24720bbe50468c1c9785404e012e224b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Hotmail’s Performance Tuning Best Practices Aladdin A. Nassar Hotmail’s Performance Champion Microsoft

Lessons Learned § § § § § We cannot defy the laws of physics The truth is always out there History is bound to repeat itself if we don’t learn from it Newer technologies ~ bigger guns to shoot ourselves with Performance is like beauty – it only shines from the inside Performance effects are asymmetric Customers do not care what we think our performance is We will always find ways to outgrow our capacity It is very easy to lose the forest in the trees Some of the best performance gains are the simplest of all

Laws of Physics § § § § The more bytes you transfer, the longer they take to load HTML is much faster & more resilient than Javascript Web Applications are thin applications WW performance is bound by network latency TCP packets cannot travel faster than the speed of light Performance Tuning is an over-constrained problem Asymmetric bandwidths can bottleneck upstream Fewer bigger files download faster than many small files
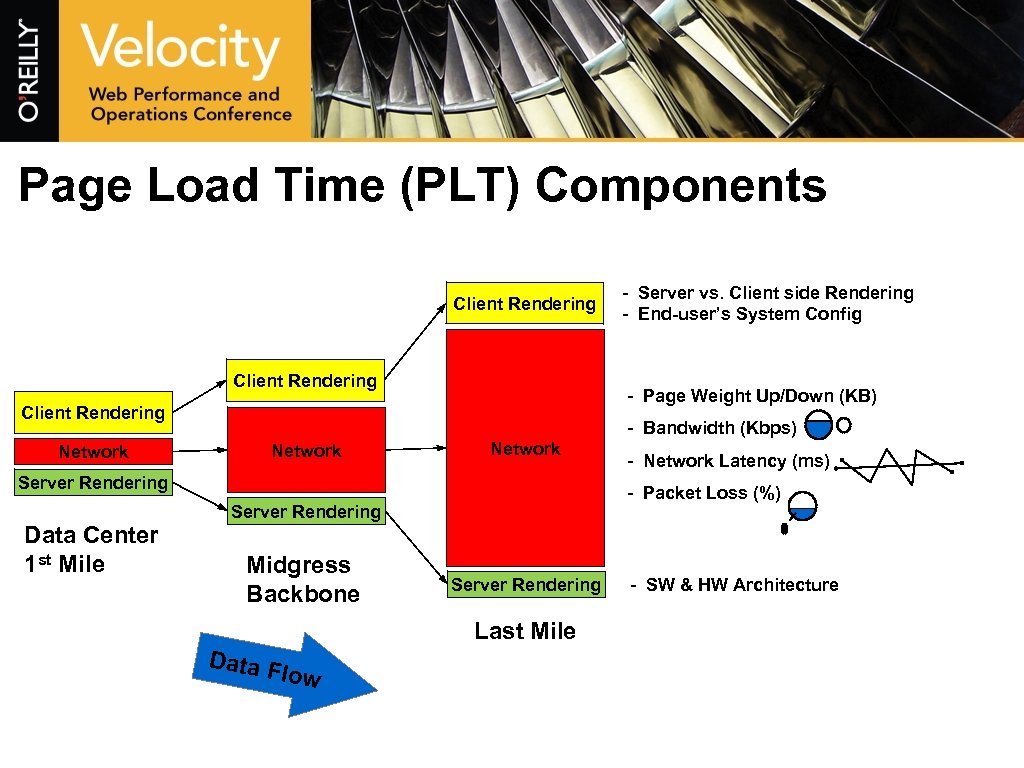
Page Load Time (PLT) Components Client Rendering - Page Weight Up/Down (KB) Client Rendering Network - Bandwidth (Kbps) Network Server Rendering Data Center 1 st Mile - Server vs. Client side Rendering - End-user’s System Config - Packet Loss (%) Server Rendering Midgress Backbone Server Rendering Last Mile Data F lo w - Network Latency (ms) - SW & HW Architecture
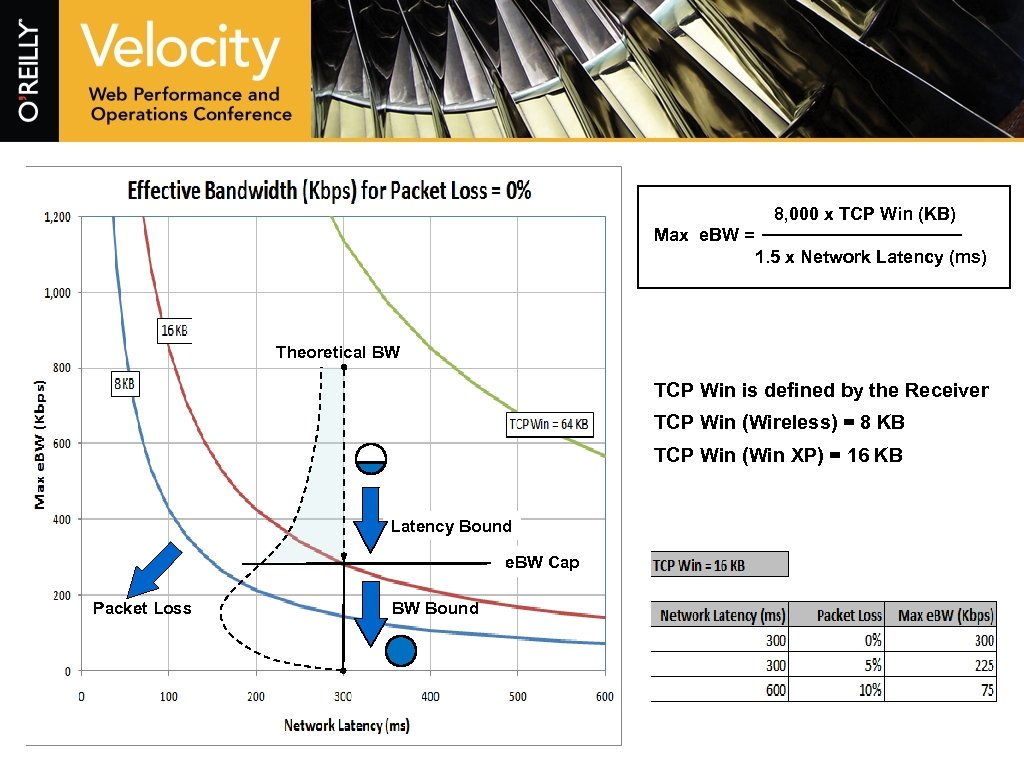
8, 000 x TCP Win (KB) Max e. BW = 1. 5 x Network Latency (ms) Theoretical BW TCP Win is defined by the Receiver TCP Win (Wireless) = 8 KB TCP Win (Win XP) = 16 KB Latency Bound e. BW Cap Packet Loss BW Bound

Performance Best Practices § § § Identify your performance bottlenecks & critical paths Trim down your page weights up/downstream Move your contents closer to your customers § § § Edge Caching Edge Computing Network Routing Optimization Geohosting Instrument performance across your entire network Build a closed feedback loop – fine tune, measure, etc.

Trim Page Weights (Downstream) § § § Trim down your features to the core minimum Render most of your content on the server side Trim down your image sizes by: § § § § Minimizing their usage Image Clustering Reducing their color palettes Delay load, slow down, cap and monitor ads Use Cache Control, Expiration Dates & e. Tags effectively Group your static content into fewer bigger files Optimize between inline and stand-alone JS & CSS Full Postbacks vs. atomic updates using Ajax

Trim Page Weights (Upstream) § § Down/up connection speeds ~ 5 which means your bottleneck is most likely upstream Trim down your cookies by: § § § Eliminating them altogether by moving your static contents to a different domain Optimizing their use Moving them away from your root domain and root path “/” Compressing them Grouping multiple smaller files into fewer bigger ones (image clustering) Trim down the number of requests and redirects (round trips)

Bandwidth Efficiency § § § § Identify your critical path Spread your downloads across multiple hostnames Hostname spreading can hurt narrowband On Demand / JIT downloading Control the sequencing of your downloads Unblock & defer your Javascript Minimize the browser’s “think time” Use appropriate tools to analyze bandwidth efficiency
The Big Picture § § § § Outgrowing Moore’s Law Performance Based Design (PBD) Effect of Ads on Performance Relative Performance Index (RPI) Performance Consortium PLT 1 vs. PLT 2 Myths Performance vs. Capacity Planning

Q&A

Performance Tools § § § § § Fiddler HTTP Watch HTTP Analyzer WANSim Net. Mon + Add-Ons RTA / VRTA / BWA Gomez Backbone/Last Mile Keynote Backbone In-House Automation Tools JS Instrumentation
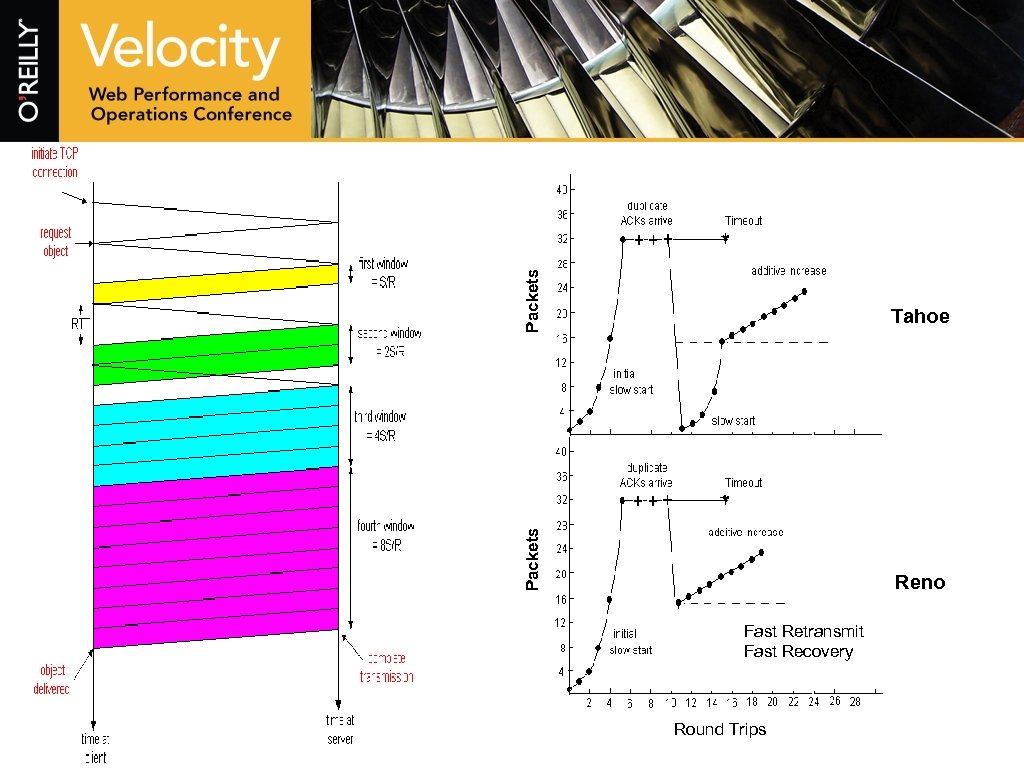
Packets Tahoe Packets Reno Fast Retransmit Fast Recovery Round Trips
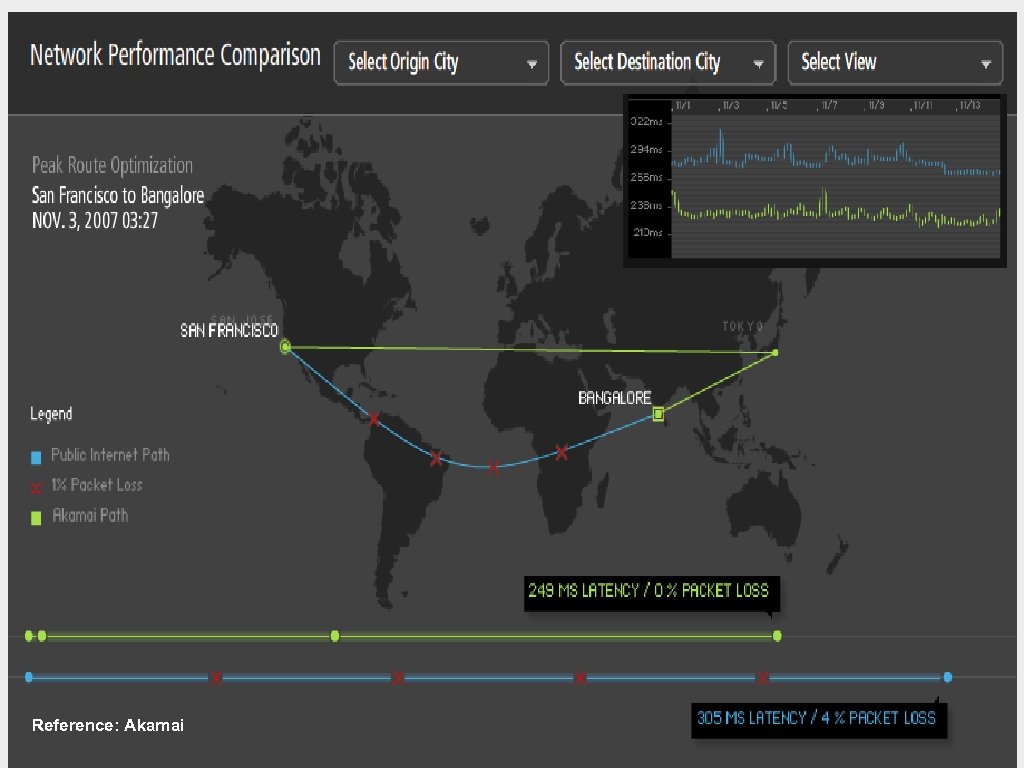
Reference: Akamai
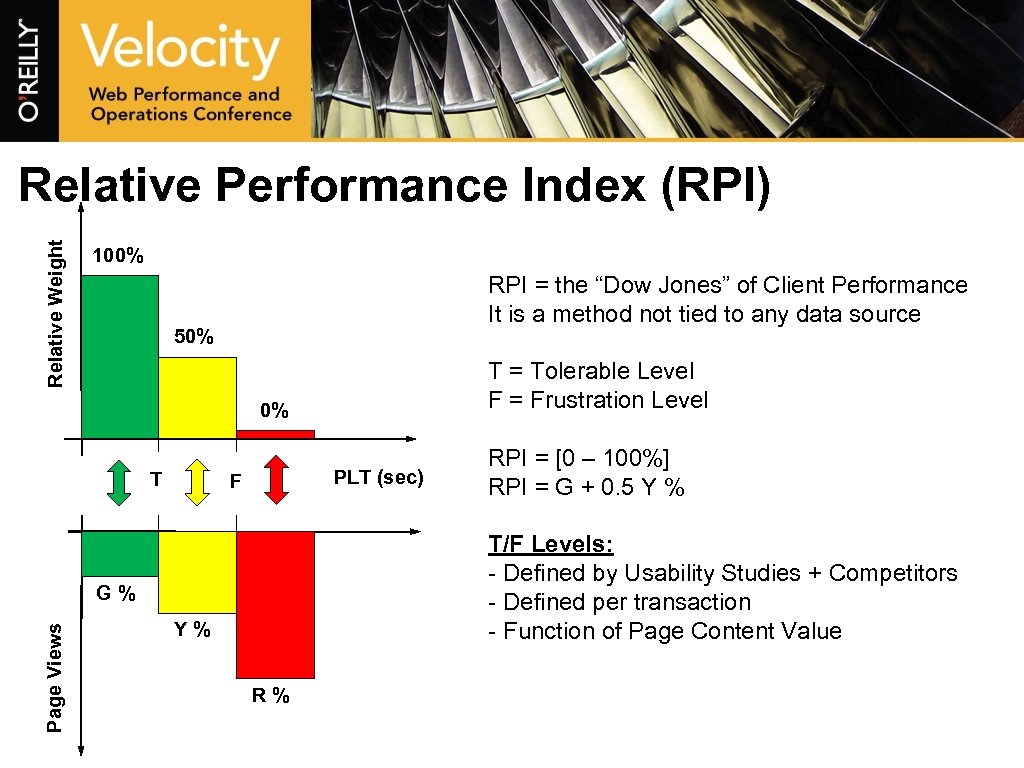
Relative Weight Relative Performance Index (RPI) 100% RPI = the “Dow Jones” of Client Performance It is a method not tied to any data source 50% T = Tolerable Level F = Frustration Level 0% T PLT (sec) F T/F Levels: - Defined by Usability Studies + Competitors - Defined per transaction - Function of Page Content Value G% Page Views RPI = [0 – 100%] RPI = G + 0. 5 Y % Y% R%
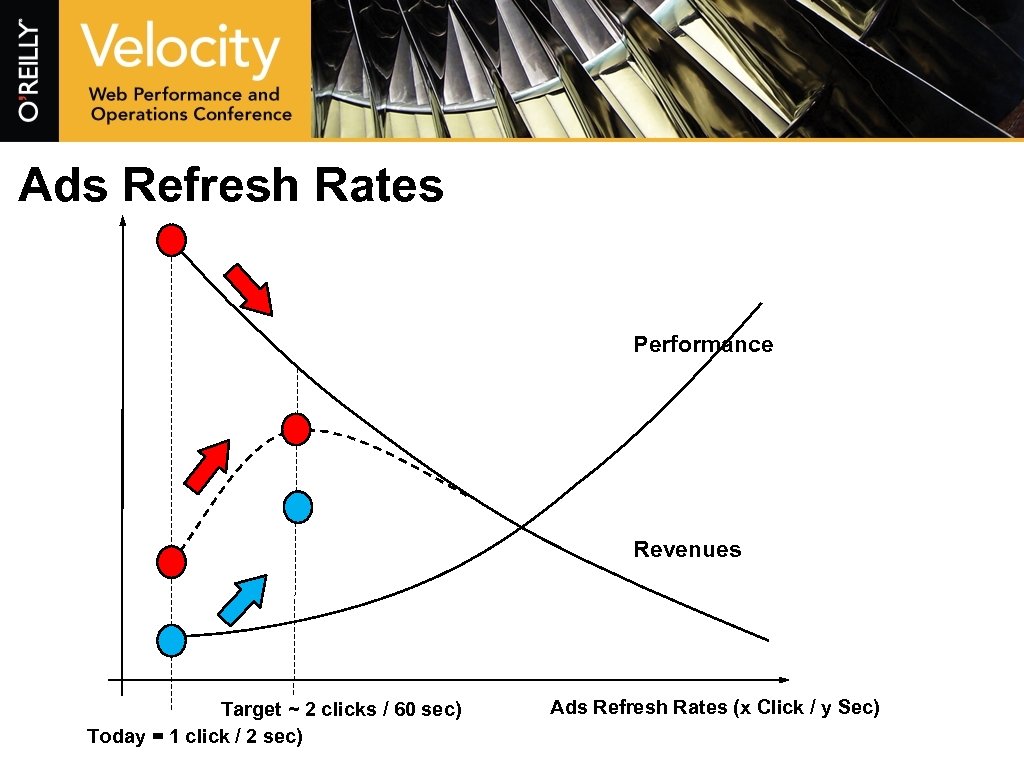
Ads Refresh Rates Performance Revenues Target ~ 2 clicks / 60 sec) Today = 1 click / 2 sec) Ads Refresh Rates (x Click / y Sec)
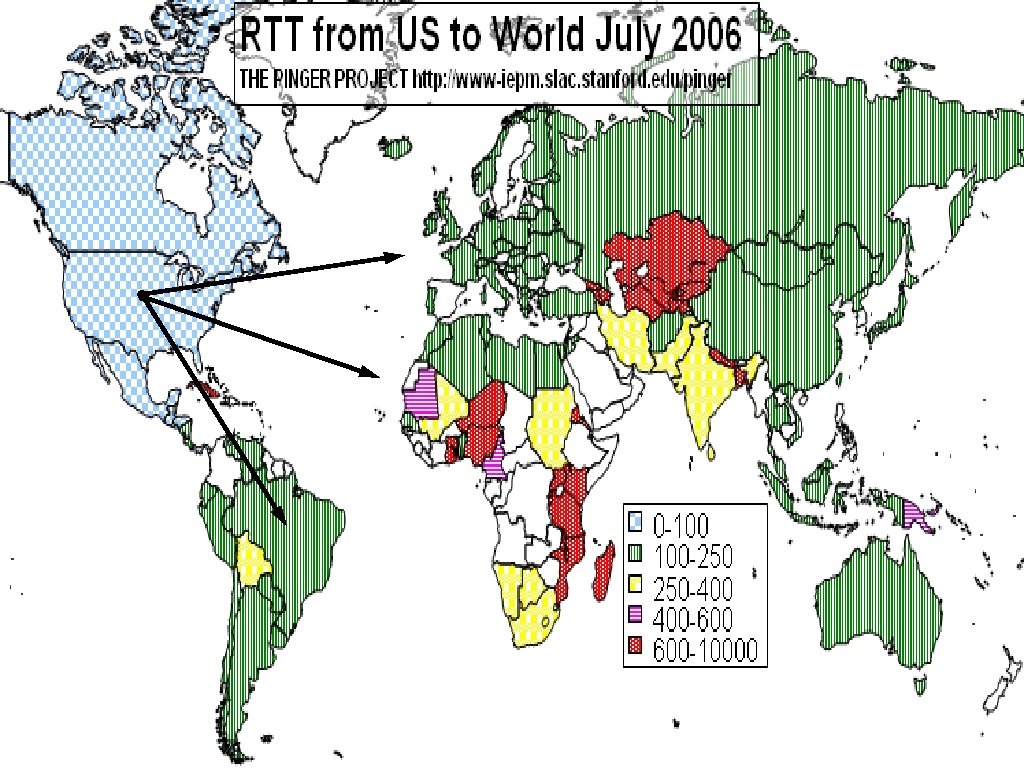
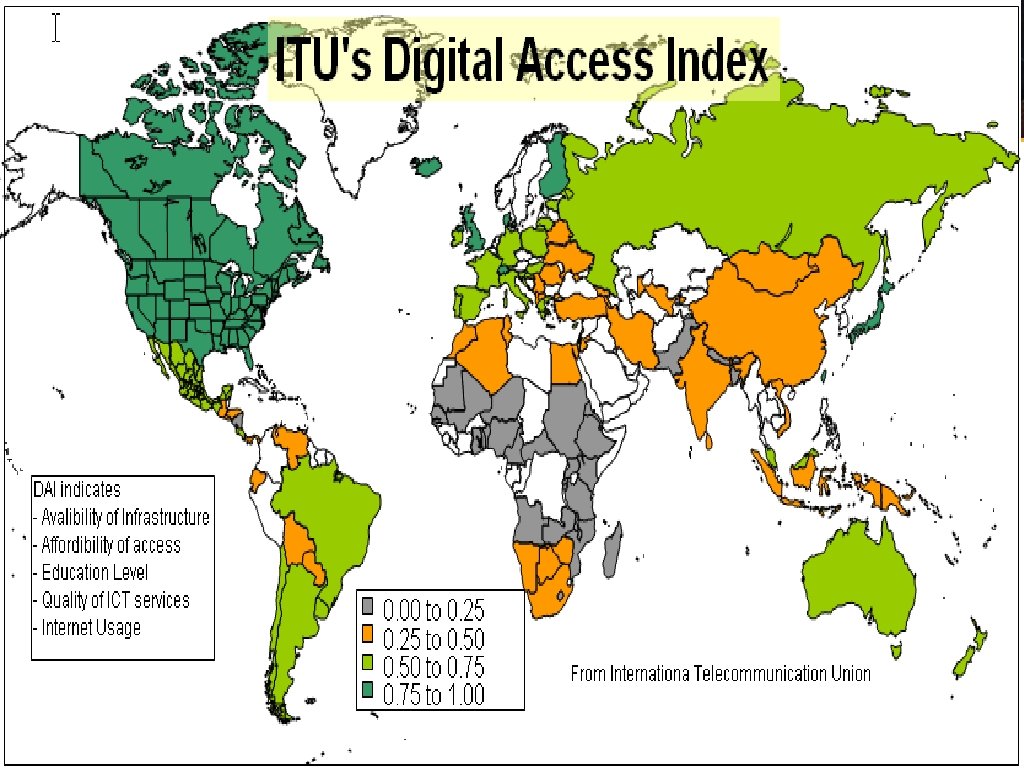
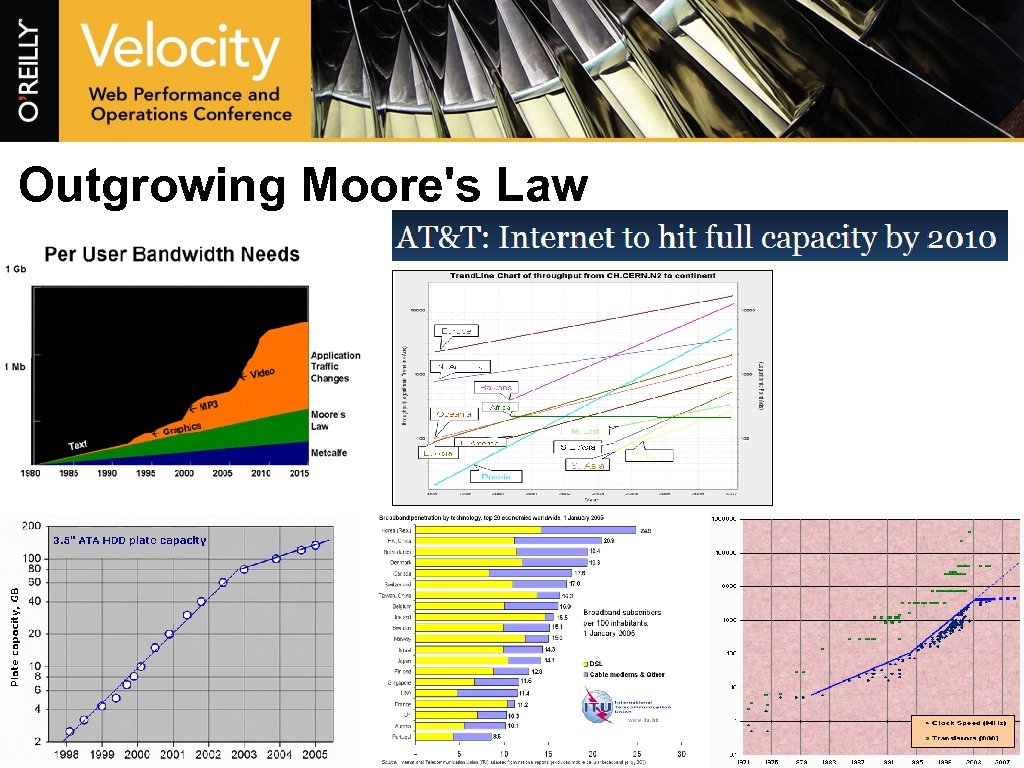
Outgrowing Moore's Law
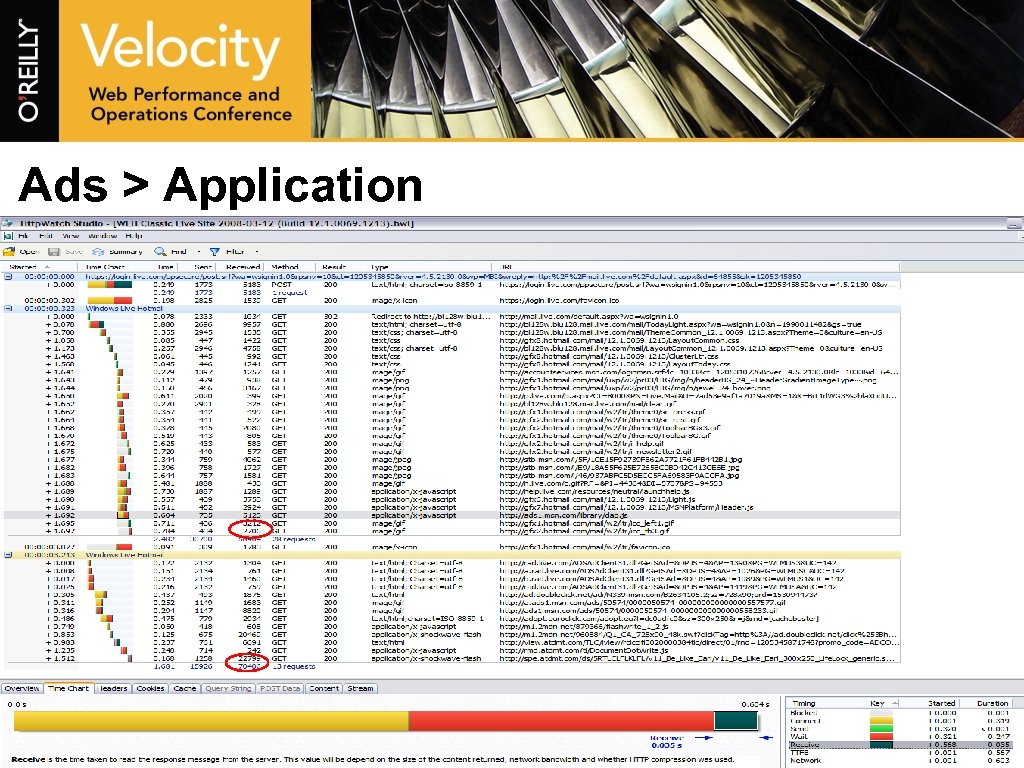
Ads > Application

The End
24720bbe50468c1c9785404e012e224b.ppt