81a798f7899a2f7efd8779464ca4f93f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58

HONEY, I BLEW UP THE KID! A SUPER Sized Medical Grand Rounds Presentor: Suzette Grace R. Kho, M. D. Resource Persons: Eric Flores, M. D. (Neurosurgery) Paolo Villanueva, M. D (Pathology) Gerardo Beltran, M. D. (Radiology) Teresa Sy-Ortin, M. D. (Radio-oncology) Moderator: Thelma Crisostomo, M. D.

Objectives To present a case of a 17 year old female with unusually tall stature To discuss differential diagnosis, & workup for patients presenting with pituitary mass to discuss pathophysiology & treatment options for patients presenting with pituitary tumors
Identifying Data F. O. 17 Female Filipino Cagayan de Oro Chief Complaint: Evaluation of Tall Stature
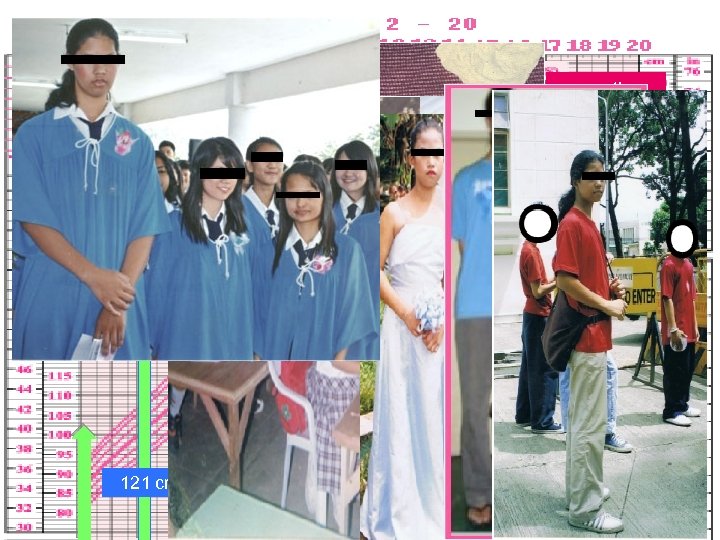

> 198 cm 191 cm 185 cm 168 cm 154 cm 121 cm 95 th %
3 mos PTA (+) “dimming” of her peripheral vision. (+) difficulty guarding her opponents, & would sometimes miss catching a pass. no consult was done until an annual school PE › Tall stature › Delayed development of secondary sexual characteristcs › Visual field abnormalities CONSULT

Review of Systems (-) rashes, (-) skin pigmentation (-) nocturia, (-) polydipsia (-) palpitations, (-) tremors, (-) heat/ cold intolerance, (-)weight gain/ weight loss (-) chest pain , (-)no difficulty of breathing, () lactation (-) easy fatigability, (-) body weakness, (-) tetany, (-) muscle cramps (-) hirsutism

Developmental History Delivered term via NSD to a 24 y/o G 2 P 1 Birth weight: 6 lbs. Birth length: claims to be within normal No delivery complications unremarkable
Family History Father- 5’ 4” (162. 54 cm) Mother- 5’ 3” (160 cm), menarche at age 12 *midparental height: 154. 77 cm 1 Sibling: Brother- 5’ 9” (175. 26 cm) tall relatives >182 cm ( 6’): mother side -8 uncles-: 6’ to 6’ 2” -1 male cousin: 6’ 1” (+) thyroid disease- aunt (+) HPN- father, uncle (+) asthma- father and brother (+) CVA- grandfather (-) DM, (-) colon cancer

Physical Examination Conscious, coherent, ambulatory, oriented to 3 spheres Vital Signs: BP 110/70 mm. Hg HR 84 bpm RR 20 cpm T 36. 3°C

Anthropometrics wt: 95. 5 kg ht: 198 cm BMI: 24. 1(overweight) upper segment: 84. 84 cm lower segment: 113 cm U/L segment: 0. 76 6’ 6 ”
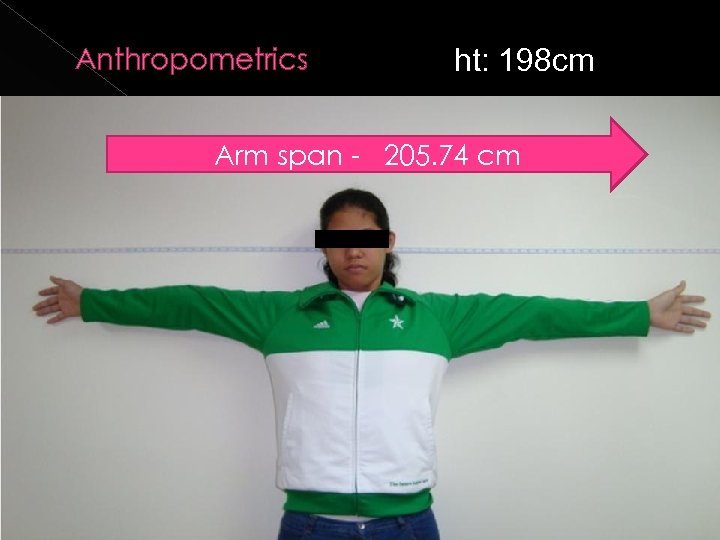
Anthropometrics ht: 198 cm Arm span - 205. 74 cm
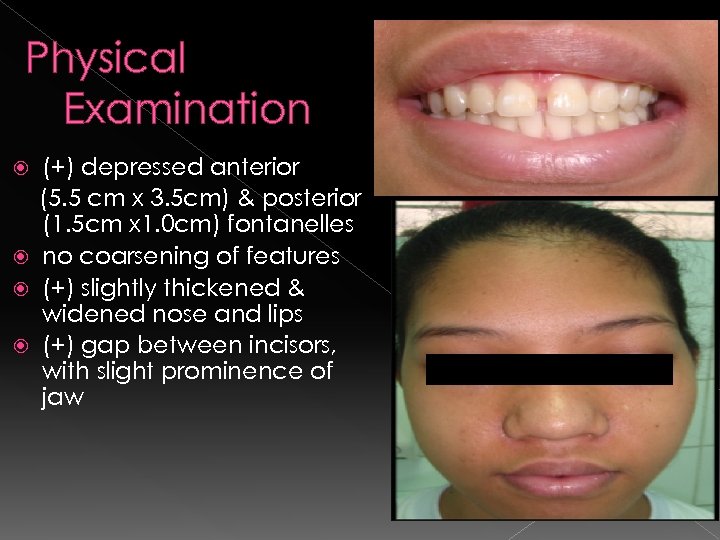
Physical Examination (+) depressed anterior (5. 5 cm x 3. 5 cm) & posterior (1. 5 cm x 1. 0 cm) fontanelles no coarsening of features (+) slightly thickened & widened nose and lips (+) gap between incisors, with slight prominence of jaw
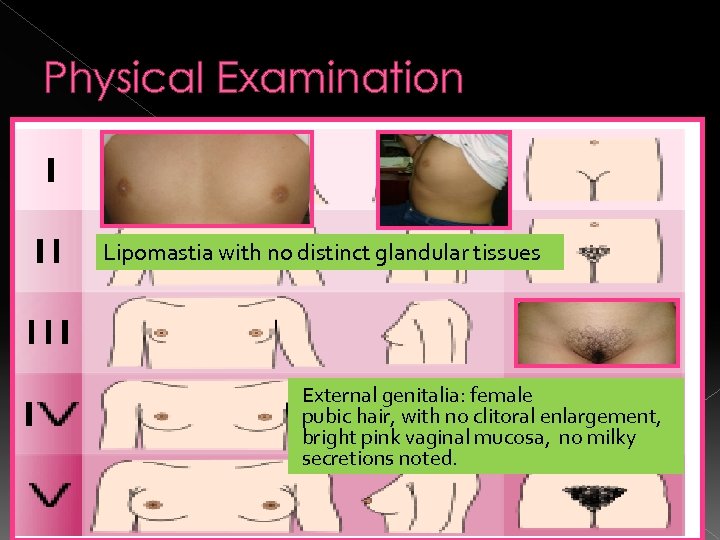
Physical Examination Lipomastia with no distinct glandular tissues External genitalia: female pubic hair, with no clitoral enlargement, bright pink vaginal mucosa, no milky secretions noted.
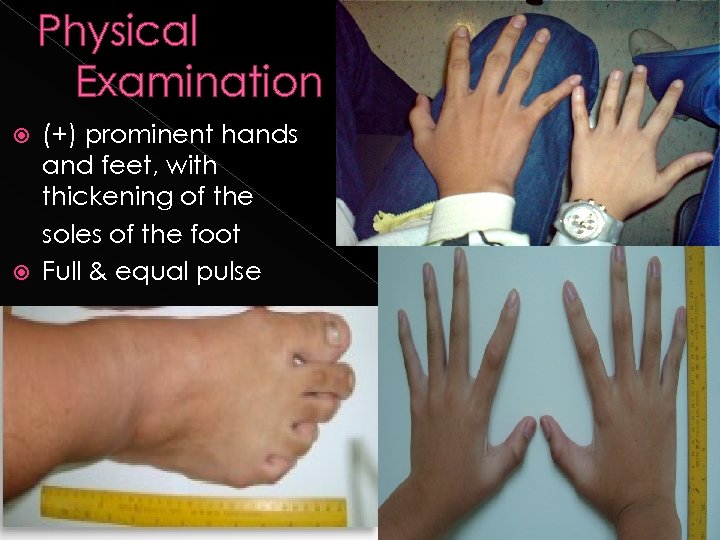
Physical Examination (+) prominent hands and feet, with thickening of the soles of the foot Full & equal pulse

Neurologic Examination Awake, alert, oriented to 3 spheres Pupils 3 -4 mm ERTL, EOM full and equal, (+) ROR, (+) visual field cuts Can smile, frown, clench teeth, tongue midline on protrusion Can shrug shoulders MMT: 5/5 on all extremities Sensory: 100% intact No dysmetria, no dysdiadokinesia (-) Brudzinski’s (-) Kernig’s (-) Babinski DTR: ++

Salient Features Depressed fontanelles slightly thickened & widened nose and lips upper tooth gap with slight prominence of jaw Prepubertal Tanner stage 1 breasts Tanner stage 3 pubic hair Prominent hands and feet 17 year old female Tall stature Delayed puberty Headaches Visual field defect
Differentials Tall Stature Familial Pituitary Mass Chromosomal Abnormalities Pubertal Delay Headache & Visual Changes Physiologic Pathologic Pituitary Mass Chromosomal Abnormalities Astigmatism Migraine Intracranial Tumor

Initial Impression Gigantism probably secondary to Growth hormone secreting pituitary adenoma with Hypogonadotrophic Hypogonadism
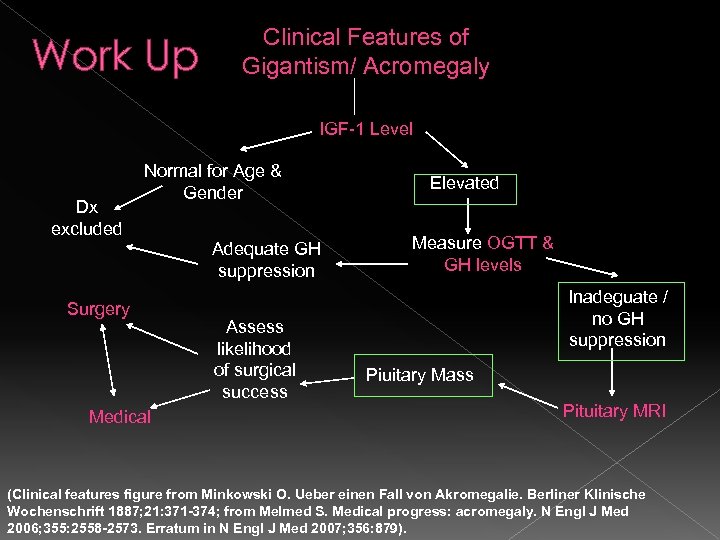
Work Up Clinical Features of Gigantism/ Acromegaly IGF-1 Level Dx excluded Normal for Age & Gender Adequate GH suppression Surgery Medical Assess likelihood of surgical success Elevated Measure OGTT & GH levels Inadeguate / no GH suppression Piuitary Mass Pituitary MRI (Clinical features figure from Minkowski O. Ueber einen Fall von Akromegalie. Berliner Klinische Wochenschrift 1887; 21: 371 -374; from Melmed S. Medical progress: acromegaly. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2558 -2573. Erratum in N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 879).
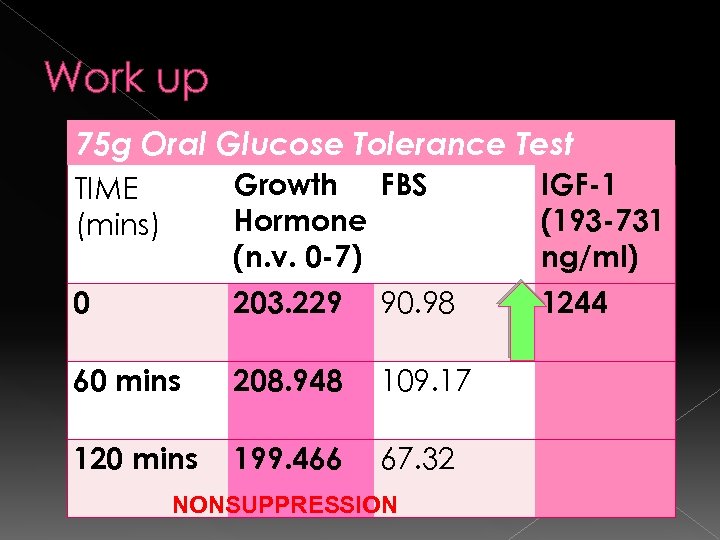
Work up 75 g Oral Glucose Tolerance Test TIME (mins) Growth FBS Hormone (n. v. 0 -7) IGF-1 (193 -731 ng/ml) 0 203. 229 90. 98 1244 60 mins 208. 948 109. 17 120 mins 199. 466 67. 32 NONSUPPRESSION
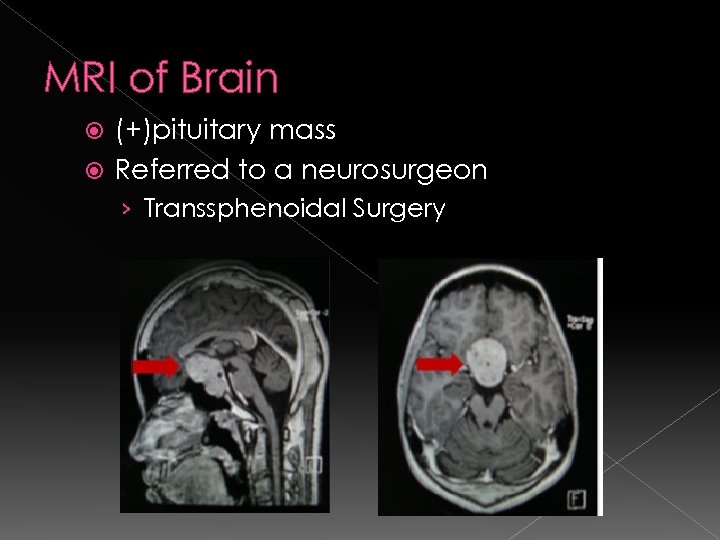
MRI of Brain (+)pituitary mass Referred to a neurosurgeon › Transsphenoidal Surgery
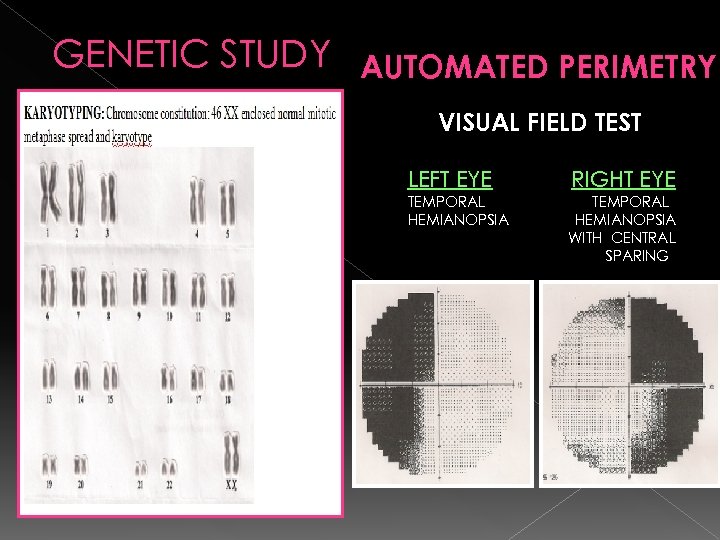
GENETIC STUDY AUTOMATED PERIMETRY VISUAL FIELD TEST LEFT EYE RIGHT EYE TEMPORAL HEMIANOPSIA WITH CENTRAL SPARING
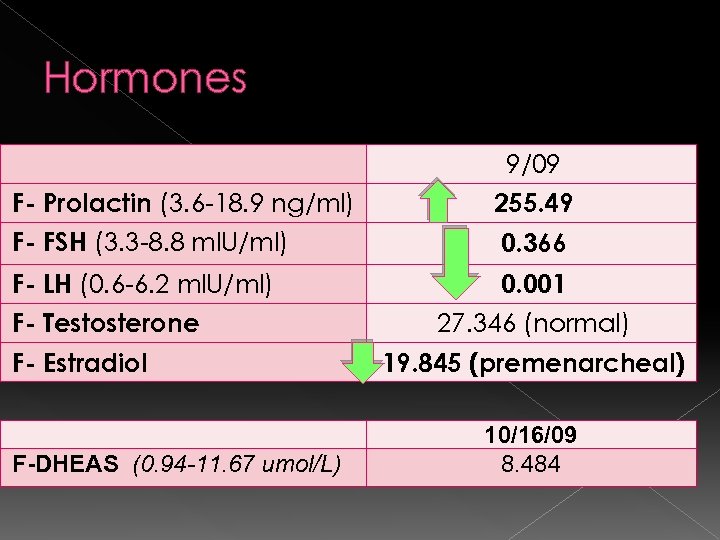
Hormones 9/09 F- Prolactin (3. 6 -18. 9 ng/ml) 255. 49 F- FSH (3. 3 -8. 8 ml. U/ml) 0. 366 F- LH (0. 6 -6. 2 ml. U/ml) 0. 001 F- Testosterone F- Estradiol F-DHEAS (0. 94 -11. 67 umol/L) 27. 346 (normal) 19. 845 (premenarcheal) 10/16/09 8. 484
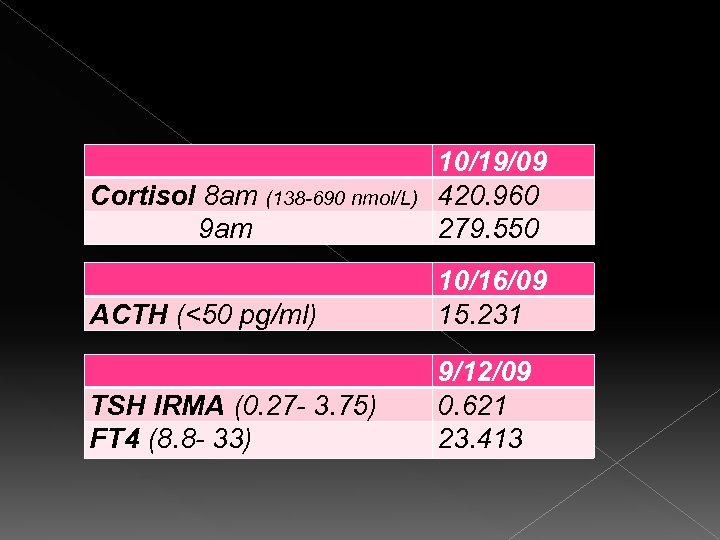
Cortisol 8 am (138 -690 nmol/L) 9 am 10/19/09 420. 960 279. 550 ACTH (<50 pg/ml) 10/16/09 15. 231 TSH IRMA (0. 27 - 3. 75) FT 4 (8. 8 - 33) 9/12/09 0. 621 23. 413
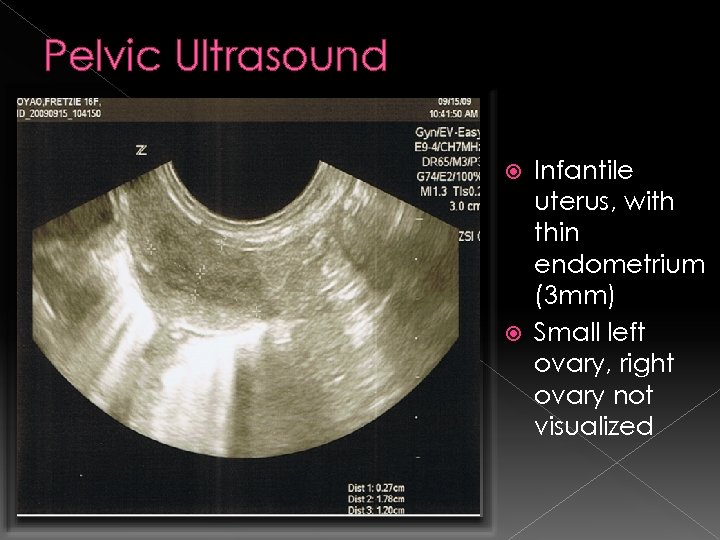
Pelvic Ultrasound Infantile uterus, with thin endometrium (3 mm) Small left ovary, right ovary not visualized
Skeletal Survey
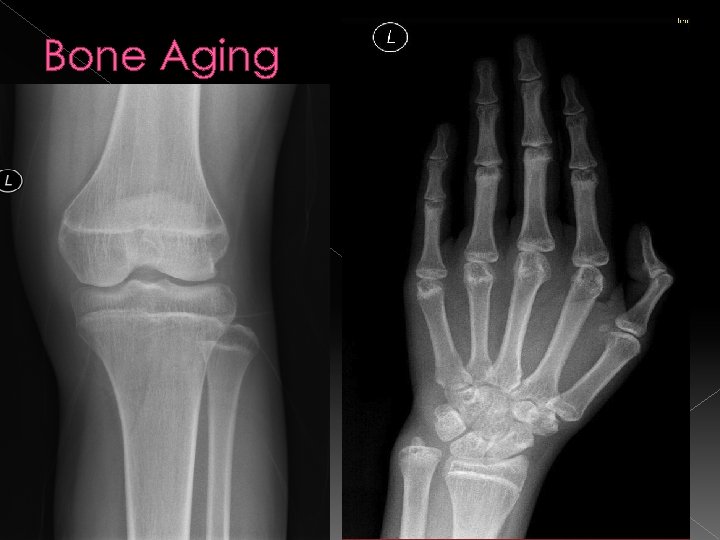
Bone Aging
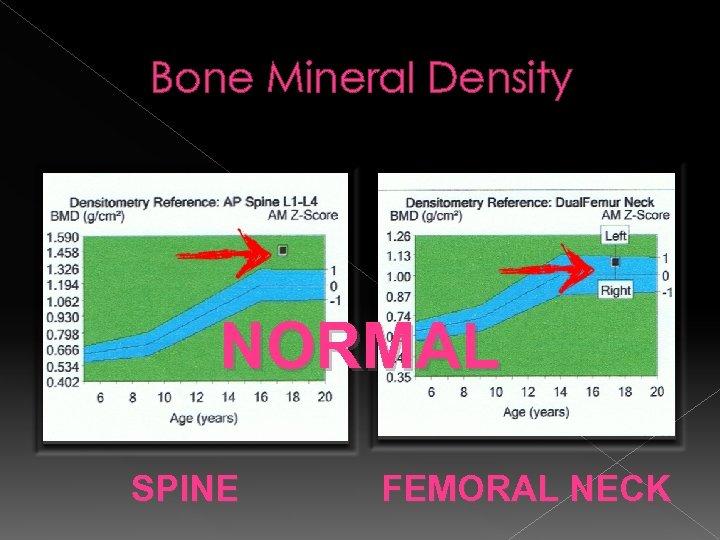
Bone Mineral Density NORMAL SPINE FEMORAL NECK
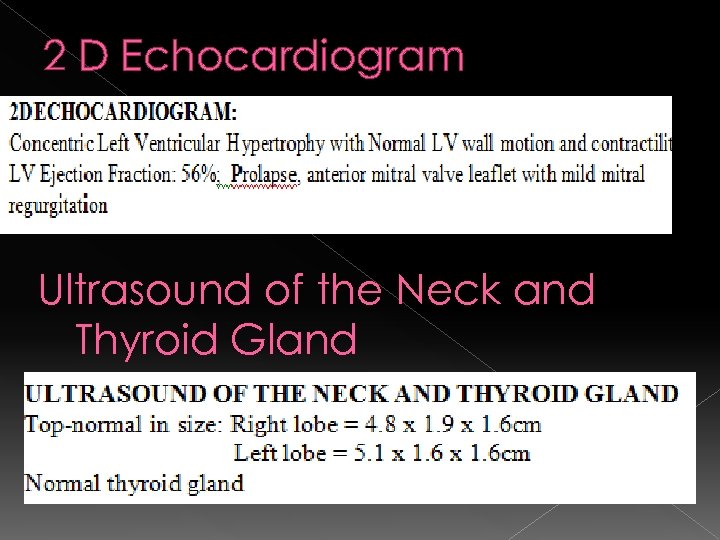
2 D Echocardiogram Ultrasound of the Neck and Thyroid Gland

Course in the Wards: Dec. 2, 2010: transnasal transphenoidal resection of the pituitary mass Post op: › (+) mild transient DI, treated with small doses Desmopressin 100 mcg/tablet › Hydrocortisone 100 mg/IV was maintained and tapered in 4 days. Transient sugar elevations noted, given insulin injections. › 7 th HD: discharged, on Prednisone 7. 5 mg/tab (5 mg- 0 -2. 5 mg).
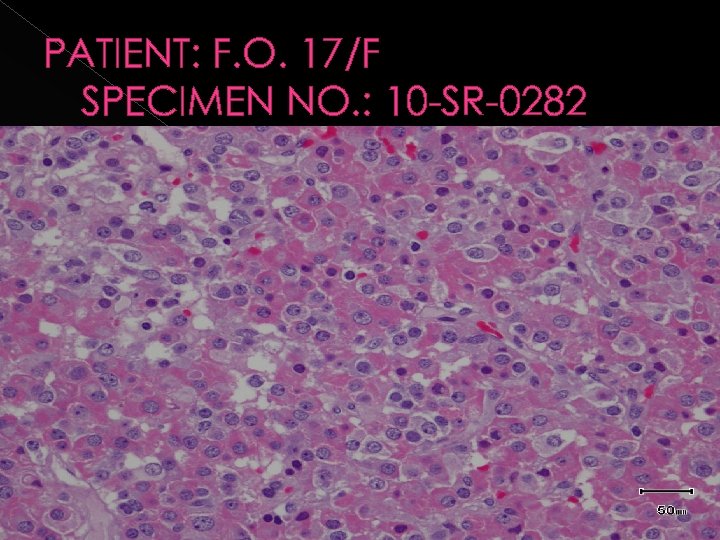
PATIENT: F. O. 17/F SPECIMEN NO. : 10 -SR-0282
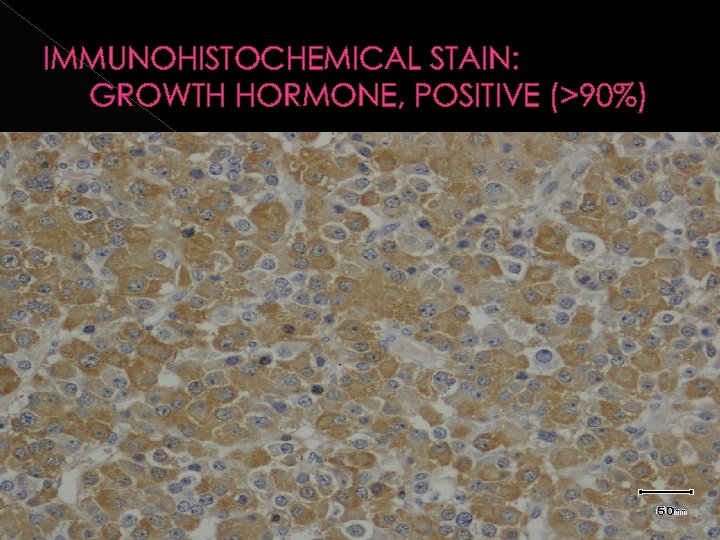
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STAIN: GROWTH HORMONE, POSITIVE (>90%)
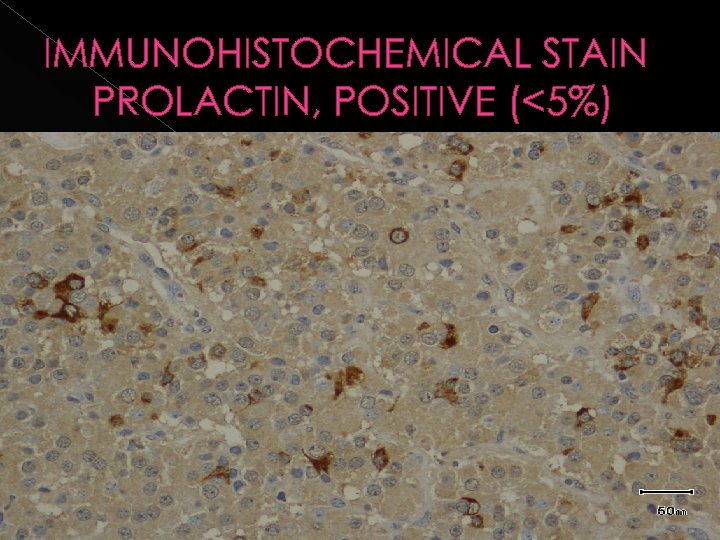
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STAIN PROLACTIN, POSITIVE (<5%)
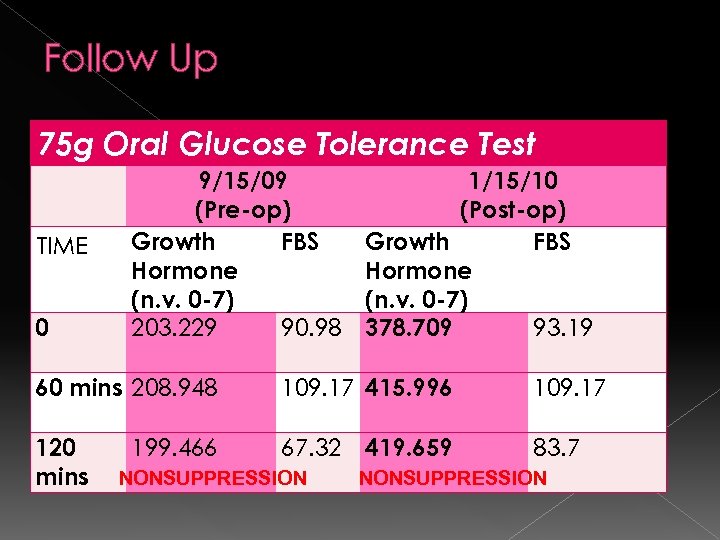
Follow Up 75 g Oral Glucose Tolerance Test TIME 0 9/15/09 (Pre-op) Growth FBS Hormone (n. v. 0 -7) 203. 229 90. 98 1/15/10 (Post-op) Growth FBS Hormone (n. v. 0 -7) 93. 19 378. 709 60 mins 208. 948 109. 17 415. 996 120 mins 67. 32 199. 466 NONSUPPRESSION 419. 659 109. 17 83. 7 NONSUPPRESSION
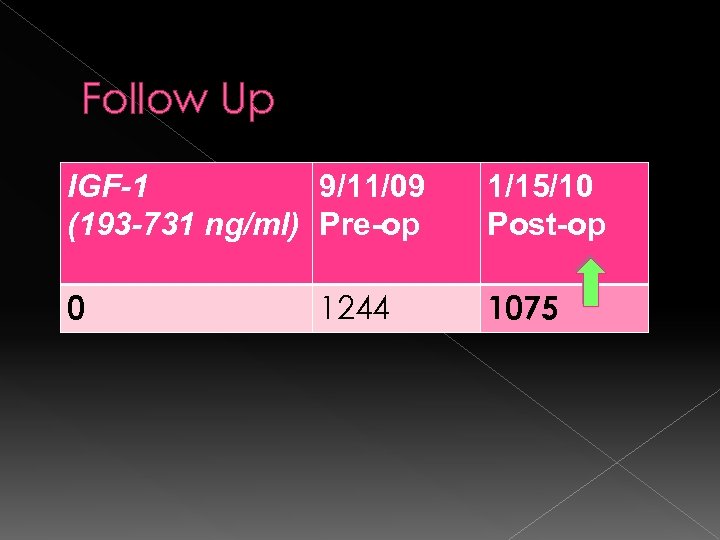
Follow Up IGF-1 9/11/09 (193 -731 ng/ml) Pre-op 1/15/10 Post-op 0 1075 1244
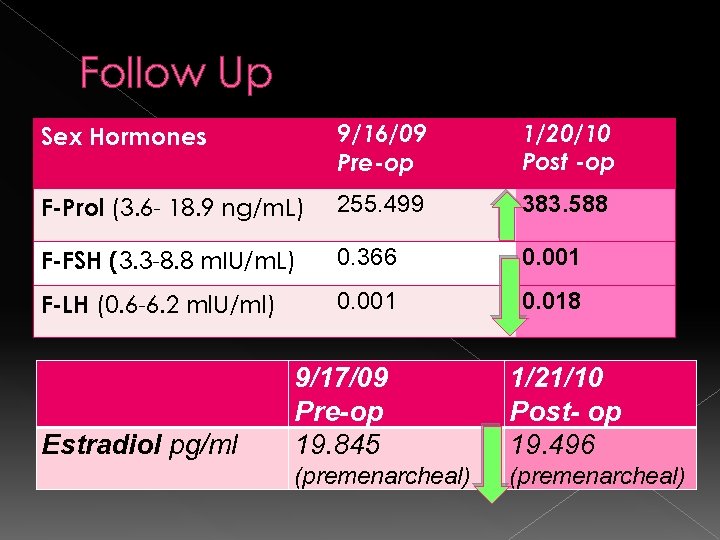
Follow Up Sex Hormones 9/16/09 Pre-op 1/20/10 Post -op F-Prol (3. 6 - 18. 9 ng/m. L) 255. 499 383. 588 F-FSH (3. 3 -8. 8 m. IU/m. L) 0. 366 0. 001 F-LH (0. 6 -6. 2 ml. U/ml) 0. 001 0. 018 Estradiol pg/ml 9/17/09 Pre-op 19. 845 1/21/10 Post- op 19. 496 (premenarcheal)
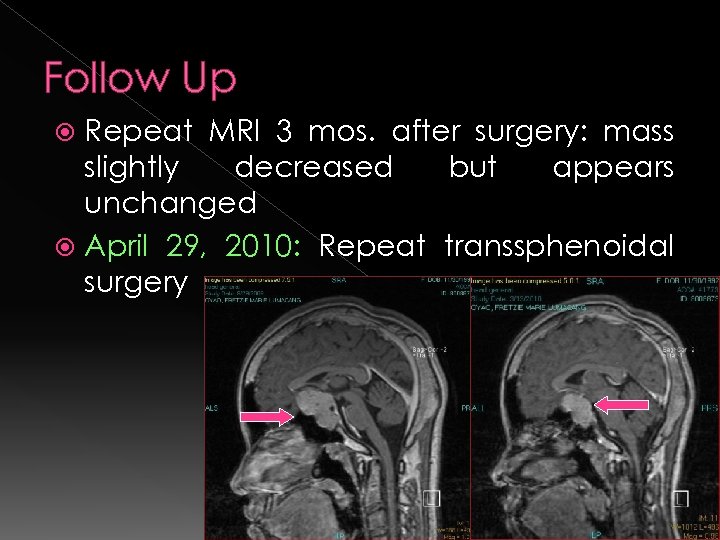
Follow Up Repeat MRI 3 mos. after surgery: mass slightly decreased but appears unchanged April 29, 2010: Repeat transsphenoidal surgery
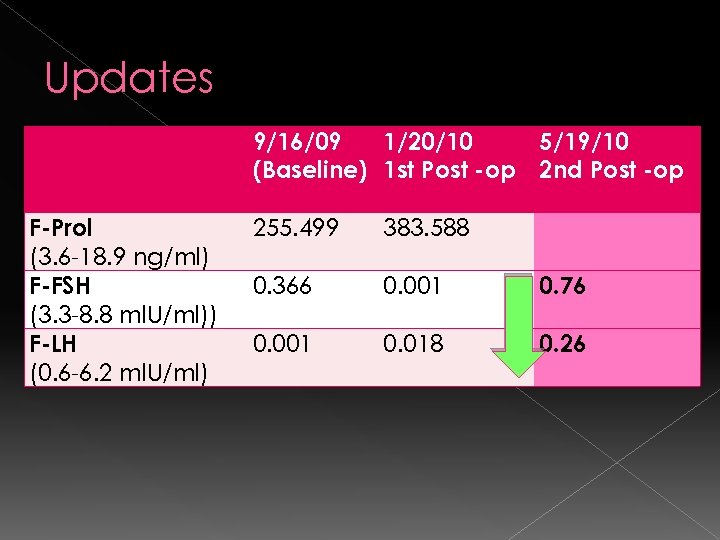
Updates 9/16/09 1/20/10 5/19/10 (Baseline) 1 st Post -op 2 nd Post -op F-Prol (3. 6 -18. 9 ng/ml) F-FSH (3. 3 -8. 8 ml. U/ml)) F-LH (0. 6 -6. 2 ml. U/ml) 255. 499 383. 588 0. 366 0. 001 0. 76 0. 001 0. 018 0. 26
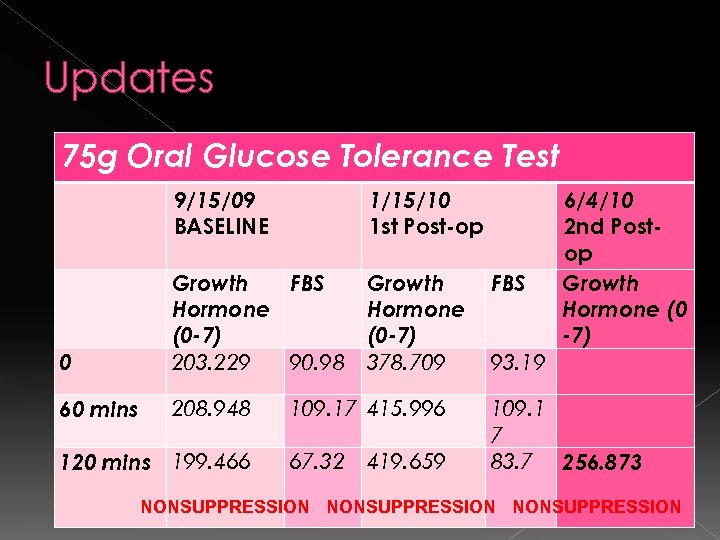
Updates 75 g Oral Glucose Tolerance Test 9/15/09 BASELINE 1/15/10 1 st Post-op 0 Growth FBS Hormone (0 -7) 203. 229 90. 98 Growth Hormone (0 -7) 378. 709 60 mins 208. 948 120 mins 199. 466 109. 17 415. 996 67. 32 419. 659 FBS 6/4/10 2 nd Postop Growth Hormone (0 -7) 93. 19 109. 1 7 83. 7 256. 873 NONSUPPRESSION
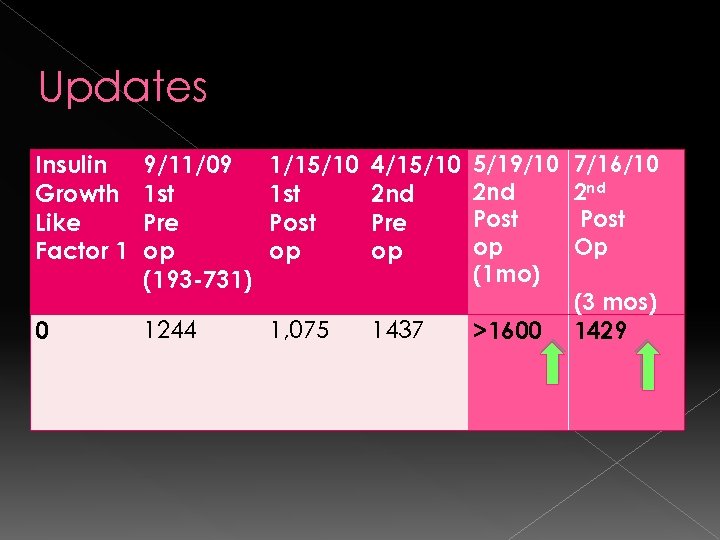
Updates Insulin Growth Like Factor 1 0 9/11/09 1 st Pre op (193 -731) 1/15/10 1 st Post op 1244 1, 075 4/15/10 2 nd Pre op 1437 5/19/10 2 nd Post op (1 mo) >1600 7/16/10 2 nd Post Op (3 mos) 1429

CASE SUMMARY 17 year old female › Tall stature › Prominently enlarged hands and feet › Slightly widened and thickened nose and lips › Widened upper tooth gap Delayed puberty Tanner stage 1 breasts tanner stage 3 pubic hair Bitemporal Hemianopsia MRI of the brain: (+) pituitary mass Histopathological & Immunohistochemical Findings: GH & Prolactin Macroadenoma Elevated ü GH levels ü Ig. F-1 level ü Prolactin level ü Prepubertal ü Estradiol ü FSH and LH level ü Infantile uterus Normal Karyotype 46 XX

Final Diagnosis Gigantism secondary to Growth Hormone and Prolactin Co- Secreting Pituitary Macroadenoma with stalk compression resulting in hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism, s/p Transnasal Transphenoidal Surgery (12/2/09 & 4/29/10)
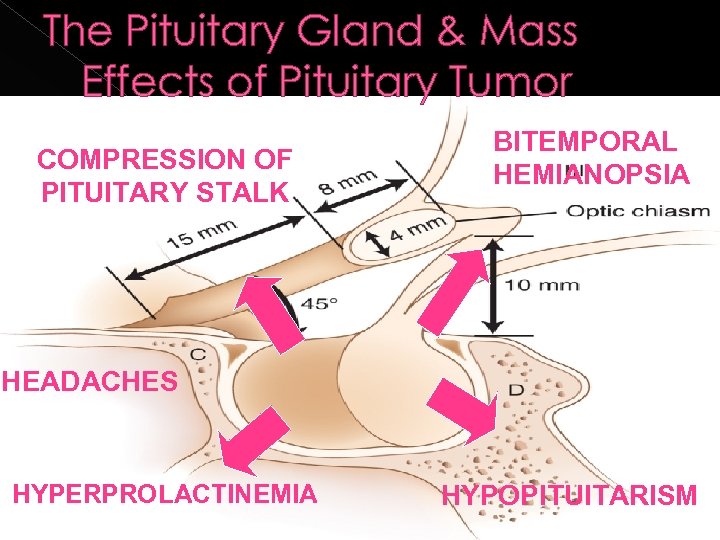
The Pituitary Gland & Mass Effects of Pituitary Tumor COMPRESSION OF PITUITARY STALK BITEMPORAL HEMIANOPSIA HEADACHES HYPERPROLACTINEMIA HYPOPITUITARISM
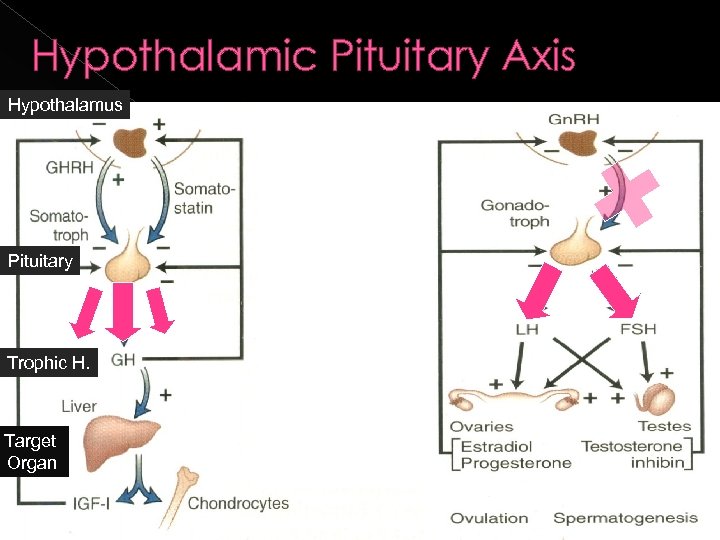
Hypothalamic Pituitary Axis Hypothalamus Pituitary Trophic H. Target Organ

In our patient. . HORMONE HYPERSECRETION Growth Hormone Secreting Adenoma (>90%) Prolactin Co-Secreting Adenoma (<5%) (Mammasomatotrophs) GIGANTISM Combined GH and Prolactin over-secretion common in early childhood gigantism Lafferty, A. R & Chrousos, G. P. , Pituitary tumors in Children & Adolescents. J. Clin. Endccinol. Metab. 1999. 84: 4317 -4323.

GIGANTISM VS. ACROMEGALY TIMING OF GH EXCESS During period of active growth Open epiphyseal plates After epiphyseal closure INCIDENCE Total cases reported only in the hundreds 3 - 4 cases/million TALL STATURE Cardinal feature 10% Cases
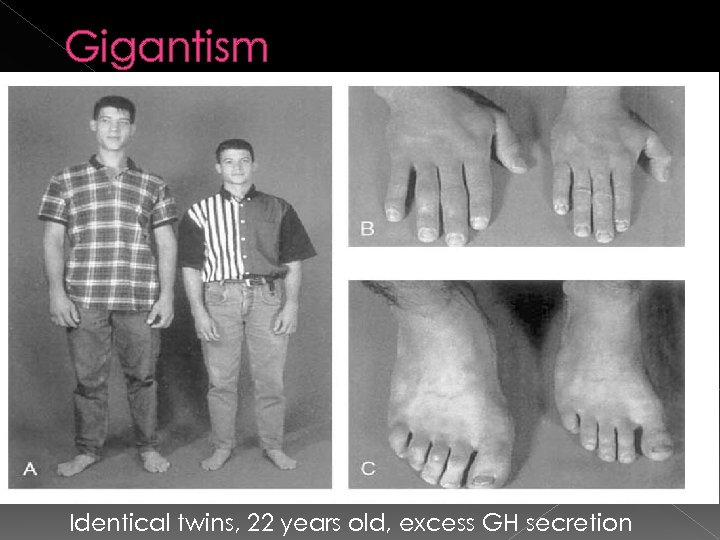
Gigantism Identical twins, 22 years old, excess GH secretion

Acromegaly
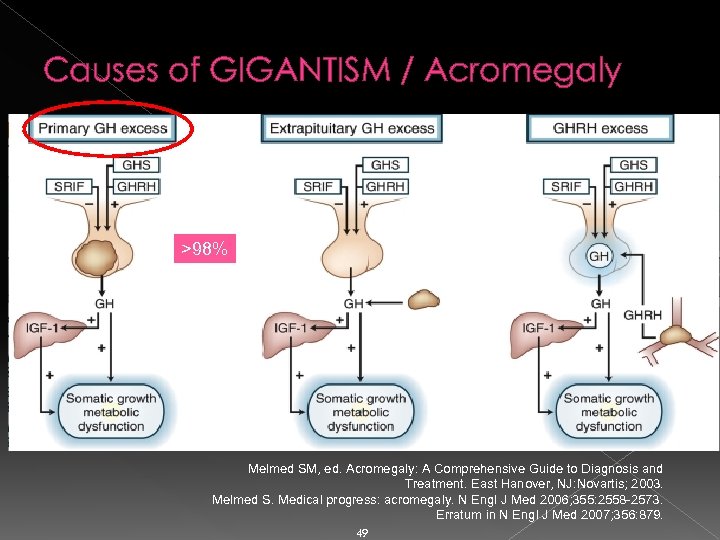
Causes of GIGANTISM / Acromegaly >98% Melmed SM, ed. Acromegaly: A Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis; 2003. Melmed S. Medical progress: acromegaly. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2558 -2573. Erratum in N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 879. 49
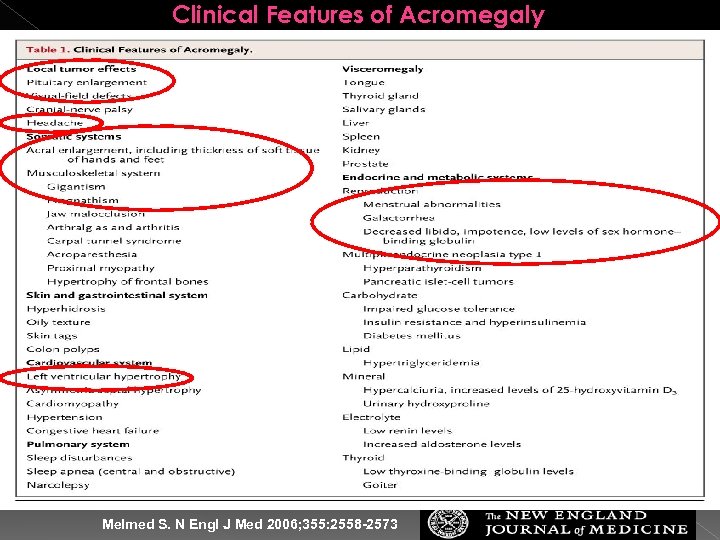
Clinical Features of Acromegaly Melmed S. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2558 -2573

Treatment Guidelines Neurosurgery: TUMOR > 2 cm = REDUCED Success Rates Medical Therapy Somatostatin Receptor Ligands Dopamine Agonists GH Receptor Antagonist Radiation Therapy
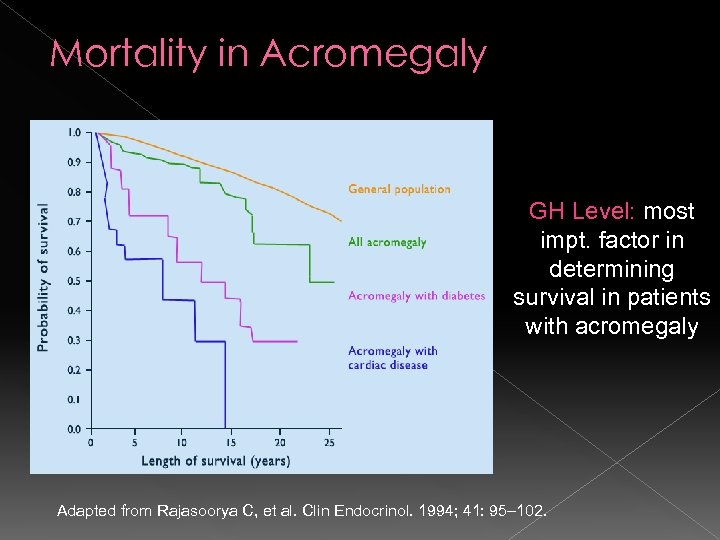
Mortality in Acromegaly GH Level: most impt. factor in determining survival in patients with acromegaly Adapted from Rajasoorya C, et al. Clin Endocrinol. 1994; 41: 95– 102.

Updates June 15, 2010: 10 days loading dose 100 mcg Somatostatin SC q 8 hrs was given, then somatostatin 300 mg/ IM once a month started (+) headaches and dizziness July 29, 2010: 2 nd Post-op MRI showed further decrease in the size of the pituitary mass Scheduled to go to Boston this September to seek further treatment at Massachusetts General Hospital with pituitary expert, Dr. Anne Klibanski

Summary Pituitary tumors develop when specific types of pituitary cells proliferate and oversecrete their respective hormones. Gigantism/ Acromegaly is a rare disorder characterized by GH hypersecretion and elevated IGF-1 levels Almost all cases (98%), of acromegaly are caused by a somatotrope adenoma Early diagnosis and treatment is important to prevent long term complications and mortality. Controlling levels of GH in patients with acromegaly improves survival

Thank you and Good Day! : )
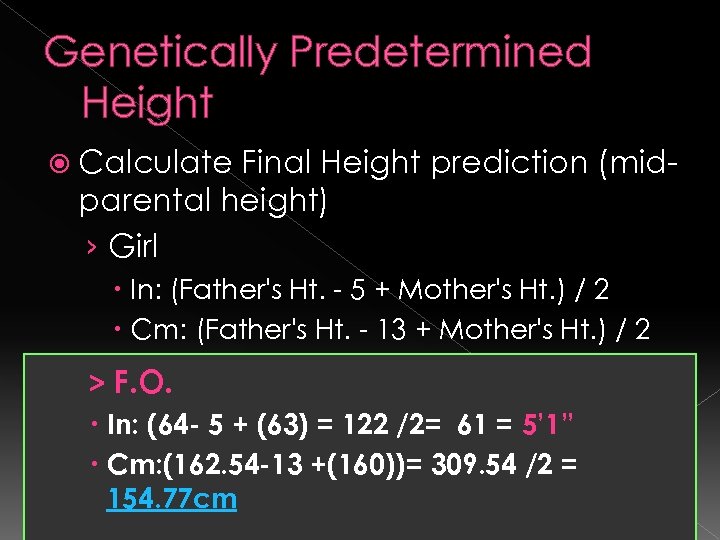
Genetically Predetermined Height Calculate Final Height prediction (midparental height) › Girl In: (Father's Ht. - 5 + Mother's Ht. ) / 2 Cm: (Father's Ht. - 13 + Mother's Ht. ) / 2 > F. O. In: (64 - 5 + (63) = 122 /2= 61 = 5’ 1” Cm: (162. 54 -13 +(160))= 309. 54 /2 = 154. 77 cm
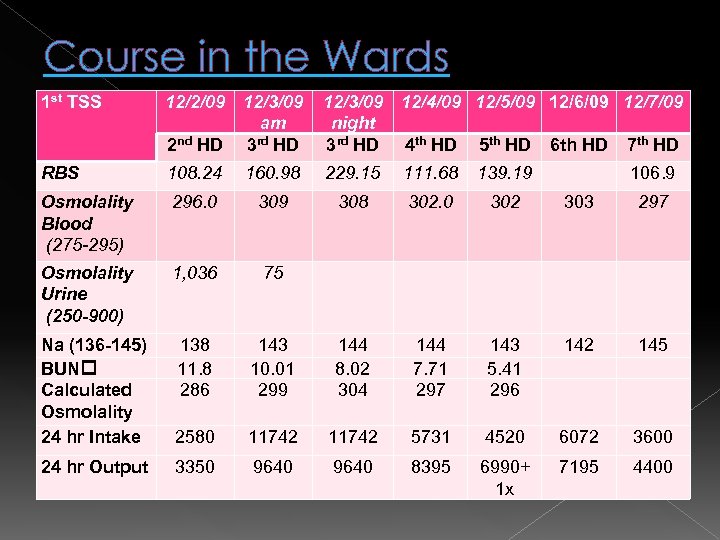
Course in the Wards 1 st TSS 12/2/09 12/3/09 am 2 nd HD 3 rd HD 12/3/09 12/4/09 12/5/09 12/6/09 12/7/09 night 3 rd HD 4 th HD 5 th HD 6 th HD 7 th HD RBS 108. 24 160. 98 229. 15 111. 68 139. 19 Osmolality Blood (275 -295) 296. 0 309 308 302. 0 302 303 297 Osmolality Urine (250 -900) 1, 036 75 Na (136 -145) BUN Calculated Osmolality 24 hr Intake 138 11. 8 286 143 10. 01 299 144 8. 02 304 144 7. 71 297 143 5. 41 296 142 145 2580 11742 5731 4520 6072 3600 24 hr Output 3350 9640 8395 6990+ 1 x 7195 4400 106. 9
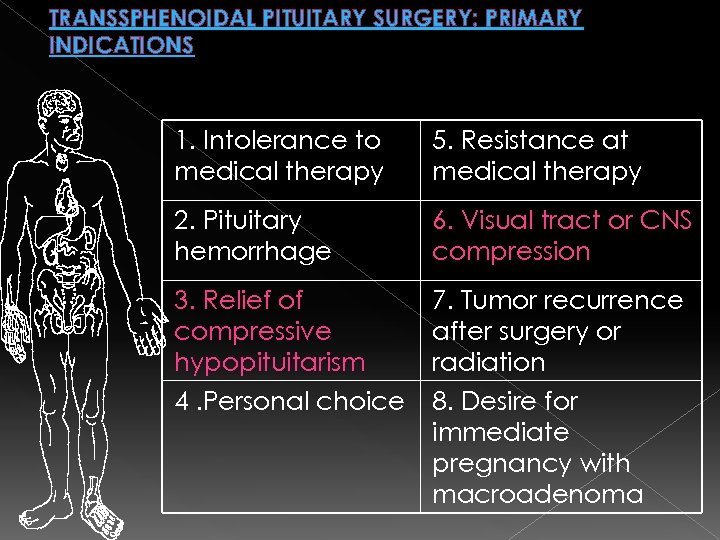
TRANSSPHENOIDAL PITUITARY SURGERY: PRIMARY INDICATIONS 1. Intolerance to medical therapy 5. Resistance at medical therapy 2. Pituitary hemorrhage 6. Visual tract or CNS compression 3. Relief of compressive hypopituitarism 4. Personal choice 7. Tumor recurrence after surgery or radiation 8. Desire for immediate pregnancy with macroadenoma
81a798f7899a2f7efd8779464ca4f93f.ppt