36e890145bda568efffbe6673cab05e5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 HKCE Macroeconomics Chapter 4: Deposit Creation and Money Supply By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 1
HKCE Macroeconomics Chapter 4: Deposit Creation and Money Supply By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 1
 Assets and Liabilities of a bank Assets: n n n Anything owned by a bank is an asset. Liquid assets are easily converted into cash, e. g. cash and short-term loans. Illiquid/Fixed assets cannot be converted into cash within a short period of time, e. g. estate and office premises. Liabilities: n Anything borrowed from others is liability. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 2
Assets and Liabilities of a bank Assets: n n n Anything owned by a bank is an asset. Liquid assets are easily converted into cash, e. g. cash and short-term loans. Illiquid/Fixed assets cannot be converted into cash within a short period of time, e. g. estate and office premises. Liabilities: n Anything borrowed from others is liability. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 2
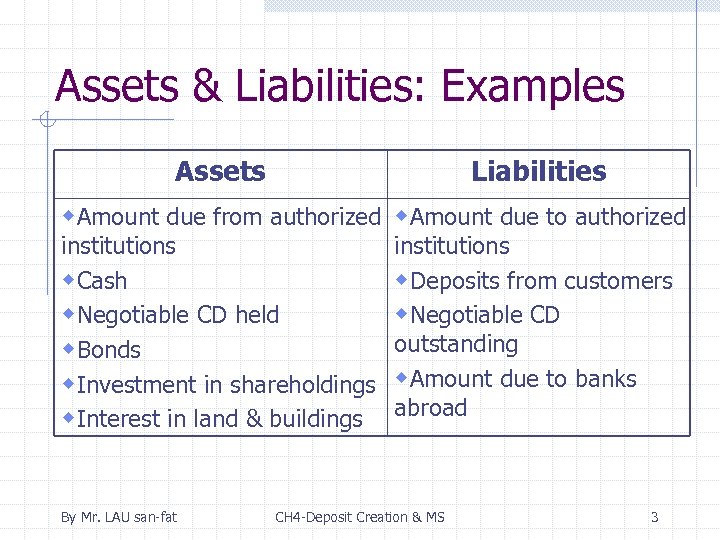 Assets & Liabilities: Examples Assets Liabilities w. Amount due from authorized w. Amount due to authorized institutions w. Cash w. Negotiable CD held w. Bonds w. Investment in shareholdings w. Interest in land & buildings By Mr. LAU san-fat institutions w. Deposits from customers w. Negotiable CD outstanding w. Amount due to banks abroad CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 3
Assets & Liabilities: Examples Assets Liabilities w. Amount due from authorized w. Amount due to authorized institutions w. Cash w. Negotiable CD held w. Bonds w. Investment in shareholdings w. Interest in land & buildings By Mr. LAU san-fat institutions w. Deposits from customers w. Negotiable CD outstanding w. Amount due to banks abroad CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 3
 Deposits & Money Supply Bank deposits are the largest component of money supply. Banks increase money supply by engaging in deposit creation. Money supply will however be contracted if banks engage in deposit withdrawals. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 4
Deposits & Money Supply Bank deposits are the largest component of money supply. Banks increase money supply by engaging in deposit creation. Money supply will however be contracted if banks engage in deposit withdrawals. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 4
 The Fractional Reserve System A fractional reserve system means that banks are required by law to keep a given fraction of their total deposits (Dd) as required or legal reserves. (Minimum) Required reserves (RR) are the minimum amount of liquid assets (e. g. cash & CDs) that must be kept in banks for withdrawals or emergency purposes. Excess reserves (ER) are the amount in excess of the required reserves. Thus, Dd=RR+ER, RR=Dd-ER, & ER=Dd-RR By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 5
The Fractional Reserve System A fractional reserve system means that banks are required by law to keep a given fraction of their total deposits (Dd) as required or legal reserves. (Minimum) Required reserves (RR) are the minimum amount of liquid assets (e. g. cash & CDs) that must be kept in banks for withdrawals or emergency purposes. Excess reserves (ER) are the amount in excess of the required reserves. Thus, Dd=RR+ER, RR=Dd-ER, & ER=Dd-RR By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 5
 The Fractional Reserve System n n The minimum required reserve ratio (RRR) is the minimum fraction of a bank's total deposits required by law to be kept in the form of cash or other liquid assets. Thus, RRR=RR/Dd. However, for the prudent/conservative purpose or insufficient loan demand, the actual reserves (AR) kept by a bank may eventually more than the required amount. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 6
The Fractional Reserve System n n The minimum required reserve ratio (RRR) is the minimum fraction of a bank's total deposits required by law to be kept in the form of cash or other liquid assets. Thus, RRR=RR/Dd. However, for the prudent/conservative purpose or insufficient loan demand, the actual reserves (AR) kept by a bank may eventually more than the required amount. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 6
 The Fractional Reserve System The actual reserves ratio (ARR) is found by dividing actual reserves by total deposits. Thus, ARR=AR/Dd. n If the actual reserves is larger than the required reserves, excess reserves were actually kept in the banking system. n Excess reserves actually kept=AR-RR n By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 7
The Fractional Reserve System The actual reserves ratio (ARR) is found by dividing actual reserves by total deposits. Thus, ARR=AR/Dd. n If the actual reserves is larger than the required reserves, excess reserves were actually kept in the banking system. n Excess reserves actually kept=AR-RR n By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 7
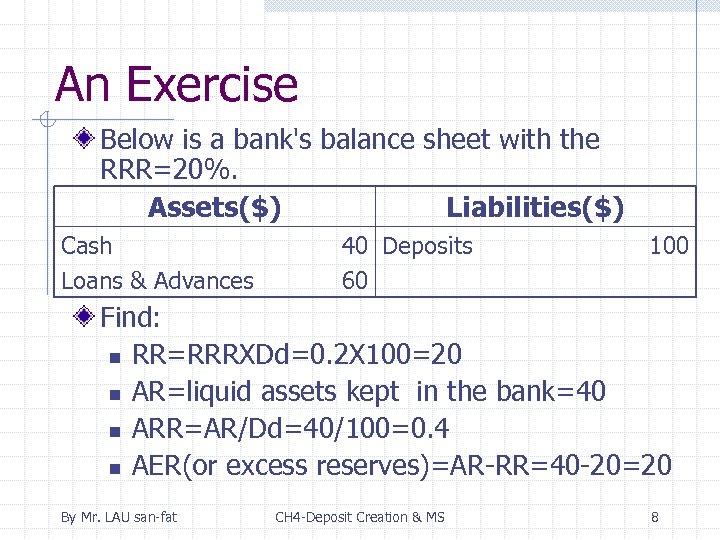 An Exercise Below is a bank's balance sheet with the RRR=20%. Assets($) Liabilities($) Cash Loans & Advances 40 Deposits 60 100 Find: n RR=RRRXDd=0. 2 X 100=20 n AR=liquid assets kept in the bank=40 n ARR=AR/Dd=40/100=0. 4 n AER(or excess reserves)=AR-RR=40 -20=20 By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 8
An Exercise Below is a bank's balance sheet with the RRR=20%. Assets($) Liabilities($) Cash Loans & Advances 40 Deposits 60 100 Find: n RR=RRRXDd=0. 2 X 100=20 n AR=liquid assets kept in the bank=40 n ARR=AR/Dd=40/100=0. 4 n AER(or excess reserves)=AR-RR=40 -20=20 By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 8
 The Fractional Reserve System n n n Cash reserve ratio specifies the minimum fraction of a bank's total deposits that is required by law to be kept in the form of cash. Liquidity ratio = (short-term liquid assets/short-term liabilities)X 100% In HK, all authorized institutions are required to meet the minimum monthly average liquidity ratio of 25%. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 9
The Fractional Reserve System n n n Cash reserve ratio specifies the minimum fraction of a bank's total deposits that is required by law to be kept in the form of cash. Liquidity ratio = (short-term liquid assets/short-term liabilities)X 100% In HK, all authorized institutions are required to meet the minimum monthly average liquidity ratio of 25%. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 9
 Assumptions behind Deposits Creation 1. Fractional reserve banking system 2. 3. 4. 5. exists. No banks keep excess reserves. No cash leakage. Sufficient loan demand exists. There is only demand deposits. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 10
Assumptions behind Deposits Creation 1. Fractional reserve banking system 2. 3. 4. 5. exists. No banks keep excess reserves. No cash leakage. Sufficient loan demand exists. There is only demand deposits. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 10
 Deposits Creation: An Illustration Assumptions: n n n There are 3 banks: Bank A, B & C. An initial amount of $1 000 was deposited in Bank A. The min. reserve ratio is 0. 25. The Question: n What will be the maximum amount of deposits created out of the initial deposits of $1 000? By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 11
Deposits Creation: An Illustration Assumptions: n n n There are 3 banks: Bank A, B & C. An initial amount of $1 000 was deposited in Bank A. The min. reserve ratio is 0. 25. The Question: n What will be the maximum amount of deposits created out of the initial deposits of $1 000? By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 11
 Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 1: $1 000 was deposited in Bank A's balance sheet Assets($) Cash By Mr. LAU san-fat Liabilities($) +1000 Deposits CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS +1000 12
Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 1: $1 000 was deposited in Bank A's balance sheet Assets($) Cash By Mr. LAU san-fat Liabilities($) +1000 Deposits CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS +1000 12
 Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 2: Bank A kept 25% of $1 000 as required reserves & loans out the rest. Bank A's balance sheet Assets($) Cash Loans By Mr. LAU san-fat Liabilities($) 250 Deposits +750 CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS +1000 13
Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 2: Bank A kept 25% of $1 000 as required reserves & loans out the rest. Bank A's balance sheet Assets($) Cash Loans By Mr. LAU san-fat Liabilities($) 250 Deposits +750 CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS +1000 13
 Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 3: Suppose the loan of $750 was finally deposited in Bank B's balance sheet Assets($) Cash By Mr. LAU san-fat Liabilities($) +750 Deposits CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS +750 14
Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 3: Suppose the loan of $750 was finally deposited in Bank B's balance sheet Assets($) Cash By Mr. LAU san-fat Liabilities($) +750 Deposits CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS +750 14
 Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 4: Bank B has to keep 25% of the total deposits as its required reserves and used the rest for loans. Bank B's balance sheet Assets($) Cash Loans By Mr. LAU san-fat Liabilities($) 187. 5 Deposits +562. 5 CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 750 15
Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 4: Bank B has to keep 25% of the total deposits as its required reserves and used the rest for loans. Bank B's balance sheet Assets($) Cash Loans By Mr. LAU san-fat Liabilities($) 187. 5 Deposits +562. 5 CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 750 15
 Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 5: Let Bank C receive $562. 5. After keeping 25% of the new deposits, $421. 9 will be loaned out. Bank C's balance sheet Assets($) Cash Loans By Mr. LAU san-fat Liabilities($) +140. 6 Deposits +421. 9 CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS +562. 5 16
Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 5: Let Bank C receive $562. 5. After keeping 25% of the new deposits, $421. 9 will be loaned out. Bank C's balance sheet Assets($) Cash Loans By Mr. LAU san-fat Liabilities($) +140. 6 Deposits +421. 9 CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS +562. 5 16
 Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 6: Total deposits being created by Banks A, B & C=$(1 000+750+562. 5)=$2 312. 5 Another bank follows the same suit: receiving a certain amount of new deposits, keeping the min. required reserves, & lending the rest. The process goes on until the decreasing deposits becomes zero. Deposits is said to be created in the sense of accounting. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 17
Deposits Creation: An Illustration Step 6: Total deposits being created by Banks A, B & C=$(1 000+750+562. 5)=$2 312. 5 Another bank follows the same suit: receiving a certain amount of new deposits, keeping the min. required reserves, & lending the rest. The process goes on until the decreasing deposits becomes zero. Deposits is said to be created in the sense of accounting. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 17
 Deposits Creation: Theoretical Process Step 1: Under the fractional reserves system, a bank will keep a fraction as the required reserves of a new deposits and lend the rest. Step 2: The amount of loans will finally be redeposited into the same or another bank. That bank will also keep a fraction as the required reserves and loan the rest out. Step 3: The process of receiving new deposits, keeping the required reserves and lending the rest will go on and on, until the decreasing deposits becomes zero. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 18
Deposits Creation: Theoretical Process Step 1: Under the fractional reserves system, a bank will keep a fraction as the required reserves of a new deposits and lend the rest. Step 2: The amount of loans will finally be redeposited into the same or another bank. That bank will also keep a fraction as the required reserves and loan the rest out. Step 3: The process of receiving new deposits, keeping the required reserves and lending the rest will go on and on, until the decreasing deposits becomes zero. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 18
 Banking Multipliers Maximum banking/money multiplier, k=1/RRR Actual banking multiplier=1/ARR By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 19
Banking Multipliers Maximum banking/money multiplier, k=1/RRR Actual banking multiplier=1/ARR By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 19
 Remarks on Deposits Creation Maximum deposits being created =initial deposits X (1/RRR) However, if banks keep excess reserves, the maximum deposits being created is lesser as less money is lent out and re-deposited. Thus, the total deposits being actually created =initial deposits X (1/ARR) Total change in deposits in the banking system =deposits created + original total deposits By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 20
Remarks on Deposits Creation Maximum deposits being created =initial deposits X (1/RRR) However, if banks keep excess reserves, the maximum deposits being created is lesser as less money is lent out and re-deposited. Thus, the total deposits being actually created =initial deposits X (1/ARR) Total change in deposits in the banking system =deposits created + original total deposits By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 20
 Remarks on Deposits Creation Maximum loans/credit being created =excess reserves X (1/RRR) By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 21
Remarks on Deposits Creation Maximum loans/credit being created =excess reserves X (1/RRR) By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 21
 Limitations of Deposits Creation Cash leakage will reduce the amount of deposits being created. Banks keep excess reserves will also reduce the deposits being created. Insufficient demand for loans will decrease the amount of deposits being created. Full reserves baking system will, however, prohibit the process multiple creation of deposits from happening. Then the deposits being created is equal to the initial deposits. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 22
Limitations of Deposits Creation Cash leakage will reduce the amount of deposits being created. Banks keep excess reserves will also reduce the deposits being created. Insufficient demand for loans will decrease the amount of deposits being created. Full reserves baking system will, however, prohibit the process multiple creation of deposits from happening. Then the deposits being created is equal to the initial deposits. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 22
 Withdrawals/Contraction of Deposits Step 1: If there is a withdrawal of deposits from a bank, the bank reserves will fall short of the legal requirement. Step 2: The bank will then call back loans or sell assets to get enough reserves. Step 3: To repay the loans or to buy assets, customers will further withdraw deposits from the other banks. Step 4: Withdrawals make bank reserves less than the legal requirement. Banks continue to call back loans. The process goes on and on. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 23
Withdrawals/Contraction of Deposits Step 1: If there is a withdrawal of deposits from a bank, the bank reserves will fall short of the legal requirement. Step 2: The bank will then call back loans or sell assets to get enough reserves. Step 3: To repay the loans or to buy assets, customers will further withdraw deposits from the other banks. Step 4: Withdrawals make bank reserves less than the legal requirement. Banks continue to call back loans. The process goes on and on. By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 23
 Remarks on Deposits Contraction Maximum deposits being withdrawn =initial withdrawal X (1/RRR) However, if banks keep excess reserves, the maximum deposits being contracted is less than expected. Thus, the total deposits being withdrawn =initial withdrawal X (1/ARR) Total change in deposits in the banking system = original total deposits - deposits withdrawn By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 24
Remarks on Deposits Contraction Maximum deposits being withdrawn =initial withdrawal X (1/RRR) However, if banks keep excess reserves, the maximum deposits being contracted is less than expected. Thus, the total deposits being withdrawn =initial withdrawal X (1/ARR) Total change in deposits in the banking system = original total deposits - deposits withdrawn By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 24
 Deposits Creation and Change in Money Supply If the initial deposits comes from currency in public circulation or cash, the change in deposits will be larger than the change in money supply. Thus, change in M 1 =deposits created – fall in cash Example: n if the initial deposits=$100, RRR=0. 2; then n Change in Deposits = $100 X(1/0. 2)=$500 n Change in M 1 = $500 - $100 = $400 By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 25
Deposits Creation and Change in Money Supply If the initial deposits comes from currency in public circulation or cash, the change in deposits will be larger than the change in money supply. Thus, change in M 1 =deposits created – fall in cash Example: n if the initial deposits=$100, RRR=0. 2; then n Change in Deposits = $100 X(1/0. 2)=$500 n Change in M 1 = $500 - $100 = $400 By Mr. LAU san-fat CH 4 -Deposit Creation & MS 25


