02395800d8d2f72244b4ede99f9bc621.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 77

Holistic management of ischemic stroke นพ. ธรวฒน รกจตร กลมงานอายรกรรม รพ. พจตร

Stroke network management • กจกรรมหลก บรการผปวยโรคหลอดเลอดสมอง – กจกรรม stroke awareness • ใหความร risk factor • คดกรองกลมเสยงและ – กจกรรม stroke alert Rx risk factor • EMS, Hotline • ประชาสมพนธอาการ และการปฏบตตวเมอเกดอาการ • ใชไดทกสทธ ทกท – Stroke fast track • จดตง และ refer – Stroke unit ดแล acute care – Rehabilitation • Acute , Chronic – Follow up หลง stroke • • 2 nd prevention Control risk factors ปองกนภาวะแทรกซอน ตดตามดแลผปวยหลง stroke ทมความพการหลงเหลออย
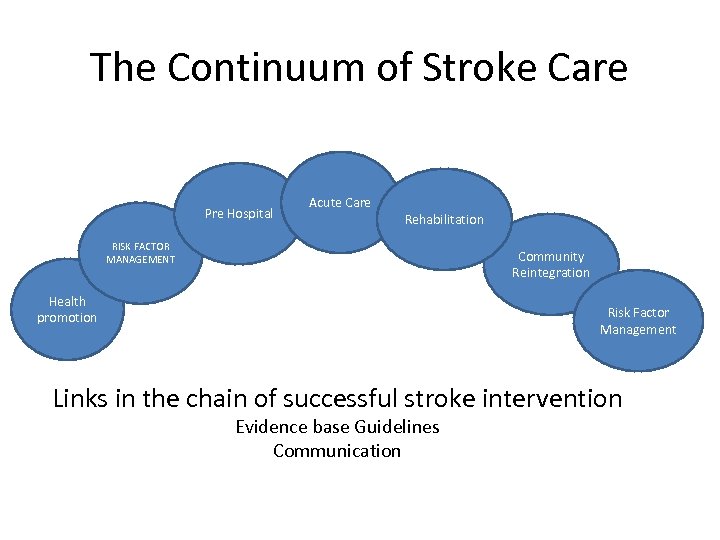
The Continuum of Stroke Care Pre Hospital Acute Care Rehabilitation RISK FACTOR MANAGEMENT Community Reintegration Health promotion Risk Factor Management Links in the chain of successful stroke intervention Evidence base Guidelines Communication

Health promotion & risk factor management • Stroke awareness • Primary prevention • Public education – Stroke signs and symptoms – Stroke risk factors

Stroke awareness & stroke alert • Identified high risk patients and control risk factors • Healthy life style campaign – High fiber , low salt – Regular exercise • Education of stroke signs and symptoms and how to do when they have stroke • Arrange transferal system

โครงการคลนกพเศษนอกเวลาราชการ เพอตรวจคดกรองความเสยงโรคห ลอดเลอดสมองและภาวะสมองเสอม • ตรวจรางกายโดยแพทยผเชยวชาญดานร ะบบประสาท – วดความดนโลหต เจาะเลอด ตรวจปสสาวะ – ตรวจคลนไฟฟาหวใจ เอกซเรยปอด – ทดสอบความจำ และตรวจพเศษอนๆ • ทกวนองคารและวนพฤหสบดเวลา 6. 008. 00 • สนใจสอบถามรายละเอยดหรอจองควรบบร การไดท งานสงเสรมคณภาพชวต ในวนและเวลาราชการเวลา 8. 00 -16. 00

Campaign media

Public education of stroke S/S

Pre hospital care • Signs and symptoms recognitions • EMS systems • Time is brain

EMS • Ability to assess clinical S/S of stroke and make accurate diagnosis • Coordinate between patient and the right hospital • Shorten time of transportation to hospital

Scale • Facial Droop Instruction Normal Abnormal • Arm Drift Instruction Normal Abnormal Ask patient to smile Both sides of face move equally One side of face does not move as well Ask patient to close eyes and extened both arms straight out for 10 seconds Both arms move the same or not at all One arm does not move or drifts down • Speech Instruction Normal Abnormal Ask patient to say “ You can ‘t teach an old dog new trick” Patient says correct words without slurring Patient slurs words, says wrong words, or is unable to speak
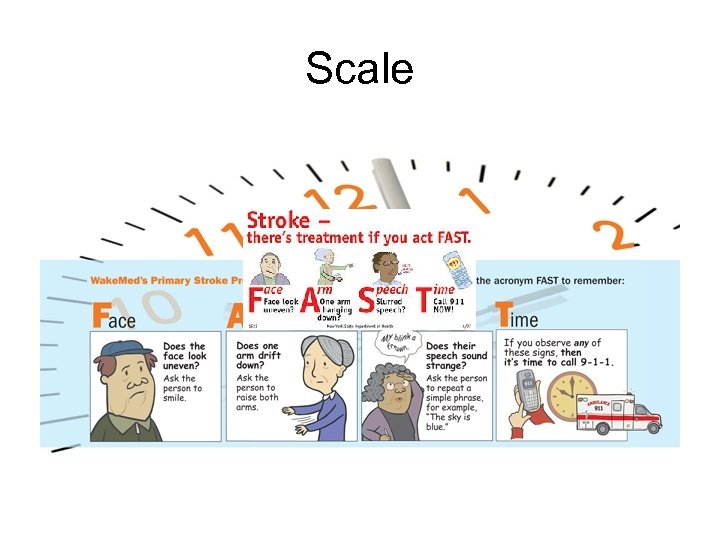
Scale

Time loss is …. Brain loss

Time is Brain • ปกตมนษยมเซลลประสาท 130 พนลานเซล • ทกๆนาท ทสมองขาดเลอด และไมไดรบการรกษา จะมเซลประสาทตาย 1. 9 ลานเซล สญเสยการทำงานหรอหนวยเชอมโยงขอ งเซลประสาท 13. 8 พนลานหนวย • ถานำเซลประสาททตายมาตอๆกน คดเปนระยะทางของเซลประสาททสญเสย 12 กโลเมตร

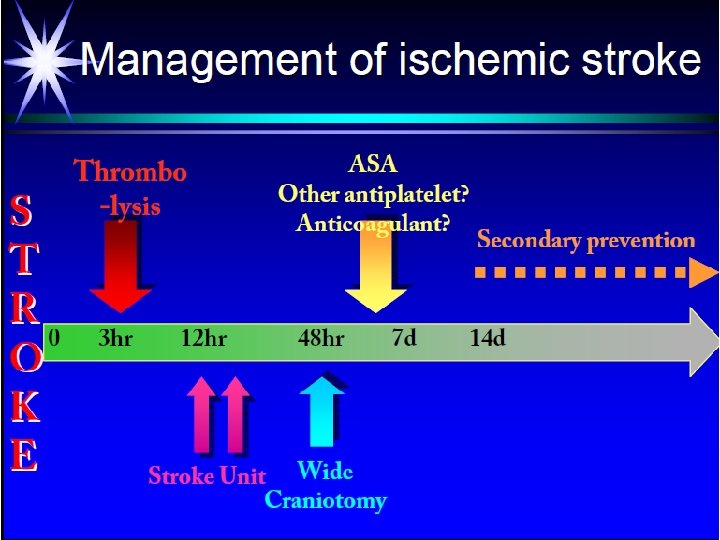
Acute stroke care • 4 evidence-base of acute care • Thrombolytic treatment in <3 ± 4. 5 hours of onset • ASA in 48 hours of onset • Stroke unit care • Hemicraniectomy of massive infarct in 48 hours
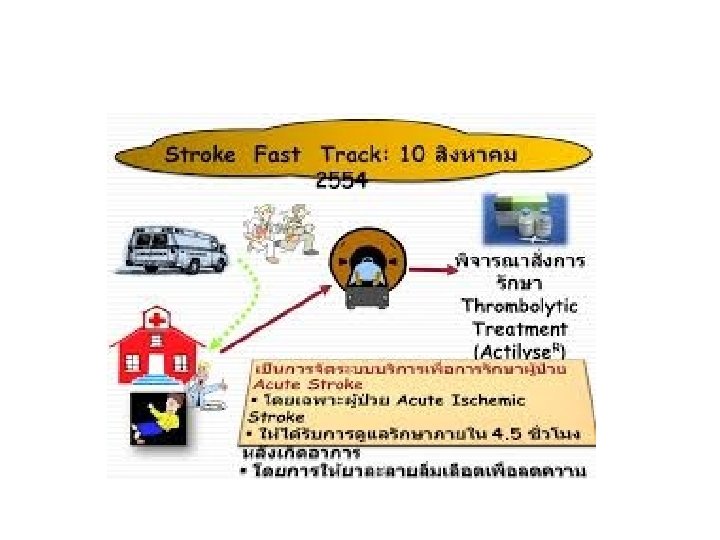


Stroke Fast Track
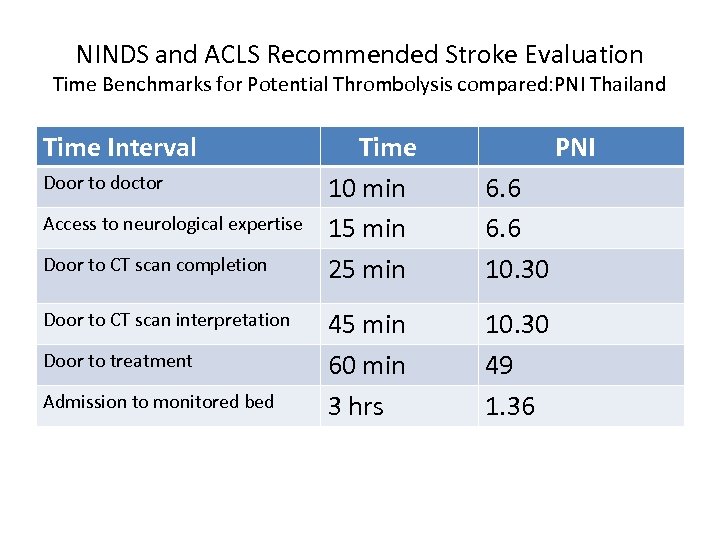
NINDS and ACLS Recommended Stroke Evaluation Time Benchmarks for Potential Thrombolysis compared: PNI Thailand Time Interval Door to doctor Access to neurological expertise Door to CT scan completion Door to CT scan interpretation Door to treatment Admission to monitored bed Time 10 min 15 min 25 min PNI 6. 6 10. 30 45 min 60 min 3 hrs 10. 30 49 1. 36

Inclusion and Exclusion Characteristics of Patients With Ischemic Stroke Who Could Be Treated With IV rt. PA Within 3 Hours From Symptom Onset • Inclusion criteria – Diagnosis of ischemic stroke causing measurable neurological deficit – Onset of symptoms < 3 hours before beginning treat – Age ≥ 18 years

• Exclusion criteria – – – – Significant head trauma or prior stroke in previous 3 months Symptoms suggest subarachnoid hemorrhage Arterial puncture at noncompressible site in previous 7 days History of previous intracranial hemorrhage Intracranial neoplasm, arteriovenous malformation, or aneurysm Recent intracranial or intraspinal surgery Elevated blood pressure (systolic >185 mm. Hg or diastolic >110 mm. Hg) Active internal bleeding Acute bleeding diathesis, including but not limited to Platelet count <100, 000/mm³ Heparin received within 48 hours, resulting in abnormality elevated Aptt greater than upper limit of normal Current use of anticoaggulant with INR >1. 7 or PT >15 seconds Currents use of direct thrombin inhibitors or direct factor Xa inhibitors with elevated sensitive laboratory tests (such as a. PTT, INR, platelet count, and ECT; TT; or appropiate factor Xa activity assays Blood glucose concentration < 50 mg/dl CT demonstrates multilobar infarction ( hypodensity > 1/3 cerebral hemisphere)

Relative exclusion criteria • Recent experience suggests that under some circumstances-with careful consideration and weighting of risk to benefit – patients may receive fibrinolytic therapy despite 1 or more relative contraindications. Condider risk to benefit of IV rt. PA administration carefully if any of these relative contraindications are present – Only minor or rapidly improving stroke symtoms ( clearing spontaneously) – Pregnancy – Seizure at onset with postictal residual neurological impairments – Major surgery or serious trauma within previous 14 days – Recent gastrointestinal or urinary tract hemorrhage (within previous 21 days) – Recent acute myocardial infarction (within previous 3 months)

• The checklist includes some FDA-approveded indications and contraindications for administration of IV rt. PA for acute ischemic stroke. Recent guideline revisions have modified the original FDA-approved indications. A physician with expertise in acute stroke care may modify this list. • Onset time is defined as either the withnessed onset of symptoms of the time last known normal if symptom onset was not withnessed. • In patients without recent use of oral anticoaggulants or heparin, treatment with IV rt. PA can be initiated before availability of coaggulation test results but should be discontinued if INR is >1. 7 or PT is abnormally elevated by local laboratory standards. • In patients without history of thrombocytopenia, treatment with IV rt. PA can be initiated before availability of platelet count but should be discontinued if platelet count is < 100, 000/mm³.

Additional exclusion criteria in time of onset 3 -4. 5 hours • • Age>80 History of previos stroke with DM On oral anticoaggulant regardless of INR NIHSS>25

NINDS rt. PA Stroke Study • 31 to 50% had a complete or near-complete recovery at three months, as • compared with 20 to 38 %of the patients given placebo • Motarity rate was similar at one year • Symptomatic brain hemorrhage, which occurred in 6. 4 percent of the patients given t. PA, as compared with 0. 6 percent of those given placebo ( 36 hrs) N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 1581 -
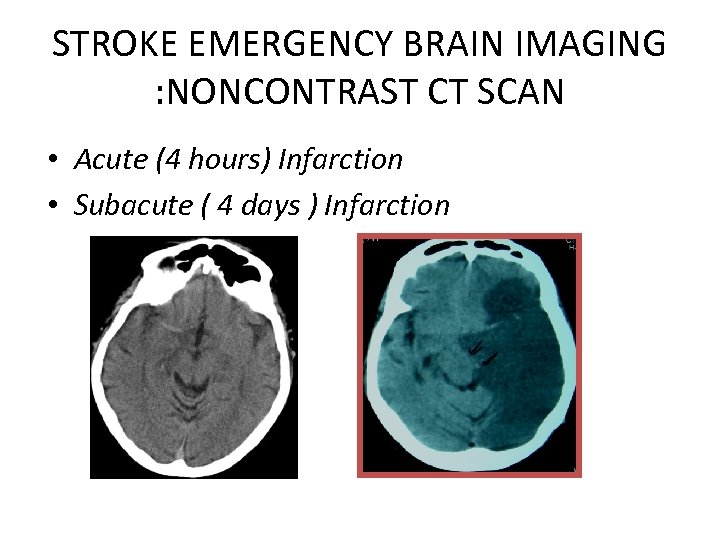
STROKE EMERGENCY BRAIN IMAGING : NONCONTRAST CT SCAN • Acute (4 hours) Infarction • Subacute ( 4 days ) Infarction
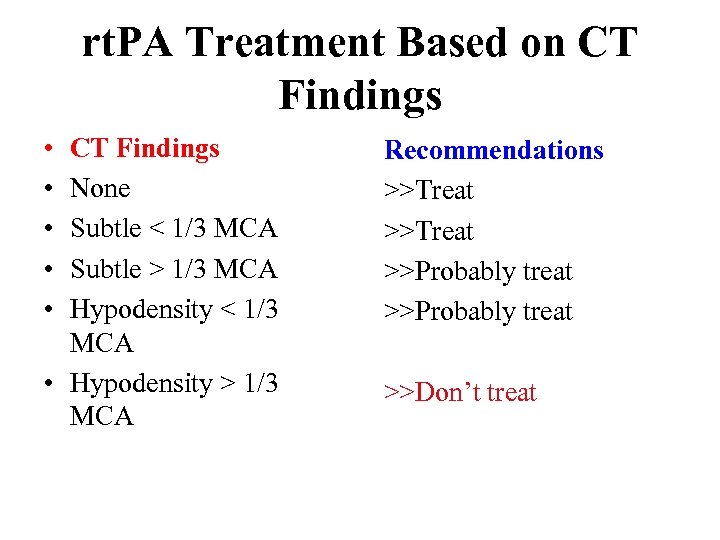
rt. PA Treatment Based on CT Findings • • • CT Findings None Subtle < 1/3 MCA Subtle > 1/3 MCA Hypodensity < 1/3 MCA • Hypodensity > 1/3 MCA Recommendations >>Treat >>Probably treat >>Don’t treat
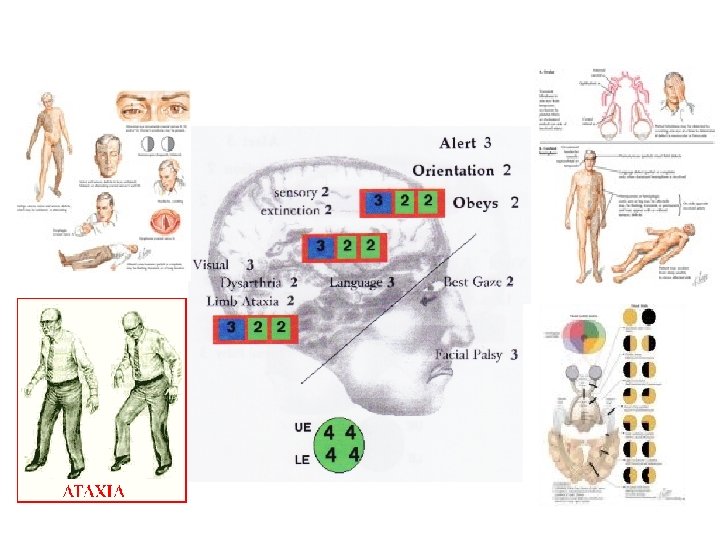

NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) The NIH stroke scale measures several aspects of brain function, including consciousness, vision, sensation, movement, speech, and language. A certain number of points are given for each impairment uncovered during a focused neurological examination. A maximal score of 42 represents the most severe and devastating stroke. Current guidelines as of 2008 allow strokes with scores greater than 4 points to be treated with t. PA.

NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) The National Institute of Health (NIH) stroke scale (NIHSS) is a standardized method used by physicians and other health care professionals to measure the level of impairment caused by a stroke.
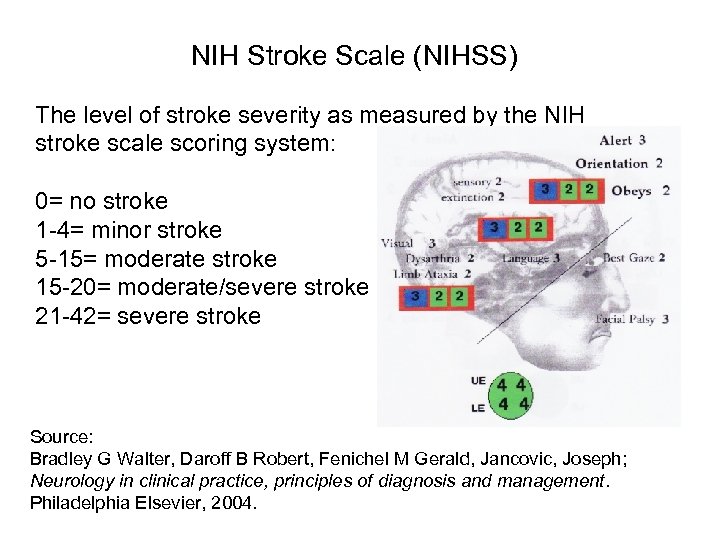
NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) The level of stroke severity as measured by the NIH stroke scale scoring system: 0= no stroke 1 -4= minor stroke 5 -15= moderate stroke 15 -20= moderate/severe stroke 21 -42= severe stroke Source: Bradley G Walter, Daroff B Robert, Fenichel M Gerald, Jancovic, Joseph; Neurology in clinical practice, principles of diagnosis and management. Philadelphia Elsevier, 2004.
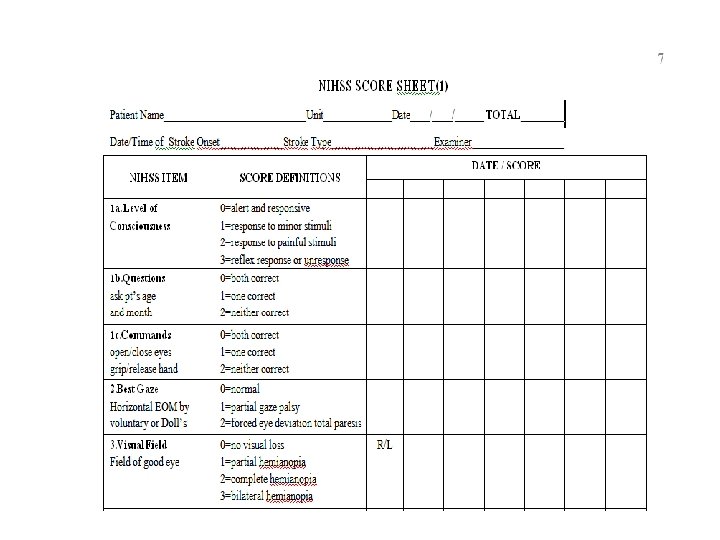
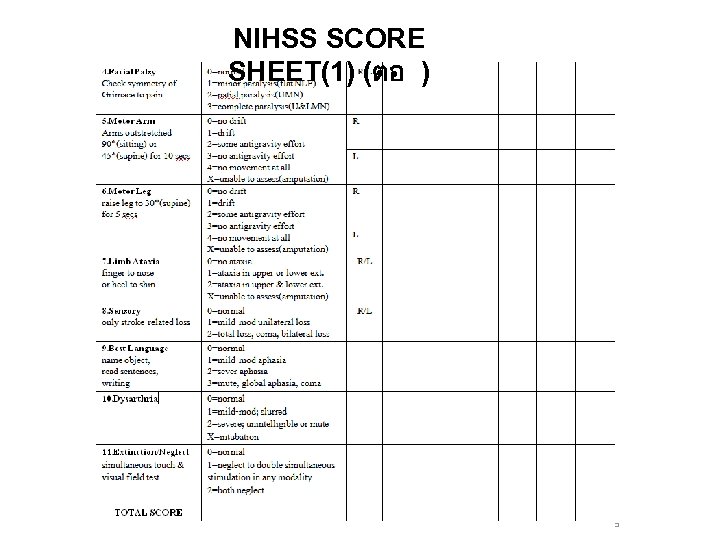
NIHSS SCORE SHEET(1) (ตอ )

Stroke unit องคประกอบหลกของการดแลผปวยโรคหลอดเลอ ดสมอง 1. Multidiscipinary ( MD) care 2. Stroke director หรอแพทยหวหนาทม มหนาทกำกบดแล ควบคมมาตรฐาน พรอมทงกำหนดนโยบาย และบรหารจดการ 3. Care protocols 4. Education (patients and family, personals) 5. Discharge planning and patient transfer protocol 6. Data collection
Stroke unit • หอผปวยเฉพาะทดแลผปวยโรคหลอดเล อดสมอง • โดยทมสหวชาชพทมความร ความเชยวชาญโรคหลอดเลอดสมอง • ดวยแผนการรกษาทเปนมาตรฐาน • พรอมทงใหความรแกผปวยและญาต • เตรยมความพรอมสำหรบผปวยกลบบาน • และมการเกบขอมลตวชวดเพอตดตา มเปรยบเทยบผลการดำเนนงาน • นำไปสการพฒนาปรบปรงการดแลรกษาผ ปวยโรคหลอดเลอดสมองใหมประสทธภาพ

ประโยชนของ stroke unit • Increase nursing contact • Early detection of deterioration • Prevent complications swallowing test, bed sore, DVT prophylaxis • Educations • Decrease LOS • Decrease mortality, morbidity and cost
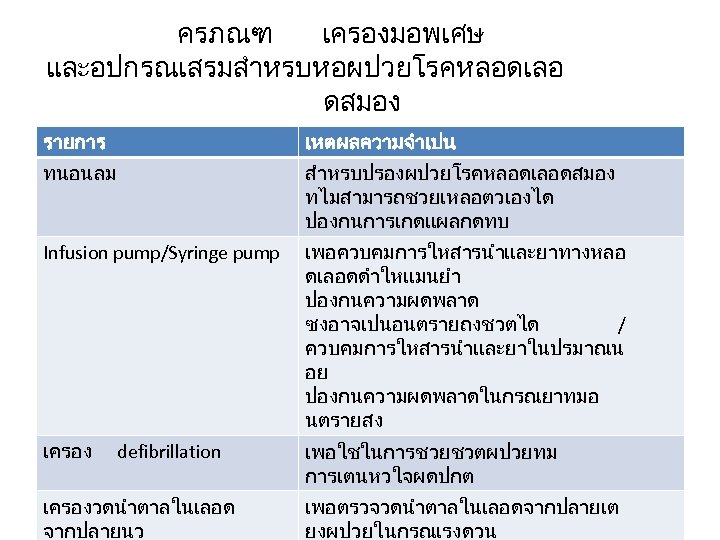
ครภณฑ เครองมอพเศษ และอปกรณเสรมสำหรบหอผปวยโรคหลอดเลอ ดสมอง รายการ เหตผลความจำเปน ทนอนลม สำหรบปรองผปวยโรคหลอดเลอดสมอง ทไมสามารถชวยเหลอตวเองได ปองกนการเกดแผลกดทบ Infusion pump/Syringe pump เพอควบคมการใหสารนำและยาทางหลอ ดเลอดดำใหแมนยำ ปองกนความผดพลาด ซงอาจเปนอนตรายถงชวตได / ควบคมการใหสารนำและยาในปรมาณน อย ปองกนความผดพลาดในกรณยาทมอ นตรายสง เครอง เพอใชในการชวยชวตผปวยทม การเตนหวใจผดปกต defibrillation เครองวดนำตาลในเลอด จากปลายนว เพอตรวจวดนำตาลในเลอดจากปลายเต ยงผปวยในกรณเรงดวน

การจดตง stroke unit • ทมสหวชาชพทเชยวชาญเฉพาะโรคหลอ ดเลอดสมอง • แพทย • Stroke manager • พยาบาล • กายภาพบำบด กจกรรมบำบด • เภสชกร • โภชนากร • จตวทยา
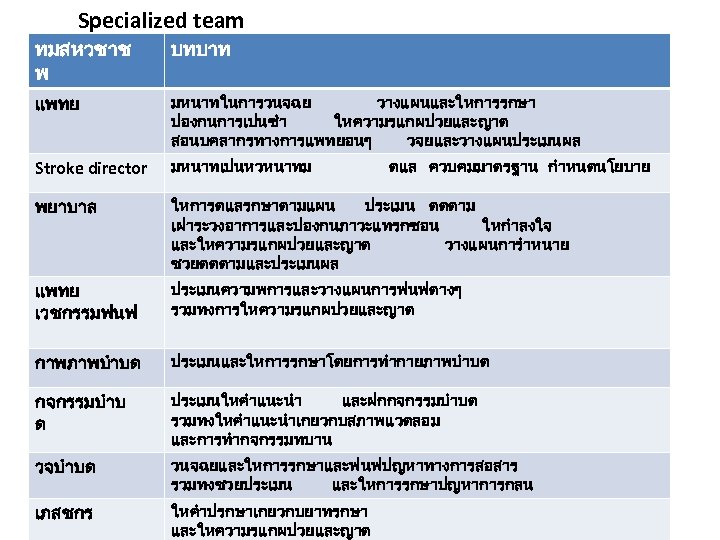
Specialized team ทมสหวชาช พ บทบาท แพทย มหนาทในการวนจฉย วางแผนและใหการรกษา ปองกนการเปนซำ ใหความรแกผปวยและญาต สอนบคลากรทางการแพทยอนๆ วจยและวางแผนประเมนผล Stroke director มหนาทเปนหวหนาทม พยาบาล ใหการดแลรกษาตามแผน ประเมน ตดตาม เฝาระวงอาการและปองกนภาวะแทรกซอน ใหกำลงใจ และใหความรแกผปวยและญาต วางแผนการำหนาย ชวยตดตามและประเมนผล แพทย เวชกรรมฟนฟ ประเมนความพการและวางแผนการฟนฟตางๆ รวมทงการใหความรแกผปวยและญาต กาพภาพบำบด ประเมนและใหการรกษาโดยการทำกายภาพบำบด กจกรรมบำบ ด ประเมนใหคำแนะนำ และฝกกจกรรมบำบด รวมทงใหคำแนะนำเกยวกบสภาพแวดลอม และการทำกจกรรมทบาน วจบำบด วนจฉยและใหการรกษาและฟนฟปญหาทางการสอสาร รวมทงชวยประเมน และใหการรกษาปญหาการกลน เภสชกร ใหคำปรกษาเกยวกบยาทรกษา และใหความรแกผปวยและญาต ดแล ควบคมมาตรฐาน กำหนดนโยบาย

Care protocols • การจดทำแผนการตรวจวนฉย การรกษาทจำเปนและสำคญ ผายนการประชมรวมกนระหวางแพทยแล ะบคลากรทางการแพทยทเกยวของในสถ านพยาบาลนนๆ โดยยดแนวทางการรกษาโรคหลอดเลอดสมอง เพอใหการรกษาในระยะเฉยบพลน ตดตามและปองกนการเกดภาวะแทรกซอน ประเมนผลการรกษาและปองกนการเกดเป นซำไดอยางมประสทธภาพ

ผปวยไดรบประโยชนจากกา รใช care map คอ • 1. ไดรบการวนจฉยรวดเรว เชน ตรวจเลอด X-Ray, ECG, เรวขน ในผปวย case care map for ischemic stroke จะไดรบการตรวจ C. T Brain non Contrast ภายใน 24 ชม. • 2. ไดรบการประเมนสภาพถกตองครบถวน แพทยมใบตรวจรางกาย ใบซกประวต พยาบาลมแบบประเมนสมรรถภาพแรกรบ , มใบ Check list for care map ischemic stroke • 3. ลดความเสยงของผปวย – ความเสยงของผปวยทอาจมอาการเลวลงจากการไ ดรบการรกษาพยาบาลลาชา – ความเสยงของผปวยทอาจเกดภาวะไตวาย จากการไดรบการฉด Contrast โดยไมจำเปนในการทำ C. T Brain • 4. ไดรบการฟนฟสมรรถภาพเรวขน
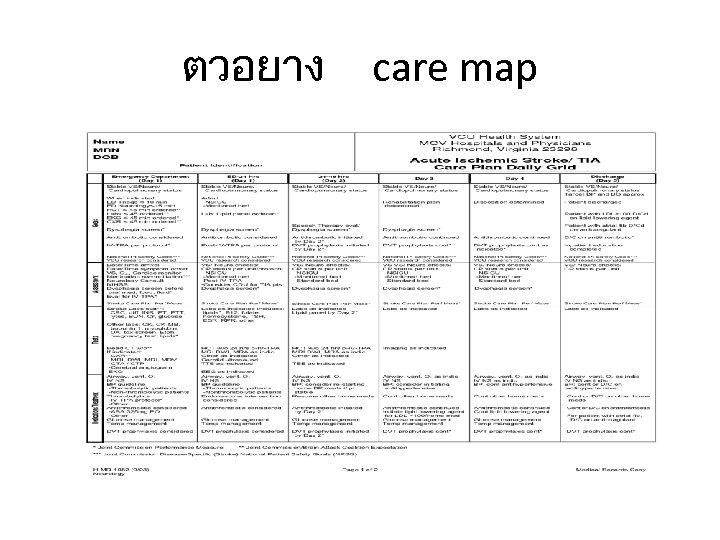
ตวอยาง care map

ตวอยางตวชวดการดแลผปวยโรคหลอ ดเลอดสมอง • ตวชวดทางดานกระบวนการ – รอยละของผปวยทไดรบการ CT/MRI สมอง – รอยละของผปวยทไดรบการตรวจระดบนำตาลในเลอด ในขณะแรกรบ – รอยละของผปวยทไดรบยาแอสไพรนภายใน 48 ชวโมงแรก ในราบทไมมขอหาม – รอยละของผปวยกลบบานทไดรบยาตานเกรดเลอด (antipl atelet) หรอยาตานการแขงตวของเลอด (anticoaggulant) ในรายทมขอบงช – รอยละของผปวยทไดรบการทำกายภาพบำบด – รอยละของผปวยทไดรบการประเมนการกลน – รอยละของผปวยทไมไดรบ Nifedipine sublingual – รอยละของผปวยกลบบานและไดรบคำแนะนำการปฏบตต วเพอปองกนการกลบเปนซำ – รอยละของผปวยทไดรบการรกษาใน Stroke unit – รอยละของผปวยทไดรบการตรวจคลนไฟฟาหวใจ

ตวอยางตวชวดการดแลผ ปวยโรคหลอดเลอดสมอง • ตวชวดทางดานผลลพท (outcomes) – อตราตาย – อตราการเกดโรคปอดอกเสบ – อตราการตดเชอทางเดนปสสาวะ – อตราการเกดแผลกดทบ – อตราการเกดพลดตกหกลม – อตราการ Re-admission ภายใน 4 สปดาห – จำนวนวนนอน – ความพการภายหลงการรกษา หรอสถานภาพขณะจำหนาย – คาใชจายของผปวยในการรกษา
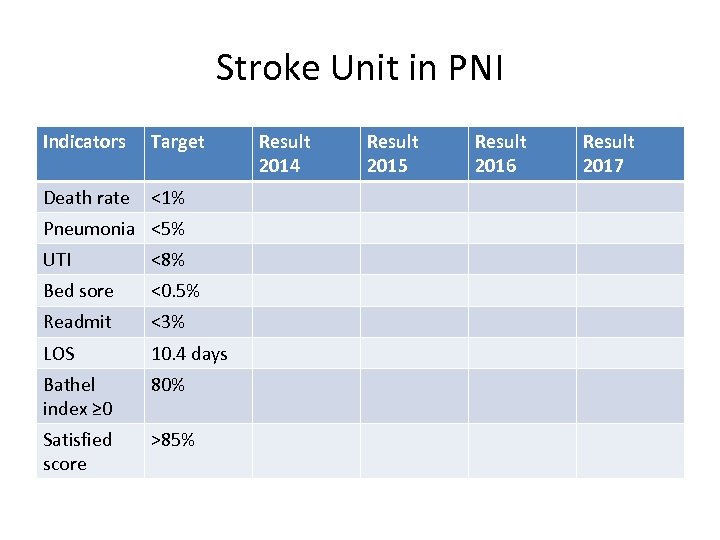
Stroke Unit in PNI Indicators Target Death rate <1% Pneumonia <5% UTI <8% Bed sore <0. 5% Readmit <3% LOS 10. 4 days Bathel index ≥ 0 80% Satisfied score >85% Result 2014 Result 2015 Result 2016 Result 2017

General management • Observe and monitor respiration and beware of hypoxemia ( keep O₂ sat ≥ 92% ) • IV fluid depend on water balance : avoid glucose solution or free water • NPO in patients with • Control BS ( 80 -140 mg/dl in non diabetic patients and 140 -180 in diabetic patients ) • Normal body temperature, treat fever • Antiepileptic drug in case of seizure • Treat underlying diseases • Precaution of DVT by early mobilization • Swallowing test

Supplemental Oxygen • Adequate tissue oxygenationingen – Prevent hypoxia and worsening of the brain injury • The most common causes of hypoxia – Partial airway obstruction – Hypoventilation – Aspiration pneumonia – Atelectasis
Temperature • Fever – Increased morbidity and mortality • Lowering body temperature – Improve prognosis – Acetaminophen 600 mg/day – Cooling devices
Cardiac Monitoring • Cardiac complications • Myocardial ischemia • Cardiac arrhythmia – – Atrial fibrillation – most common ST segment depression Inverted T waves Prominent U waves • Cardiac monitoring at least the first 24 hrs
Arterial Hypertension • Elevated BP is often detected in the first hours after stroke • Elevated BP may be secondary to – Stress – Full bladder – Nausea – Pain – Preexisting hypertension – Physiological response to hypoxia – Response to increased intracranial pressure
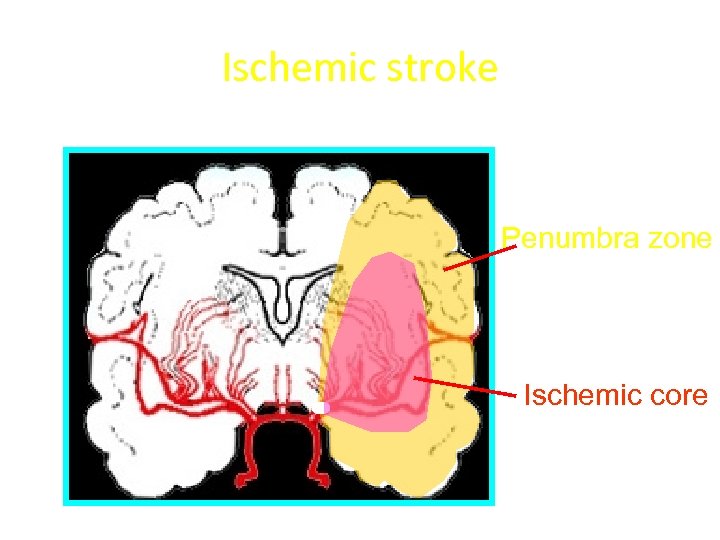
Ischemic stroke Penumbra zone Ischemic core
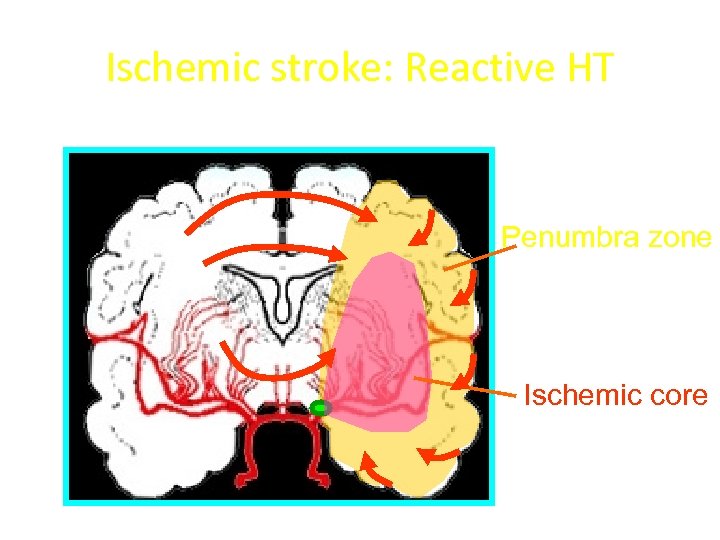
Ischemic stroke: Reactive HT Penumbra zone Ischemic core
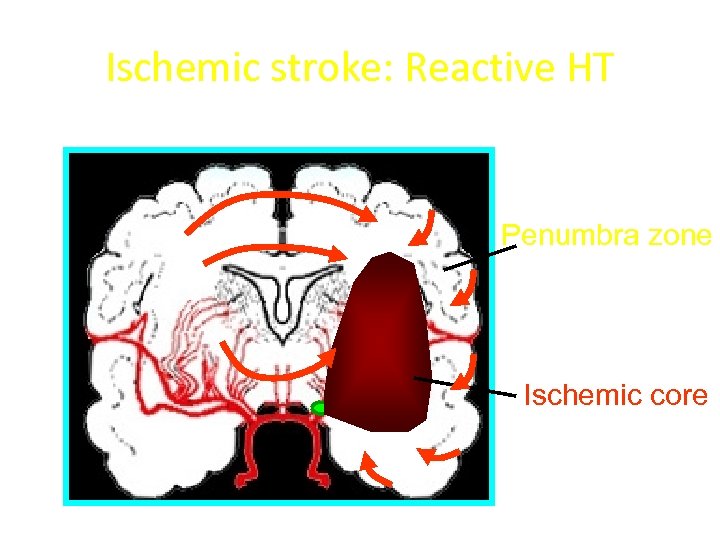
Ischemic stroke: Reactive HT Penumbra zone Ischemic core
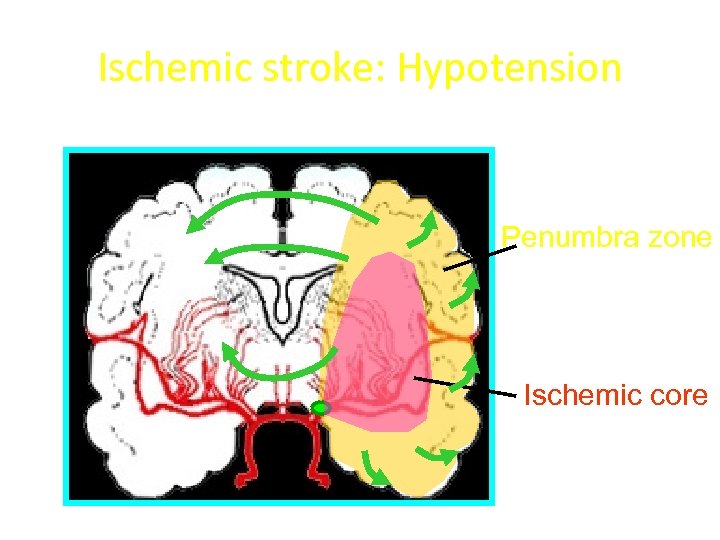
Ischemic stroke: Hypotension Penumbra zone Ischemic core
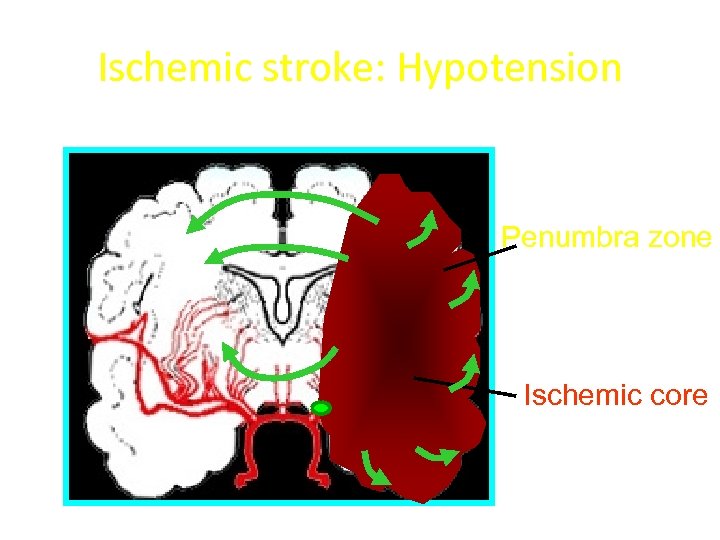
Ischemic stroke: Hypotension Penumbra zone Ischemic core

Suggested antihypertensive treatment in acute ischemic stroke - Hold previous antihypertensive medication at least 7 -10 days - Do not treat BP 220/120 mm. Hg in non-thrombolysis and/or BP 185 -115 mm. Hg in thrombolytic treatment - SBP>230 mm. Hg on repeated measure , DBP 120 -140 mm. Hg or both Captopril 6. 25 -12. 5 mg orally or iv drip calcium blocker (nicardepine) or iv Larbetalol 10 mg. - DBP>140 mm. Hg Nitroglycerine 5 mg iv. Follow by 1 -4 mg/h or Sodium nitroprusside 0. 5 µg/kg/min

ภาวะทไมถอเปนขอหามในการใหย าลดความดนโลหตในผปวย Ischemic Stroke Malignant hypertension/ hypertensive encephalopathy Acute myocardial infarction Aortic dissection Blood pressure above the upper limits of autoregulation (>220/120 mm. Hg) • Hemorrhagic transformation • Lower by 20% or within the autoregulatory range • •
Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycermia • Hypoglycermia – Brain injury • Hyperglycermia – Increasing Brain edema – Increased hemorrhagic transformation • Drsired level of BS – 80 -140 (normal poppulations) – 140 -180 ( diabeties) – Frequent monitoring of BS level – Adjustments of insulin
Complications • • Infections: pneumonia, UTI, sepsis Pressure sore DVT, pulmonary embolism Metabolic disturbances Acute MI Seizure Brain edema, hydrocephalus Bleeding : UGI bleeding
Cardiac complication • Arrhythmia – T wave changes (34%) – QTc prolonged (28%) – ST changed (25%) – Sinus tachycardia (15%) – Sinus bradycardia (11%) • Elevated cardiac enzyme – CK, CKMB , myoglobin – Troponin T remained within normal range • Myocardial infarction – co incidence stroke& MI (common)

Progressive stroke Propagation of thrombus Brain edema Recurrent emboli Metabolic causes : hypo/hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, hypo/hypernatremia, anemia, hypoxia, hypotension • Hemorrhagic transformation • •

Management Treat underlying causes Prevent brain swelling Maintain airway, blood flow, and circulation Keep BP<220/120 mm. Hg. ( no calcium blocker) Hydration keep 80%maintenance ( avoid glucose IV) • Control blood sugar (BS<140 mg/dl) • Prevent complications • • •
Treatment of increase intracranial pressure • Retain ET tube and assist ventilation when decrease consciousness • Elevate head position 20 -30° • Avoid compression of jugular vein • Steroid may increase complication and no benefit • Keep O₂ sat ≥ 92% • Avoid hypervolemia • Osmotherapy : 20% manitol IV in 20 -30 min follow by 0 • . 25 -0. 5 g/Kg IV in 10 min 4 -6 times/d • Consult neurosurgeon for decompressive craniectomy
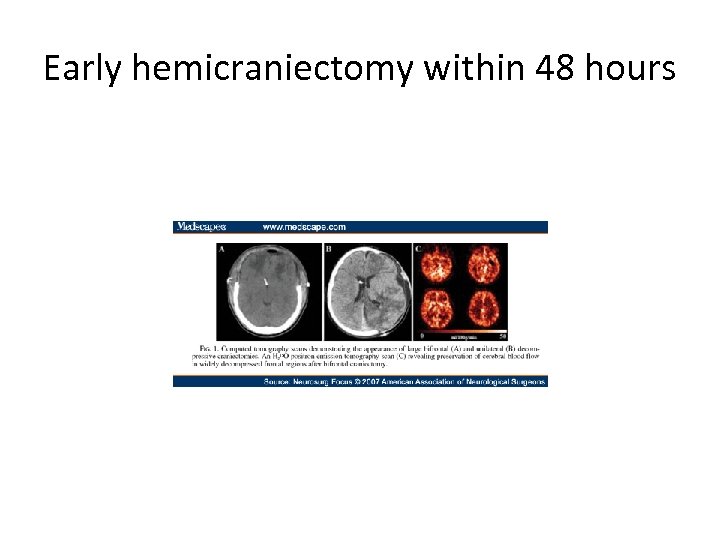
Early hemicraniectomy within 48 hours

Swallowing test • การประเมนการกลน มวตถประสงคในการประเมนสภาวะของผปวยว ามภาวะการกลนบกพรองหรอไม และพรอมทจะรบประทานอาหารทางปากไดหรอไม • ผปวยทจะสามารถรบการประเมน ควรมคณสมบตดงน – สามารถจดใหอยในทานงได – สามารถสอสารและทำตามคำสงไดพอสมควร – มระดบความรสกตวโดยประเมนจาก Glasgow coma scale > 11 คะแนน • ขอควรปฏบตกอนการประเมนการกลน มดงน

Early rehabilitation • • Prevent joint stiffness Adequate secretion toilet Prevent DVT Good outcome

Secondary prevention • • • Control risk factors Antiplatelets / anticoagulant Vascular intervention if needs Exercise and rehabilitation Good diets

Risk factor management • • • Control modifiable risk factors Public campaign and education Regular check up Secondary prevention of recurrent stroke Home help care / long term care for severe disable patients (include rehabilitation) and community support

Home health care • Follow independent patients • NG tube feedings : adequate nutrition, feeding technique, NG tube care • Prevent bed sore / wound care • Respiratory care • House adjustment for handicap person • Home PT, OT

Pitfalls in thrombolytic treatment • • • Time System Diagnosis Treatment Complications

Time of onset • Exact time of onset is crusial • Stroke on awakening, What timeis the time of onset? • Last time that witness seen of no symptom is the time of onset • TIA and progress to stroke • No definition of time of onset

• ขนตอนการบรหารยา – คำนวณปรมาณยา ตามนำหนกผปวย 0. 9 มก. /กก. ( ขนาดสงสดไมเกน 90 มก(. – ใหปรมาณยา 10% ของทคำนวณไดฉดเขาหลอดเลอดดำใน 1 นาท – ใหยาทเหลอหยดเขาหลอดเลอดดำใน 60 นาท • ขอควรระวง – หลกเลยงการใหยา antiplatelet หรอ anticoaggulant ภายใน 24 ชวโมง – ตองหยดใหยาละลายลมเลอดทนทในกรณทสงส ยวามภาวะเลอดออก – ไมควรใส NG tube หรอแทงหลอดเลอดดำใหญ ( central venous access ) หรอแทงหลอดเลอดแดงภายใน 24

การประเมนและการรกษาภาวะแทรกซอนในผปวย ทไดรบยาละลายลมเลอด • Record V/S and N/S ทก 15 นาทเปนเวลา 2 ชวโมง ตามดวยทก 30 นาท เปนเวลา 6 ชวโมง และทก 60 นาท จนครบ 24 ชวโมง • ขอควรระวงภายหลงการใหยาละลายลมเลอด – หลกเลยงการใหยา antiplatelet ภายใน 24 ชวโมง – กรณทสงสยวามเลอดออก ใหหยดยา rt-PA ทนท – ไมควรใส NG tube หรอแทง central venous/arterial line ภายใน 24 ชวโมง – หลกเลยงการใสสายสวนปสสาวะ ในชวงเวลาใหยาหรอหลงใหยา 30 นาท • ควบคม BP<180/105 mm. Hg โดยใหยา Nicardepine 5 mg/hr IV หรอ Labetalol 10 mg IV

rt-PA Pharmacokinetic properties • Alteplase is cleared rapidly from the circulating blood and metabolized mainly by the liver (plasma clearance 550 -680 ml/min). • The relevant plasma half-life t 1/2 alpha is 4 -5 minutes. • This means that after 20 minutes less than 10% of the initial value is present in the plasma. • For the residual amount remaining in a deep compartment, a beta-half-life of about 40 minutes was measured

Therapeutic usage • The reconstitued solution may be diluted with 0. 9%NSS solution for injection up to minimal concentration of 0. 2 mg alteplase per ml • Further dilution, the use of water for injections for dilution or the use of dextrose, is not recommended due to increasing formation of turbidity of the reconstituted solution. • Actilyse should not be mixed with other medicinal products neither in the same infusion vial nor the same catheter ( not even with heparin). • Shelf life – 50 mg pack sizes: 3 years – After reconstitution, an immediated use is recommended. However, the in-use stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 2°C - 8°C and for 8 hours at 25°C
02395800d8d2f72244b4ede99f9bc621.ppt