8bb84404ede71c810bb22bfedb45f64c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 How and Why Novartis is Exploiting GRID Technology? HPC and Semantic Web Prof. Manuel C. Peitsch, Ph. D Global Head of Systems Biology
How and Why Novartis is Exploiting GRID Technology? HPC and Semantic Web Prof. Manuel C. Peitsch, Ph. D Global Head of Systems Biology
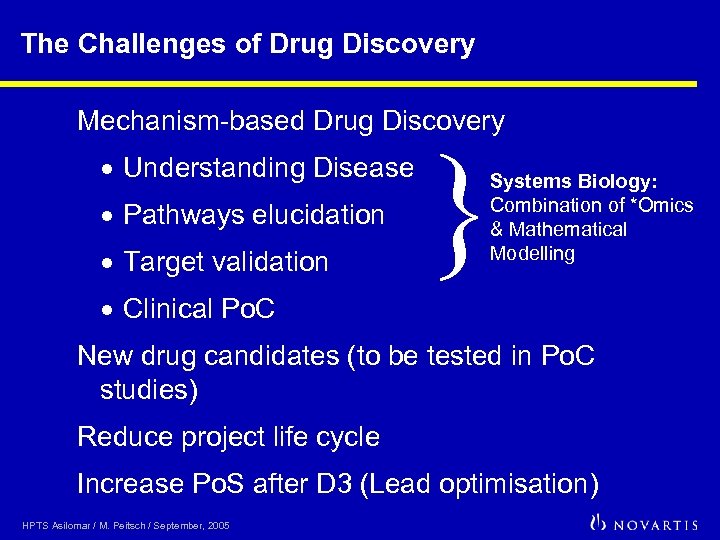 The Challenges of Drug Discovery Mechanism-based Drug Discovery · Understanding Disease · Pathways elucidation · Target validation } Systems Biology: Combination of *Omics & Mathematical Modelling · Clinical Po. C New drug candidates (to be tested in Po. C studies) Reduce project life cycle Increase Po. S after D 3 (Lead optimisation) HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
The Challenges of Drug Discovery Mechanism-based Drug Discovery · Understanding Disease · Pathways elucidation · Target validation } Systems Biology: Combination of *Omics & Mathematical Modelling · Clinical Po. C New drug candidates (to be tested in Po. C studies) Reduce project life cycle Increase Po. S after D 3 (Lead optimisation) HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
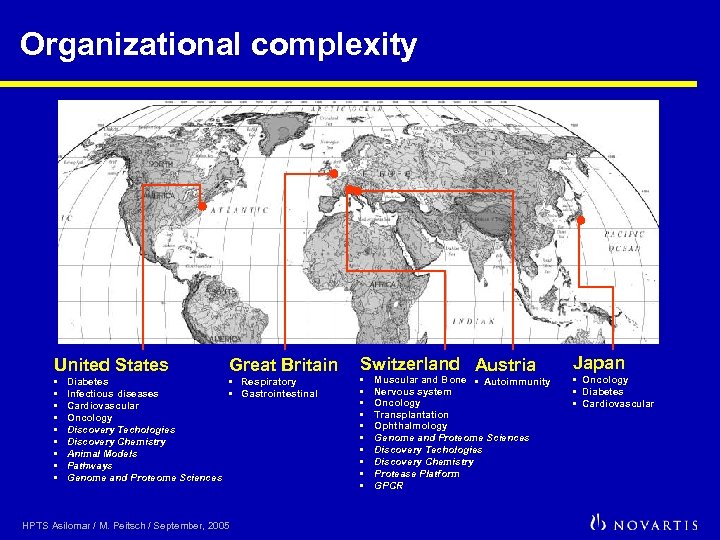 Organizational complexity United States • • • Great Britain Diabetes • Respiratory Infectious diseases • Gastrointestinal Cardiovascular Oncology Discovery Techologies Discovery Chemistry Animal Models Pathways Genome and Proteome Sciences HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Switzerland Austria • • • Muscular and Bone • Autoimmunity Nervous system Oncology Transplantation Ophthalmology Genome and Proteome Sciences Discovery Techologies Discovery Chemistry Protease Platform GPCR Japan • Oncology • Diabetes • Cardiovascular
Organizational complexity United States • • • Great Britain Diabetes • Respiratory Infectious diseases • Gastrointestinal Cardiovascular Oncology Discovery Techologies Discovery Chemistry Animal Models Pathways Genome and Proteome Sciences HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Switzerland Austria • • • Muscular and Bone • Autoimmunity Nervous system Oncology Transplantation Ophthalmology Genome and Proteome Sciences Discovery Techologies Discovery Chemistry Protease Platform GPCR Japan • Oncology • Diabetes • Cardiovascular
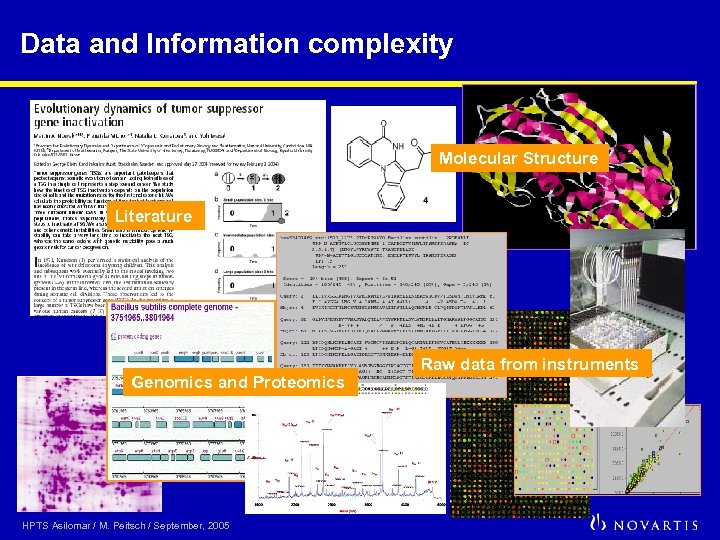 Data and Information complexity Molecular Structure Literature Genomics and Proteomics HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Raw data from instruments
Data and Information complexity Molecular Structure Literature Genomics and Proteomics HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Raw data from instruments
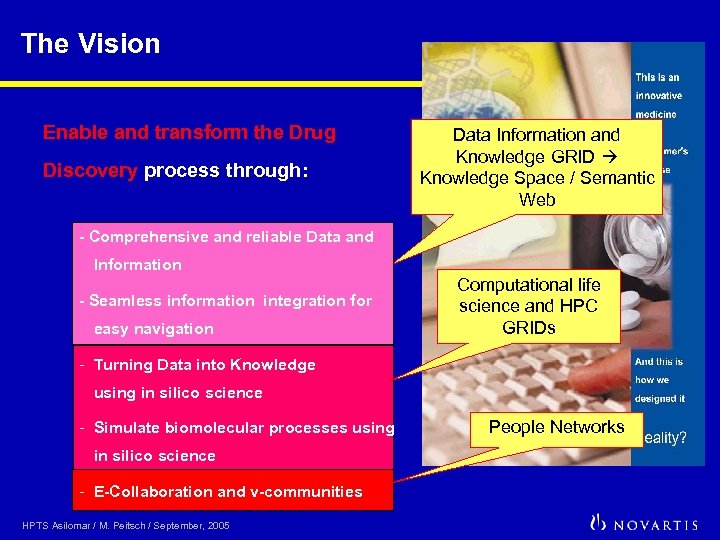 The Vision Enable and transform the Drug Discovery process through: Data Information and Knowledge GRID Knowledge Space / Semantic Web - Comprehensive and reliable Data and Information - Seamless information integration for easy navigation Computational life science and HPC GRIDs - Turning Data into Knowledge using in silico science - Simulate biomolecular processes using in silico science - E-Collaboration and v-communities HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 People Networks
The Vision Enable and transform the Drug Discovery process through: Data Information and Knowledge GRID Knowledge Space / Semantic Web - Comprehensive and reliable Data and Information - Seamless information integration for easy navigation Computational life science and HPC GRIDs - Turning Data into Knowledge using in silico science - Simulate biomolecular processes using in silico science - E-Collaboration and v-communities HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 People Networks
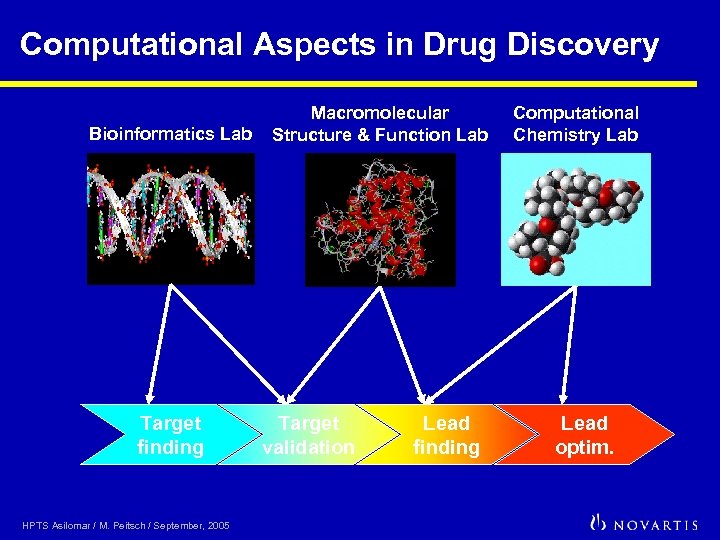 Computational Aspects in Drug Discovery Bioinformatics Lab Target finding HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Macromolecular Structure & Function Lab Target validation Lead finding Computational Chemistry Lab Lead optim.
Computational Aspects in Drug Discovery Bioinformatics Lab Target finding HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Macromolecular Structure & Function Lab Target validation Lead finding Computational Chemistry Lab Lead optim.
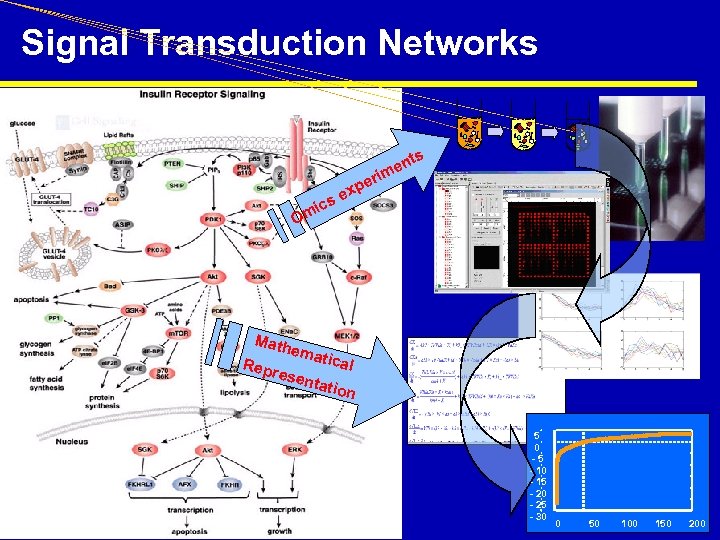 Signal Transduction Networks. . . ts en rim e xp se ic Om Math Repr e ema tical sent ation HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 5 0 -5 - 10 - 15 - 20 - 25 - 30 0 50 100 150 200
Signal Transduction Networks. . . ts en rim e xp se ic Om Math Repr e ema tical sent ation HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 5 0 -5 - 10 - 15 - 20 - 25 - 30 0 50 100 150 200
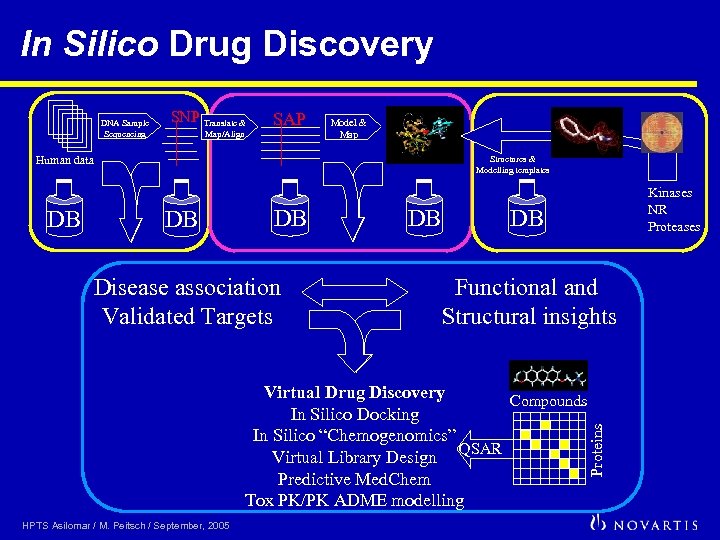 In Silico Drug Discovery SNP Translate & Map/Align SAP Model & Map Human data DB Structures & Modelling templates DB DB Disease association Validated Targets DB DB Functional and Structural insights Virtual Drug Discovery Compounds In Silico Docking In Silico “Chemogenomics” Virtual Library Design QSAR Predictive Med. Chem Tox PK/PK ADME modelling HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Kinases NR Proteases Proteins DNA Sample Sequencing
In Silico Drug Discovery SNP Translate & Map/Align SAP Model & Map Human data DB Structures & Modelling templates DB DB Disease association Validated Targets DB DB Functional and Structural insights Virtual Drug Discovery Compounds In Silico Docking In Silico “Chemogenomics” Virtual Library Design QSAR Predictive Med. Chem Tox PK/PK ADME modelling HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Kinases NR Proteases Proteins DNA Sample Sequencing
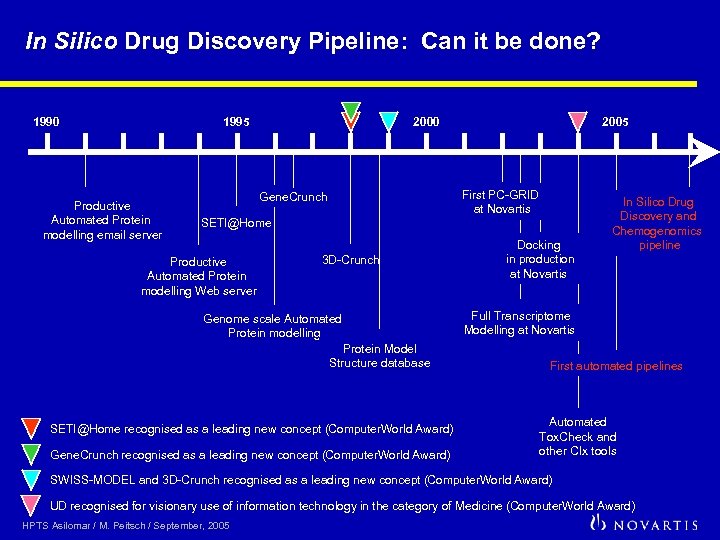 In Silico Drug Discovery Pipeline: Can it be done? 1990 1995 Productive Automated Protein modelling email server 2000 2005 First PC-GRID at Novartis Gene. Crunch SETI@Home Productive Automated Protein modelling Web server 3 D-Crunch Genome scale Automated Protein modelling Protein Model Structure database SETI@Home recognised as a leading new concept (Computer. World Award) Gene. Crunch recognised as a leading new concept (Computer. World Award) Docking in production at Novartis In Silico Drug Discovery and Chemogenomics pipeline Full Transcriptome Modelling at Novartis First automated pipelines Automated Tox. Check and other CIx tools SWISS-MODEL and 3 D-Crunch recognised as a leading new concept (Computer. World Award) UD recognised for visionary use of information technology in the category of Medicine (Computer. World Award) HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
In Silico Drug Discovery Pipeline: Can it be done? 1990 1995 Productive Automated Protein modelling email server 2000 2005 First PC-GRID at Novartis Gene. Crunch SETI@Home Productive Automated Protein modelling Web server 3 D-Crunch Genome scale Automated Protein modelling Protein Model Structure database SETI@Home recognised as a leading new concept (Computer. World Award) Gene. Crunch recognised as a leading new concept (Computer. World Award) Docking in production at Novartis In Silico Drug Discovery and Chemogenomics pipeline Full Transcriptome Modelling at Novartis First automated pipelines Automated Tox. Check and other CIx tools SWISS-MODEL and 3 D-Crunch recognised as a leading new concept (Computer. World Award) UD recognised for visionary use of information technology in the category of Medicine (Computer. World Award) HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
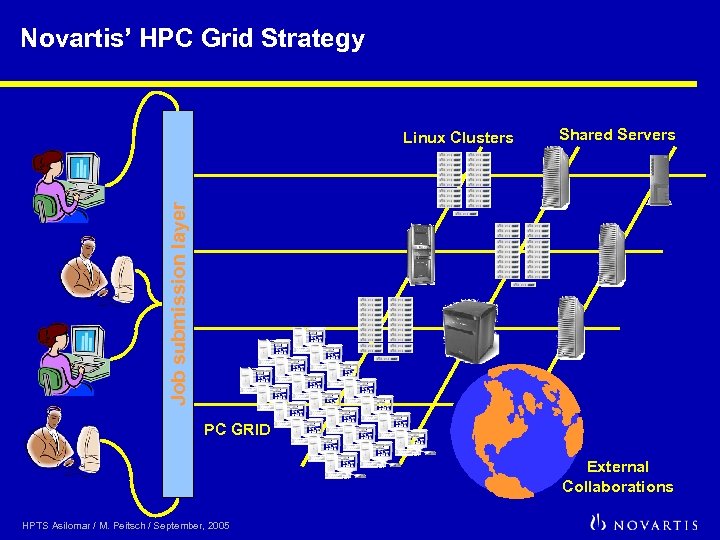 Novartis’ HPC Grid Strategy Shared Servers Job submission layer Linux Clusters PC GRID External Collaborations HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Novartis’ HPC Grid Strategy Shared Servers Job submission layer Linux Clusters PC GRID External Collaborations HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
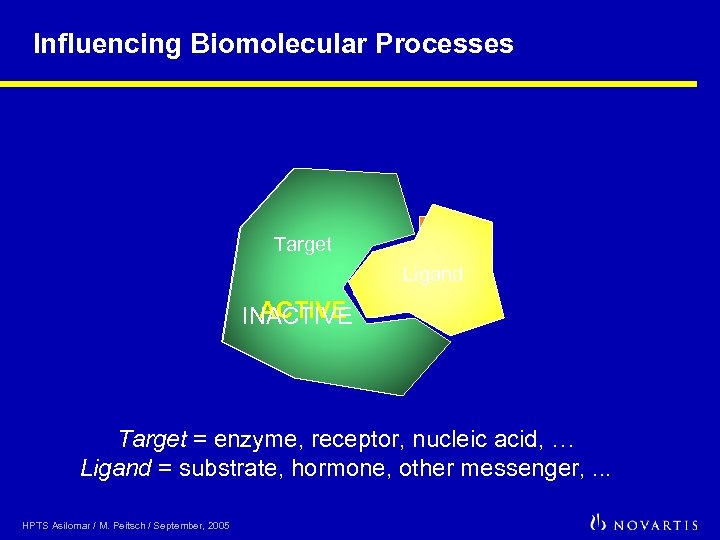 Influencing Biomolecular Processes Target Ligand Drug ACTIVE INACTIVE Target = enzyme, receptor, nucleic acid, … Ligand = substrate, hormone, other messenger, . . . HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Influencing Biomolecular Processes Target Ligand Drug ACTIVE INACTIVE Target = enzyme, receptor, nucleic acid, … Ligand = substrate, hormone, other messenger, . . . HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 PC Grid Success Story: Protein Kinase CK 2 Inhibition Target finding: Protein Kinase CK 2 has roles in cell growth, proliferation and survival. Protein Kinase CK 2 has a possible role cancer and its over expression has been associated with lymphoma. Target validation: To elucidate the different functions and roles of CK 2 and confirm it as a drug target for oncology, one needs a potent and selective inhibitor. Approach: The problem was addressed by in silico screening (docking). HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
PC Grid Success Story: Protein Kinase CK 2 Inhibition Target finding: Protein Kinase CK 2 has roles in cell growth, proliferation and survival. Protein Kinase CK 2 has a possible role cancer and its over expression has been associated with lymphoma. Target validation: To elucidate the different functions and roles of CK 2 and confirm it as a drug target for oncology, one needs a potent and selective inhibitor. Approach: The problem was addressed by in silico screening (docking). HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
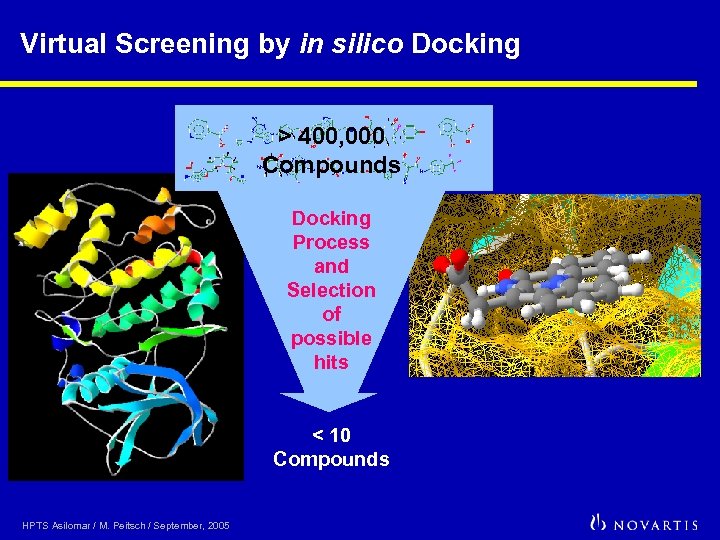 Virtual Screening by in silico Docking > 400, 000 Compounds Docking Process and Selection of possible hits < 10 Compounds HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Virtual Screening by in silico Docking > 400, 000 Compounds Docking Process and Selection of possible hits < 10 Compounds HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
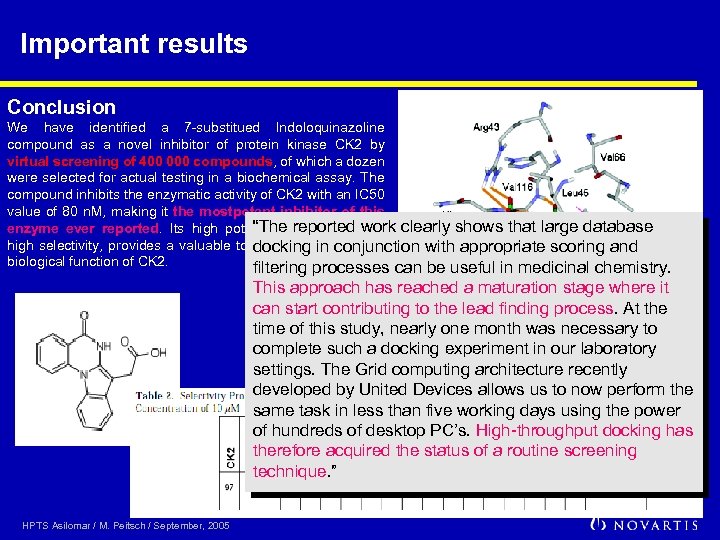 Important results Conclusion We have identified a 7 -substitued Indoloquinazoline compound as a novel inhibitor of protein kinase CK 2 by virtual screening of 400 000 compounds, of which a dozen were selected for actual testing in a biochemical assay. The compound inhibits the enzymatic activity of CK 2 with an IC 50 value of 80 n. M, making it the mostpotent inhibitor of this “The reported work enzyme ever reported. Its high potency, associated with clearly shows that large database high selectivity, provides a valuable tool for the study of the docking in conjunction with appropriate scoring and biological function of CK 2. filtering processes can be useful in medicinal chemistry. This approach has reached a maturation stage where it can start contributing to the lead finding process. At the time of this study, nearly one month was necessary to complete such a docking experiment in our laboratory settings. The Grid computing architecture recently developed by United Devices allows us to now perform the same task in less than five working days using the power of hundreds of desktop PC’s. High-throughput docking has therefore acquired the status of a routine screening technique. ” HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Important results Conclusion We have identified a 7 -substitued Indoloquinazoline compound as a novel inhibitor of protein kinase CK 2 by virtual screening of 400 000 compounds, of which a dozen were selected for actual testing in a biochemical assay. The compound inhibits the enzymatic activity of CK 2 with an IC 50 value of 80 n. M, making it the mostpotent inhibitor of this “The reported work enzyme ever reported. Its high potency, associated with clearly shows that large database high selectivity, provides a valuable tool for the study of the docking in conjunction with appropriate scoring and biological function of CK 2. filtering processes can be useful in medicinal chemistry. This approach has reached a maturation stage where it can start contributing to the lead finding process. At the time of this study, nearly one month was necessary to complete such a docking experiment in our laboratory settings. The Grid computing architecture recently developed by United Devices allows us to now perform the same task in less than five working days using the power of hundreds of desktop PC’s. High-throughput docking has therefore acquired the status of a routine screening technique. ” HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 Major benefits of GRID computing Optimization of resources utilization: · HPC platforms usage is maximized and Technology expertise is shared. · Response to additional performance requirements is easier and faster · No service downtime due to possibility to run same job on many platforms across different sites. Enable cross business units collaboration and synergies: · Single efficient access path to Data and Compute resources. · Tools are easily exchanged between scientists/programs. Favor “out of the box” thinking: · Apply HPC to areas which one would not even have considered a year ago. This has created a fertile ground for a new paradigms in Drug Discovery leading to Business Process transformation. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Major benefits of GRID computing Optimization of resources utilization: · HPC platforms usage is maximized and Technology expertise is shared. · Response to additional performance requirements is easier and faster · No service downtime due to possibility to run same job on many platforms across different sites. Enable cross business units collaboration and synergies: · Single efficient access path to Data and Compute resources. · Tools are easily exchanged between scientists/programs. Favor “out of the box” thinking: · Apply HPC to areas which one would not even have considered a year ago. This has created a fertile ground for a new paradigms in Drug Discovery leading to Business Process transformation. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 Performance of the PC-GRID (today) Computing Power: Ø Theoretical >5 Tera. FLOPS harvested from 3000 PCs in all geographical locations. Ø Acceleration of the in silico Docking process versus 1 standard 2002 PC (start of project): ~4000 x Financial: Ø Immediate savings in excess of 2 m$. Ø No need for additional data centre to support this computing power. Ø Optimally use of existing hardware (associates’ PCs) HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Performance of the PC-GRID (today) Computing Power: Ø Theoretical >5 Tera. FLOPS harvested from 3000 PCs in all geographical locations. Ø Acceleration of the in silico Docking process versus 1 standard 2002 PC (start of project): ~4000 x Financial: Ø Immediate savings in excess of 2 m$. Ø No need for additional data centre to support this computing power. Ø Optimally use of existing hardware (associates’ PCs) HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 Building a GRID: Management focus You need a champion! Do not punctuate every sentence with the GRID word and avoid the Hype! Demonstrate value through pilots: · Think “Iterative Improvement”. The conceptual layers are there, prototype are emerging, improvements and optimization is essential, maturity will follow Leadership, transcendence, entrepreneurship and tenacity are the essence of transformation! · Concepts are easy to draw on a napkin over beer! · But new and great things are hard to achieve! · Use external goodwill to create internal acceptance! HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Building a GRID: Management focus You need a champion! Do not punctuate every sentence with the GRID word and avoid the Hype! Demonstrate value through pilots: · Think “Iterative Improvement”. The conceptual layers are there, prototype are emerging, improvements and optimization is essential, maturity will follow Leadership, transcendence, entrepreneurship and tenacity are the essence of transformation! · Concepts are easy to draw on a napkin over beer! · But new and great things are hard to achieve! · Use external goodwill to create internal acceptance! HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 Peru Community projects help with acceptance HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Peru Community projects help with acceptance HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 Building a GRID: User base You need a clearly defined and communicated HP Computing strategy. · Address unmet computational needs. · Apply HPC to areas which one would not even have considered two years ago. This has created a fertile ground for a new paradigms in Drug Discovery leading to Business Process transformation. Are all problems “GRIDable”? Further applications: · Sequence identification in proteomics from LC-MS/MS data · Text Mining and semantic Web infrastructure HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Building a GRID: User base You need a clearly defined and communicated HP Computing strategy. · Address unmet computational needs. · Apply HPC to areas which one would not even have considered two years ago. This has created a fertile ground for a new paradigms in Drug Discovery leading to Business Process transformation. Are all problems “GRIDable”? Further applications: · Sequence identification in proteomics from LC-MS/MS data · Text Mining and semantic Web infrastructure HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 Building a GRID: Software The Software licensing models will have to evolve · Do not stop because of software licensing issues. · Show success with freeware and home grown algorithms. · Demonstrate business value and cost leadership. · Opportunity to develop your own code? Unification of HPC applications environment: · Ensure that applications can run on maximum number of systems. Introduce HPC software management: · Influence licensing models. The classical models do not fit the GRID and HPC paradigm. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Building a GRID: Software The Software licensing models will have to evolve · Do not stop because of software licensing issues. · Show success with freeware and home grown algorithms. · Demonstrate business value and cost leadership. · Opportunity to develop your own code? Unification of HPC applications environment: · Ensure that applications can run on maximum number of systems. Introduce HPC software management: · Influence licensing models. The classical models do not fit the GRID and HPC paradigm. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 Building a GRID: PC owners Education and awareness. · Ensure that the Help. Desk is well trained and gives the right answers. · Ensure that PC owners know about the REAL impacts, including network. The PCs are company and not personal assets! · Strategy to use them when they are idle is not a user but a company decision. · Address power saving policies in a transparent manner. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Building a GRID: PC owners Education and awareness. · Ensure that the Help. Desk is well trained and gives the right answers. · Ensure that PC owners know about the REAL impacts, including network. The PCs are company and not personal assets! · Strategy to use them when they are idle is not a user but a company decision. · Address power saving policies in a transparent manner. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
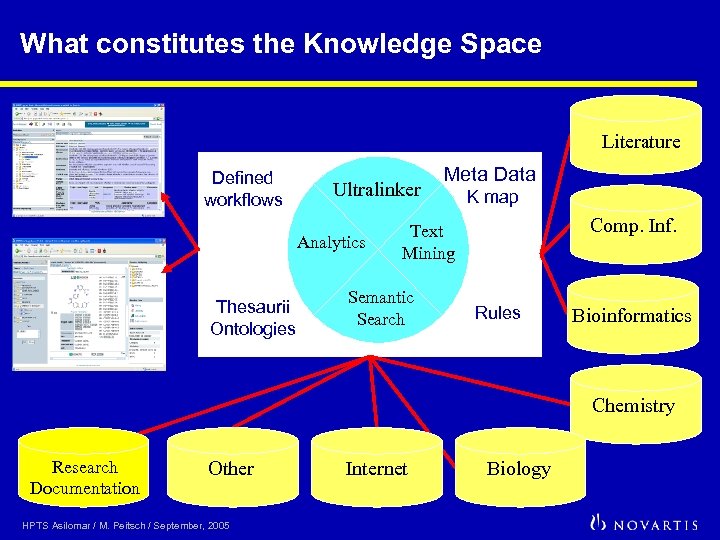
 Knowledge Space - Vision The "Knowledge Space Portal” is a Drug Discovery oriented implementation of the Semantic Web. Through a single customizable interface it: • Federates heterogeneous data resources and provide precise organization of the content • Provides quick and intuitive access to information • Provides data extraction, analysis and exploration tools • Allows data integration, data exchange and interoperability of applications • Provides mechanisms for data capture and annotation • Provides knowledge sharing and collaborative tools HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Knowledge Space - Vision The "Knowledge Space Portal” is a Drug Discovery oriented implementation of the Semantic Web. Through a single customizable interface it: • Federates heterogeneous data resources and provide precise organization of the content • Provides quick and intuitive access to information • Provides data extraction, analysis and exploration tools • Allows data integration, data exchange and interoperability of applications • Provides mechanisms for data capture and annotation • Provides knowledge sharing and collaborative tools HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 Basic principles behind the Knowledge Space The Knowledge Space consists of: The collection of all types of data and information within the scope of interest defined by a particular business. There is no conceptual difference between internal and external data/information. The Meta Data and the Knowledge Map which describe the collection in terms of content and location. The Text Mining platform which allows the identification of entities (using vocabularies) and the concepts they belong to using ontologies. The Ultralinker, which associates identified entities and concepts with specific contextual rules. A user interface. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Basic principles behind the Knowledge Space The Knowledge Space consists of: The collection of all types of data and information within the scope of interest defined by a particular business. There is no conceptual difference between internal and external data/information. The Meta Data and the Knowledge Map which describe the collection in terms of content and location. The Text Mining platform which allows the identification of entities (using vocabularies) and the concepts they belong to using ontologies. The Ultralinker, which associates identified entities and concepts with specific contextual rules. A user interface. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 What is an Ultralink? The Ultralink is an “intelligent” context-sensitive Hyperlink created at run time by the Ultralinker. The Ultralink is generally a menu of links instead of a single link. This menu will only offers sensible actions/options: · No dead ends due to a verification process ensuring that the link has a target. · The Ultralink provides direct interaction between any type of entity (gene name, compound name, mode of action, disease name, company name, etc… with an appropriate set of tools and resources as defined by the rules encoded in the Ultralinker. · The Ultralink functionality allows the selection of any portion of text in the Web browser and sends it as input to the Ultralinker for analysis and menu creation. The Ultralink allows easy navigation across the information domains contained in the Knowledge Space. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
What is an Ultralink? The Ultralink is an “intelligent” context-sensitive Hyperlink created at run time by the Ultralinker. The Ultralink is generally a menu of links instead of a single link. This menu will only offers sensible actions/options: · No dead ends due to a verification process ensuring that the link has a target. · The Ultralink provides direct interaction between any type of entity (gene name, compound name, mode of action, disease name, company name, etc… with an appropriate set of tools and resources as defined by the rules encoded in the Ultralinker. · The Ultralink functionality allows the selection of any portion of text in the Web browser and sends it as input to the Ultralinker for analysis and menu creation. The Ultralink allows easy navigation across the information domains contained in the Knowledge Space. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 How the Ultralinker works The Ultralinker is a Web service which analyses any information (such as a complete web pages) it receives for recognisable entities using text mining and pattern recognition methods. Each recognised item is mapped onto the ontologies and the Knowledge Map. The Expert System will define what can be done with the identified entities e. g. · If a gene name is recognised then Ultralinks are created to: - get its sequence and perform sequence similarity searches; - query genetic disorder databases and map it onto the chromosome; - produce a 3 D structure by comparative modelling; - look for hits from High Throughput Screening; - etc… Automated predefined processes can thus be activated by a single click (Ultraaction or work-flow). The Ultralinker will create a menu that will be sent to the User interface. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
How the Ultralinker works The Ultralinker is a Web service which analyses any information (such as a complete web pages) it receives for recognisable entities using text mining and pattern recognition methods. Each recognised item is mapped onto the ontologies and the Knowledge Map. The Expert System will define what can be done with the identified entities e. g. · If a gene name is recognised then Ultralinks are created to: - get its sequence and perform sequence similarity searches; - query genetic disorder databases and map it onto the chromosome; - produce a 3 D structure by comparative modelling; - look for hits from High Throughput Screening; - etc… Automated predefined processes can thus be activated by a single click (Ultraaction or work-flow). The Ultralinker will create a menu that will be sent to the User interface. HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 What constitutes the Knowledge Space Literature Defined workflows Ultralinker Analytics Thesaurii Ontologies Meta Data K map Comp. Inf. Text Mining Semantic Search Rules Bioinformatics Chemistry Research Documentation Other HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Internet Biology
What constitutes the Knowledge Space Literature Defined workflows Ultralinker Analytics Thesaurii Ontologies Meta Data K map Comp. Inf. Text Mining Semantic Search Rules Bioinformatics Chemistry Research Documentation Other HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Internet Biology
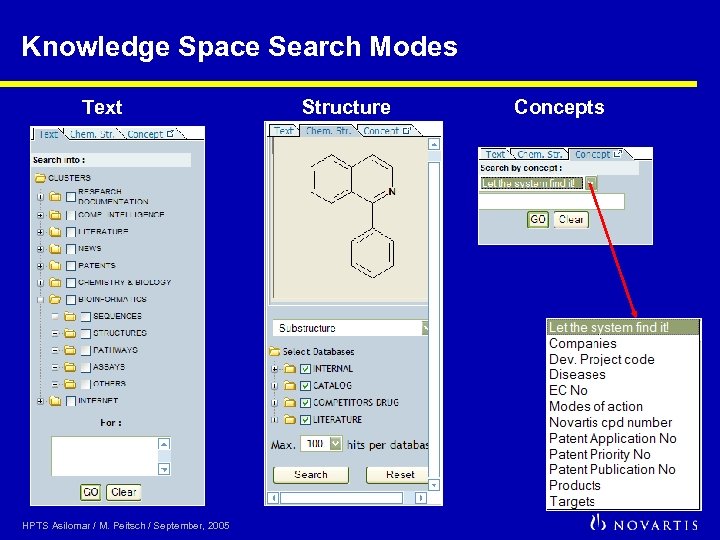 Knowledge Space Search Modes Text HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Structure Concepts
Knowledge Space Search Modes Text HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Structure Concepts
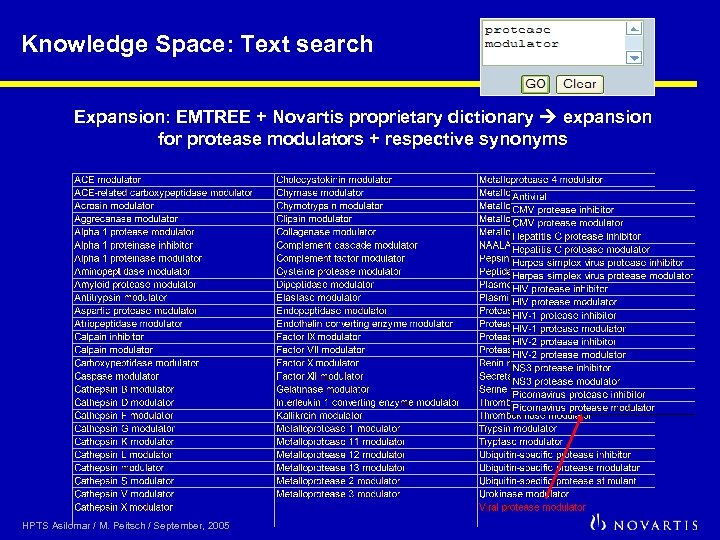 Knowledge Space: Text search Expansion: EMTREE + Novartis proprietary dictionary expansion for protease modulators + respective synonyms HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Knowledge Space: Text search Expansion: EMTREE + Novartis proprietary dictionary expansion for protease modulators + respective synonyms HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
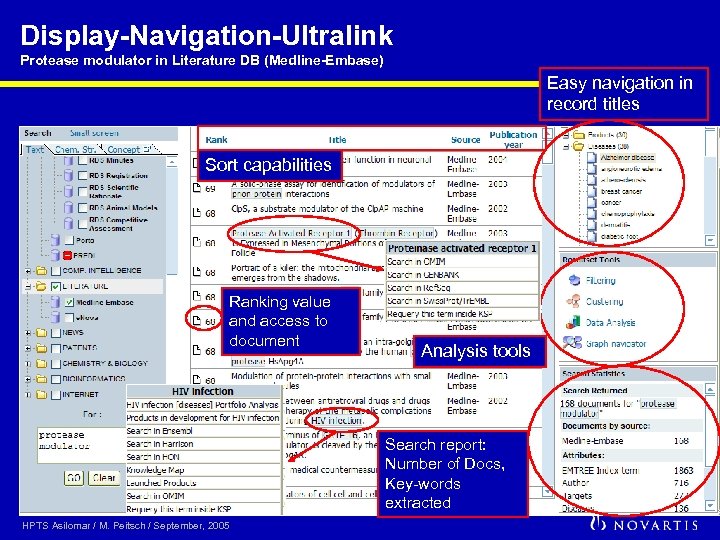 Display-Navigation-Ultralink Protease modulator in Literature DB (Medline-Embase) Easy navigation in record titles Sort capabilities Ranking value and access to document Analysis tools Search report: Number of Docs, Key-words extracted HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Display-Navigation-Ultralink Protease modulator in Literature DB (Medline-Embase) Easy navigation in record titles Sort capabilities Ranking value and access to document Analysis tools Search report: Number of Docs, Key-words extracted HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
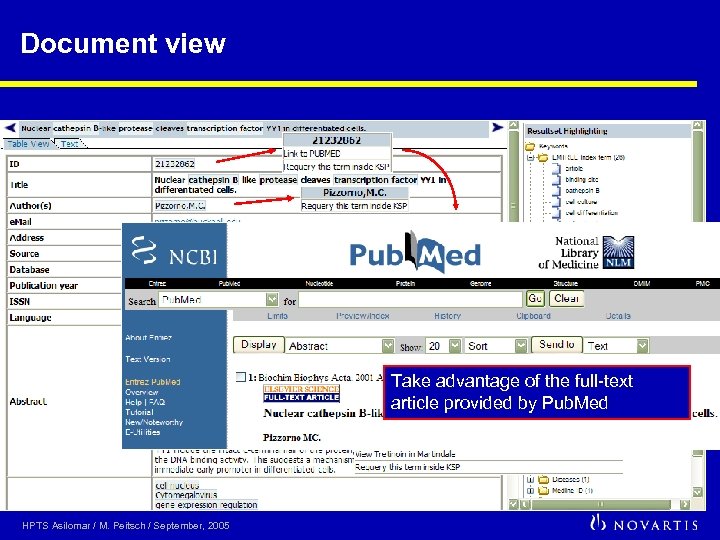 Document view Take advantage of the full-text article provided by Pub. Med HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Document view Take advantage of the full-text article provided by Pub. Med HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
 Analysis Tools HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Analysis Tools HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
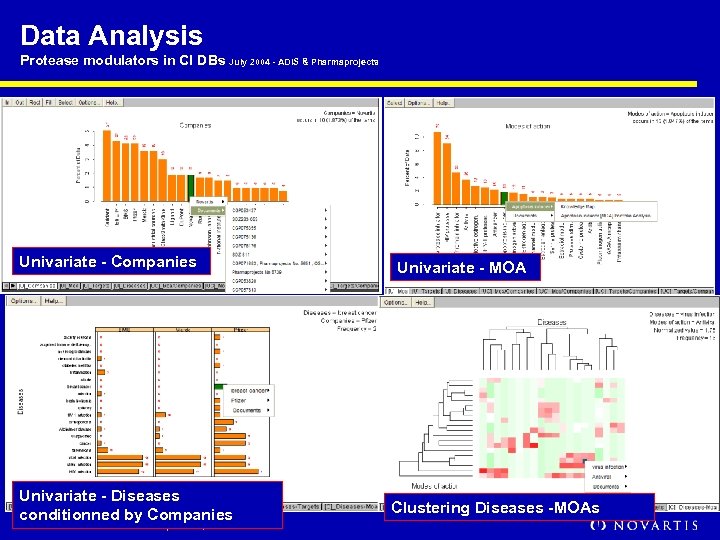 Data Analysis Protease modulators in CI DBs July 2004 - ADIS & Pharmaprojects Univariate - Companies Univariate - Diseases conditionned by Companies HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Univariate - MOA Clustering Diseases -MOAs
Data Analysis Protease modulators in CI DBs July 2004 - ADIS & Pharmaprojects Univariate - Companies Univariate - Diseases conditionned by Companies HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005 Univariate - MOA Clustering Diseases -MOAs
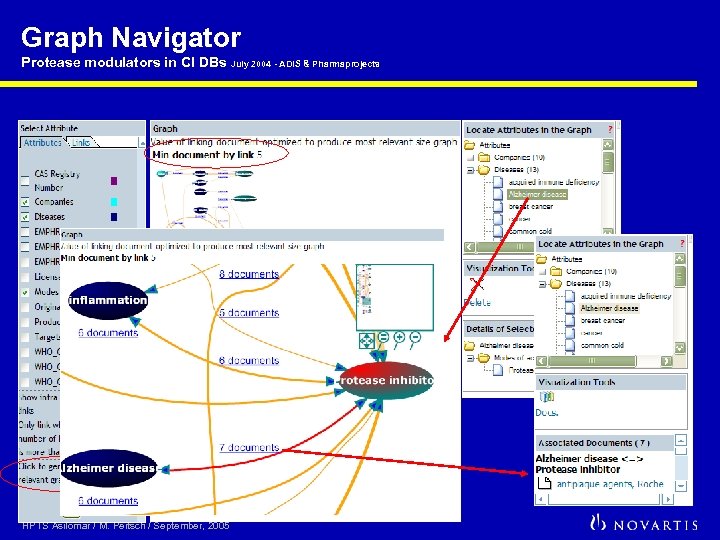 Graph Navigator Protease modulators in CI DBs July 2004 - ADIS & Pharmaprojects HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Graph Navigator Protease modulators in CI DBs July 2004 - ADIS & Pharmaprojects HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
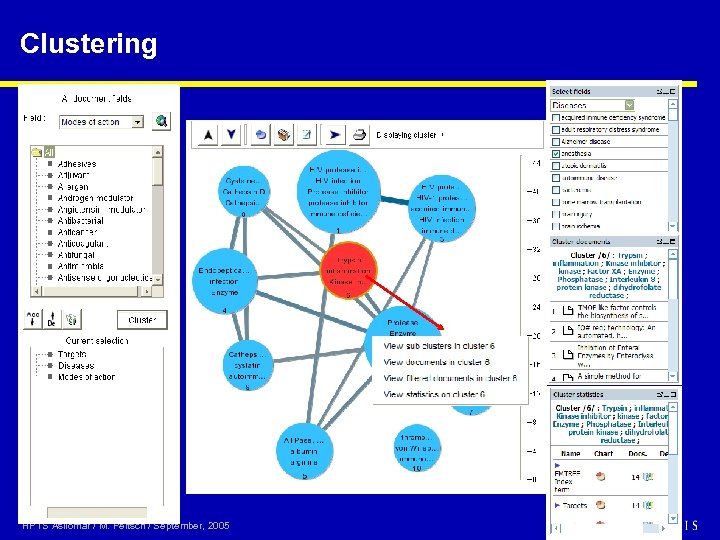 Clustering HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Clustering HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
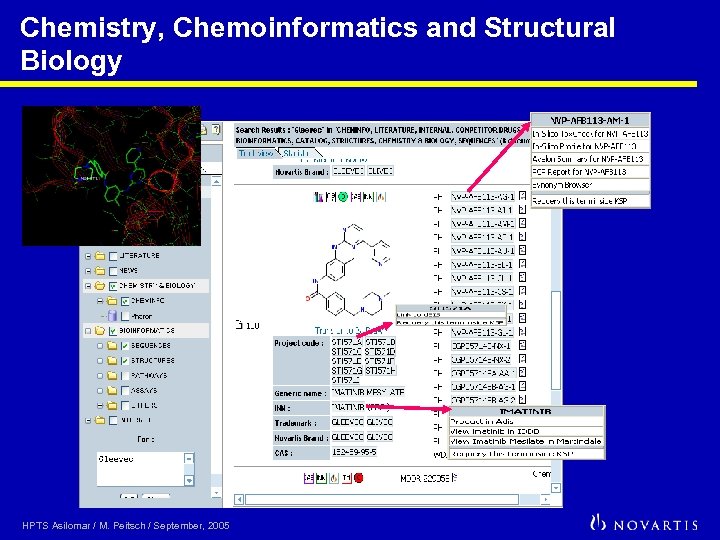 Chemistry, Chemoinformatics and Structural Biology HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005
Chemistry, Chemoinformatics and Structural Biology HPTS Asilomar / M. Peitsch / September, 2005


