bcf7a9ddf40af1bb1e09834fd8e7010c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Home Country Features © Professor Daniel F. Spulber

How much does the home country matter? Boeing (US) versus Airbus (EU/France) Airbus is a unit of the European Aeronautic Defense and Space Company (Dutch) with EU headquarters Airbus 380 Boeing 787 Dreamliner 2

Home country features When is headquarters location a source of competitive advantage / disadvantage? • Company globalization – Launching pad • Company history and culture • Managers’ background • Corporate governance • Brand nationality • Home market • Political, legal, regulatory climate Boeing (US) versus Airbus (EU/France) 3

Home country features In a global era with extreme advantage … The manager should consider: • Can the company overcome home country limits? • What critical functions are at headquarters? Brand management, human resource management, raising financial capital, research & development? • What immobile inputs do we need at the headquarters: Human capital, technology 4
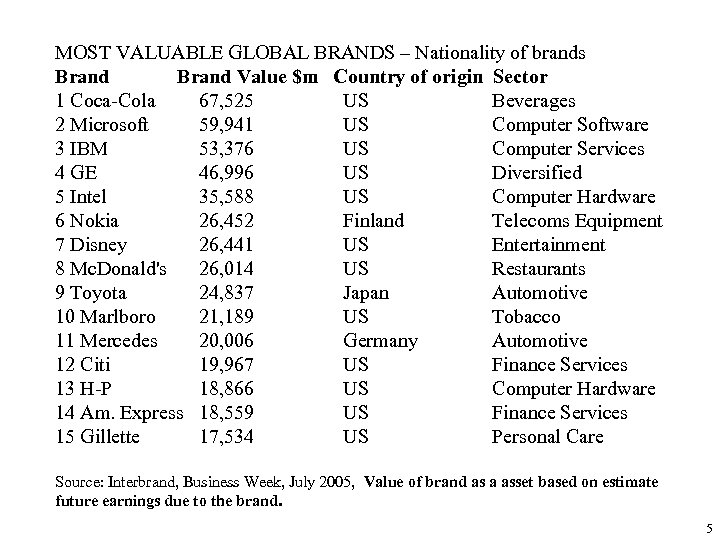
MOST VALUABLE GLOBAL BRANDS – Nationality of brands Brand Value $m Country of origin Sector 1 Coca-Cola 67, 525 US Beverages 2 Microsoft 59, 941 US Computer Software 3 IBM 53, 376 US Computer Services 4 GE 46, 996 US Diversified 5 Intel 35, 588 US Computer Hardware 6 Nokia 26, 452 Finland Telecoms Equipment 7 Disney 26, 441 US Entertainment 8 Mc. Donald's 26, 014 US Restaurants 9 Toyota 24, 837 Japan Automotive 10 Marlboro 21, 189 US Tobacco 11 Mercedes 20, 006 Germany Automotive 12 Citi 19, 967 US Finance Services 13 H-P 18, 866 US Computer Hardware 14 Am. Express 18, 559 US Finance Services 15 Gillette 17, 534 US Personal Care Source: Interbrand, Business Week, July 2005, Value of brand as a asset based on estimate future earnings due to the brand. 5
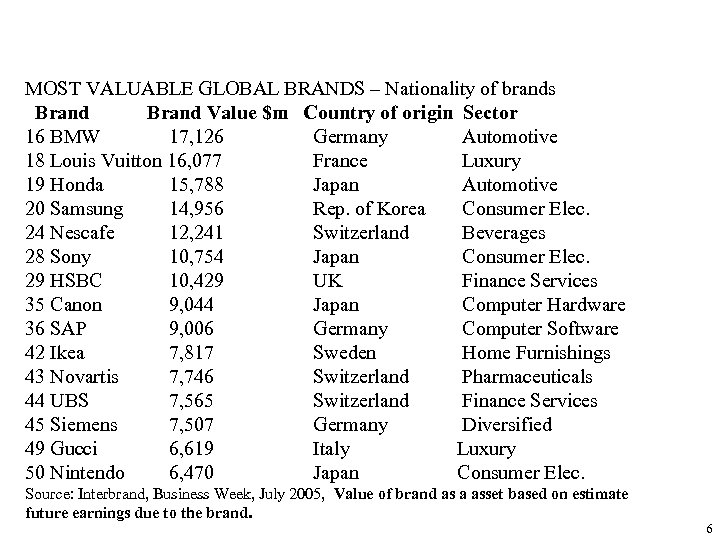
MOST VALUABLE GLOBAL BRANDS – Nationality of brands Brand Value $m Country of origin Sector 16 BMW 17, 126 Germany Automotive 18 Louis Vuitton 16, 077 France Luxury 19 Honda 15, 788 Japan Automotive 20 Samsung 14, 956 Rep. of Korea Consumer Elec. 24 Nescafe 12, 241 Switzerland Beverages 28 Sony 10, 754 Japan Consumer Elec. 29 HSBC 10, 429 UK Finance Services 35 Canon 9, 044 Japan Computer Hardware 36 SAP 9, 006 Germany Computer Software 42 Ikea 7, 817 Sweden Home Furnishings 43 Novartis 7, 746 Switzerland Pharmaceuticals 44 UBS 7, 565 Switzerland Finance Services 45 Siemens 7, 507 Germany Diversified 49 Gucci 6, 619 Italy Luxury 50 Nintendo 6, 470 Japan Consumer Elec. Source: Interbrand, Business Week, July 2005, Value of brand as a asset based on estimate future earnings due to the brand. 6

Brands can sometimes transcend the company’s home country “Consumers drink over 177 billion cups of our tea every year” (Lipton) World leader in tea, ice cream, some prepared foods Parent companies: Two headquarters: Dutch (Unilever NV) and British (Unilever PLC ) “Unilever’s strategy is to focus research and development and marketing on our leading brands, that is, those that are most in demand from consumers” 7

Unilever manages many international brands that transcend its nationality Sold 27 and 33 businesses in 2000 and 2001 including: • Bestfoods Baking Company • Elizabeth Arden • Dry soup and sauces businesses in Europe Made 20 acquisitions in 2000 including: • Bestfoods - Foods international • Amora Maille - Culinary products in France • Ben & Jerry’s - Ice cream primarily in the US • Cressida - Foods and Home & personal care in Central America • Slim-Fast - Nutritional bars and beverage products in the US 8

Location and manager knowledge Example: Hutchison Whampoa (Hong Kong) Hutchison House Courtesy of Hutchison Whampoa Limited How does Hutchison Whampoa’s HQ location affect manager’s knowledge and the competitive advantage of the company’s five core business areas? 9

Hutchison Whampoa Cheung Kong is the leading Hong Kong based multi-national conglomerate. 49. 9% The combined MARKET CAP of the Cheung Kong Group accounts for 15% of the total MARKET CAP of the Hong Kong stock market. 10

Hutchison Whampoa • Telecomm – Global network – Acquisition of Western Wireless – Divested Orange, acquired Global Crossing – Need to coordinate international network – Not dependent on HQ location • Energy and Infrastructure – Mainly Asia and Hong Kong – Infrastructure, mainly in China, some in Canada – Energy business: mostly local electric power focus – Less dependent on HQ location 11

Hutchison Whampoa • Real estate – Mainly Asia and Hong Kong – Local knowledge critical • Ports – Global – One of the world’s leading operators, Panama Canal, global network – International trade knowledge – Not dependent on HQ location • Retail and Manufacturing – Mainly Asia and Hong Kong – – A. H. Watson top Asian retailer – regional experience International trading experience Distribution JVs with Procter & Gamble Focus on regional markets 12

Home country features Home market: Demand side • A large home market can be an effective home base and launching pad for international expansion • However, the international business need not have a large home market for competitive advantage 13
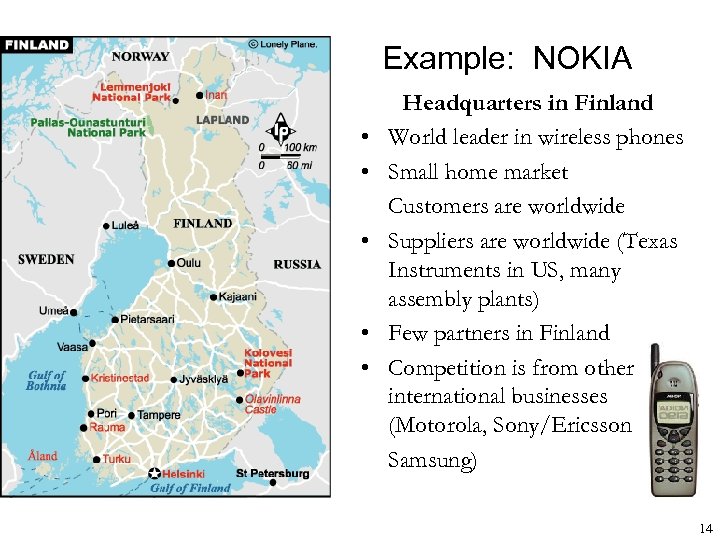
Example: NOKIA • • • Headquarters in Finland World leader in wireless phones Small home market Customers are worldwide Suppliers are worldwide (Texas Instruments in US, many assembly plants) Few partners in Finland Competition is from other international businesses (Motorola, Sony/Ericsson Samsung) 14

Home country features Home market: Supply side • Home country can be source of inputs and production advantages • However, suppliers need not be in home country for competitive advantage • Manufacturing base need not be in home country 15
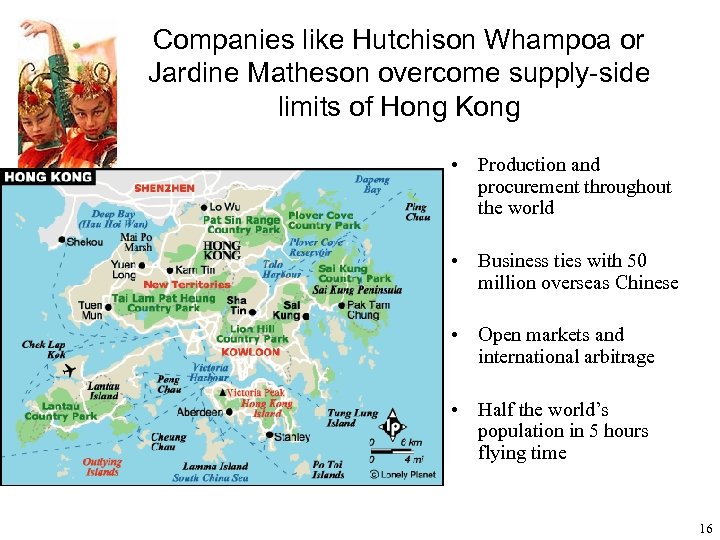
Companies like Hutchison Whampoa or Jardine Matheson overcome supply-side limits of Hong Kong • Production and procurement throughout the world • Business ties with 50 million overseas Chinese • Open markets and international arbitrage • Half the world’s population in 5 hours flying time 16
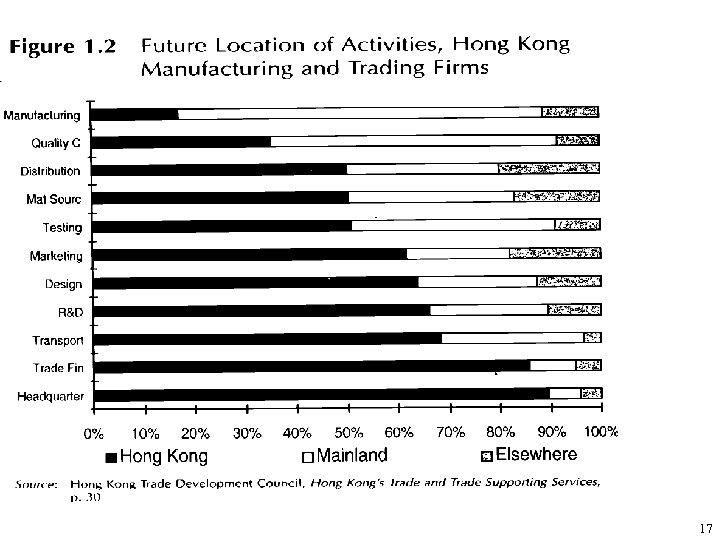
17

Home country features Manufacturer can move mobile factors to where they are needed for production Land Human Resources Technology Inputs Capital Least mobile Most mobile Some barriers to mobility: – Work force: Preferences and immigration restrictions limit human resource mobility – Trade regulations and transport costs for inputs – Capital regulations and informational home bias for finance capital 18

Home country features • Manufacturers can move production to best location outside of home country For example to countries with productive/low cost labor • Companies can purchase best products • Companies can contract with best suppliers 19
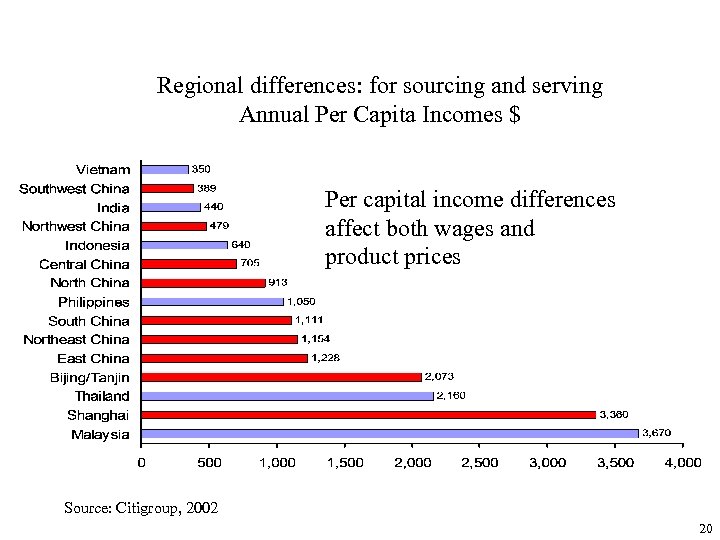
Regional differences: for sourcing and serving Annual Per Capita Incomes $ Per capital income differences affect both wages and product prices Source: Citigroup, 2002 20

Political, legal, regulatory climate • • • Political system: democracy, corruption, business risk Legal: contracts, tort Regulation: costs of doing business Trade regulations Industrial policy, subsidies Open markets reduce protection for home market incumbents • Open markets reduce costs of operating international business from home country 21
Example -- globalization Indian outsourcing industry Infosys Technologies Satyam Computer Services Tata Consultancy Services • Government policy changes ended state monopoly on Internet access and opened Indian economy • Customers located outside India • Growth in software and services, export of services online • Headquarters near source of human capital 22

Summary and Take-Away Points International business must address home country advantages/disadvantages to meet global challenges Maximize home country advantages! Transcend home country limits using global markets! (finance capital, technology and expertise, inputs, manufacturing and distribution services, final goods and services) Recognize both immobile factors for production and need to be close to customers in sales and distribution 23
bcf7a9ddf40af1bb1e09834fd8e7010c.ppt