7280ad06e2e7f54484b36c67090e111d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

How about literacy classes for literacy learners and ESOL classes for ESOL learners? Charles Hayward

acquiring vs. learning

Policy evolution in NZ • • • 1996, IALS Survey 2001, More than Words 2002, TEC (funding) 2003, Adult ESOL Strategy 2004, NZSS 2006, ALL 2007 – 2012 TES 2010 – 2015 TES 2010, Getting Results in Literacy and Numeracy • • • LN on the radar Adult Literacy Strategy Labour Govt. $$ 50, 000 / 250, 000 Kiwi English ‘Literacy Crisis’ Maori, Pasifika Priority Groups ‘literacy includes the language needed to communicate for SOL’

What’s happening in Auckland?

Similar ends different means Literacy learners • Fluent in English • Implicit grammar • Large vocabulary • Social empowerment ESOL learners • Vocab development • Grammar rules • Prosody • Linguistic approach • Confident users of (written / read) English • Confident users of English

The Great Divide

Can literacy be measured? (Brian Street) Autonomous model • Set of de-contextualised, unchangeable (fixed) skills • Deficit measured • ‘functional’ skills taught / gained James Gee • Skills for the job market, • literacy quantified (bought and sold)

The Literacy Myth Literacy autonomously : • Economic growth • Reduce poverty • Reduces crime • Promote democracy • Increase civic engagement • Prevent AIDS / other diseases (H. G. Graff, 1982) • Increase cultural diversity • Lowers birth-rates • Increase productivity • Able to participate in. . . • Less waste / re-work • Fewer accidents • Higher morale • Staff retention

Newly converted!!!

‘Unambiguously represents meaning’ • • Not dependent on knowledge of context ‘Essay-text’ form of meaning One cultural interpretation among many Ideological basis for schools and unis • Vygotsky, Scribner, Cole, - tests of explicitness
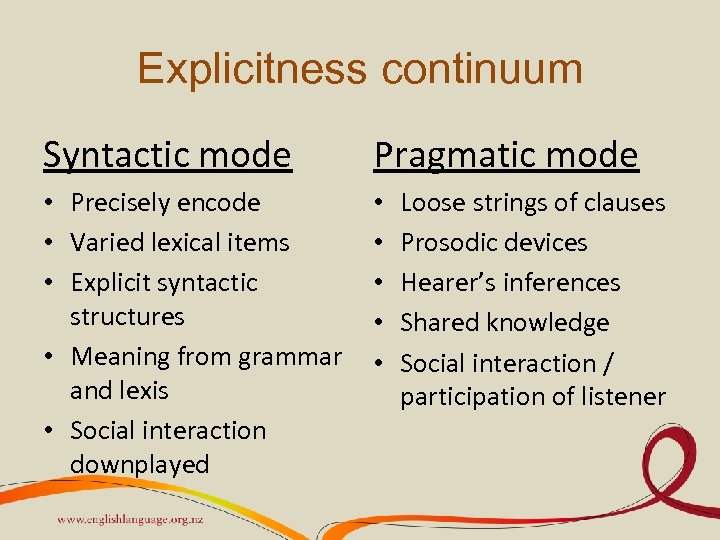
Explicitness continuum Syntactic mode Pragmatic mode • Precisely encode • Varied lexical items • Explicit syntactic structures • Meaning from grammar and lexis • Social interaction downplayed • • • Loose strings of clauses Prosodic devices Hearer’s inferences Shared knowledge Social interaction / participation of listener

syntactic mode = essay text • • Easy to measure the 4 skills Bench mark tests: IELTS, TOEIC, TOEFL 4 or 5 paragraph essay Deficit model Stair-casing / scaffolding Record incremental progress Grammar, lexis, functions

A real English teacher!

Settlement in Glasgow
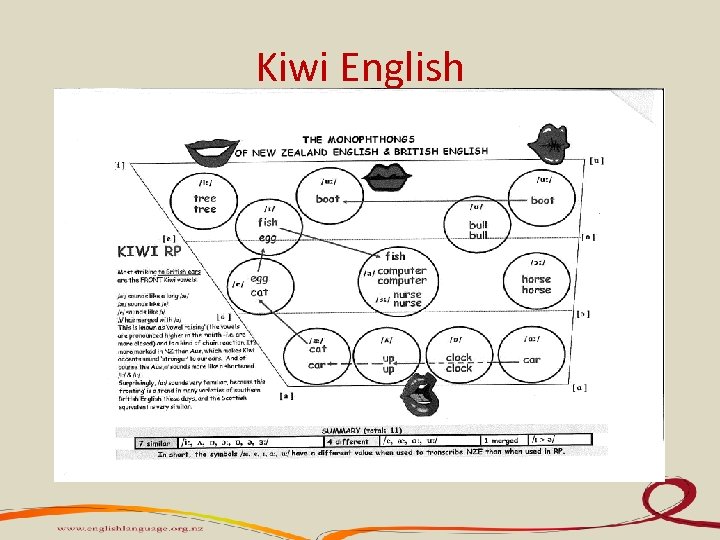
Kiwi English

pragmatic mode = context • • Community of practice Workplace culture Codes Jargon Relationships Relations of power Office politics Shared history Ideological model • Literacy practices

community of practice

Can not ‘use multiplication and division strategies to solve problems that involve proportions, ratios and rates’

Dr. Stephen Black • The ‘literacy crisis’ – crisis rhetoric • Deficit-oriented, individualistic, education via measurement and control • a range of different literacy and numeracy ‘practices’ at work rather than a set of universal literacy and numeracy ‘skills’ • This approach requires an ethnographic-type of analysis involving close observations and dialogue with those engaged with workplace practices – the workers

Phil Cave, Manufacturing Manager, Thames Timber Training Goals: • Improve the bottom line • Understand business kpi’s • Sustainable training culture for years to come • Improve Literacy, Numeracy and Leadership for (25) First Line Management leaders • Foundation and motivation for future NZQA quals

In-house Literacy, Language and Numeracy (LLN) Initiatives in New Zealand Workplaces • Department of labour 2009 • Employers who chose to set up (and meet the costs of) their own LLN initiatives • Business based outcomes vs education-based outcomes (Government / Provider) • ‘some companies will always prefer to fund and deliver their own LLN initiatives’ (Department of Labour, 2009, p. 44).
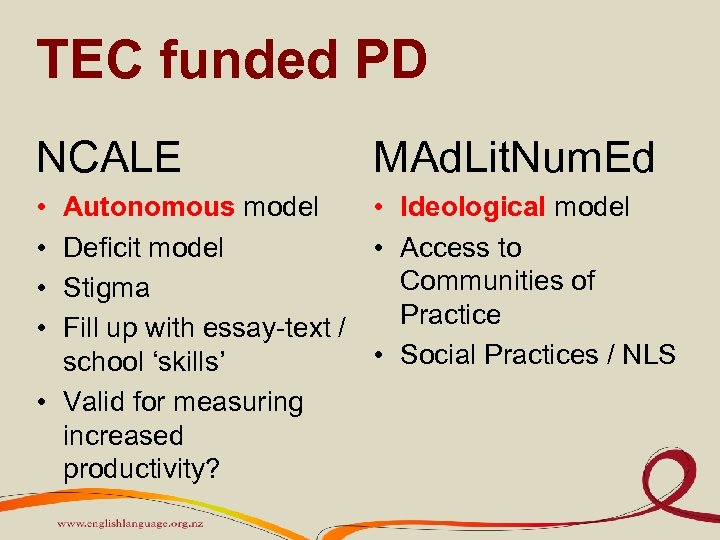
TEC funded PD NCALE • • MAd. Lit. Num. Ed Autonomous model • Ideological model Deficit model • Access to Communities of Stigma Practice Fill up with essay-text / • Social Practices / NLS school ‘skills’ • Valid for measuring increased productivity?

Traditional / emerging approaches • • • Autonomous model Syntactic mode Essay-text literacy Focus on the individual Literacy classes Standardised tests • • • Ideological model Pragmatic mode Community of practice Focus on social context Embedded learning Competence in context

How do we measure ‘pragmatic’ competence? • • • Achieving competence in unit standards (pc’s) Study skills unit standards added to quals Induction training Lean manufacturing Assessment centres

Synergies for Numerate and Literate New Zealanders Language learners • There needs to be a ‘language’ component (53% of workers in Ak were born outside NZ) • Language learners have specific needs, different from literacy learners Literacy learners NQF 1 -3 • Social practices model • Ethnographic workplace understanding • Taught in context • Assessed in context

Any questions? charles. hayward@englishlanguage. org. nz
7280ad06e2e7f54484b36c67090e111d.ppt