5c7e14d413aa1cd9ab370392590c17e1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

How Development Banks can Finance the Implementation of NAMAs UNFCCC Climate Finance Briefing Warsaw - 12 November 2013 Jochen Harnisch, KFW - Competence Center Environment and Climate Bank aus Verantwortung

About Kf. W Group › Development bank of Germany › Founded in 1948 for implementation of the Marshall Plan › More than 5000 employees › We finance investment in Germany & Europe › We provide international project & export finance › We provide support for developing countries › USD 94 bn. of new commitments in 2012 (thereof 40% climate and environment) › USD 31. 8 bn. for mitigation projects (e. g. energy, transport, waste, forestry) › USD 0. 6 bn. for adaptation projects (e. g. water sector, agriculture) › USD 2. 1 bn. of climate finance in developing countries › Instrument: Grants, concessional and commercial loans, guarantees, mezzanine and equity 2

The International Development Finance Club (IDFC) › Network of 20 leading development finance institutions with mandates for national, sub-regional, regional and international activities around the world. › Combined assets of more than USD 2, 100 billion › New commitments added up to approx. USD 390 billion › Activities : Green finance mapping, exchange on good practices in private sector mobilisation and support of GCF implementation › Current work plan: green infrastructure finance, support of SMEs, broader mapping of activities 3
IDFC Climate Finance Mapping 2013 Source: Ecofys, 2013 4

GHG Mitigation: Change Global Investment Pattern (IEA WEO 2011) 5

Dimensions of NAMAs (Nationally Appropriate Mitigation Activity) National (low carbon) development strategy Sectoral or cross-sectoral policy mechanism Individual investment decisions 6
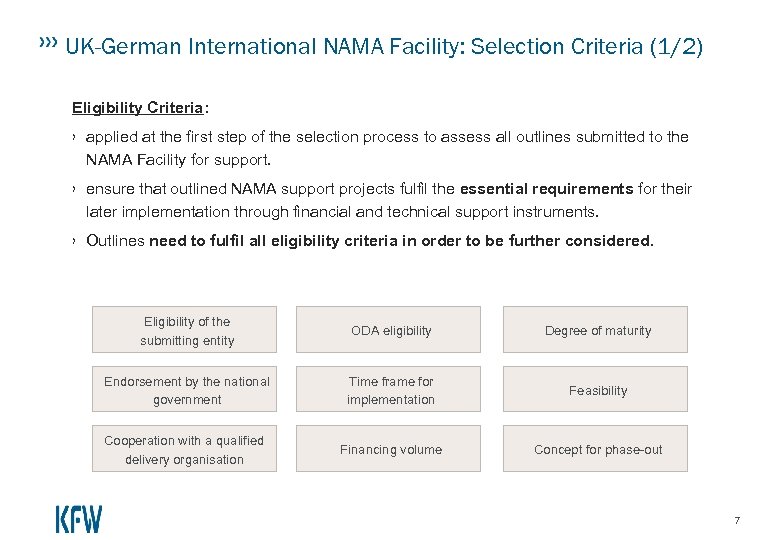
UK-German International NAMA Facility: Selection Criteria (1/2) Eligibility Criteria: › applied at the first step of the selection process to assess all outlines submitted to the NAMA Facility for support. › ensure that outlined NAMA support projects fulfil the essential requirements for their later implementation through financial and technical support instruments. › Outlines need to fulfil all eligibility criteria in order to be further considered. Eligibility of the submitting entity ODA eligibility Degree of maturity Endorsement by the national government Time frame for implementation Feasibility Cooperation with a qualified delivery organisation Financing volume Concept for phase-out 7

UK-German International NAMA Facility: Selection Criteria (2/2) Ambition Criteria: › applied to all outlines for NAMA support projects, which have successfully been assessed against the eligibility criteria › ensure that the NAMA Facility supports the most ambitious projects available › assessed on a point-grade system to allow a ranking of all submitted NAMA support projects Transformational Change Potential Does the NAMA support project contribute to a transformation of the national or sectoral development towards a less carbon-intensive development path? Co-benefits Does the NAMA support project provide important additional development cobenefits beyond the reduction of GHG emissions? Financial Ambition Does the NAMA support project foresee or enable a substantial funding contribution from other sources? Mitigation Potential Does the NAMA support project foresee substantial direct and indirect GHG emission reductions? 8
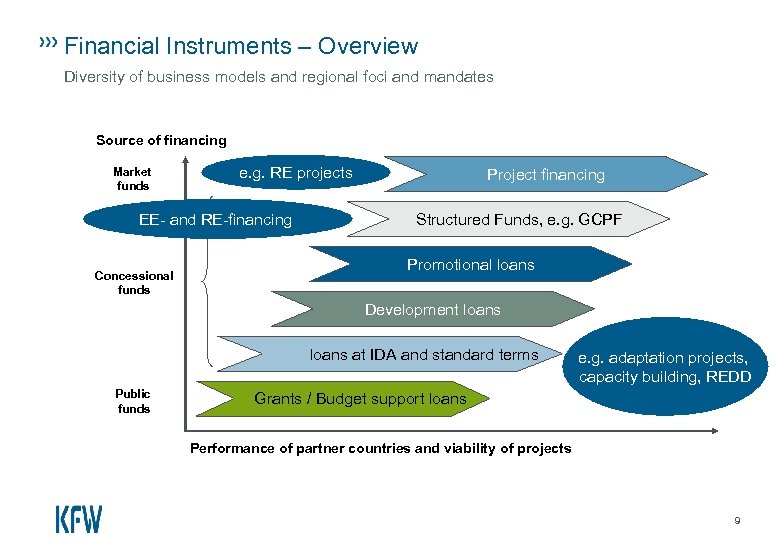
Financial Instruments – Overview Diversity of business models and regional foci and mandates Source of financing Market funds e. g. RE projects EE- and RE-financing Concessional funds Project financing Structured Funds, e. g. GCPF Promotional loans Development loans at IDA and standard terms Public funds e. g. adaptation projects, capacity building, REDD Grants / Budget support loans Performance of partner countries and viability of projects 9

Kf. W Case Study: Wind Farm Gulf of el Zayt in Egypt Approach Problem Africa's biggest wind farm with 200 MW and pilot project for bird protection › Rapidly growing energy requirements › expensive energy import › Rising pollutant emissions › Unused wind energy potential (> 10. 000 MW) › Kf. W loan (EU-NIF and EIB) for wind farm with grid connection (i. e. planning, construction, commissioning, connection, site development, consulting) Total investment ca. 340 Mio. €; Kf. W ca. 191 Mio. € /zv. loan › pilot project for bird protection (“shutdown on demand”) Impact › Efficient and ecologically sustainable electricity supply › Contribution to global climate protection and to Egypt's economic development › bird protection with a positive signal beyond the region Topic of the presentation / location / date [dd. mm. yyyy] 3 10

Kf. W Case Study: Energy Efficiency in Residential Buildings in India Problem Adopted experiences from the German subsidy practice › Share of private households on primary energy requirement: 37, 5% › Ø electricity consumption of urban middle class: 8, 000 k. Wh p. a. › Biggest economic energy saving potential in new residential housing complexes (up to 46%) Approach › Credit line to the National Housing Bank (NHB) to refinance housing loans in new energy-efficient buildings (at least 30% more efficient than reference buildings) › Introduction of an energy efficiency programme (Fraunhofer-TERI Total inv. 60 m € Kf. W financing 50 m € cooperation) and certificate) › Intensive complementary advice to NHB, building financiers and real estate developers Impact › 73 buildings in 11 housing projects certified (>20, 000 apartments, emission reduction of 32, 000 tonnes of carbon p. a. so far) › Three large housing financiers (80% market share) participating › International awards such as ADFIAP-Merit 11

Kf. W Case Study: The Global REDD Programme for Early Movers Bridge financing for pioneers Problem › Deforestation accounts for some 17% of global carbon emissions. › When the forest disappears, so do biodiversity and (poor) people's livelihoods › Decisions under the Framework Convention on Climate Impacts Approach Change have yet to be made › Innovative approach to greater outcomes orientation › Provide bridge financing between today and a future Initial investment volume: € 36. 5 m climate regime › Remunerates achievements of forest protection pioneers › Reduce emissions from forest destruction › Contribute to preserving biodiversity › Create positive REDD examples at an early stage 12

NAMA Pilot: Ecocasa Program Mexico Level of ambition › First NAMA in the sustainable housing sector › Supply of mortgage for low carbon housing and financial incentives for EE investment (incl. TA): Support for up to 27, 000 low carbon houses (-20% CO 2) and 800 passive houses (-80% CO 2) › Co-financing to provide large-scale financing of EUR 160 m and allow transformational effects Maturity and bankability › Detailed NAMA concept developed by the National Housing Commission (CONAVI) and GIZ supported by the German Environment Ministry › Detailed economic analysis of the NAMA with a National interest and ownership › Mexico as one of the first non-Annex I countries pledging to reduce its GHG emissions voluntarily › NAMA program launched by the ntl. government in 2011 and integrated into the broader national climate strategy (PECC) › Co-benefit of poverty reduction: focus on low middle income households MRV system › Robust and pragmatic MRV methodology for a baseline and different standards for energy efficient houses (Eco. Casa I, Eco. Casa II, Passive House) significant NPV › High modularity of the NAMA program 13

Results based sectoral approaches under EU AIF/LAIF 1. Carbon-Linked Incentive Scheme Indonesia (AIF) 2. Facility for Performance Based Climate Finance in Latin America (LAIF) EU KOM Kf. W Regional Partners Total EU Grant Funding: € 17 million I. Concept Development & Capacity building for Implementation EU TA grants Sector II Sector n II. Roll-out Pilot Incentive Schemes EU grants to finance perfomance based incentive schemes Governments, public & private sector, local banks, consultants Initiation of substantial investments for pilot projects including leverage through bank lending Competence for stakeholders in implementing performance based incentive schemes 14

Key Elements of Project Preparation and Execution with Kf. W 1. Project scoping and priorisation 2. Bilateral government negotiations 3. Project prepraration by project executing agency & consultant 4. Project appraisal 5. Financing decision 6. Financing agreement 7. Project implementation by project executing agency incl. monitoring 8. Start of operation and final inspection 9. Performance review and final evaluation 15

Strengthen the Pipeline of Bankable Projects › Huge uncovered investement needs and wealth of ideas for climate related projects exists › Scarcity of bankable climate projects, resulting from e. g. - weak regulatory frameworks (e. g. energy subsidies, collection of fees, lack of enforcement) - missing economic viability including concessional funding or missing sustainabilty of business model - inappropriate project implementation partner e. g. insufficient implementation capacíty, no realistic means to meet international fiduciary or environmental and social stantards, missing credit-worthiness Involve development banks and other financiers no later than in design of feasibility study 16

How to Make Supported NAMAs a Success? › Realistic expectations on private sector involvement in NAMAs implementation - simplicity, transparency and predictability are expected by private sector - be ready to accept the risk-return profiles of the private sector - state aid issues and distortion of (inter)national competition to be considered › Keep NAMA implementation simple - complexity adds perceived and real risks and transactions costs - focus on proven instruments: loans, grants, equity and guarantees - predictable selection criteria: use positive and negative lists for regions and technologies - flexible and cost-effective framework for monitoring and evaluation needed › Early focus on bankable NAMAs - firm alignment with national development priorities - transformational ambition should be commensurate with available funding - focus on win-win programmes in selected sub-sectors and countrie - involve your future financier early on 17

Contact Details Competence Center Environment and Climate Dr. Jochen Harnisch Head of Division Kf. W Bankengruppe Palmengartenstrasse 5– 9 60325 Frankfurt am Main Germany Phone +49 69 7431 - 9695 Fax +49 69 7431 - 3796 Jochen. Harnisch@kfw. de 18
5c7e14d413aa1cd9ab370392590c17e1.ppt