 HIV - infection
HIV - infection
 HIV – РNК- petrovirus HIV-infection is characterized by lymphadenopathy intoxication opportunistic infections and invasions oncological diseases заканчивается смертью больного
HIV – РNК- petrovirus HIV-infection is characterized by lymphadenopathy intoxication opportunistic infections and invasions oncological diseases заканчивается смертью больного
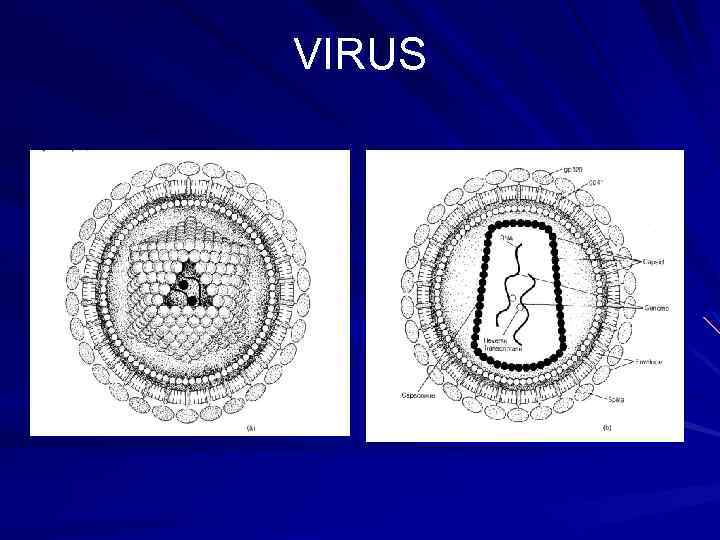 VIRUS
VIRUS
 EPYDEMIOLOGY HIV-infection is anthroponosis; source of infection – sick person in all period of the disease all biological fluids of sick person is dangerous (blood, lympha, saliva, milk, sperm, etc. )
EPYDEMIOLOGY HIV-infection is anthroponosis; source of infection – sick person in all period of the disease all biological fluids of sick person is dangerous (blood, lympha, saliva, milk, sperm, etc. )
 WAYS OF TRANSMISSION sexual (homo and heterosexual) – 80%; on hemotransfusion In drug adductors vertical (through placenta from HIV-infected women, on confinement) horizontal (при грудном вскармливании ВИЧ-инфицированной матери); on injections and on dirty instruments on transplantation;
WAYS OF TRANSMISSION sexual (homo and heterosexual) – 80%; on hemotransfusion In drug adductors vertical (through placenta from HIV-infected women, on confinement) horizontal (при грудном вскармливании ВИЧ-инфицированной матери); on injections and on dirty instruments on transplantation;
 METHODS THAT ARE NOT KNOWN TO TRANSMIT HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS. (a) Touching a doorknob; (b) a social kiss; (c) eating at a restaurant; (d) swimming at a pool; (e) donating blood; (f) drinking at a water fountain
METHODS THAT ARE NOT KNOWN TO TRANSMIT HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS. (a) Touching a doorknob; (b) a social kiss; (c) eating at a restaurant; (d) swimming at a pool; (e) donating blood; (f) drinking at a water fountain
 ОСНОВНЫЕ ГРУППЫ ПОВЫШЕННОГО РИСКА ЗАРАЖЕНИЯ ВИЧ ИНФЕКЦИЕЙ 1. гомосексуалисты и бисексуальные 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. мужчины наркоманы проститутки лица с беспорядочной половой жизнью больные, получающие препараты крови (гемофилия), трансплантация органов дети, рожденные от инфицированных матерей медицинские работники (оказывающие помощь ВИЧ-инфицированным)
ОСНОВНЫЕ ГРУППЫ ПОВЫШЕННОГО РИСКА ЗАРАЖЕНИЯ ВИЧ ИНФЕКЦИЕЙ 1. гомосексуалисты и бисексуальные 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. мужчины наркоманы проститутки лица с беспорядочной половой жизнью больные, получающие препараты крови (гемофилия), трансплантация органов дети, рожденные от инфицированных матерей медицинские работники (оказывающие помощь ВИЧ-инфицированным)
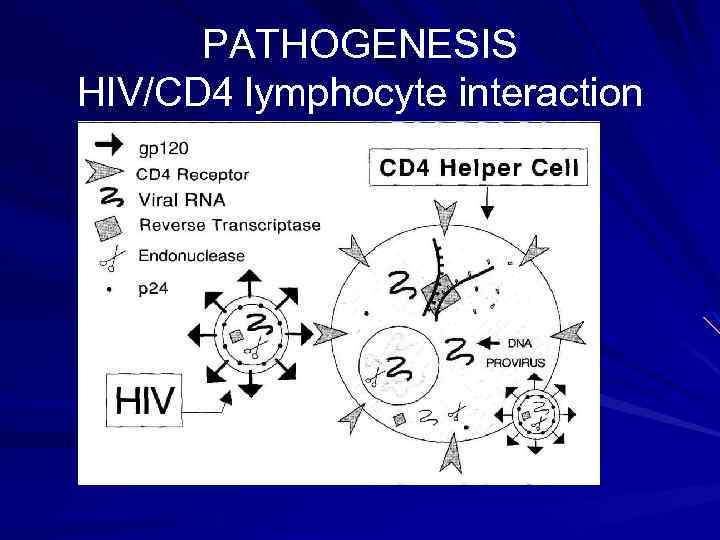 PATHOGENESIS HIV/CD 4 lymphocyte interaction
PATHOGENESIS HIV/CD 4 lymphocyte interaction
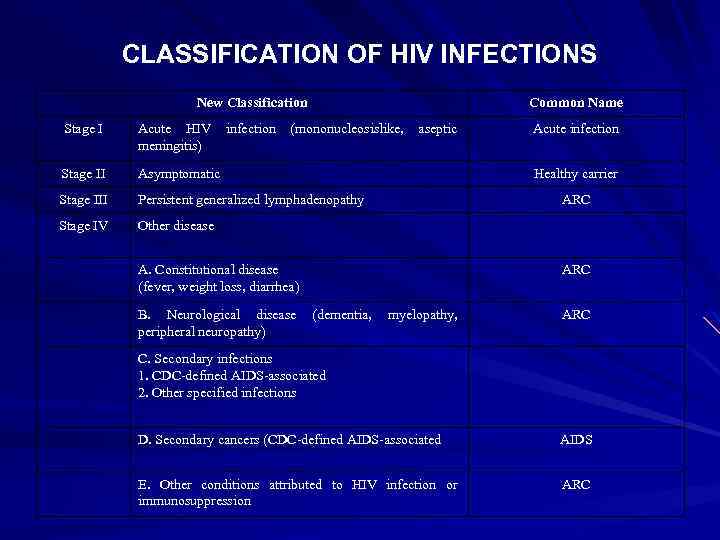 CLASSIFICATION OF HIV INFECTIONS New Classification infection Common Name Stage I Acute HIV meningitis) (mononucleosislike, Stage II Asymptomatic Stage III Persistent generalized lymphadenopathy Stage IV aseptic Other disease Healthy carrier ARC A. Constitutional disease (fever, weight loss, diarrhea) B. Neurological disease peripheral neuropathy) Acute infection ARC (dementia, myelopathy, ARC C. Secondary infections 1. CDC-defined AIDS-associated 2. Other specified infections D. Secondary cancers (CDC-defined AIDS-associated AIDS E. Other conditions attributed to HIV infection or immunosuppression ARC
CLASSIFICATION OF HIV INFECTIONS New Classification infection Common Name Stage I Acute HIV meningitis) (mononucleosislike, Stage II Asymptomatic Stage III Persistent generalized lymphadenopathy Stage IV aseptic Other disease Healthy carrier ARC A. Constitutional disease (fever, weight loss, diarrhea) B. Neurological disease peripheral neuropathy) Acute infection ARC (dementia, myelopathy, ARC C. Secondary infections 1. CDC-defined AIDS-associated 2. Other specified infections D. Secondary cancers (CDC-defined AIDS-associated AIDS E. Other conditions attributed to HIV infection or immunosuppression ARC
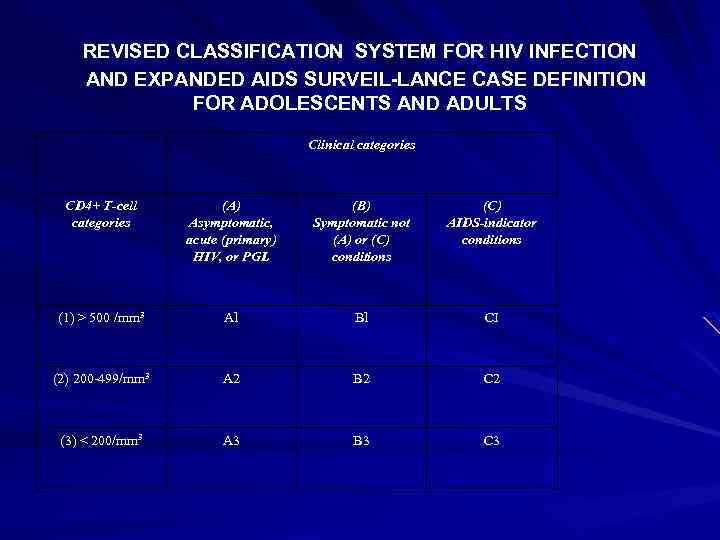 REVISED CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM FOR HIV INFECTION AND EXPANDED AIDS SURVEIL LANCE CASE DEFINITION FOR ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS Clinical categories CD 4+ T-cell categories (A) Asymptomatic, acute (primary) HIV, or PGL (B) Symptomatic not (A) or (C) conditions (C) AIDS-indicator conditions (1) > 500 /mm 3 Al Bl CI (2) 200 -499/mm 3 A 2 B 2 C 2 (3) < 200/mm 3 A 3 B 3 C 3
REVISED CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM FOR HIV INFECTION AND EXPANDED AIDS SURVEIL LANCE CASE DEFINITION FOR ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS Clinical categories CD 4+ T-cell categories (A) Asymptomatic, acute (primary) HIV, or PGL (B) Symptomatic not (A) or (C) conditions (C) AIDS-indicator conditions (1) > 500 /mm 3 Al Bl CI (2) 200 -499/mm 3 A 2 B 2 C 2 (3) < 200/mm 3 A 3 B 3 C 3
 CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF PRIMARY HIV INFECTION Fever Lymphadenopathy Lethargy Myalgia Arthralgia Gastrointestinal Pharyngitis Diarrhea Nausea or vomiting Hepatosplenomegaly Oral thrush Neurologic Headache Meningoencephalitis Peripheral neuropathy Dermatologic Truncal maculopapular rash Mucocutaneous ulcers Other Thrombocytopenia Leukopenia Increased liver function tests
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF PRIMARY HIV INFECTION Fever Lymphadenopathy Lethargy Myalgia Arthralgia Gastrointestinal Pharyngitis Diarrhea Nausea or vomiting Hepatosplenomegaly Oral thrush Neurologic Headache Meningoencephalitis Peripheral neuropathy Dermatologic Truncal maculopapular rash Mucocutaneous ulcers Other Thrombocytopenia Leukopenia Increased liver function tests
 INDEPENDENT PREDICTORS OF HIV DISEASE PROGRESSION Symptoms Constitutional symptoms Signs Hairy leukoplakia Oral candidiasis Laboratory studies CD 4 cell count CD 4: CD 8 ratio Serum 62 -microglobulin Serum and urine neopterin p 24 antigen Serum and mononuclear cell HIV titer Hl. V-related anemia Erythrocyte sedimentation rate Cutaneous anergy
INDEPENDENT PREDICTORS OF HIV DISEASE PROGRESSION Symptoms Constitutional symptoms Signs Hairy leukoplakia Oral candidiasis Laboratory studies CD 4 cell count CD 4: CD 8 ratio Serum 62 -microglobulin Serum and urine neopterin p 24 antigen Serum and mononuclear cell HIV titer Hl. V-related anemia Erythrocyte sedimentation rate Cutaneous anergy
 SOME SYMPTOMS OF HIV INFECTION, ARC, AND AIDS HIV Infection Fatigue Mild fever Sore muscles Occasional diarrhea Swollen lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy) AIDS Related Complex (ARC) Extended and extensive lymphadenopathy Weight loss of as much as 10% of normal body weight Constant low-grade fever (about 37. 8° C, or 100° F) Extensive diarrhea over several weeks Overwhelming fatigue Saturating night sweats Thrush from Candida albicans Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) Persistent lymphadenopathy Constant low-grade fever Substantial nausea and fatigue Vomiting Severe psychological stress Saturating night sweats Extensive headaches Possible wasting syndrome Unrelenting diarrhea Dramatic weight loss Severe fluid imbalance Chronic weakness and fever Possible AIDS-dementia complex Difficult muscle coordination Confusion and apathy Loss of concentration Sudden, strong emotions Memory loss Difficulty in sleeping Headache and disorientation Possible Kaposi's sarcoma Slow-growing tumors in blood-vessel linings Possible opportunistic diseases Pneumonia, esophageal diseases, blindness, brain infection, choleralike diarrhea, spinal meningitis, liver and kidney disease, tuberculosis, and many others
SOME SYMPTOMS OF HIV INFECTION, ARC, AND AIDS HIV Infection Fatigue Mild fever Sore muscles Occasional diarrhea Swollen lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy) AIDS Related Complex (ARC) Extended and extensive lymphadenopathy Weight loss of as much as 10% of normal body weight Constant low-grade fever (about 37. 8° C, or 100° F) Extensive diarrhea over several weeks Overwhelming fatigue Saturating night sweats Thrush from Candida albicans Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) Persistent lymphadenopathy Constant low-grade fever Substantial nausea and fatigue Vomiting Severe psychological stress Saturating night sweats Extensive headaches Possible wasting syndrome Unrelenting diarrhea Dramatic weight loss Severe fluid imbalance Chronic weakness and fever Possible AIDS-dementia complex Difficult muscle coordination Confusion and apathy Loss of concentration Sudden, strong emotions Memory loss Difficulty in sleeping Headache and disorientation Possible Kaposi's sarcoma Slow-growing tumors in blood-vessel linings Possible opportunistic diseases Pneumonia, esophageal diseases, blindness, brain infection, choleralike diarrhea, spinal meningitis, liver and kidney disease, tuberculosis, and many others
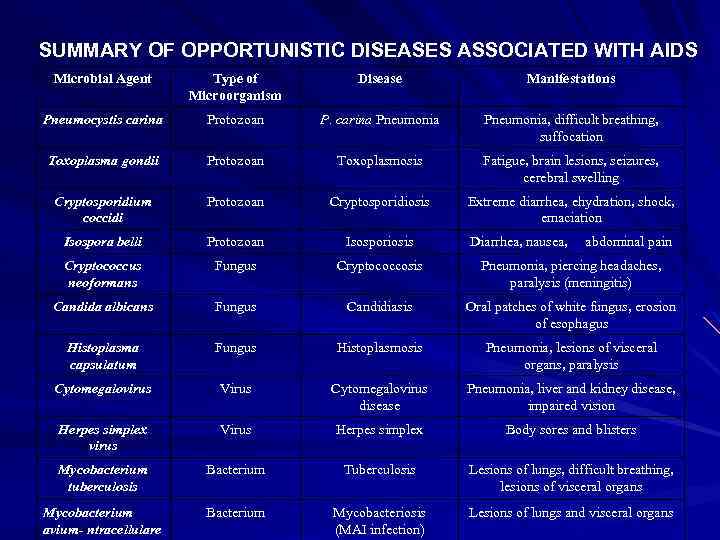 SUMMARY OF OPPORTUNISTIC DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH AIDS Microbial Agent Type of Microorganism Disease Manifestations Pneumocystis carina Protozoan P. carina Pneumonia, difficult breathing, suffocation Toxoplasma gondii Protozoan Toxoplasmosis Fatigue, brain lesions, seizures, cerebral swelling Cryptosporidium coccidi Protozoan Cryptosporidiosis Extreme diarrhea, ehydration, shock, emaciation Isospora belli Protozoan Isosporiosis Cryptococcus neoformans Fungus Cryptococcosis Pneumonia, piercing headaches, paralysis (meningitis) Candida albicans Fungus Candidiasis Oral patches of white fungus, erosion of esophagus Histoplasma capsulatum Fungus Histoplasmosis Pneumonia, lesions of visceral organs, paralysis Cytomegalovirus Virus Cytomegalovirus disease Pneumonia, liver and kidney disease, impaired vision Herpes simplex virus Virus Herpes simplex Body sores and blisters Mycobacterium tuberculosis Bacterium Tuberculosis Lesions of lungs, difficult breathing, lesions of visceral organs Mycobacterium avium- ntracellulare Bacterium Mycobacteriosis (MAI infection) Lesions of lungs and visceral organs Diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain
SUMMARY OF OPPORTUNISTIC DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH AIDS Microbial Agent Type of Microorganism Disease Manifestations Pneumocystis carina Protozoan P. carina Pneumonia, difficult breathing, suffocation Toxoplasma gondii Protozoan Toxoplasmosis Fatigue, brain lesions, seizures, cerebral swelling Cryptosporidium coccidi Protozoan Cryptosporidiosis Extreme diarrhea, ehydration, shock, emaciation Isospora belli Protozoan Isosporiosis Cryptococcus neoformans Fungus Cryptococcosis Pneumonia, piercing headaches, paralysis (meningitis) Candida albicans Fungus Candidiasis Oral patches of white fungus, erosion of esophagus Histoplasma capsulatum Fungus Histoplasmosis Pneumonia, lesions of visceral organs, paralysis Cytomegalovirus Virus Cytomegalovirus disease Pneumonia, liver and kidney disease, impaired vision Herpes simplex virus Virus Herpes simplex Body sores and blisters Mycobacterium tuberculosis Bacterium Tuberculosis Lesions of lungs, difficult breathing, lesions of visceral organs Mycobacterium avium- ntracellulare Bacterium Mycobacteriosis (MAI infection) Lesions of lungs and visceral organs Diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain
 INDICATOR CONDITIONS INCLUDED AIDS SURVEILLANCE CASE DEFINITION Candidiasis of bronchi, trachea, or lungs Candidiasis esophageal Cervical cancer, invasive Coccidioidomycosis, disseminated or extrapulmonary Cryptococcosis, extrapulmonary Cryptosporidiosis, chronic intestinal (> 1 -month duration) Cytomegalovirus disease (other than liver, spleen, or nodes) Encephalopathy, HIV-related Herpes simplex: chronic ulcer(s) (> 1 -month duration) or bronchitis or esophagitis Histoplasmosis, disseminated or extrapulmonary B Isosporiasis, chronic intestinal (> 1 -month duration) Kaposi's sarcoma Lymphoma Burkitt's (or equivalent term) Lymphoma, immunoblastic (or equivalent term) Lymphoma, primary in brain Mycobacterium avium complex or Mycobacterium kansasii, disseminated or extrapulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis, any site (pulmonary* or extrapulmonary) Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia Pneumonia, recurrent Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy Salmonella septicemia, recurrent Toxoplasmosis of brain Wasting syndrome, HIV-related
INDICATOR CONDITIONS INCLUDED AIDS SURVEILLANCE CASE DEFINITION Candidiasis of bronchi, trachea, or lungs Candidiasis esophageal Cervical cancer, invasive Coccidioidomycosis, disseminated or extrapulmonary Cryptococcosis, extrapulmonary Cryptosporidiosis, chronic intestinal (> 1 -month duration) Cytomegalovirus disease (other than liver, spleen, or nodes) Encephalopathy, HIV-related Herpes simplex: chronic ulcer(s) (> 1 -month duration) or bronchitis or esophagitis Histoplasmosis, disseminated or extrapulmonary B Isosporiasis, chronic intestinal (> 1 -month duration) Kaposi's sarcoma Lymphoma Burkitt's (or equivalent term) Lymphoma, immunoblastic (or equivalent term) Lymphoma, primary in brain Mycobacterium avium complex or Mycobacterium kansasii, disseminated or extrapulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis, any site (pulmonary* or extrapulmonary) Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia Pneumonia, recurrent Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy Salmonella septicemia, recurrent Toxoplasmosis of brain Wasting syndrome, HIV-related
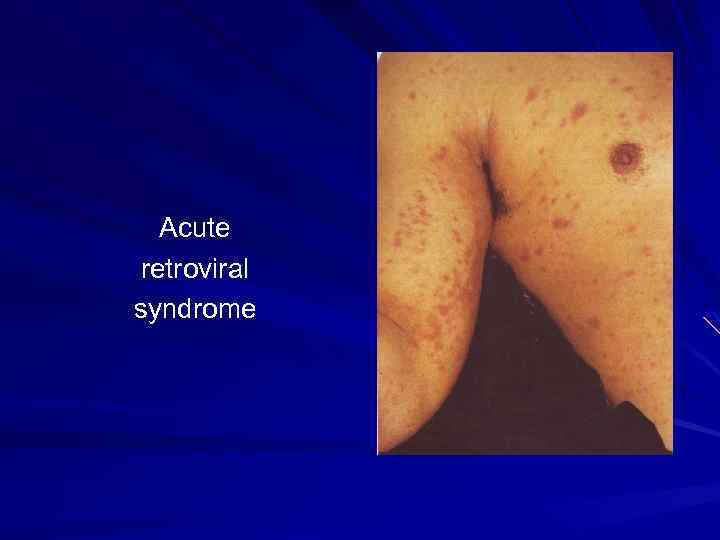 Acute retroviral syndrome
Acute retroviral syndrome
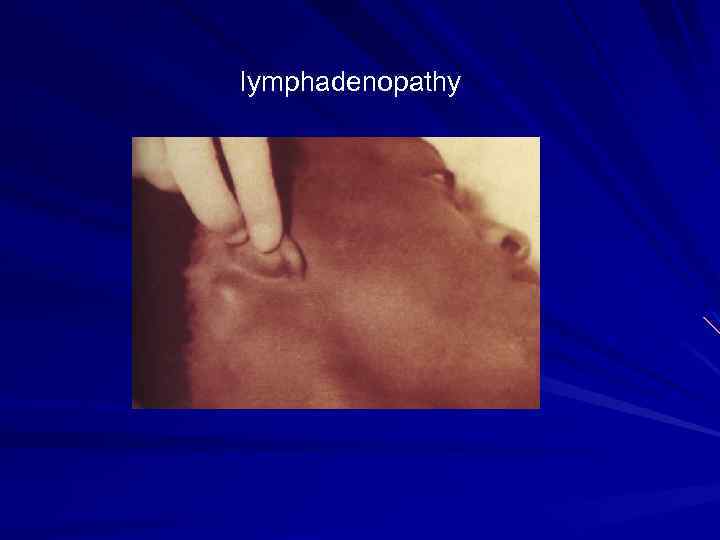 lymphadenopathy
lymphadenopathy
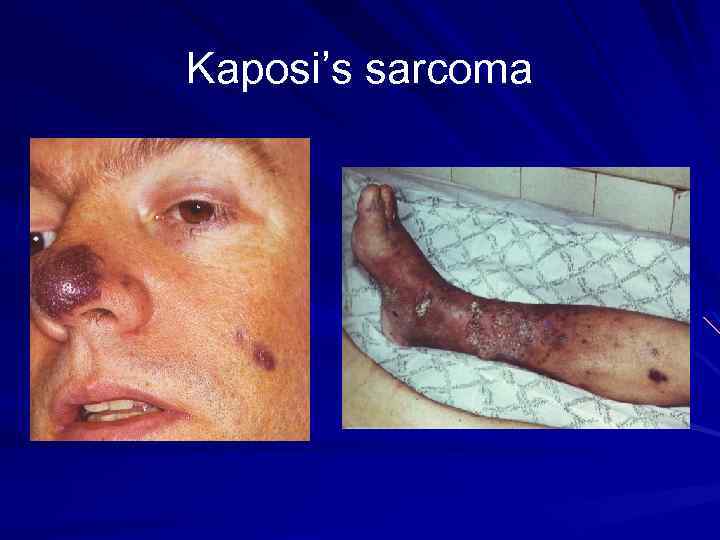 Kaposi’s sarcoma
Kaposi’s sarcoma
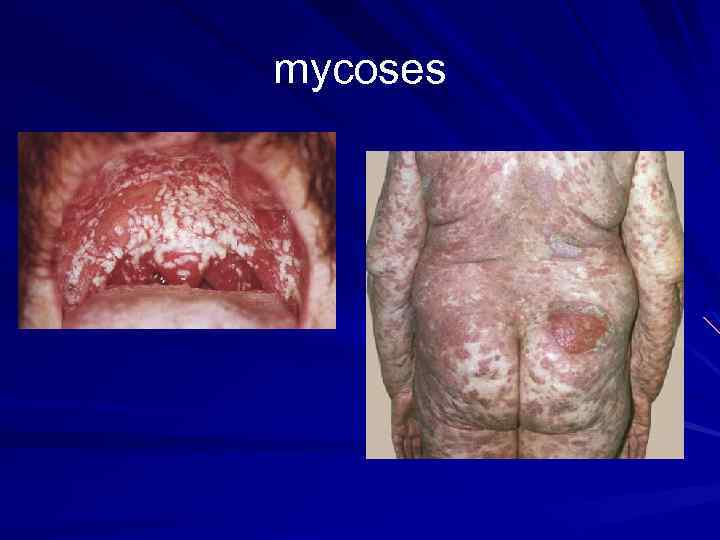 mycoses
mycoses
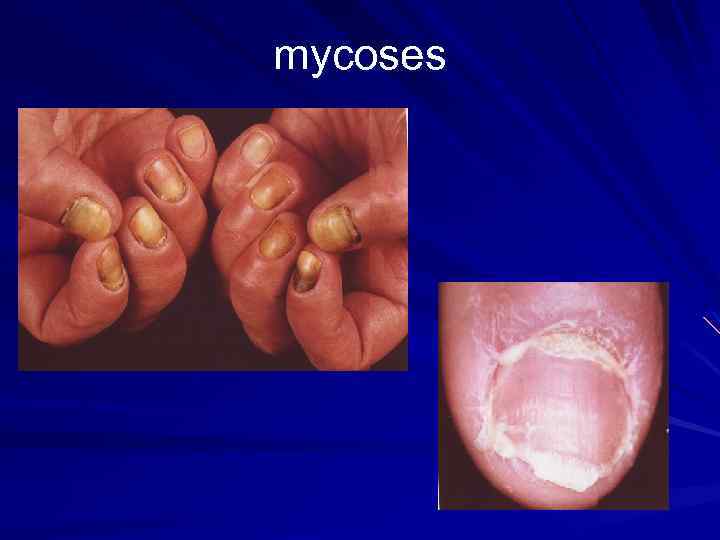 mycoses
mycoses
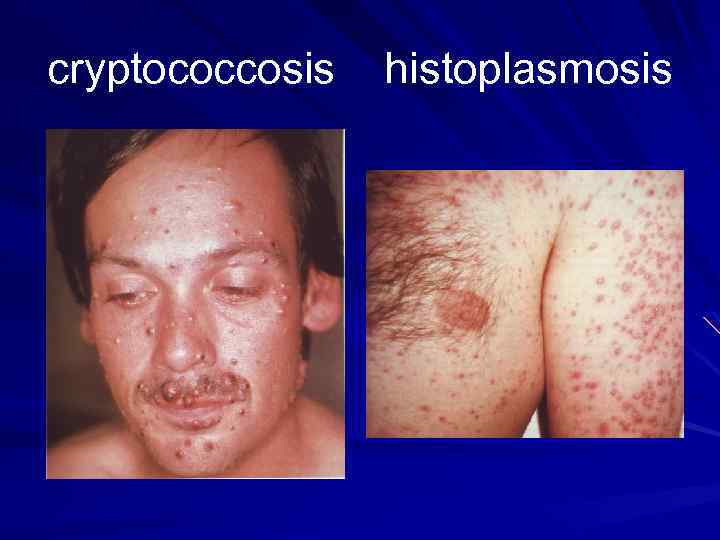 cryptococcosis histoplasmosis
cryptococcosis histoplasmosis
 DIAGNOSTICS Screening Enzyme-linked immunoassay (EIA, ELISA) for HIV-1, HIV-2, or both Latex agglutination for HIV-1 ELISA for HIV-1 detection in urine or saliva Confirmatory Western blot (WB) assay for HIV-1 WB assay for HIV-2* Indirect immunofluorescence antibody assay (IFA) for HIV-1 Radioimmunoprecipitation antibody assay (RIPA) for HIV-1 Supplemental ELISA for HIV-1 p 24 antigen HIV-1 culture* Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for HIV-1
DIAGNOSTICS Screening Enzyme-linked immunoassay (EIA, ELISA) for HIV-1, HIV-2, or both Latex agglutination for HIV-1 ELISA for HIV-1 detection in urine or saliva Confirmatory Western blot (WB) assay for HIV-1 WB assay for HIV-2* Indirect immunofluorescence antibody assay (IFA) for HIV-1 Radioimmunoprecipitation antibody assay (RIPA) for HIV-1 Supplemental ELISA for HIV-1 p 24 antigen HIV-1 culture* Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for HIV-1
 LABORATORY EVALUATION OF THE HIV INFECTED PATIENT Initial Electrolytes Renal function tests Urinalysis Liver function tests Complete blood and differential counts CD 4 cell count Glucose 6 -phosphate dehydrogenase Syphilis serology Viral hepatitis screen Toxoplasmosis serology Purified protein derivative (PPD)/anergy panel Chest radiograph in injection drug users Rectal examination/stool test for occult blood Papanicolaou (Pap) smear in women Health care maintenance Complete blood and differential counts Biochemistries (if indicated) CD 4 cell count Syphilis serology PPD/anergy panel Stool test for occult blood Pap smear in women
LABORATORY EVALUATION OF THE HIV INFECTED PATIENT Initial Electrolytes Renal function tests Urinalysis Liver function tests Complete blood and differential counts CD 4 cell count Glucose 6 -phosphate dehydrogenase Syphilis serology Viral hepatitis screen Toxoplasmosis serology Purified protein derivative (PPD)/anergy panel Chest radiograph in injection drug users Rectal examination/stool test for occult blood Papanicolaou (Pap) smear in women Health care maintenance Complete blood and differential counts Biochemistries (if indicated) CD 4 cell count Syphilis serology PPD/anergy panel Stool test for occult blood Pap smear in women
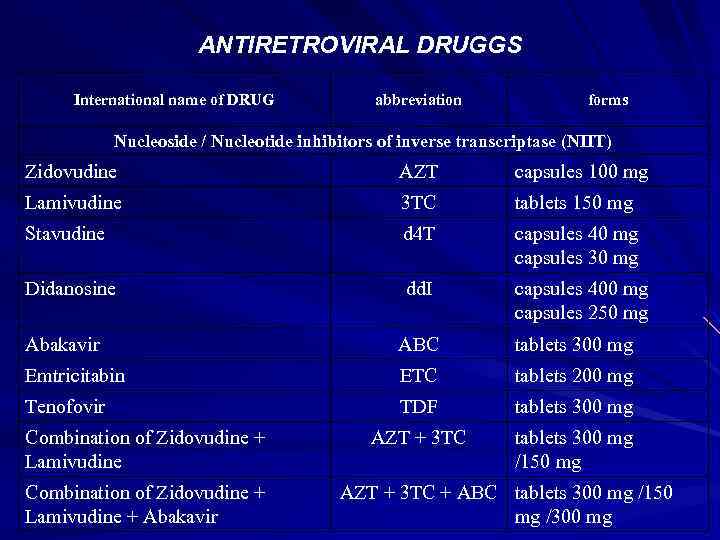 ANTIRETROVIRAL DRUGGS International name of DRUG abbreviation forms Nucleoside / Nucleotide inhibitors of inverse transcriptase (NIIT) Zidovudine AZT capsules 100 mg Lamivudine 3 TC tablets 150 mg Stavudine d 4 T capsules 40 mg capsules 30 mg Didanosine dd. I capsules 400 mg capsules 250 mg Abakavir АВС tablets 300 mg Еmtricitabin ETC tablets 200 mg Теnоfоvir TDF tablets 300 mg AZT + 3 TC tablets 300 mg /150 mg Combination of Zidovudine + Lamivudine + Аbakavir AZT + 3 TC + ABC tablets 300 mg /150 mg /300 mg
ANTIRETROVIRAL DRUGGS International name of DRUG abbreviation forms Nucleoside / Nucleotide inhibitors of inverse transcriptase (NIIT) Zidovudine AZT capsules 100 mg Lamivudine 3 TC tablets 150 mg Stavudine d 4 T capsules 40 mg capsules 30 mg Didanosine dd. I capsules 400 mg capsules 250 mg Abakavir АВС tablets 300 mg Еmtricitabin ETC tablets 200 mg Теnоfоvir TDF tablets 300 mg AZT + 3 TC tablets 300 mg /150 mg Combination of Zidovudine + Lamivudine + Аbakavir AZT + 3 TC + ABC tablets 300 mg /150 mg /300 mg
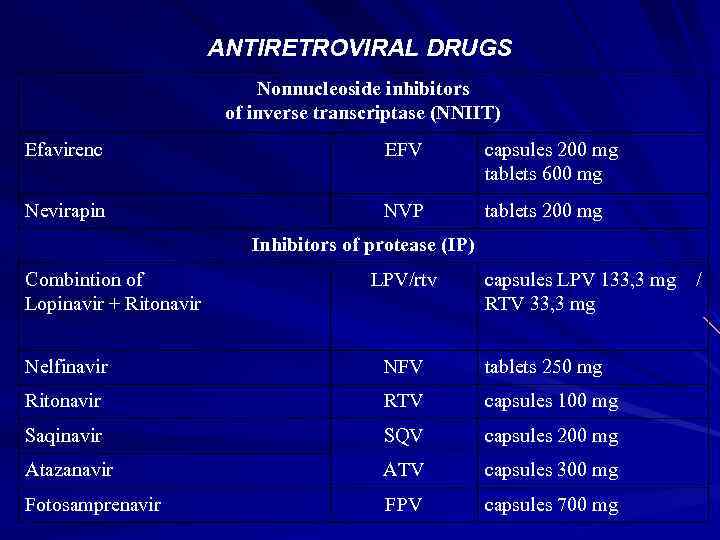 ANTIRETROVIRAL DRUGS Nonnucleoside inhibitors of inverse transcriptase (NNIIT) Efavirenc EFV capsules 200 mg tablets 600 mg Nevirapin NVP tablets 200 mg Inhibitors of protease (IP) Combintion of Lopinavir + Ritonavir LPV/rtv capsules LPV 133, 3 mg RTV 33, 3 mg Nelfinavir NFV tablets 250 mg Ritonavir RTV capsules 100 mg Saqinavir SQV capsules 200 mg Аtazanavir ATV capsules 300 mg Fotosamprenavir FPV capsules 700 mg /
ANTIRETROVIRAL DRUGS Nonnucleoside inhibitors of inverse transcriptase (NNIIT) Efavirenc EFV capsules 200 mg tablets 600 mg Nevirapin NVP tablets 200 mg Inhibitors of protease (IP) Combintion of Lopinavir + Ritonavir LPV/rtv capsules LPV 133, 3 mg RTV 33, 3 mg Nelfinavir NFV tablets 250 mg Ritonavir RTV capsules 100 mg Saqinavir SQV capsules 200 mg Аtazanavir ATV capsules 300 mg Fotosamprenavir FPV capsules 700 mg /


