HOST 1042 Module 4 - Contingency Approach & Path-Goal Theory.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 HOST 1042 Leadership & Group Dynamics with Jason Lapidus Module 4 The Contingency Approach to Leadership • Comparing Approaches to Leadership • Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Theory • Activity: What Type of Leader are You? • Activity: What Type of Follower are You? • Path-Goal Theory • Path-Goal Situations and Preferred Leader Behaviours jlapidus@georgebrown. ca
HOST 1042 Leadership & Group Dynamics with Jason Lapidus Module 4 The Contingency Approach to Leadership • Comparing Approaches to Leadership • Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Theory • Activity: What Type of Leader are You? • Activity: What Type of Follower are You? • Path-Goal Theory • Path-Goal Situations and Preferred Leader Behaviours jlapidus@georgebrown. ca
 Readings and Resources • Leadership: Trait vs Path-Goal
Readings and Resources • Leadership: Trait vs Path-Goal
 Learning Objectives • Understand how leadership is often contingent on people and situations • Apply Hersey and Blanchard’s situational theory of leader style to the level of follower readiness • Explain the Path-Goal theory of leadership
Learning Objectives • Understand how leadership is often contingent on people and situations • Apply Hersey and Blanchard’s situational theory of leader style to the level of follower readiness • Explain the Path-Goal theory of leadership
 “No man island. ” - Unknown
“No man island. ” - Unknown
 The Contingency Approach • Failure to find universal traits or behaviours that would determine effective leadership • Directed researchers to consider the “situation” in their studies • Behaviour effective in some circumstances might be ineffective under different conditions • Effectiveness of leader behaviour is contingent upon organizational situations
The Contingency Approach • Failure to find universal traits or behaviours that would determine effective leadership • Directed researchers to consider the “situation” in their studies • Behaviour effective in some circumstances might be ineffective under different conditions • Effectiveness of leader behaviour is contingent upon organizational situations
 The Contingency Approach • Contingency means that one thing depends on another
The Contingency Approach • Contingency means that one thing depends on another
 The Contingency Approach • Contingency means that one thing depends on another • Theories explain the relationship between leadership styles and effectiveness in specific situations
The Contingency Approach • Contingency means that one thing depends on another • Theories explain the relationship between leadership styles and effectiveness in specific situations
 The Contingency Approach • Leadership is not a fixed series of characteristics that can be transposed into different contexts
The Contingency Approach • Leadership is not a fixed series of characteristics that can be transposed into different contexts
 The Contingency Approach • Leadership is not a fixed series of characteristics that can be transposed into different contexts • Leadership is a set of styles that can be used in a variety of situations
The Contingency Approach • Leadership is not a fixed series of characteristics that can be transposed into different contexts • Leadership is a set of styles that can be used in a variety of situations
 The Contingency Approach • For a leader to be effective, there must be an appropriate fit between the leader’s behaviour and the styles and conditions of the situation
The Contingency Approach • For a leader to be effective, there must be an appropriate fit between the leader’s behaviour and the styles and conditions of the situation
 The Contingency Approach • Effective leadership may depend on: o Type of staff o History of the business o Culture of the business o Quality of the relationships o Nature of the changes needed o Accepted norms within the institution
The Contingency Approach • Effective leadership may depend on: o Type of staff o History of the business o Culture of the business o Quality of the relationships o Nature of the changes needed o Accepted norms within the institution
 The Contingency Approach • Contingency approaches also take into consideration the needs and maturity of the followers
The Contingency Approach • Contingency approaches also take into consideration the needs and maturity of the followers
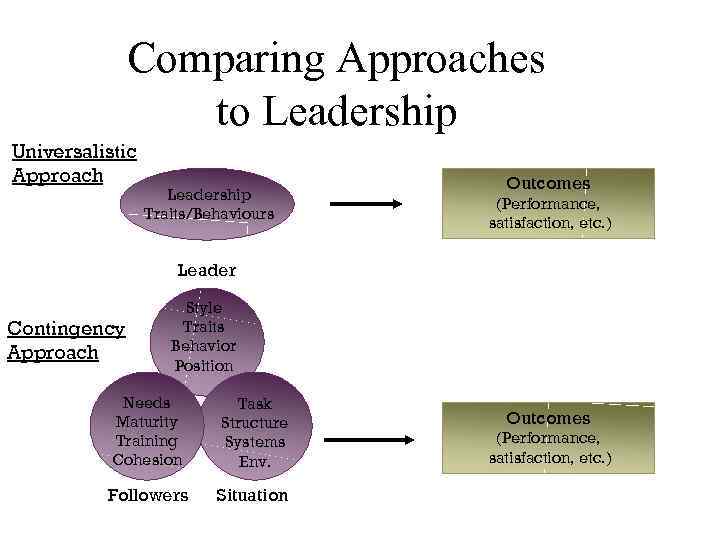 Comparing Approaches to Leadership Universalistic Approach Leadership Traits/Behaviours Outcomes (Performance, satisfaction, etc. ) Leader Contingency Approach Style Traits Behavior Position Needs Maturity Training Cohesion Task Structure Systems Env. Followers Situation Outcomes (Performance, satisfaction, etc. )
Comparing Approaches to Leadership Universalistic Approach Leadership Traits/Behaviours Outcomes (Performance, satisfaction, etc. ) Leader Contingency Approach Style Traits Behavior Position Needs Maturity Training Cohesion Task Structure Systems Env. Followers Situation Outcomes (Performance, satisfaction, etc. )
 The Contingency Approach Recap: • Contingency approaches seek to align the characteristics of leaders, situations and followers and examine the leadership styles that can be used effectively • Two main theories o Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Theory o Path-Goal Theory
The Contingency Approach Recap: • Contingency approaches seek to align the characteristics of leaders, situations and followers and examine the leadership styles that can be used effectively • Two main theories o Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Theory o Path-Goal Theory
 Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory • The characteristics of the followers are an important element of the situation, and thereby will effect the leader’s approach • According to the situational theory, a leader can adopt one of the four leadership styles, based on a combination of relationship (concern for people) and task (concern for production) The appropriate style depends on the readiness of the followers. • There are two main components to this approach: o LEADERSHIP STYLE o FOLLOWER READINESS
Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory • The characteristics of the followers are an important element of the situation, and thereby will effect the leader’s approach • According to the situational theory, a leader can adopt one of the four leadership styles, based on a combination of relationship (concern for people) and task (concern for production) The appropriate style depends on the readiness of the followers. • There are two main components to this approach: o LEADERSHIP STYLE o FOLLOWER READINESS
 Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory Four Styles of Leadership: 1. Telling Style 2. Selling Style 3. Participating Style 4. Delegating Style Each style exhibits a combination of concern for tasks and concern for people and relationships
Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory Four Styles of Leadership: 1. Telling Style 2. Selling Style 3. Participating Style 4. Delegating Style Each style exhibits a combination of concern for tasks and concern for people and relationships
 Telling Style • • High concern for tasks Low concern for people and relationship Leader defines the roles of followers Problem solving and decision making are initiated by the leader • One-way communication • Clearly involves telling people o o What to do How to do it Where to do it When to do it • And then closely supervising their performance
Telling Style • • High concern for tasks Low concern for people and relationship Leader defines the roles of followers Problem solving and decision making are initiated by the leader • One-way communication • Clearly involves telling people o o What to do How to do it Where to do it When to do it • And then closely supervising their performance
 Selling Style • High concern for tasks • High concern for people and relationship • Explains decisions and provides opportunity for clarification • Leader attempts to hear follower’s suggestions, ideas, and opinions • Two-way communication • Control over decision making remains with the Leader
Selling Style • High concern for tasks • High concern for people and relationship • Explains decisions and provides opportunity for clarification • Leader attempts to hear follower’s suggestions, ideas, and opinions • Two-way communication • Control over decision making remains with the Leader
 Participating Style • Low concern for tasks • High concern for people and relationship • Focus of control shifts to follower • Leader actively listens and shares ideas • Follower has ability and knowledge to do the task • Involves: o o o Listening to people Providing support and encouraging their efforts Facilitating their involvement in problem solving and decision making
Participating Style • Low concern for tasks • High concern for people and relationship • Focus of control shifts to follower • Leader actively listens and shares ideas • Follower has ability and knowledge to do the task • Involves: o o o Listening to people Providing support and encouraging their efforts Facilitating their involvement in problem solving and decision making
 Delegating Style • Low concern for tasks • Low concern for people and relationship o Leader discusses problems with followers o Seeks joint agreement on problem definitions o Decision making and implementation is handled by the followers they “run their own show”
Delegating Style • Low concern for tasks • Low concern for people and relationship o Leader discusses problems with followers o Seeks joint agreement on problem definitions o Decision making and implementation is handled by the followers they “run their own show”
 What Type of Leader are You? Leader’s Self Insight 3. 1 (10 minutes)
What Type of Leader are You? Leader’s Self Insight 3. 1 (10 minutes)
 Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory • Four Levels of Follower Readiness: • • Low Readiness Level Moderate Readiness Level High Readiness Level Very High Readiness Level • An effective leader will diagnose a follower’s readiness and select a leadership style that is appropriate to the level of readiness
Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory • Four Levels of Follower Readiness: • • Low Readiness Level Moderate Readiness Level High Readiness Level Very High Readiness Level • An effective leader will diagnose a follower’s readiness and select a leadership style that is appropriate to the level of readiness
 Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory • Low Readiness: Lack education, skills, experience and confidence • Moderate Readiness: Lack some education and experience but demonstrates confidence, ability, interest and willingness to learn • High Readiness: Followers have the necessary education, skills, and experience, but they may be insecure in their abilities • Very High Readiness: Followers have very high levels of education, experience, and readiness to accept responsibility
Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory • Low Readiness: Lack education, skills, experience and confidence • Moderate Readiness: Lack some education and experience but demonstrates confidence, ability, interest and willingness to learn • High Readiness: Followers have the necessary education, skills, and experience, but they may be insecure in their abilities • Very High Readiness: Followers have very high levels of education, experience, and readiness to accept responsibility
 Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory What type of follower are you? Leader’s Self Insight 3. 2 (10 minutes)
Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory What type of follower are you? Leader’s Self Insight 3. 2 (10 minutes)
 Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory • Working with a neighbour, discuss: • Part 1 • Are you a high task-oriented person or a low task-oriented person? • Are you a high people and relationship-oriented person or a low people and relationship-oriented person? • What is your corresponding leadership style orientation? • Part 2 • What is your follower readiness level? • What do you believe is the appropriate leadership style for your readiness level? • Do you believe that you and your neighbour would make a good team? Why or why not?
Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory • Working with a neighbour, discuss: • Part 1 • Are you a high task-oriented person or a low task-oriented person? • Are you a high people and relationship-oriented person or a low people and relationship-oriented person? • What is your corresponding leadership style orientation? • Part 2 • What is your follower readiness level? • What do you believe is the appropriate leadership style for your readiness level? • Do you believe that you and your neighbour would make a good team? Why or why not?
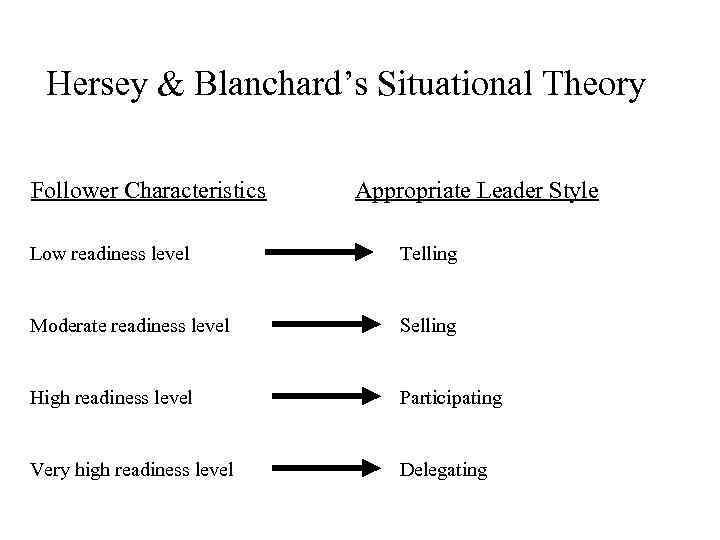 Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory Follower Characteristics Appropriate Leader Style Low readiness level Telling Moderate readiness level Selling High readiness level Participating Very high readiness level Delegating
Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Theory Follower Characteristics Appropriate Leader Style Low readiness level Telling Moderate readiness level Selling High readiness level Participating Very high readiness level Delegating
 Path-Goal Theory • The leader’s responsibility is to increase follower’s motivation to attain personal and organizational goals • A leader’s behaviour is unlikely to have a positive effect unless the leader is able to help the employee attain desired outcomes • The leader increases follower’s motivation by either o clarifying the follower’s path to the rewards that are available or o increasing the rewards that the follower values and desires • This model is considered a contingency theory because it consists of three sets of contingencies (leader style, followers, situation) • The theory examines how the effectiveness of four leader behaviours is influenced by these contingency factors
Path-Goal Theory • The leader’s responsibility is to increase follower’s motivation to attain personal and organizational goals • A leader’s behaviour is unlikely to have a positive effect unless the leader is able to help the employee attain desired outcomes • The leader increases follower’s motivation by either o clarifying the follower’s path to the rewards that are available or o increasing the rewards that the follower values and desires • This model is considered a contingency theory because it consists of three sets of contingencies (leader style, followers, situation) • The theory examines how the effectiveness of four leader behaviours is influenced by these contingency factors
 Path-Goal Theory Path clarification • The leader works with followers to help them identify and learn behaviours that will lead to successful task accomplishment and organizational rewards • Examples? Increasing rewards • The leader talks with followers to learn which rewards are important to them. o o Intrinsic rewards – rewards from the work itself Extrinsic rewards – raises or promotions • Examples? • The leader’s job is to increase the rewards and create pathways to these rewards!
Path-Goal Theory Path clarification • The leader works with followers to help them identify and learn behaviours that will lead to successful task accomplishment and organizational rewards • Examples? Increasing rewards • The leader talks with followers to learn which rewards are important to them. o o Intrinsic rewards – rewards from the work itself Extrinsic rewards – raises or promotions • Examples? • The leader’s job is to increase the rewards and create pathways to these rewards!
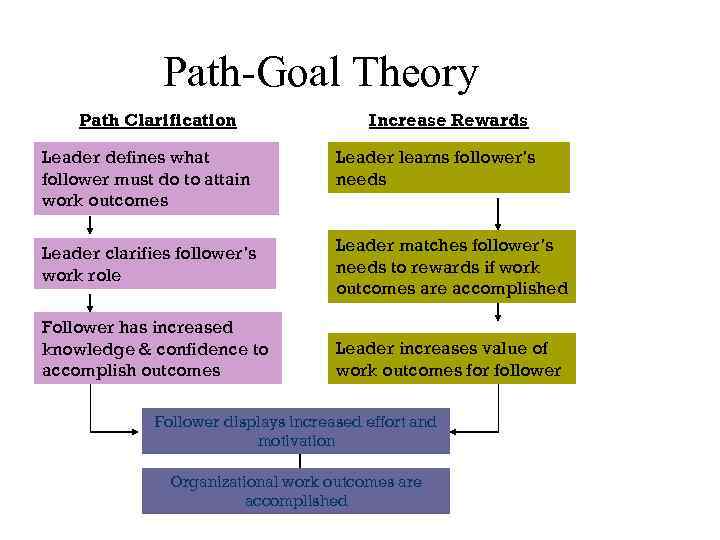 Path-Goal Theory Path Clarification Increase Rewards Leader defines what follower must do to attain work outcomes Leader learns follower’s needs Leader clarifies follower’s work role Leader matches follower’s needs to rewards if work outcomes are accomplished Follower has increased knowledge & confidence to accomplish outcomes Leader increases value of work outcomes for follower Follower displays increased effort and motivation Organizational work outcomes are accomplished
Path-Goal Theory Path Clarification Increase Rewards Leader defines what follower must do to attain work outcomes Leader learns follower’s needs Leader clarifies follower’s work role Leader matches follower’s needs to rewards if work outcomes are accomplished Follower has increased knowledge & confidence to accomplish outcomes Leader increases value of work outcomes for follower Follower displays increased effort and motivation Organizational work outcomes are accomplished
 Path-Goal Theory The Path-Goal theory suggests a four-fold classification of leader behaviours: • Supportive Leadership: friendly and approachable leader who shows concern for the status, well-being, and needs of their employees. o • Aligns with consideration (Ohio State) and people-oriented leadership. Directive Leadership: leader who lets subordinates know what is expected of them and tells them how to do it. o Aligns with initiating structure (Ohio State) and task-oriented leadership.
Path-Goal Theory The Path-Goal theory suggests a four-fold classification of leader behaviours: • Supportive Leadership: friendly and approachable leader who shows concern for the status, well-being, and needs of their employees. o • Aligns with consideration (Ohio State) and people-oriented leadership. Directive Leadership: leader who lets subordinates know what is expected of them and tells them how to do it. o Aligns with initiating structure (Ohio State) and task-oriented leadership.
 Path-Goal Theory • Participative Leadership: leader who consults with employees and asks for their suggestions, which he or she seriously considers before making a decision. o Aligns with Selling or Participating style (Hersey and Blanchard) • Achievement-Oriented Leadership: leader sets challenging goals, expects employees to perform at their highest level, and shows confidence that subordinates will meet such expectations. • These four types of leader behaviour are not considered personality traits. Rather, they reflect types of behaviour that every leader may choose to adopt, depending on the situation. • Let’s consider some possible situations. . . .
Path-Goal Theory • Participative Leadership: leader who consults with employees and asks for their suggestions, which he or she seriously considers before making a decision. o Aligns with Selling or Participating style (Hersey and Blanchard) • Achievement-Oriented Leadership: leader sets challenging goals, expects employees to perform at their highest level, and shows confidence that subordinates will meet such expectations. • These four types of leader behaviour are not considered personality traits. Rather, they reflect types of behaviour that every leader may choose to adopt, depending on the situation. • Let’s consider some possible situations. . . .
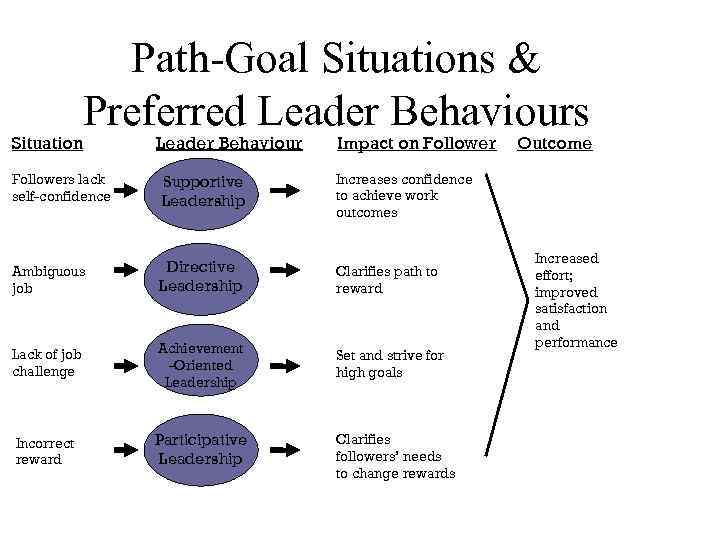 Path-Goal Situations & Preferred Leader Behaviours Situation Leader Behaviour Impact on Followers lack self-confidence Supportive Leadership Increases confidence to achieve work outcomes Ambiguous job Directive Leadership Clarifies path to reward Lack of job challenge Achievement -Oriented Leadership Set and strive for high goals Incorrect reward Participative Leadership Clarifies followers’ needs to change rewards Outcome Increased effort; improved satisfaction and performance
Path-Goal Situations & Preferred Leader Behaviours Situation Leader Behaviour Impact on Followers lack self-confidence Supportive Leadership Increases confidence to achieve work outcomes Ambiguous job Directive Leadership Clarifies path to reward Lack of job challenge Achievement -Oriented Leadership Set and strive for high goals Incorrect reward Participative Leadership Clarifies followers’ needs to change rewards Outcome Increased effort; improved satisfaction and performance
 Path-Goal Theory • Let’s compare what we’ve learned with the Trait Approach and the Path-Goal Theory Leadership: Trait vs Path-Goal
Path-Goal Theory • Let’s compare what we’ve learned with the Trait Approach and the Path-Goal Theory Leadership: Trait vs Path-Goal
 Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors
Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors
 Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors 1. Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Theory
Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors 1. Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Theory
 Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors 1. Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Theory • 4 Leadership Styles (Telling, Selling, Participating, and Delegating)
Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors 1. Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Theory • 4 Leadership Styles (Telling, Selling, Participating, and Delegating)
 Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors 1. Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Theory • 4 Leadership Styles (Telling, Selling, • Participating, and Delegating) Follower Readiness (Low, Moderate, High, and Very High)
Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors 1. Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Theory • 4 Leadership Styles (Telling, Selling, • Participating, and Delegating) Follower Readiness (Low, Moderate, High, and Very High)
 Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors 1. Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Theory • 4 Leadership Styles (Telling, Selling, Participating, and Delegating) • Follower Readiness (Low, Moderate, High, and Very High) 2. Path-Goal Theory (path clarification or increase of goals/rewards)
Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors 1. Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Theory • 4 Leadership Styles (Telling, Selling, Participating, and Delegating) • Follower Readiness (Low, Moderate, High, and Very High) 2. Path-Goal Theory (path clarification or increase of goals/rewards)
 Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors 1. Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Theory • 4 Leadership Styles (Telling, Selling, Participating, and Delegating) • Follower Readiness (Low, Moderate, High, and Very High) 2. Path-Goal Theory (path clarification or increase of goals/rewards)
Summary Contingency Approach leadership actions are contingent upon other factors 1. Hersey Blanchard’s Situational Theory • 4 Leadership Styles (Telling, Selling, Participating, and Delegating) • Follower Readiness (Low, Moderate, High, and Very High) 2. Path-Goal Theory (path clarification or increase of goals/rewards)


