162911e2af8b317a6bca7a27f6797ab1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 HOUSE CALLS 101 Sandra Qaseem MD
HOUSE CALLS 101 Sandra Qaseem MD
 Goals and objectives At the end of the presentation knowledge gained will help to • Identify patients that would likely benefit from house calls • Select the equipment necessary for a basic house call • Understand how to set up and perform a house call and bill for the service • Implement house calls as part of your regular practice
Goals and objectives At the end of the presentation knowledge gained will help to • Identify patients that would likely benefit from house calls • Select the equipment necessary for a basic house call • Understand how to set up and perform a house call and bill for the service • Implement house calls as part of your regular practice
 Background • Number of homebound is increasing- 11 million adults living at home are limited in their ability to perform ADL’s • Number of house calls is increasing- in 2010 (medicare data) The total number was 2, 517644 for house call codes and 2, 204, 351 for domiciliary care. This represents a 6. 5% increase for house call codes and a 9. 9% increase in domiciliary care codes from 2009. • Concept of medical home • Independence at Home • Face to face requirement for skilled homecare services (RN, PT, OT etc) http: //www. cdc. gov/prc/pdf/PRC_HA_fact_sheet_summer 2006. pd
Background • Number of homebound is increasing- 11 million adults living at home are limited in their ability to perform ADL’s • Number of house calls is increasing- in 2010 (medicare data) The total number was 2, 517644 for house call codes and 2, 204, 351 for domiciliary care. This represents a 6. 5% increase for house call codes and a 9. 9% increase in domiciliary care codes from 2009. • Concept of medical home • Independence at Home • Face to face requirement for skilled homecare services (RN, PT, OT etc) http: //www. cdc. gov/prc/pdf/PRC_HA_fact_sheet_summer 2006. pd
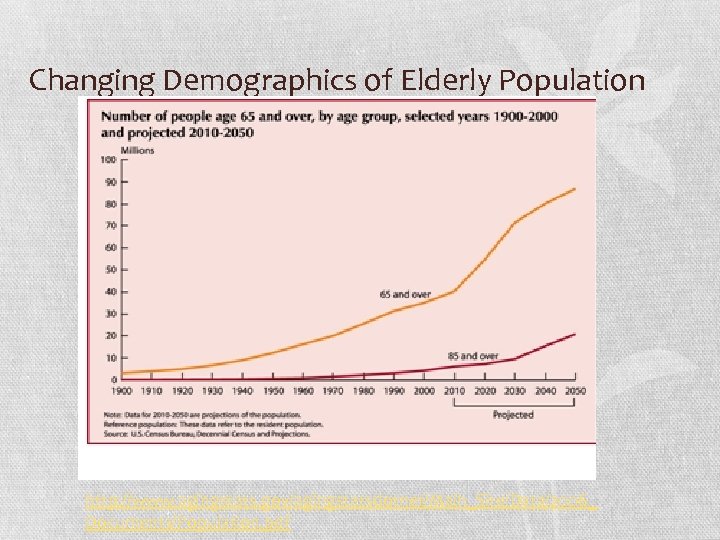 Changing Demographics of Elderly Population http: //www. agingstats. gov/agingstatsdotnet/Main_Site/Data/2006_ Documents/Population. pdf
Changing Demographics of Elderly Population http: //www. agingstats. gov/agingstatsdotnet/Main_Site/Data/2006_ Documents/Population. pdf
 Where Do Our Patients Live? • At home with or without caregiver assistance • At home with Adult Day Care Services • Assisted Living Facilities • Shelter Care or Residential Care Homes • Total care community • Nursing Homes
Where Do Our Patients Live? • At home with or without caregiver assistance • At home with Adult Day Care Services • Assisted Living Facilities • Shelter Care or Residential Care Homes • Total care community • Nursing Homes
 Why make house calls? • Patients need them and are more satisfied with treatment in the home • Patients access more regular care • Less hospitalization and use of Emergency Department translating to reduced healthcare costs • Better assessment of environmental contribution to medical problems • Evaluation of caregiver • Families are happy and caregivers less stressed • Personal satisfaction • Schedule flexibility
Why make house calls? • Patients need them and are more satisfied with treatment in the home • Patients access more regular care • Less hospitalization and use of Emergency Department translating to reduced healthcare costs • Better assessment of environmental contribution to medical problems • Evaluation of caregiver • Families are happy and caregivers less stressed • Personal satisfaction • Schedule flexibility
 Equipment- ‘The Black Bag’ • As you begin doing house calls, you will quickly customize your black bag to include those things that you find necessary and convenient. Here is a quick list of things to get you started: • Street map or GPS, • Netbook/ laptop • Stethoscope, • Blood pressure cuff (regular and large), • Pulse Oximeter • Pen light, • Tongue depressors, • Otoscope, • Prescription pad, • Phone numbers (offices, pharmacies, etc. ), • Cell phone, palm-held computer, etc. • Dictaphone/forms/progress notes, • additional pens. House Calls: Taking the Practice to the Patient James M. Giovino, MD , Fam Pract Manag. 2000 Jun; 7(6): 49 -54
Equipment- ‘The Black Bag’ • As you begin doing house calls, you will quickly customize your black bag to include those things that you find necessary and convenient. Here is a quick list of things to get you started: • Street map or GPS, • Netbook/ laptop • Stethoscope, • Blood pressure cuff (regular and large), • Pulse Oximeter • Pen light, • Tongue depressors, • Otoscope, • Prescription pad, • Phone numbers (offices, pharmacies, etc. ), • Cell phone, palm-held computer, etc. • Dictaphone/forms/progress notes, • additional pens. House Calls: Taking the Practice to the Patient James M. Giovino, MD , Fam Pract Manag. 2000 Jun; 7(6): 49 -54
 Patient Eligibility for Home Care • The visit must be “medically reasonable and necessary” • Mobility impairments • Disruptive behavior • Terminal illness • Multiple complex medical, psychiatric and social problems • Compliance issues • Not required to be as totally homebound as for skilled homecare from agency such as RN/ PT/OT
Patient Eligibility for Home Care • The visit must be “medically reasonable and necessary” • Mobility impairments • Disruptive behavior • Terminal illness • Multiple complex medical, psychiatric and social problems • Compliance issues • Not required to be as totally homebound as for skilled homecare from agency such as RN/ PT/OT
 Identify a patient (or 2) • Try to find a patient on your panel with mobility issues having great difficulty accessing care in the clinic • Ask him/ her if they would like a house call and explain the potential benefits (not everyone prefers them- for some it is a rare social event to come to the clinic!) • Set up a date and time for visit preferably at the end of the work day, if possible have a family member or caregiver present especially for the first visit
Identify a patient (or 2) • Try to find a patient on your panel with mobility issues having great difficulty accessing care in the clinic • Ask him/ her if they would like a house call and explain the potential benefits (not everyone prefers them- for some it is a rare social event to come to the clinic!) • Set up a date and time for visit preferably at the end of the work day, if possible have a family member or caregiver present especially for the first visit
 Making the visit • If possible call the patient the day before to remind them of your visit • Print out a paper copy of the patient’s recent notes, or have electronic access to the chart on the visit, include all demographic information • At the patient’s home introduce yourself and any others with you, ask if other family members present are participating in the visit • Identify a quiet place comfortable for the patient and yourself to conduct the visit • Proceed as you would for a clinic visit, identify the presenting complaint etc.
Making the visit • If possible call the patient the day before to remind them of your visit • Print out a paper copy of the patient’s recent notes, or have electronic access to the chart on the visit, include all demographic information • At the patient’s home introduce yourself and any others with you, ask if other family members present are participating in the visit • Identify a quiet place comfortable for the patient and yourself to conduct the visit • Proceed as you would for a clinic visit, identify the presenting complaint etc.
 In addition there is much to learn • Perform a medication review, and determine whether or not patient understands their medications • Observe the patient walking and functioning in their own home • Perform a home safety assessment, with permission look at the bathroom for grab bars etc • Observe interactions between the patient and the caregiver or family • Is the home clean? • With permission look in the refrigerator- is fresh food available?
In addition there is much to learn • Perform a medication review, and determine whether or not patient understands their medications • Observe the patient walking and functioning in their own home • Perform a home safety assessment, with permission look at the bathroom for grab bars etc • Observe interactions between the patient and the caregiver or family • Is the home clean? • With permission look in the refrigerator- is fresh food available?
 Wrap up • Ask if there any last questions • Set up a follow up visit • Leave written instructions for the plan of care • Return all furniture to its rightful place • Thank the patient for allowing you into their home
Wrap up • Ask if there any last questions • Set up a follow up visit • Leave written instructions for the plan of care • Return all furniture to its rightful place • Thank the patient for allowing you into their home
 Back at the office • Document the visit • Follow up paperwork • Order tests as necessary- X-ray, EKG, Laboratory tests, Cardiac Echo, Doppler and overnight oximetry can all be done in the home • Phone calls • Billing
Back at the office • Document the visit • Follow up paperwork • Order tests as necessary- X-ray, EKG, Laboratory tests, Cardiac Echo, Doppler and overnight oximetry can all be done in the home • Phone calls • Billing
 Billing Codes • Patients own home versus assisted living/ group home facility • New patient versus established patient • Level of visit- as in clinic based on complexity, number of diagnoses, medical decision making etc as in outpatient clinic • For more in depth information the American Academy of Homecare Physicians publishes a guide Making house calls a part of your practice.
Billing Codes • Patients own home versus assisted living/ group home facility • New patient versus established patient • Level of visit- as in clinic based on complexity, number of diagnoses, medical decision making etc as in outpatient clinic • For more in depth information the American Academy of Homecare Physicians publishes a guide Making house calls a part of your practice.
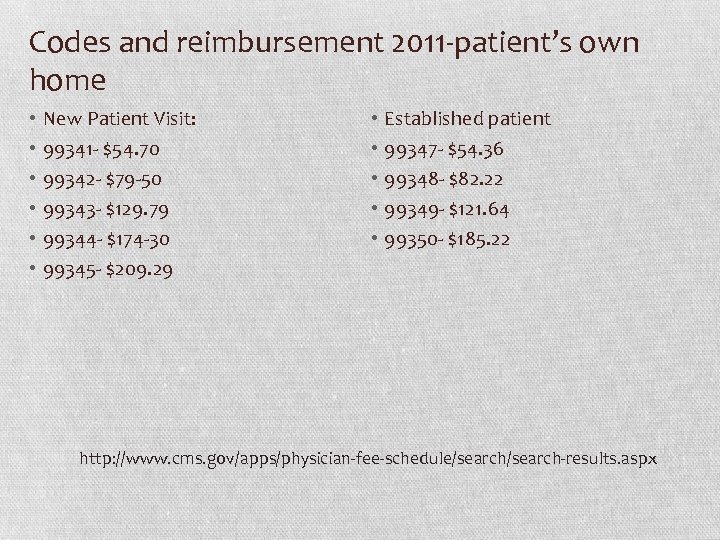 Codes and reimbursement 2011 -patient’s own home • • • New Patient Visit: 99341 - $54. 70 99342 - $79 -50 99343 - $129. 79 99344 - $174 -30 99345 - $209. 29 • • • Established patient 99347 - $54. 36 99348 - $82. 22 99349 - $121. 64 99350 - $185. 22 http: //www. cms. gov/apps/physician-fee-schedule/search-results. aspx
Codes and reimbursement 2011 -patient’s own home • • • New Patient Visit: 99341 - $54. 70 99342 - $79 -50 99343 - $129. 79 99344 - $174 -30 99345 - $209. 29 • • • Established patient 99347 - $54. 36 99348 - $82. 22 99349 - $121. 64 99350 - $185. 22 http: //www. cms. gov/apps/physician-fee-schedule/search-results. aspx
 Codes and reimbursement 2011 - Domiciliary visit • New Patient • • • 99324 - $55. 04 99325 - $79. 50 99326 - $134. 89 99327 - $177. 36 99328 - 207. 26 • Established Patient • • 99334 - $58. 44 99335 - $90. 38 99336 - $121. 74 99337 - $183. 47 http: //www. cms. gov/apps/physician-fee-schedule/search-results. aspx
Codes and reimbursement 2011 - Domiciliary visit • New Patient • • • 99324 - $55. 04 99325 - $79. 50 99326 - $134. 89 99327 - $177. 36 99328 - 207. 26 • Established Patient • • 99334 - $58. 44 99335 - $90. 38 99336 - $121. 74 99337 - $183. 47 http: //www. cms. gov/apps/physician-fee-schedule/search-results. aspx
 Care Plan Oversight and Certification for Home Health Agency Patient • These are also billable for your clinic patients receiving skilled HHA services in the community • G 0181 $104. 31 (home health)/ G 0182 $105. 67 (hospice) • Must document 30 minutes of time spent coordinating care unrelated to a face to face visit for a patient • Time spent includes telephone calls to other health professionals (NOT FAMILY), ordering and reviewing tests etc. • Time must be at least 30 minutes in 1 calendar month • a template for documentation is available in from AAHCP • G 0179 $44. 17 (initial) G 0180 $53. 00 (recertification) • Billable after reviewing and signing the ‘ 485’ orders from Home Health agencies Making House Calls a Part of Your Practice- AAHCP
Care Plan Oversight and Certification for Home Health Agency Patient • These are also billable for your clinic patients receiving skilled HHA services in the community • G 0181 $104. 31 (home health)/ G 0182 $105. 67 (hospice) • Must document 30 minutes of time spent coordinating care unrelated to a face to face visit for a patient • Time spent includes telephone calls to other health professionals (NOT FAMILY), ordering and reviewing tests etc. • Time must be at least 30 minutes in 1 calendar month • a template for documentation is available in from AAHCP • G 0179 $44. 17 (initial) G 0180 $53. 00 (recertification) • Billable after reviewing and signing the ‘ 485’ orders from Home Health agencies Making House Calls a Part of Your Practice- AAHCP
 Collaborate with Home Health Agencies and Hospices • HHA have invaluable resources to improve health outcomes in frail elderly patients • Many homebound patients will qualify for this intermittent medicare benefit and these services may help you provide excellent quality care with these added resources
Collaborate with Home Health Agencies and Hospices • HHA have invaluable resources to improve health outcomes in frail elderly patients • Many homebound patients will qualify for this intermittent medicare benefit and these services may help you provide excellent quality care with these added resources
 Documentation • H&P • Progress notes • EMR • Must be complete and comprehensive in order to provide high quality patient care and communication, maximize billing, prevent potential mismanagement/ litigation
Documentation • H&P • Progress notes • EMR • Must be complete and comprehensive in order to provide high quality patient care and communication, maximize billing, prevent potential mismanagement/ litigation
 Building up your home care practice • Gradually add another patient or 2 from a similar locality • Set aside one afternoon weekly or bimonthly as the practice grows • Typically you should be able to see 3 -4 patients in a half day at home depending on accessibility, less in rural areas • Consider building a team to help you if you have access to a Social Worker, RN case manager, pharmacist these can be invaluable members of the home care team • Many physicians now make house calls full time!
Building up your home care practice • Gradually add another patient or 2 from a similar locality • Set aside one afternoon weekly or bimonthly as the practice grows • Typically you should be able to see 3 -4 patients in a half day at home depending on accessibility, less in rural areas • Consider building a team to help you if you have access to a Social Worker, RN case manager, pharmacist these can be invaluable members of the home care team • Many physicians now make house calls full time!
 Summary • House calls are a rewarding addition to a medical based practice • Start with one or two patients and build up • Collaborate with home health agencies • Now…. . go make a home visit!
Summary • House calls are a rewarding addition to a medical based practice • Start with one or two patients and build up • Collaborate with home health agencies • Now…. . go make a home visit!


