English Когнитивная лингвокультурологическая методология иноязычного образования - .ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Historical background in the development of methodology in FLE Stages of development of theory and practice of FLE 50 th years of the XX century Aims in FLE 1. Practical aims (mastering two objects at the same time: language and speech); 2. General education aims (receiving linguistic knowledge of system, structure, levels and units of language system); 3. The educational aim – expansions of an outlook, formation of the world outlook beginnings. The theory (methodology) providing the realization of the aims of FLE Conscious-comparative approach (or theory). Conscious assimilation through the translation of language material, organized in the form of subsystems, texts, etc. (L. V. Sherba, K. A. Ganshina) Final results 1. Obtain linguistic knowledge of language 2. Formation of practical skills of the speech, but on the basis of the language – sentence.
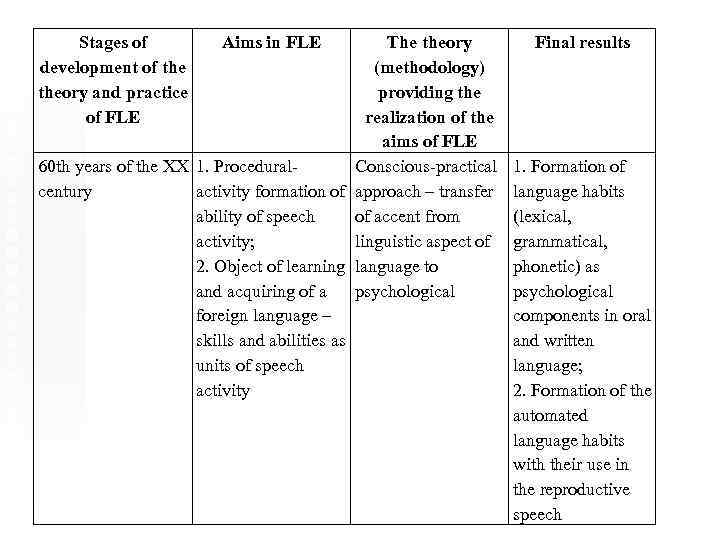
Stages of development of theory and practice of FLE Aims in FLE The theory (methodology) providing the realization of the aims of FLE 60 th years of the XX 1. Procedural. Conscious-practical century activity formation of approach – transfer ability of speech of accent from activity; linguistic aspect of 2. Object of learning language to and acquiring of a psychological foreign language – skills and abilities as units of speech activity Final results 1. Formation of language habits (lexical, grammatical, phonetic) as psychological components in oral and written language; 2. Formation of the automated language habits with their use in the reproductive speech
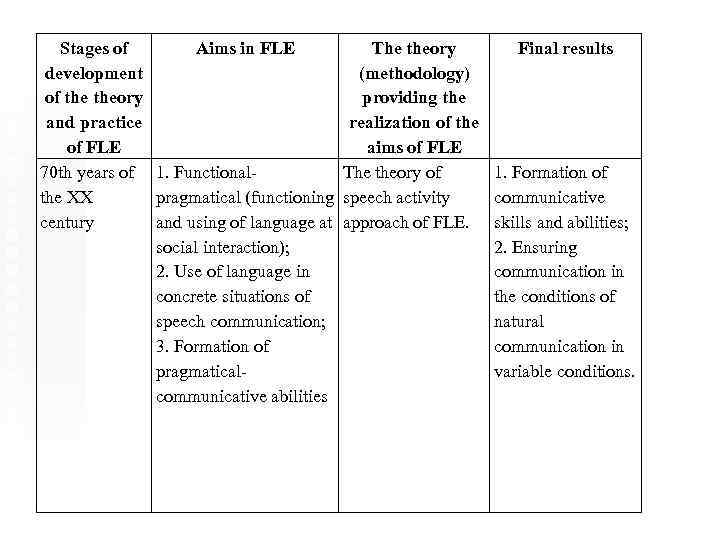
Stages of Aims in FLE development of theory and practice of FLE 70 th years of 1. Functionalthe XX pragmatical (functioning century and using of language at social interaction); 2. Use of language in concrete situations of speech communication; 3. Formation of pragmaticalcommunicative abilities The theory Final results (methodology) providing the realization of the aims of FLE The theory of 1. Formation of speech activity communicative approach of FLE. skills and abilities; 2. Ensuring communication in the conditions of natural communication in variable conditions.
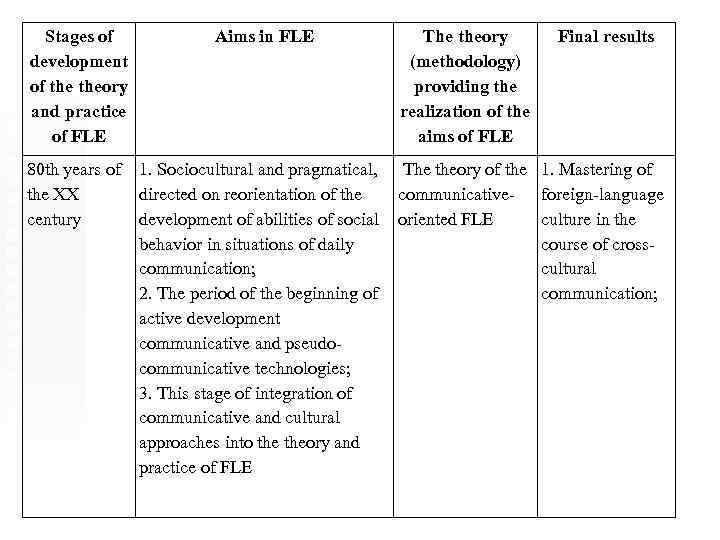
Stages of development of theory and practice of FLE Aims in FLE 80 th years of the XX century 1. Sociocultural and pragmatical, directed on reorientation of the development of abilities of social behavior in situations of daily communication; 2. The period of the beginning of active development communicative and pseudocommunicative technologies; 3. This stage of integration of communicative and cultural approaches into theory and practice of FLE The theory (methodology) providing the realization of the aims of FLE Final results The theory of the 1. Mastering of communicative- foreign-language oriented FLE culture in the course of crosscultural communication;
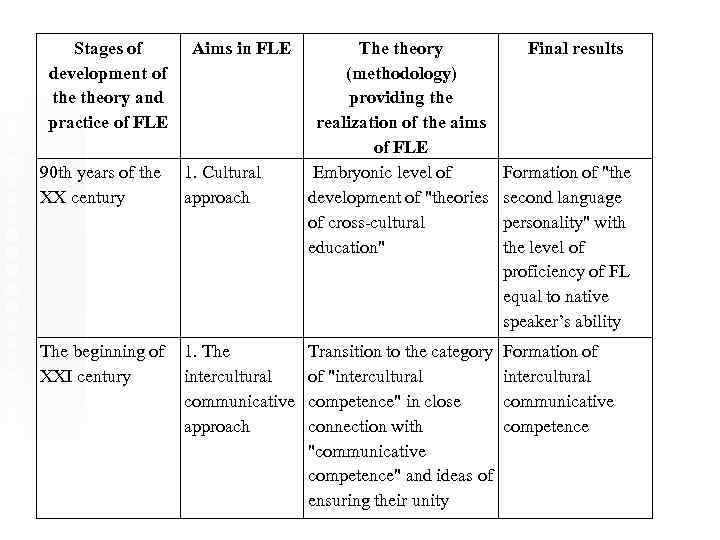
Stages of development of theory and practice of FLE Aims in FLE 90 th years of the XX century 1. Cultural approach The beginning of XXI century 1. The intercultural communicative approach The theory (methodology) providing the realization of the aims of FLE Embryonic level of development of "theories of cross-cultural education" Transition to the category of "intercultural competence" in close connection with "communicative competence" and ideas of ensuring their unity Final results Formation of "the second language personality" with the level of proficiency of FL equal to native speaker’s ability Formation of intercultural communicative competence
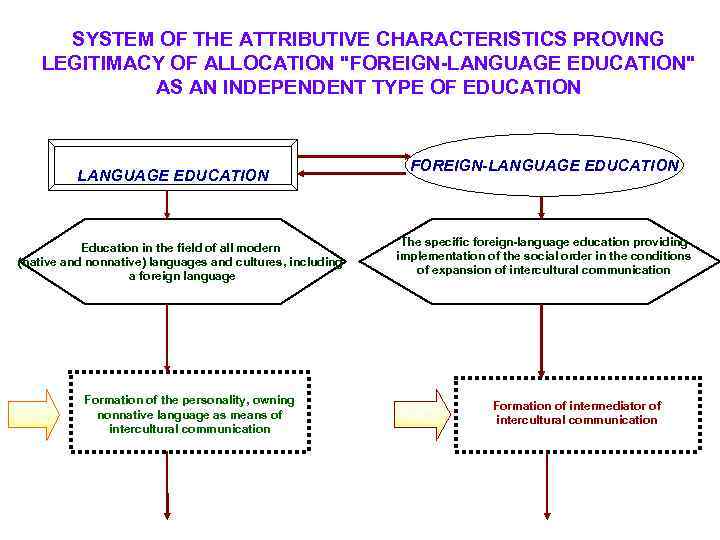
SYSTEM OF THE ATTRIBUTIVE CHARACTERISTICS PROVING LEGITIMACY OF ALLOCATION "FOREIGN-LANGUAGE EDUCATION" AS AN INDEPENDENT TYPE OF EDUCATION LANGUAGE EDUCATION Education in the field of all modern (native and nonnative) languages and cultures, including a foreign language ЦЕЛЬ Formation of the personality, owning nonnative language as means of intercultural communication FOREIGN-LANGUAGE EDUCATION The specific foreign-language education providing implementation of the social order in the conditions of expansion of intercultural communication ЦЕЛЬ Formation of intermediator of intercultural communication
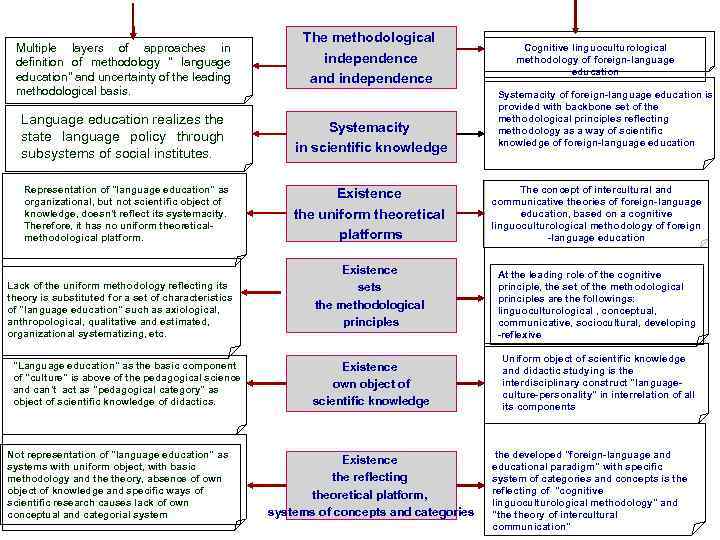
Multiple layers of approaches in definition of methodology " language education" and uncertainty of the leading methodological basis. The methodological independence and independence Language education realizes the state language policy through subsystems of social institutes. Systemacity in scientific knowledge Representation of "language education" as organizational, but not scientific object of knowledge, doesn't reflect its systemacity. Therefore, it has no uniform theoreticalmethodological platform. Existence the uniform theoretical platforms Lack of the uniform methodology reflecting its theory is substituted for a set of characteristics of "language education" such as axiological, anthropological, qualitative and estimated, organizational systematizing, etc. "Language education" as the basic component of "culture" is above of the pedagogical science and can't act as "pedagogical category" as object of scientific knowledge of didactics. Not representation of "language education" as systems with uniform object, with basic methodology and theory, absence of own object of knowledge and specific ways of scientific research causes lack of own conceptual and categorial system Existence sets the methodological principles Existence own object of scientific knowledge Existence the reflecting theoretical platform, systems of concepts and categories Cognitive linguoculturological methodology of foreign-language education Systemacity of foreign-language education is provided with backbone set of the methodological principles reflecting methodology as a way of scientific knowledge of foreign-language education The concept of intercultural and communicative theories of foreign-language education, based on a cognitive linguoculturological methodology of foreign -language education At the leading role of the cognitive principle, the set of the methodological principles are the followings: linguoculturological , conceptual, communicative, sociocultural, developing -reflexive Uniform object of scientific knowledge and didactic studying is the interdisciplinary construct "languageculture-personality" in interrelation of all its components the developed "foreign-language and educational paradigm" with specific system of categories and concepts is the reflecting of "cognitive linguoculturological methodology" and "the theory of intercultural communication"
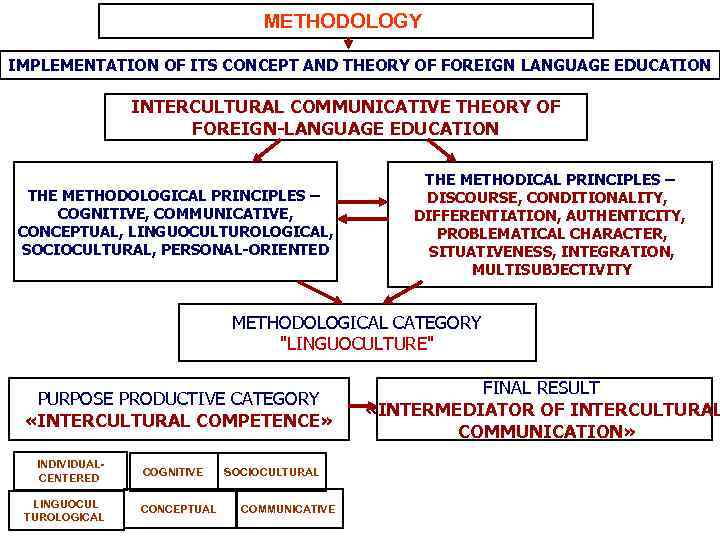
METHODOLOGY IMPLEMENTATION OF ITS CONCEPT AND THEORY OF FOREIGN LANGUAGE EDUCATION INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATIVE THEORY OF FOREIGN-LANGUAGE EDUCATION THE METHODOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES – COGNITIVE, COMMUNICATIVE, CONCEPTUAL, LINGUOCULTUROLOGICAL, SOCIOCULTURAL, PERSONAL-ORIENTED THE METHODICAL PRINCIPLES – DISCOURSE, CONDITIONALITY, DIFFERENTIATION, AUTHENTICITY, PROBLEMATICAL CHARACTER, SITUATIVENESS, INTEGRATION, MULTISUBJECTIVITY METHODOLOGICAL CATEGORY "LINGUOCULTURE" PURPOSE PRODUCTIVE CATEGORY «INTERCULTURAL COMPETENCE» INDIVIDUALCENTERED LINGUOCUL TUROLOGICAL COGNITIVE CONCEPTUAL SOCIOCULTURAL COMMUNICATIVE FINAL RESULT «INTERMEDIATOR OF INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION»
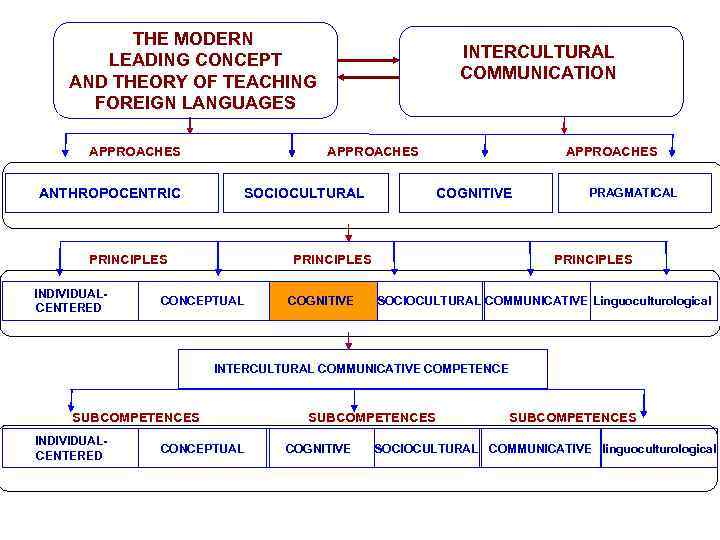
THE MODERN LEADING CONCEPT AND THEORY OF TEACHING FOREIGN LANGUAGES APPROACHES ANTHROPOCENTRIC APPROACHES SOCIOCULTURAL PRINCIPLES INDIVIDUALCENTERED INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION APPROACHES COGNITIVE PRINCIPLES CONCEPTUAL COGNITIVE PRAGMATICAL PRINCIPLES SOCIOCULTURAL COMMUNICATIVE Linguoculturological INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE SUBCOMPETENCES INDIVIDUALCENTERED CONCEPTUAL SUBCOMPETENCES COGNITIVE SUBCOMPETENCES SOCIOCULTURAL COMMUNICATIVE linguoculturological
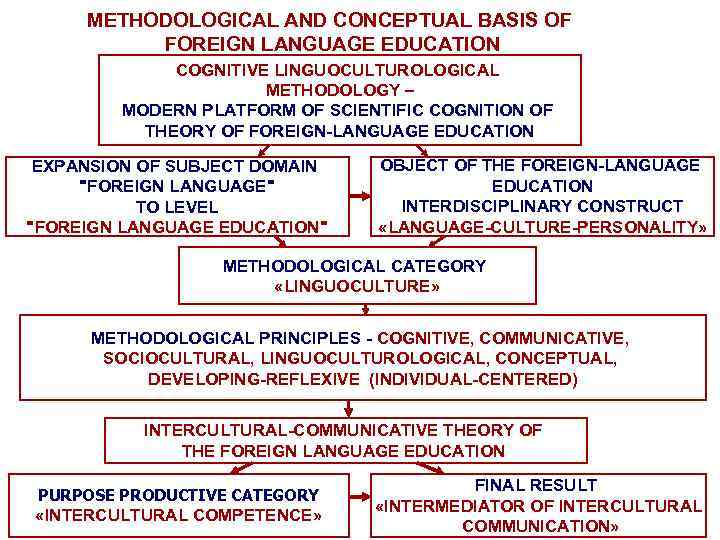
METHODOLOGICAL AND CONCEPTUAL BASIS OF FOREIGN LANGUAGE EDUCATION COGNITIVE LINGUOCULTUROLOGICAL METHODOLOGY – MODERN PLATFORM OF SCIENTIFIC COGNITION OF THEORY OF FOREIGN-LANGUAGE EDUCATION EXPANSION OF SUBJECT DOMAIN "FOREIGN LANGUAGE" TO LEVEL "FOREIGN LANGUAGE EDUCATION" OBJECT OF THE FOREIGN-LANGUAGE EDUCATION INTERDISCIPLINARY CONSTRUCT «LANGUAGE-CULTURE-PERSONALITY» METHODOLOGICAL CATEGORY «LINGUOCULTURE» METHODOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES - COGNITIVE, COMMUNICATIVE, SOCIOCULTURAL, LINGUOCULTUROLOGICAL, CONCEPTUAL, DEVELOPING-REFLEXIVE (INDIVIDUAL-CENTERED) INTERCULTURAL-COMMUNICATIVE THEORY OF THE FOREIGN LANGUAGE EDUCATION PURPOSE PRODUCTIVE CATEGORY «INTERCULTURAL COMPETENCE» FINAL RESULT «INTERMEDIATOR OF INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION»

COGNITO- LINGUOCULTUROLOGICAL METHODOLOGY MODERN PLATFORM OF SCIENTIFIC COGNITION OF THEORY OF FOREIGN-LANGUAGE EDUCATION 1. Obligatory characteristics of methodology of "foreign-language education" as theories of scientific cognition are: - systemacity in scientific cognition and research of concrete scientific area; - existence of the uniform theoretical platform providing disclosure of integrity of object, functional coherence of its components; - existence of set of the methodological principles reflecting concrete methodology of this science; existence of system of the concepts and categories reflecting a theoretical platform. 2. Legitimacy of definition of methodology of foreign-language education as "cognito-linguoculturological " locates not only expansion of object of the knowledge (foreign language - foreign culture - the personality) which is caused by need of a reconceptualization of the world when familiarizing with a new linguoculture in specific ways of scientific cognition – the methodological principles, but also the change of purposes and the end result which is defined as uniform process of formation and formation of the identity of "the intermediator of intercultural communication". Cognito-linguoculturological basis makes a substantial - conceptual and activity platformation of "the intermediator of intercultural communication".

EXPANSION OF THE SUBJECT DOMAIN "Foreign language" to the level of Foreign-language Education The intercultural and communicative theory of teaching foreign languages as the leading modern concept of foreign-language education reflects its orientation on the integrated teaching language and culture providing disclosure of language as the translator of the sociocultural specifics of national and language communities at the communication promoting their mutual understanding and interaction in the conditions of the open world. Respectively, it predetermines the change of a subject of studying and mastering – "foreign language" to the difficult and integrated concept "foreign-language education".

OBJECT OF FOREIGN-LANGUAGE EDUCATION INTERDISCIPLINARY CONSTRUCT "language-culture-personality" The methodology and the modern intercultural and communicative concept of foreign-language education systemically and completely investigates and opens complex and interdisciplinary construct "languageculture-personality" as object of scientific cognition of interrelation of all its components. Complex and difficult construct "language-culture-personality" as the object of scientific cognition of a number of sciences acts as uniform object of the scientific analysis and didactic studying of foreign-language education of that language and culture as the uniform complex as it is an integral part of process of cognition and formation of the secondary mental constructs providing new language conceptualization of the world by the personality and serves for it as system of coordinates which it uses at perception with world around in the course of familiarizing with a new linguoculturological and own formation as the intermediator of intercultural communication".

METHODOLOGICAL CATEGORY «Linguoculture» Respectively, objective manifestation of socialization of the personality is its familiarizing, mental reflection and mastering such organic unity as language and culture of a certain ethnos which has the basic and fixed form of thinking on the basis of a native linguoculture. Respectively, it is lawful to define the category "linguoculture" and as a methodological basis of concrete scientific area – theory of foreign-language education capable in the integrated refraction to provide cognition and studying of specific regularities of interaction as whole "language-culture-personality".

METHODOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES: Cognitive, communicative, sociocultural, linguoculturological , conceptual, developing-reflexive Full reflection of essence of modern methodology of theory of foreign-language education is provided with set of the methodological principles (cognitive, conceptual, communicative, linguoculturological , sociocultural, developing reflexive). intermediator of intercultural communication" can be reached by an ultimate attainable aim of teaching foreign languages in modern conditions only as a result when ensuring formation of "secondary cognitive consciousness" as an image of the world of other people as the cognitive caused process of "resocialization" with various degree of approachibility. "Resocialization" of the subject and language acquisition through culture of the country of the target language at the cognitive level shouldn't represent uniform process of formation and formation of the personality of the future "intermediator of intercultural communication". The communicative principle assumes possession of all complex of communicative behavior as set of norms and traditions of communication of the people of this or that linguoculturological community that in turn causes that fact that not formation of an adequate pragmatical component of intercultural communication and the communicative behavior typical for a linguasociety of the country of the target language is the reason of failures in situations of intercultural communication as this component realizes interrelation between speaking, the statement and a communicative context. The sociocultural principle penetrates all links of system of the intercultural communicative theory of foreignlanguage education: from the level of formation of new layer in structure of knowledge and the mental mechanism aimed at the final result – formation of the identity of "the intermediator of intercultural communication" to a substantial, methodical and technological reorganization of all educational process. The sociocultural principle is focused on formation of knowledge of the bicultural subject of communication which is based on comparative studying of data of native and foreign culture society.

INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATIVE THEORY OF FOREIGN-LANGUAGE EDUCATION The uniform theoretical platform reflecting integrity of object of scientific research and didactic studying is the modern leading concept of the "intercultural communicative" theory of foreignlanguage education based on a cognito-linguoculturological methodology which is fundamentals of modern humanistic philosophy of education. The purpose and the final result of foreign-language education – the intercultural communicative competence of personality created as "the intermediator of intercultural communication" testify to legitimacy of: - Choice and development cognito-linguoculturological methodology of theory of foreign-language education; - legitimacy of allocation of "linguoculture" as the basic and methodologically significant category synthesizing in uniform and organic whole "language-culture-personality"; - methodological adequacy of theory of "intercultural communication" as modern and the social caused concept of foreign-language education cemented in system by set of the methodological principles which is integrated and complex, the methodical concepts and categories, technologies, subject and procedural aspects of the maintenance of a foreign language which are realized within the methodical system of the same name through system, etc. ; - validity of a choice of methodology of theory of foreign-language education owing to an reflection in a cognito- linguoculturological theory of knowledge of concrete scientific area of anthropological and humanistic philosophy of education of formation of the identity of "the intermediator of intercultural communication" through his cognitive caused activity directed on a linguoculturological reconceptualization of the world when familiarizing with a new linguoculture; - scientific validity of allocation of "foreign-language education" in independent didactic area which: 1. having an object of scientific cognition; 2. representing system with backbone set of the methodological principles reflecting its methodology; 3. based on a uniform theoretical platform; 4. opening complete object (language-culture-personality); 5. having own system of concepts and categories

PURPOSE PRODUCTIVE CATEGORY «INTERCULTURAL COMPETENCE» "Intercultural competence" as the realized purpose and result of intercultural and communicative teacching is urged to reflect the result of the interconnected manifestation of the methodological principles: communicative, linguoculturological, sociocultural, conceptual, individual-centered at the leader – cognitive. Level of formation of intercultural competence is defined as the cognitive caused process of "resocialization" with various degree of approachibility, and "resocialization" of the subject and language acquisition through culture of the country of the target language at the cognitive level shouldn't represent uniform process of formation and formation of the personality of the future “intermediator of intercultural communication".

FINAL RESULT «intermediator of intercultural communication» It is expedient to understand "the intermediator of intercultural communication" as the personality with the high level of formation of cognitive and activity and communicative bases of intercultural communication, reflecting existence of "secondary cognitive consciousness" of the subject and providing ability of the personality adequately carry out intercultural communication, flexibly reacting to variable variability of situations of communication, showing thus strong fixedness socio-andlinguoculturological components of intercultural competence, the communicative and behavioral culture corresponding standards of a linguosociety. Achievements of level of the personality of “intermediator of intercultural communication": - the most achievable qualitative level in the conditions of lack of the language and sociocultural environment; - existence of elements of the created "secondary socialization" and representation of cognitive and social mental construct in consciousness of the subject as process of "resocialization" of the personality. Definition of the final result of foreign-language education as formation of level of the personality of "the intermediator of intercultural communication" is caused by that in qualitative and educational aspect this level: - is the most achievable in the conditions of lack of the language and sociocultural environment; - it is characterized by intercultural and communicative competence; - provides ability of the personality to carry out intercultural communication in variable professional and life situations. In cognitive and activity aspect achievement of this level of the personality - is provided with conscious and purposeful activity of the future “intermediator of intercultural communication", the directed formation new cognito- linguoculturological complexes included in the general cognitive mechanism of the personality in process of assimilation of foreign language and foreign culture; -assumes formation of "secondary cognitive consciousness" and process of gradual resocialization of the personality through the socializing concept of other socio-and-linguoculture;
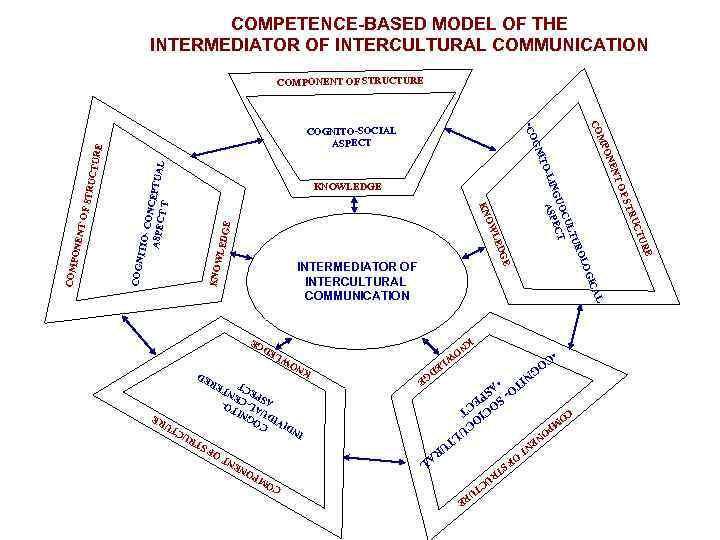
COMPETENCE-BASED MODEL OF THE INTERMEDIATOR OF INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION ITIOCONC EP ASPE CT Т TUAL DGE L ICA OG OW KN • C GE LE OG NI N U NE LT PO CU M IO T CO OC C - S SPE TO • A T OF ST KNO WLE RE TU UC TR OL INTERMEDIATOR OF INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION FS R LTU CU UO ECT ASP GE E DG TU RE LE D OW KN RE D ND IV C ID OGN UA IT O A L SP -CEN EC T TE I EN TO FS RA L C RU COGN TO NG CO MP ON TR UC TU RE F STR EN -LI LED NT O ON ITO KNOWLEDGE OW PONE MP GN COGNITO-SOCIAL ASPECT KN COM CO • CO UCTU RE COMPONENT OF STRUCTURE

Intermediator of intercultural communication It is expedient to understand "the intermediator of intercultural communication" as the personality with the high level of formation of cognitive and activity and communicative bases of intercultural communication, reflecting existence of "secondary cognitive consciousness" of the subject and providing ability of the personality adequately carry out intercultural communication, flexibly reacting to variable variability of situations of communication, showing thus strong fixedness socio-linguoculturological components of intercultural competence, the communicative and behavioral culture corresponding standards of a linguosociety.

COGNITO-SOCIAL ASPECT The cognito-social aspect is an integral part of process of cognition and formation of thinking, shown in the cognitive structures as mental education. The person perceives the world around and interacts with it as the generalized carrier of natural language, reflecting the collective consciousness which caused by social mentality of social categories of society. This component of structure of knowledge can be defined as cognito-social aspect of structure of knowledge.

COGNITO-LINGUOCULTUROLOGICAL ASPECT Cognito-linguoculturological aspect reveals regularities of cognitive processes and mechanisms of formation of the language personality and formations of its primary “conceptual picture of the world“ on base of their own culture, as linguoculturological reflection of the national language consciousness and mentality. This component structure of knowledge represents itself cognito-linguoculturological aspect of structure of knowledge.

COGNITO-SOCIOCULTURAL ASPECT Formation of the intermediator of intercultural communication is reached by formation of "secondary cognitive consciousness" as concept and an image of the world of other linguosociety, having a form of the secondary cognitive consciousness, according to a picture of the language of the world. This component is defined by us as cognitosociocultural aspect of structure of knowledge. Allocation of this aspect as independent in structure of knowledge is caused by its didactic importance in theory intercultural communication and teaching foreign language.

COGNITO-INDIVIDUAL-CENTERED ASPECT Cognitive mechanisms and cognitive processing of language in consciousness, occurring in parallel at all levels (semantic, syntactic, pragmatical) proves legitimacy of studying human language and general cognitive mechanisms of language as constructs of human personality. Thereby the anthropocentric paradigm includes with obligation the reflection of such structure as concept of the world by the language personality. Respectively, this component of structure of knowledge is defined by us as cognito-individual-centered aspect of knowledge, which joins in secondary cognitive consciousnesses of future intermediator of intercultural consciousness.

COGNITO-CONCEPTUAL ASPECT Cognitive approach in linguistics is often identified with conceptual reflection of structures of knowledge of the world. Conceptual representation of human consciousness and an identification Cognito-conceptual in the processing of information arriving from the outside, roles of memory in these processes, locates that language is understood as "a source of data about conceptual or cognitive structures of our consciousness and intelligence"; the language categorization is predetermined by a cognition (set the mental processes processing and conceptually organizing the arriving Information in blocks) which is isomorphic with mental and substantial structure of knowledge; This component of structure of knowledge can be defined as cognitoconceptual aspect of structure of knowledge.
English Когнитивная лингвокультурологическая методология иноязычного образования - .ppt