cf13c21dea5f680641e1dffcb0c2782b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 How to use ISA 95 part 3 for MES functional URS Jean Vieille www. psynapses. net/vieille
How to use ISA 95 part 3 for MES functional URS Jean Vieille www. psynapses. net/vieille
 Agenda • • What’s wrong with MES and URS? ISA 95 part 3 functional framework Methodology Conclusion
Agenda • • What’s wrong with MES and URS? ISA 95 part 3 functional framework Methodology Conclusion
 MES: between Business and Manufacturing • MES is a fuzzy area: – IT/Business community hardly understand actual manufacturing control constraints and needs – Control community doesn’t catch business mind, • MES – Crosses business processes, business tasks and control tasks – Encompassed production, quality, maintenance, and inventory execution control • Not a complex technical issue – Compared to automation: no fancy algorithmic, multipath sequencing… • However – Structure requirements and assessment process takes a unique mixture of skill sets and years of study and practice
MES: between Business and Manufacturing • MES is a fuzzy area: – IT/Business community hardly understand actual manufacturing control constraints and needs – Control community doesn’t catch business mind, • MES – Crosses business processes, business tasks and control tasks – Encompassed production, quality, maintenance, and inventory execution control • Not a complex technical issue – Compared to automation: no fancy algorithmic, multipath sequencing… • However – Structure requirements and assessment process takes a unique mixture of skill sets and years of study and practice
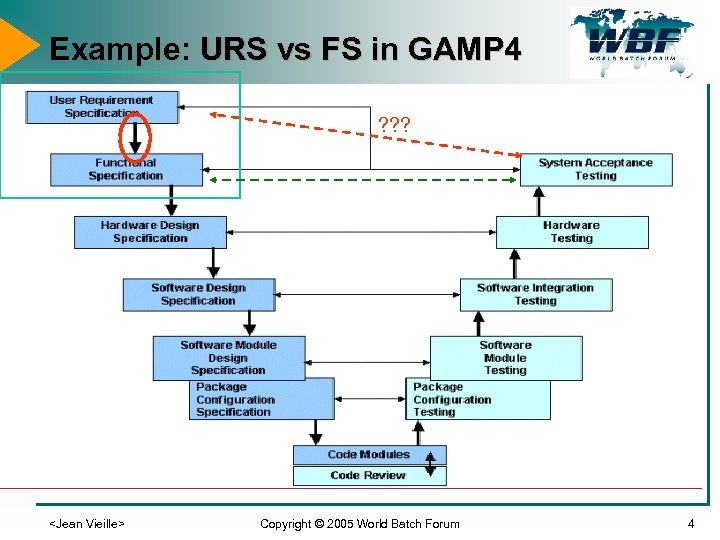 Example: URS vs FS in GAMP 4 ? ? ?
Example: URS vs FS in GAMP 4 ? ? ?
 Agenda • • What’s wrong with MES and URS? ISA 95 part 3 functional framework Methodology Conclusion
Agenda • • What’s wrong with MES and URS? ISA 95 part 3 functional framework Methodology Conclusion
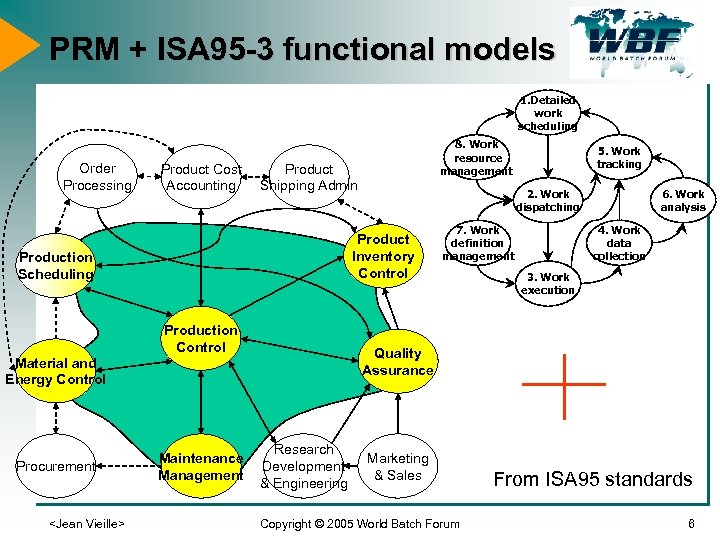 PRM + ISA 95 -3 functional models 1. Detailed work scheduling Order Processing Product Cost Accounting Product Shipping Admin Production Control
PRM + ISA 95 -3 functional models 1. Detailed work scheduling Order Processing Product Cost Accounting Product Shipping Admin Production Control
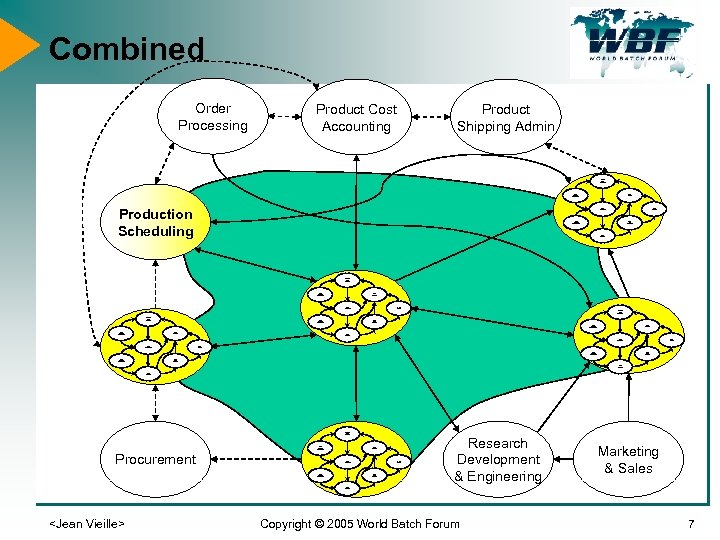 Combined Order Processing Product Cost Accounting Product Shipping Admin Detailed work scheduling Work resource management Production Scheduling Work tracking Work dispatching Work analysis Work data collection Work definition management Work execution Detailed work scheduling Work resource management Work tracking Work dispatching Work analysis Detailed work scheduling Work data collection Work definition management Work resource management Work tracking Work execution Work dispatching Work analysis Work data collection Work definition management Work execution Detailed work scheduling Work resource management Procurement Work tracking Work dispatching Work analysis Work data collection Work definition management Research Development & Engineering Marketing & Sales Work execution
Combined Order Processing Product Cost Accounting Product Shipping Admin Detailed work scheduling Work resource management Production Scheduling Work tracking Work dispatching Work analysis Work data collection Work definition management Work execution Detailed work scheduling Work resource management Work tracking Work dispatching Work analysis Detailed work scheduling Work data collection Work definition management Work resource management Work tracking Work execution Work dispatching Work analysis Work data collection Work definition management Work execution Detailed work scheduling Work resource management Procurement Work tracking Work dispatching Work analysis Work data collection Work definition management Research Development & Engineering Marketing & Sales Work execution
 Beyond Production • ISA 95 Part 3 defines the following Manufacturing Operation Categories (MOCs): – – Production Quality tests Maintenance Inventory control • Other or different MOCs can be defined. Example: – – – Distribution, Transportation Inbound, Outbound logistics, Internal transfers Tooling Cleaning … • It’s all about execution! • Advanced MES solutions take care of many aspects of product manufacturing and handling
Beyond Production • ISA 95 Part 3 defines the following Manufacturing Operation Categories (MOCs): – – Production Quality tests Maintenance Inventory control • Other or different MOCs can be defined. Example: – – – Distribution, Transportation Inbound, Outbound logistics, Internal transfers Tooling Cleaning … • It’s all about execution! • Advanced MES solutions take care of many aspects of product manufacturing and handling
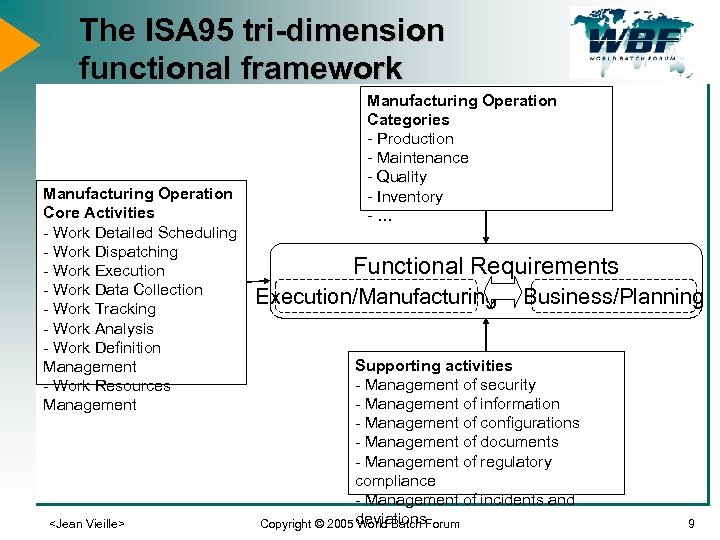 The ISA 95 tri-dimension functional framework Manufacturing Operation Core Activities - Work Detailed Scheduling - Work Dispatching - Work Execution - Work Data Collection - Work Tracking - Work Analysis - Work Definition Management - Work Resources Management
The ISA 95 tri-dimension functional framework Manufacturing Operation Core Activities - Work Detailed Scheduling - Work Dispatching - Work Execution - Work Data Collection - Work Tracking - Work Analysis - Work Definition Management - Work Resources Management
 Agenda • • What’s wrong with MES and URS? ISA 95 part 3 functional framework Methodology Conclusion
Agenda • • What’s wrong with MES and URS? ISA 95 part 3 functional framework Methodology Conclusion
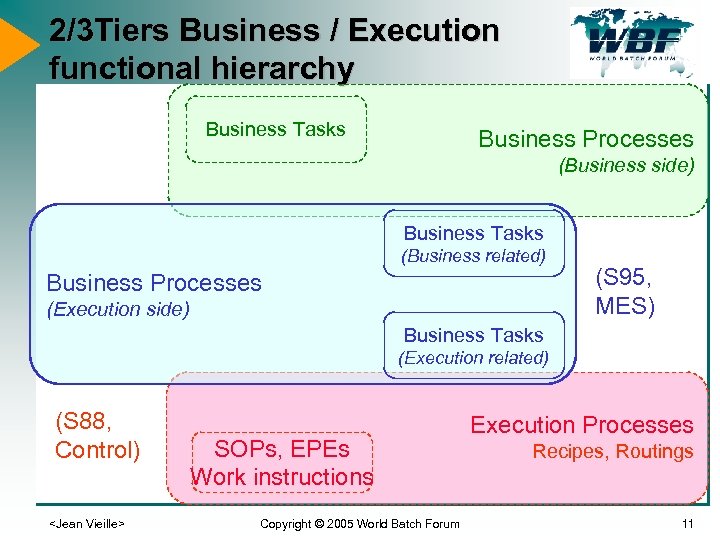 2/3 Tiers Business / Execution functional hierarchy Business Tasks Business Processes (Business side) Business Tasks (Business related) Business Processes (Execution side) (S 95, MES) Business Tasks (Execution related) (S 88, Control)
2/3 Tiers Business / Execution functional hierarchy Business Tasks Business Processes (Business side) Business Tasks (Business related) Business Processes (Execution side) (S 95, MES) Business Tasks (Execution related) (S 88, Control)
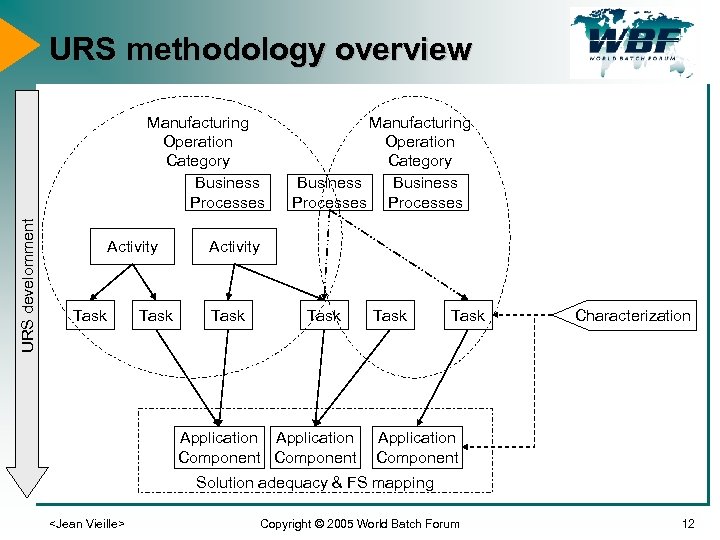 URS methodology overview URS develomment Manufacturing Operation Category Business Processes Activity Task Application Component Task Characterization Application Component Solution adequacy & FS mapping
URS methodology overview URS develomment Manufacturing Operation Category Business Processes Activity Task Application Component Task Characterization Application Component Solution adequacy & FS mapping
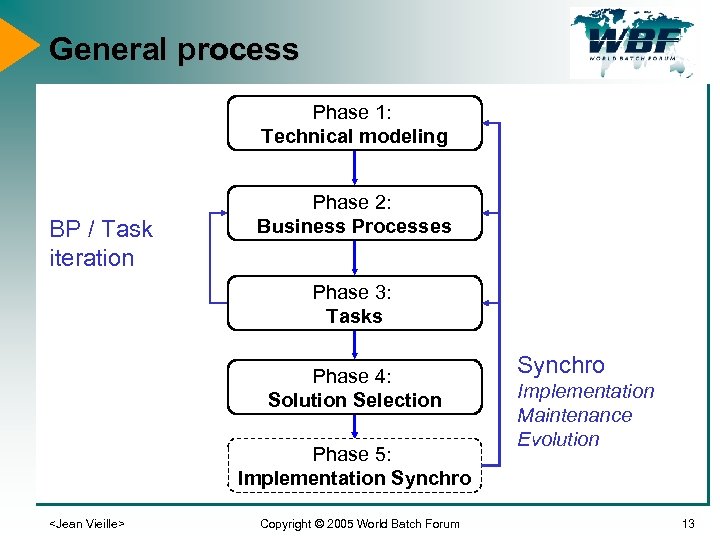 General process Phase 1: Technical modeling BP / Task iteration Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro
General process Phase 1: Technical modeling BP / Task iteration Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro
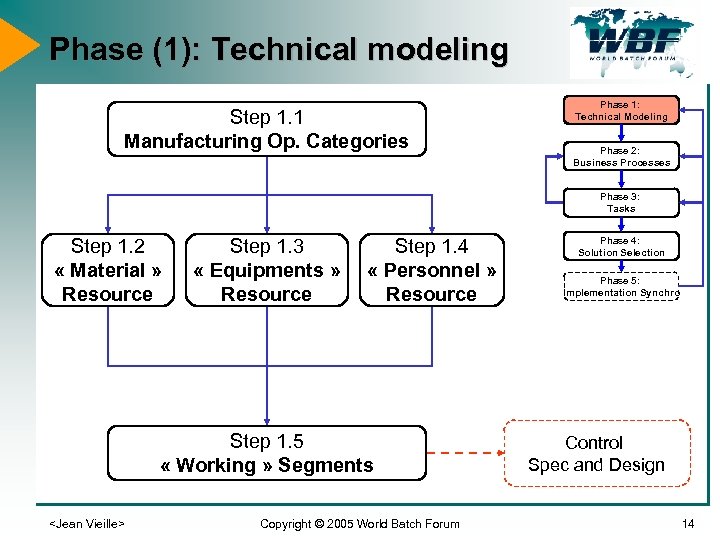 Phase (1): Technical modeling Step 1. 1 Manufacturing Op. Categories Phase 1: Technical Modeling Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Step 1. 2 « Material » Resource Step 1. 3 « Equipments » Resource Step 1. 4 « Personnel » Resource Step 1. 5 « Working » Segments
Phase (1): Technical modeling Step 1. 1 Manufacturing Op. Categories Phase 1: Technical Modeling Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Step 1. 2 « Material » Resource Step 1. 3 « Equipments » Resource Step 1. 4 « Personnel » Resource Step 1. 5 « Working » Segments
 Phase (2): Business processes • The highest functional requirement level • They illustrate situations and tasks (functional services) activation scenarios • They can be manual, semi or fully automated • They can be hierarchic – High level processes activate lower level processes – Elementary processes are tasks… Phase 1: Technical Modeling Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro • They can be compared to Manufacturing processes : ISA 88 Recipes (BP) activating EPEs (tasks)
Phase (2): Business processes • The highest functional requirement level • They illustrate situations and tasks (functional services) activation scenarios • They can be manual, semi or fully automated • They can be hierarchic – High level processes activate lower level processes – Elementary processes are tasks… Phase 1: Technical Modeling Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro • They can be compared to Manufacturing processes : ISA 88 Recipes (BP) activating EPEs (tasks)
 Business processes classification Phase 1: Technical Modeling 1. Execution management – Work organization and execution – MOC specific or shared Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks 2. Resources management – Resources, not work related activities 3. Operations management Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro – Dashboards, performance indicators, activity reports not specifically linked to work orders 4. Repository synchronization Depend on business management options
Business processes classification Phase 1: Technical Modeling 1. Execution management – Work organization and execution – MOC specific or shared Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks 2. Resources management – Resources, not work related activities 3. Operations management Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro – Dashboards, performance indicators, activity reports not specifically linked to work orders 4. Repository synchronization Depend on business management options
 BPs highlight interfaces requirements • Some processes are shared – Between several MOCs – Between Business and Execution • These situations indicates communication links and likely transactions.
BPs highlight interfaces requirements • Some processes are shared – Between several MOCs – Between Business and Execution • These situations indicates communication links and likely transactions.
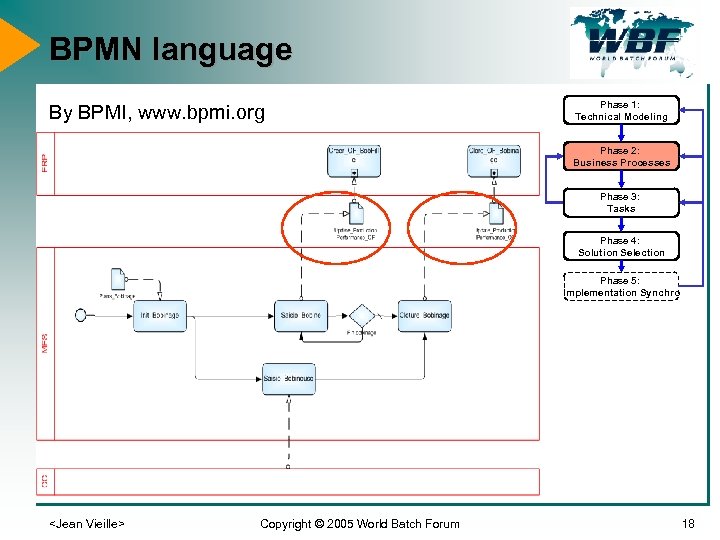 BPMN language By BPMI, www. bpmi. org Phase 1: Technical Modeling Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro
BPMN language By BPMI, www. bpmi. org Phase 1: Technical Modeling Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro
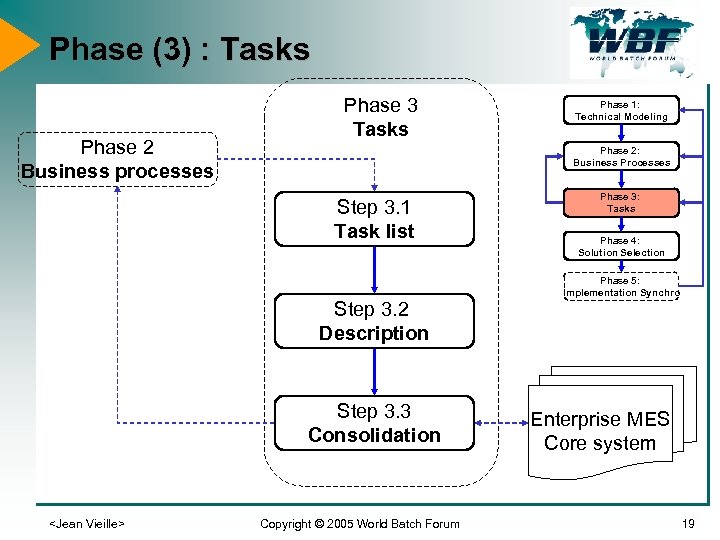 Phase (3) : Tasks Phase 2 Business processes Phase 3 Tasks Phase 1: Technical Modeling Phase 2: Business Processes Step 3. 1 Task list Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro Step 3. 2 Description Step 3. 3 Consolidation
Phase (3) : Tasks Phase 2 Business processes Phase 3 Tasks Phase 1: Technical Modeling Phase 2: Business Processes Step 3. 1 Task list Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro Step 3. 2 Description Step 3. 3 Consolidation
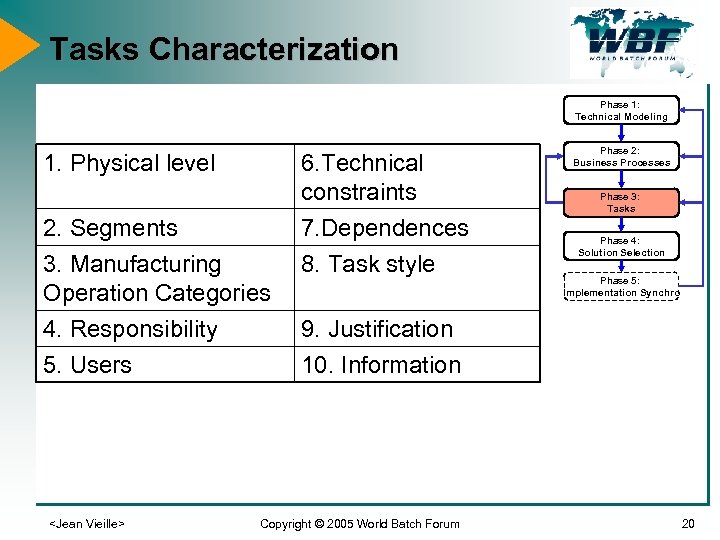 Tasks Characterization Phase 1: Technical Modeling 1. Physical level 6. Technical constraints 2. Segments 7. Dependences 3. Manufacturing Operation Categories 8. Task style 4. Responsibility Phase 3: Tasks 9. Justification 5. Users Phase 2: Business Processes 10. Information
Tasks Characterization Phase 1: Technical Modeling 1. Physical level 6. Technical constraints 2. Segments 7. Dependences 3. Manufacturing Operation Categories 8. Task style 4. Responsibility Phase 3: Tasks 9. Justification 5. Users Phase 2: Business Processes 10. Information
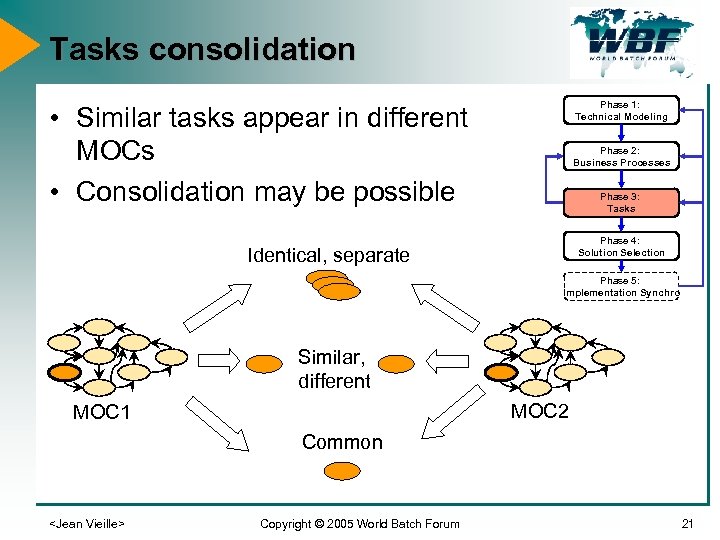 Tasks consolidation Phase 1: Technical Modeling • Similar tasks appear in different MOCs • Consolidation may be possible Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Identical, separate Phase 5: Implementation Synchro Similar, different MOC 2 MOC 1 Common
Tasks consolidation Phase 1: Technical Modeling • Similar tasks appear in different MOCs • Consolidation may be possible Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Identical, separate Phase 5: Implementation Synchro Similar, different MOC 2 MOC 1 Common
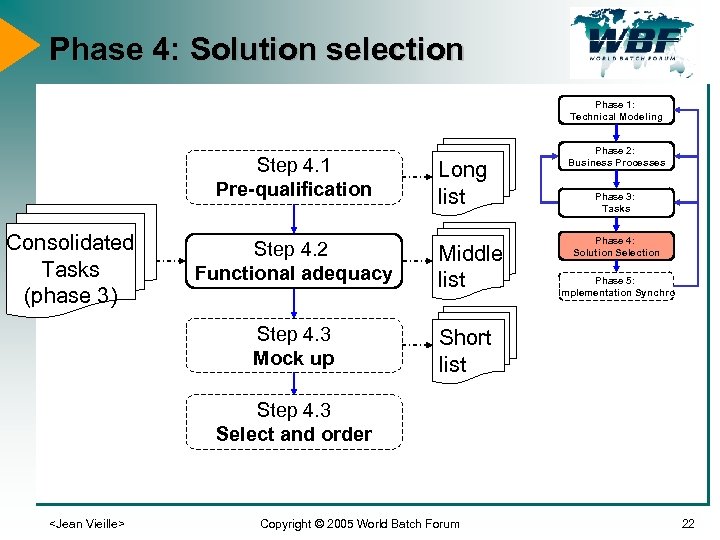 Phase 4: Solution selection Phase 1: Technical Modeling Step 4. 1 Pre-qualification Consolidated Tasks (phase 3) Long list Step 4. 2 Functional adequacy Middle list Step 4. 3 Mock up Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Short list Phase 5: Implementation Synchro Step 4. 3 Select and order
Phase 4: Solution selection Phase 1: Technical Modeling Step 4. 1 Pre-qualification Consolidated Tasks (phase 3) Long list Step 4. 2 Functional adequacy Middle list Step 4. 3 Mock up Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Short list Phase 5: Implementation Synchro Step 4. 3 Select and order
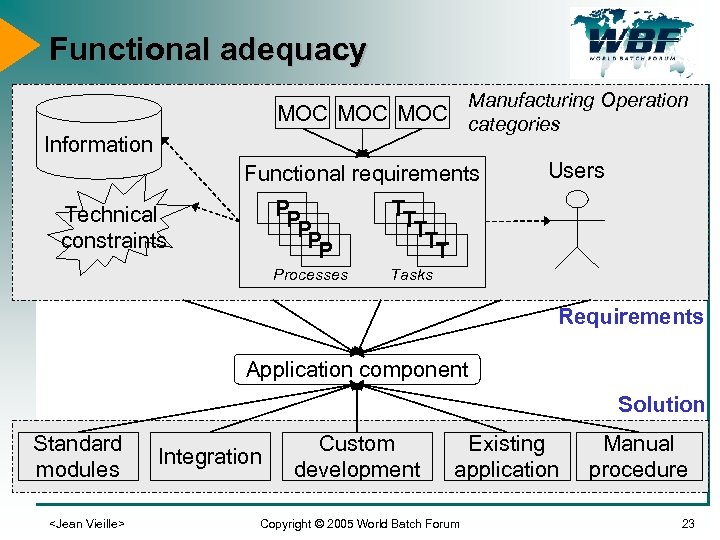 Functional adequacy Manufacturing Operation MOC MOC categories Information Functional requirements PP PP P TT TT T Processes Technical constraints Users Tasks Requirements Application component Solution Standard modules
Functional adequacy Manufacturing Operation MOC MOC categories Information Functional requirements PP PP P TT TT T Processes Technical constraints Users Tasks Requirements Application component Solution Standard modules
 Agenda • • What’s wrong with MES and URS? ISA 95 part 3 functional framework Methodology Conclusion
Agenda • • What’s wrong with MES and URS? ISA 95 part 3 functional framework Methodology Conclusion
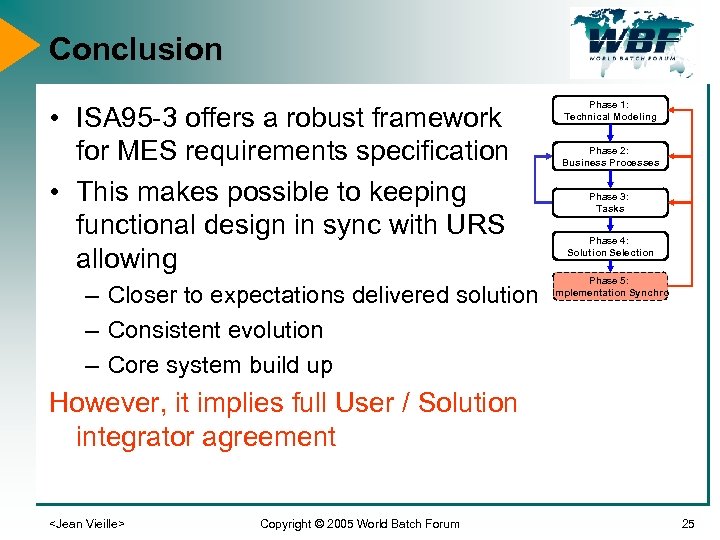 Conclusion • ISA 95 -3 offers a robust framework for MES requirements specification • This makes possible to keeping functional design in sync with URS allowing – Closer to expectations delivered solution – Consistent evolution – Core system build up Phase 1: Technical Modeling Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro However, it implies full User / Solution integrator agreement
Conclusion • ISA 95 -3 offers a robust framework for MES requirements specification • This makes possible to keeping functional design in sync with URS allowing – Closer to expectations delivered solution – Consistent evolution – Core system build up Phase 1: Technical Modeling Phase 2: Business Processes Phase 3: Tasks Phase 4: Solution Selection Phase 5: Implementation Synchro However, it implies full User / Solution integrator agreement


