9116037446455de53ba66530af333a2e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 80

Home and Community Based Services Supporting Individuals in Their Homes and Community

Who Qualifies for Medicaid? Medicaid is a health insurance program for certain groups of people based on income levels and eligibility groups. Specifically, in Iowa, the groups are: v A child under the age of 21 v A parent living with a child under the age of 18 v A woman who is pregnant v A person who is elderly (age 65 or older) v A person is disabled according to Social Security standards v A woman in need of treatment for breast or cervical cancer v Others may qualify (see list below)

What are Home and Community Based Waivers? v Waive traditional Medicaid guidelines to allow non- traditional Medicaid funded services in the home and community v Supports individualized services v Draw down federal $’s to fund needed services v Serve adults and children, based on the specific waiver eligibility criteria

Waivers are not: v Daycare v Academic education v Replacement of parental responsibility v Cadillac service v The only funding source

Roles v IMW – reviews the application and determines financial v v eligibility SW/CM/IHH – reviews need for services and monitors comprehensive service plan implementation IME Medical Services – reviews level of care based on an assessment tool and accompanying information Funder – IME allocates a funding slot and approves individual services and costs via an ISIS milestone Providers – agencies or persons enrolled/certified to provide HCBS services

Iowa HCBS Waiver Programs v Intellectual Disabilities v Brain Injury v Health and Disability v Elderly v AIDS/HIV v Physical Disability v Children’s Mental Health

What Do Waivers Have In Common v Availability- Statewide – first come first serve v Target Population – age- diagnosis - disability v Level of Care - SNF, ICF/ID, PMIC v Maximum $ per Month and/ or per Service • Services must be cost effective v Interdisciplinary Team (IDT) led by the member v Person Centered Service Plan coordinated and monitored by a DHS SW, TCM or IHH

Intellectual Disabilities Waiver v Age v v • no limit Availability • statewide Target Population • diagnosis of ID /functioning in the range of ID Level of Care • ICF/ID Maximum $ per Month • cost effective

ID Waiver Services • Adult Daycare • Consumer Directed Attendant Care • Personal Emergency Response • Pre-vocational • Day Habilitation • Respite • Home & Vehicle • Supported Community Living Modification • Home Health Aide • Residential-Based Supported Community Living • Interim Medical Monitoring • Supported Employment and Treatment • Nursing • Transportation
Brain Injury Waiver v Age • No age limit v Availability • statewide v Target Population • diagnosis of specific BI, according to IAC v Level of Care • ICF/ID • NF • SNF v Maximum $ per Month

BI Waiver Services • Adult Daycare • Personal Emergency • Behavioral Programming • Case Management • • Consumer Directed • Attendant Care • Family Counseling and Training • Home and Vehicle Modification • Interim Medical Monitoring and Treatment • • Response Pre-vocational Respite Specialized Medical Equipment Supported Community Living Supported Employment Transportation
Health and Disability Waiver v Age • Under age 65 v Availability • statewide v Target Population • blind/disabled - SSI/SSDI or DD • If over 21, ineligible for SSI - SSDI is OK v Level of Care • ICF/MR • SNF • NF

Health and Disability Waiver v v v v Adult Day Care Homemaker Home health Respite care Nursing Counseling Consumer-Directed Attendant Care (CDAC) Interim medical monitoring and treatment Home and vehicle modification Personal emergency response system Home-delivered meals Nutritional counseling Consumer Choices Option (CCO)

Elderly Waiver v Age • Over 65 v Availability • Statewide v Target Population • age 65 and over v Level of Care • NF • SNF

Elderly Waiver Services v v v v Adult Day Care Adaptive Devices Case Management Chore Consumer Directed Attendant Care (CDAC) Personal Emergency Response System Home Delivered meals Home Health Aide Homemaker Home and Vehicle Modifications Mental Health Outreach Nursing Nutritional Counseling Respite Consumer Choices Option (CCO)
AIDS/HIV Waiver v Age v v • no limit Availability • statewide Target Population • diagnosis of AIDS/HIV Level of care • SNF • NF Maximum $ per Month

AIDS/HIV Waiver Services v v v v v Counseling, Home Health Aide Homemaker Nursing care Respite care Home-delivered meals Adult day care Consumer-Directed Attendant Care Consumer Choices Option (CCO)

Physical Disability Waiver v Age v v • 18 to 64 Availability • Statewide Target Population • diagnosis of physical disability/not eligible for MR waiver Level of Care • SNF • ICF Maximum $ per Month

Physical Disability Waiver Services v. Consumer-Directed Attendant Care v Home and vehicle modification v Personal Emergency Response System, v Transportation v Specialized medical equipment v. Consumer Choices Option

Children’s Mental Health Waiver v Age v v • Under age 18 Availability • Statewide Target Population • diagnosis of serious emotional disturbance Level of Care • Psychiatric Hospital serving children under the age of 21 (Psychiatric Medical Institution for Children (PMIC) Maximum $ per Month

Children’s Mental Health Waiver Services v Environmental modifications, adaptive devices and therapeutic resources v Family and community support services; v In-home family therapy v Respite care.

State Plan HCBS Habilitation v Income must be at or below 150% FPL v Age • No age criteria, primarily serves adults v Availability • Statewide v Target Population – Individual who has met at least one of the following risk factors: • Has undergone or is currently undergoing psychiatric treatment more intensive than outpatient care, more than once in a lifetime (e. g. , emergency services, alternative home care, partial hospitalization or inpatient hospitalization). OR • Has a history of psychiatric illness resulting in at least one episode of continuous, professional supportive care other than hospitalization.

State Plan HCBS Habilitation v Need for Assistance • Need for assistance – the person has a need for assistance demonstrated by meeting at least two of the following criteria on a continuing or intermittent basis for at least two years: – Is unemployed, is employed in a sheltered setting, or has markedly limited skills and a poor work history – Requires financial assistance for out-of-hospital maintenance and is unable to procure this assistance without help – Shows severe inability to establish or maintain a personal social support system – Requires help in basic skills such as self-care, money management, housekeeping, cooking and medication management – Exhibits inappropriate social behavior that results in a demand for intervention *CM by qualified agency

Habilitation Services & Supports ¨ Services designed to assist in acquiring, retaining and improving the self-help, socialization and adaptive skills necessary to reside successfully in home and community-based settings. ¨ Case Management for members not enrolled in an Integrated Health Home (IHH) ¨ Habilitation – Day Habilitation – Home-Based Habilitation – Prevocational Habilitation – Supported Employment Habilitation 24
Role of the Targeted Case Manager (TCM), Community Based Case Manager (CBCM) and Integrated Health Home (IHH) v HCBS Elderly, BI and ID Waiver services are coordinated and monitored by a TCM or MCO CBCM v HCBS CMH Waiver services are coordinated and monitored by an Integrated Health Home (IHH) Team. v HCBS Health and Disability , Physical Disability and AIDS/HIV Waiver services are coordinated and monitored by a DHS TCM or MCO CBCM v State Plan HCBS Habilitation Services are coordinated and monitored by a Targeted Case Manger or Integrated Health Home (IHH) Team.

Role of the Targeted Case Manager (TCM), Community Based Case Manager (CBCM) and Integrated Health Home (IHH v Help individuals meet their needs, promote their v v v v independence, and self determination Act as an advocate Facilitate the individual’s access to the service system Facilitate access to health and mental health care Coordinate the delivery of services and develop the person-centered service plan Promote ongoing communication Monitor service utilization Monitor the service plan to ensure that services are being received and that the services are meeting the individual's needs


What is different? v Members can directly hire employees to provide services- Service providers do not need to be a certified/enrolled Medicaid provider v Members can use their Medicaid HCBS Waiver $’s to purchase goods/services example: hire a co-worker to be their job coach example: hire a neighbor to provide transportation v Financial Management Service provider to help manage the individual budget v Additional counseling and advice through an Independent Support Broker

What remains the same? v All consumers will have a service plan v Skilled services such as Nursing, Counseling, Home Health Aide, etc. will continue to be provided by Medicaid providers v Case Management will continue to monitor services

Service options v Self-directed Personal Care- cleaning, meal preparation, showering assistance, respite v Self-directed Community and Employment Supports- social skills development, career placement, cooking skills development v Individual Directed Goods and Services- HVM, snow removal, lawn care services, home delivered meals

Web Resources Department of Human Services: http: //www. dhs. iowa. gov/ Iowa Medicaid Enterprises: http: //dhs. iowa. gov/ime/about Iowa Medicaid Enterprise Member Information: http: //dhs. iowa. gov/ime/members HCBS Home: http: //dhs. iowa. gov/ime/members/medicaid-a-to-z/hcbs/waivers DHS Office of Policy Analysis (Rules): http: //dhs. iowa. gov/ime/providers/rulesandpolicies Iowa COMPASS Disability Resource Database: http: //search. iowacompass. org/

Accessing HCBS Rules, Provider Manual and Informational Letters http: //dhs. iowa. gov/ime/providers/rulesandpolicies

HCBS Waiver Program Managers: Aids/HIV, Physical Disability & Health and Disability: Lin Christensen 515 256 -4639 lchrist@dhs. state. ia. us Intellectual Disability & Consumer Choices Option (CCO): Brain Wines 515 -256 -4661 bwines@dhs. state. ia. us Brain Injury Waiver & Habilitation Le. Ann Moskowitz 515 -256 -4653 lmoskow@dhs. state. ia. us TCM , Children’s Mental Health & Elderly Waiver Leann Howland 515 -256 -4642 lhowlan@dhs. state. ia. us

What do you know about VR?

Our Purpose To work with individuals who have disabilities to reach their employment goals.

Who We Serve: ¨ To be eligible for IVRS services: – The individual must have a disability – The disability must affect the individual’s ability to be employed – The individual must need rehabilitation services in order to work

Eligibility cont. ¨ Vocational Rehabilitation does not use income to decide eligibility, although some specific services are based on financial need.

Vocational Rehabilitation can provide a variety of services once you are eligible and able to be served.

Employment Plan (IEP) ¨ Your counselor and You will develop an IEP that will outline the services and resources that you will need to achieve successful employment.

What We Do: ¨ Typical Services: – Career Counseling – Skill/Academic Training – Assistive Technology – Physical Restoration

What We Do: – Mental Restoration – Job Development – Placement – Employer education – Employer follow-up

What We Do: – Specialized Services – Tools/Work Equipment – Consultation to employers regarding accommodations

What We Provide: VR is a highly individualized process whereby the counselor and the client work together as partners to: • Identify vocational interest and aptitudes • Determine a vocational goal • Develop an action plan to achieve the goal

Vocational Counseling Vocational counseling can help you make good employment choices. You can discuss your skills, interest and abilities with your counselor. You may take tests or try different job tasks to help you determine what type of work you can do in the future.

Assistance With Job Placement ¨ Learn how to find a job ¨ Where to look for jobs ¨ How to fill out applications ¨ Write resumes ¨ Interviewing skills

Vocational Rehabilitation has contacts with the Iowa Workforce Centers and other community programs as well as Employers that may help you in finding a job.

Assistive Technology You may need equipment or a device to help you do a job task because of your disability. If needed, your counselor can help you find or buy this equipment. Often the employer has responsibility to help you get or pay for the equipment you need to do your job.

Training You may need training to be able to work. Training may be done by an employer, by another community agency, by a vocational-technical school or by a college. You may need to apply for financial aid to help pay for training.

Tools, Licenses or Equipment Needed to Work Sometimes when you start a job you may need to bring your own tools, have a license or have your own equipment. VR can help you get what is necessary to start the job.
Transportation VR can help to pay for temporary transportation, (for example: bus passes or gas money) as needed to reach your employment goals. VR cannot buy cars.

Help Starting A Small Business ¨ VR can help with the planning and starting of a small business. VR works closely with other programs which help you plan and find funding to start your own business.

Some General Laws: ¨ VR does not pay for services for which someone else has responsibility to pay such as private insurance or Worker’s Compensation. ¨ Some services, such as college training, are based on pre-set determinations of the monetary amount we are able to assist
¨ VR has limits on how much it can pay for some services. ¨ VR has requirements to determine services needed.

Employment Follow-Up After you find a job, your counselor will keep in contact with you for at least 90 days to be sure things are going well. The counselor is available to help you solve problems on the job.

Manage your disability to improve your chances of becoming employed.

Waiting List ¨ Category 2 – MSD (most significantly disabled) – Immediate service ¨ Category 4 – SD (significantly disabled) – Short waiting list ¨ Category 6 – Other Eligibility – Long waiting list

Questions?

Supplemental Security Income (SSI) 59

Under age 18 Ø Child must not be working and earning Ø Ø Ø over SGA Child must have a physical or mental condition Be expected to last at least 12 months, or result in death If child’s condition results in “marked and severe functional limitations” for at least 12 months Household income or resources Apply/ Redetermination Age 18 60

Parent to Child Deeming (under 18) Ø Parental income/resources shared with the child is “deemed” Ø Doesn’t matter if the money is actually provided to child Ø Not all income/resources count Ø Deemed income from a parent to an eligible child is treated as unearned income Ø May be used as for a PASS 61

Age 18 Redetermination Ø SSA will gather medical and other information to see if the 18 year old is eligible to receive benefits as an adult Ø A person receiving benefits as a child may not be eligible under the adult rules Ø Be prepared!!!!! 62

Strategies for Redetermination Ø Don’t assume that the student will get SSA benefits as a adult Ø Start Planning Early Ø Document Work Expense Ø Understand the purpose of the Questions Ø Appeal if determined ineligible 63

Adult Definition of Disability Ø Same for SSDI & SSI Ø The inability to engage in any substantial gainful activity (SGA) because of a medically determinable physical or mental impairment that can be expected to last for at least 12 months or that ends in death. 64

What are the differences between SSI & SSDI(CDB)? Ø SSI Ø Is needs based. That is why all your resources and income are monitored. Ø You receive Medicaid (Title 19) Ø SSDI Ø Is insurance paid through taxes. Must have work credits. Resources are not an issue, but income is. Ø Receive Medicare after a 24 month waiting period. Ø CDB Ø Disabled before the age of 22 and the child of an insured worker who is either disabled, retired or deceased. Ø Same as SSDI Ø If SSCDB marries, benefits end unless to another SSDI/SSCDB beneficiary. 65

Rental Liability Ø Separate Household Development Ø In-Kind Support – if the landlord would charge a higher rate to another renter Ø Presumed Maximum Value – 1/3 reduction 66

Work Incentives 67

SSI Work Incentives Ø Basic Earned Income Calculation Ø Impairment-Related Work Expenses (IRWE) Ø Plan for Achieving Self-Support (PASS) Ø Student-Earned Income Exclusion (SEIE) Ø 1619 (a) & (b) Ø Blind Work Expense (BWE) Ø Property Essential to Self Support (PESS) Ø Expedited Reinstatement 68
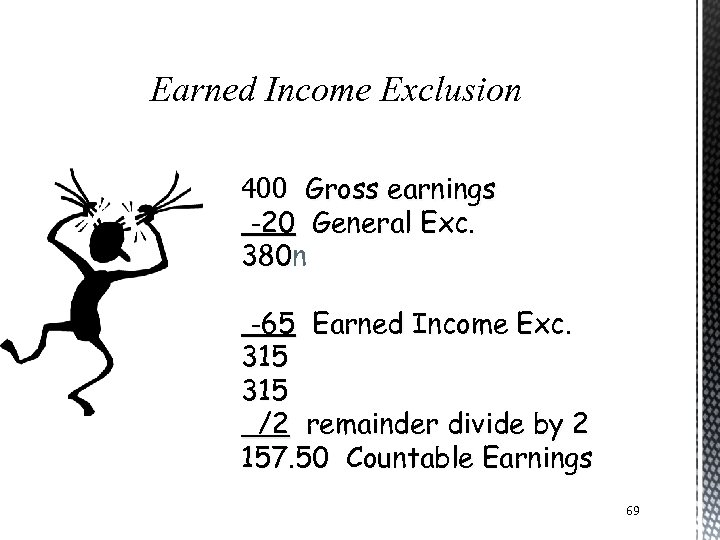
Earned Income Exclusion 400 Gross earnings -20 General Exc. 380 n 380 -65 Earned Income Exc. 315 /2 remainder divide by 2 157. 50 Countable Earnings 69

733 2016 Federal Benefit Rate - 157. 50 Countable Earnings 575. 50 Reduced SSI payment +400 gross Income $975. 50 Total monthly gross income 70

Student Earned Income Exclusion Ø Must be under 22 Ø regularly attending school College 8 hrs a week Grades 7 -12 12 hrs a week Training Course 12 hrs a week Home study due to disability can also be considered Ø Allows student to exclude $1, 640 per month/maximum of $6, 600 per year and their SSI is not reduced in 2011 71

Other important Work Incentives Ø 1619 b Ø Impairment Related Work Expense Ø Blind Work Expense Ø Plan for Achieving Self Support Ø Property Essential to Self Support Ø Section 301 72

Plan for Achieving Self-Support (PASS Plan) Allows an individual to set aside income and/or resources for a specified period of time to achieve their work goal. 73

PASS facts Ø Already receiving SSI or must meet eligibility Ø Ø Ø requirements Must have income/resources to set aside To increase or maintain income producing capability A chance to achieve a vocational goal To make it financially feasible to set aside or save income/resources PASS can start as early as 14 years old. 74

PASS Expenditures ØSupported Employment services ØItems & Capital for a Business ØEducational & Training expenses ØAttendant Care ØChild Care ØEquipment or tools ØUniforms or special clothing ØEtc 75

If benefits ended because you worked and had earnings, you can request to have your benefits started again without having to complete a new application. You can request that your benefits start again if: Benefits stopped because of earnings from work. Are not performing SGA in the month you request reinstatement Have an impairment that is the same as or related to the original impairment that you received benefits for. Request reinstatement within 5 years from the month that the individuals entitlement or eligibility is terminated. 76

Have worked and paid Social Security taxes (FICA), be a qualified worker, or an adult disabled child of a qualified worker. 77

ØTrial Work Period ØExtended Period of Eligibility ØIRWE ØHigher SGA for Blind ØSubsidy ØPASS ØExtended Medicare coverage ØExpedited Reinstatement ØUnincurred Business expenses ØUnsuccessful Work Attempt ØContinued payment under a VR or similar program 78

Medicaid for Employed People With Disabilities ~ Title 19 ØMust be disabled ØMust have earned income from employment ØMust be under age 65 ØMust meet income and resource requirements (higher than SSI requirements) ØSame as Title 19 - administered by DHS ØSome individuals may pay a premium 79

For more information Sheila Stoeckel Iowa. WORKS North Iowa 641 -424 -1524 ext. 44500 Sheila. stoeckel@iwd. iowa. gov
9116037446455de53ba66530af333a2e.ppt