a33c63eda6f0339019e223a550d21fee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 HIPSSA Project Support for Harmonization of the ICT Policies in Sub-Sahara Africa Data protection principles and the model-law Jean-Marc Van Gyseghem, HIPSSA expert International Telecommunication Union
HIPSSA Project Support for Harmonization of the ICT Policies in Sub-Sahara Africa Data protection principles and the model-law Jean-Marc Van Gyseghem, HIPSSA expert International Telecommunication Union
 Table of contents § Study framework; § Analyzed references § Determination of the principles: Ø Openness; Ø Definitions; Ø Purposes; Ø Legitimacy; Ø Necessity/proportionality; Ø Data quality; Ø Special categories of data; 2
Table of contents § Study framework; § Analyzed references § Determination of the principles: Ø Openness; Ø Definitions; Ø Purposes; Ø Legitimacy; Ø Necessity/proportionality; Ø Data quality; Ø Special categories of data; 2
 Table of contents Ø Security; Ø Confidentiality; Ø Accountability Ø Rights of the data subject; Ø Sanction; Ø Protection authority; Ø Transborder data flows. § Skeleton of the Draft of the model-law 3
Table of contents Ø Security; Ø Confidentiality; Ø Accountability Ø Rights of the data subject; Ø Sanction; Ø Protection authority; Ø Transborder data flows. § Skeleton of the Draft of the model-law 3
 Framework of the analysis § Objectives: Ø Suggest an analysis of the international frameworks on data protection; Ø Suggest a panorama of: § International references; § Principles mentionned in the international references; Ø Suggest a model-law taking in accound these principles. 4
Framework of the analysis § Objectives: Ø Suggest an analysis of the international frameworks on data protection; Ø Suggest a panorama of: § International references; § Principles mentionned in the international references; Ø Suggest a model-law taking in accound these principles. 4
 International references analyzed 5 § Africa: Ø draft on the establishment of a credible legal framework for cyber security in Africa; Ø Supplementary act a/sa…/12/09 on guidelines on personal data protection within ECOWAS Ø Protocol on Health (SADC) Ø Protocol against corruption (SADC) Ø Protocol on extradition (SADC) Ø Protocol on mutual legal assistance in criminal matters (SADC) Ø Cybersecurity draft policy Guidelines (COMESA) Ø Comesa model law on electronic transactions and guide to enactment 2010 (COMESA) Ø Supplementary act a/sa. 1/01/07 on the harmonization of policies and of the regulatory framework for the information and communication technology (ict) sector
International references analyzed 5 § Africa: Ø draft on the establishment of a credible legal framework for cyber security in Africa; Ø Supplementary act a/sa…/12/09 on guidelines on personal data protection within ECOWAS Ø Protocol on Health (SADC) Ø Protocol against corruption (SADC) Ø Protocol on extradition (SADC) Ø Protocol on mutual legal assistance in criminal matters (SADC) Ø Cybersecurity draft policy Guidelines (COMESA) Ø Comesa model law on electronic transactions and guide to enactment 2010 (COMESA) Ø Supplementary act a/sa. 1/01/07 on the harmonization of policies and of the regulatory framework for the information and communication technology (ict) sector
 International references analyzed § United Nations: Ø Guidelines for the Regulation of Computerized Personal Data Files § OECD Ø Guidelines on the Protection of Privacy and Transborder Flows of Personal Data Ø OECD Recommendation on Cross-border Cooperation in the Enforcement of Laws Protecting Privacy 6
International references analyzed § United Nations: Ø Guidelines for the Regulation of Computerized Personal Data Files § OECD Ø Guidelines on the Protection of Privacy and Transborder Flows of Personal Data Ø OECD Recommendation on Cross-border Cooperation in the Enforcement of Laws Protecting Privacy 6
 International references analyzed 7 § Council of Europe Ø Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms Ø Convention for the Protection of Individuals with regard to Automatic Processing of Personal Data Ø Additional Protocol to the Convention for the Protection of Individuals with regard to Automatic Processing of Personal Data, regarding supervisory authorities and transborder data flows
International references analyzed 7 § Council of Europe Ø Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms Ø Convention for the Protection of Individuals with regard to Automatic Processing of Personal Data Ø Additional Protocol to the Convention for the Protection of Individuals with regard to Automatic Processing of Personal Data, regarding supervisory authorities and transborder data flows
 International references analyzed § European Union Ø Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union Ø Directive 95/46 on the protection of individuals with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data Convention for the Protection of Individuals with regard to Automatic Processing of Personal Data Ø Directive 2002/58 on electronic communications was adopted (2002). It's also known as the e. Privacy Directive 8
International references analyzed § European Union Ø Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union Ø Directive 95/46 on the protection of individuals with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data Convention for the Protection of Individuals with regard to Automatic Processing of Personal Data Ø Directive 2002/58 on electronic communications was adopted (2002). It's also known as the e. Privacy Directive 8
 International references analyzed § Conference of Madrid (2009) Ø Madrid Resolution § Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Ø Privacy framework 9
International references analyzed § Conference of Madrid (2009) Ø Madrid Resolution § Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Ø Privacy framework 9
 Determination of the principles 10 § Openness ØMost important principle; ØOpenness towards the data subject; ØOther principles stem from this one: § Information of the data subject; § Rights of access; § Notification to protection authority (https: //www. privacycommission. be/elg/public. Register. htm ? dec. Archive. Id=36689) § Etc. ØArticle 23 (and articles 14, 15, 24, etc)
Determination of the principles 10 § Openness ØMost important principle; ØOpenness towards the data subject; ØOther principles stem from this one: § Information of the data subject; § Rights of access; § Notification to protection authority (https: //www. privacycommission. be/elg/public. Register. htm ? dec. Archive. Id=36689) § Etc. ØArticle 23 (and articles 14, 15, 24, etc)
 Determination of the principles § Definitions ØAllow a comprehension of the various terms used in the given legislation; ØAllow a standardization; ØArticle 1 11
Determination of the principles § Definitions ØAllow a comprehension of the various terms used in the given legislation; ØAllow a standardization; ØArticle 1 11
 12
12
 Determination of the principles 13 § Specified purpose ØAllow data subjetc to know what his/her data are processed for; ØAllow the data subject to control the processing of his/her personal data (informational auto determination); ØSet a time of storage of the personal data before the deletion/anonymisation. ØArticle 10.
Determination of the principles 13 § Specified purpose ØAllow data subjetc to know what his/her data are processed for; ØAllow the data subject to control the processing of his/her personal data (informational auto determination); ØSet a time of storage of the personal data before the deletion/anonymisation. ØArticle 10.
 Determination of the principles § Necessity/proprotionnality ØProcessing necessary to the specified purpose (choice of the less invasive way); ØData which are necessary for the processing ØChapters 3 & 4. 14
Determination of the principles § Necessity/proprotionnality ØProcessing necessary to the specified purpose (choice of the less invasive way); ØData which are necessary for the processing ØChapters 3 & 4. 14
 Determination of the principles § Legitimacy ØMust be in accordance with the expectation of the individuals; ØIn accordance with the law ØChapter 4, sections 2 & 3 15
Determination of the principles § Legitimacy ØMust be in accordance with the expectation of the individuals; ØIn accordance with the law ØChapter 4, sections 2 & 3 15
 Determination of the principles § Special categories of data ØReligion; ØEthnic; ØHealth ØSexuality; ØFiliation; ØEtc ØArticles 8 and following 16
Determination of the principles § Special categories of data ØReligion; ØEthnic; ØHealth ØSexuality; ØFiliation; ØEtc ØArticles 8 and following 16
 Determination of the principles § Security/confidentiality Ø Security: two levels: § Organizational: – Training given to the people who process personal data; – Establishment of a structure to avoid: – Lost of data; – Unauthorized access; – Etc. Ø Technical: § Access management; § Management of the lasting quality of the data (against deletion, deterioration, etc) Ø Chapter 5, sections 2 & 3. 17
Determination of the principles § Security/confidentiality Ø Security: two levels: § Organizational: – Training given to the people who process personal data; – Establishment of a structure to avoid: – Lost of data; – Unauthorized access; – Etc. Ø Technical: § Access management; § Management of the lasting quality of the data (against deletion, deterioration, etc) Ø Chapter 5, sections 2 & 3. 17
 Determination of the principles § Data processing ØWork under the instruction of the data controller; ØContract between data controller and data processor; ØArticles 17 & 18. 18
Determination of the principles § Data processing ØWork under the instruction of the data controller; ØContract between data controller and data processor; ØArticles 17 & 18. 18
 Determination of the principles § Accountability: Øto make the data controller and data processor aware of their responsibilities ; ØObligation to give explanation to the protection authorities and data subject. ØArticle 23 19
Determination of the principles § Accountability: Øto make the data controller and data processor aware of their responsibilities ; ØObligation to give explanation to the protection authorities and data subject. ØArticle 23 19
 Determination of the principles § Data subject rights Øaccess; ØRectification; ØEtc. ØChapter 6 20
Determination of the principles § Data subject rights Øaccess; ØRectification; ØEtc. ØChapter 6 20
 Determination of the principles 21 § Sanctions ØCivil (liability) ØCriminal with a preventive action and a repressive action; ØAdministrative (protection authority) with a preventive action and a repressive action; ØChapter 7, section 15 & chapters 8, 9 and 10.
Determination of the principles 21 § Sanctions ØCivil (liability) ØCriminal with a preventive action and a repressive action; ØAdministrative (protection authority) with a preventive action and a repressive action; ØChapter 7, section 15 & chapters 8, 9 and 10.
 Determination of the principles § Protection authority ØIndependent; ØProtect the principles mentioned before ØPreventive action; ØRepressive action; ØPunisher; Ø… ØChapter 7 22
Determination of the principles § Protection authority ØIndependent; ØProtect the principles mentioned before ØPreventive action; ØRepressive action; ØPunisher; Ø… ØChapter 7 22
 Determination of the principles § Transborder data flow: ØBased an a equivalent protection in case of transfer to another country: § By legal rules; § By contract; § By hybrid systems (safe harbor principle) § Chapter 12 23
Determination of the principles § Transborder data flow: ØBased an a equivalent protection in case of transfer to another country: § By legal rules; § By contract; § By hybrid systems (safe harbor principle) § Chapter 12 23
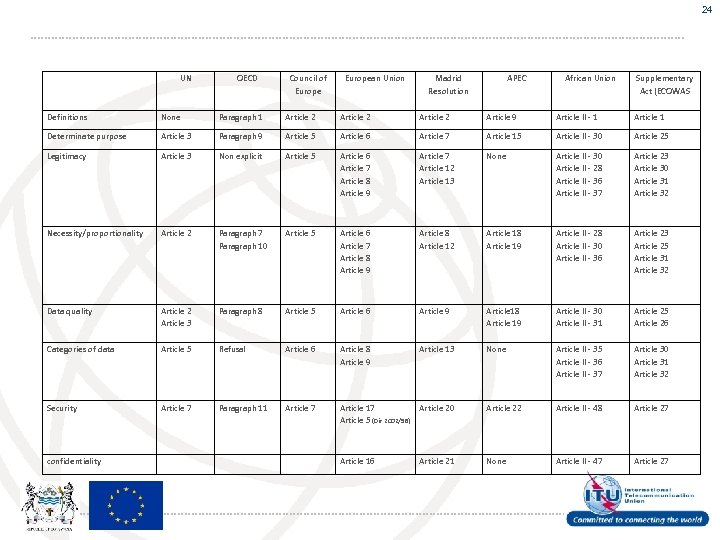 24 UN OECD Council of European Union Madrid Resolution APEC African Union Supplementary Act (ECOWAS Definitions None Paragraph 1 Article 2 Article 9 Article II - 1 Article 1 Determinate purpose Article 3 Paragraph 9 Article 5 Article 6 Article 7 Article 15 Article II - 30 Article 25 Legitimacy Article 3 Non explicit Article 5 Article 6 Article 7 Article 8 Article 9 Article 7 Article 12 Article 13 None Article II - 30 Article II - 28 Article II - 36 Article II - 37 Article 23 Article 30 Article 31 Article 32 Necessity/proportionality Article 2 Paragraph 7 Paragraph 10 Article 5 Article 6 Article 7 Article 8 Article 9 Article 8 Article 12 Article 18 Article 19 Article II - 28 Article II - 30 Article II - 36 Article 23 Article 25 Article 31 Article 32 Data quality Article 2 Article 3 Paragraph 8 Article 5 Article 6 Article 9 Article 18 Article 19 Article II - 30 Article II - 31 Article 25 Article 26 Categories of data Article 5 Refusal Article 6 Article 8 Article 9 Article 13 None Article II - 35 Article II - 36 Article II - 37 Article 30 Article 31 Article 32 Security Article 7 Paragraph 11 Article 7 Article 17 Article 20 Article 5 (Dir 2002/58) Article 22 Article II - 48 Article 27 confidentiality Article 16 None Article II - 47 Article 21
24 UN OECD Council of European Union Madrid Resolution APEC African Union Supplementary Act (ECOWAS Definitions None Paragraph 1 Article 2 Article 9 Article II - 1 Article 1 Determinate purpose Article 3 Paragraph 9 Article 5 Article 6 Article 7 Article 15 Article II - 30 Article 25 Legitimacy Article 3 Non explicit Article 5 Article 6 Article 7 Article 8 Article 9 Article 7 Article 12 Article 13 None Article II - 30 Article II - 28 Article II - 36 Article II - 37 Article 23 Article 30 Article 31 Article 32 Necessity/proportionality Article 2 Paragraph 7 Paragraph 10 Article 5 Article 6 Article 7 Article 8 Article 9 Article 8 Article 12 Article 18 Article 19 Article II - 28 Article II - 30 Article II - 36 Article 23 Article 25 Article 31 Article 32 Data quality Article 2 Article 3 Paragraph 8 Article 5 Article 6 Article 9 Article 18 Article 19 Article II - 30 Article II - 31 Article 25 Article 26 Categories of data Article 5 Refusal Article 6 Article 8 Article 9 Article 13 None Article II - 35 Article II - 36 Article II - 37 Article 30 Article 31 Article 32 Security Article 7 Paragraph 11 Article 7 Article 17 Article 20 Article 5 (Dir 2002/58) Article 22 Article II - 48 Article 27 confidentiality Article 16 None Article II - 47 Article 21
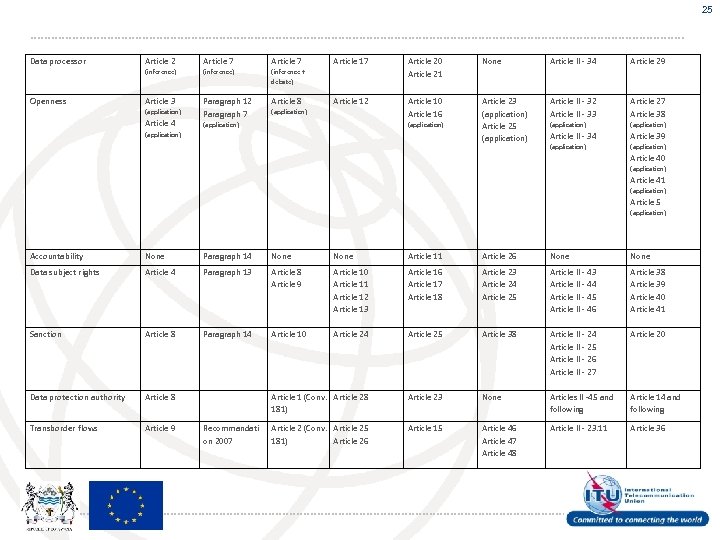 25 Data processor Article 7 (inference) Openness Article 2 (inference) (inference + debate) Article 3 Paragraph 12 Paragraph 7 Article 8 (application) Article 4 Article 17 Article 20 Article 21 None Article II - 34 Article 29 Article 12 Article 10 Article 16 Article 23 (application) Article 25 (application) Article II - 32 Article II - 33 Article 27 Article 38 (application) Article II - 34 Article 39 (application) (application) Article 40 (application) Article 41 (application) Article 5 (application) Accountability None Paragraph 14 None Article 11 Article 26 None Data subject rights Article 4 Paragraph 13 Article 8 Article 9 Article 10 Article 11 Article 12 Article 13 Article 16 Article 17 Article 18 Article 23 Article 24 Article 25 Article II - 43 Article II - 44 Article II - 45 Article II - 46 Article 38 Article 39 Article 40 Article 41 Sanction Article 8 Paragraph 14 Article 10 Article 24 Article 25 Article 38 Article II - 24 Article II - 25 Article II - 26 Article II - 27 Article 20 Data protection authority Article 8 Article 1 (Conv. Article 28 181) Article 23 None Articles II -45 and following Article 14 and following Transborder flows Article 9 Recommandati on 2007 Article 2 (Conv. Article 25 181) Article 26 Article 15 Article 46 Article 47 Article 48 Article II - 23. 11 Article 36
25 Data processor Article 7 (inference) Openness Article 2 (inference) (inference + debate) Article 3 Paragraph 12 Paragraph 7 Article 8 (application) Article 4 Article 17 Article 20 Article 21 None Article II - 34 Article 29 Article 12 Article 10 Article 16 Article 23 (application) Article 25 (application) Article II - 32 Article II - 33 Article 27 Article 38 (application) Article II - 34 Article 39 (application) (application) Article 40 (application) Article 41 (application) Article 5 (application) Accountability None Paragraph 14 None Article 11 Article 26 None Data subject rights Article 4 Paragraph 13 Article 8 Article 9 Article 10 Article 11 Article 12 Article 13 Article 16 Article 17 Article 18 Article 23 Article 24 Article 25 Article II - 43 Article II - 44 Article II - 45 Article II - 46 Article 38 Article 39 Article 40 Article 41 Sanction Article 8 Paragraph 14 Article 10 Article 24 Article 25 Article 38 Article II - 24 Article II - 25 Article II - 26 Article II - 27 Article 20 Data protection authority Article 8 Article 1 (Conv. Article 28 181) Article 23 None Articles II -45 and following Article 14 and following Transborder flows Article 9 Recommandati on 2007 Article 2 (Conv. Article 25 181) Article 26 Article 15 Article 46 Article 47 Article 48 Article II - 23. 11 Article 36
 The skeleton of the draft of a model-law
The skeleton of the draft of a model-law
 Chapter 1 § Definitions: ØDatasubject; ØUnder age child; ØSensitive data; Ø…
Chapter 1 § Definitions: ØDatasubject; ØUnder age child; ØSensitive data; Ø…
 Chapter 2 § Scope: Ø= any processing of personal data perform wholly or partly by automated means, and to the processing of personal data otherwise than by automated means of personal data which forms part of a filing system or is intended to form part of a filing system Ø≠ processing of personal data by a natural person in the course of purely personal or household activities
Chapter 2 § Scope: Ø= any processing of personal data perform wholly or partly by automated means, and to the processing of personal data otherwise than by automated means of personal data which forms part of a filing system or is intended to form part of a filing system Ø≠ processing of personal data by a natural person in the course of purely personal or household activities
![Chapter 2 § Applicable law: Øactivities of any controller permanently established on [given country] Chapter 2 § Applicable law: Øactivities of any controller permanently established on [given country]](https://present5.com/presentation/a33c63eda6f0339019e223a550d21fee/image-29.jpg) Chapter 2 § Applicable law: Øactivities of any controller permanently established on [given country] territory or in a place where [given country] law applies by virtue of international public law; Øif the means used, which can be automatic or other means located on [given country] territory, are not the same as the means used for processing personal data only for the purposes of transit of personal data through [given country] territory.
Chapter 2 § Applicable law: Øactivities of any controller permanently established on [given country] territory or in a place where [given country] law applies by virtue of international public law; Øif the means used, which can be automatic or other means located on [given country] territory, are not the same as the means used for processing personal data only for the purposes of transit of personal data through [given country] territory.
 Chapter 3 § Quality of the data: ØAdequate, relevant and not excessive to the purpose ØAccurate and up-to-date ØUnder an identifying way only for the length of the processing ØEtc.
Chapter 3 § Quality of the data: ØAdequate, relevant and not excessive to the purpose ØAccurate and up-to-date ØUnder an identifying way only for the length of the processing ØEtc.
 Chapter 4 § General rules on the lawfulness: ØGenerality ØPurpose ØLegitimacy § Non-sensitive data § Sensitive data ØEtc.
Chapter 4 § General rules on the lawfulness: ØGenerality ØPurpose ØLegitimacy § Non-sensitive data § Sensitive data ØEtc.
 Chapter 5 § Duties of the data controller and data processor: Øinformation Øconfidentiality ØNotification to the protection authority ØPublicity of the processing Øaccountability
Chapter 5 § Duties of the data controller and data processor: Øinformation Øconfidentiality ØNotification to the protection authority ØPublicity of the processing Øaccountability
 Chapter 6 § Rights of the data subject: ØRight of access ØRight of rectification, deletion, temporary limitation of access ØDelays ØCapacitation ØAutomated decision ØRepresentation of the data subject
Chapter 6 § Rights of the data subject: ØRight of access ØRight of rectification, deletion, temporary limitation of access ØDelays ØCapacitation ØAutomated decision ØRepresentation of the data subject
 Chapter 7 § Protection authority ØStatus and composition ØCompetencies ØFinancing
Chapter 7 § Protection authority ØStatus and composition ØCompetencies ØFinancing
 Chapter 8 § Recourses to the judicial authority ØAccess to the judicial authority; ØClass action
Chapter 8 § Recourses to the judicial authority ØAccess to the judicial authority; ØClass action
 Chapter 9 § Responsability ØCompensation; ØData controller’s liability strengthening
Chapter 9 § Responsability ØCompensation; ØData controller’s liability strengthening
 Chapter 10 § Sanctions
Chapter 10 § Sanctions
 Chapter 11 § Limitations: ØNational security; ØJournalism; ØEtc …
Chapter 11 § Limitations: ØNational security; ØJournalism; ØEtc …
 Chapter 12 § Transborder flows: ØMember States of SADC; ØNon member States of SADC;
Chapter 12 § Transborder flows: ØMember States of SADC; ØNon member States of SADC;
 Chapter 13 § Code of conduct
Chapter 13 § Code of conduct
 Chapter 14 § Whistelblowing
Chapter 14 § Whistelblowing
 42 Thanks a lot for your attention Jean-Marc Van Gyseghem jmvangyseghem@rawlingsgiles. be jean-marc. vangyseghem@fundp. ac. be Member of the Bar of Brussels (Belgium) Head of a Research Unit at the University of Namur (Belgium) Union Internationale des Télécommunications International Telecommunication Union
42 Thanks a lot for your attention Jean-Marc Van Gyseghem jmvangyseghem@rawlingsgiles. be jean-marc. vangyseghem@fundp. ac. be Member of the Bar of Brussels (Belgium) Head of a Research Unit at the University of Namur (Belgium) Union Internationale des Télécommunications International Telecommunication Union


