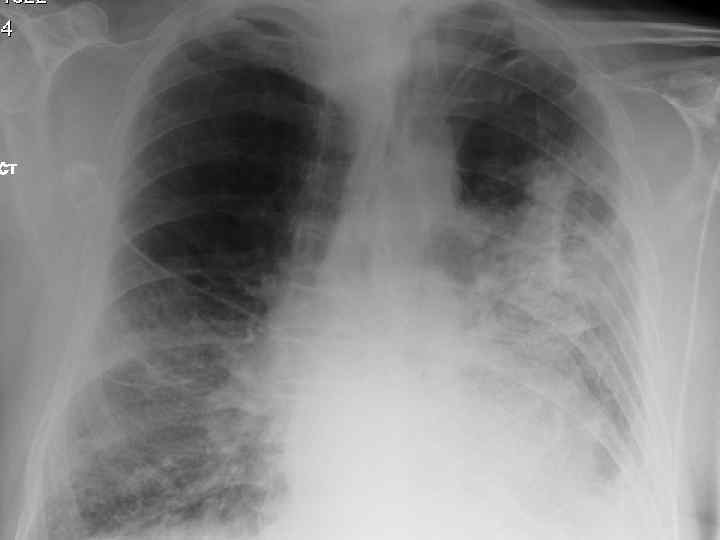
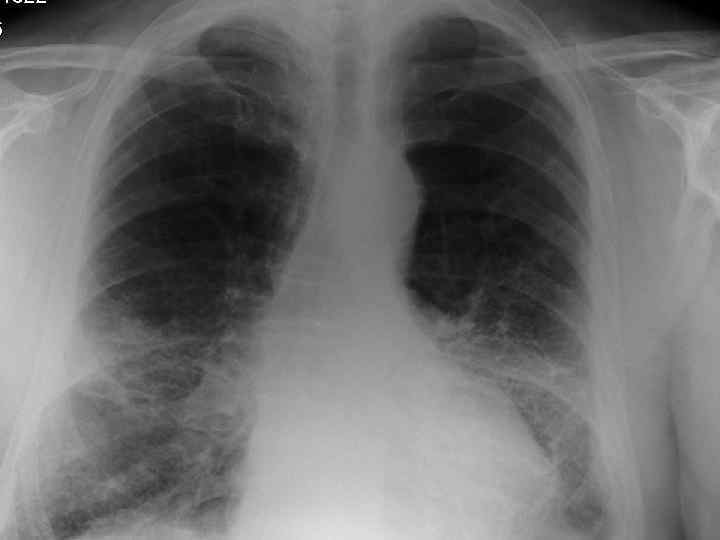
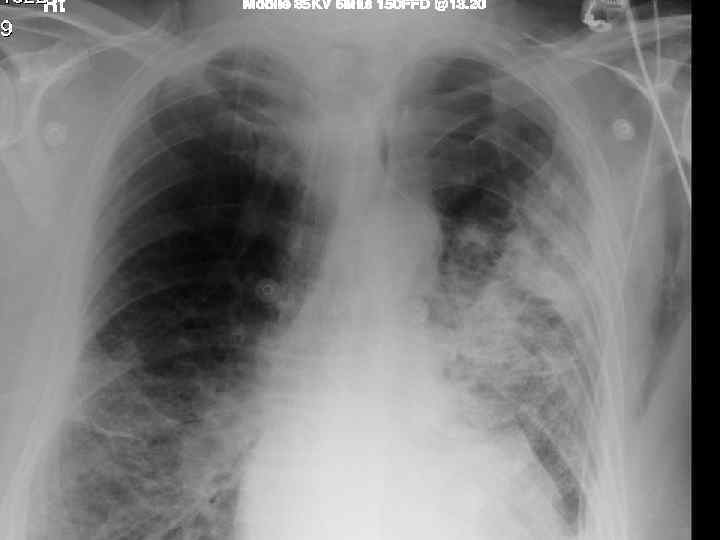
History n Mr X is a 74 year old Caucasian male n PC: Acute SOB n HPC: SOB episode began at 10 -11 am this morning gradually worsening, but suddenly became acutely worse. Noticed by neighbour. Ambulance blue lighted to AE resus
History n Mr X is a 74 year old Caucasian male n PC: Acute SOB n HPC: SOB episode began at 10 -11 am this morning gradually worsening, but suddenly became acutely worse. Noticed by neighbour. Ambulance blue lighted to AE resus
 ‘A short of breath radio operator’ Dr Antonios
‘A short of breath radio operator’ Dr Antonios
 PMH n n n AHA diagnosed 1988 MI 1999 Fibrosing alveolitis diagnosed 1993 Hypercholestolaemia 1993 Multiple admissions for SOB, 6 times in the last 6/12
PMH n n n AHA diagnosed 1988 MI 1999 Fibrosing alveolitis diagnosed 1993 Hypercholestolaemia 1993 Multiple admissions for SOB, 6 times in the last 6/12
 DH n n n n n Salbutamol 100 mg 2 puffs qds Ipratropium Bromide tds 2 puffs Beconase nasal spray 2 puffs Bumetanide 1 md od Simvastatin 20 mg Asprin 75 mg od Azatioprine 50 mg Folic acid 5 mg Lansoprazole 15 mg Calcichew 500 mg tds
DH n n n n n Salbutamol 100 mg 2 puffs qds Ipratropium Bromide tds 2 puffs Beconase nasal spray 2 puffs Bumetanide 1 md od Simvastatin 20 mg Asprin 75 mg od Azatioprine 50 mg Folic acid 5 mg Lansoprazole 15 mg Calcichew 500 mg tds
 SH n Ex radio operator for the army n Lives alone in a flat n Not married, no children n Smoked for most of life n Ex- heavy alcohol drinker.
SH n Ex radio operator for the army n Lives alone in a flat n Not married, no children n Smoked for most of life n Ex- heavy alcohol drinker.
 CVS n Ankle oedema 4 months ago R > L n. Resp n n n SOB for 15 years getting worse, can’t complete sentences SOB on 1 flight of stairs No PND 2 pillow orthopnia Same throughout the year, no variation to day/night or climate change.
CVS n Ankle oedema 4 months ago R > L n. Resp n n n SOB for 15 years getting worse, can’t complete sentences SOB on 1 flight of stairs No PND 2 pillow orthopnia Same throughout the year, no variation to day/night or climate change.
 n Sputum produced throughout the year, difficult to clear, White in colour Autoimmune Haemolytic anaemia diagnosed 15 years ago drug controlled by Azathioprine and folic acid, Predisolone was discontinued 2 years ago n Cryptogenic Fibrosing alveolitis for 10 years n
n Sputum produced throughout the year, difficult to clear, White in colour Autoimmune Haemolytic anaemia diagnosed 15 years ago drug controlled by Azathioprine and folic acid, Predisolone was discontinued 2 years ago n Cryptogenic Fibrosing alveolitis for 10 years n
 Examination n n n Anxious, gasping for breath, holding arms on trolley, Abdominal muscles used for breathing Central cyanosis Pulse 106 bmp regular HS I + II + 0 Apex beat laterally displaced Pitting right ankle oedema No sacral oedema
Examination n n n Anxious, gasping for breath, holding arms on trolley, Abdominal muscles used for breathing Central cyanosis Pulse 106 bmp regular HS I + II + 0 Apex beat laterally displaced Pitting right ankle oedema No sacral oedema
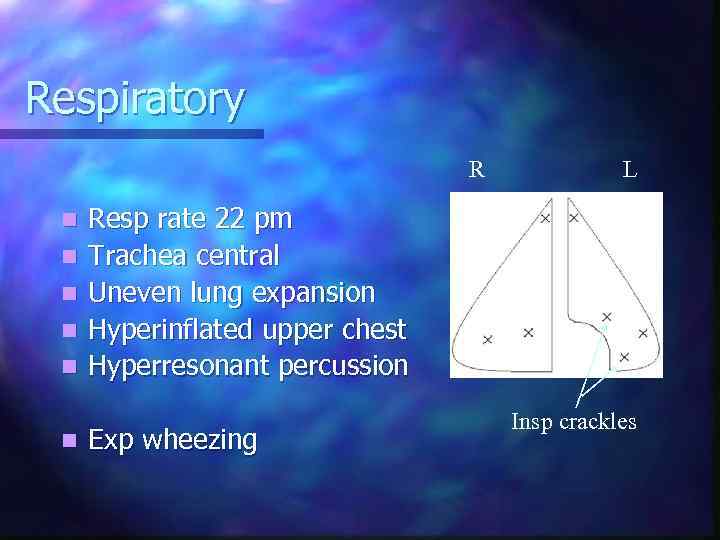 Respiratory R n n n L Resp rate 22 pm Trachea central Uneven lung expansion Hyperinflated upper chest Hyperresonant percussion Exp wheezing Insp crackles
Respiratory R n n n L Resp rate 22 pm Trachea central Uneven lung expansion Hyperinflated upper chest Hyperresonant percussion Exp wheezing Insp crackles
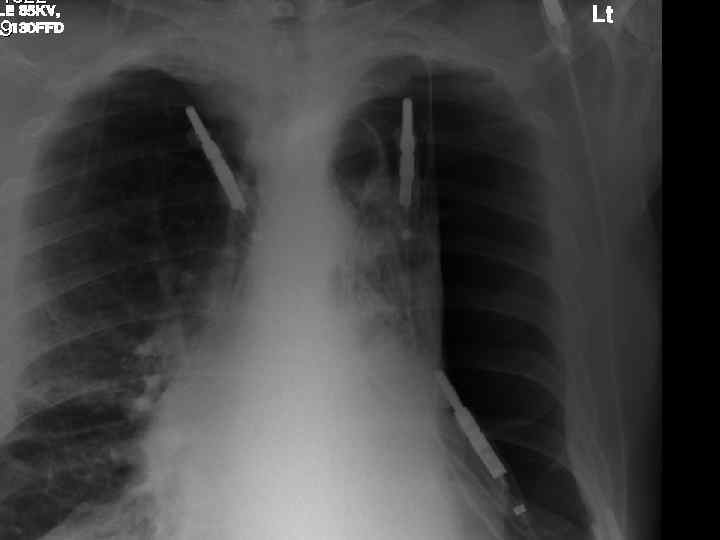
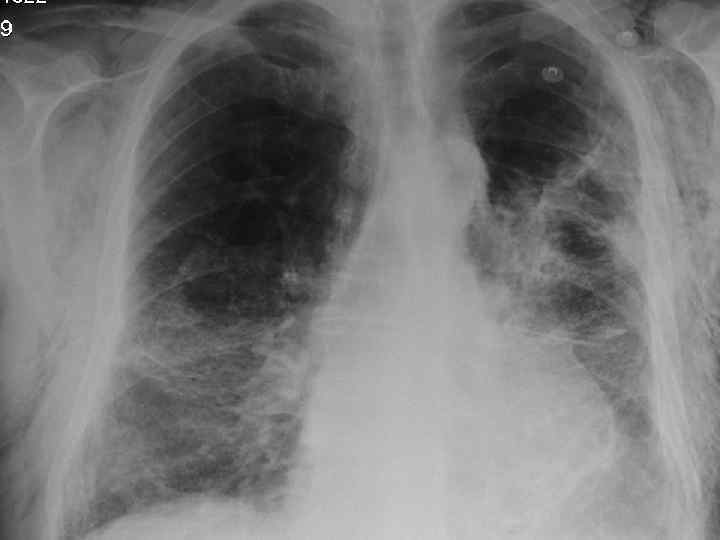
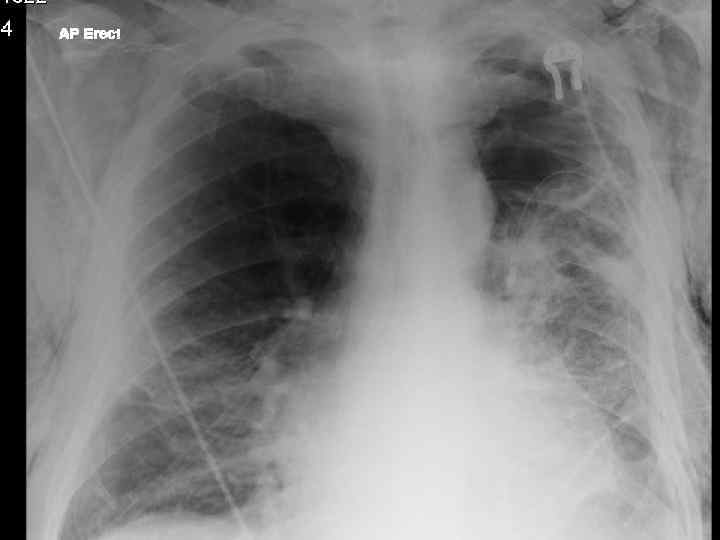
 Impressions n Pneumothorax n COPD/Fibrosing alveolitis n AHA n Congestive heart failure n Newly diagnosed Diabetes mellitus
Impressions n Pneumothorax n COPD/Fibrosing alveolitis n AHA n Congestive heart failure n Newly diagnosed Diabetes mellitus
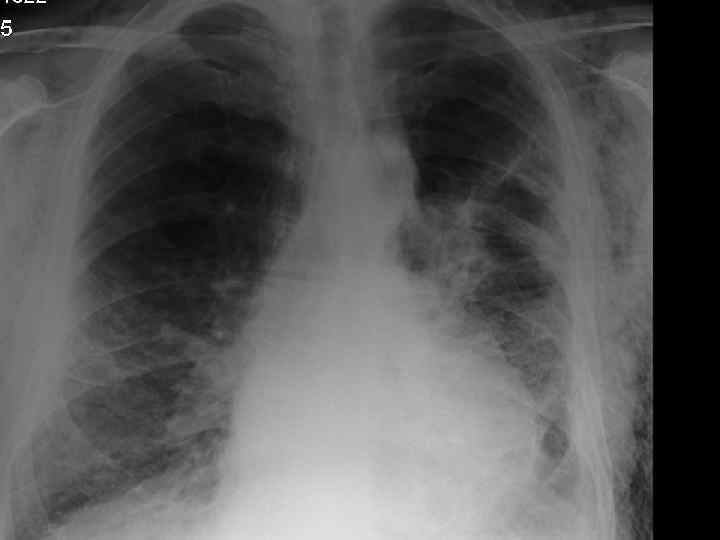
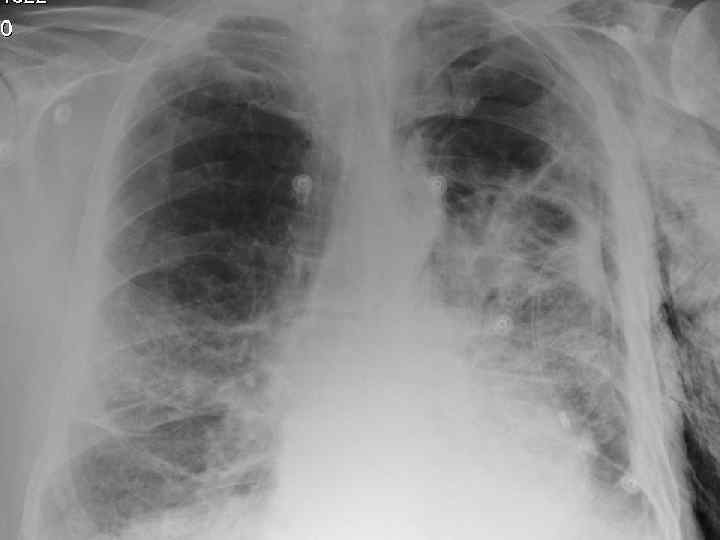
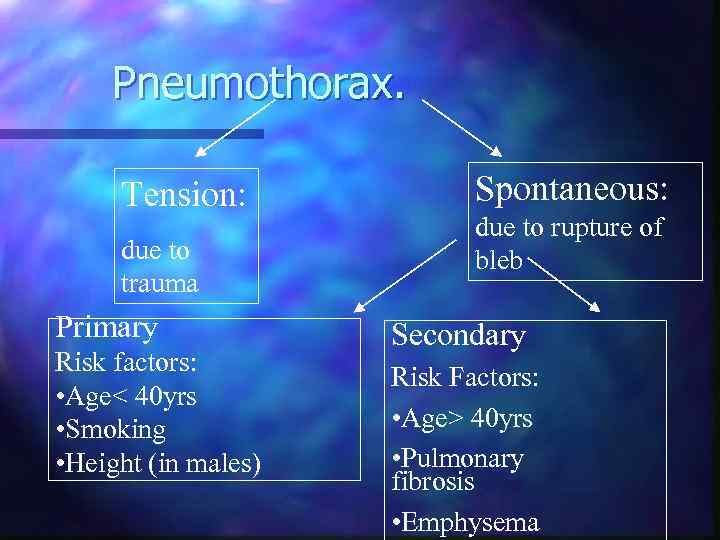 Pneumothorax. Tension: due to trauma Primary Risk factors: • Age< 40 yrs • Smoking • Height (in males) Spontaneous: due to rupture of bleb Secondary Risk Factors: • Age> 40 yrs • Pulmonary fibrosis • Emphysema
Pneumothorax. Tension: due to trauma Primary Risk factors: • Age< 40 yrs • Smoking • Height (in males) Spontaneous: due to rupture of bleb Secondary Risk Factors: • Age> 40 yrs • Pulmonary fibrosis • Emphysema
 Epidemiology. n Incidence - 1. 2 -6/100, 000 women - 18 -28/100, 000 men n Hospital admission rates 5. 8/100, 000 per year for women n 16. 7/100, 000 per year for men n n Mortality rates 0. 62/million per year for women n 1. 26/million per year for men n (between 1991 -1995)
Epidemiology. n Incidence - 1. 2 -6/100, 000 women - 18 -28/100, 000 men n Hospital admission rates 5. 8/100, 000 per year for women n 16. 7/100, 000 per year for men n n Mortality rates 0. 62/million per year for women n 1. 26/million per year for men n (between 1991 -1995)
 Signs and Symptoms. n Sudden SOB n Small (<2 cm)- few signs n Large (>2 cm) Pallor n Tachycardia n chest wall movement n breath sounds n
Signs and Symptoms. n Sudden SOB n Small (<2 cm)- few signs n Large (>2 cm) Pallor n Tachycardia n chest wall movement n breath sounds n
 Investigations. n CXR n CT n Arterial blood gases
Investigations. n CXR n CT n Arterial blood gases
 Treatment of spontaneous pneumothorax. n Depends on: Age n Levels of dyspnoea n Results of CXR n
Treatment of spontaneous pneumothorax. n Depends on: Age n Levels of dyspnoea n Results of CXR n
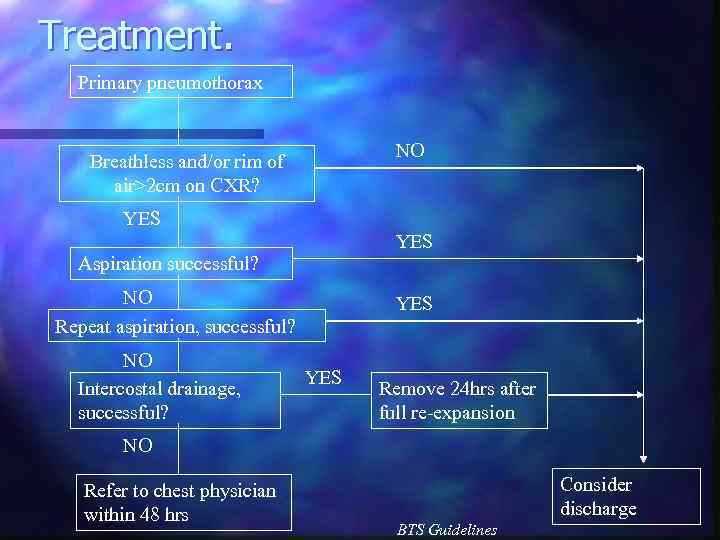 Treatment. Primary pneumothorax NO Breathless and/or rim of air>2 cm on CXR? YES Aspiration successful? NO Repeat aspiration, successful? NO Intercostal drainage, successful? YES Remove 24 hrs after full re-expansion NO Refer to chest physician within 48 hrs Consider discharge BTS Guidelines
Treatment. Primary pneumothorax NO Breathless and/or rim of air>2 cm on CXR? YES Aspiration successful? NO Repeat aspiration, successful? NO Intercostal drainage, successful? YES Remove 24 hrs after full re-expansion NO Refer to chest physician within 48 hrs Consider discharge BTS Guidelines
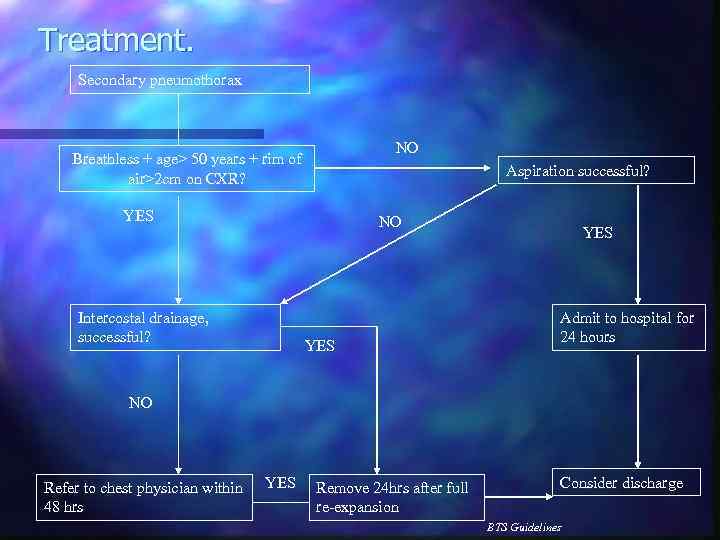 Treatment. Secondary pneumothorax NO Breathless + age> 50 years + rim of air>2 cm on CXR? Aspiration successful? YES NO Intercostal drainage, successful? YES Admit to hospital for 24 hours NO Refer to chest physician within 48 hrs YES Remove 24 hrs after full re-expansion Consider discharge BTS Guidelines
Treatment. Secondary pneumothorax NO Breathless + age> 50 years + rim of air>2 cm on CXR? Aspiration successful? YES NO Intercostal drainage, successful? YES Admit to hospital for 24 hours NO Refer to chest physician within 48 hrs YES Remove 24 hrs after full re-expansion Consider discharge BTS Guidelines
 Simple aspiration.
Simple aspiration.
 Intercostal drainage n Chest drain into triangle marked by: Apex of axilla n Nipple (4 th ics, mid clav. line) n Base of scapula n n Complications: Penetration of major organs n Pleural infection n Surgical emphysema n
Intercostal drainage n Chest drain into triangle marked by: Apex of axilla n Nipple (4 th ics, mid clav. line) n Base of scapula n n Complications: Penetration of major organs n Pleural infection n Surgical emphysema n
 Surgical emphysema n Air filled space in subcutaneous tissue n Felt on skin as bubble wrap n Severe respiratory compromise n Rx- skin incision
Surgical emphysema n Air filled space in subcutaneous tissue n Felt on skin as bubble wrap n Severe respiratory compromise n Rx- skin incision
 Follow up n Unsuccessful referral to resp. physician n Successful discharge with: Chest clinic appointment (after 7 -10 days) n No air travel for 3 mths n Back to hospital if symptoms worsen n
Follow up n Unsuccessful referral to resp. physician n Successful discharge with: Chest clinic appointment (after 7 -10 days) n No air travel for 3 mths n Back to hospital if symptoms worsen n
 Fibrosing alveolitis n Affects less than 3 in 10, 000 n Onset usually after 50 years of age n Affects twice as many men as women n Twice as common in smokers than nonsmokers
Fibrosing alveolitis n Affects less than 3 in 10, 000 n Onset usually after 50 years of age n Affects twice as many men as women n Twice as common in smokers than nonsmokers
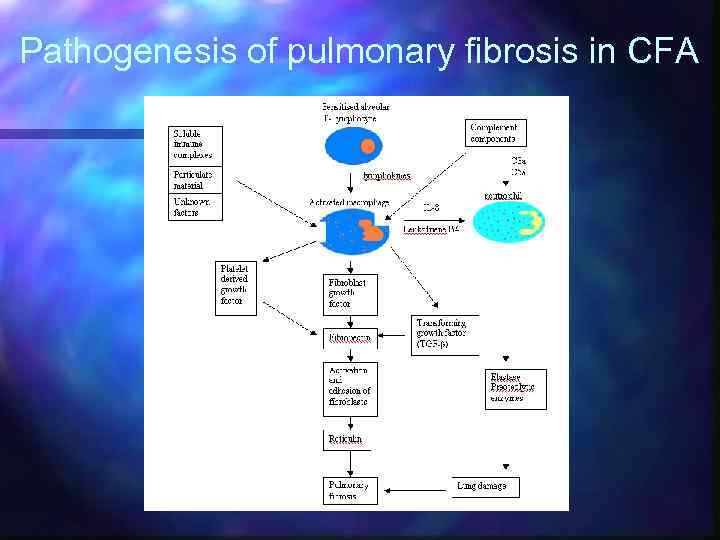 Pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis in CFA
Pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis in CFA
 Histological features of CFA n Cellular infiltration and thickening of alveolar walls n Alveolitis – increased number of cells within the alveolar space
Histological features of CFA n Cellular infiltration and thickening of alveolar walls n Alveolitis – increased number of cells within the alveolar space
 Clinical features n Progressive breathlessness n Cyanosis n Pulmonary hypertension/cor pulmonale n Clubbing n Bilateral fine end insp. Crackles n X-ray shows ground glass appearance
Clinical features n Progressive breathlessness n Cyanosis n Pulmonary hypertension/cor pulmonale n Clubbing n Bilateral fine end insp. Crackles n X-ray shows ground glass appearance
 Investigations n Chest X-ray n High res. CT scan n Respiratory function tests n Blood gasses n ANF, RF, ESR n Bronchoalveolar lavage n Biopsy
Investigations n Chest X-ray n High res. CT scan n Respiratory function tests n Blood gasses n ANF, RF, ESR n Bronchoalveolar lavage n Biopsy
 Differential diagnosis n Extrinsic allergic alveolitis n Bronchiectasis n Chronic LHF n Sarcoidosis n Industrial lung disease n Lymphangitis carcinomatosa
Differential diagnosis n Extrinsic allergic alveolitis n Bronchiectasis n Chronic LHF n Sarcoidosis n Industrial lung disease n Lymphangitis carcinomatosa
 Treatment n Corticosteroids: Prednisolone n Other immunosuppresants: Azathioprine n Oxygen therapy n Single lung transplant
Treatment n Corticosteroids: Prednisolone n Other immunosuppresants: Azathioprine n Oxygen therapy n Single lung transplant