1be89aaff29f2c029d3b19c5657af08e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 66

HL 7 Work Group Report September 20 - 25, 2009 - Atlanta, GA USA Gov. Projects, SOA, EHR, PHER HL 7 Project Prototype: EHR System Design Reference Model (EHR-SD RM) Immunization and Adverse Event Reporting Nancy Orvis, HL 7 Project Co-Chair Stephen Hufnagel Ph. D, HL 7 Project Facilitator September 22, 2009 presentation October 10, 2009 update F
Contents EHR System Design Reference Model (EHR-SD RM) • Background – – • What Changed in 2009 – – • Jan 2009 baseline project Sep 2009 Information Model (IM) additions 2010 EHR SD RM Model with HITSP Capabilities, IM & ARRA Vaccination and Adverse Event Reporting Prototype – – – • ARRA (American Reinvestment and Recovery Act) HITSP Harmonization Framework for reuse HITSP Capabilities • Information Exchanges Interface Standards Specifications HITSP Service Collaborations EHR SD RM Model – – – • 2008 Project Results 2009 HL 7 EHR SD RM Project plan AHIC Use Cases EHR-S FM HITSP Capabilities Next Steps 2

Introduction • In 2004, Executive Orders 13335 set the objective for National Electronic Healthcare Record (EHR) Interoperability by 2014 • In 2006, Executive Order 13410 mandated Federal agencies to begin transformation to Healthcare Information Technology Standards Panel (HITSP) conformant EHR interoperable systems by 2007 • We present a standards-based strategic approach for interoperability at the service level to construct semantically consistent interoperable Enterprise Architectures (EAs) – It builds upon the functional foundation of the HL 7 EHR System Functional Model (EHR-S) and the technical foundation of Thomas Erl’s Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) model to specify a standard Healthcare SOA Reference Architecture (H-SOA-RA) – Information Exchange Requirements (IERs) are used to identify services and as the key to traceability from requirements to 3
HL 7 Project Intent • Implement a step in HL 7 roadmap – Identify gaps and overlaps in HL 7’s portfolio – Identify gaps in the EHR-S FM – Pilot HL 7 ARB SAEAF methodology • Create H-SOA-RA Version 2 • Create Healthcare SOA EHR-SD Reference Model based on EHR System Functional Model (EHR-S FM) • Create prototype architectural case study using HL 7 HSSP Practical Guide for SOA in Healthcare “sample health” and service specifications, EHR-S FM, EHR-SD RM, AHIC Use Cases, HITSP Interoperability Specifications and NHIN services • Demonstrate standards-based Model Driven Architecture (MDA) approach 4

HL 7 Project Scope • This project will mature the April 2008 H-SOA-RA version 1. 0 into H-SOARA Version 2. 0 and integrate it into an EHR-SD RM using – – – • Emphasis will be placed on maintaining AHIC, HITSP, NHIN and CCHIT conformance by maintaining IERs and Data Requirements (DRs) traceability – • HL 7 (SA)EAF, HITSP Capabilities, and EHR System Functional Model (EHR-S FM) Mapping and analysis of the HL 7 product portfolio against the EHR-S FM will be used to integrate the reference architecture with HL 7 product lines and initially mature the resulting model as a technical white papers, then an informative reference model and finally a standard reference model An HSSP based prototype case study architectural specification will be built to validate the effort using the AHIC-HITSP Immunization and Response Management and Public Health Case Reporting use cases 5

HL 7 Project Schedule • Sep 2008 – Healthcare SOA Reference Architecture (H-SOA-RA) • Jan 2009 – harmonize and catalogue priority IERs, DRs and candidate services • Mar 2009 – map priority IERs, DRs and candidate services to EHR-S FM • Jun 2009 - Mappings of V 2. 5, V 3 products to EHR-S FM • Jun 2009 - Present at HL 7 SOA Conference (for peer feedback) • Sep 2009 – Report on Vaccination and Adverse Event Prototype • Oct 2009 – Healthcare SOA Reference Architecture (H-SOA-RA) version 2. 0 • Nov 2009 - HSSP Practical Guide for SOA in Health Care, Part II: Case Study • Jan 2010 - EHR-SD RM white paper for HL 7 committee comments, to 6

2008 Project Goal Healthcare SOA Reference Architecture (H-SOA-RA) Identifying Opportunities to Leverage Technology and Alleviate Redundancy or Agency IT Overlap TIO RA BO LL A Healthcare Industry VA/ Do. D Interagency Do. D Key Architectural Objective Standardized Technical Solutions aligned with Core Business Processes. N IO AT GR CO Federated TE National IN N Key Business Driver Patient Centric Processes TMA Military Services INTER-AGENCY Joining Forces to Improve Effectiveness, Efficiency, and Service delivery 7
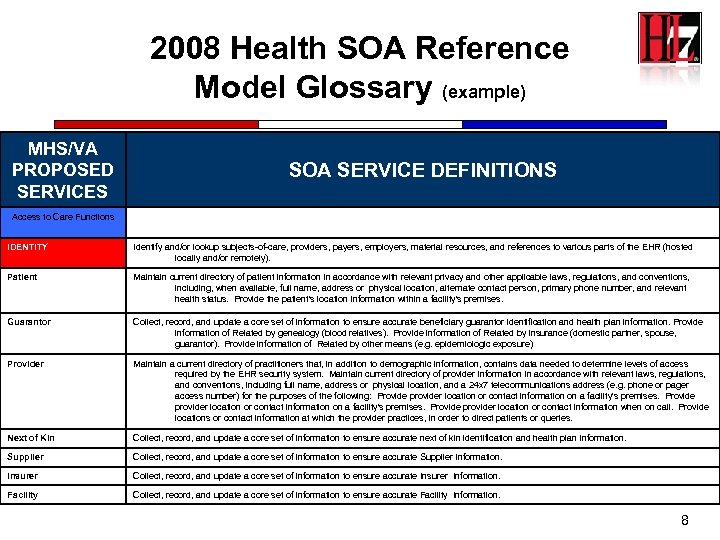
2008 Health SOA Reference Model Glossary (example) MHS/VA PROPOSED SERVICES SOA SERVICE DEFINITIONS Access to Care Functions IDENTITY Identify and/or lookup subjects-of-care, providers, payers, employers, material resources, and references to various parts of the EHR (hosted locally and/or remotely). Patient Maintain current directory of patient information in accordance with relevant privacy and other applicable laws, regulations, and conventions, including, when available, full name, address or physical location, alternate contact person, primary phone number, and relevant health status. Provide the patient's location information within a facility's premises. Guarantor Collect, record, and update a core set of information to ensure accurate beneficiary guarantor identification and health plan information. Provide information of Related by genealogy (blood relatives). Provide information of Related by insurance (domestic partner, spouse, guarantor). Provide information of Related by other means (e. g. epidemiologic exposure) Provider Maintain a current directory of practitioners that, in addition to demographic information, contains data needed to determine levels of access required by the EHR security system. Maintain current directory of provider information in accordance with relevant laws, regulations, and conventions, including full name, address or physical location, and a 24 x 7 telecommunications address (e. g. phone or pager access number) for the purposes of the following: Provide provider location or contact information on a facility's premises. Provide provider location or contact information when on call. Provide locations or contact information at which the provider practices, in order to direct patients or queries. Next of Kin Collect, record, and update a core set of information to ensure accurate next of kin identification and health plan information. Supplier Collect, record, and update a core set of information to ensure accurate Supplier Information. Insurer Collect, record, and update a core set of information to ensure accurate Insurer Information. Facility Collect, record, and update a core set of information to ensure accurate Facility Information. 8
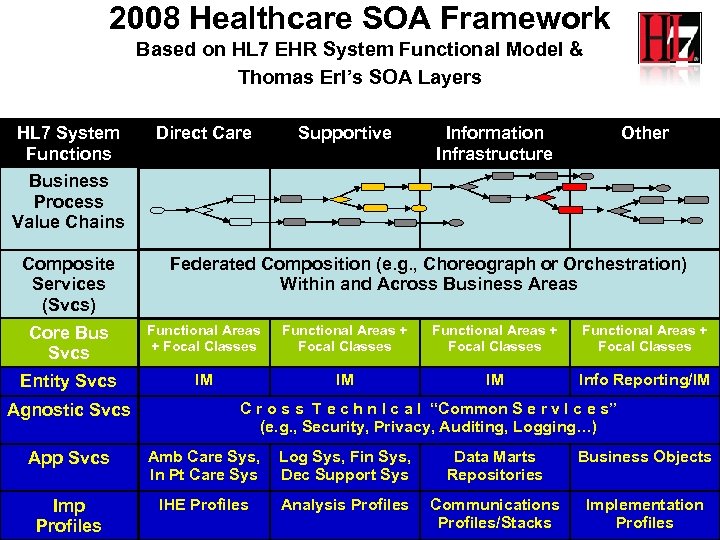
2008 Healthcare SOA Framework Based on HL 7 EHR System Functional Model & Thomas Erl’s SOA Layers HL 7 System Functions Direct Care Supportive Information Infrastructure Other Business Process Value Chains Composite Services (Svcs) Federated Composition (e. g. , Choreograph or Orchestration) Within and Across Business Areas Core Bus Svcs Functional Areas + Focal Classes Entity Svcs IM IM IM Info Reporting/IM Agnostic Svcs C r o s s T e c h n I c a l “Common S e r v I c e s” (e. g. , Security, Privacy, Auditing, Logging…) App Svcs Amb Care Sys, In Pt Care Sys Log Sys, Fin Sys, Dec Support Sys Data Marts Repositories Business Objects Imp Profiles IHE Profiles Analysis Profiles Communications Profiles/Stacks Implementation Profiles 9 9
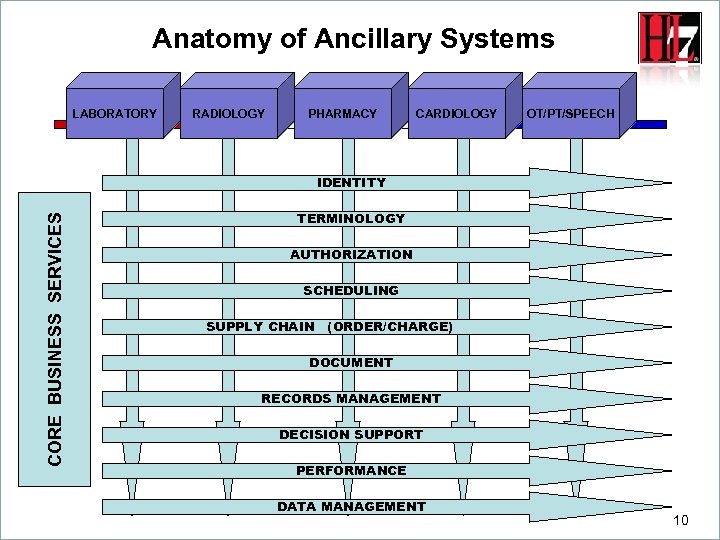
Anatomy of Ancillary Systems LABORATORY RADIOLOGY PHARMACY CARDIOLOGY OT/PT/SPEECH CORE BUSINESS SERVICES IDENTITY s TERMINOLOGY AUTHORIZATION SCHEDULING SUPPLY CHAIN (ORDER/CHARGE) DOCUMENT RECORDS MANAGEMENT DECISION SUPPORT PERFORMANCE DATA MANAGEMENT 10
Contents EHR System Design Reference Model (EHR-SD RM) • Background – – • What Changed in 2009 – – • Jan 2009 baseline project Sep 2009 Information Model (IM) additions 2010 EHR SD RM Model with HITSP Capabilities, IM & ARRA Vaccination and Adverse Event Reporting Prototype – – – • ARRA (American Reinvestment and Recovery Act) HITSP Harmonization Framework for reuse HITSP Capabilities • Information Exchanges Interface Standards Specifications HITSP Service Collaborations EHR SD RM Model – – – • 2008 Project Results 2009 HL 7 EHR SD RM Project plan AHIC Use Cases EHR-S FM HITSP Capabilities Next Steps 11
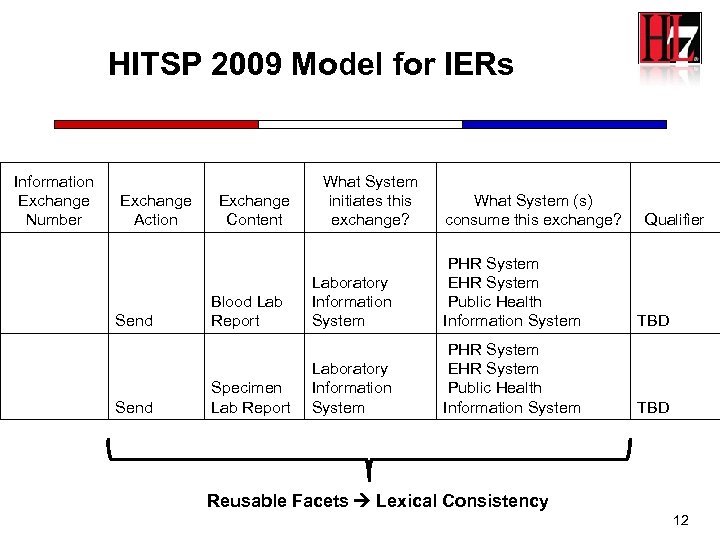
HITSP 2009 Model for IERs Information Exchange Number Exchange Action Send Exchange Content Blood Lab Report Specimen Lab Report What System initiates this exchange? What System (s) consume this exchange? Qualifier Laboratory Information System PHR System EHR System Public Health Information System TBD Reusable Facets Lexical Consistency 12

A new 2009 concept HITSP Capability • A HITSP capability is an implementable business service that specifies interoperable information exchanges using HITSP constructs. • It is meant to supports stakeholder requirements and as part of its design, it includes workflow, information content, infrastructure, security and privacy. • Capabilities include constraints and operate on specific network topologies (contexts) • Capabilities have options: subsets of the data content can be sent or received as appropriate by a system implementing a capability.
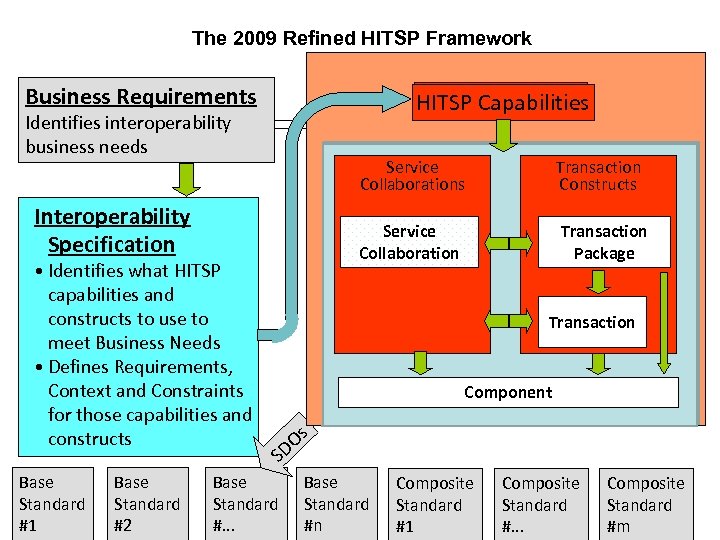
The 2009 Refined HITSP Framework Business Requirements Constructs HITSP Capabilities Identifies interoperability business needs Service Collaborations Interoperability Specification • Identifies what HITSP capabilities and constructs to use to meet Business Needs • Defines Requirements, Context and Constraints for those capabilities and constructs Base Standard #1 Base Standard #2 Transaction Constructs Transaction Package Service Collaboration Transaction Component Available for Component Internal reuse or repurposing Os D S Base Standard #. . . Base Standard #n Composite Standard #1 Composite Standard #. . . Composite Standard #m
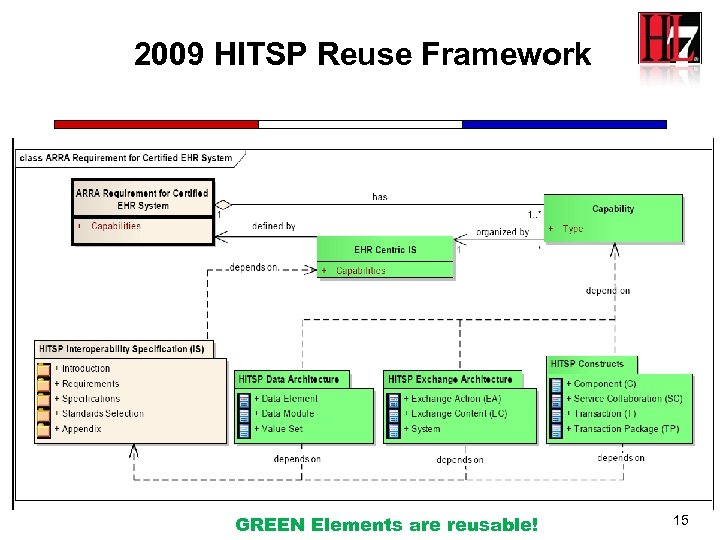
2009 HITSP Reuse Framework GREEN Elements are reusable! 15
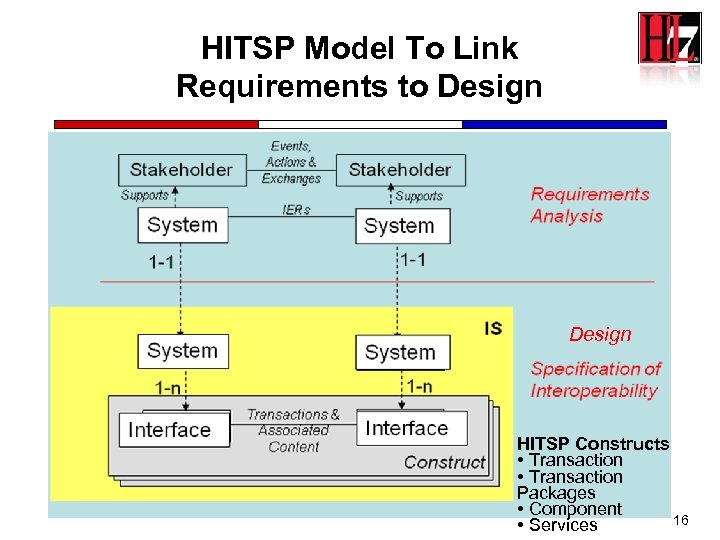
HITSP Model To Link Requirements to Design HITSP Constructs • Transaction Packages • Component 16 • Services
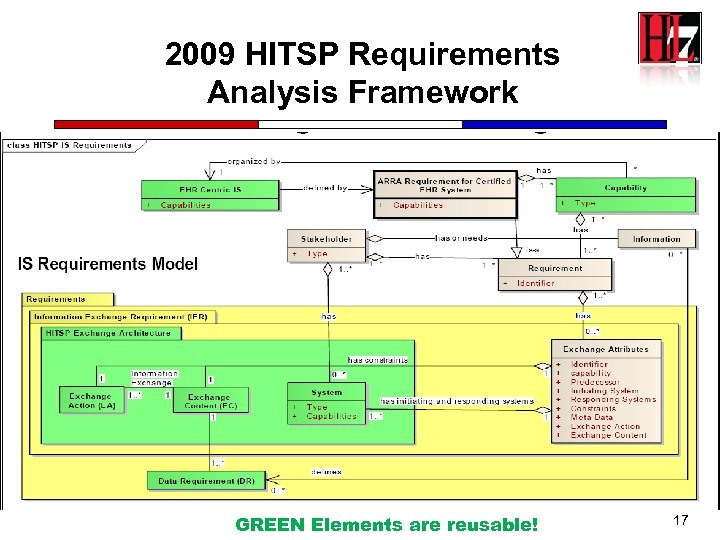
2009 HITSP Requirements Analysis Framework GREEN Elements are reusable! 17
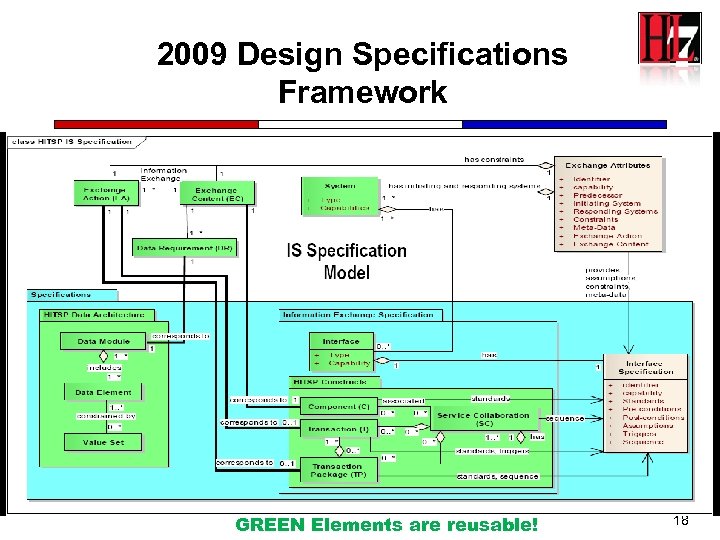
2009 Design Specifications Framework GREEN Elements are reusable! 18

HITSP List of Priority Information Exchanges 1. Demographics 8. Laboratory Results 2. Problem List 9. Microbiology 3. Medications 10. Images 4. Immunizations/ Adverse Event Reporting 11. Administrative Transactions 5. Allergies 6. Progress Notes and Other Narrative Documents (History and Physical, Operative Notes, Discharge Summary) 7. (Benefits/Eligibility, Referral/Authorization, Claims/Remittance) 12. Quality Measures 13. Privacy and Security Departmental Reports (Pathology/Cytology, GI, Pulmonary, Cardiology etc. ) 19

HITSP List of Priority Capabilities 1. HITSP/CAP 117 Communicate Ambulatory and 14. Long Term Care Prescription 2. HITSP/CAP 118 Communicate Hospital Prescription 3. 4. 5. HITSP/CAP 130 Communicate Quality Measure Specification 15. HITSP/CAP 131 Update Immunization Registry 16. HITSP/CAP 119 Communicate Structured Document HITSP/CAP 132 Retrieve Immunization Registry Information 17. HITSP/CAP 120 Communicate Unstructured Document HITSP/CAP 133 Communicate Immunization Summary 18. HITSP/CAP 135 Retrieve and Populate Form HITSP/CAP 136 Communicate Emergency Alert 6. HITSP/CAP 121 Communicate Clinical Referral 19. Request 20. HITSP/CAP 122 Retrieve Medical Knowledge 7. HITSP/CAP 123 Retrieve Existing Data HITSP/CAP 138 Retrieve Pseudonym 8. HITSP/CAP 124 Establish Secure Web Access 22. HITSP/CAP 125 Retrieve Genomic Decision 23. Support HITSP/CAP 139 Communicate Resource Utilization 10. HITSP/CAP 126 Communicate Lab Results Message 24. HITSP/CAP 141 Communicate Referral Authorization 11. HITSP/CAP 127 Communicate Lab Results 25. HITSP/CAP 142 Retrieve Communications 9. 21. HITSP/CAP 137 Communicate Encounter Information Message HITSP/CAP 140 Communicate Benefits and Eligibility 20
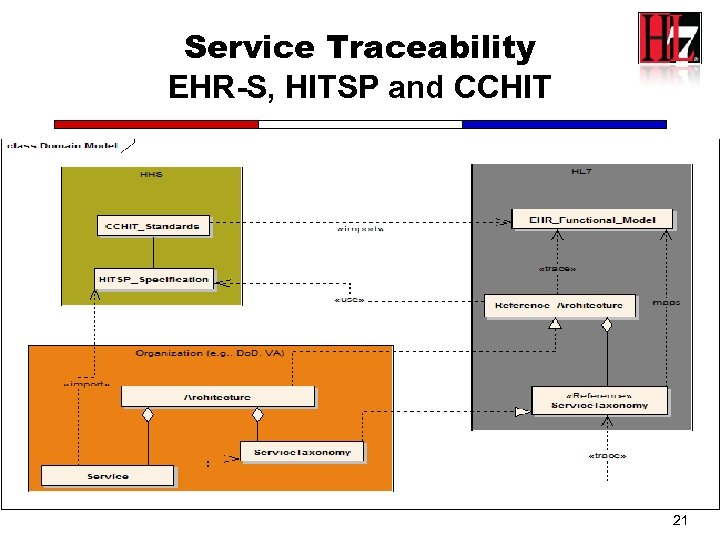
Service Traceability EHR-S, HITSP and CCHIT 21
Contents EHR System Design Reference Model (EHR-SD RM) • Background – – • What Changed in 2009 – – • Jan 2009 baseline project Sep 2009 Information Model (IM) additions 2010 EHR SD RM Model with HITSP Capabilities, IM & ARRA Vaccination and Adverse Event Reporting Prototype – – – • ARRA (American Reinvestment and Recovery Act) HITSP Harmonization Framework for reuse HITSP Capabilities • Information Exchanges Interface Standards Specifications HITSP Service Collaborations EHR SD RM Model – – – • 2008 Project Results 2009 HL 7 EHR SD RM Project plan AHIC Use Cases EHR-S FM HITSP Capabilities Next Steps 22
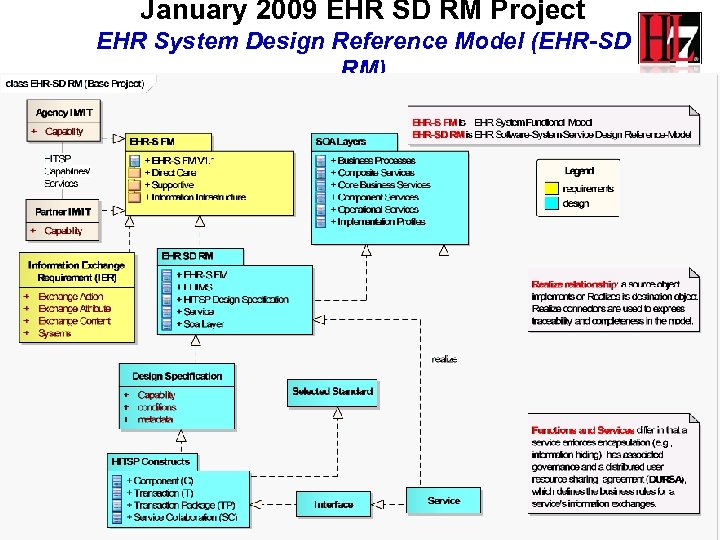
January 2009 EHR SD RM Project EHR System Design Reference Model (EHR-SD RM) 23
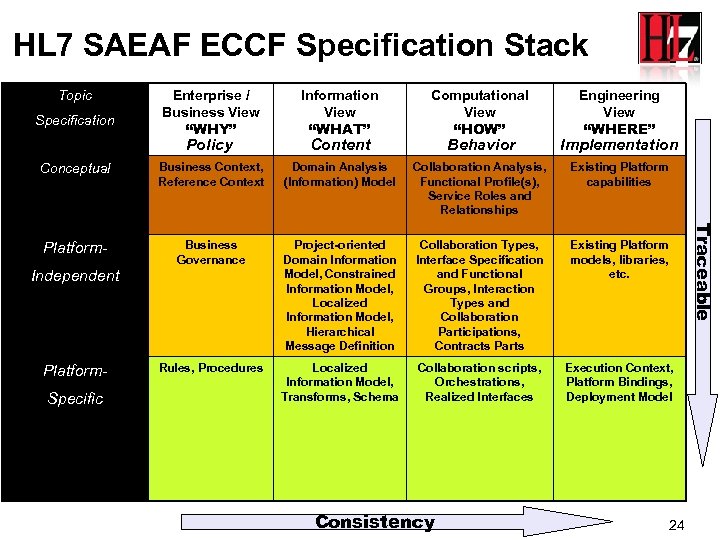
HL 7 SAEAF ECCF Specification Stack Topic Information View “WHAT” Computational View “HOW” Behavior Implementation Conceptual Business Context, Reference Context Domain Analysis (Information) Model Collaboration Analysis, Functional Profile(s), Service Roles and Relationships Existing Platform capabilities Platform- Business Governance Project-oriented Domain Information Model, Constrained Information Model, Localized Information Model, Hierarchical Message Definition Collaboration Types, Interface Specification and Functional Groups, Interaction Types and Collaboration Participations, Contracts Parts Existing Platform models, libraries, etc. Rules, Procedures Localized Information Model, Transforms, Schema Collaboration scripts, Orchestrations, Realized Interfaces Execution Context, Platform Bindings, Deployment Model Specification Policy Independent Platform. Specific Content Consistency Engineering View “WHERE” Traceable Enterprise / Business View “WHY” 24
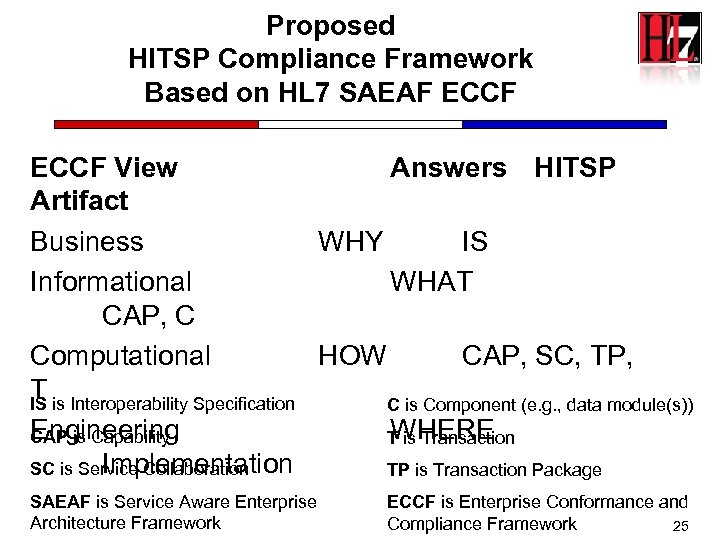
Proposed HITSP Compliance Framework Based on HL 7 SAEAF ECCF View Answers HITSP Artifact Business WHY IS Informational WHAT CAP, C Computational HOW CAP, SC, TP, T IS is Interoperability Specification C is Component (e. g. , data module(s)) Engineering WHERE CAP is Capability T is Transaction Implementation SC is Service Collaboration TP is Transaction Package SAEAF is Service Aware Enterprise Architecture Framework ECCF is Enterprise Conformance and Compliance Framework 25
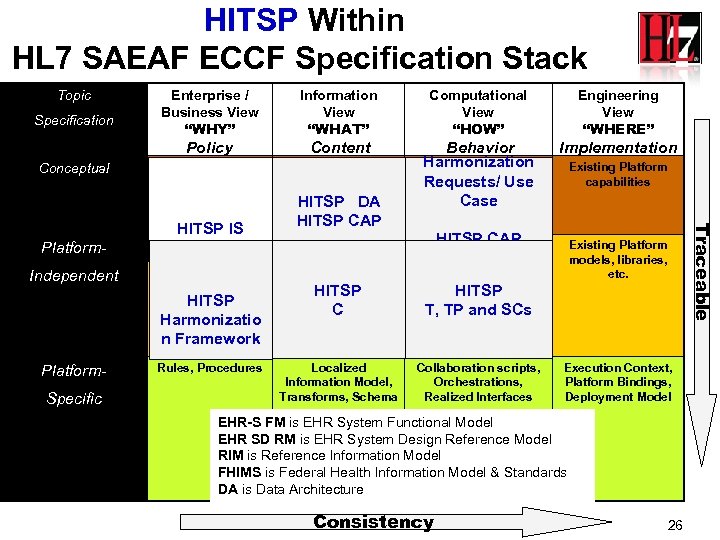
HITSP Within HL 7 SAEAF ECCF Specification Stack Topic Conceptual Information View “WHAT” Policy Specification Enterprise / Business View “WHY” Content Business Context, Reference Context Domain Analysis (Information) Model Platform- Business Governance Independent HITSP Harmonizatio n Framework Platform. Specific Rules, Procedures Engineering View “WHERE” Behavior Implementation Harmonization Collaboration Analysis, Existing Platform Functional Profile(s), capabilities Requests/ Use Service Roles and Case Relationships Project-oriented Domain Information Model, Constrained Information Model, HITSP Localized C Information Model, Hierarchical Message Definition HITSP CAP Collaboration Types, Interface Specification and Functional Groups, Interaction HITSP Types and T, Collaboration TP and SCs Participations, Contracts Parts Localized Information Model, Transforms, Schema Collaboration scripts, Orchestrations, Realized Interfaces Traceable HITSP IS HITSP DA HITSP CAP Computational View “HOW” Existing Platform models, libraries, etc. Execution Context, Platform Bindings, Deployment Model EHR-S FM is EHR System Functional Model EHR SD RM is EHR System Design Reference Model RIM is Reference Information Model FHIMS is Federal Health Information Model & Standards DA is Data Architecture Consistency 26
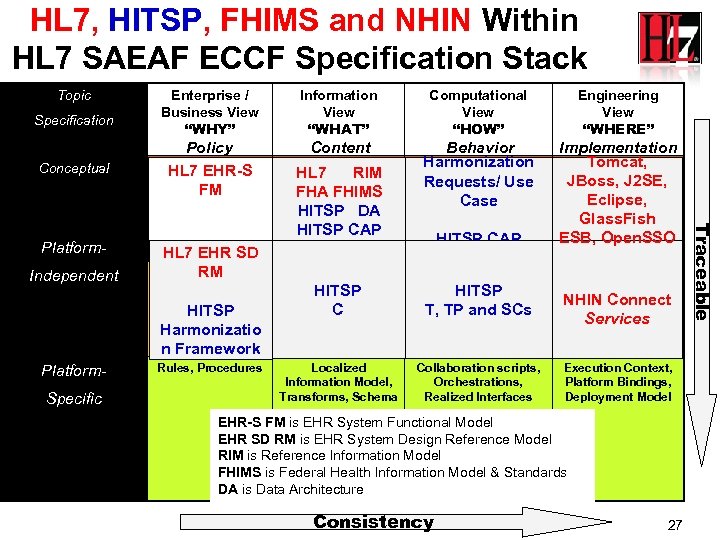
HL 7, HITSP, FHIMS and NHIN Within HL 7 SAEAF ECCF Specification Stack Topic Specification Conceptual Independent Information View “WHAT” Policy Business Context, HL 7 EHR-S Reference Context FM Content Business HITSP SD HL 7 EHRIS Governance RM HITSP Harmonizatio n Framework Platform. Specific Rules, Procedures Domain Analysis HL 7 RIM (Information) Model FHA FHIMS HITSP DA HITSP CAP Project-oriented Domain Information Model, Constrained Information Model, HITSP Localized C Information Model, Hierarchical Message Definition Localized Information Model, Transforms, Schema Computational View “HOW” Engineering View “WHERE” Behavior Implementation Tomcat, Harmonization Collaboration Analysis, Existing Platform Functional Profile(s), capabilities JBoss, J 2 SE, Requests/ Use Service Roles and Eclipse, Case Relationships Glass. Fish ESB, Open. SSO HITSP CAP Collaboration Types, Existing Platform Interface Specification and Functional Groups, Interaction HITSP Types and T, Collaboration TP and SCs Participations, Contracts Parts models, libraries, etc. NHIN Connect Services Collaboration scripts, Orchestrations, Realized Interfaces Execution Context, Platform Bindings, Deployment Model EHR-S FM is EHR System Functional Model EHR SD RM is EHR System Design Reference Model RIM is Reference Information Model FHIMS is Federal Health Information Model & Standards DA is Data Architecture Consistency 27 Traceable Platform- Enterprise / Business View “WHY”
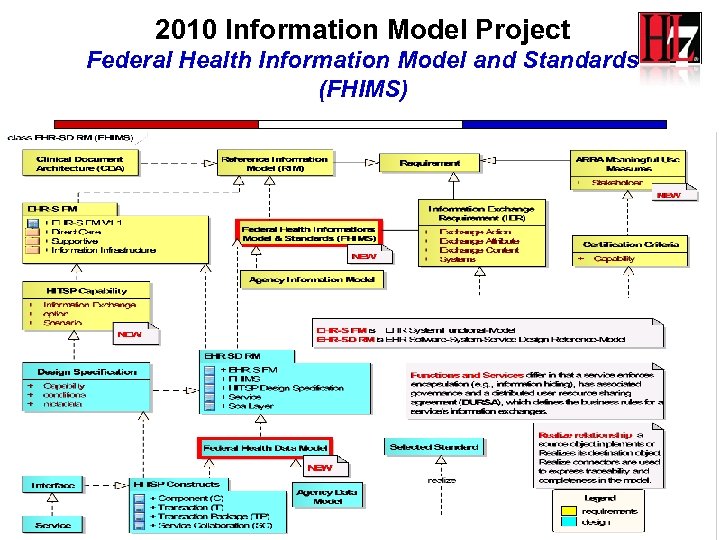
2010 Information Model Project Federal Health Information Model and Standards (FHIMS) 28

2010 Project Integrated EHR-SD RM, FHIMS, HITSP Capabilities and ARRA Meaningful Use 29
Benefits 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Faster, Better, Cheaper Integrated Requirements-Design Process Strategic Plan based on International and National Standards Objective Investment Portfolio Cost Estimation Minimize the Chance of Year of Execution Unfunded Requirements (UFRs) IM and IT aligned on Consistent Catalogue of Services MHS EHR Interoperability alignment with National Agenda 1. Manage Care Support Contractor (MCSC) interoperability 2. VA interoperability 30 Consistent with Enterprise Architecture

Prototype Approach • Build Integrated Requirements Design CONOPS package based on – Service Oriented Architecture categorized and populated by • Candidate Services Derived from following Thomas Erl’s Service Oriented Design Principles • HL 7 EHR System Functional Model Requirements and 31
Contents EHR System Design Reference Model (EHR-SD RM) • Background – – • What Changed in 2009 – – • Jan 2009 baseline project Sep 2009 Information Model (IM) additions 2010 EHR SD RM Model with HITSP Capabilities, IM & ARRA Vaccination and Adverse Event Reporting Prototype – – – • ARRA (American Reinvestment and Recovery Act) HITSP Harmonization Framework for reuse HITSP Capabilities • Information Exchanges Interface Standards Specifications HITSP Service Collaborations EHR SD RM Model – – – • 2008 Project Results 2009 HL 7 EHR SD RM Project plan AHIC Use Cases EHR-S FM HITSP Capabilities Next Steps 32

EHR-SD RM Prototype Requirements from 2008 AHIC Use Cases • • Use Case 1: Immunization and Response Management (IRM) and Use Case 2: Public Health Case Reporting (PHCR) – – The IRM AHIC Use Case and HITSP Interoperability Specification are intended to support current interoperability approaches between EHRs and Immunization Information Systems while allowing for a migration toward emerging interoperability implementations and document sharing environments where PHRs are able to be included in the information flow The Interoperability Specification also allows for basic electronic information exchanges to enable requirement communications and alerting mechanisms and to lay the foundation for future clinical support capabilities The Public Health Case Reporting AHIC Use Case and HITSP Interoperability Specification supports the bi-directional information exchanges of the Public Health Case Reporting process The Public Health Case Reporting Use Case addresses numerous domains which have similar content and processes at a high level, but 33
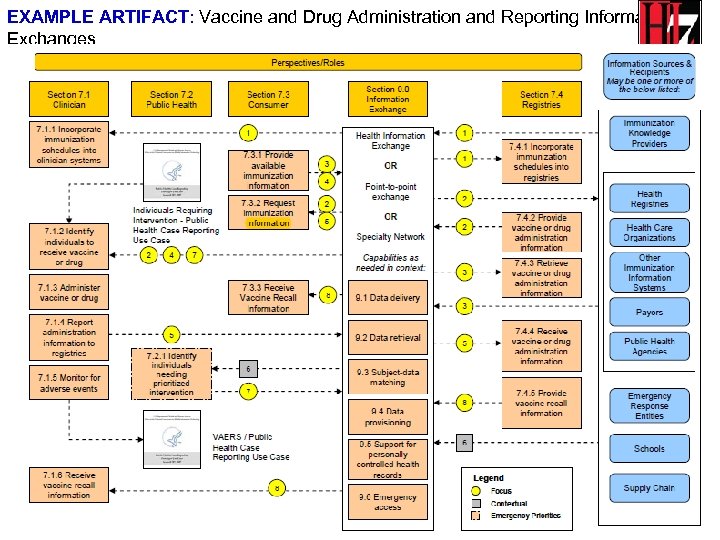
EXAMPLE ARTIFACT: Vaccine and Drug Administration and Reporting Information Exchanges 34

EXAMPLE ARTIFACT Vaccine and Drug Administration and Reporting Use Case Full use case available at: http: //healthit. hhs. gov/portal/server. pt? open=512&obj. ID=1255&parentname=Community. Page&parentid=1&mode=2&in_hi_userid= 10741&cached=true 35
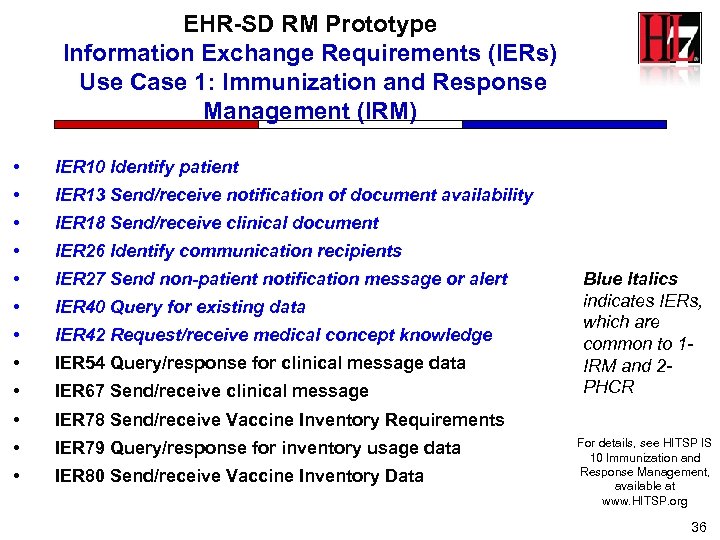
EHR-SD RM Prototype Information Exchange Requirements (IERs) Use Case 1: Immunization and Response Management (IRM) • IER 10 Identify patient • IER 13 Send/receive notification of document availability • IER 18 Send/receive clinical document • IER 26 Identify communication recipients • IER 27 Send non-patient notification message or alert • IER 40 Query for existing data • IER 42 Request/receive medical concept knowledge • IER 54 Query/response for clinical message data • IER 67 Send/receive clinical message • IER 78 Send/receive Vaccine Inventory Requirements • IER 79 Query/response for inventory usage data • IER 80 Send/receive Vaccine Inventory Data Blue Italics indicates IERs, which are common to 1 IRM and 2 PHCR For details, see HITSP IS 10 Immunization and Response Management, available at www. HITSP. org 36
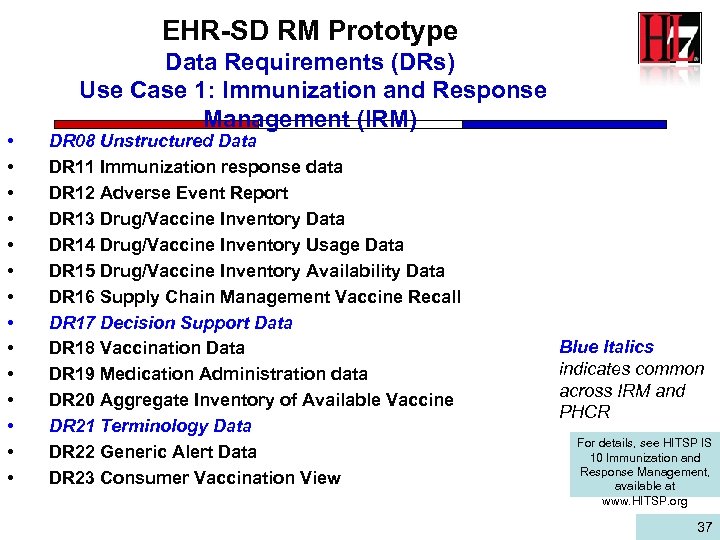
EHR-SD RM Prototype • • • • Data Requirements (DRs) Use Case 1: Immunization and Response Management (IRM) DR 08 Unstructured Data DR 11 Immunization response data DR 12 Adverse Event Report DR 13 Drug/Vaccine Inventory Data DR 14 Drug/Vaccine Inventory Usage Data DR 15 Drug/Vaccine Inventory Availability Data DR 16 Supply Chain Management Vaccine Recall DR 17 Decision Support Data DR 18 Vaccination Data DR 19 Medication Administration data DR 20 Aggregate Inventory of Available Vaccine DR 21 Terminology Data DR 22 Generic Alert Data DR 23 Consumer Vaccination View Blue Italics indicates common across IRM and PHCR For details, see HITSP IS 10 Immunization and Response Management, available at www. HITSP. org 37 37
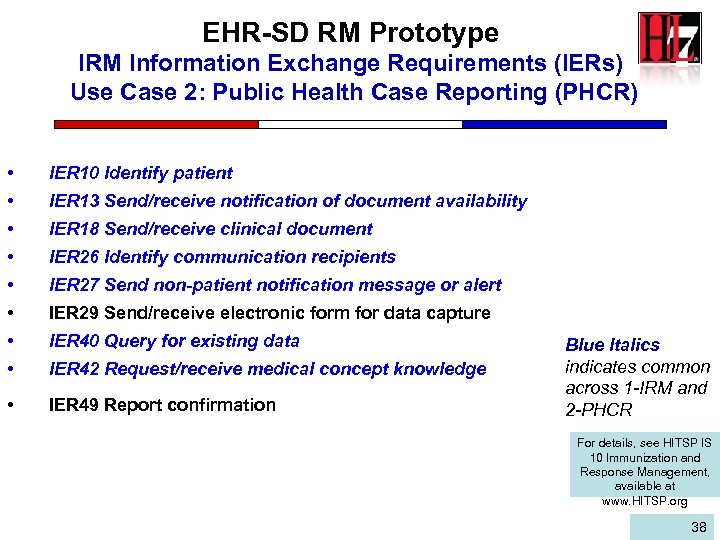
EHR-SD RM Prototype IRM Information Exchange Requirements (IERs) Use Case 2: Public Health Case Reporting (PHCR) • IER 10 Identify patient • IER 13 Send/receive notification of document availability • IER 18 Send/receive clinical document • IER 26 Identify communication recipients • IER 27 Send non-patient notification message or alert • IER 29 Send/receive electronic form for data capture • IER 40 Query for existing data • IER 42 Request/receive medical concept knowledge • IER 49 Report confirmation Blue Italics indicates common across 1 -IRM and 2 -PHCR For details, see HITSP IS 10 Immunization and Response Management, available at www. HITSP. org 38 38
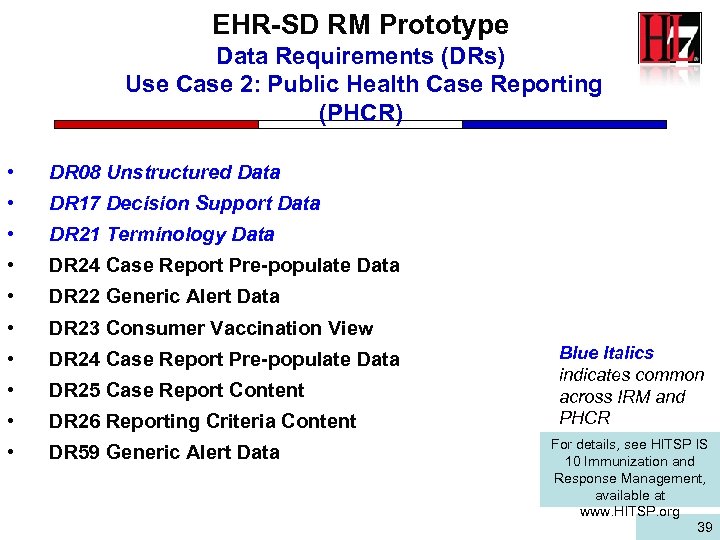
EHR-SD RM Prototype Data Requirements (DRs) Use Case 2: Public Health Case Reporting (PHCR) • DR 08 Unstructured Data • DR 17 Decision Support Data • DR 21 Terminology Data • DR 24 Case Report Pre-populate Data • DR 22 Generic Alert Data • DR 23 Consumer Vaccination View • DR 24 Case Report Pre-populate Data • DR 25 Case Report Content • DR 26 Reporting Criteria Content • DR 59 Generic Alert Data Blue Italics indicates common across IRM and PHCR For details, see HITSP IS 10 Immunization and Response Management, available at www. HITSP. org 39 39
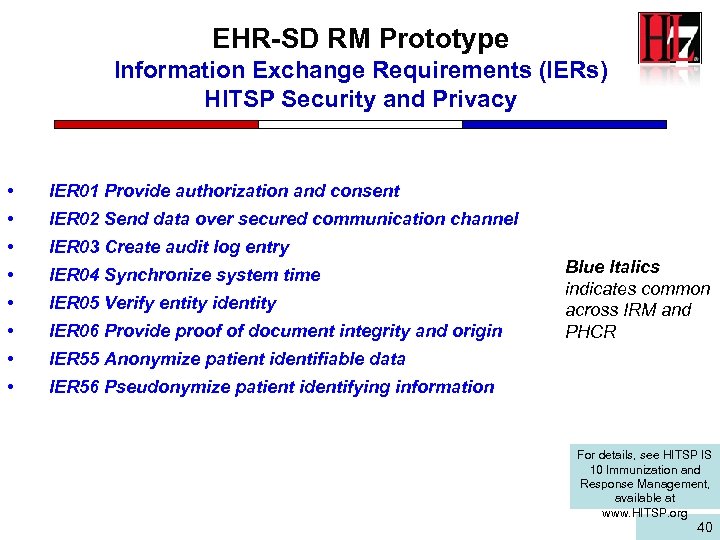
EHR-SD RM Prototype Information Exchange Requirements (IERs) HITSP Security and Privacy • IER 01 Provide authorization and consent • IER 02 Send data over secured communication channel • IER 03 Create audit log entry • IER 04 Synchronize system time • IER 05 Verify entity identity • IER 06 Provide proof of document integrity and origin • IER 55 Anonymize patient identifiable data • IER 56 Pseudonymize patient identifying information Blue Italics indicates common across IRM and PHCR For details, see HITSP IS 10 Immunization and Response Management, available at www. HITSP. org 40 40
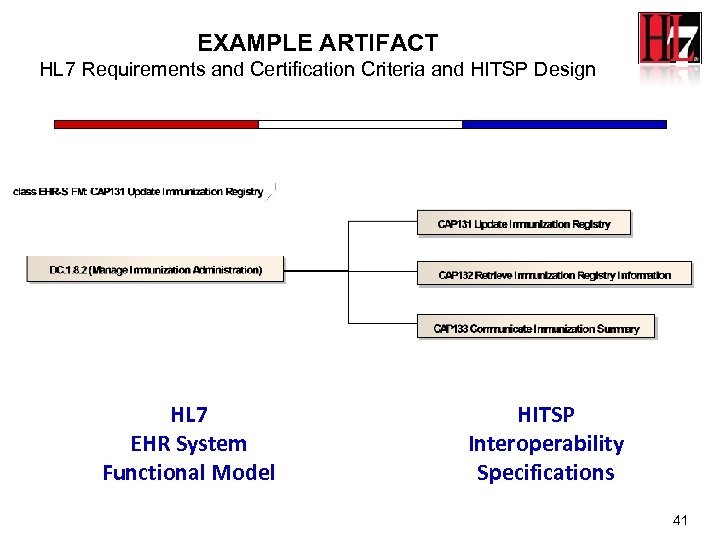
EXAMPLE ARTIFACT HL 7 Requirements and Certification Criteria and HITSP Design HL 7 EHR System Functional Model HITSP Interoperability Specifications 41
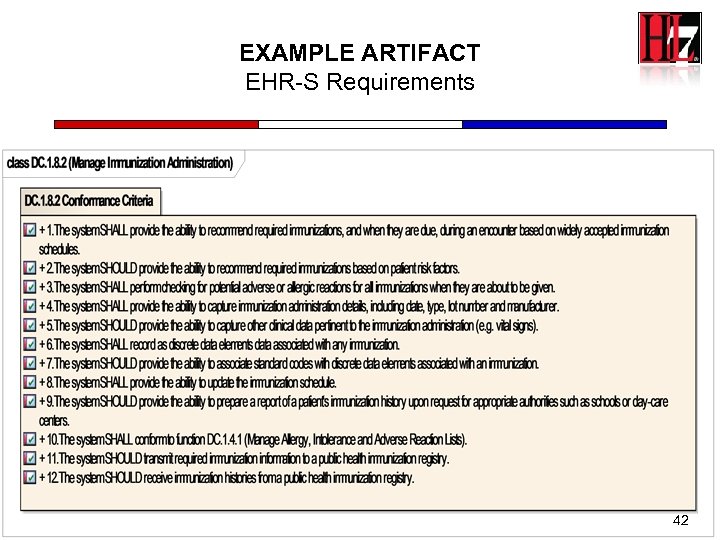
EXAMPLE ARTIFACT EHR-S Requirements 42
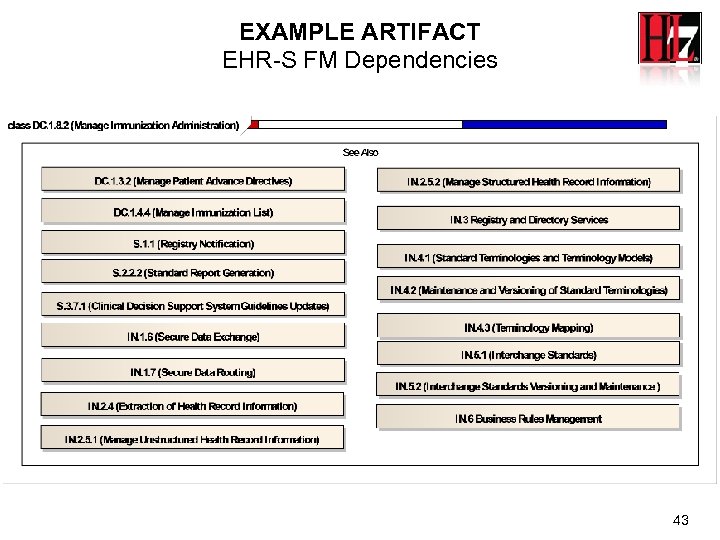
EXAMPLE ARTIFACT EHR-S FM Dependencies 43
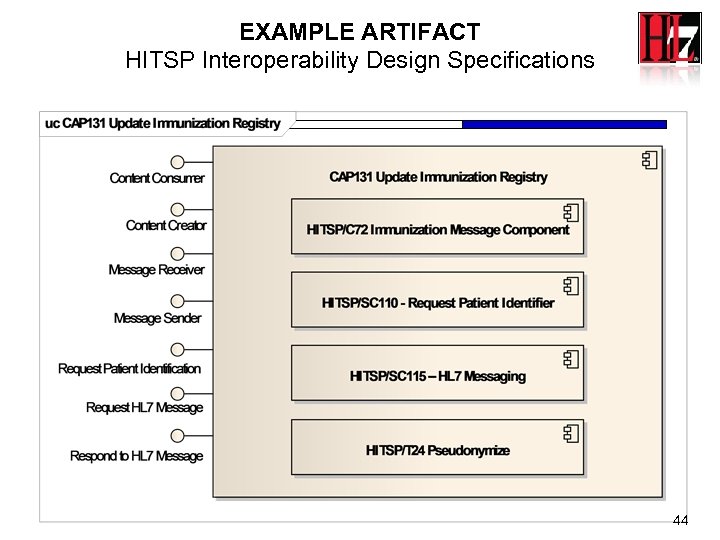
EXAMPLE ARTIFACT HITSP Interoperability Design Specifications 44
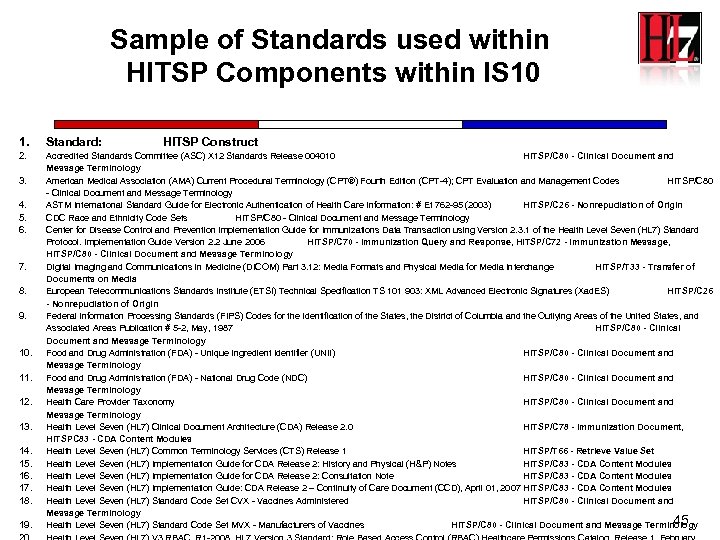
Sample of Standards used within HITSP Components within IS 10 1. Standard: 2. Accredited Standards Committee (ASC) X 12 Standards Release 004010 HITSP/C 80 - Clinical Document and Message Terminology American Medical Association (AMA) Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) Fourth Edition (CPT-4); CPT Evaluation and Management Codes HITSP/C 80 - Clinical Document and Message Terminology ASTM International Standard Guide for Electronic Authentication of Health Care Information: # E 1762 -95 (2003) HITSP/C 26 - Nonrepudiation of Origin CDC Race and Ethnicity Code Sets HITSP/C 80 - Clinical Document and Message Terminology Center for Disease Control and Prevention Implementation Guide for Immunizations Data Transaction using Version 2. 3. 1 of the Health Level Seven (HL 7) Standard Protocol. Implementation Guide Version 2. 2 June 2006 HITSP/C 70 - Immunization Query and Response, HITSP/C 72 - Immunization Message, HITSP/C 80 - Clinical Document and Message Terminology Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) Part 3. 12: Media Formats and Physical Media for Media Interchange HITSP/T 33 - Transfer of Documents on Media European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) Technical Specification TS 101 903: XML Advanced Electronic Signatures (Xad. ES) HITSP/C 26 - Nonrepudiation of Origin Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) Codes for the Identification of the States, the District of Columbia and the Outlying Areas of the United States, and Associated Areas Publication # 5 -2, May, 1987 HITSP/C 80 - Clinical Document and Message Terminology Food and Drug Administration (FDA) - Unique Ingredient Identifier (UNII) HITSP/C 80 - Clinical Document and Message Terminology Food and Drug Administration (FDA) - National Drug Code (NDC) HITSP/C 80 - Clinical Document and Message Terminology Health Care Provider Taxonomy HITSP/C 80 - Clinical Document and Message Terminology Health Level Seven (HL 7) Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) Release 2. 0 HITSP/C 78 - Immunization Document, HITSPC 83 - CDA Content Modules Health Level Seven (HL 7) Common Terminology Services (CTS) Release 1 HITSP/T 66 - Retrieve Value Set Health Level Seven (HL 7) Implementation Guide for CDA Release 2: History and Physical (H&P) Notes HITSP/C 83 - CDA Content Modules Health Level Seven (HL 7) Implementation Guide for CDA Release 2: Consultation Note HITSP/C 83 - CDA Content Modules Health Level Seven (HL 7) Implementation Guide: CDA Release 2 – Continuity of Care Document (CCD), April 01, 2007 HITSP/C 83 - CDA Content Modules Health Level Seven (HL 7) Standard Code Set CVX - Vaccines Administered HITSP/C 80 - Clinical Document and Message Terminology 45 Health Level Seven (HL 7) Standard Code Set MVX - Manufacturers of Vaccines HITSP/C 80 - Clinical Document and Message Terminology 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. HITSP Construct

Work Plans EHR-SD RM Next Steps 1. EHR SD RM Framework – 2. Information Model – – 3. 4. 5. 6. Populate the framework with candidate healthcare Information Exchanges/ capabilities/ services, based on HL 7 EHR-S Functional Model Loosely-coupled top-down Framework Rigorously specified bottom up structure/ content Publish HL 7 HSSP Practical Guide for SOA in Healthcare Part 2: Case Study Socialize EHR SD RM Collaborate with others Informative ballot in 2010 46

Questions? ? What was omitted? Suggestions for improvement? How should the model be represented? What should be balloted in 2010? 47

Questions? Contact us: • Nancy. Orvis@tma. osd. mil • Stephen. Hufnagel. ctr@tma. osd. mil Project info available at: • http: //hitsp. wikispaces. com/HITSP+MODEL • http: //hssp. wikispaces. com/Reference+Architecture 48
Backup 49
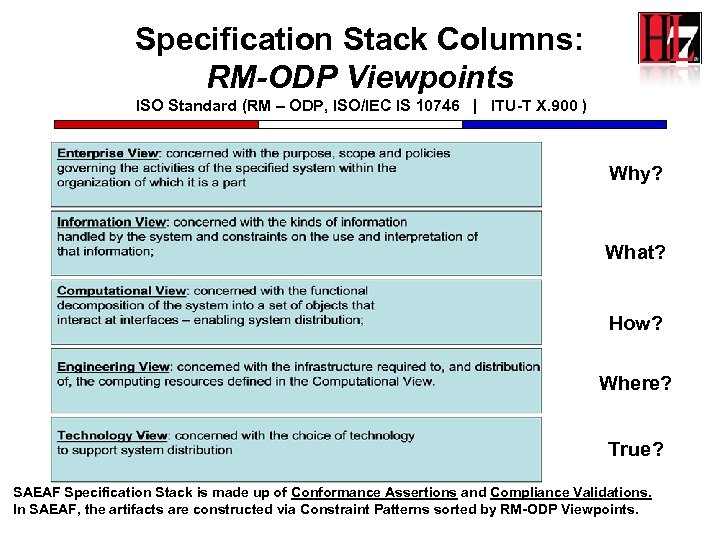
Specification Stack Columns: RM-ODP Viewpoints ISO Standard (RM – ODP, ISO/IEC IS 10746 | ITU-T X. 900 ) Why? What? How? Where? True? SAEAF Specification Stack is made up of Conformance Assertions and Compliance Validations. In SAEAF, the artifacts are constructed via Constraint Patterns sorted by RM-ODP Viewpoints.
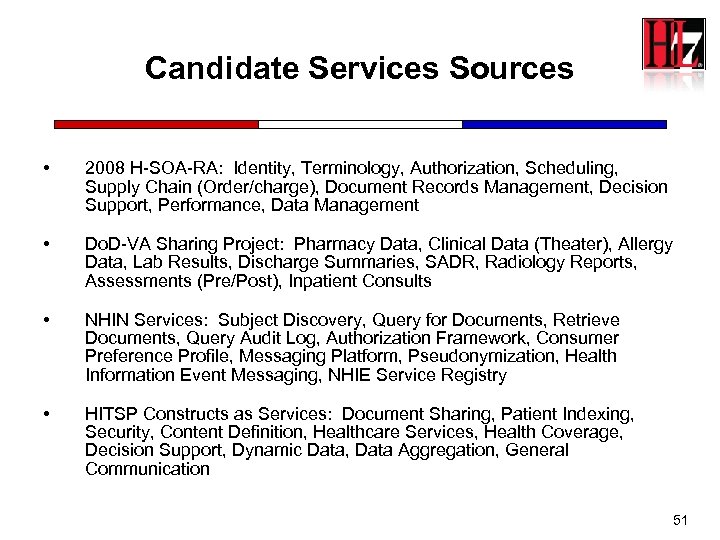
Candidate Services Sources • 2008 H-SOA-RA: Identity, Terminology, Authorization, Scheduling, Supply Chain (Order/charge), Document Records Management, Decision Support, Performance, Data Management • Do. D-VA Sharing Project: Pharmacy Data, Clinical Data (Theater), Allergy Data, Lab Results, Discharge Summaries, SADR, Radiology Reports, Assessments (Pre/Post), Inpatient Consults • NHIN Services: Subject Discovery, Query for Documents, Retrieve Documents, Query Audit Log, Authorization Framework, Consumer Preference Profile, Messaging Platform, Pseudonymization, Health Information Event Messaging, NHIE Service Registry • HITSP Constructs as Services: Document Sharing, Patient Indexing, Security, Content Definition, Healthcare Services, Health Coverage, Decision Support, Dynamic Data, Data Aggregation, General Communication 51

2008 Results Healthcare SOA Reference Architecture H-SOA-RA • H-SOA-RA: Overall Goal – Service Traceability – EHR System Functional Model (EHR-S) – Healthcare SOA Reference Architecture – Notional Functional Example 52
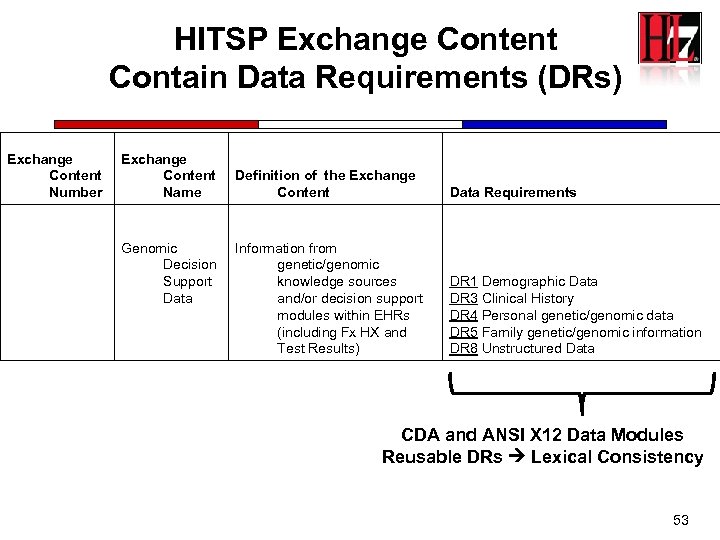
HITSP Exchange Content Contain Data Requirements (DRs) Exchange Content Number Exchange Content Name Genomic Decision Support Data Definition of the Exchange Content Data Requirements Information from genetic/genomic knowledge sources and/or decision support modules within EHRs (including Fx HX and Test Results) DR 1 Demographic Data DR 3 Clinical History DR 4 Personal genetic/genomic data DR 5 Family genetic/genomic information DR 8 Unstructured Data CDA and ANSI X 12 Data Modules Reusable DRs Lexical Consistency 53
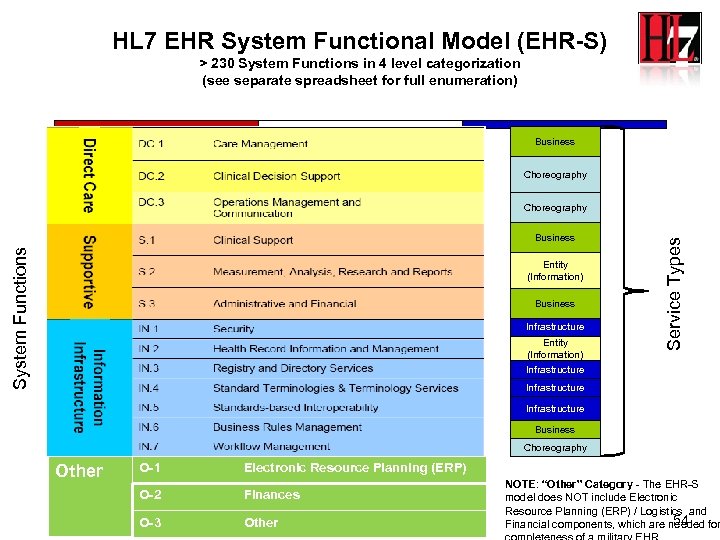
HL 7 EHR System Functional Model (EHR-S) > 230 System Functions in 4 level categorization (see separate spreadsheet for full enumeration) Business Choreography System Functions Business Entity (Information) Business Infrastructure Entity (Information) Infrastructure Service Types Choreography Infrastructure Business Choreography Other O-1 Electronic Resource Planning (ERP) O-2 Finances O-3 Other NOTE: “Other” Category - The EHR-S model does NOT include Electronic Resource Planning (ERP) / Logistics and 54 Financial components, which are needed for
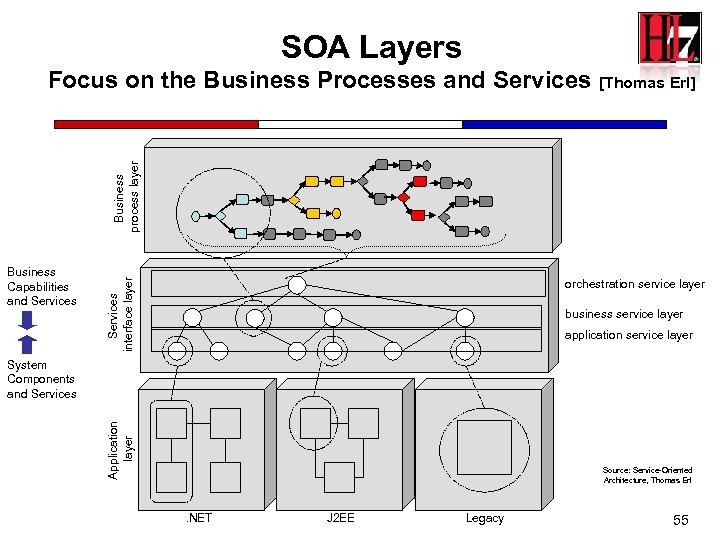
SOA Layers Business Capabilities and Services interface layer Business process layer Focus on the Business Processes and Services [Thomas Erl] orchestration service layer business service layer application service layer Application layer System Components and Services Source: Service-Oriented Architecture, Thomas Erl . NET J 2 EE Legacy 55
![SOA Service Models Potential Service Layers [Thomas Erl] Service Model Application Service Business Service SOA Service Models Potential Service Layers [Thomas Erl] Service Model Application Service Business Service](https://present5.com/presentation/1be89aaff29f2c029d3b19c5657af08e/image-56.jpg)
SOA Service Models Potential Service Layers [Thomas Erl] Service Model Application Service Business Service Controller Service Coordinator Services Description A generic category used to represent services that contain logic derived from a solution or technical platform. Services are generally distinguished as application services when creating abstraction layers. A generic category used to represent services that contain business logic. When establishing specialized service layers, services that fall into the business service layers are collectively referred to as business. However, individually these services are classified as entity-centric (e. g. , information) or task-centric business services. A Service that composes others. Variations of this model exist, depending on the position of the controller in the composition hierarchy. The patent controller service can be classified as the master controller and a service that composes a subset of a larger composition can be labeled as sub-controller. Three service models are derived from the concept of coordination: the coordinator, the atomic transaction coordinator, and the business activity coordinator. All three models are specific to the WS-Coordination specification and related protocols. 56
![SOA Service Models Potential Service Layers [Thomas Erl] (cont) Service Model Description Entity-centric Business SOA Service Models Potential Service Layers [Thomas Erl] (cont) Service Model Description Entity-centric Business](https://present5.com/presentation/1be89aaff29f2c029d3b19c5657af08e/image-57.jpg)
SOA Service Models Potential Service Layers [Thomas Erl] (cont) Service Model Description Entity-centric Business Service A business process-agnostic variation of the business service that represents one or more related business entities. This type of service is created when establishing a business service layer. Hybrid Service A service that contains both business and application logic. Most services created as part of traditional distributed solutions fall into this category. When organizing services into abstraction layers, hybrid services are considered part of the application service layer. Integration Service An application service that also acts as an endpoint to a solution for cross-referencing integration purposes. Process Service A service that represents a business process as implemented by an orchestration platform and described by a process definition. Process services reside in the orchestration service layer. Task-Centric Business Service A business process-specific variation of the business service that represents an atomic unit of process logic. Task-centric services are different from process services in that the process logic is provided by the underlying service logic, not by a separate process definition. 57
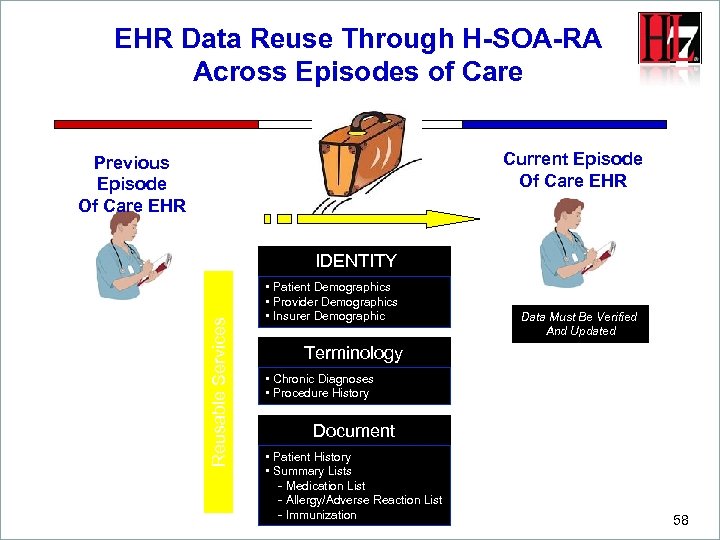
EHR Data Reuse Through H-SOA-RA Across Episodes of Care Current Episode Of Care EHR Previous Episode Of Care EHR Reusable Services IDENTITY • Patient Demographics • Provider Demographics • Insurer Demographic Data Must Be Verified And Updated Terminology • Chronic Diagnoses • Procedure History Document • Patient History • Summary Lists - Medication List - Allergy/Adverse Reaction List - Immunization 58
![Federated Services [1] • • Federation is a state achieved by extending SOA into Federated Services [1] • • Federation is a state achieved by extending SOA into](https://present5.com/presentation/1be89aaff29f2c029d3b19c5657af08e/image-59.jpg)
Federated Services [1] • • Federation is a state achieved by extending SOA into the realm of service-oriented integration • A number of key WS-* extensions provide feature-sets that support the attainment of federation • Most notable among these are the specifications that implement the concepts of orchestration and choreography Establishing SOA within an enterprise does not necessarily require that you replace what you already have • One of the most attractive aspects of this architecture is its ability to introduce unity across previously non-federated environments • While web-services enable federation, SOA promotes this cause by establishing and standardizing the ability to encapsulate legacy and non-legacy application logic and by exposing it via a common, open, and standardized communications framework • WSRP (Web Services for Remote Portals) is the cornerstone of federated services • SAML (Security Assertions Markup Language) is commonly used • ALSO: WS-Security, WS-Trust, WS-Policy, WS-Federation • Additional info at: https: //www 120. livemeeting. com/cc/bea/view. Reg [1] SOA: Principles of Service Design, by Thomas Erl, Prentice 59
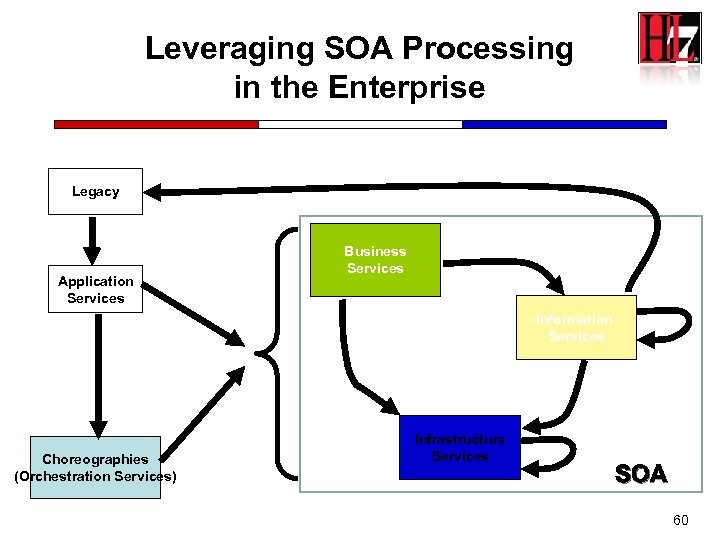
Leveraging SOA Processing in the Enterprise Legacy Application Services Business Services Information Services Choreographies (Orchestration Services) Infrastructure Services SOA 60
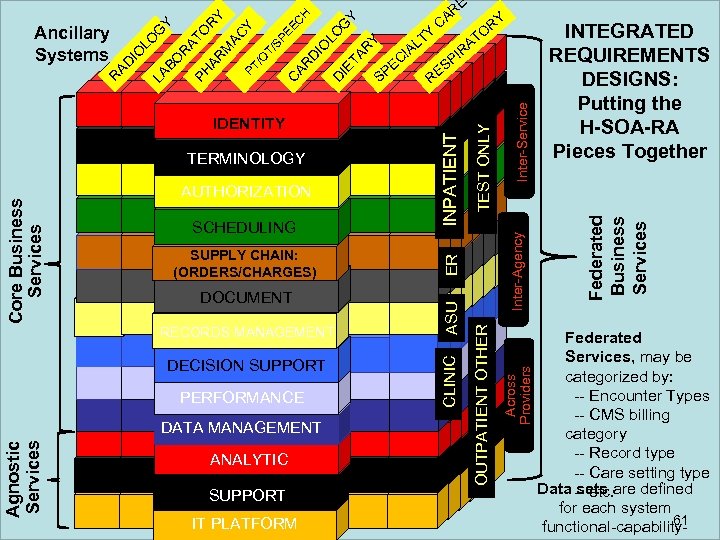
DOCUMENT RECORDS MANAGEMENT DECISION SUPPORT PERFORMANCE Agnostic Services DATA MANAGEMENT ANALYTIC SUPPORT IT PLATFORM ER SUPPLY CHAIN: (ORDERS/CHARGES) ASU AUTHORIZATION SCHEDULING CLINIC Core Business Services TERMINOLOGY INPATIENT IDENTITY INTEGRATED REQUIREMENTS DESIGNS: Putting the H-SOA-RA Pieces Together Federated Business Services R Inter-Service S I P ES Inter-Agency TA R I C PE O AT R Across Providers Y LO D IE IO T AL RY TEST ONLY G Y OUTPATIENT OTHER Y C H EE C AR D SP T/ T/ O BO R AT PH O R AR Y M AC P Y G LO LA R AD IO Ancillary Systems Y E R CA Federated Services, may be categorized by: -- Encounter Types -- CMS billing category -- Record type -- Care setting type Data sets are defined -- etc. for each system 61 functional-capability-
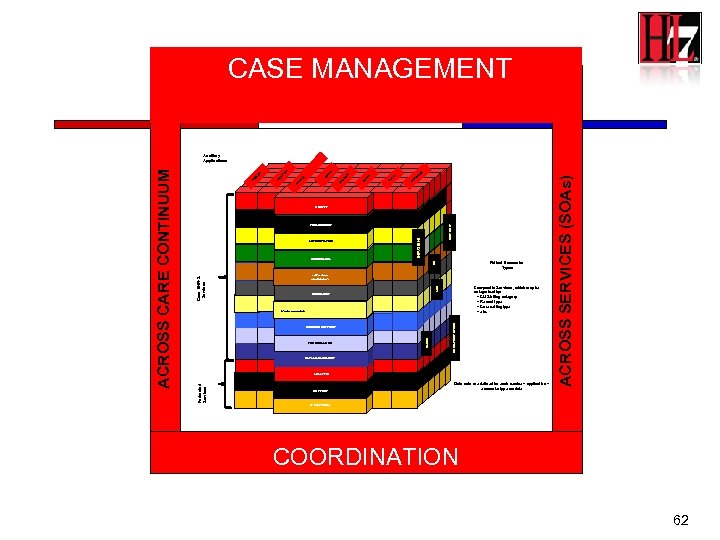
CASE MANAGEMENT H C EE TA IE RY PH C D IO D AR M AR R LO /O PT Y AC Y T/ G H Y SP AT R BO LA AT IR SP RE TEST ONLY AUTHORIZATION Patient Encounter Types ER SCHEDULING INPATIENT TERMINOLOGY Composite Services, which may be categorized by: -- CMS billing category -- Record type -- Care setting type -- etc. ASU Core EHR-S Services SUPPLY CHAIN: (ORDER/CHARGE) DOCUMENT DECISION SUPPORT CLINIC PERFORMANCE OUTPATIENT OTHER RECORDS MANAGEMENT DATA MANAGEMENT ANALYTIC SUPPORT Data sets are defined for each service – application – encounter type module ACROSS SERVICES (SOAs) Y R O Y G LO IO AD R O RE CA Y LT IA EC SP IDENTITY Federated Services ACROSS CARE CONTINUUM Ancillary Applications IT PLATFORM COORDINATION 62
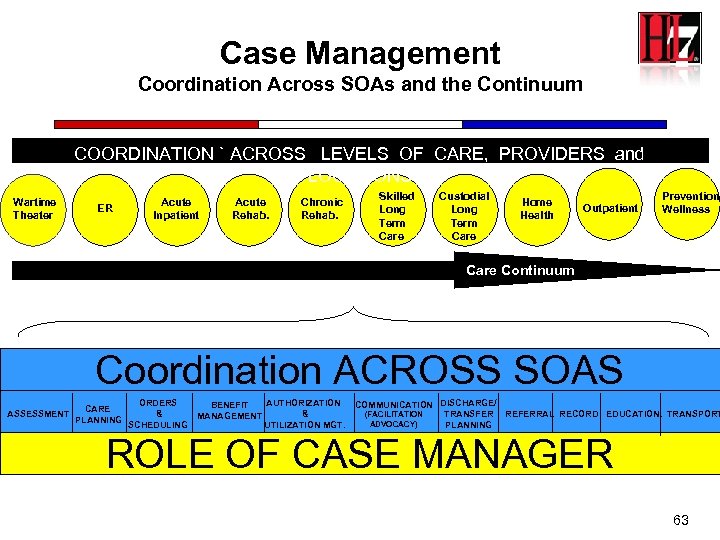
Case Management Coordination Across SOAs and the Continuum c COORDINATION ` ACROSS LEVELS OF CARE, PROVIDERS and LOCATIONS Wartime Theater ER Acute Inpatient Acute Rehab. Chronic Rehab. Skilled Long Term Care Custodial Long Term Care Home Health Outpatient Prevention/ Wellness Care Continuum Coordination ACROSS SOAS ASSESSMENT CARE PLANNING ORDERS & SCHEDULING AUTHORIZATION BENEFIT & MANAGEMENT UTILIZATION MGT. COMMUNICATION DISCHARGE/ TRANSFER REFERRAL RECORD EDUCATION. TRANSPORT (FACILITATION ADVOCACY) PLANNING ROLE OF CASE MANAGER 63

Potential Benefits: Process Improvement through H-SOA-RA Elimination of Process Obstacles would result in: – – – – Length of Stay Reduction Improved Patient Outcomes / Reduced Risk Revenue Improvement Staff Efficiencies Improved Patient and Staff Satisfaction Reduced IT Expenditure/Maintenance Costs Improved Information Accuracy and Availability 64

Addressing Real Business Issues Through H-SOA-RA • Incomplete/Inaccurate Demographic Data – Identity Service • Incomplete/Inaccurate Insurance Information – Authorization Service • Unauthorized Service – Authorization Service • Diagnosis/Procedure Coding Errors – Terminology Service • Service Delays – Scheduling Service • Incomplete and Inefficient Charge Capture – Supply Chain Service 65

Addressing Real Business Issues Through H-SOA-RA • Non-indicated or Contra-indicated Services • – Decision Support/Authorization Services Delays in EHR Document Production and Provision – Document Service) • Billing Delays and Errors – (Supply Chain/ Billing/Collection Services) • Not fully coordinated Scheduling – Scheduling Service) • Lack of fully integrated Patient Assessment and Treatment Plan – (Document Service/ Decision Support Service) • Delayed or Lack of Medical Record Access – (Record Service) 66
1be89aaff29f2c029d3b19c5657af08e.ppt