94e96dd64c8133e7763cc55be503c0d3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 History & Govn’t of the United States & Canada
History & Govn’t of the United States & Canada
 How did Climate & Location Affect Early People? • Arctic Tundra: people had to hunt caribou and other animals—too cold to grow crops! • Pacific Coast: mild climate allowed people to harvest salmon from the ocean and to split trees to make canoes and houses • SW Deserts: used irrigation techniques (moving water from a lake or river to dry area) to be able to farm on the dry land. • Great Plains: use of buffalo for food, clothing, shelter & tools. • Native Americans living east of the Mississippi: Built ceremonial mounds, hunted, grew crops and traded (shells & seawater pearls) • NE Woodlands: Natives living in tight-knit villages hunted turkey, geese, squirrels & deer.
How did Climate & Location Affect Early People? • Arctic Tundra: people had to hunt caribou and other animals—too cold to grow crops! • Pacific Coast: mild climate allowed people to harvest salmon from the ocean and to split trees to make canoes and houses • SW Deserts: used irrigation techniques (moving water from a lake or river to dry area) to be able to farm on the dry land. • Great Plains: use of buffalo for food, clothing, shelter & tools. • Native Americans living east of the Mississippi: Built ceremonial mounds, hunted, grew crops and traded (shells & seawater pearls) • NE Woodlands: Natives living in tight-knit villages hunted turkey, geese, squirrels & deer.
 European Settlement: 1500 s • The Spanish owned… – Florida & land west of the Mississippi • The French owned… – St. Lawrence R. & Mississippi R. near the Gulf • The British owned… – Atlantic coast & around Hudson Bay
European Settlement: 1500 s • The Spanish owned… – Florida & land west of the Mississippi • The French owned… – St. Lawrence R. & Mississippi R. near the Gulf • The British owned… – Atlantic coast & around Hudson Bay
 Why did they immigrate? ? God, Glory & Gold • Spanish settlements were founded as military posts or as missions (communities who converted Natives to Christianity) • French set up a fur trade along the St. Lawrence and Mississippi Rivers • British set up colonies along the Atlantic and around Hudson Bay in Canada – Upper: excellent harbor, poor soil (Canadian Shield). Used for shipbuilding & harbors – Middle: longer growing season, wide river valleys (growth & transportation) – South: EXCELLENT soil + extended growing season = large plantations slaves
Why did they immigrate? ? God, Glory & Gold • Spanish settlements were founded as military posts or as missions (communities who converted Natives to Christianity) • French set up a fur trade along the St. Lawrence and Mississippi Rivers • British set up colonies along the Atlantic and around Hudson Bay in Canada – Upper: excellent harbor, poor soil (Canadian Shield). Used for shipbuilding & harbors – Middle: longer growing season, wide river valleys (growth & transportation) – South: EXCELLENT soil + extended growing season = large plantations slaves
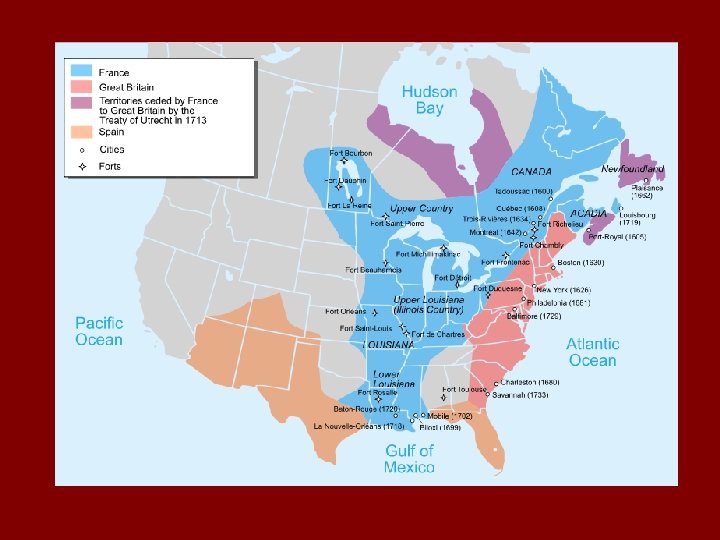
 English Colonies in 1700 s • Upper: excellent harbor, poor soil (Canadian Shield). Used for shipbuilding & harbors, fishing • Middle: longer growing season, wide river valleys (growth & transportation) • South: EXCELLENT soil + extended growing season = large plantations need for slaves • Eventually, the English would go on to be the most powerful group among European colonists (THEY WERE RICH!! The French became poor after a war in France)
English Colonies in 1700 s • Upper: excellent harbor, poor soil (Canadian Shield). Used for shipbuilding & harbors, fishing • Middle: longer growing season, wide river valleys (growth & transportation) • South: EXCELLENT soil + extended growing season = large plantations need for slaves • Eventually, the English would go on to be the most powerful group among European colonists (THEY WERE RICH!! The French became poor after a war in France)
 New Countries • 1763 – France forced to give up North American Empire to British, causing conflict between Natives & Europeans. – Europeans pushed Natives out, causing the destruction of the Native culture • In 1760 s, Britain began imposing taxes & 1775: American Revolution began • After victory, America set up a republic • Constitution signed in 1787
New Countries • 1763 – France forced to give up North American Empire to British, causing conflict between Natives & Europeans. – Europeans pushed Natives out, causing the destruction of the Native culture • In 1760 s, Britain began imposing taxes & 1775: American Revolution began • After victory, America set up a republic • Constitution signed in 1787
 Republic • Rejects monarchy • People elect their officials • George Washington (leader of Cont. Army) was 1 st president
Republic • Rejects monarchy • People elect their officials • George Washington (leader of Cont. Army) was 1 st president
 New Countries • Colonists who did NOT want to break away are called Loyalists – Moved to present-day Canada • Loyalists & French ppl formed Dominion of Canada (1867) – w/in British Empire – Own country 1931 – Monarch still head of state
New Countries • Colonists who did NOT want to break away are called Loyalists – Moved to present-day Canada • Loyalists & French ppl formed Dominion of Canada (1867) – w/in British Empire – Own country 1931 – Monarch still head of state
 Growth • 1803: Louisiana Purchase – Bought land b/w Mississippi River and Rockies from France • War with Mexico gave U. S. more land – Texas became free from Mexico in 1836, then joined U. S. in 1845 – Why Texas? • Rich soil + warm climate = $$$$$$ • 1840 s: won more land through war – California, Nevada & Utah – Parts of Colorado, Wyoming, Arizona & New Mexico
Growth • 1803: Louisiana Purchase – Bought land b/w Mississippi River and Rockies from France • War with Mexico gave U. S. more land – Texas became free from Mexico in 1836, then joined U. S. in 1845 – Why Texas? • Rich soil + warm climate = $$$$$$ • 1840 s: won more land through war – California, Nevada & Utah – Parts of Colorado, Wyoming, Arizona & New Mexico
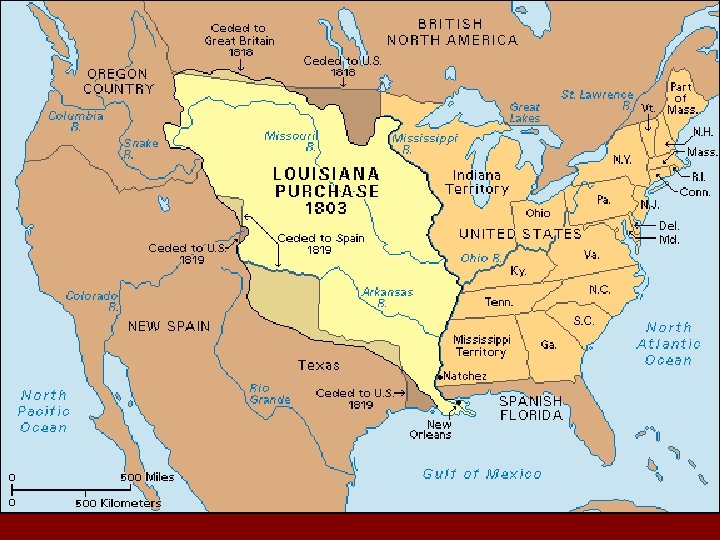
 Growth • California Gold Rush: 1849 – Discovery of gold movement westward – San Francisco 49 ers. . • USA bought Alaska from Russia in 1867 – Alaska did not become a state until 1959 – Eventually bought Hawaii as well
Growth • California Gold Rush: 1849 – Discovery of gold movement westward – San Francisco 49 ers. . • USA bought Alaska from Russia in 1867 – Alaska did not become a state until 1959 – Eventually bought Hawaii as well
 Growth • Emphasis on settlement in Great Plains (interior) –Ease crowding in Eastern cities (NYC) because of recent European immigration –Farming in the region more food for urban, highly populated areas
Growth • Emphasis on settlement in Great Plains (interior) –Ease crowding in Eastern cities (NYC) because of recent European immigration –Farming in the region more food for urban, highly populated areas
 Growth • What effect did westward growth have on Native Americans? –Steady loss of lands –Restrictions on traditional ways of life
Growth • What effect did westward growth have on Native Americans? –Steady loss of lands –Restrictions on traditional ways of life
 Growth • Northeast U. S. - industry, manufacturing (coal mines) – Result: $$$ • Midwest U. S. - business, transport (lots of rivers) – Profit!! $$$ • South- Cotton cash crop (needed for textile industry) – Result: $$$ & need for slaves
Growth • Northeast U. S. - industry, manufacturing (coal mines) – Result: $$$ • Midwest U. S. - business, transport (lots of rivers) – Profit!! $$$ • South- Cotton cash crop (needed for textile industry) – Result: $$$ & need for slaves
 Division • South used slave labor on plantations –Some escaped to Canada (where slavery is illegal) –Used Underground Railroad • Series of “safe houses” used to help slaves escape to the north
Division • South used slave labor on plantations –Some escaped to Canada (where slavery is illegal) –Used Underground Railroad • Series of “safe houses” used to help slaves escape to the north

 Division • Disputes over slavery and economic issues South left the U. S. • Civil War (1861 -1865) • North won under Pres. Lincoln • Slavery abolished, given equal rights eventually
Division • Disputes over slavery and economic issues South left the U. S. • Civil War (1861 -1865) • North won under Pres. Lincoln • Slavery abolished, given equal rights eventually
 Amendments • 13 th: abolished slavery • 14 th: African-Americans now citizens th: Any race can vote • 15 th: Any race & sex can • 19 vote (women)
Amendments • 13 th: abolished slavery • 14 th: African-Americans now citizens th: Any race can vote • 15 th: Any race & sex can • 19 vote (women)
 Social Change • Late 1800 s: transcontinental railroads built –Chinese, Irish, and Mexican immigrants used to build RRs • Early 1900 s: assembly line allows for mass production (esp. cars)
Social Change • Late 1800 s: transcontinental railroads built –Chinese, Irish, and Mexican immigrants used to build RRs • Early 1900 s: assembly line allows for mass production (esp. cars)
 Social Change • WWI and WWII sparked economic growth for U. S. & Canada –Trade partnership grew (more than any 2 countries in the world)
Social Change • WWI and WWII sparked economic growth for U. S. & Canada –Trade partnership grew (more than any 2 countries in the world)
 Social Change • Women, African Americans & Hispanics are participating in politics and in the workplace • Native rights also improving –Inuit in Canada: independence in 1999; creation of Nunavut
Social Change • Women, African Americans & Hispanics are participating in politics and in the workplace • Native rights also improving –Inuit in Canada: independence in 1999; creation of Nunavut
 Government • Both countries have… –DEMOCRACIES –Constitutions –National govn’t shares power with state/provincial govn’ts. –Supreme court w/ 9 judges – 3 branches
Government • Both countries have… –DEMOCRACIES –Constitutions –National govn’t shares power with state/provincial govn’ts. –Supreme court w/ 9 judges – 3 branches
 Government • U. S. has 3 branches 1. Executive (Pres. , Vice Pres. , 2. 3. • • & Cabinet) Judicial (9 judges) Legislative (Congress) Senate House of Representatives
Government • U. S. has 3 branches 1. Executive (Pres. , Vice Pres. , 2. 3. • • & Cabinet) Judicial (9 judges) Legislative (Congress) Senate House of Representatives
 • Government Canada has 3 branches 1. Executive (Prime minister, cabinet, and appointed governor -general) 2. Judicial (9 judges) 3. Legislative (Parliament) – Senate – House of Commons
• Government Canada has 3 branches 1. Executive (Prime minister, cabinet, and appointed governor -general) 2. Judicial (9 judges) 3. Legislative (Parliament) – Senate – House of Commons


