54bfee5fd182af42a30fd4456b53c52a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Housing Initiative for Eastern Europe – IWO e. V. for the Support of Market-oriented Structures in the Housing and Construction Sector in Eastern Europe “Strategies and Instruments Supporting Energy Efficient Refurbishment (EER) in Germany” Knut Höller, Britta Schmigotzki IWO e. V. , Berlin / Germany Tallinn, 29. November 2006
Housing Initiative for Eastern Europe – IWO e. V. for the Support of Market-oriented Structures in the Housing and Construction Sector in Eastern Europe “Strategies and Instruments Supporting Energy Efficient Refurbishment (EER) in Germany” Knut Höller, Britta Schmigotzki IWO e. V. , Berlin / Germany Tallinn, 29. November 2006
 Structure of Presentation 1. IWO e. V. – tasks and structure 2. German experiences in energy efficient refurbishment of prefabricated housing estates – „The Berlin Strategy“ - after reunification 3. German strategy for energy efficient refurbishment (EER) – today’s approach
Structure of Presentation 1. IWO e. V. – tasks and structure 2. German experiences in energy efficient refurbishment of prefabricated housing estates – „The Berlin Strategy“ - after reunification 3. German strategy for energy efficient refurbishment (EER) – today’s approach
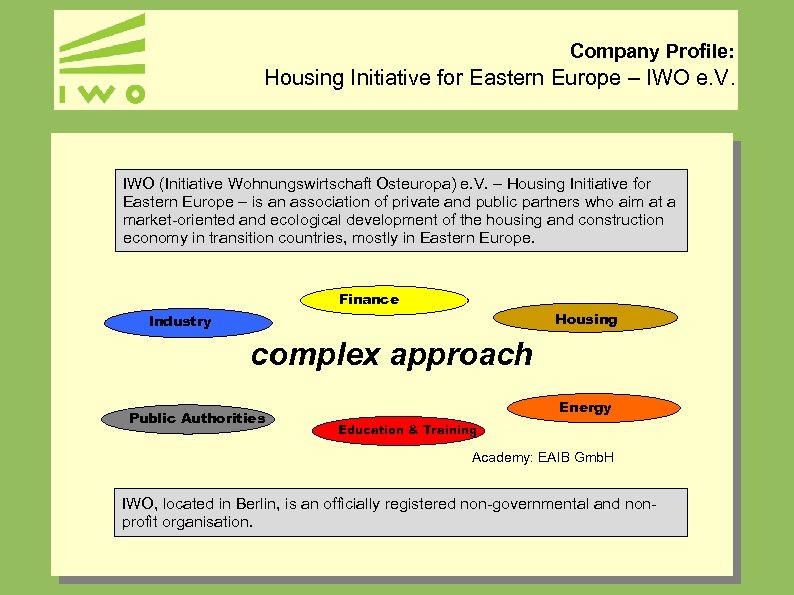 Company Profile: Housing Initiative for Eastern Europe – IWO e. V. IWO (Initiative Wohnungswirtschaft Osteuropa) e. V. – Housing Initiative for Eastern Europe – is an association of private and public partners who aim at a market-oriented and ecological development of the housing and construction economy in transition countries, mostly in Eastern Europe. Finance Housing Industry complex approach Public Authorities Energy Education & Training Academy: EAIB Gmb. H IWO, located in Berlin, is an officially registered non-governmental and nonprofit organisation.
Company Profile: Housing Initiative for Eastern Europe – IWO e. V. IWO (Initiative Wohnungswirtschaft Osteuropa) e. V. – Housing Initiative for Eastern Europe – is an association of private and public partners who aim at a market-oriented and ecological development of the housing and construction economy in transition countries, mostly in Eastern Europe. Finance Housing Industry complex approach Public Authorities Energy Education & Training Academy: EAIB Gmb. H IWO, located in Berlin, is an officially registered non-governmental and nonprofit organisation.
 German experiences in energy efficient refurbishment „The Berlin Strategy“ Initial situation after 1990: § Eastern part of Berlin: 632, 000 dwellings, of these 360, 000 built after 2 WW § 273, 000 dwellings in prefabricated multi-family buildings. 800, 000 people, i. e. 2/3 of the inhabitants in Eastern Berlin, live in these flats. They are located mainly in the districts Marzahn, Hellersdorf, Lichtenberg and Hohenschönhausen § Berlin government quickly decided that the maintenance of the existing stock and the immediate refurbishment with new support instruments should by applied instead of adopting a policy of wait and see.
German experiences in energy efficient refurbishment „The Berlin Strategy“ Initial situation after 1990: § Eastern part of Berlin: 632, 000 dwellings, of these 360, 000 built after 2 WW § 273, 000 dwellings in prefabricated multi-family buildings. 800, 000 people, i. e. 2/3 of the inhabitants in Eastern Berlin, live in these flats. They are located mainly in the districts Marzahn, Hellersdorf, Lichtenberg and Hohenschönhausen § Berlin government quickly decided that the maintenance of the existing stock and the immediate refurbishment with new support instruments should by applied instead of adopting a policy of wait and see.
 German experiences in energy efficient refurbishment „The Berlin Strategy“ The main elements in the strategy: 1. Legal assignment of the property and reorganisation of the housing administration/housing economy. 2. Improvement of the residential environment 3. Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Ø Main difference to situation in CEE: No Privatisation. Housing stock administrated by municipal companies. Rental housing stock!!!
German experiences in energy efficient refurbishment „The Berlin Strategy“ The main elements in the strategy: 1. Legal assignment of the property and reorganisation of the housing administration/housing economy. 2. Improvement of the residential environment 3. Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Ø Main difference to situation in CEE: No Privatisation. Housing stock administrated by municipal companies. Rental housing stock!!!
 „The Berlin Strategy“: Improvement of the residential environment
„The Berlin Strategy“: Improvement of the residential environment
 „The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock The approach: § At the beginning of the 90 s the Berlin Senate ordered extensive structural studies, to determine the renovation and modernisation need of the different buildings types. § A „measure/cost-matrix“ was developed relating 17 building series with 21 renovation measures, and stating an average price for the measure and the overall sum per flat. Prices varied from 7, 000 €/flat (newer buildings) to 34, 000 €/flat (QP 59). The matrix was the basis for the Berlin support guidelines. § Measures listed included: - improvement of thermal insulation and heating system, - new sanitation, - new windows and balconies, - renovation of elevators as well as - modernisation of the housing entrances and staircases.
„The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock The approach: § At the beginning of the 90 s the Berlin Senate ordered extensive structural studies, to determine the renovation and modernisation need of the different buildings types. § A „measure/cost-matrix“ was developed relating 17 building series with 21 renovation measures, and stating an average price for the measure and the overall sum per flat. Prices varied from 7, 000 €/flat (newer buildings) to 34, 000 €/flat (QP 59). The matrix was the basis for the Berlin support guidelines. § Measures listed included: - improvement of thermal insulation and heating system, - new sanitation, - new windows and balconies, - renovation of elevators as well as - modernisation of the housing entrances and staircases.
 „The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock In October 1993, the pilot phase of the programme supporting the refurbishment of prefabricated housing estates started. . .
„The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock In October 1993, the pilot phase of the programme supporting the refurbishment of prefabricated housing estates started. . .
 „The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock . . . and from 1994 on, the renovation programme was implemented on a large scale (over a period of 10 years).
„The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock . . . and from 1994 on, the renovation programme was implemented on a large scale (over a period of 10 years).
 „The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock
„The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock
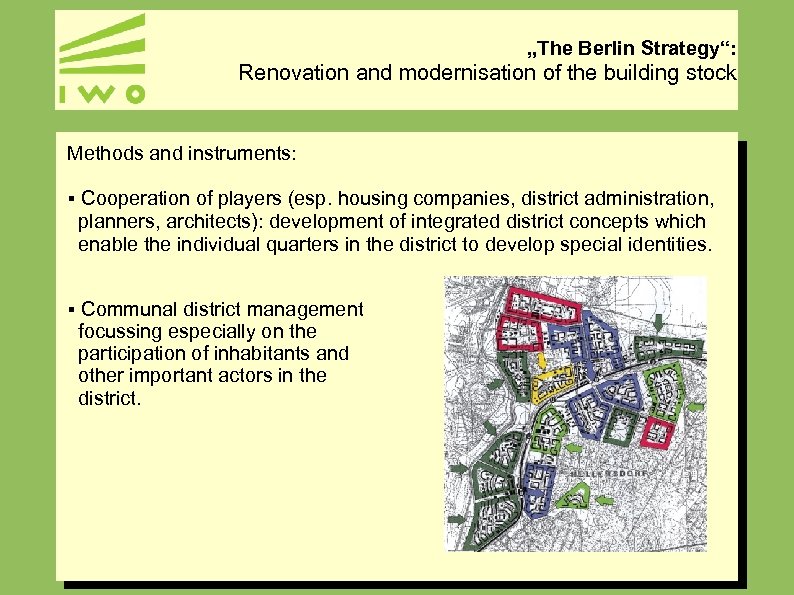 „The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Methods and instruments: § Cooperation of players (esp. housing companies, district administration, planners, architects): development of integrated district concepts which enable the individual quarters in the district to develop special identities. § Communal district management focussing especially on the participation of inhabitants and other important actors in the district.
„The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Methods and instruments: § Cooperation of players (esp. housing companies, district administration, planners, architects): development of integrated district concepts which enable the individual quarters in the district to develop special identities. § Communal district management focussing especially on the participation of inhabitants and other important actors in the district.
 „The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Basic principles of financing: § Nearly all refurbishment measures were financed with long-term loans with reduced interest rates § Every credit was secured by mortgages § When necessary: additional state or municipal guarantees were provided § Two levels providing support: - Federal Government - Municipality of Berlin
„The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Basic principles of financing: § Nearly all refurbishment measures were financed with long-term loans with reduced interest rates § Every credit was secured by mortgages § When necessary: additional state or municipal guarantees were provided § Two levels providing support: - Federal Government - Municipality of Berlin
 „The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Financing / Main support programmes: a. The „Kf. W-dwelling modernisation prgramme“ of the Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (Kf. W), provided reduced interest rate loans which were supported by the German government. Alltogether, loans of around 3 Billion € were used for the renovation of the housing stock in Eastern Berlin. b. The „Prefabricated buildings renovation programme“. In accordance with the so-called „Inst. Mod. RL“ the Berlin government provided long term interest subsidies for buildings, where renovation costs could not be covered by rents and with Kf. W-loans alone. Approximately 650 Mio. € were provided in the form of long term interest subsidies by the Berlin government.
„The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Financing / Main support programmes: a. The „Kf. W-dwelling modernisation prgramme“ of the Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (Kf. W), provided reduced interest rate loans which were supported by the German government. Alltogether, loans of around 3 Billion € were used for the renovation of the housing stock in Eastern Berlin. b. The „Prefabricated buildings renovation programme“. In accordance with the so-called „Inst. Mod. RL“ the Berlin government provided long term interest subsidies for buildings, where renovation costs could not be covered by rents and with Kf. W-loans alone. Approximately 650 Mio. € were provided in the form of long term interest subsidies by the Berlin government.
 „The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Consequences for the residents: § The costs for the complex refurbishment of the buildings amounted to 23, 000 Euro per flat § Measures have been refinanced through the rents § Rents have been increased by 11 percent annually § The average rent in refurbished dwellings included approx. 135 Euro costs for the refurbishment § On average, the rents in renovated buildings amount to 25 percent of the net household income
„The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Consequences for the residents: § The costs for the complex refurbishment of the buildings amounted to 23, 000 Euro per flat § Measures have been refinanced through the rents § Rents have been increased by 11 percent annually § The average rent in refurbished dwellings included approx. 135 Euro costs for the refurbishment § On average, the rents in renovated buildings amount to 25 percent of the net household income
 „The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Overall results: Ø 60 % of the stock has been extensively refurbished 25 % 15 % “ “ has been partly refurbished has not been refurbished Ø Between 1993 and 2003 around 6. 2 Billion € have been invested in the renovation and modernisation of the prefabricated building stock in Eastern Berlin, that is on average 23, 000 € per flat, of which ~8, 500 € used for energy efficient measures.
„The Berlin Strategy“: Renovation and modernisation of the building stock Overall results: Ø 60 % of the stock has been extensively refurbished 25 % 15 % “ “ has been partly refurbished has not been refurbished Ø Between 1993 and 2003 around 6. 2 Billion € have been invested in the renovation and modernisation of the prefabricated building stock in Eastern Berlin, that is on average 23, 000 € per flat, of which ~8, 500 € used for energy efficient measures.
 German strategy for EER in the housing stock - today Strategies and Instruments 1. Legal: e. g. Energy Conservation Ordinance En. EV 2. Financial: - Financing programmes by Kf. W - Financing programmes by regional governments and municipalities 3. Information and Transparency 4. Research and increase of know-how
German strategy for EER in the housing stock - today Strategies and Instruments 1. Legal: e. g. Energy Conservation Ordinance En. EV 2. Financial: - Financing programmes by Kf. W - Financing programmes by regional governments and municipalities 3. Information and Transparency 4. Research and increase of know-how
 German strategy for EER in the housing stock - today Main Financing Instruments 1. Promotion mainly by the Federal Government through the (Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (Kf. W) - Reconstruction Loan Corporation) 2. Promotion by 3. - reduced-interest loans 4. - grants 5. - tax-relief 6.
German strategy for EER in the housing stock - today Main Financing Instruments 1. Promotion mainly by the Federal Government through the (Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (Kf. W) - Reconstruction Loan Corporation) 2. Promotion by 3. - reduced-interest loans 4. - grants 5. - tax-relief 6.
 Promotion of EER by Kf. W programmes What is the Kf. W? Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (Kf. W) = “Reconstruction Loan Corporation”: § Owned by federal government (80 %) and federal states (20 %) § Kf. W Förderbank = Kf. W Promotional Bank § Funding areas: housing construction, modernisation, energy conservation
Promotion of EER by Kf. W programmes What is the Kf. W? Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (Kf. W) = “Reconstruction Loan Corporation”: § Owned by federal government (80 %) and federal states (20 %) § Kf. W Förderbank = Kf. W Promotional Bank § Funding areas: housing construction, modernisation, energy conservation
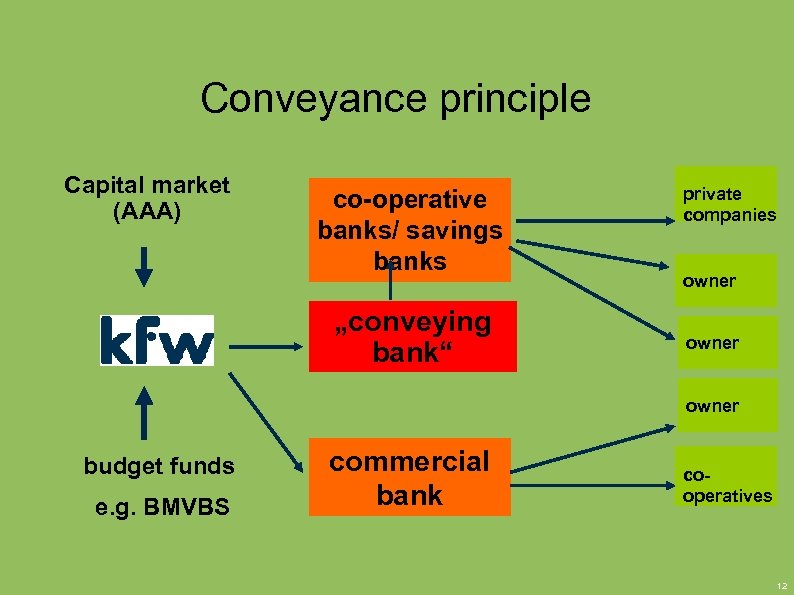 Conveyance principle Capital market (AAA) co-operative banks/ savings banks „conveying bank“ private companies owner budget funds e. g. BMVBS commercial bank cooperatives 12
Conveyance principle Capital market (AAA) co-operative banks/ savings banks „conveying bank“ private companies owner budget funds e. g. BMVBS commercial bank cooperatives 12
 Promotion of EER by Kf. W programmes Financing Principles Ø Long-term, low-interest financing for projects that reduce CO 2 Ø Interest rate is set considerably below capital market level Ø Interest rate fixed for 10 years – reliable basis for calculation Ø Financing of up to 100 % of the investment costs Ø Partial dept relief for the Kf. W loan once the level of a low-energy house has been attained Ø Possibility of combination with other promotional funds and with other Kf. W programmes
Promotion of EER by Kf. W programmes Financing Principles Ø Long-term, low-interest financing for projects that reduce CO 2 Ø Interest rate is set considerably below capital market level Ø Interest rate fixed for 10 years – reliable basis for calculation Ø Financing of up to 100 % of the investment costs Ø Partial dept relief for the Kf. W loan once the level of a low-energy house has been attained Ø Possibility of combination with other promotional funds and with other Kf. W programmes
 Promotion of EER by Kf. W programmes Eligible Applicants and Programmes Applicants: § Whoever wants to invest in owner occupied or rented residential buildings (Private individuals, Housing companies, Housing cooperatives, other investors, municipalities, districts etc. ) Relevant Programmes: a. CO 2 Building Rehabilitation Programme: 4 fixed packages of extensive energy refurbishment measures - high interest rate reduction b. Housing Modernisation Programme: certain energy efficient measures (ÖKO-Plus) or modernisation in general (STANDARD) – comparatively low interest rate reduction
Promotion of EER by Kf. W programmes Eligible Applicants and Programmes Applicants: § Whoever wants to invest in owner occupied or rented residential buildings (Private individuals, Housing companies, Housing cooperatives, other investors, municipalities, districts etc. ) Relevant Programmes: a. CO 2 Building Rehabilitation Programme: 4 fixed packages of extensive energy refurbishment measures - high interest rate reduction b. Housing Modernisation Programme: certain energy efficient measures (ÖKO-Plus) or modernisation in general (STANDARD) – comparatively low interest rate reduction
 Promotion of EER by Kf. W programmes Volume of the CO 2 building rehabilitation programme § Total amount approx. 1. 4 billion EUR state support per year, of these - 1. 0 billion EUR for CO 2 Building Rehabilitation Programme, divided in * 600 million EUR reduced interest loans for residential buildings * 200 million EUR grants for residential buildings * 200 million EUR for schools, kindergarten etc. § From 2001 to 2005 approx. 5 billion EUR have been granted for loans in the programme, for the energy efficient refurbishment of 304, 820 dwellings. § 2005: Average size of daily (!) received application amounted to 5 million EUR.
Promotion of EER by Kf. W programmes Volume of the CO 2 building rehabilitation programme § Total amount approx. 1. 4 billion EUR state support per year, of these - 1. 0 billion EUR for CO 2 Building Rehabilitation Programme, divided in * 600 million EUR reduced interest loans for residential buildings * 200 million EUR grants for residential buildings * 200 million EUR for schools, kindergarten etc. § From 2001 to 2005 approx. 5 billion EUR have been granted for loans in the programme, for the energy efficient refurbishment of 304, 820 dwellings. § 2005: Average size of daily (!) received application amounted to 5 million EUR.
 German strategy for EER in the housing stock - today Current state of the programme: § Improved conditions since February 2006 lead to the approval of loans amounting to 7. 5 billion EUR until August 2006. § Due to the huge demand for the programme, an additional amount of 350 million EUR has been approved by the budget committee of the German Parliament. § Currently discussion about re-launch of modified programme from January 2007 on.
German strategy for EER in the housing stock - today Current state of the programme: § Improved conditions since February 2006 lead to the approval of loans amounting to 7. 5 billion EUR until August 2006. § Due to the huge demand for the programme, an additional amount of 350 million EUR has been approved by the budget committee of the German Parliament. § Currently discussion about re-launch of modified programme from January 2007 on.
 “Strategies and Instruments Supporting Energy Efficient Refurbishment in Germany” Thank you very much for your attention!!! Contact: Initiative Wohnungswirtschaft Osteuropa (IWO e. V. ) Knut Höller / Britta Schmigotzki Friedrichstraße 95 10117 Berlin (Germany) Phone: +49 30 20 67 98 02 Fax: +49 30 20 67 98 04 mail@iwoev. org www. iwoev. org
“Strategies and Instruments Supporting Energy Efficient Refurbishment in Germany” Thank you very much for your attention!!! Contact: Initiative Wohnungswirtschaft Osteuropa (IWO e. V. ) Knut Höller / Britta Schmigotzki Friedrichstraße 95 10117 Berlin (Germany) Phone: +49 30 20 67 98 02 Fax: +49 30 20 67 98 04 mail@iwoev. org www. iwoev. org


