564ea1e67b3ae1ac1cbbe4a6b8891359.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Hosted by The Future of Windows in the Enterprise John Enck Vice President and Research Director Server and Directory Strategies Copyright © 2003, Gartner
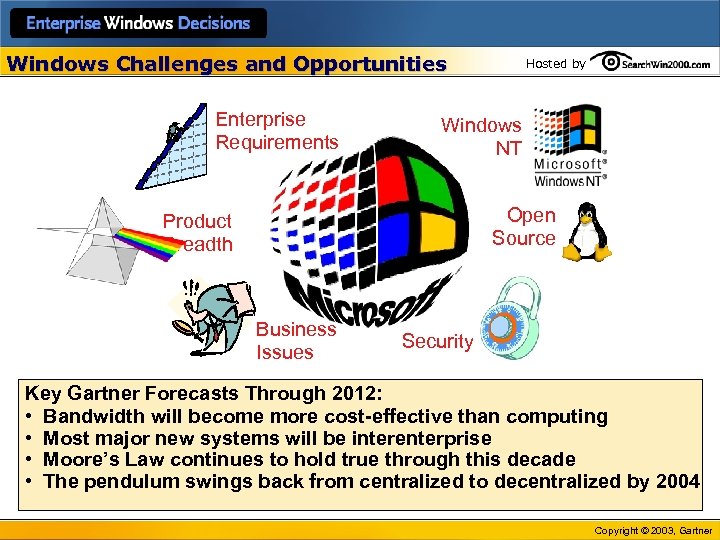
Windows Challenges and Opportunities Enterprise Requirements Hosted by Windows NT Open Source Product Breadth Business Issues Security Key Gartner Forecasts Through 2012: • Bandwidth will become more cost-effective than computing • Most major new systems will be interenterprise • Moore’s Law continues to hold true through this decade • The pendulum swings back from centralized to decentralized by 2004 Copyright © 2003, Gartner
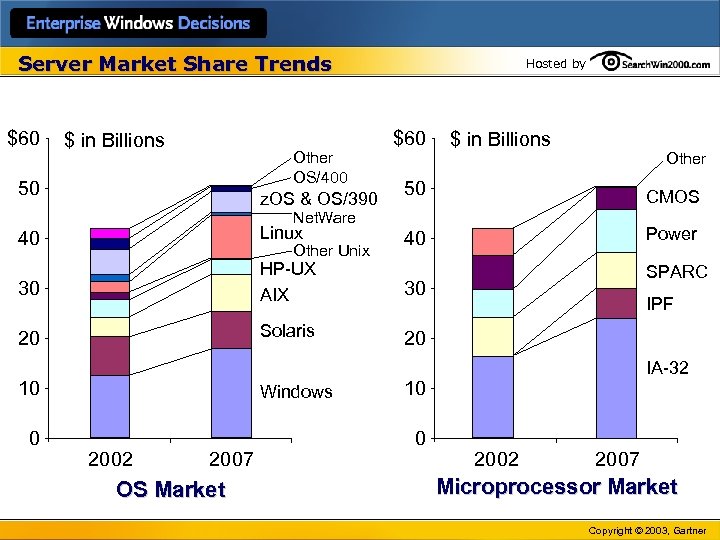
Server Market Share Trends $60 $ in Billions Other OS/400 50 z. OS & OS/390 Hosted by $60 $ in Billions Other 50 CMOS 40 Power Net. Ware 40 Linux 30 HP-UX AIX 30 20 Solaris 20 Other Unix 10 0 Windows 2002 2007 OS Market SPARC IPF IA-32 10 0 2002 2007 Microprocessor Market Copyright © 2003, Gartner
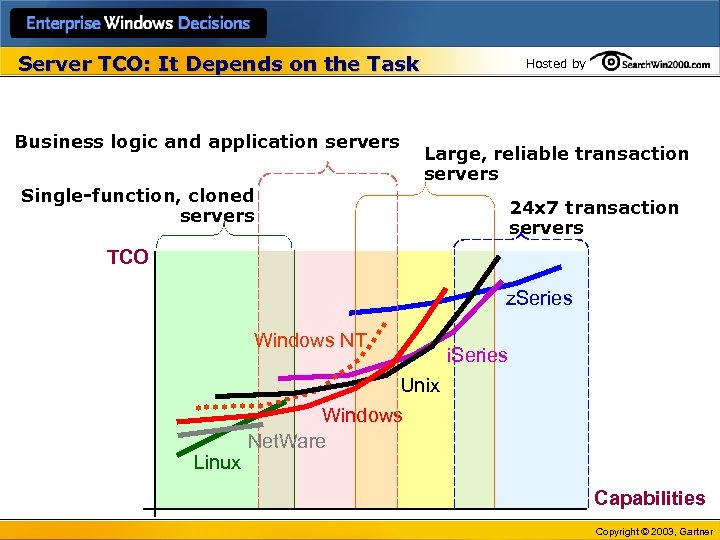
Server TCO: It Depends on the Task Business logic and application servers Hosted by Large, reliable transaction servers Single-function, cloned servers 24 x 7 transaction servers TCO z. Series Windows NT Linux i. Series Unix Windows Net. Ware Capabilities Copyright © 2003, Gartner
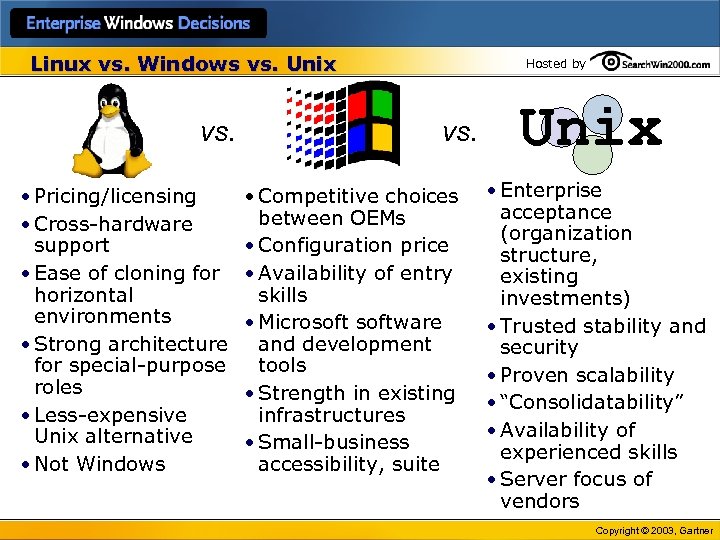
Linux vs. Windows vs. Unix vs. • Pricing/licensing • Cross-hardware support • Ease of cloning for horizontal environments • Strong architecture for special-purpose roles • Less-expensive Unix alternative • Not Windows Hosted by vs. • Competitive choices between OEMs • Configuration price • Availability of entry skills • Microsoftware and development tools • Strength in existing infrastructures • Small-business accessibility, suite Unix • Enterprise acceptance (organization structure, existing investments) • Trusted stability and security • Proven scalability • “Consolidatability” • Availability of experienced skills • Server focus of vendors Copyright © 2003, Gartner
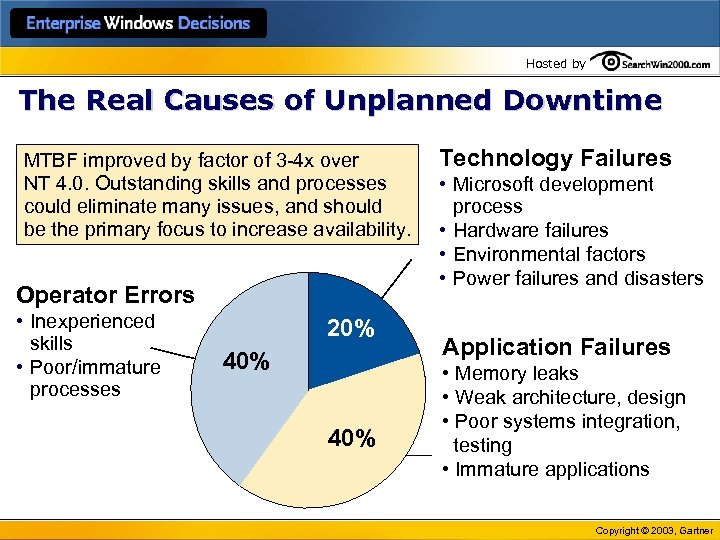
Hosted by The Real Causes of Unplanned Downtime MTBF improved by factor of 3 -4 x over NT 4. 0. Outstanding skills and processes could eliminate many issues, and should be the primary focus to increase availability. Operator Errors • Inexperienced skills • Poor/immature processes 20% 40% Technology Failures • Microsoft development process • Hardware failures • Environmental factors • Power failures and disasters Application Failures • Memory leaks • Weak architecture, design • Poor systems integration, testing • Immature applications Copyright © 2003, Gartner
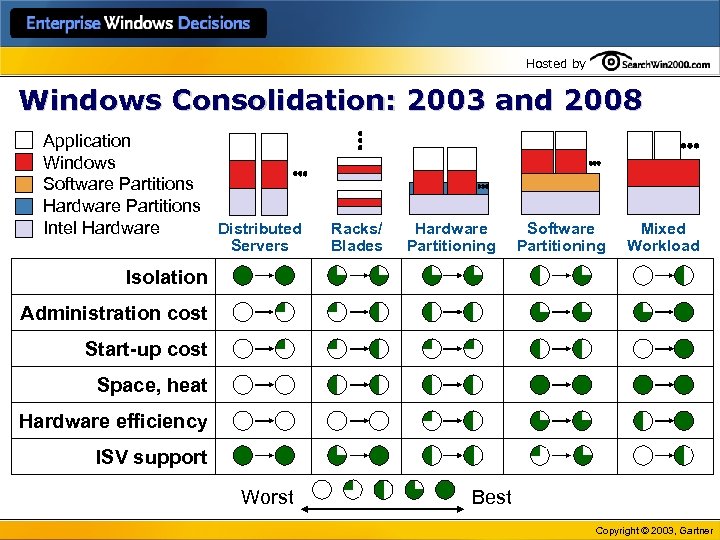
Hosted by Windows Consolidation: 2003 and 2008 Application Windows Software Partitions Hardware Partitions Intel Hardware Distributed Servers Racks/ Blades Hardware Partitioning Software Partitioning Mixed Workload Isolation Administration cost Start-up cost Space, heat Hardware efficiency ISV support Worst Best Copyright © 2003, Gartner

Hosted by VMware: Software Partitioning What It Does • ESX: Machine interface kernel OS (unique drivers required) • GSX: OS-hosted partition manager (host OS drivers/tools utilized) • Consolidates many small workloads on SMP systems • Windows and Linux • Dynamically reallocates resources • Processors: any percentage • Network bandwidth: average/maximum • I/O bandwidth: average/maximum What It Doesn’t Do • Eliminate multiple OS administration • Eliminate multiple OS license costs Risks/Issues • ISV support risk (especially Microsoft) • Driver support (ESX) • Microsoft’s workload strategy Use When • Multiple underutilized single processor workloads • Benefit from dynamic allocation • Application isolation important • New OS images and applications need to be deployed quickly • Strong OEM relationship available • Without rapid ROI in mind • GSX: Flexibility, MS support critical • ESX: Performance critical Copyright © 2003, Gartner

Hosted by The Promise of WSRM What It Does • Not just processor “affinity” • Dynamically adjusted processor utilization (via priority-setting) • Dynamically set limits on physical and virtual memory use of processes • Exceeding memory limit results in choice of warning or termination • GUI, command line, scripting • Accounting data created • Unused resource dynamically reallocated What It Doesn’t Do • Manage I/O or network bandwidth • Eliminate existing application collision problems Risks/Issues • Compatibility testing needed • ISV support limited — with slow ramp up (little motivation) Use When • Vendors can certify compatibility (e. g. , all Microsoft) • Microsoft develops tools/guidelines for easy in-house testing • Isolation less critical than reducing administration costs • Applications are more CPU-bound than I/O-bound • Note: Availability 6/2003, but significant ISV support will lag by six to 18 months Copyright © 2003, Gartner
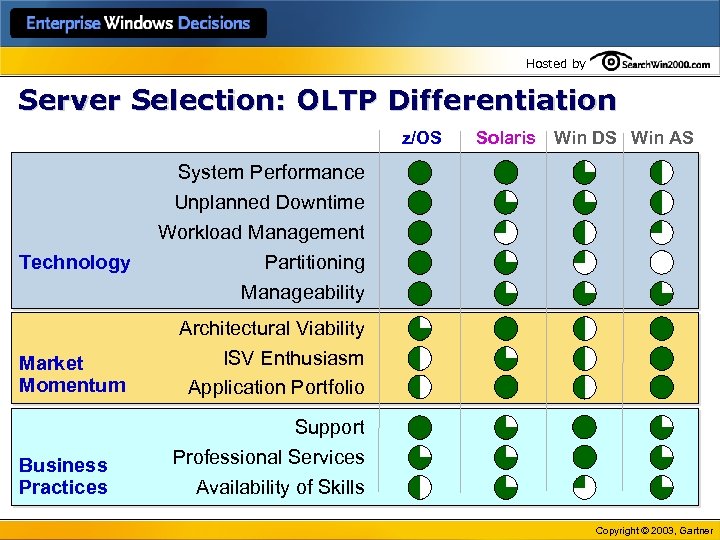
Hosted by Server Selection: OLTP Differentiation z/OS Technology Market Momentum Business Practices Solaris Win DS Win AS System Performance Unplanned Downtime Workload Management Partitioning Manageability Architectural Viability ISV Enthusiasm Application Portfolio Support Professional Services Availability of Skills Copyright © 2003, Gartner
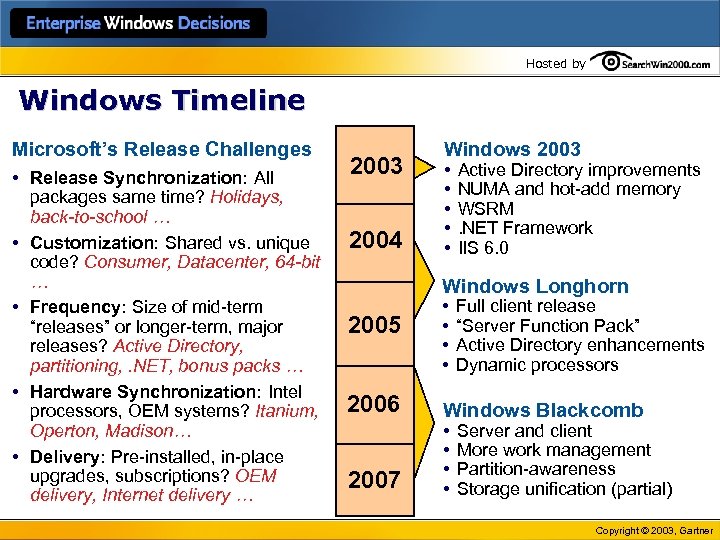
Hosted by Windows Timeline Microsoft’s Release Challenges • Release Synchronization: All packages same time? Holidays, back-to-school … • Customization: Shared vs. unique code? Consumer, Datacenter, 64 -bit … • Frequency: Size of mid-term “releases” or longer-term, major releases? Active Directory, partitioning, . NET, bonus packs … • Hardware Synchronization: Intel processors, OEM systems? Itanium, Operton, Madison… • Delivery: Pre-installed, in-place upgrades, subscriptions? OEM delivery, Internet delivery … 2003 2004 Windows 2003 • • • Active Directory improvements NUMA and hot-add memory WSRM. NET Framework IIS 6. 0 Windows Longhorn 2005 2006 2007 • • Full client release “Server Function Pack” Active Directory enhancements Dynamic processors Windows Blackcomb • • Server and client More work management Partition-awareness Storage unification (partial) Copyright © 2003, Gartner
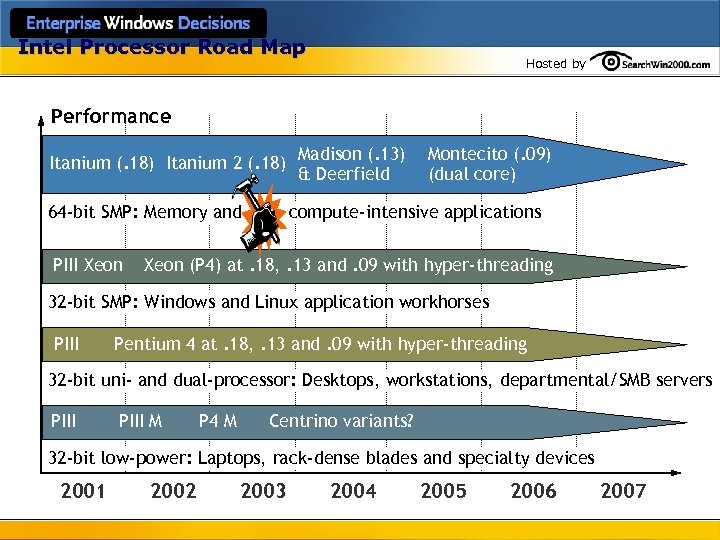
Intel Processor Road Map Hosted by Performance Itanium (. 18) Itanium 2 (. 18) Madison (. 13) & Deerfield 64 -bit SMP: Memory and PIII Xeon Montecito (. 09) (dual core) compute-intensive applications Xeon (P 4) at. 18, . 13 and. 09 with hyper-threading 32 -bit SMP: Windows and Linux application workhorses PIII Pentium 4 at. 18, . 13 and. 09 with hyper-threading 32 -bit uni- and dual-processor: Desktops, workstations, departmental/SMB servers PIII M P 4 M Centrino variants? 32 -bit low-power: Laptops, rack-dense blades and specialty devices 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007

What is Windows Server 2003 All About? Packaging Scalability • Web Edition • 64 -bit • NUMA. NET • Hot-add memory • IIS 6. 0, • WSRM • ASP. NET • . NET Framework • Enterprise UDDI Hosted by Active Directory • *Domain rename trusts • *Forest-level rootschema extensions • *Ability to deleteapplication partitions • Introduction of • Support for LDAP inet. Org. Person object • Support for multiple binds over one LDAP connection Management and Recovery • Global catalog no longer required in each site • Scripting/command line tools • Support for directory initialization from • Automated system recovery media • System tracing • Improved intersite replication topology • Emergency management generation service • Group membership replication for remote recovery improvements • Device driver rollback • Group size limitations removed • Remote control (single-user • Improved migration and management terminal services) tools * * * Only available with 100 percent Windows Server 2003 domain controllers © 2003, Gartner Copyright
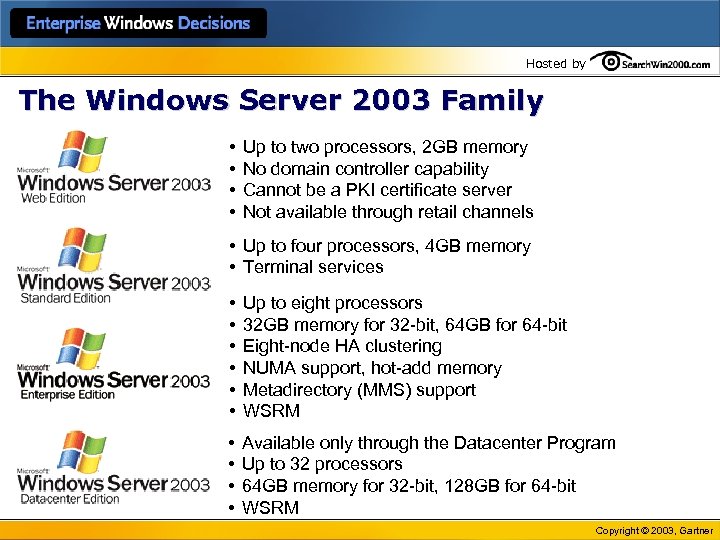
Hosted by The Windows Server 2003 Family • • Up to two processors, 2 GB memory No domain controller capability Cannot be a PKI certificate server Not available through retail channels • Up to four processors, 4 GB memory • Terminal services • • • Up to eight processors 32 GB memory for 32 -bit, 64 GB for 64 -bit Eight-node HA clustering NUMA support, hot-add memory Metadirectory (MMS) support WSRM • • Available only through the Datacenter Program Up to 32 processors 64 GB memory for 32 -bit, 128 GB for 64 -bit WSRM Copyright © 2003, Gartner
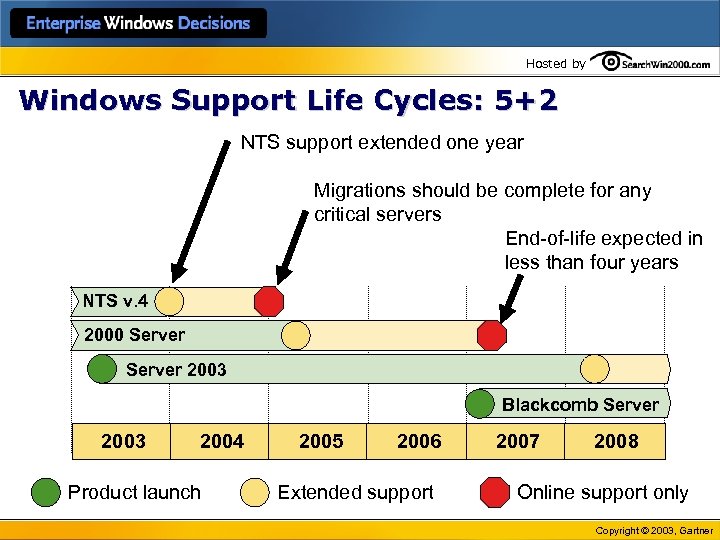
Hosted by Windows Support Life Cycles: 5+2 NTS support extended one year Migrations should be complete for any critical servers End-of-life expected in less than four years NTS v. 4 2000 Server 2003 Blackcomb Server 2003 2004 Product launch 2005 2006 Extended support 2007 2008 Online support only Copyright © 2003, Gartner
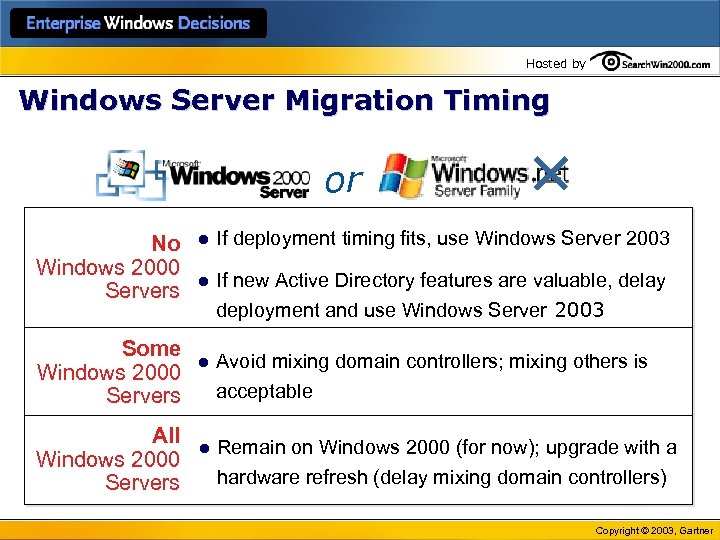
Hosted by Windows Server Migration Timing or No Windows 2000 Servers Some Windows 2000 Servers All Windows 2000 Servers l If deployment timing fits, use Windows Server 2003 l If new Active Directory features are valuable, delay deployment and use Windows Server 2003 l Avoid mixing domain controllers; mixing others is acceptable l Remain on Windows 2000 (for now); upgrade with a hardware refresh (delay mixing domain controllers) Copyright © 2003, Gartner
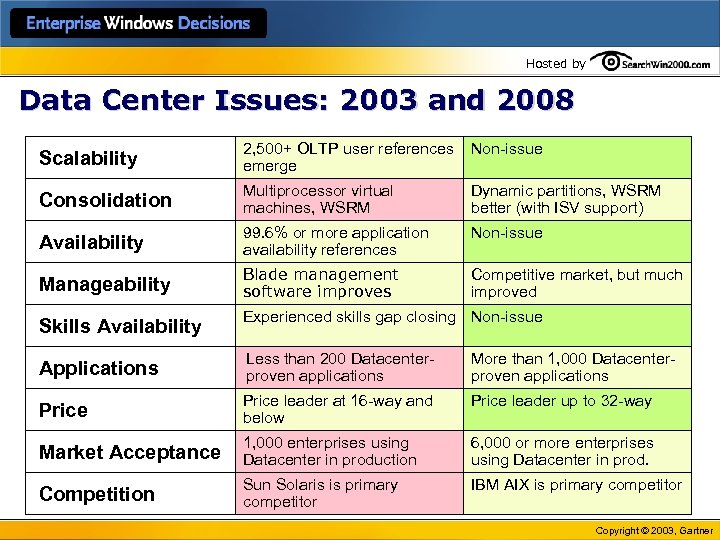
Hosted by Data Center Issues: 2003 and 2008 Scalability 2, 500+ OLTP user references emerge Non-issue Consolidation Multiprocessor virtual machines, WSRM Dynamic partitions, WSRM better (with ISV support) Availability 99. 6% or more application availability references Non-issue Manageability Blade management software improves Competitive market, but much improved Skills Availability Experienced skills gap closing Non-issue Applications Less than 200 Datacenterproven applications More than 1, 000 Datacenterproven applications Price leader at 16 -way and below Price leader up to 32 -way Market Acceptance 1, 000 enterprises using Datacenter in production 6, 000 or more enterprises using Datacenter in prod. Competition Sun Solaris is primary competitor IBM AIX is primary competitor Copyright © 2003, Gartner

Hosted by Microsoft & RTI: “Must Have” Technology Focus • Development tools and application architecture standards (“operationally aware” applications) • XML and Web services as the primary foundation • Distributed server manageability improvements (WMI, MOM, SMS, Application Center) • OS server consolidation improvements Assets …and. NET Enterprise Servers …and developers Challenges • Defining Strategy: Microsoft has not yet publicly defined an RTI strategy • Part of Problem: Windows server proliferation is the primary server management problem today and Windows lags in support for server consolidation tools • Non-Windows: Enterprises do not want unique management solutions for Windows only • Linux Velocity: Linux will gain momentum if its RTI capabilities improve faster than Windows’ • Limited Services: And limited direct management expertise Copyright © 2003, Gartner

Recommendations Hosted by · 64 -Bit: Consider 64 -bit Windows as a niche solution for specific applications, not as a general-purpose growth path. · Availability: The best way to maximize Windows availability is through skills and processes. · Partitions: Enterprises should consider VMware for projects that can provide an ROI in two years or less, but which also have an exit strategy — for example, test and development, migration, product demonstrations or low-end server consolidations. · Mixed Workload: Consider WSRM use for applications that can be proven to run effectively in a mixed environment only. · Windows NT 4. 0: Enterprises should plan to migrate critical servers away from NT Server version 4. 0 by year-end 2004 at the latest. · Windows Server 2003: Enterprises should view Windows Server 2003 as a point release and “slipstream” it into current Windows 2000 migration programs accordingly (starting 2 H 03). · “Function Packs”: Enterprises should prepare for Microsoft starting to offer optional server function pack between releases. · Windows Blackcomb: Enterprises should not plan on major improvements in Windows consolidation until Blackcomb (by 1 H 07). Copyright © 2003, Gartner
564ea1e67b3ae1ac1cbbe4a6b8891359.ppt