fe26ac1d1f8247ccbf53337973bfc46b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 HIPAA SECURITY How not to get lost in the Big Ocean of Portable Electronic Health Records: Riding the Wave of Digital Health Information Spring Conference April 4, 2008 Gary Beatty President EC Integrity, Inc Vice-Chair ASC X 12
HIPAA SECURITY How not to get lost in the Big Ocean of Portable Electronic Health Records: Riding the Wave of Digital Health Information Spring Conference April 4, 2008 Gary Beatty President EC Integrity, Inc Vice-Chair ASC X 12
 Influencing the move to e. Healthcare Need to reduce the cost of health care Increase quality of health care Consumer driven health care Online health records Payer support for community health records Transparency in health care Pay for performance programs Governmental
Influencing the move to e. Healthcare Need to reduce the cost of health care Increase quality of health care Consumer driven health care Online health records Payer support for community health records Transparency in health care Pay for performance programs Governmental
 Terminology HR EMR EHR CCR PHR Acronyms Hybrids PHI
Terminology HR EMR EHR CCR PHR Acronyms Hybrids PHI
 Terminology Health Records (AHIMA) The legal business record for a healthcare organization. Individually identifiable information Any medium Collected, processed, stored, displayed
Terminology Health Records (AHIMA) The legal business record for a healthcare organization. Individually identifiable information Any medium Collected, processed, stored, displayed
 Terminology Health Records contain Diagnosis Medications Procedures Problems Clinical Notes Diagnostic Results Images Graphs Other items deemed necessary
Terminology Health Records contain Diagnosis Medications Procedures Problems Clinical Notes Diagnostic Results Images Graphs Other items deemed necessary
 Terminology Health Records Support continuity of care Planning patient care Provides planning information Resource allocation Trend analysis Forecasting Workload management Justification for billing information
Terminology Health Records Support continuity of care Planning patient care Provides planning information Resource allocation Trend analysis Forecasting Workload management Justification for billing information
 Terminology Electronic Medical Record (EMR) (HIMSS) An application environment composed of: Clinical Data Repository (CDR) Clinical Decision Support (CDS) Controlled medical terminology Order entry Computerized provider order entry Pharmacy Clinical document applications Enterprise support Inpatient and Outpatient Use to document, monitor and manage delivery of health care Electronic Medical Record (EMR) (HIMSS) The EMR is the legal record Owned by the Care Delivery Organization (CDO)
Terminology Electronic Medical Record (EMR) (HIMSS) An application environment composed of: Clinical Data Repository (CDR) Clinical Decision Support (CDS) Controlled medical terminology Order entry Computerized provider order entry Pharmacy Clinical document applications Enterprise support Inpatient and Outpatient Use to document, monitor and manage delivery of health care Electronic Medical Record (EMR) (HIMSS) The EMR is the legal record Owned by the Care Delivery Organization (CDO)
 Terminology Electronic Health Record (EHR) (HIMSS) Longitutal electronic medical record across encounters in any care delivery setting. Resource for clinicians Secure Real-time Point-of-care Patient centric information source Aids collection of data for other uses Billing Quality management Outcomes reporting Resource planning Public health disease surveillance Reporting
Terminology Electronic Health Record (EHR) (HIMSS) Longitutal electronic medical record across encounters in any care delivery setting. Resource for clinicians Secure Real-time Point-of-care Patient centric information source Aids collection of data for other uses Billing Quality management Outcomes reporting Resource planning Public health disease surveillance Reporting
 Terminology Electronic Health Record (EHR) (HIMSS) Includes: Patient demographics Progress notes Problems Medications Vital signs Past medical history Immunizations Laboratory data Radiology reports
Terminology Electronic Health Record (EHR) (HIMSS) Includes: Patient demographics Progress notes Problems Medications Vital signs Past medical history Immunizations Laboratory data Radiology reports
 Terminology Electronic Health Record (EHR) (HIMSS) Automates / streamlines clinicians workflow Complete record of clinical encounter Supports other care-related activities Evidence-based decision support Quality management Outcome reporting
Terminology Electronic Health Record (EHR) (HIMSS) Automates / streamlines clinicians workflow Complete record of clinical encounter Supports other care-related activities Evidence-based decision support Quality management Outcome reporting
 Terminology Personal Health Record (PHR) Created by the individual Summarizes health and medical history Gathered from many sources Format of PHR Paper Personal computer Internet based Portable storage
Terminology Personal Health Record (PHR) Created by the individual Summarizes health and medical history Gathered from many sources Format of PHR Paper Personal computer Internet based Portable storage
 Terminology Continuity of Care Record (CCR) Patient Health Summary Standard ASTM / MMS / HIMSS / AAFP / AAP codevelopment Core health care components Sent from one provider to another Includes Patient demographics Insurance information Diagnosis and problem Medications Allergies Care plan
Terminology Continuity of Care Record (CCR) Patient Health Summary Standard ASTM / MMS / HIMSS / AAFP / AAP codevelopment Core health care components Sent from one provider to another Includes Patient demographics Insurance information Diagnosis and problem Medications Allergies Care plan
 Terminology Hybrid Health Record Both Paper health records Electronic health records
Terminology Hybrid Health Record Both Paper health records Electronic health records
 Terminology Protected Health Information (PHI) Any health care information linked to a person Health Status Provision of Health Care Payment of Health Care Includes • Names • Geographic subdivision smaller than a state • Dates related to an individual • Phone Numbers • Fax Numbers • Email Addresses • SSN • Medical Record Numbers • Beneficiary Numbers • Account Numbers • Certificate/license numbers; • Vehicle identifiers and serial numbers • license plate numbers • Device identifiers and serial numbers • Web Universal Resource Locators (URLs) • Internet Protocol (IP) address numbers • Biometric identifiers • Finger • voice prints • Full face photographic images and any comparable images • Any other unique identifying number, characteristic, or code
Terminology Protected Health Information (PHI) Any health care information linked to a person Health Status Provision of Health Care Payment of Health Care Includes • Names • Geographic subdivision smaller than a state • Dates related to an individual • Phone Numbers • Fax Numbers • Email Addresses • SSN • Medical Record Numbers • Beneficiary Numbers • Account Numbers • Certificate/license numbers; • Vehicle identifiers and serial numbers • license plate numbers • Device identifiers and serial numbers • Web Universal Resource Locators (URLs) • Internet Protocol (IP) address numbers • Biometric identifiers • Finger • voice prints • Full face photographic images and any comparable images • Any other unique identifying number, characteristic, or code
 Security Concerns Privacy Authentication Did it arrive exactly as sent? Non-repudiation of receipt How do I know who sent it? Data Integrity Can anyone else read it? Can the receiver deny receipt? How do I know it got there? How do I track these activities?
Security Concerns Privacy Authentication Did it arrive exactly as sent? Non-repudiation of receipt How do I know who sent it? Data Integrity Can anyone else read it? Can the receiver deny receipt? How do I know it got there? How do I track these activities?
 Modes of Communication Internet / Intranet Wired Wireless Wifi (802. 11 a, b, g, i, n) Bluetooth (Personal Area Network - PAN) Voi. P Dial-up Mobile Devices Smart Phones Mobile Standards (GSM, GPRS, etc. ) PDA Tablet PC’s Physical Media Magnetic, optical, flash (thumb drives), others
Modes of Communication Internet / Intranet Wired Wireless Wifi (802. 11 a, b, g, i, n) Bluetooth (Personal Area Network - PAN) Voi. P Dial-up Mobile Devices Smart Phones Mobile Standards (GSM, GPRS, etc. ) PDA Tablet PC’s Physical Media Magnetic, optical, flash (thumb drives), others
 Wireless Security RC 4 (ARC 4 /ARCFOUR) – Stream Cypher (easily broken) Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) WEP Wire Equivalent Privacy WPA Wi. Fi Protected Access WPA 2 (based upon 802. 11 i) Data Encryption Standards (DES) Advanced Encryption Standards (AES) Government strength encryption
Wireless Security RC 4 (ARC 4 /ARCFOUR) – Stream Cypher (easily broken) Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) WEP Wire Equivalent Privacy WPA Wi. Fi Protected Access WPA 2 (based upon 802. 11 i) Data Encryption Standards (DES) Advanced Encryption Standards (AES) Government strength encryption
 Internet Security Firewall machines IP address selection ID + Passwords Security techniques Encryption Digital Signatures Data Integrity Verification Non-repudiation Trading Partner Agreements (TPA)
Internet Security Firewall machines IP address selection ID + Passwords Security techniques Encryption Digital Signatures Data Integrity Verification Non-repudiation Trading Partner Agreements (TPA)
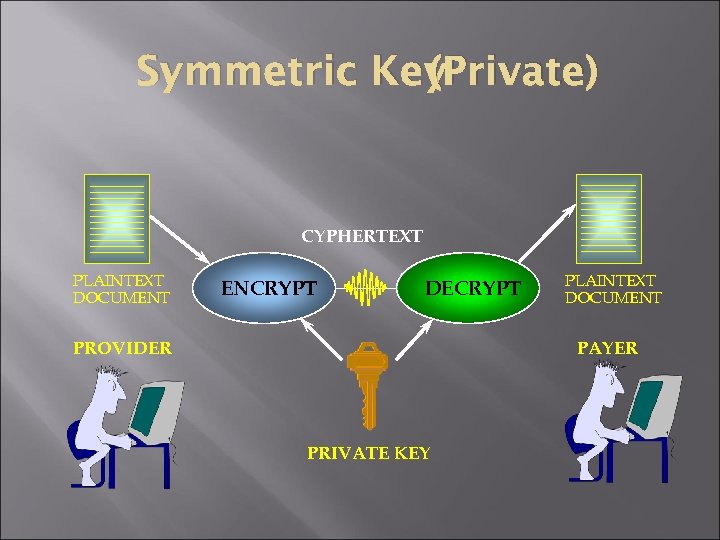 (Private) Symmetric Key CYPHERTEXT PLAINTEXT DOCUMENT ENCRYPT DECRYPT PROVIDER PLAINTEXT DOCUMENT PAYER PRIVATE KEY
(Private) Symmetric Key CYPHERTEXT PLAINTEXT DOCUMENT ENCRYPT DECRYPT PROVIDER PLAINTEXT DOCUMENT PAYER PRIVATE KEY
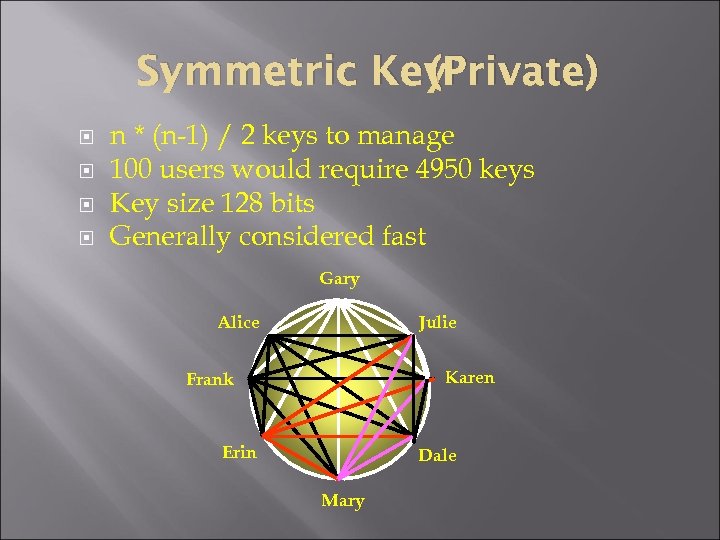 (Private) Symmetric Key n * (n-1) / 2 keys to manage 100 users would require 4950 keys Key size 128 bits Generally considered fast Gary Alice Julie Karen Frank Erin Dale Mary
(Private) Symmetric Key n * (n-1) / 2 keys to manage 100 users would require 4950 keys Key size 128 bits Generally considered fast Gary Alice Julie Karen Frank Erin Dale Mary
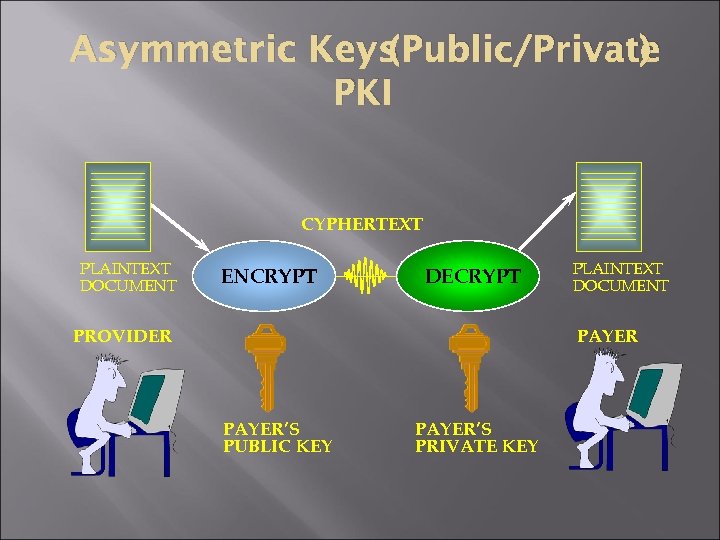 (Public/Private ) Asymmetric Keys PKI CYPHERTEXT PLAINTEXT DOCUMENT ENCRYPT DECRYPT PROVIDER PLAINTEXT DOCUMENT PAYER’S PUBLIC KEY PAYER’S PRIVATE KEY
(Public/Private ) Asymmetric Keys PKI CYPHERTEXT PLAINTEXT DOCUMENT ENCRYPT DECRYPT PROVIDER PLAINTEXT DOCUMENT PAYER’S PUBLIC KEY PAYER’S PRIVATE KEY
 (Public/Private) Asymmetric Keys n key pairs needed for n partners key size (128, 768, 1024, 2048 bits) Generally considered slower What happens if you lose your key? Gary Alice Julie Public Key Directory Gary Alice Frank Erin Frank Mary Dale Karen Julie Erin E F G H Karen Dale Mary
(Public/Private) Asymmetric Keys n key pairs needed for n partners key size (128, 768, 1024, 2048 bits) Generally considered slower What happens if you lose your key? Gary Alice Julie Public Key Directory Gary Alice Frank Erin Frank Mary Dale Karen Julie Erin E F G H Karen Dale Mary
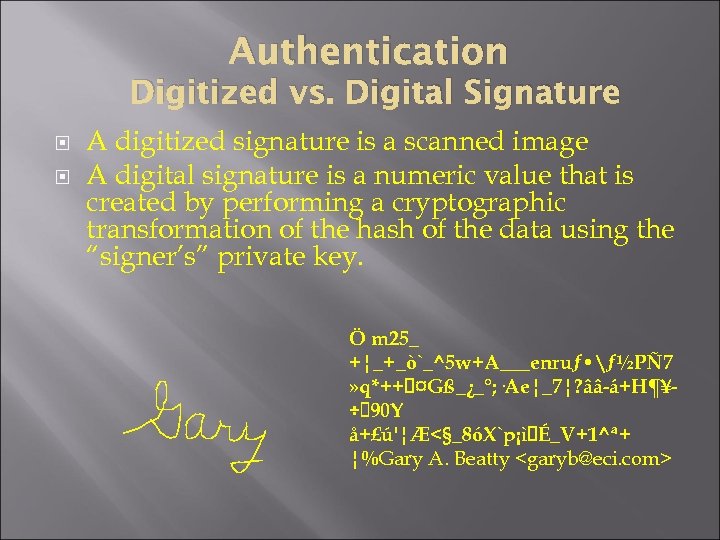 Authentication Digitized vs. Digital Signature A digitized signature is a scanned image A digital signature is a numeric value that is created by performing a cryptographic transformation of the hash of the data using the “signer’s” private key. Ö m 25_ +¦_+_ò`_^5 w+A___enruƒ • ƒ½PÑ 7 » q*++ ¤Gß_¿_°; ·Ae¦_7¦? ââ-á+H¶¥÷ 90 Y å+£ú'¦Æ<§_8óX`p¡ì É_V+1^ª+ ¦%Gary A. Beatty
Authentication Digitized vs. Digital Signature A digitized signature is a scanned image A digital signature is a numeric value that is created by performing a cryptographic transformation of the hash of the data using the “signer’s” private key. Ö m 25_ +¦_+_ò`_^5 w+A___enruƒ • ƒ½PÑ 7 » q*++ ¤Gß_¿_°; ·Ae¦_7¦? ââ-á+H¶¥÷ 90 Y å+£ú'¦Æ<§_8óX`p¡ì É_V+1^ª+ ¦%Gary A. Beatty
 Data Integrity Part of the digital signature process A secure one way hashing algorithm used to create a hash of the data PROVIDER A EHR Provider B PUBLIC KEY Encoded Provider B Cypher PROVIDER A PRIVATE KEY Cypher Encoded PROVIDER A PUBLIC KEY EHR Provider B PRIVATE KEY
Data Integrity Part of the digital signature process A secure one way hashing algorithm used to create a hash of the data PROVIDER A EHR Provider B PUBLIC KEY Encoded Provider B Cypher PROVIDER A PRIVATE KEY Cypher Encoded PROVIDER A PUBLIC KEY EHR Provider B PRIVATE KEY
 Applicability Statement Standards EDIINT Workgroup of IETF AS 1 – Applicability Statement 1 Email exchange of electronic transactions S/MIME – Secure Multi-Purpose Internet Mail Extensions Uses SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) Satisfies Security Requirements Encryption Authentication Integrity Non-repudiation What’s needed Email capability Electronic Transaction Digital Certificate
Applicability Statement Standards EDIINT Workgroup of IETF AS 1 – Applicability Statement 1 Email exchange of electronic transactions S/MIME – Secure Multi-Purpose Internet Mail Extensions Uses SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) Satisfies Security Requirements Encryption Authentication Integrity Non-repudiation What’s needed Email capability Electronic Transaction Digital Certificate
 Applicability Statement Standards EDIINT Workgroup of IETF AS 2 – Applicability Statement 2 HTTP exchange of electronic transactions S/MIME – Secure Multi-Purpose Internet Mail Extensions Uses HTTPS Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer Allows for REAL TIME delivery Satisfies Security Requirements Encryption Authentication Integrity Non-repudiation What’s needed Web Server (static IP address) Electronic Transaction Digital Certificate
Applicability Statement Standards EDIINT Workgroup of IETF AS 2 – Applicability Statement 2 HTTP exchange of electronic transactions S/MIME – Secure Multi-Purpose Internet Mail Extensions Uses HTTPS Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer Allows for REAL TIME delivery Satisfies Security Requirements Encryption Authentication Integrity Non-repudiation What’s needed Web Server (static IP address) Electronic Transaction Digital Certificate
 Applicability Statement Standards EDIINT Workgroup of IETF AS 3 – Applicability Statement 3 FTP exchange of electronic transactions S/MIME – Secure Multi-Purpose Internet Mail Extensions Uses FTP – File Transfer Protocol Allows for REAL TIME delivery Satisfies Security Requirements Encryption Authentication Integrity Non-repudiation What’s needed FTP Server Electronic Transaction Digital Certificate
Applicability Statement Standards EDIINT Workgroup of IETF AS 3 – Applicability Statement 3 FTP exchange of electronic transactions S/MIME – Secure Multi-Purpose Internet Mail Extensions Uses FTP – File Transfer Protocol Allows for REAL TIME delivery Satisfies Security Requirements Encryption Authentication Integrity Non-repudiation What’s needed FTP Server Electronic Transaction Digital Certificate
 Digital Certificates Electronic Credit Card Issues by Credential Authority Establishes “Credentials” for electronic transactions Name Serial Number Expiration Dates Certificate Holder’s Public Key Digital Certificate of Certification Authority Verified by Registration Authority X. 509 Standards Registry of Digital Certificates Access with HIPAA Identifiers
Digital Certificates Electronic Credit Card Issues by Credential Authority Establishes “Credentials” for electronic transactions Name Serial Number Expiration Dates Certificate Holder’s Public Key Digital Certificate of Certification Authority Verified by Registration Authority X. 509 Standards Registry of Digital Certificates Access with HIPAA Identifiers
 Security – Weak Links We can secure transmission of data! Weakest link – usually when data is AT REST! Paper On the screen Waste baskets Physical Security Building access Data Center access Electronic Security Screen Savers Auto Logoff
Security – Weak Links We can secure transmission of data! Weakest link – usually when data is AT REST! Paper On the screen Waste baskets Physical Security Building access Data Center access Electronic Security Screen Savers Auto Logoff
 Thank you Spring Conference April 4, 2008 Gary Beatty President EC Integrity, Inc Vice-Chair ASC X 12
Thank you Spring Conference April 4, 2008 Gary Beatty President EC Integrity, Inc Vice-Chair ASC X 12


