03bda2173b0a3e373ff7801d0b39dac2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 HIP proxy Patrik Salmela 2004 -12 -01
HIP proxy Patrik Salmela 2004 -12 -01
 Contents Background: ID-locator split ¢ HIP ¢ Why a HIP proxy ¢ Functionality of a HIP proxy ¢ The prototype ¢ Performance ¢ Conclusions ¢ 2 2004 -12 -01
Contents Background: ID-locator split ¢ HIP ¢ Why a HIP proxy ¢ Functionality of a HIP proxy ¢ The prototype ¢ Performance ¢ Conclusions ¢ 2 2004 -12 -01
 Background: ID – locator split ¢ Currently: IP address serves 2 purposes l Locator POW: l • Node moves -> new locator: OK l Identifier POW: • Node moves -> new identifier: NOT OK l Identifier requirements: • Stay constant regardless of location and time 3 2004 -12 -01
Background: ID – locator split ¢ Currently: IP address serves 2 purposes l Locator POW: l • Node moves -> new locator: OK l Identifier POW: • Node moves -> new identifier: NOT OK l Identifier requirements: • Stay constant regardless of location and time 3 2004 -12 -01
 Background (cont. ) Some ID – locator split solutions ¢ GSE proposal for IPv 6 l ¢ FARA l ¢ Part of address serves as ID, constant Framework for designing new architectures Peer. Net l DHT and peer-to-peer thinking ¢ I 3 l ¢ 4 IDs registered at I 3 servers HIP 2004 -12 -01
Background (cont. ) Some ID – locator split solutions ¢ GSE proposal for IPv 6 l ¢ FARA l ¢ Part of address serves as ID, constant Framework for designing new architectures Peer. Net l DHT and peer-to-peer thinking ¢ I 3 l ¢ 4 IDs registered at I 3 servers HIP 2004 -12 -01
 The HIP way l ID-locator split • ID: HI (-> HIT / LSI) locator: IP address ID locator • Packets sent to ID, routed using locator ID l Security • IPsec ESP, SAs created during base exchange l Mobility • Connections between IDs (HITs) • Location update messages l Multihoming • Packets sent to ID, the routing is irrelevant ID ¢ 5 The ID is the base for all these features 2004 -12 -01
The HIP way l ID-locator split • ID: HI (-> HIT / LSI) locator: IP address ID locator • Packets sent to ID, routed using locator ID l Security • IPsec ESP, SAs created during base exchange l Mobility • Connections between IDs (HITs) • Location update messages l Multihoming • Packets sent to ID, the routing is irrelevant ID ¢ 5 The ID is the base for all these features 2004 -12 -01
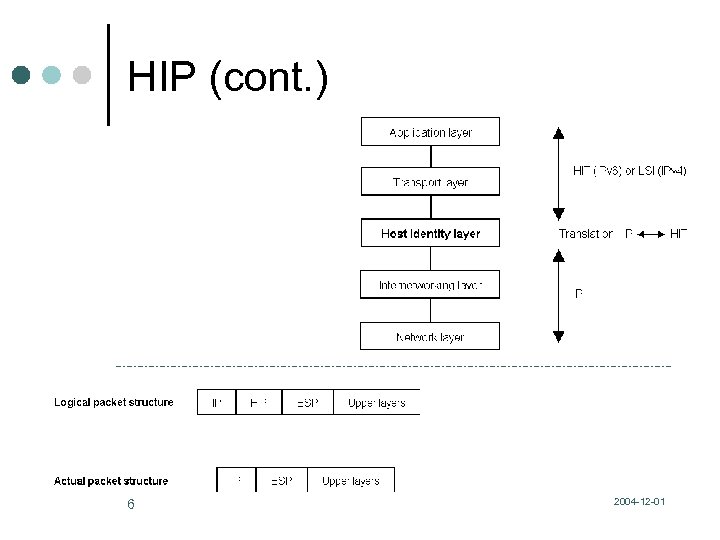 HIP (cont. ) 6 2004 -12 -01
HIP (cont. ) 6 2004 -12 -01
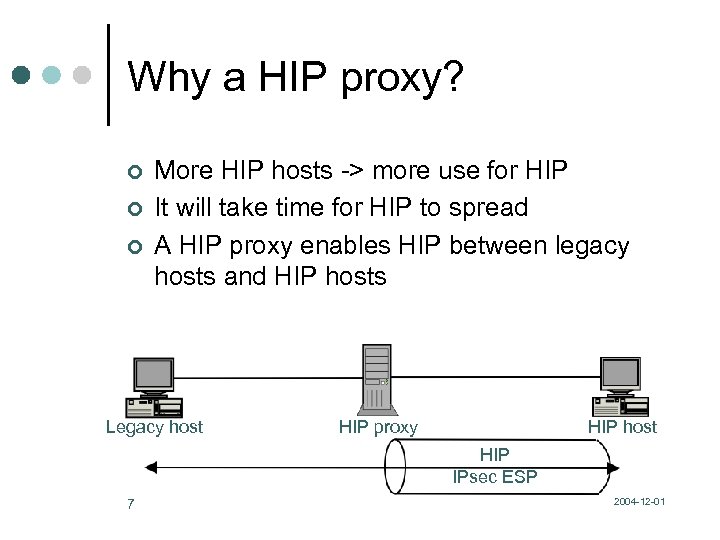 Why a HIP proxy? ¢ ¢ ¢ More HIP hosts -> more use for HIP It will take time for HIP to spread A HIP proxy enables HIP between legacy hosts and HIP hosts Legacy host HIP proxy HIP host HIP IPsec ESP 7 2004 -12 -01
Why a HIP proxy? ¢ ¢ ¢ More HIP hosts -> more use for HIP It will take time for HIP to spread A HIP proxy enables HIP between legacy hosts and HIP hosts Legacy host HIP proxy HIP host HIP IPsec ESP 7 2004 -12 -01
 Why a HIP proxy (cont. ) ¢ Promotes HIP • New possibilities to use HIP ¢ Can be used as ”try-then-buy” for HIP • Easier to enable HIP for hosts in a network • In the long run an all HIP solution is better; less configuration, more freedom/features • If satisfied by services provided by HIP (proxy) -> upgrade to a HIP host/network 8 2004 -12 -01
Why a HIP proxy (cont. ) ¢ Promotes HIP • New possibilities to use HIP ¢ Can be used as ”try-then-buy” for HIP • Easier to enable HIP for hosts in a network • In the long run an all HIP solution is better; less configuration, more freedom/features • If satisfied by services provided by HIP (proxy) -> upgrade to a HIP host/network 8 2004 -12 -01
 Restrictions for a HIP proxy l No security between proxy and legacy host • Solution: Proxy on the border of a private network l HIP host unaware of proxy, security problem • Solution: Add indication into base exchange l Legacy hosts cannot use all HIP features • Solution: Upgrade to HIP host 9 2004 -12 -01
Restrictions for a HIP proxy l No security between proxy and legacy host • Solution: Proxy on the border of a private network l HIP host unaware of proxy, security problem • Solution: Add indication into base exchange l Legacy hosts cannot use all HIP features • Solution: Upgrade to HIP host 9 2004 -12 -01
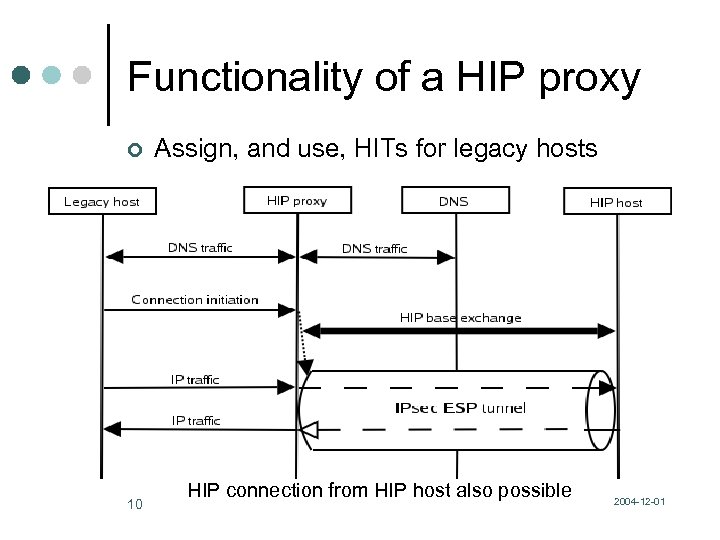 Functionality of a HIP proxy ¢ 10 Assign, and use, HITs for legacy hosts HIP connection from HIP host also possible 2004 -12 -01
Functionality of a HIP proxy ¢ 10 Assign, and use, HITs for legacy hosts HIP connection from HIP host also possible 2004 -12 -01
 The prototype HIP proxy ¢ Free. BSD 5. 2, Ericsson Finland’s HIP impl. ¢ IPv 6 only ¢ No HIP modified DNS -> HIT-IP mappings in configuration file ¢ Proxy between two small LANs ¢ Uses ip 6 fw and divert 6 11 2004 -12 -01
The prototype HIP proxy ¢ Free. BSD 5. 2, Ericsson Finland’s HIP impl. ¢ IPv 6 only ¢ No HIP modified DNS -> HIT-IP mappings in configuration file ¢ Proxy between two small LANs ¢ Uses ip 6 fw and divert 6 11 2004 -12 -01
 The prototype (cont. ) ¢ Packets diverted to proxy for processing l All packets coming from priv. net. • Locate HIT-IP mappings • Replace IP addresses with HITs l Packets from pub. net. with HITs in header • Locate HIT-IP mappings • Replace HITs with IP addresses 12 2004 -12 -01
The prototype (cont. ) ¢ Packets diverted to proxy for processing l All packets coming from priv. net. • Locate HIT-IP mappings • Replace IP addresses with HITs l Packets from pub. net. with HITs in header • Locate HIT-IP mappings • Replace HITs with IP addresses 12 2004 -12 -01
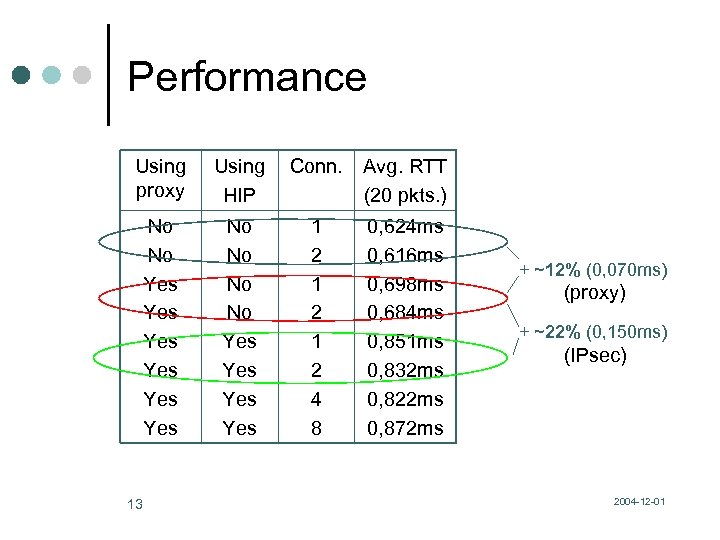 Performance Using proxy Using HIP Conn. Avg. RTT (20 pkts. ) No No Yes Yes Yes No No Yes Yes 1 2 1 2 4 8 0, 624 ms 0, 616 ms 0, 698 ms 0, 684 ms 0, 851 ms 0, 832 ms 0, 822 ms 0, 872 ms 13 + ~12% (0, 070 ms) (proxy) + ~22% (0, 150 ms) (IPsec) 2004 -12 -01
Performance Using proxy Using HIP Conn. Avg. RTT (20 pkts. ) No No Yes Yes Yes No No Yes Yes 1 2 1 2 4 8 0, 624 ms 0, 616 ms 0, 698 ms 0, 684 ms 0, 851 ms 0, 832 ms 0, 822 ms 0, 872 ms 13 + ~12% (0, 070 ms) (proxy) + ~22% (0, 150 ms) (IPsec) 2004 -12 -01
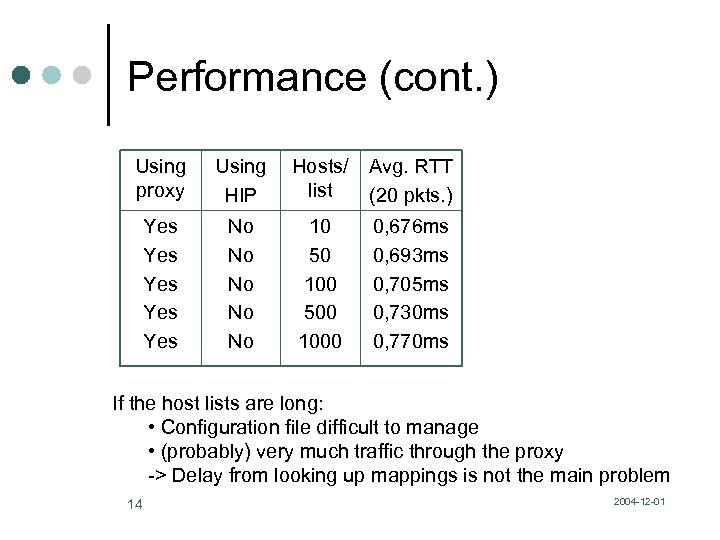 Performance (cont. ) Using proxy Using HIP Hosts/ list Avg. RTT (20 pkts. ) Yes Yes Yes No No No 10 50 100 500 1000 0, 676 ms 0, 693 ms 0, 705 ms 0, 730 ms 0, 770 ms If the host lists are long: • Configuration file difficult to manage • (probably) very much traffic through the proxy -> Delay from looking up mappings is not the main problem 14 2004 -12 -01
Performance (cont. ) Using proxy Using HIP Hosts/ list Avg. RTT (20 pkts. ) Yes Yes Yes No No No 10 50 100 500 1000 0, 676 ms 0, 693 ms 0, 705 ms 0, 730 ms 0, 770 ms If the host lists are long: • Configuration file difficult to manage • (probably) very much traffic through the proxy -> Delay from looking up mappings is not the main problem 14 2004 -12 -01
 Further work ¢ IP version independent HIP proxy • Work in progress… ¢ Improve proxy configuration • E. g. check if configuration file has been edited 15 2004 -12 -01
Further work ¢ IP version independent HIP proxy • Work in progress… ¢ Improve proxy configuration • E. g. check if configuration file has been edited 15 2004 -12 -01
 Conclusions ¢ HIP proxy prototype intended as proof -of-concept • concept proven Can be used as base for new, improved, version ¢ HIP proxy can be used as a stepping stone when going legacy -> HIP ¢ 16 2004 -12 -01
Conclusions ¢ HIP proxy prototype intended as proof -of-concept • concept proven Can be used as base for new, improved, version ¢ HIP proxy can be used as a stepping stone when going legacy -> HIP ¢ 16 2004 -12 -01
 Comments / Questions? 17 2004 -12 -01
Comments / Questions? 17 2004 -12 -01


