9828d152017fc13342e218b3fc888e74.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

How to Beat The High Cost of Obamacare Chief Executive Summit Kingsgate Marriott October 25, 2013

2010 Changes Tax Provisions Healthcare Provisions Certain small businesses with up to 25 employees get credit of up to 35% of the cost of providing employee health benefits Insurance companies cannot deny children coverage for pre-existing conditions Plans can no longer set lifetime limits on coverage 10% excise tax on indoor tanning services using certain UV lights Children can remain on parents’ plan until age 26 Medicare Part D recipients entering “donut hole” get $250 rebate

2011 Changes Tax Provisions Penalty tax for Health Savings Account/Medical Savings Account distributions not used for health care expenses doubles from 10% to 20%. Healthcare Provisions Medicare Part D recipients entering “donut hole” get 50% discount on certain prescriptions

2012 Changes Tax Provisions W 2 reporting requirements apply for employers with 250+ employees Healthcare Provisions Medical Loss Ratio rules require carriers to issue rebates if losses fall below 85% of premiums.
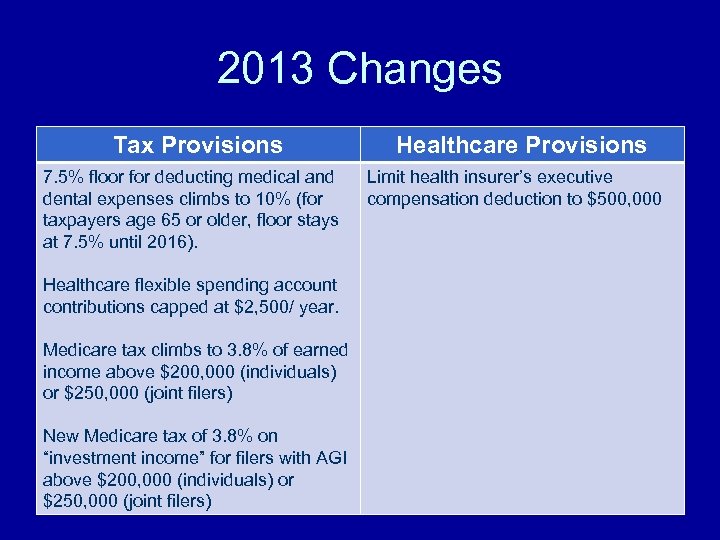
2013 Changes Tax Provisions Healthcare Provisions 7. 5% floor for deducting medical and Limit health insurer’s executive dental expenses climbs to 10% (for compensation deduction to $500, 000 taxpayers age 65 or older, floor stays at 7. 5% until 2016). Healthcare flexible spending account contributions capped at $2, 500/ year. Medicare tax climbs to 3. 8% of earned income above $200, 000 (individuals) or $250, 000 (joint filers) New Medicare tax of 3. 8% on “investment income” for filers with AGI above $200, 000 (individuals) or $250, 000 (joint filers)

2014 Changes Tax Provisions Most individuals must maintain “minimum essential coverage” or face penalties Healthcare Provisions Insurance companies cannot deny adults coverage for pre-existing conditions Businesses with >50 employees must Plans can no longer set annual limits offer health coverage or pay penalty of on coverage $2, 000/employee Medicaid expands to cover all Americans with income up to 133% of poverty line State-run insurance “exchanges” begin offering coverage to individuals and small businesses

2018 Changes Tax Provisions Impose 40% excise tax on “Cadillac plans” costing above $10, 200 (singles) or $27, 500 (families) Healthcare Provisions

Tax Credits for Employers • Must pay 50% of premium • <25 employees • <$50, 000 average wage

Tax Credits for Employers
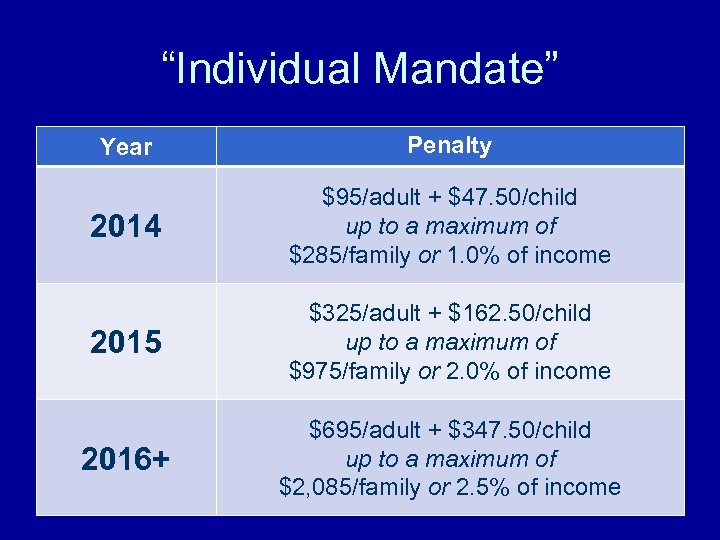
“Individual Mandate” Year Penalty 2014 $95/adult + $47. 50/child up to a maximum of $285/family or 1. 0% of income 2015 $325/adult + $162. 50/child up to a maximum of $975/family or 2. 0% of income 2016+ $695/adult + $347. 50/child up to a maximum of $2, 085/family or 2. 5% of income

Enforcing the Mandate “The penalty is assessed through the Code and accounted for as an additional amount of Federal tax owed. However, it is not subject to the enforcement provisions of subtitle F of the Code. The use of liens and seizures otherwise authorized for collection of taxes does not apply to the collection of this penalty. Non-compliance with the personal responsibility requirement to have health coverage is not subject to criminal or civil penalties under the Code and interest does not accrue for failure to pay such assessments in a timely manner. ” Joint Committee on Taxation

Insurance “Exchanges” • State or federal • Online comparison • Guaranteed issue
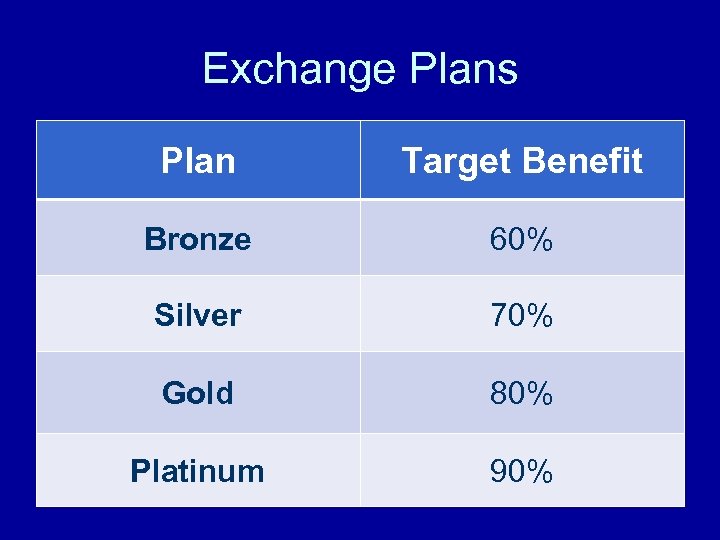
Exchange Plans Plan Target Benefit Bronze 60% Silver 70% Gold 80% Platinum 90%

Premium Subsidies • Household income < 400% poverty level • Premium > 9. 5% of “household income”
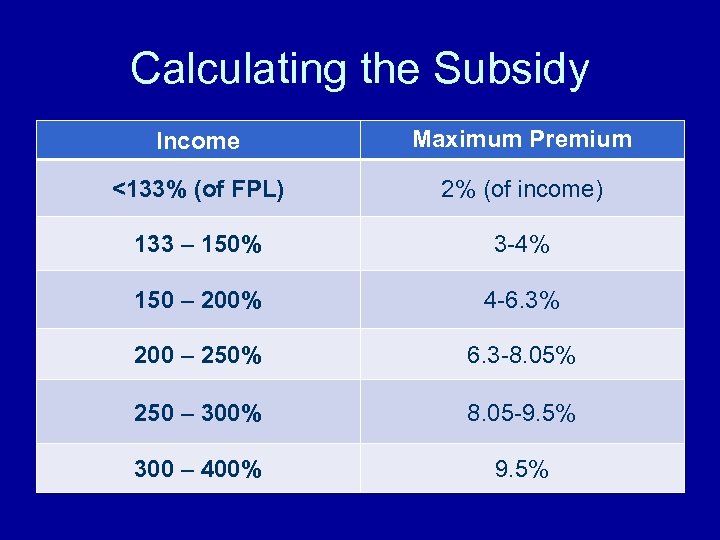
Calculating the Subsidy Income Maximum Premium <133% (of FPL) 2% (of income) 133 – 150% 3 -4% 150 – 200% 4 -6. 3% 200 – 250% 6. 3 -8. 05% 250 – 300% 8. 05 -9. 5% 300 – 400% 9. 5%

Employer Requirements Size Requirements <51 • No requirement to provide coverage • Employees qualify for subsidies on exchange >50 • Must cover those working 30+ hours/week • Must start coverage 90 days after hire • Subject to “free rider” penalty

Free-Rider Penalty Employer owes penalty if: • More than 50 employees or FTEs and. . . • One or more employees receives premium subsidies to buy insurance on an exchange
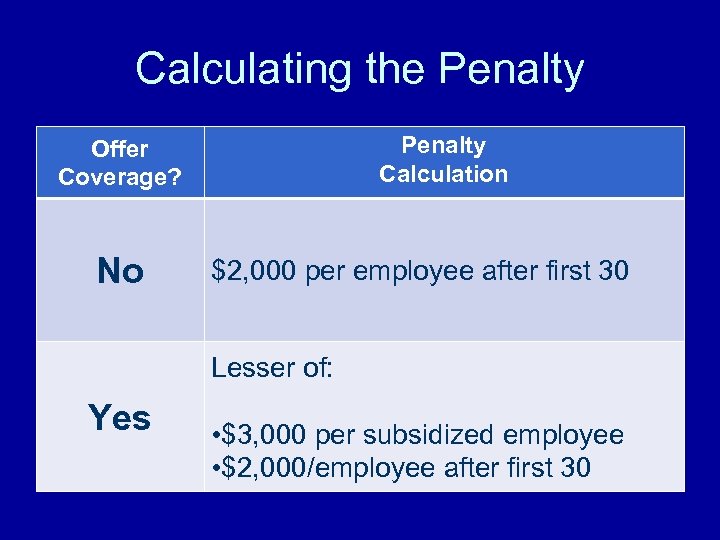
Calculating the Penalty Calculation Offer Coverage? No $2, 000 per employee after first 30 Lesser of: Yes • $3, 000 per subsidized employee • $2, 000/employee after first 30

Options for Individuals • • • Do nothing Keep current plan Turn to exchange MERP Health Savings Accounts

MERP/105 Plan • Employee benefit plan – Married: Hire spouse (no salary necessary) – Not married: C-corp • Reimburse employee for medical expenses incurred for self, spouse, and dependents • Works with any insurance – Choose your own – Supplement spouse’s coverage

MERP/105 Plan • Major medical, LTC, Medicare, “Medigap” • Co-pays, deductibles, prescriptions • Dental, vision, and chiropractic • Braces, fertility treatments, special schools • Nonprescription medications and supplies

MERP/105 Plan • Written plan document • No pre-funding required – Reimburse employee – Pay provider directly • Bypass 10% floor • Minimize self-employment tax

MERP/105 Plan • Must cover “eligible employees” • Exclusions – Under age 25 – Under 35 hours/week – Under 9 months/year – Under 3 years service – Collective bargaining agreement • Excise tax on Form 720

Health Savings Accounts 1. “High deductible health plan” - $1, 250+ deductible (individual coverage) - $2, 500+ deductible (family coverage) Plus 2. Tax-deductible “Health Savings Account” - Contribute & deduct up to $3, 250/$6, 450 per year - Account grows tax-free - Tax-free withdrawals for qualified expenses

Options for Employers (<51) • • Do nothing Keep current plan Cut employees loose Consider Medicaid/CHIP plans

Medicaid/CHIP • Medicaid available up to 138% of FPL • CHIP coverage typically available up to 200% of FPL • Coverage is free to employees

Options for Employers (51+) • Do nothing • Keep current plan • Modify current plan

Options for Self-Insured Plans • Cover costs directly • Buy stop-loss to limit risk • Use Obamacare to cut risk

New Medicare Taxes • 0. 9% Medicare surtax • $200, 000+ for individuals • $250, 000 for joint filers

“Unearned Income Medicare Contribution” • 3. 8% tax • Individuals >$200 k • Joint filers >$250 k “Investment Income” • Interest • Dividends • Capital gains • Rents • Royalties • Annuities

Avoid the Tax • Choose tax-efficient investments • Match gains and losses

Home Sales: Rumor vs. Reality Rumor • $475, 000 sale X 3. 8% tax rate = $ 18, 050 tax Reality • $475, 000 sale - $125, 000 “basis” - $ 50, 000 improvements - $250, 000 exclusion = $ 50, 000 gain X 3. 8% tax rate = $ 1, 900 tax

Red Tape Alert!

Who’s In Charge?

Continuing Challenges • Repeal efforts • State challenges/nullification • Congressional nullification

Where Do We Go From Here? • Track developments • Get the right advice
9828d152017fc13342e218b3fc888e74.ppt