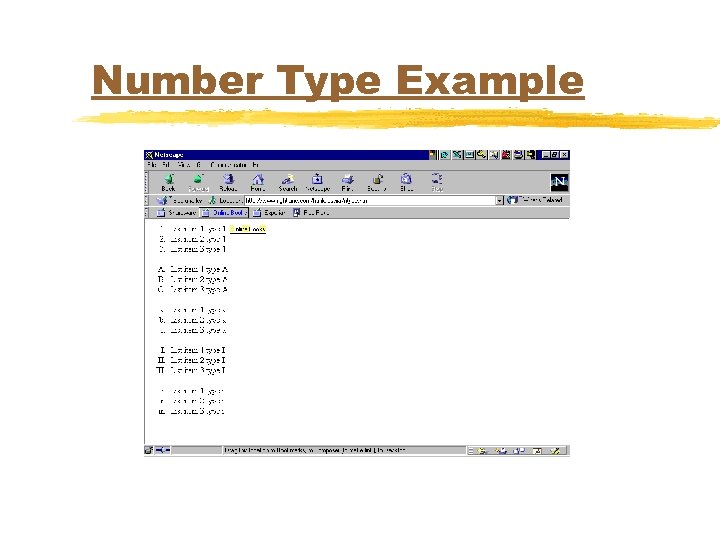
Number Type Example

Definition List Tag u. Used to format a glossary or dictionary type of structure u. All list items must be enclosed between definition list tags u<DL> u</DL> u. Terms are identified by the <DT> tag u. Definitions are defined by the <DD> tag

Definition List Example <DL> <DT>HTML <DD>Hypertext Markup Language <DT>World Wide Web <DD>One of the services available on the Internet </DL>
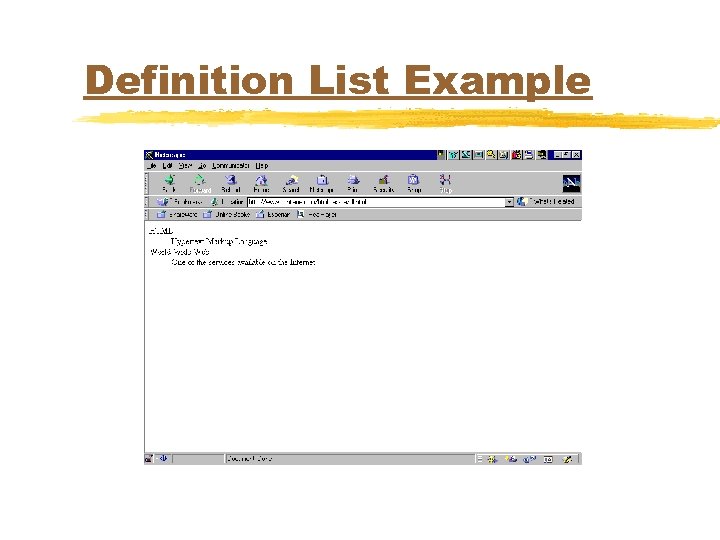
Definition List Example

Nested Lists u. You can embed or “nest” lists within lists u. Just about any nested list combination imaginable

Nested Lists Example <OL> <LI>Go to the market and buy: </LI> <UL> <LI>Milk</LI> <LI>Eggs</LI> </UL> <LI>Go to the cleaners and pick up: </LI> <UL> <LI>Shirts</LI> <LI>Dresses</LI> </UL> <LI>Remember: </LI> <DL> <DT>Survive <DD>My motto of the day </DL> </OL>
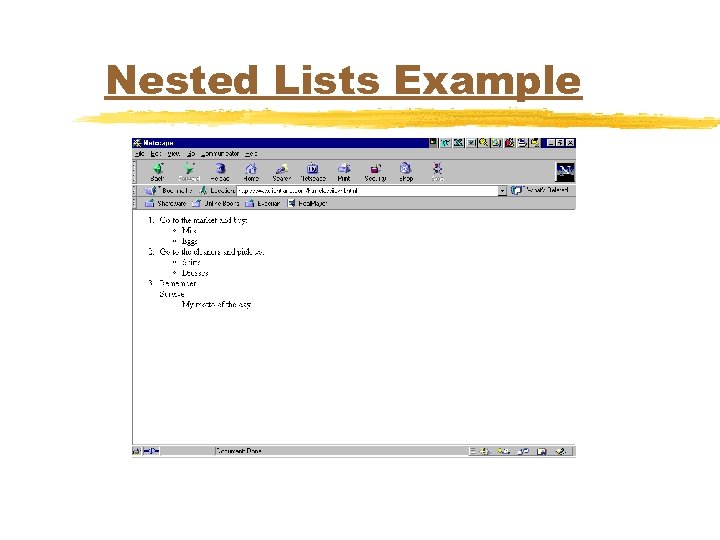
Nested Lists Example

Formatting Within Lists u. Decreasing Space u. Use the COMPACT attribute in the <UL>, <SL>, <OL> or <DL> tag uexample: <UL COMPACT> u. Increasing Space u. Put the <P> tag after each </LI> tag

Tables u. Intended for display of columnar data u. Can be used to align data on the screen u. Not just for text - images, blank space, form fields and other tables
How Tables are Organized u. The fundamental building blocks of tables are called cells u. Cells contain a data element of the table or a heading for a column of data u. Related cells are grouped into rows u. Rows are grouped together to make up a table

TABLE Tag u. All elements in a table are enclosed between the table tags u<TABLE> u</TABLE>
Table Row Tag u. Rows are defined with the Table Row tags u<TR> u</TR> u. You can place as many <TR> and </TR> tag pairs inside a table as you want u. Each pair counts for one row

Creating a Table Cell u. Two types of table cells: u. Table Headers u. Data Cells

Table Header Tag u. Table headers are defined with the table header tags u<TH> u</TH> u. Table Header cells are automatically centered and boldface u. Usually the first row of a table

Table Data Tag u. Data cells are defined with the table data tags u<TD> u</TD> u. Data cells are left justified u. Formatted with the usual tags
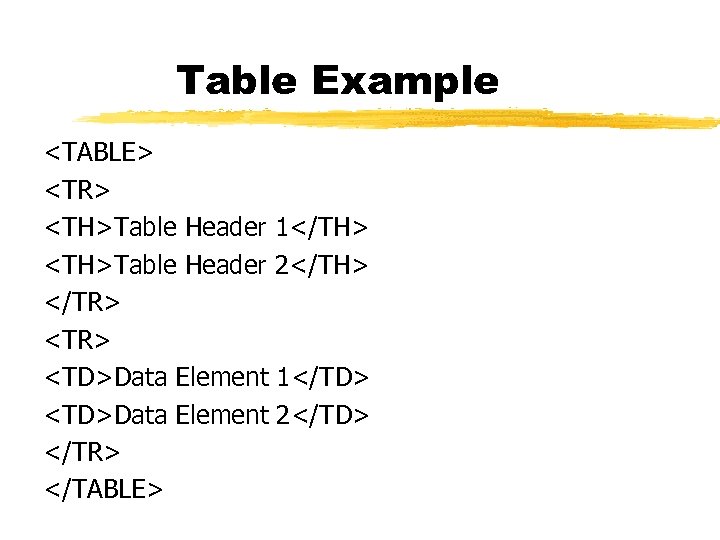
Table Example <TABLE> <TR> <TH>Table Header 1</TH> <TH>Table Header 2</TH> </TR> <TD>Data Element 1</TD> <TD>Data Element 2</TD> </TR> </TABLE>
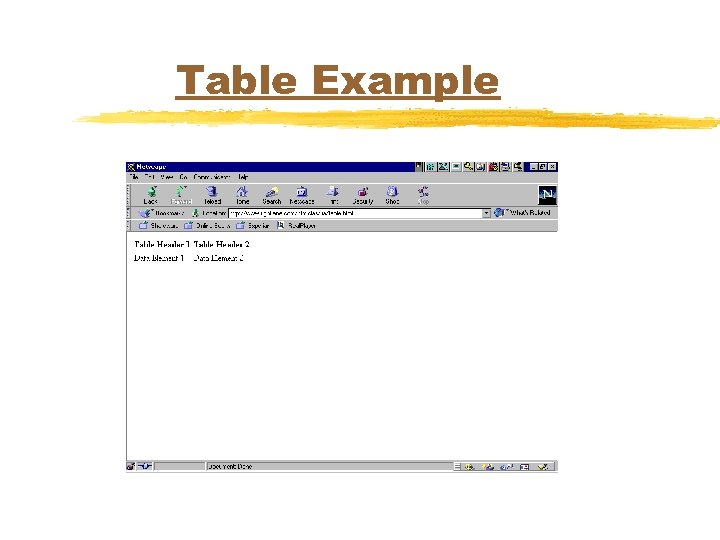
Table Example
Table Alignment u. Vertical Alignment u. Horizontal Alignment u. Entire Table u. Within a Row u. Within a Cell
Vertical Alignment u. Refers to alignment between the top and bottom of a cell u. Set the VALIGN attribute to u. TOP u. MIDDLE u. BOTTOM uexample: <TD VALIGN=TOP>

Horizontal Alignment u. Refers to alignment of an element across the width of the cell or of a table across a page u. Set the ALIGN attribute to u. LEFT u. CENTER u. RIGHT uexample: <TD VALIGN=RIGHT>

Aligning the Entire Table u. Set ALIGN=LEFT or ALGIN=RIGHT to float the table in the left or right margin <TABLE ALIGN=LEFT> u. Set ALIGN=CENTER to center the table in the browser window <TABLE ALIGN=CENTER> u. Enclose the table in <CENTER></CENTER> tags

Aligning a Row u. Use the VALIGN and ALIGN attributes of the <TR> tag to make the alignment the same for every cell in a given row u<TR VALIGN=TOP> u. Any alignment specified in the <TR> tag will override all defaults

Aligning a Cell u. Use the VALIGN and ALIGN attributes in the <TH> or <TD> tags u<TD ALIGN=RIGHT> u. Overrides any default alignments and any alignments specified in a <TR> tag

Other TABLE Attributes u. Captions u. Table Width u. Borders u. Spacing within and between cells u. How many rows or columns a cell should occupy

Adding a Caption u. Enclose the caption text between the caption tags u<CAPTION> u</CAPTION> u. Appears centered over the table u. Use ALIGN=BOTTOM attribute to place the caption below the table <CAPTION ALIGN=BOTTOM>

Setting the Table Width u. Use the WIDTH attribute u. Specify the table with in % of the browser window u<TABLE WIDTH=50%> u. Specify the table width in pixels u<TABLE WIDTH=600>
Adding a Border u. Use the BORDER attribute u. Set the BORDER to the number of pixels wide u<TABLE BORDER=3> u. You can specify no border u<TABLE BORDER=0>

Cell Spacing u. Use the CELLPADDING attribute to specify spacing in pixels within a cell u<TABLE CELLPADDING=6> u. Use the CELLSPACING attribute to specify spacing in pixels between cells u<TABLE CELLSPACING=3>

Spanning Multiple Rows or Columns u. Use the COLSPAN attribute of a <TH> or <TD> tag to make the cell occupy multiple columns u<TH COLSPAN=2> u. Use the ROWSPAN attribute of a <TH> or <TD> tag to make the cell occupy multiple rows u<TD ROWSPAN=3>
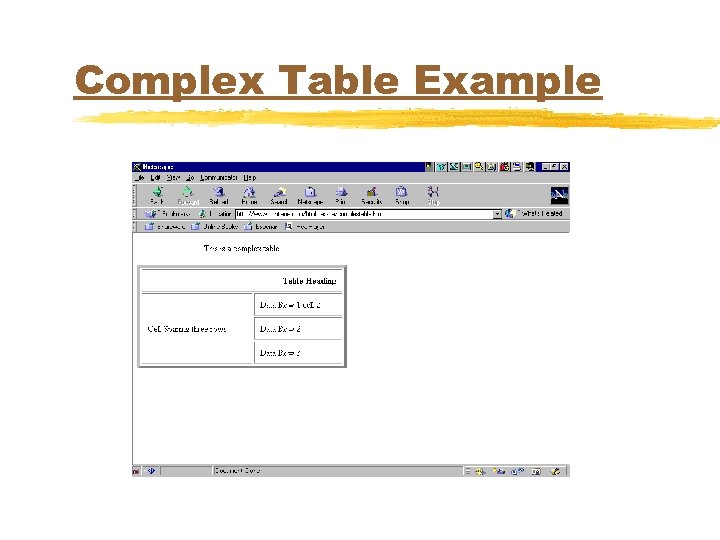
Complex Table Example <TABLE WIDTH=50% BORDER=5 CELLSPACING=3 CELLPADDING=10> <CAPTION>This is a complex table</CAPTION> <TR ALIGN=RIGHT> <TH COLSPAN=2>Table Heading</TH> </TR> <TD ROWSPAN=3>Cell Spaning three rows</TD> <TD>Data Row 1 cell 2</TD> </TR>
Complex Table Example <TR> <TD>Data Row 2</TD> </TR> <TD>Data Row 3</TD> </TR> </TABLE>
Complex Table Example
b2f06a0af55aea45f2d046f89125add4.ppt