65b98529f528ae88017e58f00938f1b6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 How DNS Misnaming Distorts Internet Topology Mapping Ming Zhang, Microsoft Research Yaoping Ruan, IBM Research Vivek Pai, Jennifer Rexford, Princeton University June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC
How DNS Misnaming Distorts Internet Topology Mapping Ming Zhang, Microsoft Research Yaoping Ruan, IBM Research Vivek Pai, Jennifer Rexford, Princeton University June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC
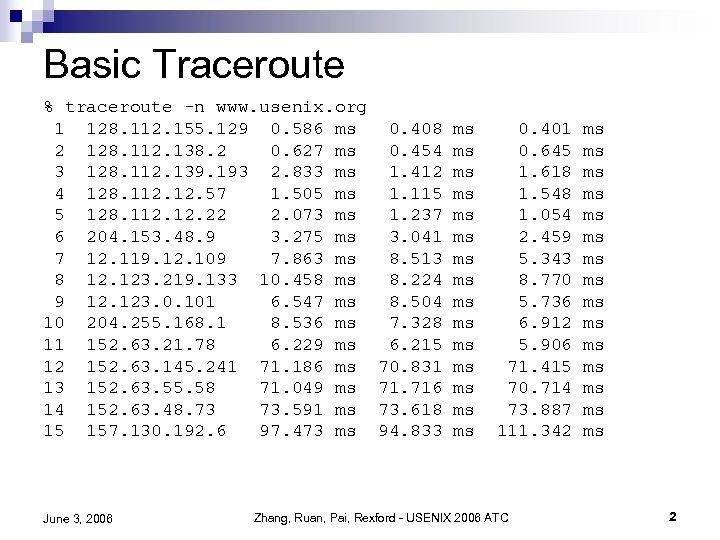 Basic Traceroute % traceroute -n www. usenix. org 1 128. 112. 155. 129 0. 586 ms 2 128. 112. 138. 2 0. 627 ms 3 128. 112. 139. 193 2. 833 ms 4 128. 112. 57 1. 505 ms 5 128. 112. 22 2. 073 ms 6 204. 153. 48. 9 3. 275 ms 7 12. 119. 12. 109 7. 863 ms 8 12. 123. 219. 133 10. 458 ms 9 12. 123. 0. 101 6. 547 ms 10 204. 255. 168. 1 8. 536 ms 11 152. 63. 21. 78 6. 229 ms 12 152. 63. 145. 241 71. 186 ms 13 152. 63. 55. 58 71. 049 ms 14 152. 63. 48. 73 73. 591 ms 15 157. 130. 192. 6 97. 473 ms June 3, 2006 0. 408 0. 454 1. 412 1. 115 1. 237 3. 041 8. 513 8. 224 8. 504 7. 328 6. 215 70. 831 71. 716 73. 618 94. 833 ms ms ms ms 0. 401 0. 645 1. 618 1. 548 1. 054 2. 459 5. 343 8. 770 5. 736 6. 912 5. 906 71. 415 70. 714 73. 887 111. 342 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC ms ms ms ms 2
Basic Traceroute % traceroute -n www. usenix. org 1 128. 112. 155. 129 0. 586 ms 2 128. 112. 138. 2 0. 627 ms 3 128. 112. 139. 193 2. 833 ms 4 128. 112. 57 1. 505 ms 5 128. 112. 22 2. 073 ms 6 204. 153. 48. 9 3. 275 ms 7 12. 119. 12. 109 7. 863 ms 8 12. 123. 219. 133 10. 458 ms 9 12. 123. 0. 101 6. 547 ms 10 204. 255. 168. 1 8. 536 ms 11 152. 63. 21. 78 6. 229 ms 12 152. 63. 145. 241 71. 186 ms 13 152. 63. 55. 58 71. 049 ms 14 152. 63. 48. 73 73. 591 ms 15 157. 130. 192. 6 97. 473 ms June 3, 2006 0. 408 0. 454 1. 412 1. 115 1. 237 3. 041 8. 513 8. 224 8. 504 7. 328 6. 215 70. 831 71. 716 73. 618 94. 833 ms ms ms ms 0. 401 0. 645 1. 618 1. 548 1. 054 2. 459 5. 343 8. 770 5. 736 6. 912 5. 906 71. 415 70. 714 73. 887 111. 342 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC ms ms ms ms 2
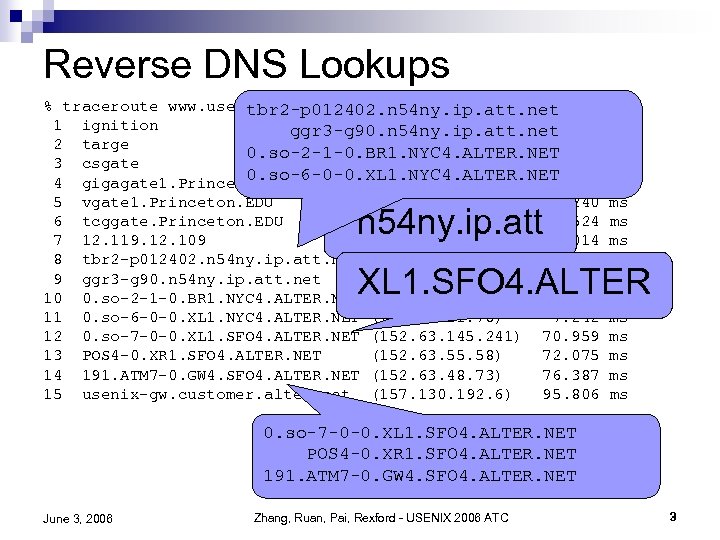 Reverse DNS Lookups % traceroute www. usenix. org tbr 2 -p 012402. n 54 ny. ip. att. net 1 ignition (128. 112. 155. 129) 0. 542 ggr 3 -g 90. n 54 ny. ip. att. net 2 targe (128. 112. 138. 2) 0. 894 0. so-2 -1 -0. BR 1. NYC 4. ALTER. NET 3 csgate (128. 112. 139. 193) 1. 592 0. so-6 -0 -0. XL 1. NYC 4. ALTER. NET 4 gigagate 1. Princeton. EDU (128. 112. 57) 1. 768 5 vgate 1. Princeton. EDU (128. 112. 22) 1. 240 6 tcggate. Princeton. EDU (204. 153. 48. 9) 2. 524 7 12. 119. 12. 109 (12. 119. 12. 109) 9. 014 8 tbr 2 -p 012402. n 54 ny. ip. att. net (12. 123. 219. 133) 6. 708 9 ggr 3 -g 90. n 54 ny. ip. att. net (12. 123. 0. 101) 6. 510 10 0. so-2 -1 -0. BR 1. NYC 4. ALTER. NET (204. 255. 168. 1) 6. 806 11 0. so-6 -0 -0. XL 1. NYC 4. ALTER. NET (152. 63. 21. 78) 7. 242 12 0. so-7 -0 -0. XL 1. SFO 4. ALTER. NET (152. 63. 145. 241) 70. 959 13 POS 4 -0. XR 1. SFO 4. ALTER. NET (152. 63. 55. 58) 72. 075 14 191. ATM 7 -0. GW 4. SFO 4. ALTER. NET (152. 63. 48. 73) 76. 387 15 usenix-gw. customer. alter. net (157. 130. 192. 6) 95. 806 n 54 ny. ip. att ms ms ms ms XL 1. SFO 4. ALTER 0. so-7 -0 -0. XL 1. SFO 4. ALTER. NET POS 4 -0. XR 1. SFO 4. ALTER. NET 191. ATM 7 -0. GW 4. SFO 4. ALTER. NET June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 3
Reverse DNS Lookups % traceroute www. usenix. org tbr 2 -p 012402. n 54 ny. ip. att. net 1 ignition (128. 112. 155. 129) 0. 542 ggr 3 -g 90. n 54 ny. ip. att. net 2 targe (128. 112. 138. 2) 0. 894 0. so-2 -1 -0. BR 1. NYC 4. ALTER. NET 3 csgate (128. 112. 139. 193) 1. 592 0. so-6 -0 -0. XL 1. NYC 4. ALTER. NET 4 gigagate 1. Princeton. EDU (128. 112. 57) 1. 768 5 vgate 1. Princeton. EDU (128. 112. 22) 1. 240 6 tcggate. Princeton. EDU (204. 153. 48. 9) 2. 524 7 12. 119. 12. 109 (12. 119. 12. 109) 9. 014 8 tbr 2 -p 012402. n 54 ny. ip. att. net (12. 123. 219. 133) 6. 708 9 ggr 3 -g 90. n 54 ny. ip. att. net (12. 123. 0. 101) 6. 510 10 0. so-2 -1 -0. BR 1. NYC 4. ALTER. NET (204. 255. 168. 1) 6. 806 11 0. so-6 -0 -0. XL 1. NYC 4. ALTER. NET (152. 63. 21. 78) 7. 242 12 0. so-7 -0 -0. XL 1. SFO 4. ALTER. NET (152. 63. 145. 241) 70. 959 13 POS 4 -0. XR 1. SFO 4. ALTER. NET (152. 63. 55. 58) 72. 075 14 191. ATM 7 -0. GW 4. SFO 4. ALTER. NET (152. 63. 48. 73) 76. 387 15 usenix-gw. customer. alter. net (157. 130. 192. 6) 95. 806 n 54 ny. ip. att ms ms ms ms XL 1. SFO 4. ALTER 0. so-7 -0 -0. XL 1. SFO 4. ALTER. NET POS 4 -0. XR 1. SFO 4. ALTER. NET 191. ATM 7 -0. GW 4. SFO 4. ALTER. NET June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 3
 Network Debugging & Research n DNS now a critical tool, errors problematic n For humans annoying ¨ Assuming n For mapping small problems ¨ Relatively n you can detect it contained For derived data magnified problems ¨ “Worst” June 3, 2006 problems can be fictional Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 4
Network Debugging & Research n DNS now a critical tool, errors problematic n For humans annoying ¨ Assuming n For mapping small problems ¨ Relatively n you can detect it contained For derived data magnified problems ¨ “Worst” June 3, 2006 problems can be fictional Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 4
 Automating the Process n Generate large number of traceroutes ¨ e. g. , n use Planet. Lab and/or Script. Route Extract geography from names ¨ undns tool from Rocket. Fuel ¨ Understands conventions for tons of ISPs Merge cities into POPs n Now, reverse-engineer paths, peering decisions, routing, etc. n June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 5
Automating the Process n Generate large number of traceroutes ¨ e. g. , n use Planet. Lab and/or Script. Route Extract geography from names ¨ undns tool from Rocket. Fuel ¨ Understands conventions for tons of ISPs Merge cities into POPs n Now, reverse-engineer paths, peering decisions, routing, etc. n June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 5
 DNS Misnaming Problems n Reverse DNS names not critical for ISP ¨ Especially in routers – debugging tool ¨ Often no forward DNS mapping n Reasons for misnaming ¨ Router gets moved ¨ Linecards swapped (IP per linecard) ¨ Reuse old IP addresses ¨ Peering ISPs share IP addresses June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 6
DNS Misnaming Problems n Reverse DNS names not critical for ISP ¨ Especially in routers – debugging tool ¨ Often no forward DNS mapping n Reasons for misnaming ¨ Router gets moved ¨ Linecards swapped (IP per linecard) ¨ Reuse old IP addresses ¨ Peering ISPs share IP addresses June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 6
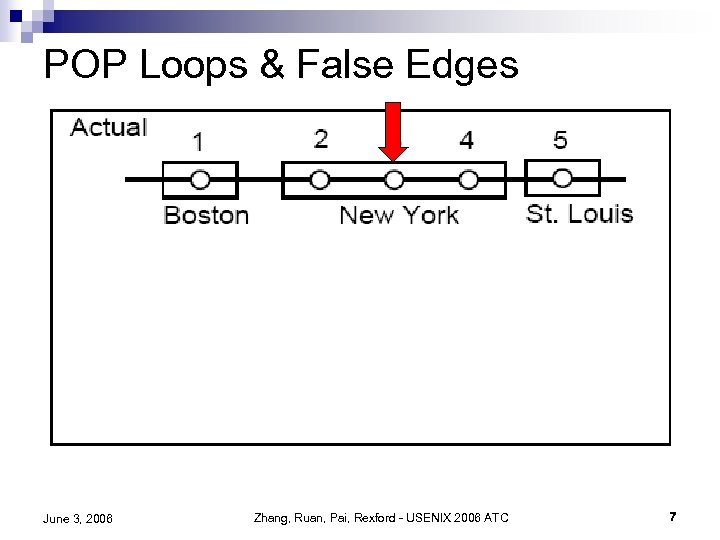 POP Loops & False Edges June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 7
POP Loops & False Edges June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 7
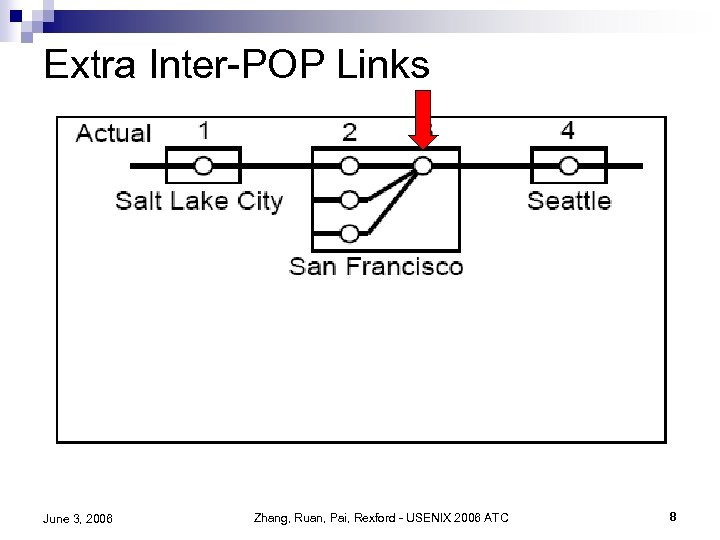 Extra Inter-POP Links June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 8
Extra Inter-POP Links June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 8
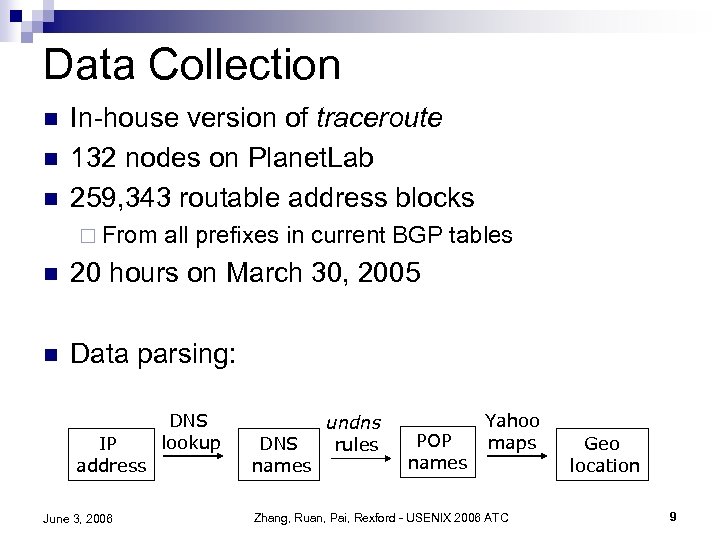 Data Collection n In-house version of traceroute 132 nodes on Planet. Lab 259, 343 routable address blocks ¨ From all prefixes in current BGP tables n 20 hours on March 30, 2005 n Data parsing: IP address June 3, 2006 DNS lookup DNS names undns rules POP names Yahoo maps Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC Geo location 9
Data Collection n In-house version of traceroute 132 nodes on Planet. Lab 259, 343 routable address blocks ¨ From all prefixes in current BGP tables n 20 hours on March 30, 2005 n Data parsing: IP address June 3, 2006 DNS lookup DNS names undns rules POP names Yahoo maps Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC Geo location 9
 Resolving POP-level loop n Greedy algorithm: ¨ Get all fishy IPs ¨ Pick IP that Resolves most loops n Rarely appears good n ¨ Remove IP’s loops, report IP ¨ Repeat n The correct location of a misnamed IP is decided by voting based on its neighbors June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 10
Resolving POP-level loop n Greedy algorithm: ¨ Get all fishy IPs ¨ Pick IP that Resolves most loops n Rarely appears good n ¨ Remove IP’s loops, report IP ¨ Repeat n The correct location of a misnamed IP is decided by voting based on its neighbors June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 10
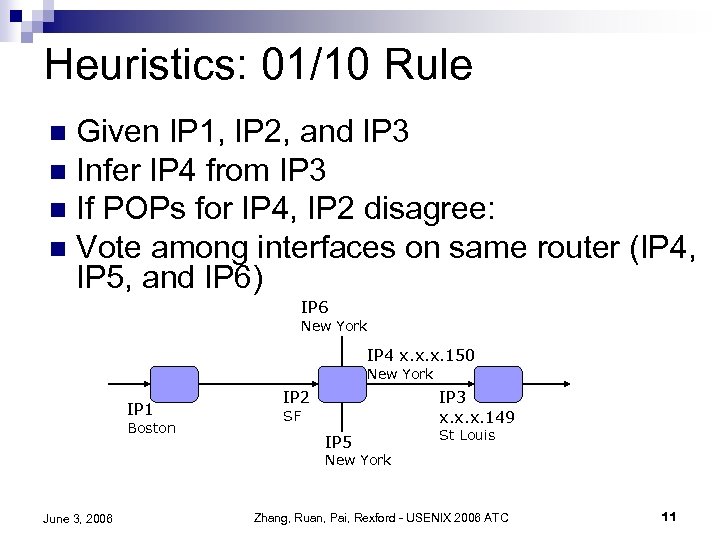 Heuristics: 01/10 Rule Given IP 1, IP 2, and IP 3 n Infer IP 4 from IP 3 n If POPs for IP 4, IP 2 disagree: n Vote among interfaces on same router (IP 4, IP 5, and IP 6) n IP 6 New York IP 4 x. x. x. 150 New York IP 1 Boston IP 2 IP 3 x. x. x. 149 SF IP 5 St Louis New York June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 11
Heuristics: 01/10 Rule Given IP 1, IP 2, and IP 3 n Infer IP 4 from IP 3 n If POPs for IP 4, IP 2 disagree: n Vote among interfaces on same router (IP 4, IP 5, and IP 6) n IP 6 New York IP 4 x. x. x. 150 New York IP 1 Boston IP 2 IP 3 x. x. x. 149 SF IP 5 St Louis New York June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 11
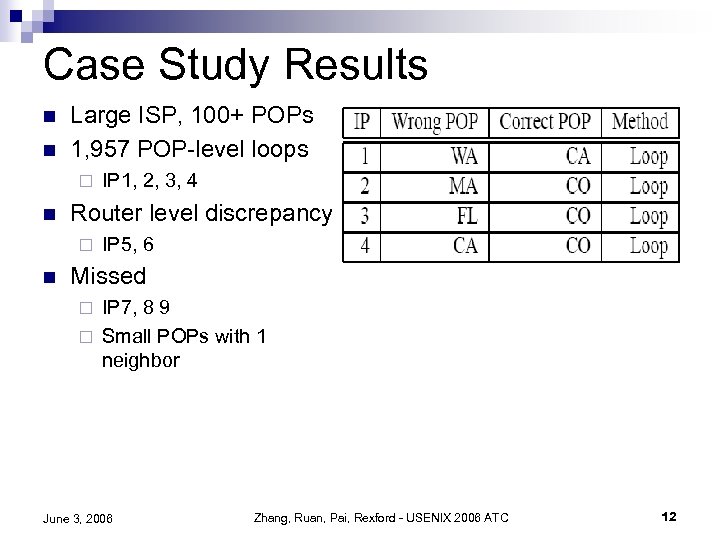 Case Study Results n n Large ISP, 100+ POPs 1, 957 POP-level loops ¨ n Router level discrepancy ¨ n IP 1, 2, 3, 4 IP 5, 6 Missed IP 7, 8 9 ¨ Small POPs with 1 neighbor ¨ June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 12
Case Study Results n n Large ISP, 100+ POPs 1, 957 POP-level loops ¨ n Router level discrepancy ¨ n IP 1, 2, 3, 4 IP 5, 6 Missed IP 7, 8 9 ¨ Small POPs with 1 neighbor ¨ June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 12
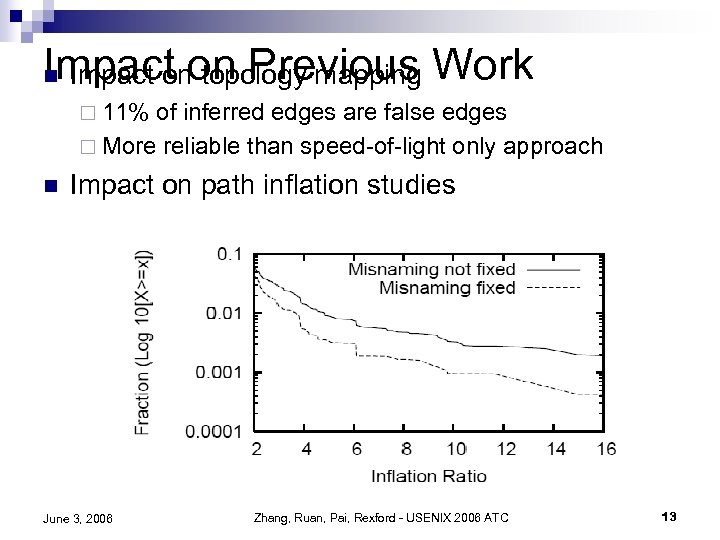 Impact on Previous Work n Impact on topology mapping ¨ 11% of inferred edges are false edges ¨ More reliable than speed-of-light only approach n Impact on path inflation studies June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 13
Impact on Previous Work n Impact on topology mapping ¨ 11% of inferred edges are false edges ¨ More reliable than speed-of-light only approach n Impact on path inflation studies June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 13
 Conclusion DNS misnaming can be serious for network researchers n We study two heuristics to identify and fix the wrong names n Case study confirms the effectiveness of our approach n June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 14
Conclusion DNS misnaming can be serious for network researchers n We study two heuristics to identify and fix the wrong names n Case study confirms the effectiveness of our approach n June 3, 2006 Zhang, Ruan, Pai, Rexford - USENIX 2006 ATC 14


