ccab63d52ab5ada445941ea25759819c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Homework in class and lecture at home? Experience with active learning in engineering Ron K. Cytron and Cindy M. Grimm Computer Science and Engineering Washington University
Homework in class and lecture at home? Experience with active learning in engineering Ron K. Cytron and Cindy M. Grimm Computer Science and Engineering Washington University
 How did we get here? • Ken Goldman (on leave at Google) – CPATH funding from NSF • Olin College of Engineering – Highly collaborative environment – Problem-focus, knowledge-based inquiry – Lynn Stein’s visit to our department • WU art/architecture studio courses – Peter Mac. Keith – Observation of studio format • Keith Sawyer – Conversations about teaching modes
How did we get here? • Ken Goldman (on leave at Google) – CPATH funding from NSF • Olin College of Engineering – Highly collaborative environment – Problem-focus, knowledge-based inquiry – Lynn Stein’s visit to our department • WU art/architecture studio courses – Peter Mac. Keith – Observation of studio format • Keith Sawyer – Conversations about teaching modes
 How did we get here? • CSE is a naturally collaborative discipline – All programs that could be written by one person have already been written • Collaborative nature not apparent in school – Single-person assignments – Dire warnings about inappropriate collaboration – Little to foster communication and interpersonal skills until late in the curriculum • Real-world demands collaboration • Collaboration attracts underrepresented groups – Juan Gilbert, Auburn (ACM speaker on this topic) – Brochures featuring geek computer scientists working solo in are a big turn-off
How did we get here? • CSE is a naturally collaborative discipline – All programs that could be written by one person have already been written • Collaborative nature not apparent in school – Single-person assignments – Dire warnings about inappropriate collaboration – Little to foster communication and interpersonal skills until late in the curriculum • Real-world demands collaboration • Collaboration attracts underrepresented groups – Juan Gilbert, Auburn (ACM speaker on this topic) – Brochures featuring geek computer scientists working solo in are a big turn-off
 How are we different? • Olin College is new, could rethink curriculum from the ground up – No service community (calc, intro cs, etc. ) – Holistic engineering programming • Funded to develop new modes of teaching – Faculty research not emphasized • Students Olin College – Up front about active learning, knowledge-based inquiry – Unique admissions process • 250 applicants chosen as finalists (end of January) • They visit and participate in design project and team exercises (Feb/March) • Yield of 84 this past year
How are we different? • Olin College is new, could rethink curriculum from the ground up – No service community (calc, intro cs, etc. ) – Holistic engineering programming • Funded to develop new modes of teaching – Faculty research not emphasized • Students Olin College – Up front about active learning, knowledge-based inquiry – Unique admissions process • 250 applicants chosen as finalists (end of January) • They visit and participate in design project and team exercises (Feb/March) • Yield of 84 this past year
 How are we different? • Existing and successful program – Diverse service community (artsci, b school, eng) • CPATH funding modest compared to Olin • Students WU – Faculty buy-in, unexpectedly successful – Students largely unaware of our new approach when they apply – Only vaguely aware of the approach when they arrive – Only half our students are CSE when they arrive
How are we different? • Existing and successful program – Diverse service community (artsci, b school, eng) • CPATH funding modest compared to Olin • Students WU – Faculty buy-in, unexpectedly successful – Students largely unaware of our new approach when they apply – Only vaguely aware of the approach when they arrive – Only half our students are CSE when they arrive
 Adaptation of the Idea • Lecture is rarely interactive, especially with large classes – If one-way, why not shift “lecture” to time outside of class? – Lectures recorded online allow flexibility and review • Use class time for problem-solving sessions – Students collaborate and work with professor/TA supervision – Professors observe process, not just product
Adaptation of the Idea • Lecture is rarely interactive, especially with large classes – If one-way, why not shift “lecture” to time outside of class? – Lectures recorded online allow flexibility and review • Use class time for problem-solving sessions – Students collaborate and work with professor/TA supervision – Professors observe process, not just product
 Nice idea, but… • Many students were not watching the lecture prior to attending class – Mix of prepared / unprepared students – Collaborative work awkward • Remedy: short in-class quiz over lecture material. – – Students watch lecture before class Professor reviews material briefly, asks for questions Quiz given Collaborative problem solving ensues • Some students felt new structure is unfair – – 3 unit course 3 contact hours as scheduled Required watching of video, also 3 hours, outside of class Remedy: regulate overall commitment
Nice idea, but… • Many students were not watching the lecture prior to attending class – Mix of prepared / unprepared students – Collaborative work awkward • Remedy: short in-class quiz over lecture material. – – Students watch lecture before class Professor reviews material briefly, asks for questions Quiz given Collaborative problem solving ensues • Some students felt new structure is unfair – – 3 unit course 3 contact hours as scheduled Required watching of video, also 3 hours, outside of class Remedy: regulate overall commitment
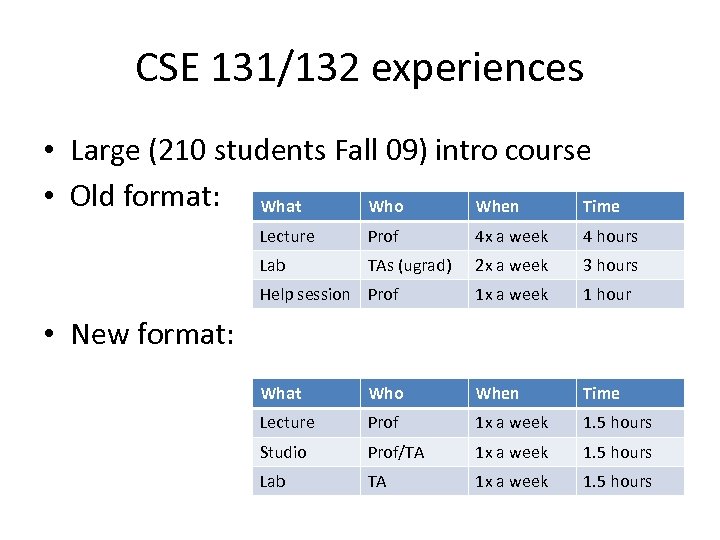 CSE 131/132 experiences • Large (210 students Fall 09) intro course • Old format: What Who When Time Lecture Prof 4 x a week 4 hours Lab TAs (ugrad) 2 x a week 3 hours Help session Prof 1 x a week 1 hour What Who When Time Lecture Prof 1 x a week 1. 5 hours Studio Prof/TA 1 x a week 1. 5 hours Lab TA 1 x a week 1. 5 hours • New format:
CSE 131/132 experiences • Large (210 students Fall 09) intro course • Old format: What Who When Time Lecture Prof 4 x a week 4 hours Lab TAs (ugrad) 2 x a week 3 hours Help session Prof 1 x a week 1 hour What Who When Time Lecture Prof 1 x a week 1. 5 hours Studio Prof/TA 1 x a week 1. 5 hours Lab TA 1 x a week 1. 5 hours • New format:
 Studio sessions • Students arrive, form groups of 2 -4 people • Physically arranged so they share a display – Large displays in our new studio space – Use multiple regular computers in old space • Studio script provided – – Checkpoints with TAs Interactions with other groups Document and turn in findings TAs/prof evaluate group performance • No a priori expectations about how far a group will go – Depth and exploration emphasized over quantity
Studio sessions • Students arrive, form groups of 2 -4 people • Physically arranged so they share a display – Large displays in our new studio space – Use multiple regular computers in old space • Studio script provided – – Checkpoints with TAs Interactions with other groups Document and turn in findings TAs/prof evaluate group performance • No a priori expectations about how far a group will go – Depth and exploration emphasized over quantity
 Group formation: one bad approach • Mix strong and weak students in the same group – Strong members will help the weak members – Provides “teaching moments” for some – Encourages learning from peers • Result: frustration – Strong students want to push ahead unencumbered – Weak students feel lost, inadequate
Group formation: one bad approach • Mix strong and weak students in the same group – Strong members will help the weak members – Provides “teaching moments” for some – Encourages learning from peers • Result: frustration – Strong students want to push ahead unencumbered – Weak students feel lost, inadequate
 Group formation: a better approach • Aim eventually for students of like abilities in the same group • Difficult to do this right the first time, so… – Let students form groups on their own – Provided basis and encouragement for switching groups in subsequent sessions • Students have an almost pheromonal ability to seek compatible studio partners
Group formation: a better approach • Aim eventually for students of like abilities in the same group • Difficult to do this right the first time, so… – Let students form groups on their own – Provided basis and encouragement for switching groups in subsequent sessions • Students have an almost pheromonal ability to seek compatible studio partners
 Observations from 131 studios • Awkward first session – – 18 -year olds First week of college ~30 students in each studio section Prof felt like “cruise ship social director” • Second week – Some switches in groups, most stay put – Only one or two students who needed extra help getting situated • By third week – Students show up prepared – Students waiting for team to arrive
Observations from 131 studios • Awkward first session – – 18 -year olds First week of college ~30 students in each studio section Prof felt like “cruise ship social director” • Second week – Some switches in groups, most stay put – Only one or two students who needed extra help getting situated • By third week – Students show up prepared – Students waiting for team to arrive
 Observations from 131 studios • 2008 course evaluation, specific question “How useful were the studio sessions for this course? ” – 14 “not useful” – 36 expressed mixed reaction – 37 expressed favorable to strongly favorable reaction • 2009, question was accidentally dropped, but students volunteered information: – 2 expressed mixed feelings – 10 expressed strongly positive feelings • “Best thing about the class” • “Working with others” • “Supplementing lecture material”
Observations from 131 studios • 2008 course evaluation, specific question “How useful were the studio sessions for this course? ” – 14 “not useful” – 36 expressed mixed reaction – 37 expressed favorable to strongly favorable reaction • 2009, question was accidentally dropped, but students volunteered information: – 2 expressed mixed feelings – 10 expressed strongly positive feelings • “Best thing about the class” • “Working with others” • “Supplementing lecture material”
 CSE 431 • Upper-level software course, 26 students • Students (and professor) had no prior studio experiences • “What did you like most about the course” – 7/11 mentioned studio • Studio sessions – Planned after course began – Took the place of a lecture slot – Held as needed, not on a regular schedule
CSE 431 • Upper-level software course, 26 students • Students (and professor) had no prior studio experiences • “What did you like most about the course” – 7/11 mentioned studio • Studio sessions – Planned after course began – Took the place of a lecture slot – Held as needed, not on a regular schedule
 CSE 431 • Sessions were initially very collaborative in nature • Students approached prof, saying – Collaboration is OK – Want some element of competition • Next studio featured competitive element – – – Design given for a component Tests given to measure component correctness Test given to time the component’s performance Times posted throughout the studio session Winning team earned Coldstone gift certificate Very exciting studio session! • Students loved this
CSE 431 • Sessions were initially very collaborative in nature • Students approached prof, saying – Collaboration is OK – Want some element of competition • Next studio featured competitive element – – – Design given for a component Tests given to measure component correctness Test given to time the component’s performance Times posted throughout the studio session Winning team earned Coldstone gift certificate Very exciting studio session! • Students loved this
 Quasi-Evaluation • Exam scores – Similar exams, compare per-question • Evaluations – Unfortunately, lost 4 useful questions • Student interviews – External evaluator (Mark Tranel) • Follow-on cpath grant (Amherst, Univ of Oregon) – Active learning in a wide variety of classes
Quasi-Evaluation • Exam scores – Similar exams, compare per-question • Evaluations – Unfortunately, lost 4 useful questions • Student interviews – External evaluator (Mark Tranel) • Follow-on cpath grant (Amherst, Univ of Oregon) – Active learning in a wide variety of classes
 All studio, all the time (cse 320) • Focus is on design, implement, test, reimplement – Real problem (student driven) – Group work • Students are responsible for: – Devising own grading scheme/sharing of work load – Critiquing each other
All studio, all the time (cse 320) • Focus is on design, implement, test, reimplement – Real problem (student driven) – Group work • Students are responsible for: – Devising own grading scheme/sharing of work load – Critiquing each other
 CSE 320 format • Two 1 ½ hour sessions per week – Lab time(1/3) – Design discussions – Student-student evaluation • Designs • Code • Functionality – User studies
CSE 320 format • Two 1 ½ hour sessions per week – Lab time(1/3) – Design discussions – Student-student evaluation • Designs • Code • Functionality – User studies
 What works • Bi-modal response • Most really like – 1 -2 usually hate • Like the fact that they implement something “real” • Develop good appreciation for – Good design – User studies – Team work
What works • Bi-modal response • Most really like – 1 -2 usually hate • Like the fact that they implement something “real” • Develop good appreciation for – Good design – User studies – Team work
 What doesn’t work • Student-student evaluation – Not critical enough • Re-implementation – Finding right incentives for students to fix what’s wrong • Bad group dynamics – Same group all semester, hard to fix • I need a psychology degree…
What doesn’t work • Student-student evaluation – Not critical enough • Re-implementation – Finding right incentives for students to fix what’s wrong • Bad group dynamics – Same group all semester, hard to fix • I need a psychology degree…
 CSE 241/240/441 • Logic, data structures, algorithms – Difficult material to understand – Large (40 -80) students • Shift some, not all, lecture to pre-recorded • In class exercises – Best is walk them through data structure/proof, present to class for critiquing • Time consuming
CSE 241/240/441 • Logic, data structures, algorithms – Difficult material to understand – Large (40 -80) students • Shift some, not all, lecture to pre-recorded • In class exercises – Best is walk them through data structure/proof, present to class for critiquing • Time consuming
 What works • Designing data structures or physically implementing algorithm – Have students sort themselves by their last name • Recorded lectures – Useful to have around; need to be indexed/cleaned up
What works • Designing data structures or physically implementing algorithm – Have students sort themselves by their last name • Recorded lectures – Useful to have around; need to be indexed/cleaned up
 What doesn’t work • In-class exercises tend to look like homework – Students unclear as to usefulness • Very slow going – 10 times slower for students to derive algorithm • Exam scores approximately the same • Course evaluation scores same or lower
What doesn’t work • In-class exercises tend to look like homework – Students unclear as to usefulness • Very slow going – 10 times slower for students to derive algorithm • Exam scores approximately the same • Course evaluation scores same or lower
 Depends a lot on instructor • How they teach material – Focus on proofs or on applications • Lecturing style/skill – Easier for some people to do a really good lecture
Depends a lot on instructor • How they teach material – Focus on proofs or on applications • Lecturing style/skill – Easier for some people to do a really good lecture
 Better evaluation • Hard to know where students are learning material – Lectures? Homeworks? Studying for exams? Study groups? • Different learning modes – Skill sets very different amongst students
Better evaluation • Hard to know where students are learning material – Lectures? Homeworks? Studying for exams? Study groups? • Different learning modes – Skill sets very different amongst students
 Where are we going? • Refine use of active learning exercises in entry level courses – 240 first time • See how skill sets of students change – Already see a big change in how comfortable students are with designing their own problems – Might make group/design work easier to incorporate in upper-level courses
Where are we going? • Refine use of active learning exercises in entry level courses – 240 first time • See how skill sets of students change – Already see a big change in how comfortable students are with designing their own problems – Might make group/design work easier to incorporate in upper-level courses


