f62fa1e08dac633ac302afb5c426df9c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 How are you solving the puzzle? Integrated Risk Management Plans SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
How are you solving the puzzle? Integrated Risk Management Plans SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Strategic Risk Management Conference Supporting the FRS IRMP Process Mike Vicary (mike. v@orhltd. com) Graham Holland (graham. h@orhltd. com) Paul Murray (paul. m@orhltd. com) SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Strategic Risk Management Conference Supporting the FRS IRMP Process Mike Vicary (mike. v@orhltd. com) Graham Holland (graham. h@orhltd. com) Paul Murray (paul. m@orhltd. com) SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Presentation Ø Work undertaken in supporting FRSs in producing their IRMPs Ø Overview of systems and methodologies employed Ø Some of the pitfalls/challenges faced Ø Plans for future development of systems SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Presentation Ø Work undertaken in supporting FRSs in producing their IRMPs Ø Overview of systems and methodologies employed Ø Some of the pitfalls/challenges faced Ø Plans for future development of systems SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 ORH SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
ORH SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Company Summary Ø ORH Limited was established in 1986 Ø Over 400 studies undertaken in UK and Overseas Ø Main Study Areas – Health & Emergency Services Ø Main Clients – Service providers/commissioners and Government Departments Ø ORH specialises in modelling systems involving transport and access, particularly for the emergency services, to improve cost-effectiveness SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Company Summary Ø ORH Limited was established in 1986 Ø Over 400 studies undertaken in UK and Overseas Ø Main Study Areas – Health & Emergency Services Ø Main Clients – Service providers/commissioners and Government Departments Ø ORH specialises in modelling systems involving transport and access, particularly for the emergency services, to improve cost-effectiveness SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 ORH General Approach Ø Consultancy with specialised modelling software (developed in-house) Ø Expertise in analysis and modelling Ø We apply Operational Research modelling techniques to resource planning problems Operational Research is a management science that uses mathematical or computer modelling techniques to solve resource planning problems in operational service delivery SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
ORH General Approach Ø Consultancy with specialised modelling software (developed in-house) Ø Expertise in analysis and modelling Ø We apply Operational Research modelling techniques to resource planning problems Operational Research is a management science that uses mathematical or computer modelling techniques to solve resource planning problems in operational service delivery SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Supporting the FRS IRMP Process SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Supporting the FRS IRMP Process SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 How are you solving the puzzle? Integrated Risk Management Plans SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
How are you solving the puzzle? Integrated Risk Management Plans SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
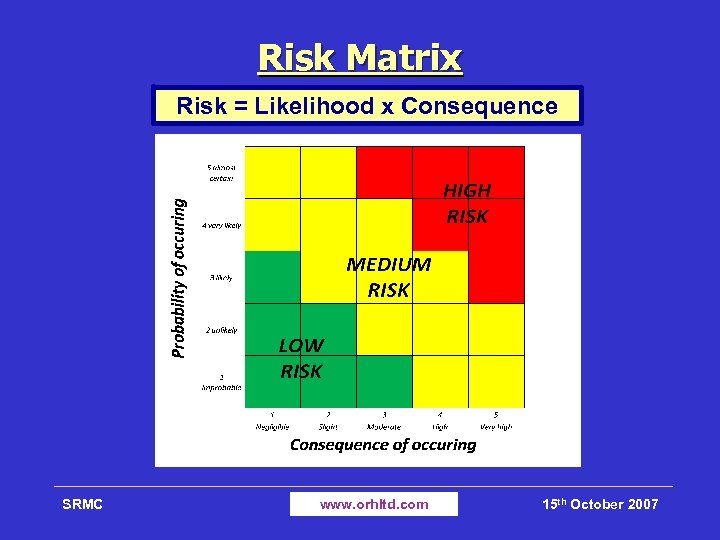 Risk Matrix Risk = Likelihood x Consequence SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Risk Matrix Risk = Likelihood x Consequence SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
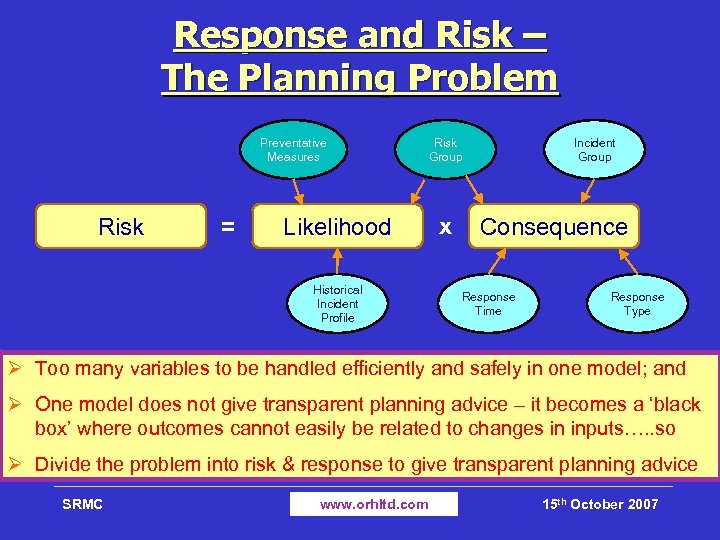 Response and Risk – The Planning Problem Preventative Measures Risk = Likelihood Historical Incident Profile Risk Group x Incident Group Consequence Response Time Response Type Ø Too many variables to be handled efficiently and safely in one model; and Ø One model does not give transparent planning advice – it becomes a ‘black box’ where outcomes cannot easily be related to changes in inputs…. . so Ø Divide the problem into risk & response to give transparent planning advice SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Response and Risk – The Planning Problem Preventative Measures Risk = Likelihood Historical Incident Profile Risk Group x Incident Group Consequence Response Time Response Type Ø Too many variables to be handled efficiently and safely in one model; and Ø One model does not give transparent planning advice – it becomes a ‘black box’ where outcomes cannot easily be related to changes in inputs…. . so Ø Divide the problem into risk & response to give transparent planning advice SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
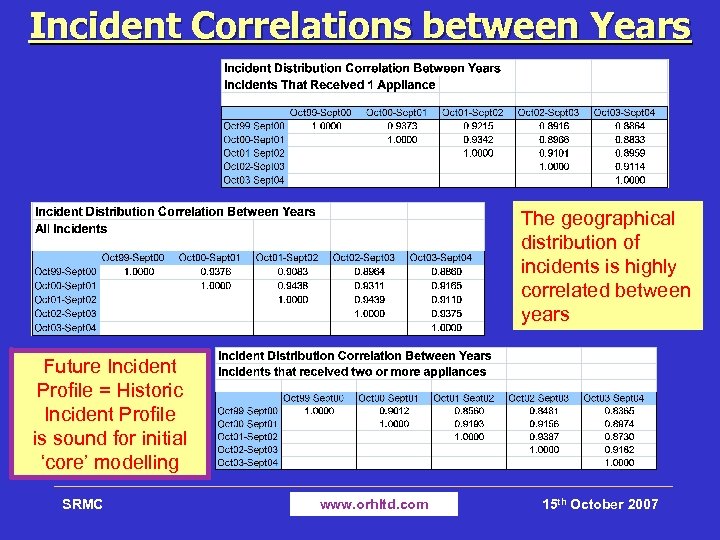 Incident Correlations between Years The geographical distribution of incidents is highly correlated between years Future Incident Profile = Historic Incident Profile is sound for initial ‘core’ modelling SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Incident Correlations between Years The geographical distribution of incidents is highly correlated between years Future Incident Profile = Historic Incident Profile is sound for initial ‘core’ modelling SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
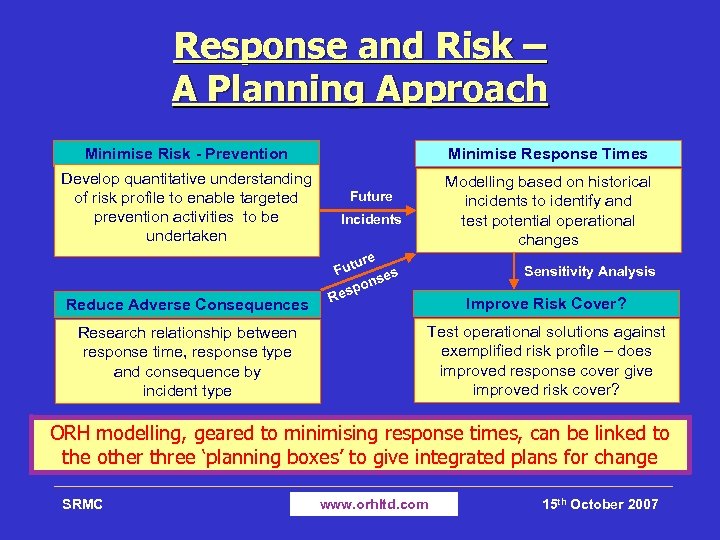 Response and Risk – A Planning Approach Minimise Risk - Prevention Minimise Response Times Develop quantitative understanding of risk profile to enable targeted prevention activities to be undertaken Modelling based on historical incidents to identify and test potential operational changes Reduce Adverse Consequences Research relationship between response time, response type and consequence by incident type Future Incidents ure Fut es ons p Res Sensitivity Analysis Improve Risk Cover? Test operational solutions against exemplified risk profile – does improved response cover give improved risk cover? ORH modelling, geared to minimising response times, can be linked to the other three ‘planning boxes’ to give integrated plans for change SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Response and Risk – A Planning Approach Minimise Risk - Prevention Minimise Response Times Develop quantitative understanding of risk profile to enable targeted prevention activities to be undertaken Modelling based on historical incidents to identify and test potential operational changes Reduce Adverse Consequences Research relationship between response time, response type and consequence by incident type Future Incidents ure Fut es ons p Res Sensitivity Analysis Improve Risk Cover? Test operational solutions against exemplified risk profile – does improved response cover give improved risk cover? ORH modelling, geared to minimising response times, can be linked to the other three ‘planning boxes’ to give integrated plans for change SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Risk, Response and Range Ø Separating response from risk allows powerful response models to examine a wide range of operational options quickly and with confidence Ø Response can be modelled with simulation techniques, taking account of all key controllable and uncontrollable input variables Ø Range cover (assumes static resources) allows optimisation modelling techniques to be used, and the solutions tested by simulating response Response v Risk – to allow a transparent planning process Range v Response – to allow range optimisation modelling SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Risk, Response and Range Ø Separating response from risk allows powerful response models to examine a wide range of operational options quickly and with confidence Ø Response can be modelled with simulation techniques, taking account of all key controllable and uncontrollable input variables Ø Range cover (assumes static resources) allows optimisation modelling techniques to be used, and the solutions tested by simulating response Response v Risk – to allow a transparent planning process Range v Response – to allow range optimisation modelling SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Overview of Models Used SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Overview of Models Used SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
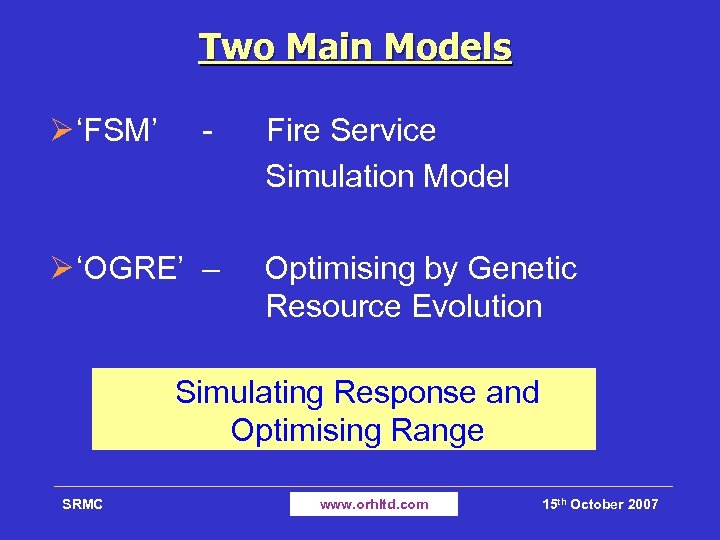 Two Main Models Ø ‘FSM’ - Ø ‘OGRE’ – Fire Service Simulation Model Optimising by Genetic Resource Evolution Simulating Response and Optimising Range SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Two Main Models Ø ‘FSM’ - Ø ‘OGRE’ – Fire Service Simulation Model Optimising by Genetic Resource Evolution Simulating Response and Optimising Range SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
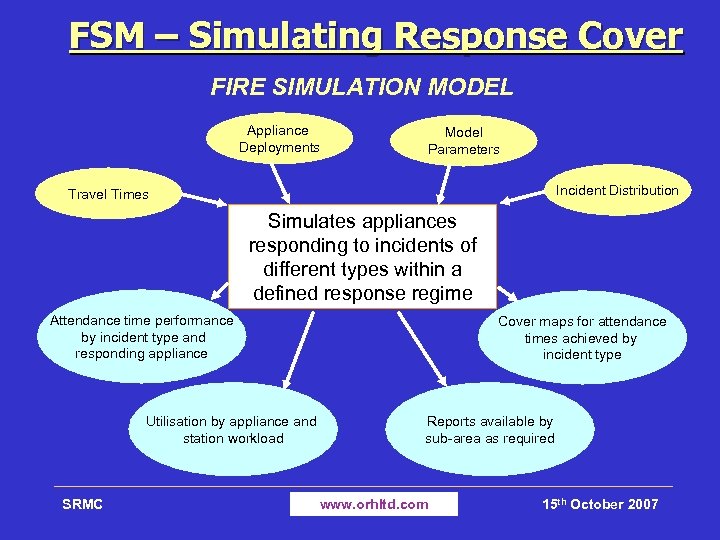 FSM – Simulating Response Cover FIRE SIMULATION MODEL Appliance Deployments Model Parameters Incident Distribution Travel Times Simulates appliances responding to incidents of different types within a defined response regime Attendance time performance by incident type and responding appliance Utilisation by appliance and station workload SRMC Cover maps for attendance times achieved by incident type Reports available by sub-area as required www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
FSM – Simulating Response Cover FIRE SIMULATION MODEL Appliance Deployments Model Parameters Incident Distribution Travel Times Simulates appliances responding to incidents of different types within a defined response regime Attendance time performance by incident type and responding appliance Utilisation by appliance and station workload SRMC Cover maps for attendance times achieved by incident type Reports available by sub-area as required www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 What FSM Can Do Simulates the cover impact of changes in: Ø appliance deployments Ø the balance between wholetime, ‘day only’ and retained stations Ø station locations and the overall configuration Ø improved mobilisation Ø shift systems and staff deployment Ø demand levels – future projected Ø combinations of above and others SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
What FSM Can Do Simulates the cover impact of changes in: Ø appliance deployments Ø the balance between wholetime, ‘day only’ and retained stations Ø station locations and the overall configuration Ø improved mobilisation Ø shift systems and staff deployment Ø demand levels – future projected Ø combinations of above and others SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
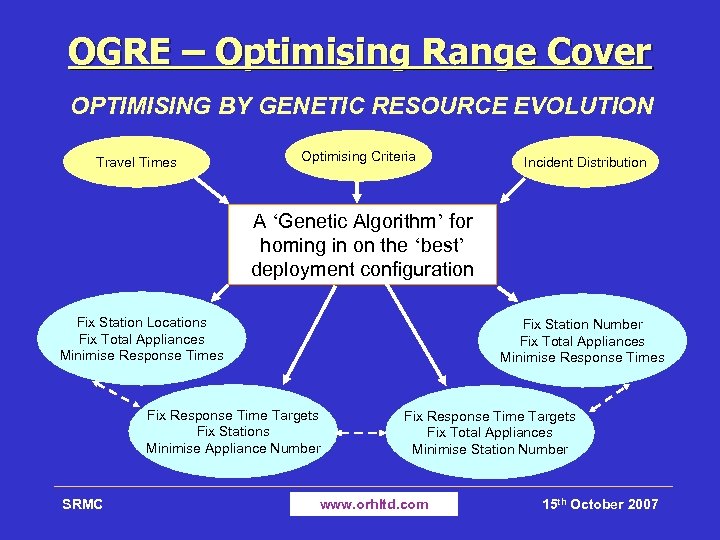 OGRE – Optimising Range Cover OPTIMISING BY GENETIC RESOURCE EVOLUTION Travel Times Optimising Criteria Incident Distribution A ‘Genetic Algorithm’ for homing in on the ‘best’ deployment configuration Fix Station Locations Fix Total Appliances Minimise Response Times Fix Station Number Fix Total Appliances Minimise Response Times Fix Response Time Targets Fix Stations Minimise Appliance Number SRMC Fix Response Time Targets Fix Total Appliances Minimise Station Number www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
OGRE – Optimising Range Cover OPTIMISING BY GENETIC RESOURCE EVOLUTION Travel Times Optimising Criteria Incident Distribution A ‘Genetic Algorithm’ for homing in on the ‘best’ deployment configuration Fix Station Locations Fix Total Appliances Minimise Response Times Fix Station Number Fix Total Appliances Minimise Response Times Fix Response Time Targets Fix Stations Minimise Appliance Number SRMC Fix Response Time Targets Fix Total Appliances Minimise Station Number www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 What OGRE Can Do Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø OGRE optimises the location of appliances Targets relate to appliance cover for incidents Embraces targets for 1 st, 2 nd, etc attendance Embraces targets for different incident types FRS determines appropriate optimisation function Optimises to greenfield sites or around fixed points Optimises with fixed or variable appliance number Optimises with fixed or variable station number Can optimise the location of ‘special appliances’ SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
What OGRE Can Do Ø Ø Ø Ø Ø OGRE optimises the location of appliances Targets relate to appliance cover for incidents Embraces targets for 1 st, 2 nd, etc attendance Embraces targets for different incident types FRS determines appropriate optimisation function Optimises to greenfield sites or around fixed points Optimises with fixed or variable appliance number Optimises with fixed or variable station number Can optimise the location of ‘special appliances’ SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
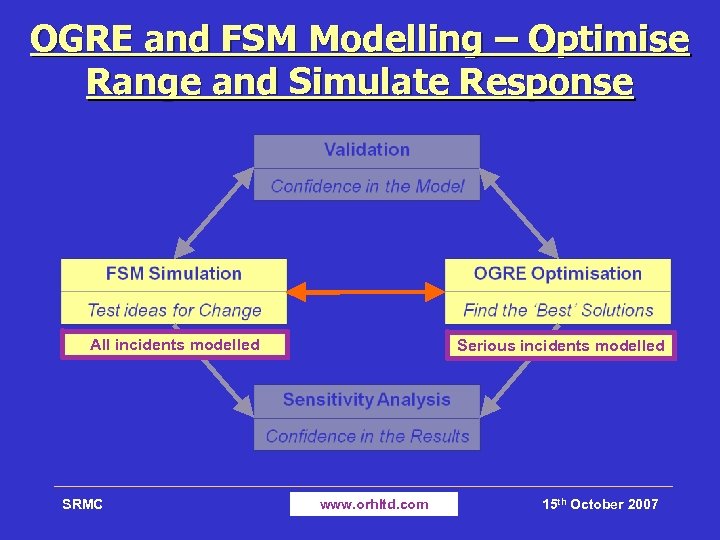 OGRE and FSM Modelling – Optimise Range and Simulate Response All incidents modelled SRMC Serious incidents modelled www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
OGRE and FSM Modelling – Optimise Range and Simulate Response All incidents modelled SRMC Serious incidents modelled www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Examples SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Examples SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
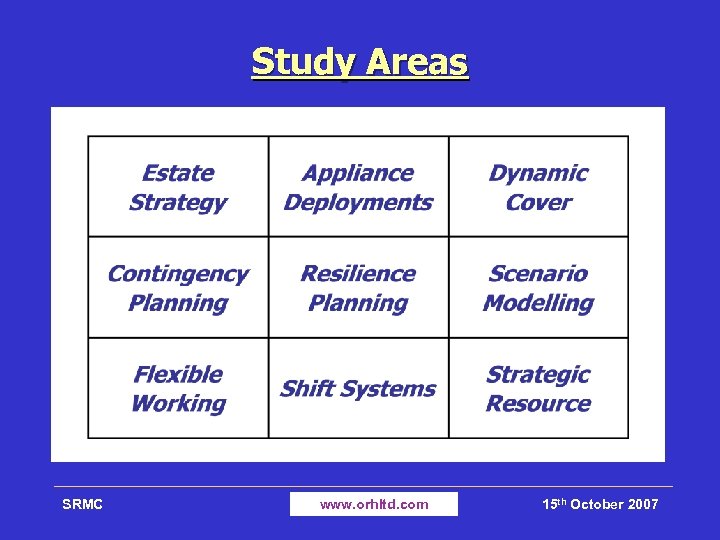 Study Areas SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Study Areas SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Overview and Methodology Employed SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Overview and Methodology Employed SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
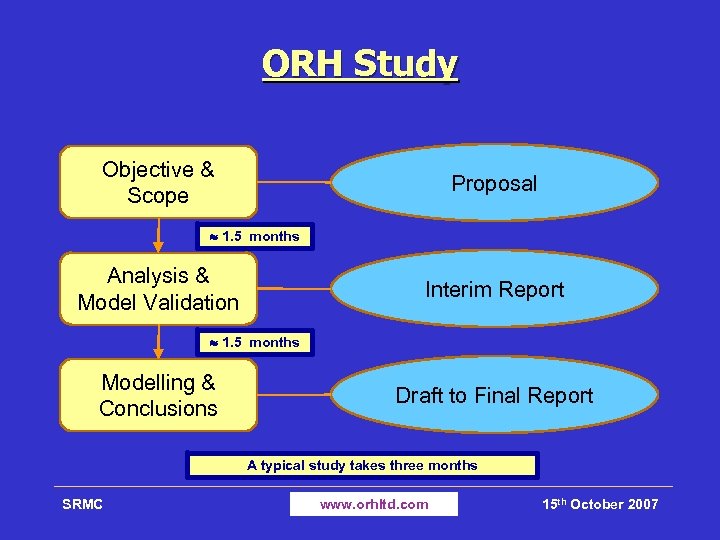 ORH Study Objective & Scope Proposal 1. 5 months Analysis & Model Validation Interim Report 1. 5 months Modelling & Conclusions Draft to Final Report A typical study takes three months SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
ORH Study Objective & Scope Proposal 1. 5 months Analysis & Model Validation Interim Report 1. 5 months Modelling & Conclusions Draft to Final Report A typical study takes three months SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
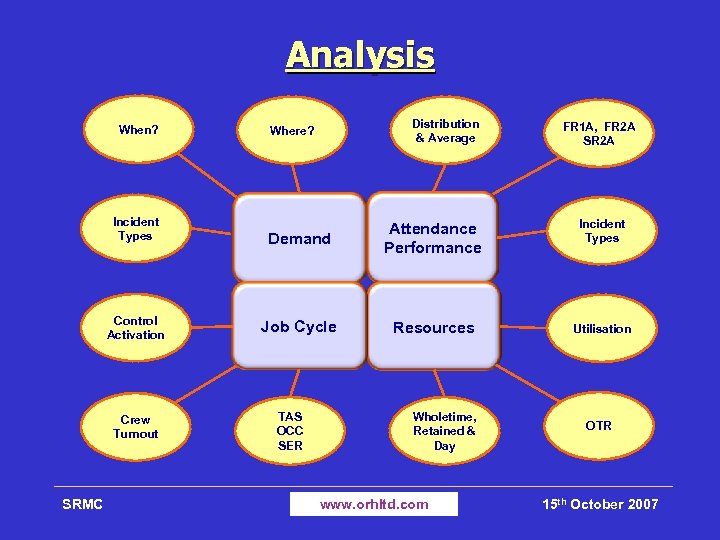 Analysis When? Incident Types Control Activation Crew Turnout SRMC Distribution & Average Where? FR 1 A, FR 2 A SR 2 A Demand Attendance Performance Incident Types Job Cycle Resources Utilisation TAS OCC SER Wholetime, Retained & Day www. orhltd. com OTR 15 th October 2007
Analysis When? Incident Types Control Activation Crew Turnout SRMC Distribution & Average Where? FR 1 A, FR 2 A SR 2 A Demand Attendance Performance Incident Types Job Cycle Resources Utilisation TAS OCC SER Wholetime, Retained & Day www. orhltd. com OTR 15 th October 2007
 Analysis Outcomes Ø Quantifies current cover characteristics Ø Provides insights into study objectives Ø Prepares inputs/outputs for model validation Ø Informs the modelling phase of the study SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Analysis Outcomes Ø Quantifies current cover characteristics Ø Provides insights into study objectives Ø Prepares inputs/outputs for model validation Ø Informs the modelling phase of the study SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
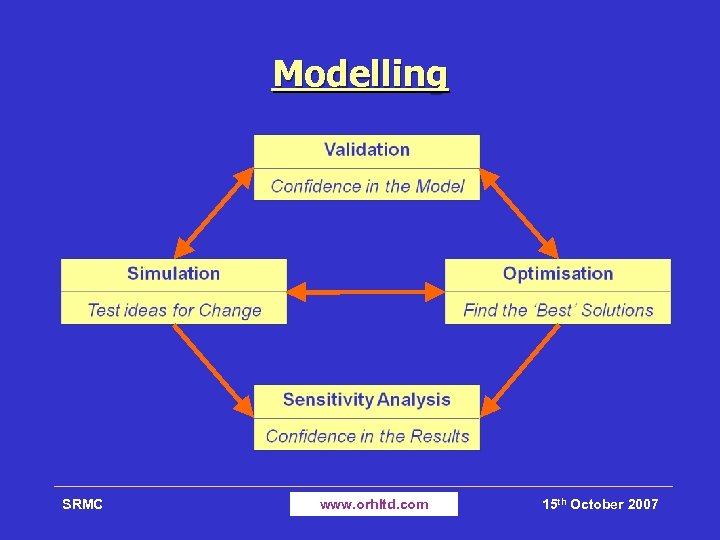 Modelling SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Modelling SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Modelling Outcomes Ø Response model validated for local FRS Ø Model, once validated, gives a powerful tool Ø Informs a range of planning issues Ø Model runs are very quick (decades in minutes) Ø Can be used iteratively in consultation with FRS Ø Solutions tested by sensitivity analysis Ø Can check solutions developed in-house Ø Provides robust information for consultation SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Modelling Outcomes Ø Response model validated for local FRS Ø Model, once validated, gives a powerful tool Ø Informs a range of planning issues Ø Model runs are very quick (decades in minutes) Ø Can be used iteratively in consultation with FRS Ø Solutions tested by sensitivity analysis Ø Can check solutions developed in-house Ø Provides robust information for consultation SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Future Development of Systems SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Future Development of Systems SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Future ORH Systems Development Ø Improve real-time dynamic cover model Ø Use OGRE to optimise against risk proxies Ø Develop response/risk modelling relationship Ø Model special appliances alongside ‘pumps’ Ø Develop method for projecting future incidents Ø Research response/consequence relationship Ø Developments required by future FRS clients! SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Future ORH Systems Development Ø Improve real-time dynamic cover model Ø Use OGRE to optimise against risk proxies Ø Develop response/risk modelling relationship Ø Model special appliances alongside ‘pumps’ Ø Develop method for projecting future incidents Ø Research response/consequence relationship Ø Developments required by future FRS clients! SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Summary SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Summary SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 Summary Ø The IRMP planning process is complex Ø Separating response modelling from risk analysis - but with a link between them - works well Ø Modelling should inform plans in a transparent way, ensuring that impacts of change are clear Ø In-house skills/software combined with ORH modelling support can be a strong combination Ø Using specialist ORH modelling will give more confidence in plans for change SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Summary Ø The IRMP planning process is complex Ø Separating response modelling from risk analysis - but with a link between them - works well Ø Modelling should inform plans in a transparent way, ensuring that impacts of change are clear Ø In-house skills/software combined with ORH modelling support can be a strong combination Ø Using specialist ORH modelling will give more confidence in plans for change SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
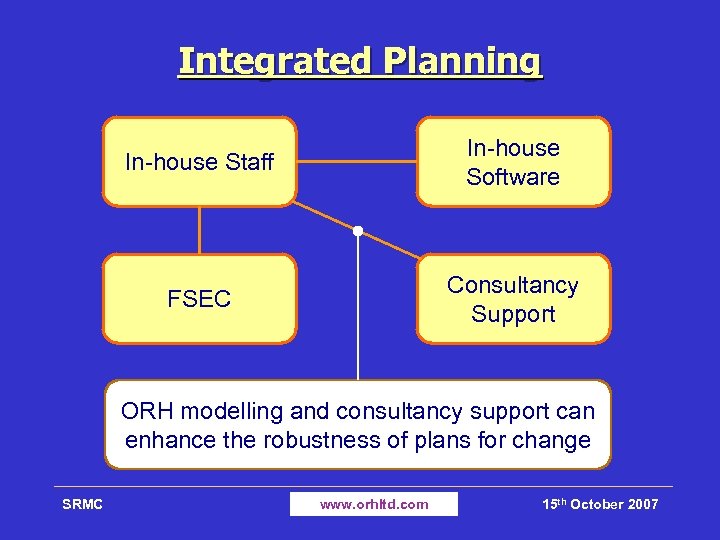 Integrated Planning In-house Staff In-house Software FSEC Consultancy Support ORH modelling and consultancy support can enhance the robustness of plans for change SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
Integrated Planning In-house Staff In-house Software FSEC Consultancy Support ORH modelling and consultancy support can enhance the robustness of plans for change SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
 How are you solving the puzzle? Make ORH part of your solution SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007
How are you solving the puzzle? Make ORH part of your solution SRMC www. orhltd. com 15 th October 2007


