e8f955068111485fb512f09514c59936.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57

 • How Do We Predict Weather? • General Weather Information Clouds, rain, thunderstorms, etc.
• How Do We Predict Weather? • General Weather Information Clouds, rain, thunderstorms, etc.
 What is the National Weather Service? ?
What is the National Weather Service? ?
 Organizational Structure… U. S. Department of Commerce (International Trade, US Business Growth, Aid in Technological Advancement) National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) (Climate, Ocean Life, Satellites, Research) National Weather Service (Forecasts, Warnings, River Data, Weather Safety)
Organizational Structure… U. S. Department of Commerce (International Trade, US Business Growth, Aid in Technological Advancement) National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) (Climate, Ocean Life, Satellites, Research) National Weather Service (Forecasts, Warnings, River Data, Weather Safety)
 What We Do Produce Weather, Water and Climate Forecasts and Warnings - For All Americans -To Protect Life and Property -To Enhance the National Economy Data and Products: - Government Agencies -Private Sector -The Public -Global Communities Weather and data are becoming more important to the economy and business decisions
What We Do Produce Weather, Water and Climate Forecasts and Warnings - For All Americans -To Protect Life and Property -To Enhance the National Economy Data and Products: - Government Agencies -Private Sector -The Public -Global Communities Weather and data are becoming more important to the economy and business decisions
 National Weather Service Our Primary Mission: The protection of lives and property Watches, warnings, and advisories for: -Severe Thunderstorms -Tornados -Floods -Flash Floods -Winter Storms
National Weather Service Our Primary Mission: The protection of lives and property Watches, warnings, and advisories for: -Severe Thunderstorms -Tornados -Floods -Flash Floods -Winter Storms
 Advisory: Just so you know… Watch: Stay Alert! Warning: Take Cover NOW!
Advisory: Just so you know… Watch: Stay Alert! Warning: Take Cover NOW!
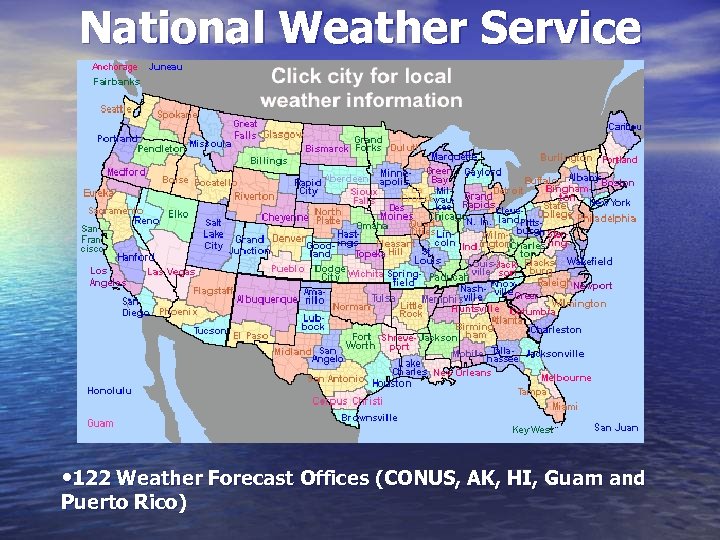 National Weather Service • 122 Weather Forecast Offices (CONUS, AK, HI, Guam and Puerto Rico)
National Weather Service • 122 Weather Forecast Offices (CONUS, AK, HI, Guam and Puerto Rico)
 National Weather Service Forecast Office Austin/San Antonio, TX
National Weather Service Forecast Office Austin/San Antonio, TX
 WEATHER FORECASTING This problem has two parts. . . Analyze: What’s going on right now? Forecast: What’s going to happen?
WEATHER FORECASTING This problem has two parts. . . Analyze: What’s going on right now? Forecast: What’s going to happen?
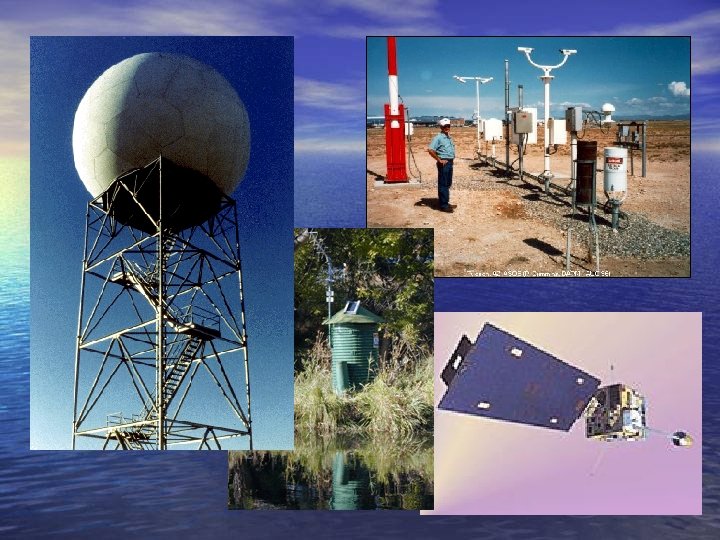

 Analyzing the Weather Surface Observations. . . mostly at airports. . . can be taken by people Or by machines such as the ASOS Automated Surface Observing System
Analyzing the Weather Surface Observations. . . mostly at airports. . . can be taken by people Or by machines such as the ASOS Automated Surface Observing System
 COOPERATIVE OBSERVERS • Volunteer weather observers • Daily temperature and precipitation reports • River level reports • Important for ground truth
COOPERATIVE OBSERVERS • Volunteer weather observers • Daily temperature and precipitation reports • River level reports • Important for ground truth
 Of course, we can’t forget radar! It can see father - with greater detail and more power than any other weather radar in the world!! So sensitive. . . it can detect birds. . . bats. . . bugs and pollen in the air. . . and leaves rustling on nearby trees.
Of course, we can’t forget radar! It can see father - with greater detail and more power than any other weather radar in the world!! So sensitive. . . it can detect birds. . . bats. . . bugs and pollen in the air. . . and leaves rustling on nearby trees.
 But observations are not limited to surface conditions. Aircraft reports of winds and weather are important. And observations from upper air balloons launched twice a day at around 120 sites are the basis of upper air analysis.
But observations are not limited to surface conditions. Aircraft reports of winds and weather are important. And observations from upper air balloons launched twice a day at around 120 sites are the basis of upper air analysis.
 Dozens of satellites keep a constant watch over the earth each day. Some are geosynchronous (stay in the same position over the earth) while others orbit around the earth.
Dozens of satellites keep a constant watch over the earth each day. Some are geosynchronous (stay in the same position over the earth) while others orbit around the earth.
 FORECASTING There are 3 basic methods of forecasting: • Persistence • Experience • Computer Modeling
FORECASTING There are 3 basic methods of forecasting: • Persistence • Experience • Computer Modeling
 PERSISTENCE: • Not much is going to change. • Tomorrow will be like today. • Works great in summer. • Not so good the rest of the year.
PERSISTENCE: • Not much is going to change. • Tomorrow will be like today. • Works great in summer. • Not so good the rest of the year.
 EXPERIENCE: • Forecast what was seen before to repeat. • This is good for 1 to 2 day forecasts. • Works great a lot of the time. • Problem when something new happens.
EXPERIENCE: • Forecast what was seen before to repeat. • This is good for 1 to 2 day forecasts. • Works great a lot of the time. • Problem when something new happens.
 MODELS: • They are better than people past 3 days. • Works great most of the time. • Problem when bad data gets put in or if something really new occurs.
MODELS: • They are better than people past 3 days. • Works great most of the time. • Problem when bad data gets put in or if something really new occurs.
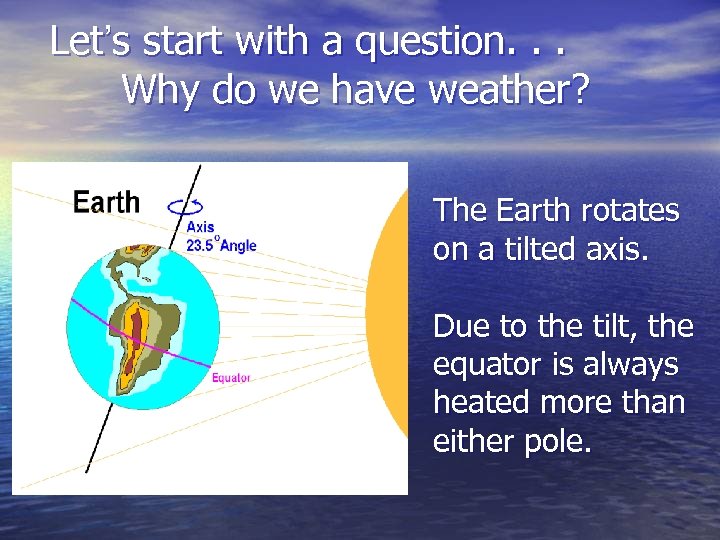 Let’s start with a question. . . Why do we have weather? The Earth rotates on a tilted axis. Due to the tilt, the equator is always heated more than either pole.
Let’s start with a question. . . Why do we have weather? The Earth rotates on a tilted axis. Due to the tilt, the equator is always heated more than either pole.
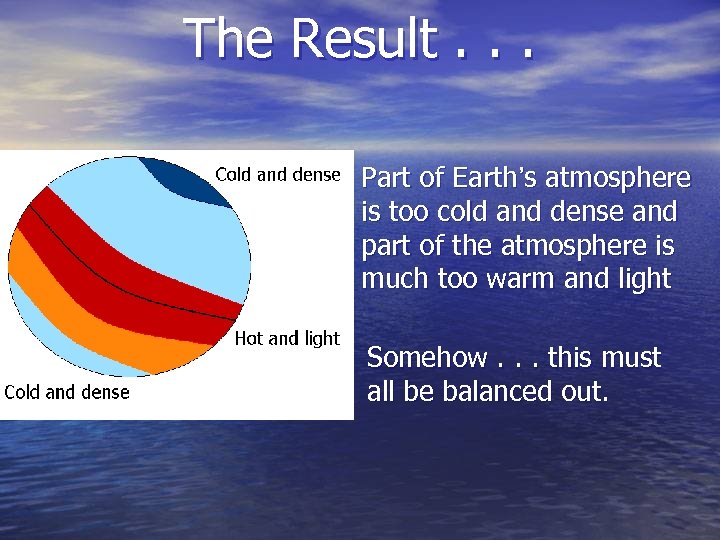 The Result. . . Part of Earth’s atmosphere is too cold and dense and part of the atmosphere is much too warm and light Somehow. . . this must all be balanced out.
The Result. . . Part of Earth’s atmosphere is too cold and dense and part of the atmosphere is much too warm and light Somehow. . . this must all be balanced out.
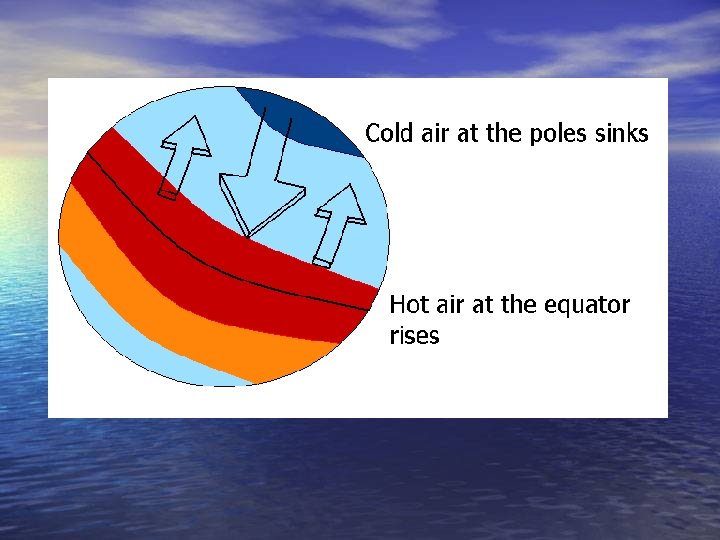
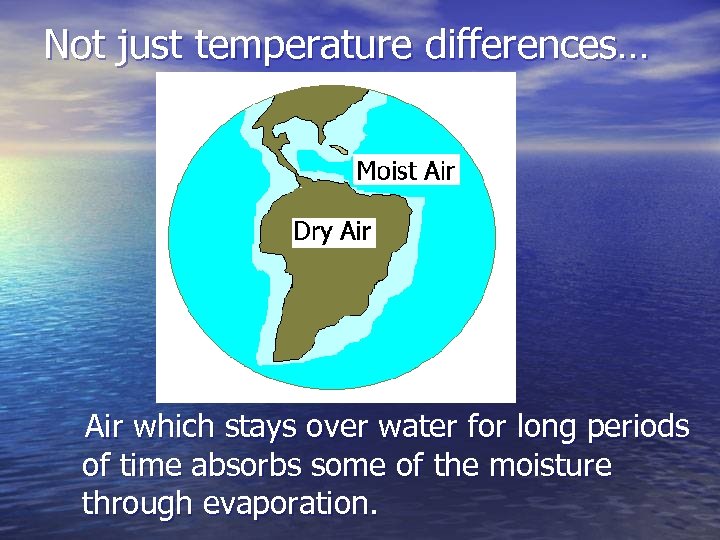 Not just temperature differences… Air which stays over water for long periods of time absorbs some of the moisture through evaporation.
Not just temperature differences… Air which stays over water for long periods of time absorbs some of the moisture through evaporation.
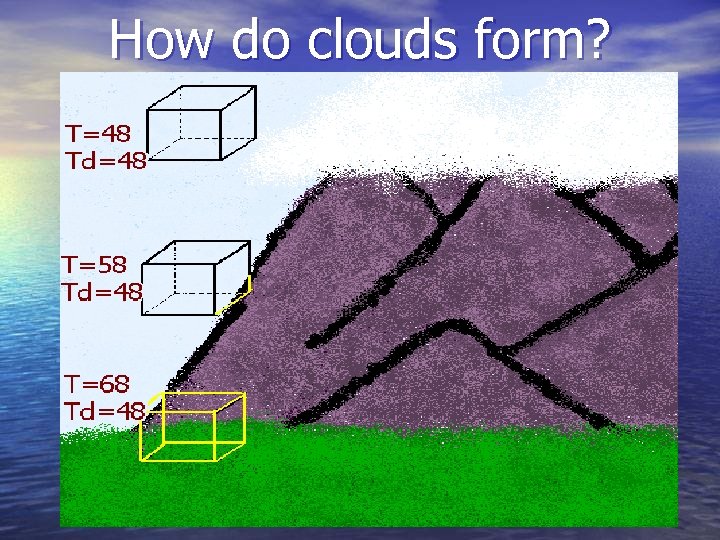 How do clouds form?
How do clouds form?
 CLOUDS • Cirrus • Stratus • Cumulus • Nimbus
CLOUDS • Cirrus • Stratus • Cumulus • Nimbus
 Cirrus Clouds • High-level clouds • Usually only ice crystals • Generally in fair weather
Cirrus Clouds • High-level clouds • Usually only ice crystals • Generally in fair weather
 Stratus Clouds • Base is usually only a few hundred feet above the ground • Little to no vertical development • Can cover entire sky
Stratus Clouds • Base is usually only a few hundred feet above the ground • Little to no vertical development • Can cover entire sky
 Cumulus Clouds • Base is at low level, but tops can reach 60, 000 feet (11 miles) high • Made of both ice and water droplets • Puffy like cotton balls
Cumulus Clouds • Base is at low level, but tops can reach 60, 000 feet (11 miles) high • Made of both ice and water droplets • Puffy like cotton balls
 Nimbus Clouds • Generally form 7, 000 to 15, 000 feet (1 to 3 miles) above ground • Steady precipitation
Nimbus Clouds • Generally form 7, 000 to 15, 000 feet (1 to 3 miles) above ground • Steady precipitation
 PRECIPITATION Two basic ways precipitation forms: • “Collision” process (warm clouds) • “Ice Crystal” process (cold clouds)
PRECIPITATION Two basic ways precipitation forms: • “Collision” process (warm clouds) • “Ice Crystal” process (cold clouds)
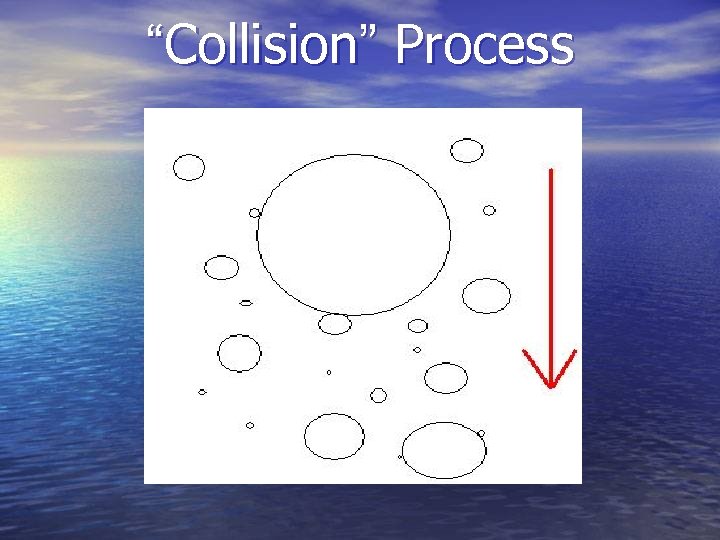 “Collision” Process
“Collision” Process
 “Ice Crystal” Process Easier for water vapor to deposit directly onto ice crystals. Crystals then grow heavy enough to start falling.
“Ice Crystal” Process Easier for water vapor to deposit directly onto ice crystals. Crystals then grow heavy enough to start falling.
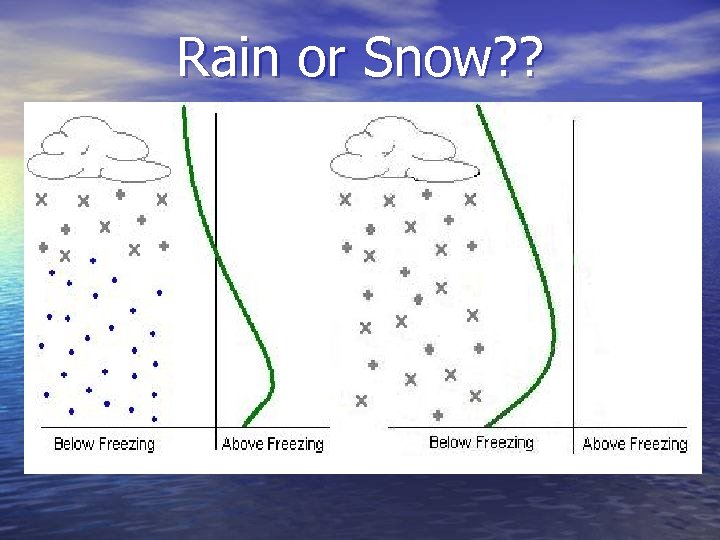 Rain or Snow? ?
Rain or Snow? ?
 THUNDERSTORMS In order to form, thunderstorms need: • Moisture • Instability • Lifting
THUNDERSTORMS In order to form, thunderstorms need: • Moisture • Instability • Lifting
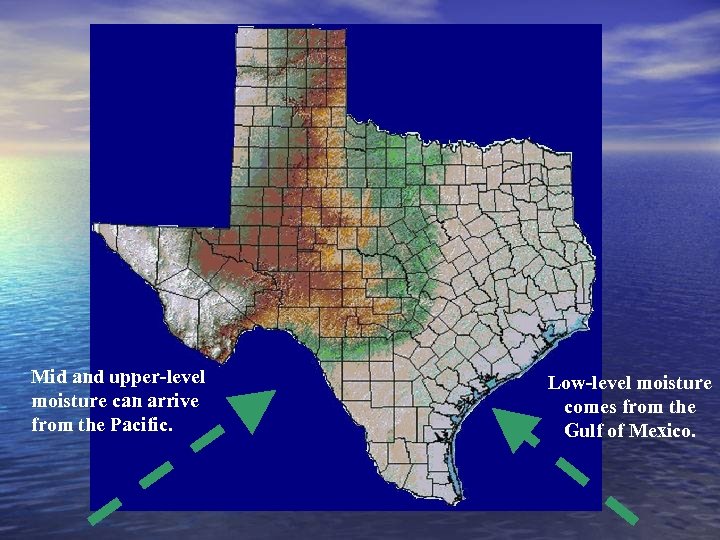 Mid and upper-level moisture can arrive from the Pacific. Low-level moisture comes from the Gulf of Mexico.
Mid and upper-level moisture can arrive from the Pacific. Low-level moisture comes from the Gulf of Mexico.
 INSTABILITY • If air is stable, it will try to go back to where it was • If air is unstable, it will continue in the direction it was pushed
INSTABILITY • If air is stable, it will try to go back to where it was • If air is unstable, it will continue in the direction it was pushed
 LIFT • Differences in heating • Terrain • Fronts, boundaries, drylines
LIFT • Differences in heating • Terrain • Fronts, boundaries, drylines
 The three stages in a thunderstorm’s life:
The three stages in a thunderstorm’s life:
 Thunderstorm Hazards • Hail • Damaging Winds • Tornados • Flash Floods
Thunderstorm Hazards • Hail • Damaging Winds • Tornados • Flash Floods
 HAIL
HAIL
 DAMAGING WINDS Damage from a downburst Damage from a tornado
DAMAGING WINDS Damage from a downburst Damage from a tornado
 TORNADOS F-Scale • Named after its creator, Dr. Fujita • Used to describe how fast winds in a tornado are • Actually goes all the way to F 12, which is the speed of sound
TORNADOS F-Scale • Named after its creator, Dr. Fujita • Used to describe how fast winds in a tornado are • Actually goes all the way to F 12, which is the speed of sound
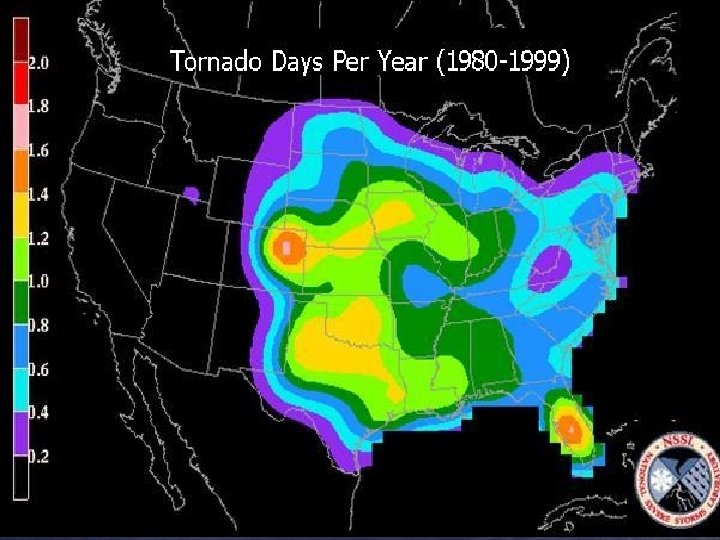
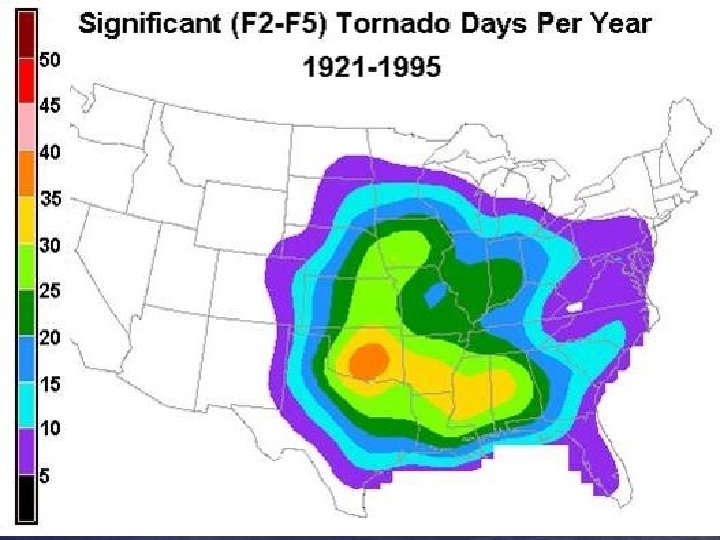
 Minimal Tornado - F 0, F 1 - 67% of S. C. TX Tornadoes - Causes 5% of all deaths - Life span 1 to 2 minutes - Path length less than 1 mile - Path width less than 100 yards - Wind speeds up to 110 mph
Minimal Tornado - F 0, F 1 - 67% of S. C. TX Tornadoes - Causes 5% of all deaths - Life span 1 to 2 minutes - Path length less than 1 mile - Path width less than 100 yards - Wind speeds up to 110 mph
 Strong Tornado - F 2, F 3 - 30% of S. C. TX Tornadoes - Causes 30% of all deaths - Life span 15 to 20 minutes - Path up to 15 miles - Path width up to 500 yards - Wind speeds up to 200 mph
Strong Tornado - F 2, F 3 - 30% of S. C. TX Tornadoes - Causes 30% of all deaths - Life span 15 to 20 minutes - Path up to 15 miles - Path width up to 500 yards - Wind speeds up to 200 mph
 Violent Tornado - F 4, F 5 - 3% of S. C. TX Tornadoes - Causes 65% of all deaths - Life span to several hours - Path length dozens of miles - Path width to 1 1/ 2 miles - Wind speeds over 300 mph
Violent Tornado - F 4, F 5 - 3% of S. C. TX Tornadoes - Causes 65% of all deaths - Life span to several hours - Path length dozens of miles - Path width to 1 1/ 2 miles - Wind speeds over 300 mph
 Jarrell, TX — May 27, 1997
Jarrell, TX — May 27, 1997
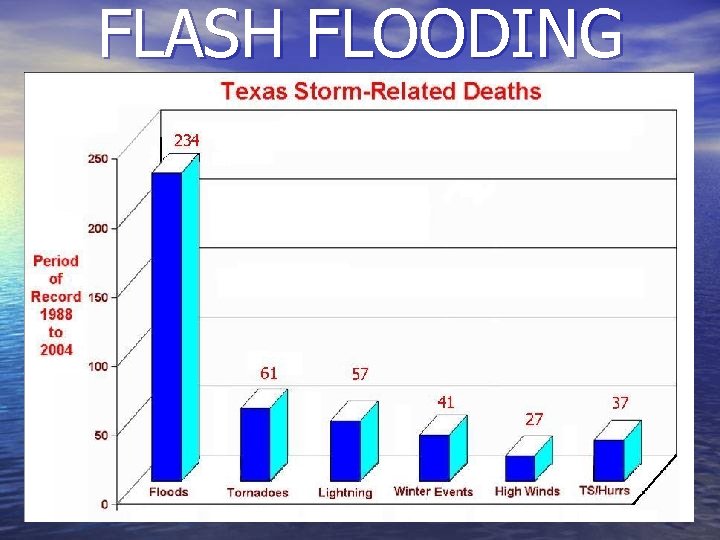 FLASH FLOODING
FLASH FLOODING
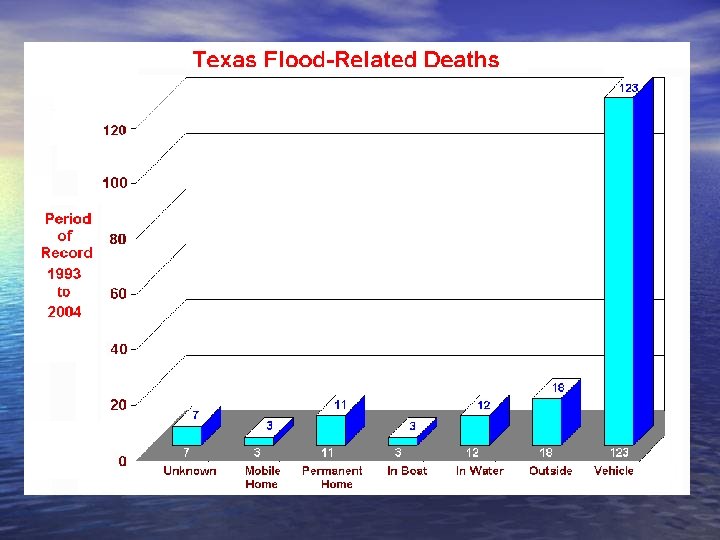
 For each foot of rising water, a car weighs 1500 pounds less! As little as 18 inches of water can float a truck! It takes only 12 to 14 inches of water to float a car!
For each foot of rising water, a car weighs 1500 pounds less! As little as 18 inches of water can float a truck! It takes only 12 to 14 inches of water to float a car!
 Tire 8” wide, 30” diameter floats 816 lbs of car weight Tire 12” wide, 30” diameter floats 1225 lbs of car weight
Tire 8” wide, 30” diameter floats 816 lbs of car weight Tire 12” wide, 30” diameter floats 1225 lbs of car weight

 For Current Weather Information: NOAA Weather Radio Or: www. weather. gov Clickable map of the entire U. S. www. srh. noaa. gov/ewx NWS Austin/San Antonio’s Homepage
For Current Weather Information: NOAA Weather Radio Or: www. weather. gov Clickable map of the entire U. S. www. srh. noaa. gov/ewx NWS Austin/San Antonio’s Homepage
 QUESTIONS? Marianne Sutton@noaa. gov National Weather Service Austin/San Antonio 2090 Airport Road New Braunfels, TX 78130
QUESTIONS? Marianne Sutton@noaa. gov National Weather Service Austin/San Antonio 2090 Airport Road New Braunfels, TX 78130


