9c55a18f480b2fbb49feb121ee550867.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
How to use Lab. VIEW February 2011

Contents q What is Lab. VIEW? q How does Lab. VIEW work? Block diagram Front panel Palettes q Data flow programming. Functions. q Lab. VIEW Programming Structures (Formula, Case structure …) q What is a sub. VI? Using a VI as a sub. VI. q How to use Lab. VIEW with data acquisition (DAQ) software Measurements and automation explorer (MAX) I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
What is Lab. VIEW? Lab. VIEW – Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench is a graphical (visual) programming from National istruments (NI). The purpose is automating the usage of processing and measuring equipment in any laboratory setup. Originally released for the Apple Macintosh in 1986, the graphical language at the heart of Lab. VIEW is called "G". C language Dataflow programming language uses icons instead of lines of text to create programs The graphical approach of Lab. VIEW allows non-programmers to build programs by dragging and dropping virtual representations of lab equipment with which they are already familiar. Cross-platform I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
Price Desktop PC Lab. VIEW Professional Development System http: //www. ni. com/labview/buy/ I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Laptop PDA
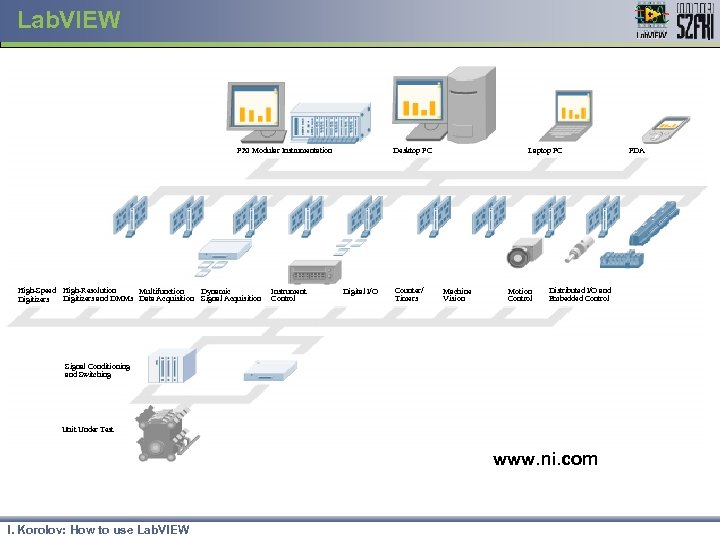
Lab. VIEW PXI Modular Instrumentation High-Speed High-Resolution Multifunction Dynamic Digitizers and DMMs Data Acquisition Signal Acquisition Digitizers Instrument Control Laptop PC Desktop PC Digital I/O Counter/ Timers Machine Vision Motion Control Distributed I/O and Embedded Control Signal Conditioning and Switching Unit Under Test www. ni. com I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW PDA

How does Lab. VIEW work? I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
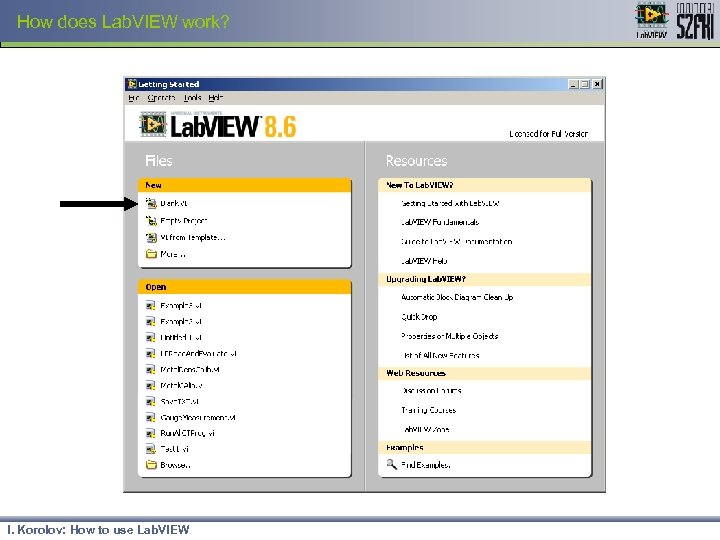
How does Lab. VIEW work? I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
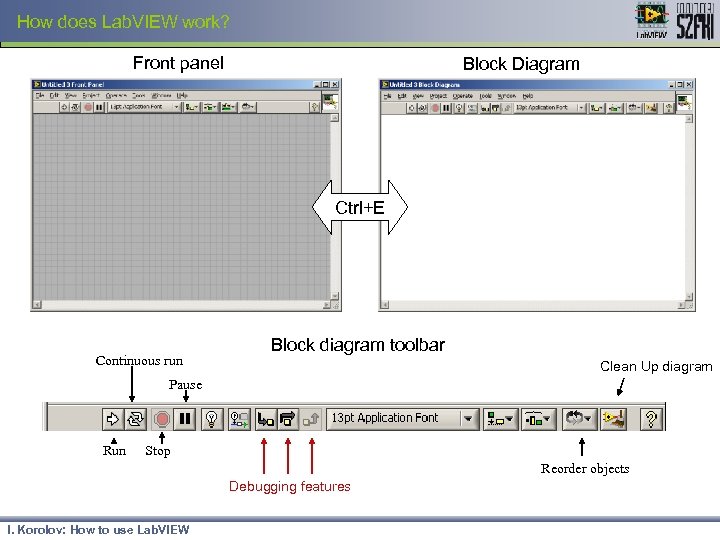
How does Lab. VIEW work? Front panel Block Diagram Ctrl+E Continuous run Block diagram toolbar Clean Up diagram Pause Run Stop Reorder objects Debugging features I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
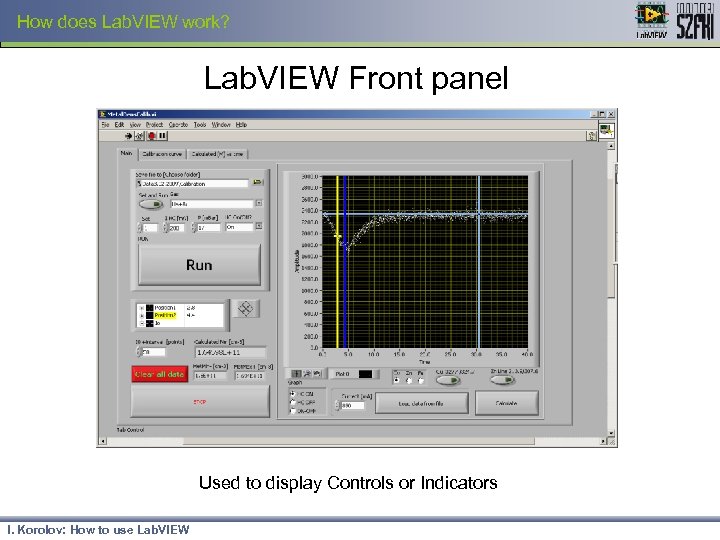
How does Lab. VIEW work? Lab. VIEW Front panel Used to display Controls or Indicators I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
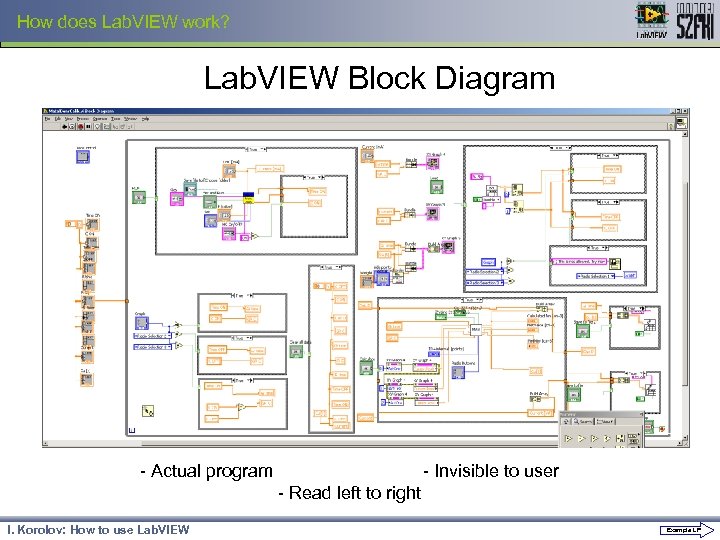
How does Lab. VIEW work? Lab. VIEW Block Diagram - Actual program - Invisible to user - Read left to right I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example LP
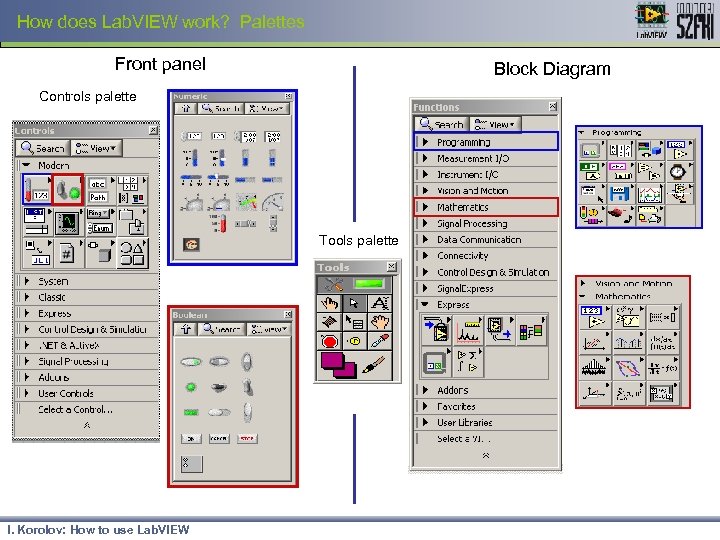
How does Lab. VIEW work? Palettes Front panel Block Diagram Controls palette Tools palette I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
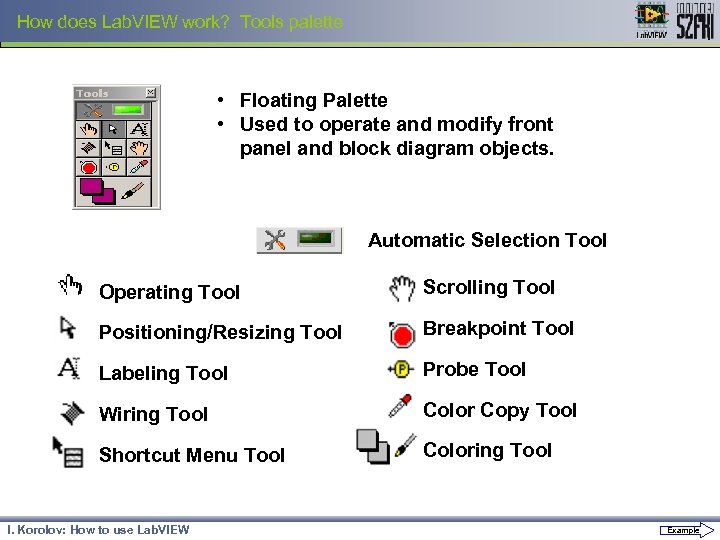
How does Lab. VIEW work? Tools palette • Floating Palette • Used to operate and modify front panel and block diagram objects. Automatic Selection Tool Operating Tool Scrolling Tool Positioning/Resizing Tool Breakpoint Tool Labeling Tool Probe Tool Wiring Tool Color Copy Tool Shortcut Menu Tool Coloring Tool I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example

Data flow programming I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
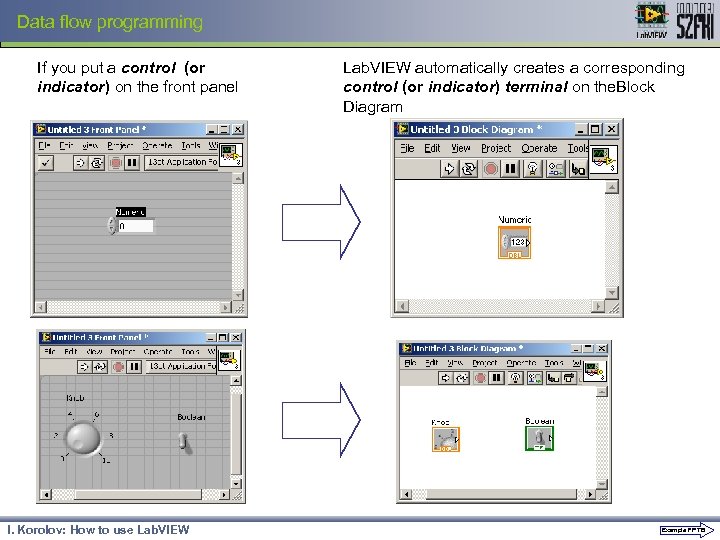
Data flow programming If you put a control (or indicator) on the front panel I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW automatically creates a corresponding control (or indicator) terminal on the. Block Diagram Example FP TB
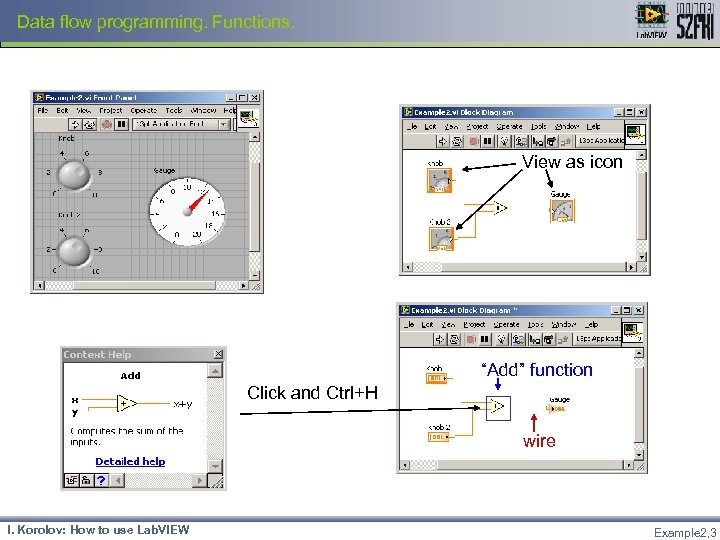
Data flow programming. Functions. View as icon “Add” function Click and Ctrl+H wire I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example 2, 3
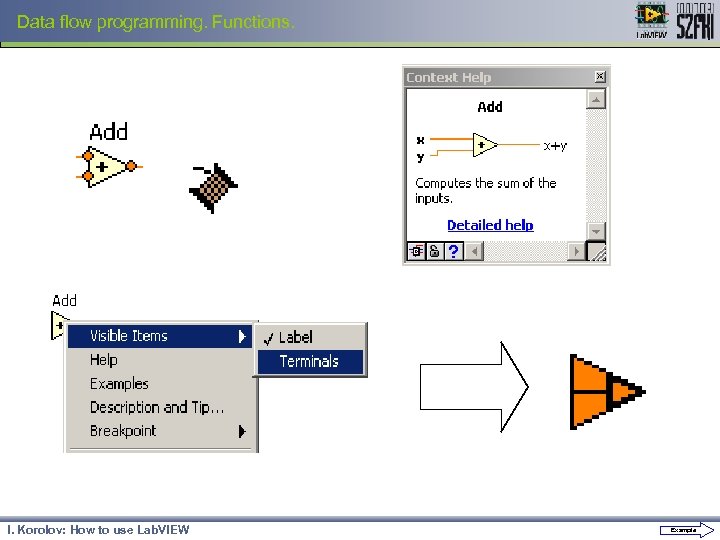
Data flow programming. Functions. I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example
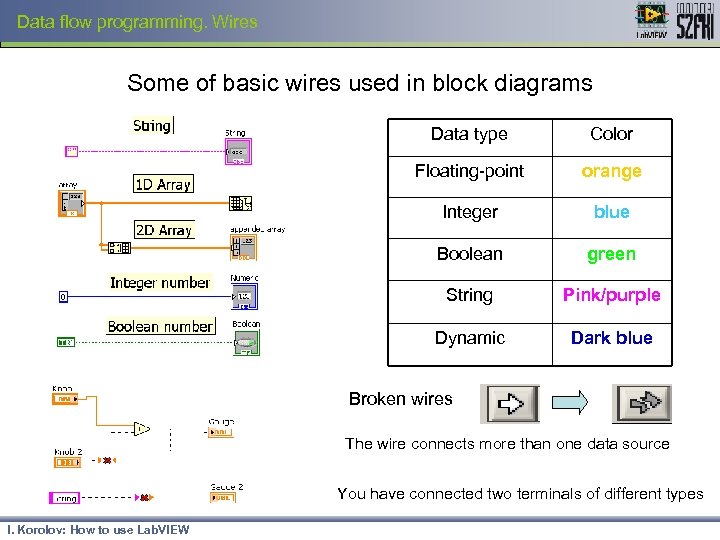
Data flow programming. Wires Some of basic wires used in block diagrams Data type Color Floating-point orange Integer blue Boolean green String Pink/purple Dynamic Dark blue Broken wires The wire connects more than one data source You have connected two terminals of different types I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
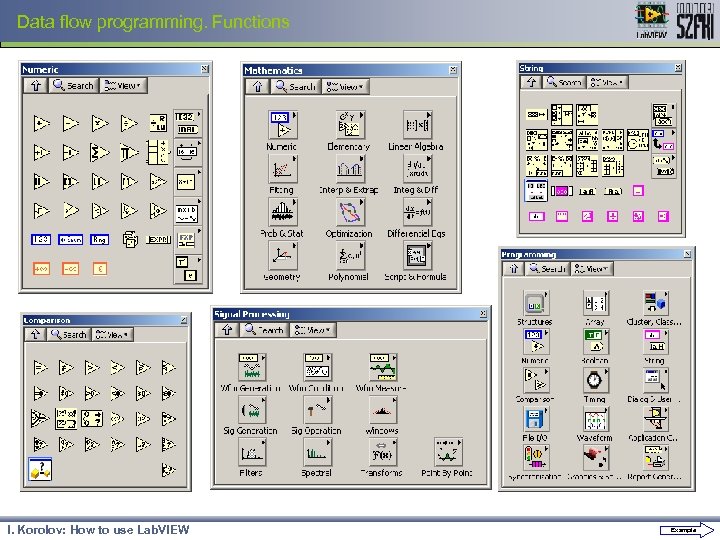
Data flow programming. Functions I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example
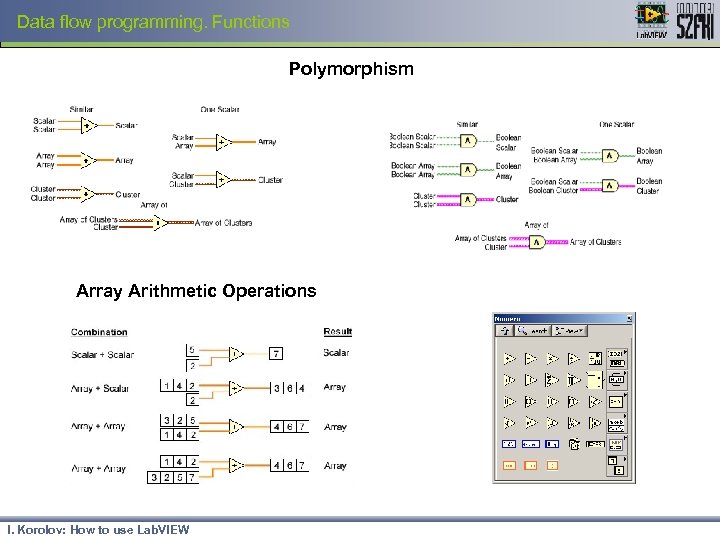
Data flow programming. Functions Polymorphism Array Arithmetic Operations I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW

Programming structures I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
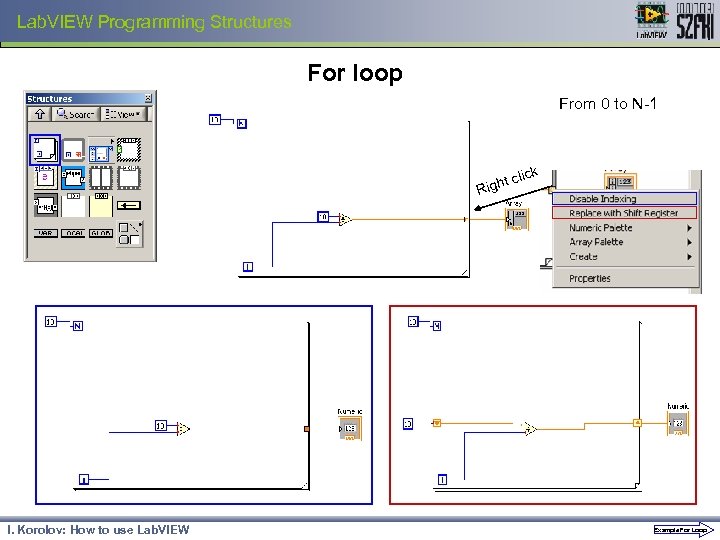
Lab. VIEW Programming Structures For loop From 0 to N-1 click ight R I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example For Loop
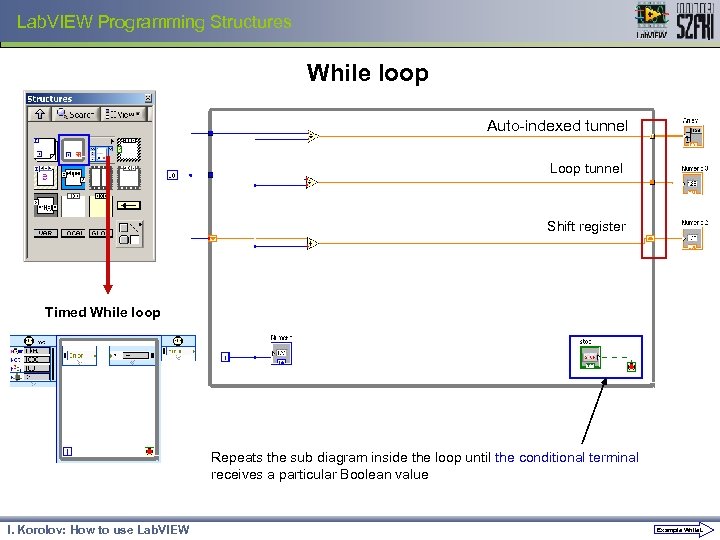
Lab. VIEW Programming Structures While loop Auto-indexed tunnel Loop tunnel Shift register Timed While loop Repeats the sub diagram inside the loop until the conditional terminal receives a particular Boolean value I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example While. L
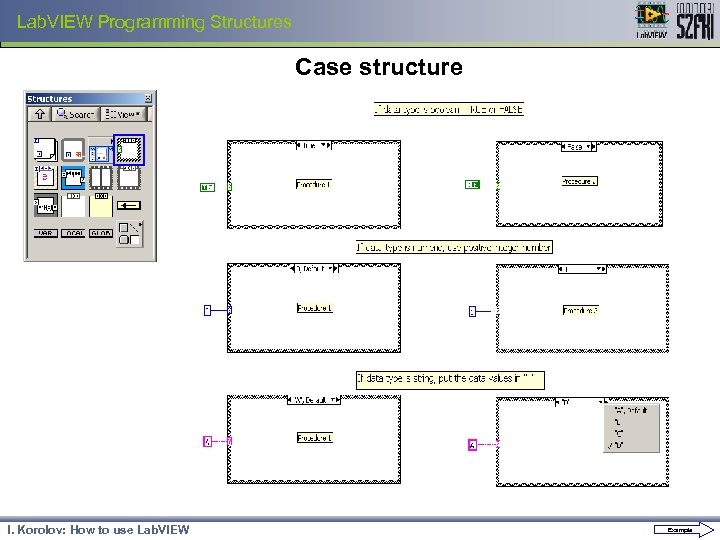
Lab. VIEW Programming Structures Case structure I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example
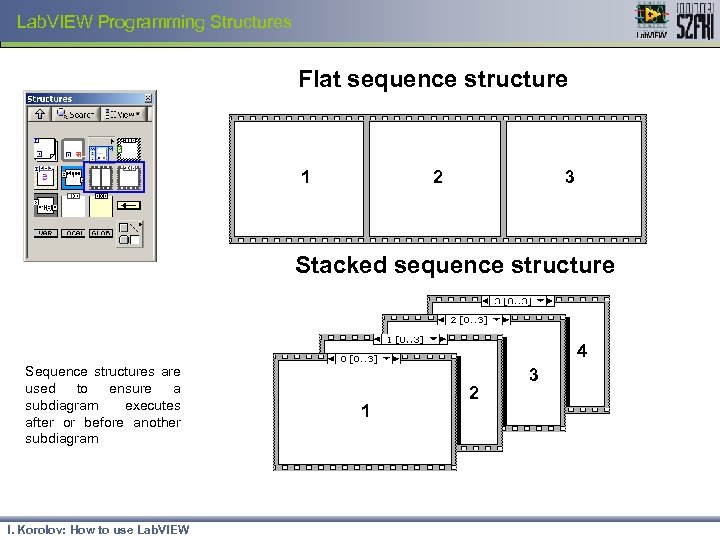
Lab. VIEW Programming Structures Flat sequence structure 1 2 3 Stacked sequence structure 4 Sequence structures are used to ensure a subdiagram executes after or before another subdiagram I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW 1 2 3
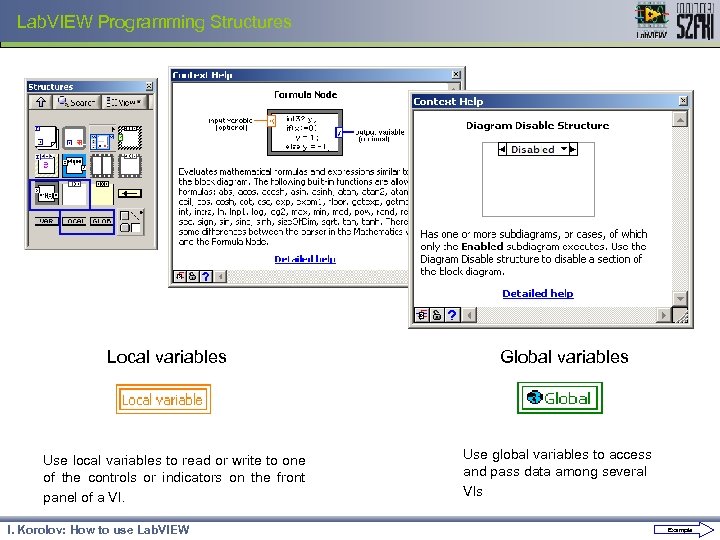
Lab. VIEW Programming Structures Local variables Use local variables to read or write to one of the controls or indicators on the front panel of a VI. I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Global variables Use global variables to access and pass data among several VIs Example
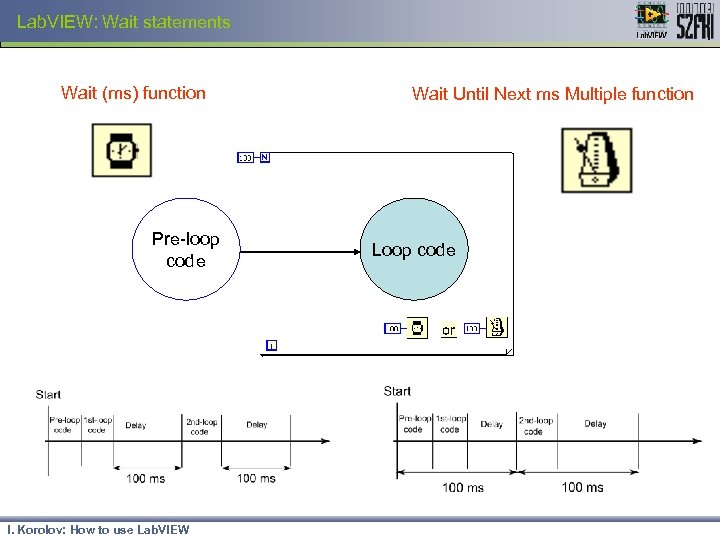
Lab. VIEW: Wait statements Wait (ms) function Pre-loop code I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Wait Until Next ms Multiple function Loop code
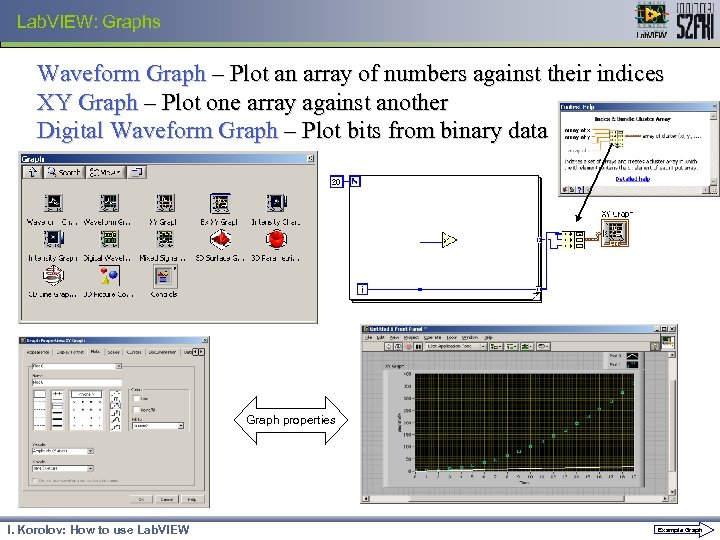
Lab. VIEW: Graphs Waveform Graph – Plot an array of numbers against their indices XY Graph – Plot one array against another Digital Waveform Graph – Plot bits from binary data Graph properties I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example Graph
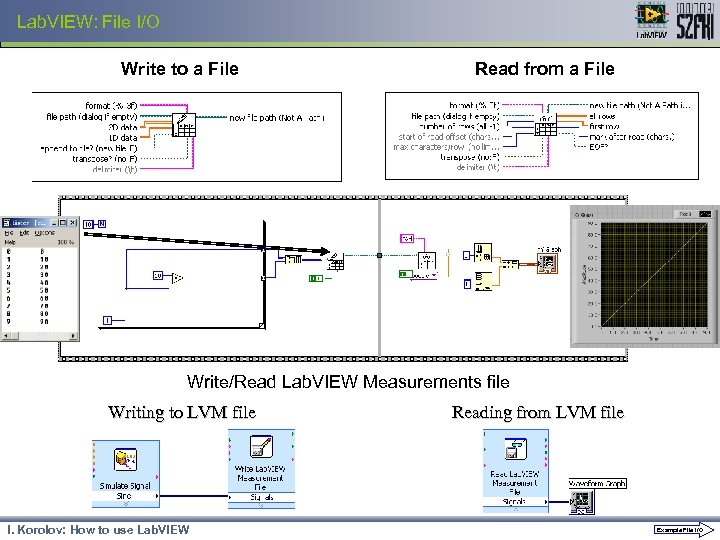
Lab. VIEW: File I/O Write to a File Read from a File Write/Read Lab. VIEW Measurements file Writing to LVM file I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Reading from LVM file Example File I/O

Sub. VI I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
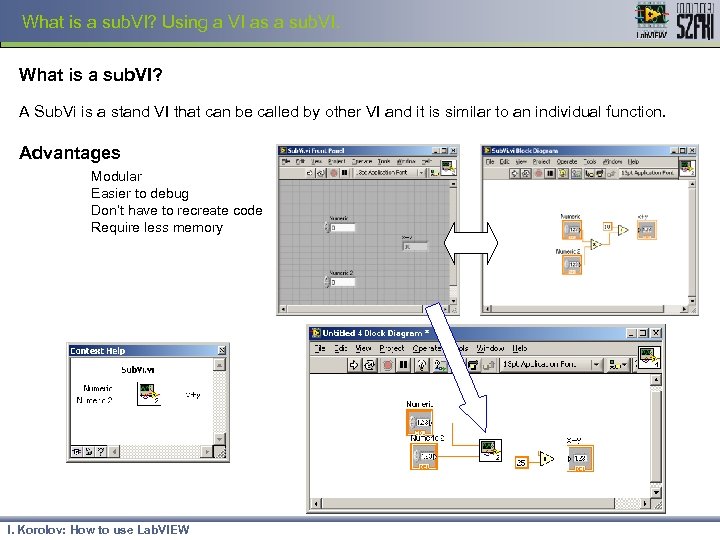
What is a sub. VI? Using a VI as a sub. VI. What is a sub. VI? A Sub. Vi is a stand VI that can be called by other VI and it is similar to an individual function. Advantages Modular Easier to debug Don’t have to recreate code Require less memory I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW

What is a sub. VI? Using a VI as a sub. VI. How to create a sub. VI? A Sub. Vi is a stand VI that can be called by other VI and it is similar to an individual function. ü Create/Edit the Icon ü Create the Connector ü Assign Terminals to controls and indicators ü Add description (optional) ü Save the VI ü Insert the VI into a Top Level VI 1 Create/Edit the Icon Right-click on the icon in the block diagram or front panel I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
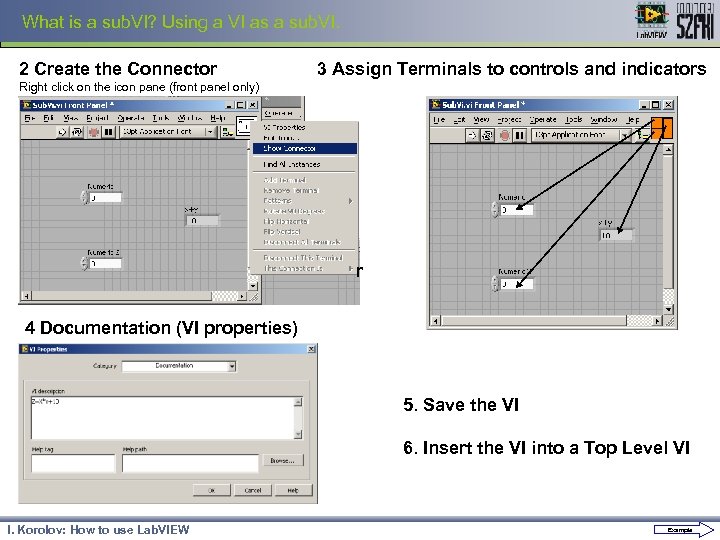
What is a sub. VI? Using a VI as a sub. VI. 2 Create the Connector 3 Assign Terminals to controls and indicators Right click on the icon pane (front panel only) r 4 Documentation (VI properties) 5. Save the VI 6. Insert the VI into a Top Level VI I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example

Data acquisition I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
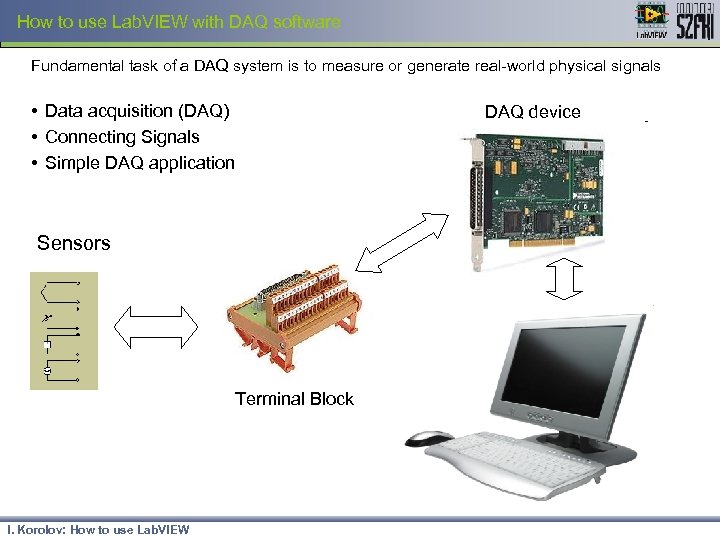
How to use Lab. VIEW with DAQ software Fundamental task of a DAQ system is to measure or generate real-world physical signals • Data acquisition (DAQ) • Connecting Signals • Simple DAQ application DAQ device Sensors Terminal Block I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
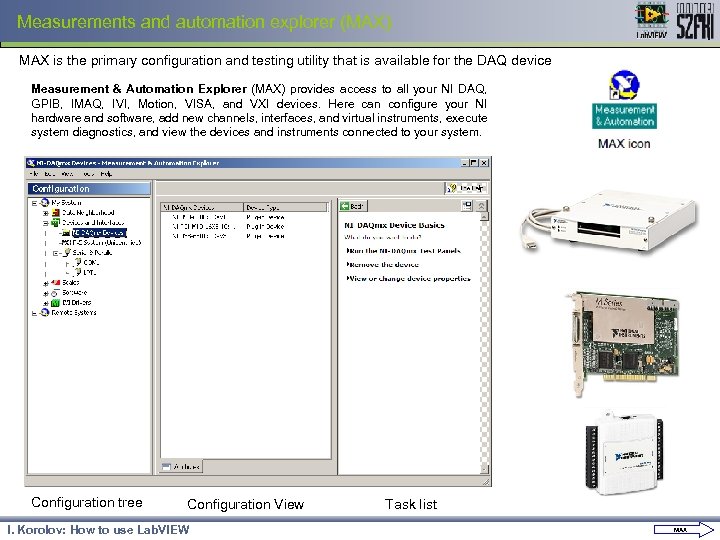
Measurements and automation explorer (MAX) MAX is the primary configuration and testing utility that is available for the DAQ device Measurement & Automation Explorer (MAX) provides access to all your NI DAQ, GPIB, IMAQ, IVI, Motion, VISA, and VXI devices. Here can configure your NI hardware and software, add new channels, interfaces, and virtual instruments, execute system diagnostics, and view the devices and instruments connected to your system. Configuration tree Configuration View I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Task list MAX
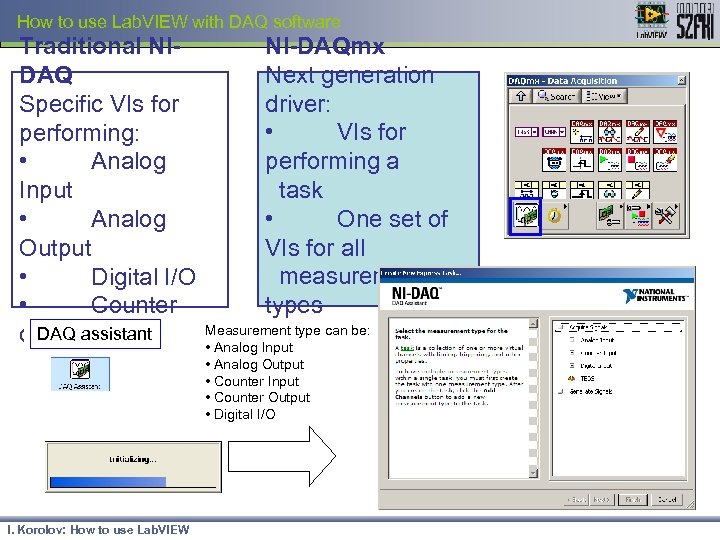
How to use Lab. VIEW with DAQ software Traditional NIDAQ Specific VIs for performing: • Analog Input • Analog Output • Digital I/O • Counter DAQ assistant operations I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW NI-DAQmx Next generation driver: • VIs for performing a task • One set of VIs for all measurement types Measurement type can be: • Analog Input • Analog Output • Counter Input • Counter Output • Digital I/O
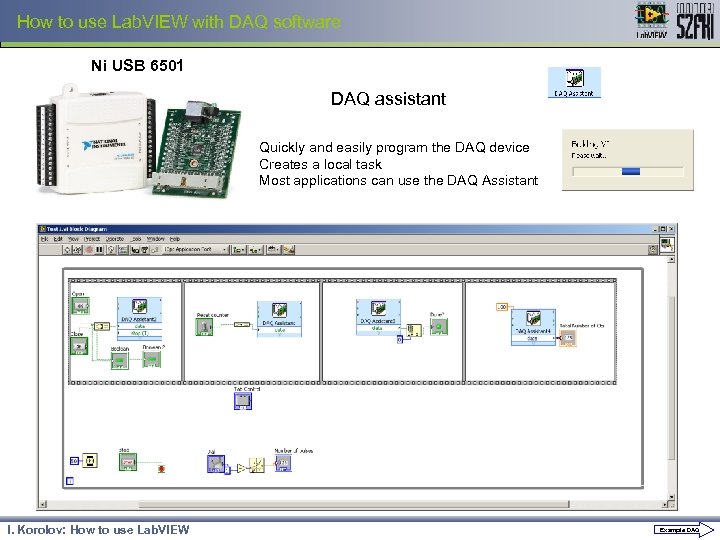
How to use Lab. VIEW with DAQ software Ni USB 6501 DAQ assistant Quickly and easily program the DAQ device Creates a local task Most applications can use the DAQ Assistant I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW Example DAQ

How to use Lab. VIEW ? Tips and tricks q GPIB Communication and Configuration q Virtual Instrument Software Architecture (VISA) Serial Port Communication q Instrument Drivers (How to create and use *. dll in Lab. VIEW) q Application control (property node and invoke node) q How to execute a system command q Remote panel connection manager and Web publishing tool q … I. Korolov: How to use Lab. VIEW
9c55a18f480b2fbb49feb121ee550867.ppt