6f77fee20ca7a4ef473b30c25e7a5630.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60

How and When to Order Blood Tests Tammy Pifer Than, MS, OD, FAAO Carl Vinson VAMC Dublin, GA tammy. than@va. gov

Getting the Job Done. . . • PCP • External laboratory • In-office sampling v is it ok?

Before You Order Tests. . . • • good case hx narrow ddx avoid “shot gun” approach comprehensive ocular exam

If You Order Tests. . . • interpret v Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures 4 th edition - 2004 § Chernecky and Berger § – includes Herbal interactions ISBN 0721603882 § $41. 95 § • communicate • treat • refer

Random Blood Glucose • note when patient ate last e. g. 220 mg/d. L pp 3 hours v pp = post-prandial v • diabetic if: v 200 mg/d. L with symptoms • can do in-office • encourage patients to do this!
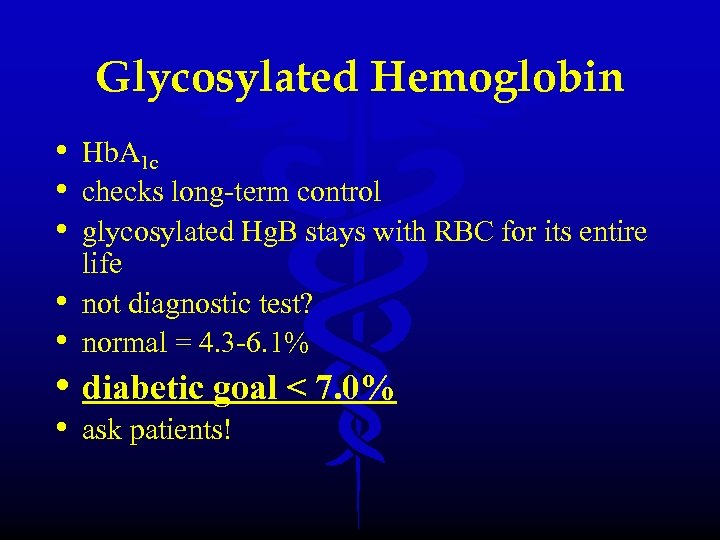
Glycosylated Hemoglobin • Hb. A 1 c • checks long-term control • glycosylated Hg. B stays with RBC for its entire • • life not diagnostic test? normal = 4. 3 -6. 1% • diabetic goal < 7. 0% • ask patients!

Fasting Plasma Glucose • fluctuating vision v • • get stable reading before new Sp. Rx retinopathy diplopia vascular occlusions optic neuropathy

CASE EXAMPLES

Case #1. This is an easy one! • • 17 year old male CC: eyes look “real bad” Symptoms: no pain Pertinent Hx: county fair last night

Subconjunctival Hemorrhage • History frequency v medications v activity v • Examination
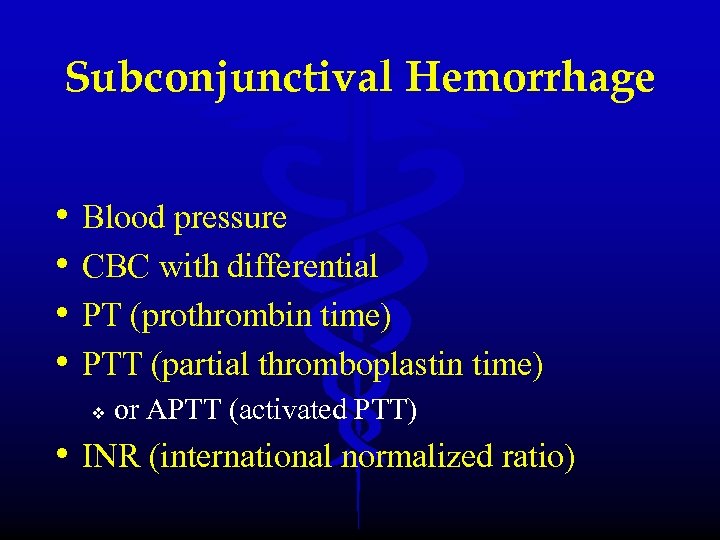
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage • • Blood pressure CBC with differential PT (prothrombin time) PTT (partial thromboplastin time) v or APTT (activated PTT) • INR (international normalized ratio)

Prothrombin Time (PT) • prothrombin: v v vitamin-K dependent glycoprotein produced by liver needed for firm fibrin clot formation • PT – measures time for clot formation v reagent tissue thromboplastin and calcium are added to citrate plasma • avoid coffee and alcohol for 24 hours before test
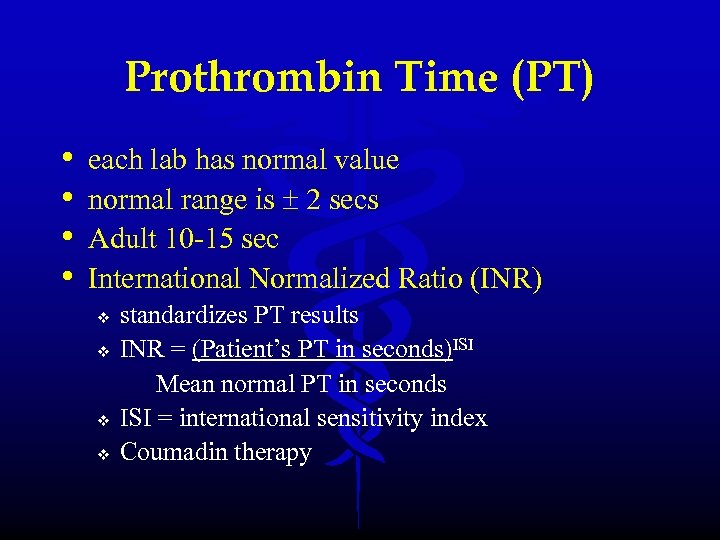
Prothrombin Time (PT) • • each lab has normal value normal range is 2 secs Adult 10 -15 sec International Normalized Ratio (INR) v v standardizes PT results INR = (Patient’s PT in seconds)ISI Mean normal PT in seconds ISI = international sensitivity index Coumadin therapy

Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT) • evaluates how well coagulation sequence is • • functioning time for recalcified, citrate plasma takes to clot after partial thromboplastin is added Activated PTT v v commercial activating materials used to standardize the test current method of the test • Standardized times reported by each lab v < 35 seconds

CBC with differential • routine part of health care • inexpensive • screening: anemia v leukemia v infection v inflammation v

WBC (Part of CBC) • Total overall number v first line of defense v decreased in aplastic anemia v elevated in infections, leukemia v

WBC (Part of CBC) • Differential 100 white blood cells v % of each v neutrophils v lymphocytes v monocytes v eosinophils & basophils v

CBC • • RBC count hemoglobin morphology hematocrit volume of RBC in 100 m. L v 3 x Hgb v • platelets

Coagulation Studies • • recurrent subconjunctival hemorrhages non-traumatic hyphema artery or vein occlusion pre-op cataract surgery?

Case #2. To Treat or not to Treat. • • 34 YOWF CC: HAs, double vision, dizzy OHx: no trauma, LEE in 1999 - normal MHx: Voltaren, Zantac
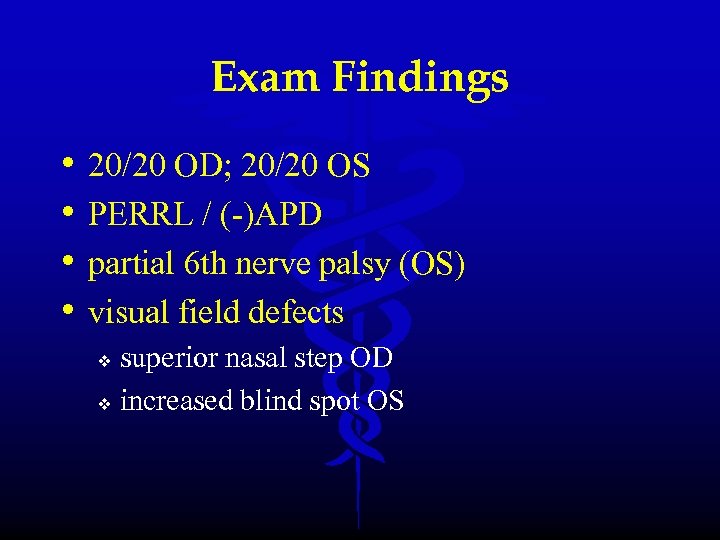
Exam Findings • • 20/20 OD; 20/20 OS PERRL / (-)APD partial 6 th nerve palsy (OS) visual field defects superior nasal step OD v increased blind spot OS v

Fundus: What’s Your Diagnosis? • • papilledema R/O mass R/O infection placing your bets. . . v Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension

Workup • CT or MRI v unremarkable • LP normal CSF content v elevated pressure v

Management • weight loss • acetazolamide v Diamox • steroids? ? • ON sheath decompression • LP shunt

Before you prescribe Diamox • baseline electrolytes • CBC with differential v R/O blood dyscrasias • monitor every 6 months

Electrolytes • Na+ v 135. 0 – 145. 0 mmol/L • K+ v 3. 60 – 5. 00 mmol/L • Clv 101. 0 – 111. 0 mmol/L

CO 2 total content blood • 21. 0 – 31. 0 mmol/L • Increased v v alcoholism airway obstruction pneumonia drugs (e. g. antacids) • Decreased v v dehydration Diamox § v measures compliance - < 20 m. Eq/L tetracyclines
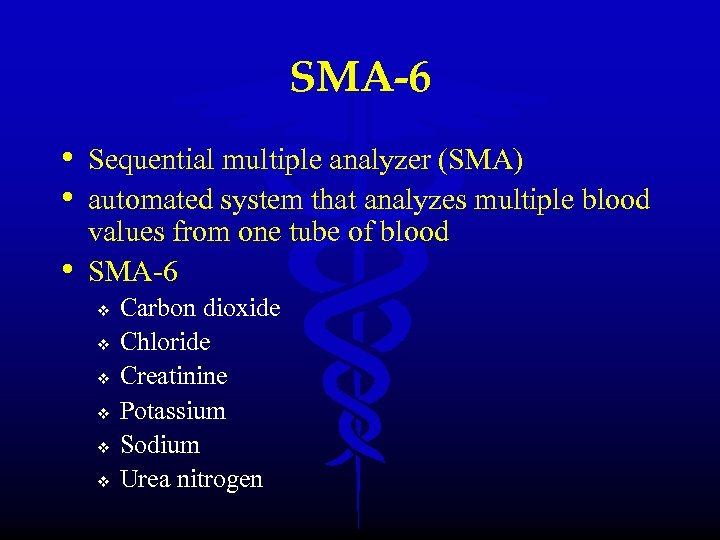
SMA-6 • Sequential multiple analyzer (SMA) • automated system that analyzes multiple blood • values from one tube of blood SMA-6 v v v Carbon dioxide Chloride Creatinine Potassium Sodium Urea nitrogen

SMA-7 Carbon dioxide v Chloride v Creatinine v Glucose v Potassium v Sodium v Urea nitrogen v

SMA-12 v v v Albumin Alkaline phosphatase Aspartate aminotransferase Bilirubin Calcium Cholesterol Glucose Lactate dehydrogenase Phosphorus Protein Urea nitrogen Uric acid • Also SMA-20

Eyelid Xanthoma • • dermis infiltrated with xanthoma cells yellow bilateral plaque medial aspect UL management: v cautery v laser v anything else?
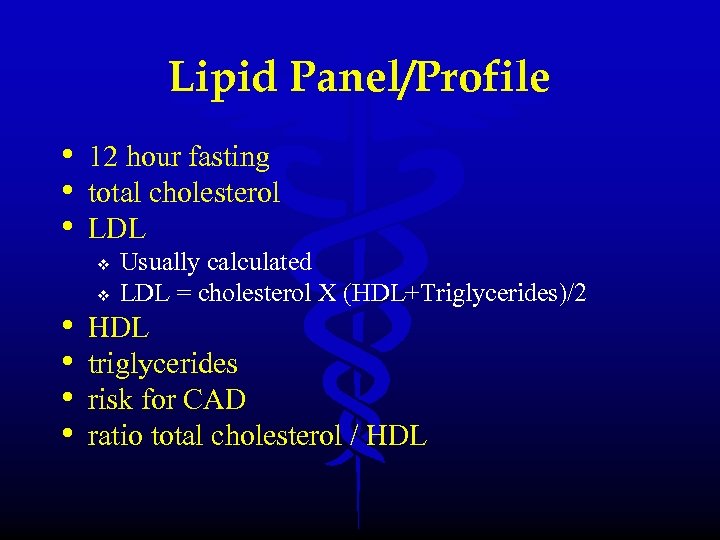
Lipid Panel/Profile • 12 hour fasting • total cholesterol • LDL v • • v Usually calculated LDL = cholesterol X (HDL+Triglycerides)/2 HDL triglycerides risk for CAD ratio total cholesterol / HDL

Cholesterol • over half of adults in US have cholesterol > • • 200 mg/d. L desirable: 160 -200 mg/d. L borderline: 200 -239 mg/d. L high 240 mg/d. L Outside US v v cholesterol x 0. 0259 mmoles/L (international units) 200 mg/d. L = 5. 18 mmol/L

More Numbers… • HDL v good 35 mg/d. L § v women probably 45 mg/d. L 1 mg/m. L risk of CHD 2 -3% § Helsinki Heart Study (gemfibrizol in men ) • LDL v v good < 130 mg/d. L high 190 mg/d. L • Ratio (Total / HDL) v < 5: 1 § Female < 4. 4

Triglycerides • normal < 200 mg/d. L v women probably < 150 • borderline 200 -400 • high 400 -1000 • very high > 1000

Lipid Panel • arcus v young patients • occlusive disease • optic neuropathy • xanthoma

CASE #3

Case #3 • • • 52 YOWM CC: “inferior vision OS is dim” MHx: diabetic x 20 years; poor control VAs: OD 20/20 OS 20/20 -2 LEE: 6 month prior v two dot hemorrhages OD

Initial Presentation • OD – unremarkable

What is your tentative diagnosis? • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy Retrobulbar mass Papilledema Diabetic papillopathy Optic Neuritis Papillitis Other?

What Should You Do?

ESR • • • erythrocyte sedimentation rate nonspecific test for inflammation mm/hr M: age/2 F: (age+10)/2 usually > 60 mm/hr in GCA
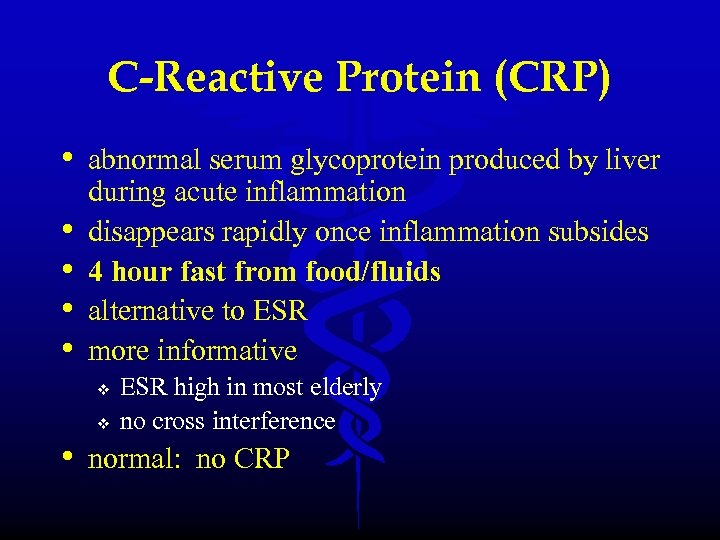
C-Reactive Protein (CRP) • abnormal serum glycoprotein produced by liver • • during acute inflammation disappears rapidly once inflammation subsides 4 hour fast from food/fluids alternative to ESR more informative v v ESR high in most elderly no cross interference • normal: no CRP

Causes of Optic Nerve Edema • • • Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Nonarteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Compressive Optic Nerve Head Tumor Diabetic Papillopathy Infiltration of Optic Nerve Head Malignant Hypertension Papilledema Papillitis Papillophlebitis Thyroid Ophthalmopathy

Diabetic Papillopathy • 0. 4 – 2% of diabetics • characteristics sectoral or total ON edema v ± peripapillary hemorrhages v ± nerve fiber layer infarcts v ± macular edema v • unilateral or bilateral v asymmetric

Diabetic Papillopathy • retinopathy does not need to be present • small optic nerve cupping v 0. 3/0. 3 • usually associated with Type 1 DM? • prognosis: signficant or complete recovery in several months v may have residual pallor and VF defect v • pathophysiology is unclear

Diabetic Papillopathy • Eye 2005 19: 45 -51 6 eyes v Betamethasone – Subtenons’ injection v duration decreased from 5 months to 3 weeks v • Am J Ophth 2004 137(6) 1151 -3 1 case – intravitreal triamcinolone v significant improvement in visual acuity v

CASE #4

“Phone A Friend” • • • 40 YOBF CC: “Decrease vision for 3 weeks” HPI: OS worse than OD; no pain; acute MHx: unremarkable Meds: None NKMA

“Phone A Friend” • Entering Acuities v v OD 20/60 PH 20/30 OS 20/50 PH 20/30 • Refraction v OD -2. 00 – 1. 75 x 135 20/25 § -2. 00 – 5. 00 x 167 20/50 § • K readings… v v OD 39. 75 / 44. 12 @ 095 OS 36. 75 / 43. 50 @ 095 • Cornea v central corneal edema with “haziness”

What’s Your Tentative Diagnosis? • 1. Keratoconus • 2. Keratoconus with Acute Corneal • • • Hydrops 3. Corneal Ulcer 4. Corneal Dystrophy / Corneal Degeneration 5. Dry Eye Syndrome 6. Herpes Simplex Keratitis 7. Other

What Was Actually Done… • Cycloplegic • Muro 128 qid • RTC 1 day

Interstitial Keratitis • cellular infiltration of the corneal stroma • no primary involvement of epi or endo • characterized by: v acute: dense, white stromal necrosis § vascularization (salmon patch of Hutchinson) § v later: scarring and thinning § ghost vessels §

Interstitial Keratitis • • Syphilis (Congenital or Acquired) TB Lyme Parasitic infection HSV Sarcoidosis Leprosy Misc.

Syphilis: Ever Had It? • FTA-ABS fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test v ordered more frequently v positive even after treatment v • MHA-TP v microhemagglutination treponemal pallidum test

Syphilis: Do you have it now? • RPR v rapid plasma reagin test • VDRL v venereal disease research laboratory test • Treat If: v (+) RPR and (+)FTA-ABS • What if: v (+)RPR and (-)FTA-ABS

PPD • purified protein • • • derivative TB skin test inject under skin check in 48 -72 hours positive is >10 mm wheal Positive for active and inactive TB

Lyme titer • In endemic areas. . . • Normal: negative

ACE • angiotensin converting enzyme • Enzyme found primarily in lung epithelial cells v v Some in blood vessels and renal tissue Converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a vasopressor that also stimulates adrenal cortex to produce aldosterone • best for patients > 20 YO • helps confirm dx of sarcoidosis v ACE elevated in 60%

Interstitial Keratitis • Active 70% of unilateral Herpes Simplex Virus v 60% of bilateral Idiopathic v • Inactive v 50% of bilateral Syphilis • All cases v 20% attributed to syphilis
6f77fee20ca7a4ef473b30c25e7a5630.ppt