68471482f6ca3813f1f69ea3a59562e4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 How to design and refine effective EMR tools for CRC screening Gloria D. Coronado, Ph. D Beverly Green, MD, MPH
How to design and refine effective EMR tools for CRC screening Gloria D. Coronado, Ph. D Beverly Green, MD, MPH
 Technological advances
Technological advances
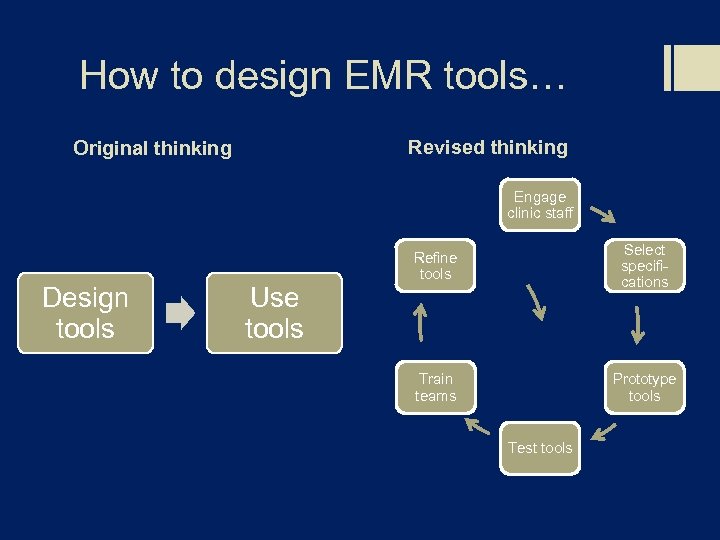 How to design EMR tools… Revised thinking Original thinking Engage clinic staff Design tools Use tools Refine tools Select specifications Train teams Prototype tools Test tools
How to design EMR tools… Revised thinking Original thinking Engage clinic staff Design tools Use tools Refine tools Select specifications Train teams Prototype tools Test tools
 Key messages § How to build effective EMR tools: § Assemble your team; § Identify goals – save time, accurately identify patients, improve rates, avoid unintended consequences – choose specifications; § Consider workflows and data sources § Anticipate unintended consequences § Train, re-train § Revise workflows and tools § PDSA § EMR work sessions
Key messages § How to build effective EMR tools: § Assemble your team; § Identify goals – save time, accurately identify patients, improve rates, avoid unintended consequences – choose specifications; § Consider workflows and data sources § Anticipate unintended consequences § Train, re-train § Revise workflows and tools § PDSA § EMR work sessions
 https: //www. kpchr. org/stopcrc/public/stopcrcpublic. aspx? pageid=10&Site. ID=1
https: //www. kpchr. org/stopcrc/public/stopcrcpublic. aspx? pageid=10&Site. ID=1
 Assemble your team § Leadership buy-in § Clinical staff (providers, MAs, front desk staff, etc. ) § Quality improvement leads for testing § Training, and re-training
Assemble your team § Leadership buy-in § Clinical staff (providers, MAs, front desk staff, etc. ) § Quality improvement leads for testing § Training, and re-training
 Select design specifications § What is important? § What is possible? § Review what others have done Possible § Real-time data § Sustainability and long-term use § Rely on Health Maintenance and STOP CRC codes § Over time can rely on Health Maintenance § Automate as much as possible § Design could be used across EMR platforms Important
Select design specifications § What is important? § What is possible? § Review what others have done Possible § Real-time data § Sustainability and long-term use § Rely on Health Maintenance and STOP CRC codes § Over time can rely on Health Maintenance § Automate as much as possible § Design could be used across EMR platforms Important
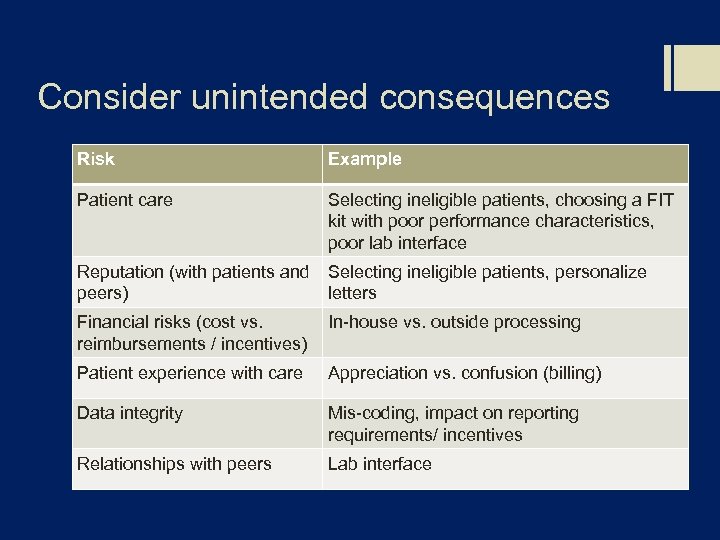 Consider unintended consequences Risk Example Patient care Selecting ineligible patients, choosing a FIT kit with poor performance characteristics, poor lab interface Reputation (with patients and Selecting ineligible patients, personalize peers) letters Financial risks (cost vs. reimbursements / incentives) In-house vs. outside processing Patient experience with care Appreciation vs. confusion (billing) Data integrity Mis-coding, impact on reporting requirements/ incentives Relationships with peers Lab interface
Consider unintended consequences Risk Example Patient care Selecting ineligible patients, choosing a FIT kit with poor performance characteristics, poor lab interface Reputation (with patients and Selecting ineligible patients, personalize peers) letters Financial risks (cost vs. reimbursements / incentives) In-house vs. outside processing Patient experience with care Appreciation vs. confusion (billing) Data integrity Mis-coding, impact on reporting requirements/ incentives Relationships with peers Lab interface
 Think about workflows and data sources… Original thinking Revised thinking
Think about workflows and data sources… Original thinking Revised thinking
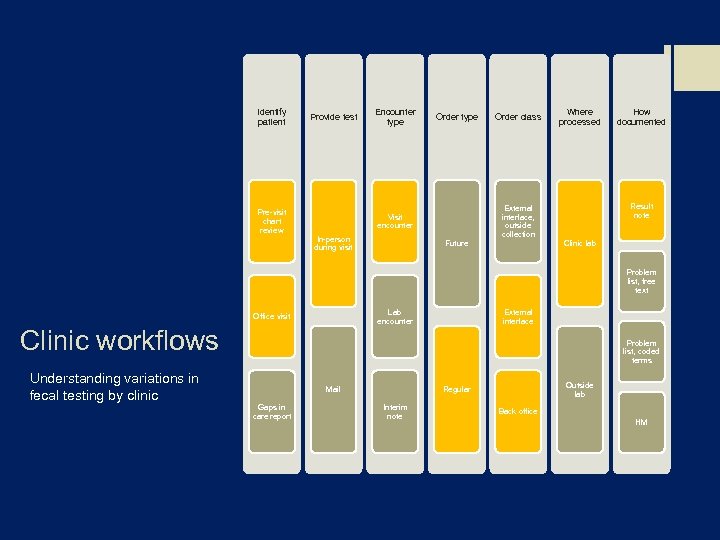 Identify patient Provide test Pre-visit chart review Encounter type Order type Where processed Future How documented Result note External interface, outside collection Visit encounter In-person during visit Order class Clinic lab Problem list, free text Lab encounter Office visit Clinic workflows Understanding variations in fecal testing by clinic External interface Problem list, coded terms Mail Gaps in care report Outside lab Regular Interim note Back office HM
Identify patient Provide test Pre-visit chart review Encounter type Order type Where processed Future How documented Result note External interface, outside collection Visit encounter In-person during visit Order class Clinic lab Problem list, free text Lab encounter Office visit Clinic workflows Understanding variations in fecal testing by clinic External interface Problem list, coded terms Mail Gaps in care report Outside lab Regular Interim note Back office HM
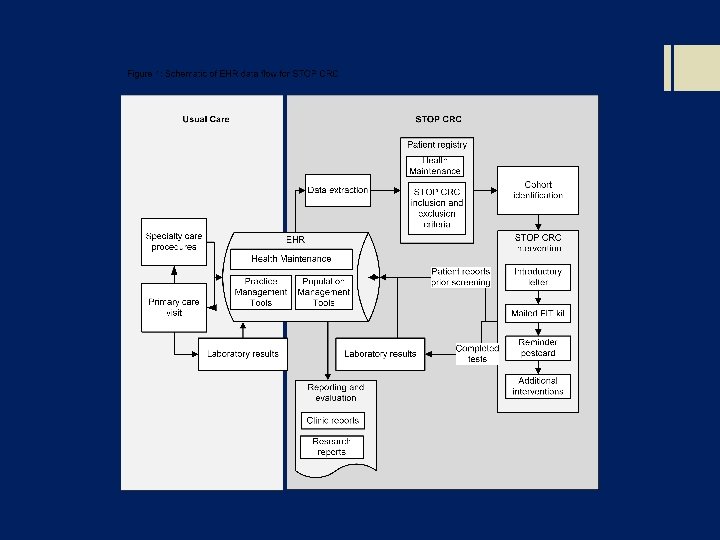
 Step 1: Mail Introductory letter Step-wise exclusions EMR tools in Reporting Workbench, driven by Health Maintenance; Step-wise exclusions for: • Invalid address • Self-reported prior screening • Completion of CRC screening Step 2: Mail FIT kit Step 3: Mail Reminder Postcard
Step 1: Mail Introductory letter Step-wise exclusions EMR tools in Reporting Workbench, driven by Health Maintenance; Step-wise exclusions for: • Invalid address • Self-reported prior screening • Completion of CRC screening Step 2: Mail FIT kit Step 3: Mail Reminder Postcard
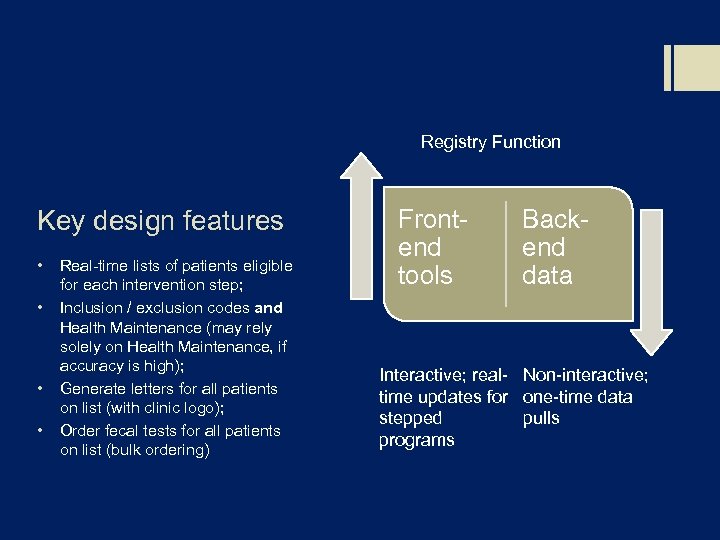 Registry Function Key design features • • Real-time lists of patients eligible for each intervention step; Inclusion / exclusion codes and Health Maintenance (may rely solely on Health Maintenance, if accuracy is high); Generate letters for all patients on list (with clinic logo); Order fecal tests for all patients on list (bulk ordering) Frontend tools Backend data Interactive; real- Non-interactive; time updates for one-time data stepped pulls programs
Registry Function Key design features • • Real-time lists of patients eligible for each intervention step; Inclusion / exclusion codes and Health Maintenance (may rely solely on Health Maintenance, if accuracy is high); Generate letters for all patients on list (with clinic logo); Order fecal tests for all patients on list (bulk ordering) Frontend tools Backend data Interactive; real- Non-interactive; time updates for one-time data stepped pulls programs
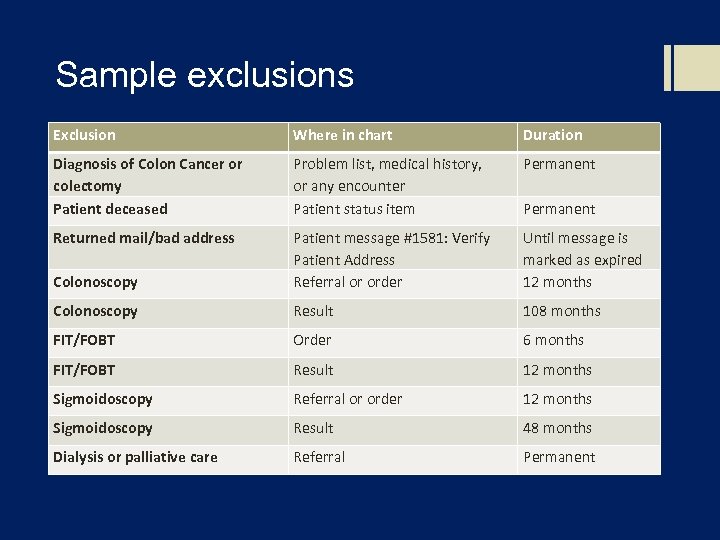 Sample exclusions Exclusion Where in chart Duration Diagnosis of Colon Cancer or colectomy Patient deceased Problem list, medical history, or any encounter Patient status item Permanent Returned mail/bad address Colonoscopy Patient message #1581: Verify Patient Address Referral or order Until message is marked as expired 12 months Colonoscopy Result 108 months FIT/FOBT Order 6 months FIT/FOBT Result 12 months Sigmoidoscopy Referral or order 12 months Sigmoidoscopy Result 48 months Dialysis or palliative care Referral Permanent
Sample exclusions Exclusion Where in chart Duration Diagnosis of Colon Cancer or colectomy Patient deceased Problem list, medical history, or any encounter Patient status item Permanent Returned mail/bad address Colonoscopy Patient message #1581: Verify Patient Address Referral or order Until message is marked as expired 12 months Colonoscopy Result 108 months FIT/FOBT Order 6 months FIT/FOBT Result 12 months Sigmoidoscopy Referral or order 12 months Sigmoidoscopy Result 48 months Dialysis or palliative care Referral Permanent
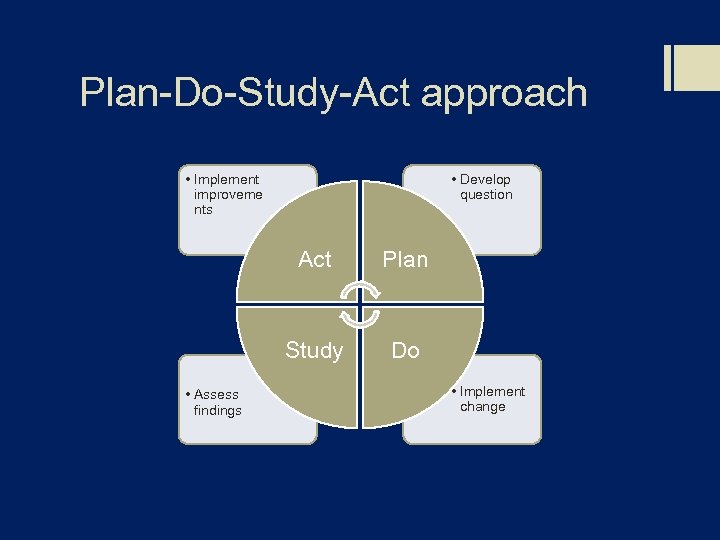 Plan-Do-Study-Act approach • Implement improveme nts • Develop question Act Study • Assess findings Plan Do • Implement change
Plan-Do-Study-Act approach • Implement improveme nts • Develop question Act Study • Assess findings Plan Do • Implement change
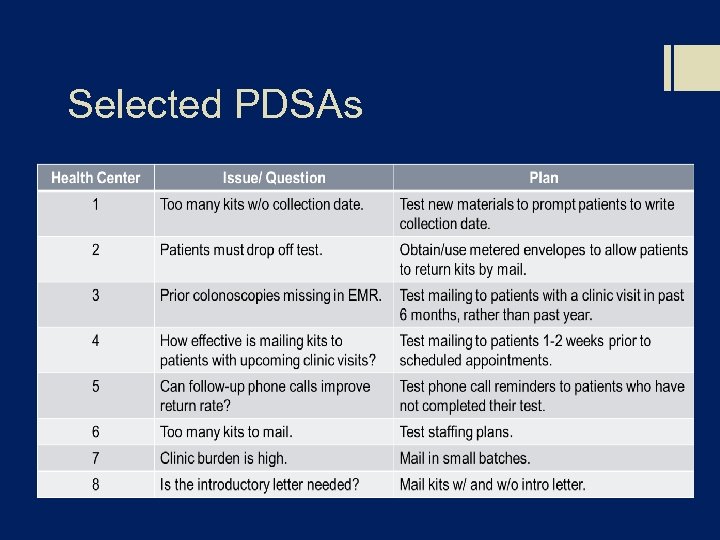 Selected PDSAs
Selected PDSAs
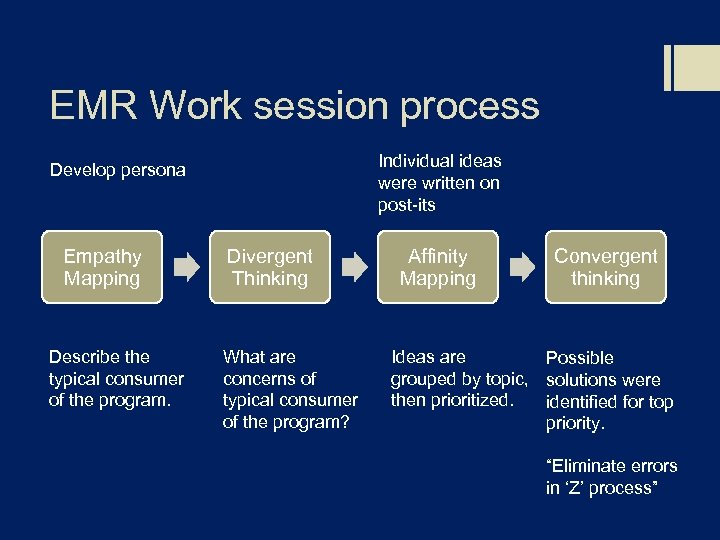 EMR Work session process Individual ideas were written on post-its Develop persona Empathy Mapping Describe the typical consumer of the program. Divergent Thinking What are concerns of typical consumer of the program? Affinity Mapping Convergent thinking Ideas are Possible grouped by topic, solutions were then prioritized. identified for top priority. “Eliminate errors in ‘Z’ process”
EMR Work session process Individual ideas were written on post-its Develop persona Empathy Mapping Describe the typical consumer of the program. Divergent Thinking What are concerns of typical consumer of the program? Affinity Mapping Convergent thinking Ideas are Possible grouped by topic, solutions were then prioritized. identified for top priority. “Eliminate errors in ‘Z’ process”
 Vote on the Most Important § § § Eliminate manual scrubbing and improve info at a glance Decrease time to mail kit Increase match between communication methods and patient preference Decrease number of reports Increase provider buy-in on FIT Kits Increase interoperability between modules (PL, Surg hx, HMA) Reduce time in searching for previous colonoscopy Improve process by eliminating printing delay Reduce time spent creating orders Reduce time and materials by increasing patient portal use. Reduce staff time by understanding individual status with a patient report
Vote on the Most Important § § § Eliminate manual scrubbing and improve info at a glance Decrease time to mail kit Increase match between communication methods and patient preference Decrease number of reports Increase provider buy-in on FIT Kits Increase interoperability between modules (PL, Surg hx, HMA) Reduce time in searching for previous colonoscopy Improve process by eliminating printing delay Reduce time spent creating orders Reduce time and materials by increasing patient portal use. Reduce staff time by understanding individual status with a patient report
 Conclusion § Multiple, iterative steps in designing and refining EMR tools for long-term use: § § § Assemble team Select specifications Develop and refine tools Train staff Repeat § Understanding clinic workflow and where data are stored in the EMR is important; § Start small, consider unintended consequences, and prepare for iterative process.
Conclusion § Multiple, iterative steps in designing and refining EMR tools for long-term use: § § § Assemble team Select specifications Develop and refine tools Train staff Repeat § Understanding clinic workflow and where data are stored in the EMR is important; § Start small, consider unintended consequences, and prepare for iterative process.
 Acknowledgments Funding source: NIH Common Fund [UH 2 AT 007782 and 4 UH 3 CA 188640 -02] and Kaiser Permanente Community Benefit § STOP CRC Research Team; § OCHIN; § Participating Clinics § STOP CRC Advisory Board
Acknowledgments Funding source: NIH Common Fund [UH 2 AT 007782 and 4 UH 3 CA 188640 -02] and Kaiser Permanente Community Benefit § STOP CRC Research Team; § OCHIN; § Participating Clinics § STOP CRC Advisory Board


